steering OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 1006 of 6000
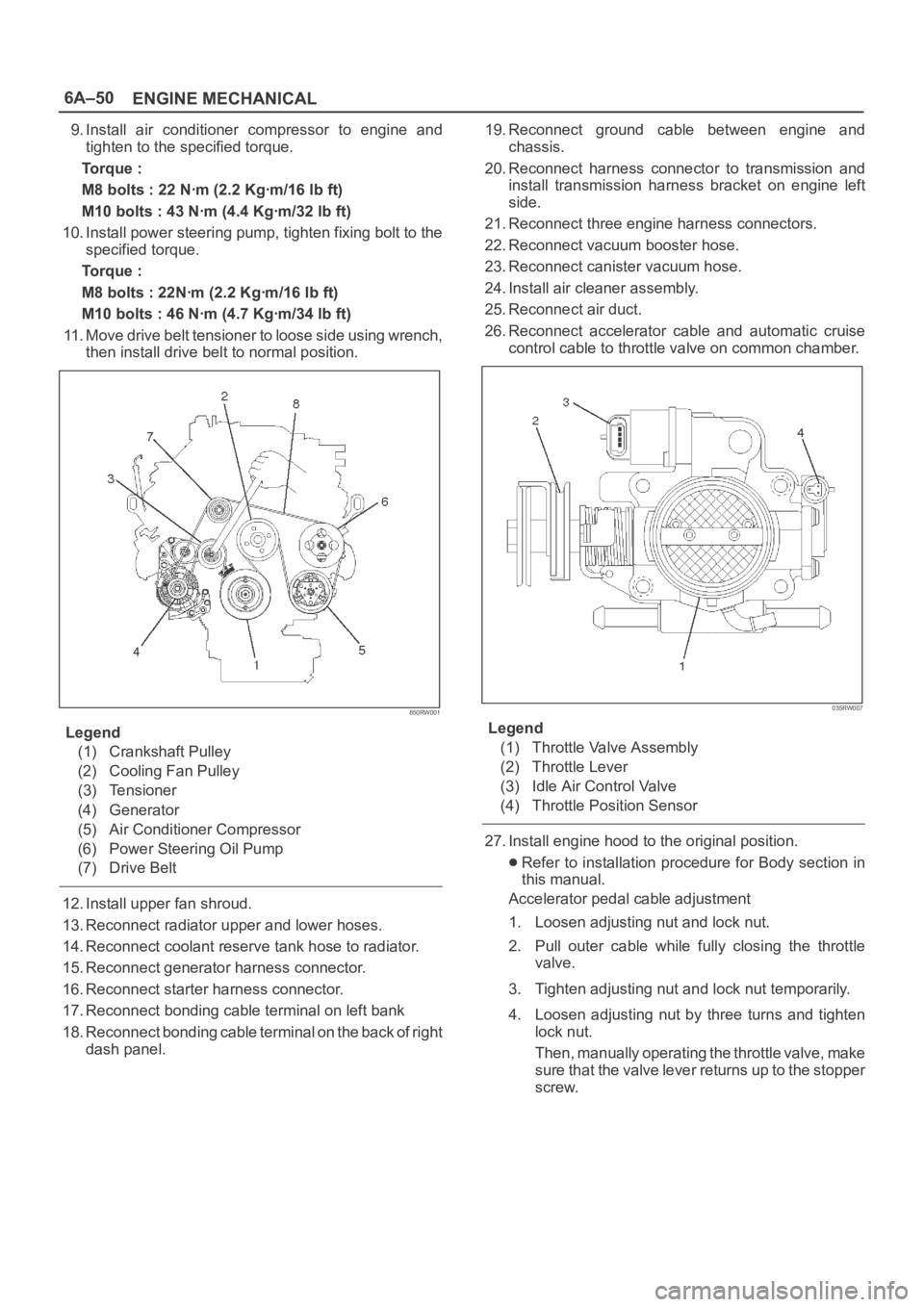
6A–50
ENGINE MECHANICAL
9. Install air conditioner compressor to engine and
tighten to the specified torque.
Torque :
M8 bolts : 22 Nꞏm (2.2 Kgꞏm/16 lb ft)
M10 bolts : 43 Nꞏm (4.4 Kgꞏm/32 lb ft)
10. Install power steering pump, tighten fixing bolt to the
specified torque.
Torque :
M8 bolts : 22Nꞏm (2.2 Kgꞏm/16 lb ft)
M10 bolts : 46 Nꞏm (4.7 Kgꞏm/34 lb ft)
11. Move drive belt tensioner to loose side using wrench,
then install drive belt to normal position.
850RW001
Legend
(1) Crankshaft Pulley
(2) Cooling Fan Pulley
(3) Tensioner
(4) Generator
(5) Air Conditioner Compressor
(6) Power Steering Oil Pump
(7) Drive Belt
12. Install upper fan shroud.
13. Reconnect radiator upper and lower hoses.
14. Reconnect coolant reserve tank hose to radiator.
15. Reconnect generator harness connector.
16. Reconnect starter harness connector.
17. Reconnect bonding cable terminal on left bank
18. Reconnect bonding cable terminal on the back of right
dash panel.19. Reconnect ground cable between engine and
chassis.
20. Reconnect harness connector to transmission and
install transmission harness bracket on engine left
side.
21. Reconnect three engine harness connectors.
22. Reconnect vacuum booster hose.
23. Reconnect canister vacuum hose.
24. Install air cleaner assembly.
25. Reconnect air duct.
26. Reconnect accelerator cable and automatic cruise
control cable to throttle valve on common chamber.
035RW007
Legend
(1) Throttle Valve Assembly
(2) Throttle Lever
(3) Idle Air Control Valve
(4) Throttle Position Sensor
27. Install engine hood to the original position.
Refer to installation procedure for Body section in
this manual.
Accelerator pedal cable adjustment
1. Loosen adjusting nut and lock nut.
2. Pull outer cable while fully closing the throttle
valve.
3. Tighten adjusting nut and lock nut temporarily.
4. Loosen adjusting nut by three turns and tighten
lock nut.
Then, manually operating the throttle valve, make
s u r e t h a t t h e v a l v e l e v e r r e t u r n s u p t o t h e s t o p p e r
screw.
Page 1065 of 6000

6B–12
ENGINE COOLING
Drive Belt and Cooling Fan
Drive Belt and Associated Parts
015RW005
Legend
(1) Crankshaft Pulley
(2) Generator
(3) Power Steering Pump(4) Water Pump and Cooling Fan Pulley
(5) Idle Pulley
(6) Tension Pulley
(7) Drive Belt
The drive belt adjustment is not required as automatic
drive belt tensioner is equipped.
Inspection
Check drive belt for wear or damage, and replace with a
new one as necessary.
Installation
Install cooling fan assembly and tighten bolts/nuts to the
specified torque.
Torque : 22 Nꞏm (2.2 Kgꞏm/16 lb ft) for fan pulley
and fan bracket.
Torque : 10 Nꞏm (1.0 Kgꞏm/88.5 lb in) for fan and
clutch assembly.
NOTE: Fan belts for 6VE1 Gasoline Engine mounted on
98MY (UX) have been brought into one. As a result, the
rotating direction of a fan belt is opposite to the direction
o f c o o l i n g f a n f o r 9 2 t o 9 7 M Y 6 V D 1 w i t h n o
interchangeability.
Therefore, incorrect installation of a fan may cause the air
for cooling to flow in the opposite direction, this resulting
in the poor performance of the air-conditioner and a rise
temperature in engine cooling water.
Page 1120 of 6000

6E–3 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0351
Ignition 1 Control Circuit 6E–206. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0352
Ignition 2 Control Circuit 6E–209. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0353
Ignition 3 Control Circuit 6E–212. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0354
Ignition 4 Control Circuit 6E–215. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0355
Ignition 5 Control Circuit 6E–218. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0356
Ignition 6 Control Circuit 6E–221. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0402
EGR Pintle Crank Error 6E–224. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0404
EGR Open Stuck 6E–226. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0405
EGR Low Voltage 6E–228. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0406
EGR High Voltage 6E–231. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0502
VSS Circuit Low Input 6E–234. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0562
System Voltage Low 6E–237. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0563
System Voltage High 6E–239. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0601
PCM Memory 6E–240. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1154
HO2S Circuit Transition Time Ratio Bank 2
Sensor 1 6E–241. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1171
Fuel System Lean During Acceleration 6E–245. . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1380
ABS Rough Road ABS System Fault 6E–248. . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1404
EGR Closed Stuck 6E–249. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1508
IAC System Low RPM 6E–251. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1509
IAC System High RPM 6E–254. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1618
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) PCM
Interprocessor Communication Error 6E–257. . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1625
PCM Unexpected Reset 6E–258. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1640
Driver-1-Input High Voltage 6E–259. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Symptom Diagnosis 6E–262. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Default Matrix Table 6E–288. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor 6E–291. . . . . . . . . .
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor 6E–292. . . . . . . . .
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor 6E–292.
Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) 6E–293. . . . . . . . . . .
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor 6E–295. . . . . . .
Knock Sensor (KS) 6E–296. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor 6E–297. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor 6E–297.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) 6E–298. . . . . . . . . .
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) 6E–298. . . . . . . . .
EEPROM 6E–300. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Steering Pressure (PSP) Switch 6E–300
. . . .
Throttle Position (TP) Sensor 6E–301. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) 6E–302. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Air Cleaner/Air Filter 6E–303. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve 6E–304. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Common Chamber 6E–305. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accelerator Cable Assembly 6E–305. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accelerator Pedal Replacement 6E–308. . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Filter Cap 6E–310. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Filter 6E–310. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Gauge Unit 6E–313. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Injectors 6E–314. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Pressure Regulator 6E–315. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Metering System 6E–317. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Pump Assembly 6E–318. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Pump Relay 6E–319. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Rail Assembly 6E–319. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Tank 6E–321. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Throttle Body (TB) 6E–323. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electronic Ignition System 6E–324. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Catalytic Converter 6E–325. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Air Conditioning Relay 6E–325. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EVAP Canister Hoses 6E–326. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EVAP Canister 6E–326. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid 6E–327. . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Tank Vent Valve 6E–328. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) Valve 6E–328. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) Valve 6E–329.
Wiring and Connectors 6E–330. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Connectors and Terminals 6E–330. . . . . . . . . . .
Wire Harness Repair: Twisted Shielded
Cable 6E–330. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Twisted Leads 6E–331. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Weather-Pack Connector 6E–332. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Com-Pack III 6E–333. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Metri-Pack 6E–333. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description 6E–335. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description (PCM and Sensors) 6E–335. . .
58X Reference PCM Input 6E–335. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A/C Request Signal 6E–335. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor 6E–335. . . . . . .
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor and
Signal 6E–335. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor 6E–335
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read
Only Memory (EEPROM) 6E–336. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Control Heated Oxygen Sensors 6E–336. . . .
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor 6E–336. . . . .
Page 1136 of 6000
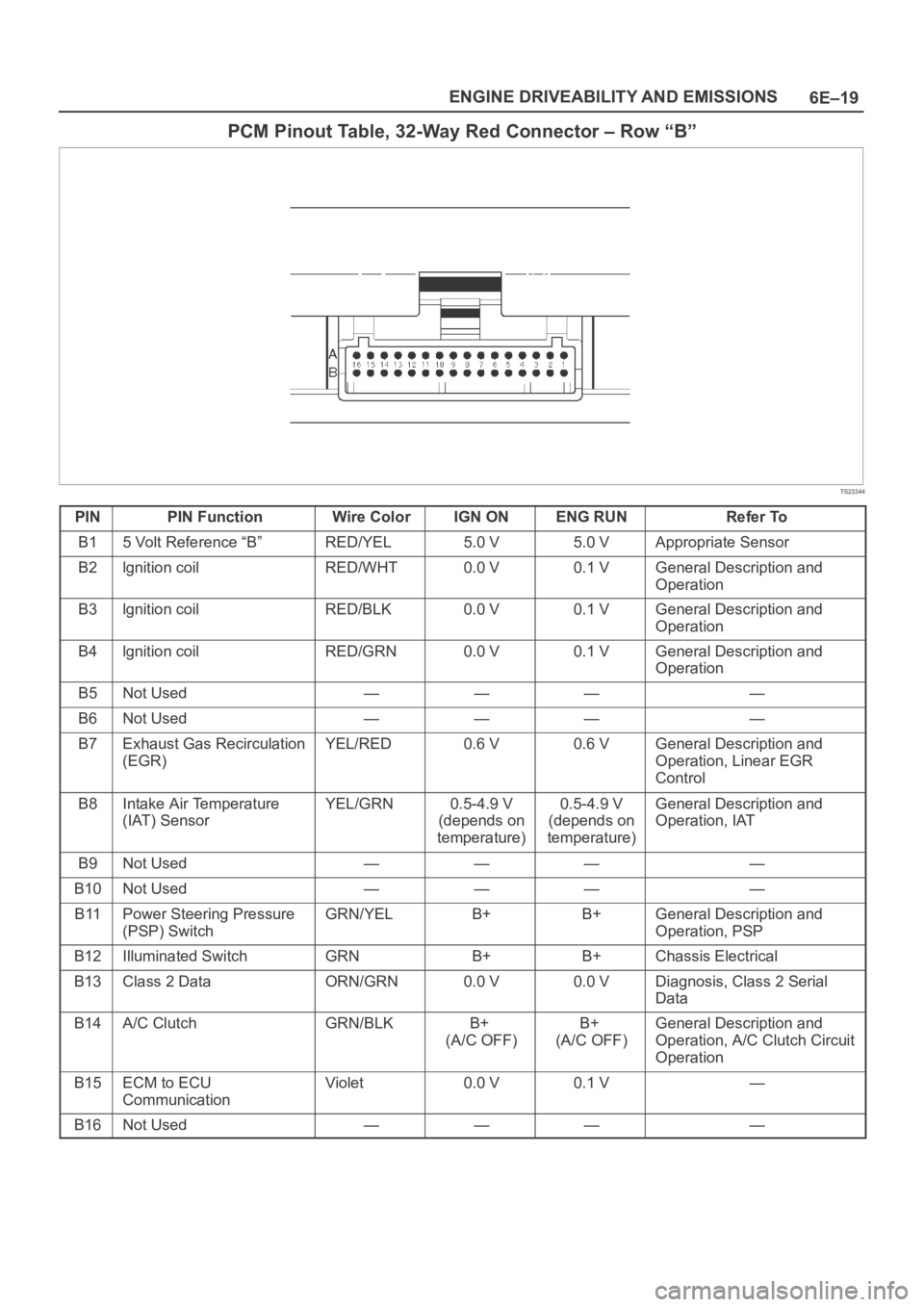
6E–19 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way Red Connector – Row “B”
TS23344
PINPIN FunctionWire ColorIGN ONENG RUNRefer To
B15 Volt Reference “B”RED/YEL5.0 V5.0 VAppropriate Sensor
B2lgnition coilRED/WHT0.0 V0.1 VGeneral Description and
Operation
B3lgnition coilRED/BLK0.0 V0.1 VGeneral Description and
Operation
B4lgnition coilRED/GRN0.0 V0.1 VGeneral Description and
Operation
B5Not Used————
B6Not Used————
B7Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR)YEL/RED0.6 V0.6 VGeneral Description and
Operation, Linear EGR
Control
B8Intake Air Temperature
(IAT) SensorYEL/GRN0.5-4.9 V
(depends on
temperature)0.5-4.9 V
(depends on
temperature)General Description and
Operation, IAT
B9Not Used————
B10Not Used————
B11Power Steering Pressure
(PSP) SwitchGRN/YELB+B+General Description and
Operation, PSP
B12Illuminated SwitchGRNB+B+Chassis Electrical
B13Class 2 DataORN/GRN0.0 V0.0 VDiagnosis, Class 2 Serial
Data
B14A/C ClutchGRN/BLKB+
(A/C OFF)B+
(A/C OFF)General Description and
Operation, A/C Clutch Circuit
Operation
B15ECM to ECU
CommunicationViolet0.0 V0.1 V—
B16Not Used————
Page 1171 of 6000

6E–54
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
A/C Clutch Control Circuit Diagnosis
D06RW085
Circuit Description
When air conditioning and blower fan are selected, and if
the system has a sufficient refrigerant charge, a 12-volt
signal is supplied to the A/C request input of the
powertrain control module (PCM). The A/C request
signal may be temporarily canceled during system
operation by the electronic thermostat in the evaporator
case. The electronic thermostat may intermittently
remove the control circuit ground for the A/C thermostat
relay to prevent the evaporator from forming ice. When
the A/C request signal is received by the PCM, the PCM
supplies a ground from the compressor clutch relay if the
engine operating conditions are within acceptable
ranges. With the A/C compressor relay energized,
voltage is supplied to the compressor clutch coil.
The PCM will enable the compressor clutch to engage
whenever A/C has been selected with the engine running,
unless any of the following conditions are present:
The throttle is greater than 90%.
The ignition voltage is below 10.5 volts.
The engine speed is greater than 4500 RPM for 5
seconds or 5400 RPM.
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is greater than
125
C (257 F).
The intake air temperature (IAT) is less than 5C
(41
F).
The power steering pressure switch signals a cramped
position.
Diagnostic Aids
To diagnose an the intermittent fault, check for the
following conditions:
Poor connection at the PCM–Inspect connections for
backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken locks,
improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal-to-wire connection.
Page 1417 of 6000

6E–300
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
4. Disconnect the red, white, and blue electrical
connectors at the PCM.
5. Remove the two screws in the front of the PCM.
6. Remove the one screw at the left rear of the PCM.
7. Pull the PCM straight out from the dashboard.
TS23757
Installation Procedure
1. Insert the PCM into the dashboard.
Line up the holes in front for the mounting screws.
2. Install the PCM with two screws in the front and one
screw at the left rear.
3. Plug the red, white, and blue connectors into the
appropriate sockets.
TS23757
EEPROM
General Description
The Electronically Erasable Programmable Read Only
Memory (EEPROM) is a permanent memory that is
physically soldered within the PCM. The EEPROM
contains program and calibration information that the
PCM needs to control powertrain operation.
EEPROM Programming
1. Step-up – Ensure that the following conditions have
been met:
The battery is fully charged.
The ignition is “ON.”
The Vehicle Interface Module cable connection at
the DLC is secure.
2. Program the PCM using the latest software matching
the vehicle. Refer to up-to-date Techline equipment
user’s instructions.
3. If the PCM fails to program, Refer to
UBS 98 model
year Immobilizer Workshop Manual.
Functional Check
1. Perform the On-Board Diagnostic System Check.
2. Start the engine and run for one minute.
3. Scan for DTCs using the Tech 2.
Power Steering Pressure (PSP)
Switch
General Description
The Power Steering Pressure (PSP) switch closes when
the hydraulic pressure reaches 3920
690 kPa (570
100 psi). This causes the PCM to actuate the idle air
control valve in order to prevent the additional load from
slowing down the engine. The switch opens when the
hydraulic pressure drops to 2970
560 kPa (430 80
psi).
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the PSP switch pigtail from the wiring
harness.
The pigtail is permanently attached to the switch.
Do not attempt to remove the wires from the
sensor.
Have a container ready to catch the power steering
fluid that leaks out of the line when the switch is
removed.
Page 1418 of 6000

6E–301 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
2. Remove the PSP switch from the power steering line.
Plug the line to prevent excessive loss of fluid and
possible contamination of the power steering
system.
TS23760
Installation Procedure
1. Install the PSP switch in the power steering line.
TS23760
2. Connect the PSP switch pigtail to the wiring harness.
3. Check the power steering fluid level. Refer to
Power
Steering
.
4. Start the engine. Watch the PSP switch for signs of
fluid leakage.
Throttle Position (TP) Sensor
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the TPS electrical connector.3. Remove the bolts and the TP sensor from the throttle
body.
TS23747
NOTE: Do not clean the TP sensor by soaking it in
solvent. The sensor will be damaged as a result.
Function Check
Use a Tech 2 to check the TP sensor output voltage at
closed throttle.
The voltage should be under 0.85 volt.
If the reading is greater than 0.85 volt, check the
throttle shaft to see if it is binding. Check that the
throttle cable is properly adjusted, also. Refer to
Throttle Cable Adjustment.
If the throttle shaft is not binding and the throttle cable
is properly adjusted, install a new TP sensor.
Installation Procedure
1. Install the TP sensor on the throttle body with the
bolts.
TS23747
Page 1456 of 6000

6E–339 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
0005
PCM Components
The PCM is designed to maintain exhaust emission levels
to government mandated standards while providing
excellent driveability and fuel efficiency. The PCM
monitors numerous engine and vehicle functions via
electronic sensors such as the throttle position (TP)
sensor, heated oxygen sensor (HO2S), and vehicle
speed sensor (VSS). The PCM also controls certain
engine operations through the following:
Fuel injector control
Ignition control module
Knock sensor
Automatic transmission shift functions
Cruise control
A/C clutch control
PCM Voltage Description
The PCM supplies a buffered voltage to various switches
and sensors. It can do this because resistance in the
PCM is so high in value that a test light may not illuminate
when connected to the circuit. An ordinary shop
voltmeter may not give an accurate reading because the
voltmeter input impedance is too low. Use a 10-megohm
input impedance digital voltmeter (such as J 39200) to
assure accurate voltage readings.
The input/output devices in the PCM include
analog-to-digital converters, signal buffers, counters,
and special drivers. The PCM controls most components
with electronic switches which complete a ground circuit
when turned “ON.” These switches are arranged in
groups of 4 and 7, called either a surface-mounted quad
driver module (QDM), which can independently control up
to 4 output terminals, or QDMs which can independently
control up to 7 outputs. Not all outputs are always used.
PCM Input/Outputs
Inputs – Operating Conditions Read
Air Conditioning “ON” or “OFF”
Engine Coolant Temperature
Crankshaft Position
Exhaust Oxygen Content
Electronic Ignition
Manifold Absolute Pressure
Battery Voltage
Throttle Position
Vehicle Speed
Fuel Pump Voltage
Power Steering Pressure
Intake Air Temperature
Mass Air Flow
Engine Knock
Camshaft Position
Outputs – Systems Controlled
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
Ignition Control
Fuel Control
Idle Air Control
Electric Fuel Pump
Air Conditioning
Diagnostics
– Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Service Engine Soon
lamp)
– Data Link Connector (DLC)
– Data Output
Transmission Control Module
Alternator Gain Control
PCM Service Precautions
The PCM is designed to withstand normal current draws
associated with vehicle operation. Avoid overloading any
circuit. When testing for opens and shorts, do not ground
or apply voltage to any of the PCM’s circuits unless
instructed to do so. These circuits should only be tested
Tech-2. The PCM should remain connected to the PCM
or to a recommended breakout box.
Reprogramming The PCM
The Trooper allow reprogramming of the PCM without
removing it from the vehicle . This provides a flexible and
cost-effective method of making changes in software
calibrations.
The service programming system (SPS) will not allow
incorrect software programming or incorrect calibration
changes.
Refer to the UBS 98model year Immobilizer Workshop
Manual.
Throttle Position (TP) Sensor
The throttle position (TP) sensor is a potentiometer
connected to the throttle shaft on the throttle body. The
PCM monitors the voltage on the signal line and
calculates throttle position. As the throttle valve angle is
changed (accelerator pedal moved), the TP sensor signal
also changes. At a closed throttle position, the output of
Page 1486 of 6000

6G–7 ENGINE LUBRICATION
Oil Pan and Crankcase
Removal
1. Disconnect battery ground cable.
2. Drain engine oil.
3. Lift vehicle by supporting the frame.
4. Remove front wheels.
5. Remove oil level dipstick from level gauge tube.
6. Remove stone guard.
7. Remove radiator under fan shroud.
8. Remove suspension cross member fixing bolts, 2 pcs
each per side and remove suspension cross member.
9. Remove pitman arm and relay lever assembly, using
the 5–8840–2005–0 remover, remove pitman arm
from the steering unit and remove four fixing bolts for
relay lever assembly.
10. Remove axle housing assembly four fixing bolts from
housing isolator side and mounting bolts from wheel
side. At this time support the axle with a garage jack
and remove axle housing assembly.
11. Remove oil pan fixing bolts.
12. Remove oil pan, using 5–8840–2153–0 sealer cutter,
remove oil pan.
013RS003
13. Remove crankcase fixing bolts.
14. Remove crankcase, using 5–8840–2153–0 sealer
cutter, remove crankcase.
NOTE: Do not deform or damage the flange of oil pan and
crankcase.
Replace the oil pan and/or crankcase if deformed or dam-
aged.
013RS003
Installation
1. Install crankcase.
1. Remove residual sealant, lubricant and moisture
from mounting surface, then dry thoroughly.
2. Properly apply a 4.5 mm (0.7 in) wide bead of
sealant (TB-1207C or equivalent) to mounting
surface of crankcase.
Sealant beat must be continuous.
The crankcase must be installed within 5
minutes after sealant application before the
sealant hardens.
013RW010
Page 1487 of 6000

6G–8
ENGINE LUBRICATION
3. Install crankcase, tighten crankcase fixing bolts
to the specified torque.
Torque : 10 Nꞏm (1.0 Kgꞏm/89 lb in)
013RW004
2. Install oil pan
1. Remove residual sealant, lubricant and moisture
from mounting surface, then dry thoroughly.
2. Properly apply a 4.5 mm (07 in) wide bead of
sealant (TB-1207C or equivalent) to mounting
surface of oil pan.
Sealant beat must be continuous.
The crankcase must be installed within 5
minutes after sealant application befor the
sealant hardens.
013RW003
3. Install oil pan, tighten oil pan fixing bolts to the
specified torque.
Torque : 25 Nꞏm (2.5 Kgꞏm/18 lb ft)3. Install axle housing assembly and tighten fixing bolts
to the specified torque.
Axle case bolts
Torque : 82 Nꞏm (8.4 Kgꞏm/60 lb ft)
Mounting bolts
Torque : 152 Nꞏm (15.5 Kgꞏm/112 lb ft)
013RW005
4. Install relay lever assembly and tighten fixing bolts.
Torque: 44 Nꞏm (4.5 Kgꞏm/32 lb ft)
5. Engage teeth of pitman arm and steering unit, and
tighten nut to the specified torque.
Torque : 216 Nꞏm (22.0 Kgꞏm/159 lb ft)
013RW006
Legend
(1) Pitman Arm
(2) Relay Lever