ignition OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 2262 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–17
Menu
The following table shows, which functions are
used the available equipment versions.
F0: Diagnostic Trouble Codes
F0: Read DTC Info Ordered By Priority
F1: Clear DTC Information
F2: DTC Information
F0: History
F1: MIL SVS or Message Requested
F2: Last Test Failed
F3: Test Failed Since Code Cleared
F4: Not Ran Since Code Cleared
F5: Failed This Ignition
F1: Data Display
3. DVOM
When instructed to use a voltmeter or ohmmeter
within a troubleshooting procedure, use only a high
impedance DVOM (Digital Volt Ohmmeter) such as
J–39200 or equivalent.
Page 2265 of 6000
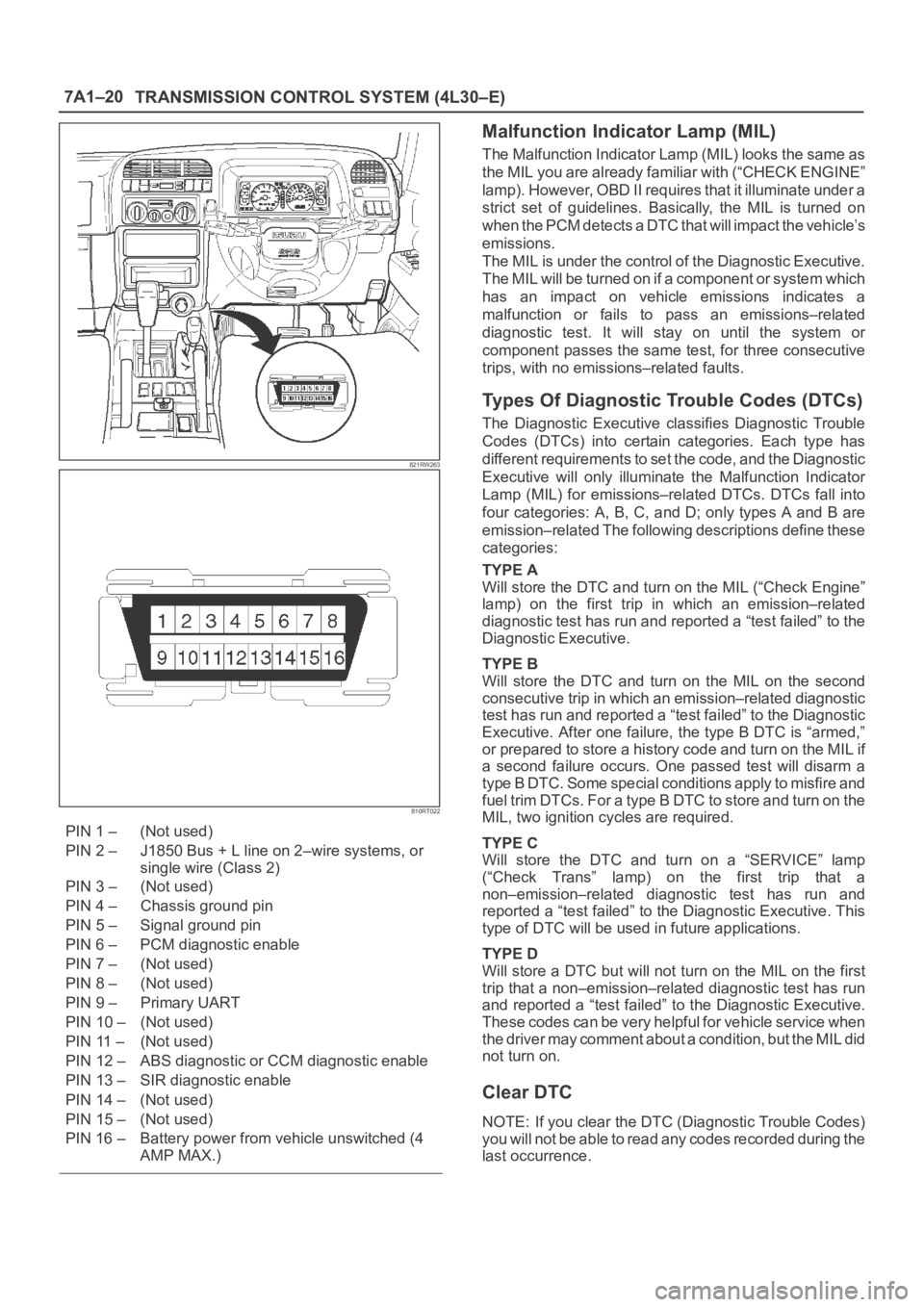
7A1–20
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
821RW263
810RT022
PIN 1 – (Not used)
PIN 2 – J1850 Bus + L line on 2–wire systems, or
single wire (Class 2)
PIN 3 – (Not used)
PIN 4 – Chassis ground pin
PIN 5 – Signal ground pin
PIN 6 – PCM diagnostic enable
PIN 7 – (Not used)
PIN 8 – (Not used)
PIN 9 – Primary UART
PIN 10 – (Not used)
PIN 11 – (Not used)
PIN 12 – ABS diagnostic or CCM diagnostic enable
PIN 13 – SIR diagnostic enable
PIN 14 – (Not used)
PIN 15 – (Not used)
PIN 16 – Battery power from vehicle unswitched (4
AMP MAX.)
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) looks the same as
the MIL you are already familiar with (“CHECK ENGINE”
lamp). However, OBD II requires that it illuminate under a
strict set of guidelines. Basically, the MIL is turned on
when the PCM detects a DTC that will impact the vehicle’s
emissions.
The MIL is under the control of the Diagnostic Executive.
The MIL will be turned on if a component or system which
has an impact on vehicle emissions indicates a
malfunction or fails to pass an emissions–related
diagnostic test. It will stay on until the system or
component passes the same test, for three consecutive
trips, with no emissions–related faults.
Types Of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
The Diagnostic Executive classifies Diagnostic Trouble
Codes (DTCs) into certain categories. Each type has
different requirements to set the code, and the Diagnostic
Executive will only illuminate the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) for emissions–related DTCs. DTCs fall into
four categories: A, B, C, and D; only types A and B are
emission–related The following descriptions define these
categories:
TYPE A
Will store the DTC and turn on the MIL (“Check Engine”
lamp) on the first trip in which an emission–related
diagnostic test has run and reported a “test failed” to the
Diagnostic Executive.
TYPE B
Will store the DTC and turn on the MIL on the second
consecutive trip in which an emission–related diagnostic
test has run and reported a “test failed” to the Diagnostic
Executive. After one failure, the type B DTC is “armed,”
or prepared to store a history code and turn on the MIL if
a second failure occurs. One passed test will disarm a
type B DTC. Some special conditions apply to misfire and
fuel trim DTCs. For a type B DTC to store and turn on the
MIL, two ignition cycles are required.
TYPE C
Will store the DTC and turn on a “SERVICE” lamp
(“Check Trans” lamp) on the first trip that a
non–emission–related diagnostic test has run and
reported a “test failed” to the Diagnostic Executive. This
type of DTC will be used in future applications.
TYPE D
Will store a DTC but will not turn on the MIL on the first
trip that a non–emission–related diagnostic test has run
and reported a “test failed” to the Diagnostic Executive.
These codes can be very helpful for vehicle service when
the driver may comment about a condition, but the MIL did
not turn on.
Clear DTC
NOTE: If you clear the DTC (Diagnostic Trouble Codes)
you will not be able to read any codes recorded during the
last occurrence.
Page 2266 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–21
NOTE: To use the DTC again to identify a problem, you
will need to reproduce the fault or the problem. This may
require a new test drive or just turning the ignition on (this
depends on the nature of the fault).
1. IF you have a Tech2:
1. Connect the Tech2 if it is still not connected
GOTHROUGH Tech2 OBD II CONNECTION.
2. Push “F4” and answer “Yes” to the question “Do
you really want to clear the codes?”
a. When a malfunction remains as it is the Tech2
displays “4L30E CODES NOT CLEARED”. This
means that the problem is still there or that the
recovery was not done. Please GOTO DTC
CHECK.
b. When a malfunction has been repaired and the
recovery is done. The Tech2 displays “4L30E
CODES CLEARED”.
2. IF you have no Tech2:
To clear the DTC, remove Fuse “Stop, A/T CONT”
(C–14, 15A) for at least 10 seconds.
DTC Check
1. Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) have been identified
by Tech2.
2. You have written the list of the DTCs. The order of the
malfunctions has no meanings for this PCM. Usually
only one or two malfunctions should be set for a given
problem.
3. Check directly the DTCs you identified. The DTCs are
sorted by number. Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) Identification in this section.
PCM Precaution
The PCM can be damaged by:
1. Electrostatic discharge
2. The short circuit of some terminals to voltage or to
ground.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage Description:
1. Electronic components used to control systems are
often designed to carry very low voltage, and are very
susceptible to damage caused by electrostatic
discharge. It is possible for less than 100 volts of
static electricity to cause damage to some electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as
4,000 volts for a person to even feel the zap of a static
discharge.2. There are several ways for a person to become
statically charged. The most common methods of
charging are by friction and induction. An example of
charging by friction is a person sliding across a car
seat, in which a charge of as much as 25,000 volts
can build up. Charging by induction occurs when a
person with well insulated shoes stands near a highly
charged object and momentarily touches ground.
Charges for the same polarity are drained off, leaving
the person highly charged with the opposite polarity.
Static charges of either type can cause damage,
therefore, it is important to use care when handling
and testing electronic components.
NOTICE: To prevent possible electrostatic
discharge damage:
1. Do not touch the PCM connector pins or soldered
components on the PCM circuit board.
2. Be sure to follow the guidelines listed below if
servicing any of these electronic components:
3. Do not open the replacement part package until it is
time to install the part.
4. Avoid touching electrical terminals of the part.
5. Before removing the part from its package, ground
the package to a known good ground on the vehicle.
6. Always touch a known good ground before handling
the part. This step should be repeated before
installing the part if the part has been handled while
sliding across the seat, while sitting down from a
standing position or while walking some distance.
Information On PCM
1. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is located in
the center console and is the control center of the
electronic transmission control system.
2. The PCM must be maintained at a temperature below
185
F (85C) at all times. This is most essential if the
vehicle is put through a paint baking process. The
PCM will become inoperative if its temperature
exceeds 85
C (185F). Therefore, it is
recommended that the PCM be removed or that
temporary insulation be placed around the PCM
during the time the vehicle is in a paint oven or other
high temperature process.
3. The PCM is designed to process the various inputs
and then respond by sending the appropriate
electrical signals to control transmission upshift,
downshift, shift feel and torque converter clutch
engagement.
4. The PCM constantly interprets information from the
various sensors, and controls the systems that affect
transmission and vehicle performance. By analyzing
operational problems, the PCM is able to perform a
diagnostic function by displaying DTC(s) and aid the
technician in making repairs.
Intermittent Conditions
If the Tech2 displays a diagnostic trouble code as
intermittent, or if after a test drive a DTC does not
reappear though the detection conditions for this DTC are
present, the problem is most likely a faulty electrical
Page 2270 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–25
DTC P0218 Transmission Fluid Over Temperature
D07RW029
Circuit Description
The Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) sensor is a
thermister that controls the signal voltage to the PCM.
The PCM supplies a 5–volt reference to the sensor on
circuit RED/BLK–GRN/RED. When the transmission fluid
is cold, the sensor resistance is high and the PCM will
sense high signal voltage. As the fluid temperature
warms to a normal transmission operating temperature of
100
C (212F), the sensor resistance becomes less and
the voltage decreases to 1.5 to 2.0 volts.
This DTC detects a high transmission temperature for a
long period of time. This is a type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
No TFT DTCs P0712 or P0713.
TFT is greater than 135C (275F).
All conditions met for 21 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
Hot mode TCC Shift Pattern.
The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
ATF Lamp ON. (TFT is greater than 145C (293F).)
Disable E–side TCC OFF request.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
The DTC will be cleared from history when the vehicle
has achieved 40 warm–up cycles without a failure
reported.
The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled “off”
long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the PCM and at the transmission 16–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed, or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal tension
as well.
Also check for a chafed wire that could short to bare
metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken wire inside
the insulation.
When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
Check harness routing for a potential short to ground
in circuit RED/BLK–GRN/RED.
Scan tool TFT sensor temperature should rise
steadily to about 100
C (212F), then stabilize.
Check for a “skewed” (mis–scaled) sensor by
comparing the TFT sensor temperature to the
ambient temperature after a vehicle cold soak. A
“skewed” sensor can cause delayed garage shifts or
TCC complaints.
Check for a possible torque converter stator problem.
Verify customer driving habits, trailer towing, etc.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart.
3. This test checks for a “skewed” sensor or shorted
circuit.
4. This test simulates a TFT DTC P0713.
Page 2271 of 6000

7A1–26
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
DTC P0218 Transmission Fluid Over Temperature
StepActionYe sNo
1Perform the following checks:
Check for possible engine system problems.
Transmission fluid checking procedure. Refer to Checking
Transmission Fluid Level and Condition in Automatic
Transmission (4L30–E) Section.
Were the checks performed?
Go to Step 2—
21. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine “off”, turn the ignition switch “on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record “Failure
Records” for reference, as data will be lost when “Clear Info”
function is used.
3. Record the DTC “Failure Records”.
Is the TFT sensor signal voltage less than 0.33 volts?
Go to Step 3
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
31. Turn the ignition “off”.
2. Disconnect the transmission 16–way connector H–53
(additional DTCs may set).
Is the TFT sensor signal voltage greater than 4.92 volts?
Go to Internal
Wiring Harness
Check.
Go to Step 4
4Inspect/repair circuit RED/BLK–GRN/RED for a short to ground.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 6Go to Step 5
51. Inspect the PCM for poor connections.
2. Replace the PCM if no poor connections were found.
Is the replacement complete?
Go to Step 6—
61. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select “DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and ensure the following conditions
are met:
TFT is less than 125
C (257F) for at least 10 seconds.
2. Review the scan tool “DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified
Exit DTC table
Page 2272 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–27
DTC P0560 System Voltage Malfunction
D07RW030
Circuit Description
Circuit WHT is the battery voltage feed for the PCM.
Circuit RED/BLU is the ignition voltage feed for the PCM.
This DTC detects a low voltage or a high voltage. This is a
type “C” DTC.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
System Voltage Low:
Engine speed is greater than 1,000 rpm.
System voltage is less than 10 volts at a maximum
transmission temperature of 150
C (302F).
System voltage is less than 7.3 volts at a minimum
transmission temperature of –40
C (–40F).
All conditions met for 4 seconds.
System Voltage High:
System voltage is greater than 16 volts for 2 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
Fixed to 4th gear.
Maximum line pressure.
Inhibit TCC engagement.
The PCM will illuminate the CHECK TRANS Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
The PCM will turn off the CHECK TRANS Lamp after
three consecutive ignition cycles without a failure
reported.
The DTC will be cleared from history when the vehicle
has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a failure
reported.
The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled “off”
long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
Charging the battery with a battery charger and jump
starting an engine may set DTC(s). If DTC(s) set
when an accessory is operated, check for faulty
connections or excessive current draw.
Check for faulty connections at the starter solenoid or
fusible link.
Check for loose/damaged terminals at generator.
Check belt wear/tension.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart.
4. This test checks charging system voltage.
5. This test checks battery voltage input at the PCM.
7. This test checks ignition voltage input at the PCM.
Page 2273 of 6000

7A1–28
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
DTC P0560 System Voltage Malfunction
StepActionYe sNo
11. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine “off”, turn the ignition switch “on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record “Failure
Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the “Clear Info”
function is used.
3. Record the DTC “Failure Records”. Note: If any other DTCs
are present, refer to their applicable diagnostic charts before
continuing.
4. Using the J–39200 DVOM, measure the battery voltage
across the battery terminals. Record the measurement for
future reference.
Is the voltage higher than 10.5 volts?
Go to Step 2
Go to Engine
Electrical in
Engine section
2Start the engine and warm to normal operating temperature.
Is the generator/check engine light “on”?Go to Starting
and Charging
System in Engine
section
Go to Step 3
31. Increase the engine speed to 1,000–1,500 rpm.
2. Observe scan tool system voltage.
Is the system voltage within 13–15 volts.
Go to Step 4
Go to Starting
and Charging
System in Engine
section
41. Turn the ignition switch “off”.
2. Disconnect the J1(RED) and J3 (BLUE) PCM connector
(additional DTCs will set).
3. With the engine “off”, turn the ignition switch “on”.
4. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the battery voltage input at
PCM connector terminals J1–A4 and J3–E16.
Is there a voltage variance between the voltage measured at the
battery (taken in Step 1) and at terminals J1–A4 and J3–E16 that
is greater than 0.5 volts?
Go to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Repair the high resistance condition in circuit WHT.
Was the circuit repaired?
Go to Step 10—
61. Disconnect the J3 (BLUE) PCM connector.
2. Measure the ignition voltage input at PCM connector terminals
J3–E16 and J3–F16.
Is there a voltage variance between the voltage measured at the
battery (taken in Step 1) and at terminals J3–E16 and J3–F16 that
is greater than 0.5 volts?
Go to Step 7Go to Step 8
7Repair the high resistance condition is circuit RED/BLU.
Was the circuit repaired?
Go to Step 10—
8Check PCM connector terminals J1–A4, J3–E16 and J3–F16 for
bent, damaged, or backed out connector pins. Also check for
weak terminal tension.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 10Go to Step 9
Page 2275 of 6000

7A1–30
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
DTC P0705 Transmission Range Switch (Mode Switch) Illegal Position
D07RW031
Circuit Description
The range switch supplies the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) with information regarding the selector
lever position: P, R, N, D 3, 2 or L. The selector lever
position is indicated by the state of four ON/OFF
contracts. The range switch is located on one side of
the transmission. It is on the transmission manual
shaft and is fixed to the main case.
The range switch is also used to provide the
information P or N to the engine crank wiring. The
engine can be cranked only if connector M–25
terminal 4(H) is connected to terminal 1(E) which is
connected to ground.
The range switch is also used to provide the backup
lamp power in reverse. This is why the range switch is
supplied through a 10A fuse (C–3). This fuse can
burn due to a short circuit in the backup lamp.
This DTC detects when a fuse is open or the range switch
circuit does not work. This is a type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
Range switch illegal positions met for 5 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
Default to D position.
Inhibit torque management.
Maximum line pressure.
The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
The DTC will be cleared from history when the vehicle
has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a failure
reported.
The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled “off”
long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
Refer to accompanying chart for the normal range
signals and the illegal combinations.
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the PCM and at the transmission 8–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal tension
as we ll. A lso ch eck fo r a ch af e d w ire th at cou l d s ho r t
to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken wire
inside the insulation.
When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
Page 2276 of 6000
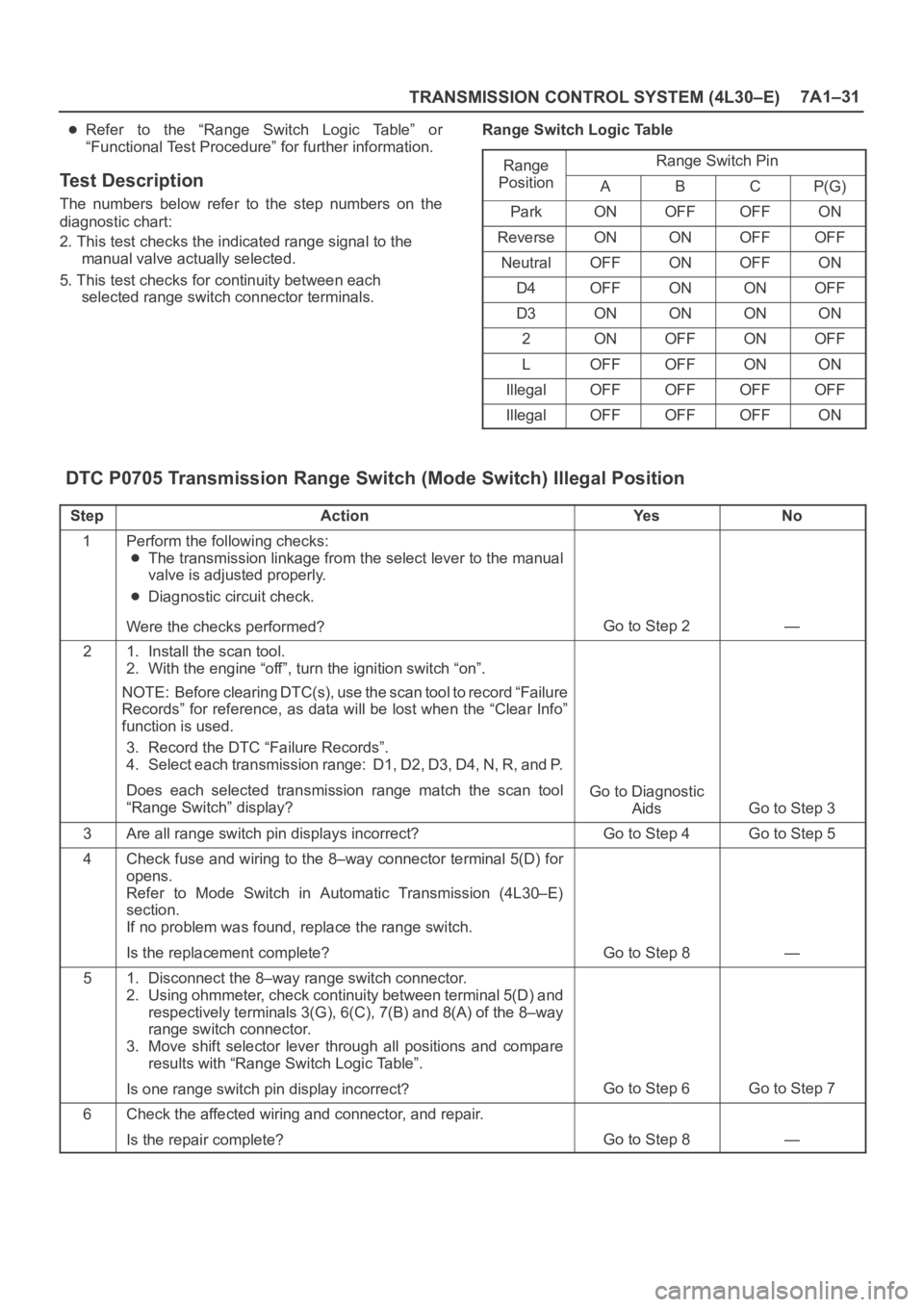
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–31
Refer to the “Range Switch Logic Table” or
“Functional Test Procedure” for further information.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
2. This test checks the indicated range signal to the
manual valve actually selected.
5. This test checks for continuity between each
selected range switch connector terminals.Range Switch Logic Table
Range
Range Switch Ping
PositionABCP(G)
ParkONOFFOFFON
ReverseONONOFFOFF
NeutralOFFONOFFON
D4OFFONONOFF
D3ONONONON
2ONOFFONOFF
LOFFOFFONON
IllegalOFFOFFOFFOFF
IllegalOFFOFFOFFON
DTC P0705 Transmission Range Switch (Mode Switch) Illegal Position
StepActionYe sNo
1Perform the following checks:
The transmission linkage from the select lever to the manual
valve is adjusted properly.
Diagnostic circuit check.
Were the checks performed?
Go to Step 2—
21. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine “off”, turn the ignition switch “on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record “Failure
Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the “Clear Info”
function is used.
3. Record the DTC “Failure Records”.
4. Select each transmission range: D1, D2, D3, D4, N, R, and P.
Does each selected transmission range match the scan tool
“Range Switch” display?
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 3
3Are all range switch pin displays incorrect?Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
4Check fuse and wiring to the 8–way connector terminal 5(D) for
opens.
Refer to Mode Switch in Automatic Transmission (4L30–E)
section.
If no problem was found, replace the range switch.
Is the replacement complete?
Go to Step 8—
51. Disconnect the 8–way range switch connector.
2. Using ohmmeter, check continuity between terminal 5(D) and
respectively terminals 3(G), 6(C), 7(B) and 8(A) of the 8–way
range switch connector.
3. Move shift selector lever through all positions and compare
results with “Range Switch Logic Table”.
Is one range switch pin display incorrect?
Go to Step 6Go to Step 7
6Check the affected wiring and connector, and repair.
Is the repair complete?
Go to Step 8—
Page 2278 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–33
DTC P0706 Transmission Range Switch (Mode Switch) Performance
D07RW031
Circuit Description
The range switch supplies the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) with information regarding the selector
l e v e r p o s i t i o n : P, R , N , D , 3 , 2 o r L . T h e s e l e c t o r l e v e r
position is indicated by the state of four ON/OFF
contracts. The range switch is located on one side of
the transmission. It is on the transmission manual
shaft and is fixed to the main case.
The range switch is also used to provide the
information P or N to the engine crank wiring. The
engine can be cranked only if connector M–25
terminal 4(H) is connected to terminal 1(E) which is
connected to ground.
The range switch is also used to provide the backup
lamp power in reverse. This is why the mode switch is
supplied through a 10A fuse (C–3). This fuse can
burn due to a shot circuit in the backup lamp.
This DTC detects an invalid state of the range switch
or the range switch circuit by deciphering the range
switch inputs. This is a type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
This DTC will set if any of the following conditions occurs:
Condition 1 (“R” bad position):
Engine is running.
No output speed DTCP0722, P0723.
Output speed greater then 3,200 RPM.
Range switch indicates “R”.
All conditions met for 4 seconds.
Condition 2 (“P” or “N” bad position):
Engine is running.
No TPS codes.
Engine speed is less than 3,000 RPM.
TP angle is greater than 20%.
Range switch indicates “P” or “N”.
All conditions met for 4 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
Default to “D” position.
The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
The DTC will be cleared from history when the vehicle
has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a failure
reported.
The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled “off”
long enough to power down the PCM.