ignition OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 2118 of 6000

6E–225 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
General Description
(ECM and Sensors)
57X Reference ECM Input
The engine control module (ECM) uses this signal from
the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor to calculate engine
RPM and crankshaft position at all engine speeds. The
ECM also uses the pulses on this circuit to initiate injector
pulses. If the ECM receives no pulses on this circuit, DTC
P0337 will set. The engine will not start and run without
using the 57X reference signal.
A/C Request Signal
This signal tells the ECM when the A/C mode is selected
at the A/C control head.
Refer to
A/C Clutch Circuit Diagnosis for A/C wiring
diagrams and diagnosis for the A/C electrical system.
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor provides a signal
used by the engine control module (ECM) to calculate the
ignition sequence. The CKP sensor initiates the 57X
reference pulses which the ECM uses to calculate RPM
and crankshaft position.
Refer to
Electronic Ignition System for additional
information.
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor and
Signal
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor sends a CMP signal
to the ECM. The ECM uses this signal as a “cylinder
distinction” to trigger the injectors in the power order. If the
ECM detects an incorrect CMP signal while the engine is
running, DTC P0341 will set, and the ECM triggers the
injectors in the power order.
Refer to
DTC P0341.
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a
thermistor (a resistor which changes value based on
temperature) mounted in the engine coolant stream. Low
coolant temperature produces a high resistance of
100,000 ohms at –40
C (–40F). High temperature
causes a low resistance of 70 ohms at 130
C (266F).
The ECM supplies a 5-volt signal to the ECT sensor
through resistors in the ECM and measures the voltage.
The signal voltage will be high when the engine is cold and
low when the engine is hot. By measuring the voltage, the
ECM calculates the engine coolant temperature. Engine
coolant temperature affects most of the systems that the
ECM controls.
The Tech 2 displays engine coolant temperature in
degrees. After engine start-up, the temperature should
rise steadily to about 85
C (185F). It then stabilizes
when the thermostat opens. If the engine has not been
run for several hours (overnight), the engine coolanttemperature and intake air temperature displays should
be close to each other. A hard fault in the engine coolant
sensor circuit will set DTC P0117 or DTC P0118.
0016
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read
Only Memory (EEPROM)
The electrically erasable programmable read only
memory (EEPROM) is a permanent memory chip that is
physically soldered within the ECM. The EEPROM
contains the program and the calibration information that
the ECM needs to control powertrain operation.
Unlike the PROM used in past applications, the EEPROM
is not replaceable. If the ECM is replaced, the new ECM
will need to be programmed. Equipment containing the
correct program and calibration for the vehicle is required
to program the ECM.
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is a thermistor
which changes its resistance based on the temperature of
air entering the engine. Low temperature produces a high
resistance of 100,000 ohms at –40
C (–40F). High
temperature causes low resistance of 70 ohms at 130
C
(266
F) . The ECM supplies a 5-volt signal to the sensor
through a resistor in the ECM and monitors the signal
voltage. The voltage will be high when the incoming air is
cold. The voltage will be low when the incoming air is hot.
By measuring the voltage, the ECM calculates the
incoming air temperature.
The Tech 2 displays the temperature of the air entering
the engine. The temperature should read close to the
ambient air temperature when the engine is cold and rise
as underhood temperature increases. If the engine has
not been run for several hours (overnight), the IAT sensor
temperature and engine coolant temperature should read
close to each other. A fault in the IAT sensor circuit will set
DTC P0112 or DTC P0113.
Page 2119 of 6000

6E–226
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
0018
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure. The MAP sensor
signal voltage to the ECM varies from below 2 volts at idle
(high vacuum) to above 4 volts.
The MAP sensor is used to determine the following:
Boost pressure for injector control.
Barometric pressure (BARO).
If the ECM detects a voltage that is lower than the
possible range of the MAP sensor, DTC P0107 will be set.
A signal voltage higher than the possible range of the
sensor will set DTC P0108. An intermittent low or high
voltage will set DTC P1107 or DTC P1106, respectively.
The ECM can detect a shifted MAP sensor. The ECM
compares the MAP sensor signal to a calculated MAP
based on throttle position and various engine load factors.
If the ECM detects a MAP signal that varies excessively
above or below the calculated value, DTC P0106 will set.
Engine Control Module (ECM)
The engine control module (ECM) is located in the engine
room.
The ECM constantly observes the information from
various sensors. The ECM controls the systems that
affect vehicle performance. The ECM performs the
diagnostic function of the system. It can recognize
operational problems, alert the driver through the MIL
(Service Engine Soon lamp), and store diagnostic trouble
codes (DTCs). DTCs identify the problem areas to aid the
technician in making repairs.
ECM Function
The ECM supplies 5, 12 and 110 volts to power various
sensors or switches. The power is supplied through
resistances in the ECM which are so high in value that a
test light will not light when connected to the circuit. In
some cases, even an ordinary shop voltmeter will not give
an accurate reading because its resistance is too low.
Therefore, a digital voltmeter with at least 10 megohms
input impedance is required to ensure accurate voltage
readings. The ECM controls output circuits such as theinjectors, glow relays, etc., by controlling the ground or
the power feed circuit through transistors or through
either of the following two devices:
Output Driver Module (ODM)
Quad Driver Module (QDM)
ECM Components
The ECM is designed to maintain exhaust emission levels
to government mandated standards while providing
excellent driveability and fuel efficiency. The ECM
monitors numerous engine and vehicle functions via
electronic sensors such as the crankshaft position (CKP)
sensor, and vehicle speed sensor (VSS). The ECM also
controls certain engine operations through the following:
Fuel injector control
Rail pressure control
ECM Voltage Description
The ECM supplies a buffered voltage to various switches
and sensors. It can do this because resistance in the
ECM is so high in value that a test light may not illuminate
when connected to the circuit. An ordinary shop
voltmeter may not give an accurate reading because the
voltmeter input impedance is too low. Use a 10-megohm
input impedance digital voltmeter to assure accurate
voltage readings.
The input/output devices in the ECM include
analog-to-digital converters, signal buffers, counters,
and special drivers. The ECM controls most components
with electronic switches which complete a ground circuit
when turned “ON.” These switches are arranged in
groups of 4 and 7, called either a surface-mounted quad
driver module (QDM), which can independently control up
to 4 output terminals, or QDMs which can independently
control up to 7 outputs. Not all outputs are always used.
ECM Input/Outputs
Inputs – Operating Conditions Read
Air Conditioning “ON” or “OFF”
Engine Coolant Temperature
Crankshaft Position
Electronic Ignition
Manifold Absolute Pressure
Battery Voltage
Intake Throttle Position
Vehicle Speed
Fuel Temperature
Oil Temperature
Intake Air Temperature
EGR boost pressure
Oil rail pressure
Camshaft Position
Accelerator position
Outputs – Systems Controlled
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
Injector Control
QWS
Page 2165 of 6000
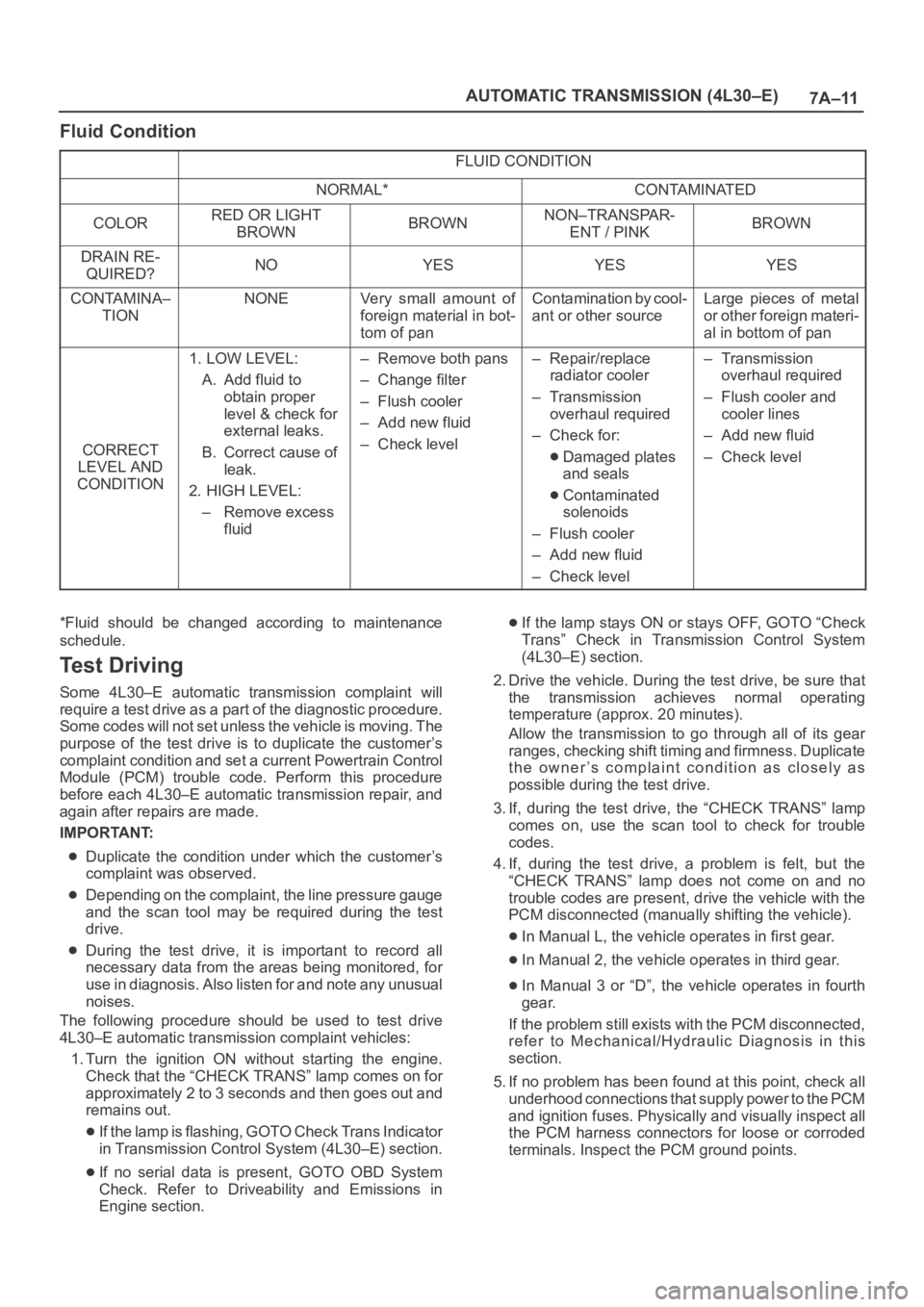
7A–11 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Fluid Condition
FLUID CONDITION
NORMAL*CONTAMINATED
COLORRED OR LIGHT
BROWNBROWNNON–TRANSPAR-
ENT / PINKBROWN
DRAIN RE-
QUIRED?NOYESYESYES
CONTAMINA–
TIONNONEVery small amount of
foreign material in bot-
tom of panContamination by cool-
ant or other sourceLarge pieces of metal
or other foreign materi-
al in bottom of pan
CORRECT
LEVEL AND
CONDITION
1. LOW LEVEL:
A. Add fluid to
obtain proper
level & check for
external leaks.
B. Correct cause of
leak.
2. HIGH LEVEL:
– Remove excess
fluid– Remove both pans
– Change filter
– Flush cooler
– Add new fluid
– Check level– Repair/replace
radiator cooler
–Transmission
overhaul required
– Check for:
Damaged plates
and seals
Contaminated
solenoids
– Flush cooler
– Add new fluid
– Check level
–Transmission
overhaul required
– Flush cooler and
cooler lines
– Add new fluid
– Check level
*Fluid should be changed according to maintenance
schedule.
Te s t D r i v i n g
Some 4L30–E automatic transmission complaint will
require a test drive as a part of the diagnostic procedure.
Some codes will not set unless the vehicle is moving. The
purpose of the test drive is to duplicate the customer’s
complaint condition and set a current Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) trouble code. Perform this procedure
before each 4L30–E automatic transmission repair, and
again after repairs are made.
IMPORTANT:
Duplicate the condition under which the customer’s
complaint was observed.
Depending on the complaint, the line pressure gauge
and the scan tool may be required during the test
drive.
During the test drive, it is important to record all
necessary data from the areas being monitored, for
use in diagnosis. Also listen for and note any unusual
noises.
The following procedure should be used to test drive
4L30–E automatic transmission complaint vehicles:
1. Turn the ignition ON without starting the engine.
Check that the “CHECK TRANS” lamp comes on for
approximately 2 to 3 seconds and then goes out and
remains out.
If the lamp is flashing, GOTO Check Trans Indicator
in Transmission Control System (4L30–E) section.
If no serial data is present, GOTO OBD System
Check. Refer to Driveability and Emissions in
Engine section.
If the lamp stays ON or stays OFF, GOTO “Check
Trans” Check in Transmission Control System
(4L30–E) section.
2. Drive the vehicle. During the test drive, be sure that
the transmission achieves normal operating
temperature (approx. 20 minutes).
Allow the transmission to go through all of its gear
ranges, checking shift timing and firmness. Duplicate
the owner’s complaint condition as closely as
possible during the test drive.
3. If, during the test drive, the “CHECK TRANS” lamp
comes on, use the scan tool to check for trouble
codes.
4. If, during the test drive, a problem is felt, but the
“CHECK TRANS” lamp does not come on and no
trouble codes are present, drive the vehicle with the
PCM disconnected (manually shifting the vehicle).
In Manual L, the vehicle operates in first gear.
In Manual 2, the vehicle operates in third gear.
In Manual 3 or “D”, the vehicle operates in fourth
gear.
If the problem still exists with the PCM disconnected,
refer to Mechanical/Hydraulic Diagnosis in this
section.
5. If no problem has been found at this point, check all
underhood connections that supply power to the PCM
and ignition fuses. Physically and visually inspect all
the PCM harness connectors for loose or corroded
terminals. Inspect the PCM ground points.
Page 2182 of 6000
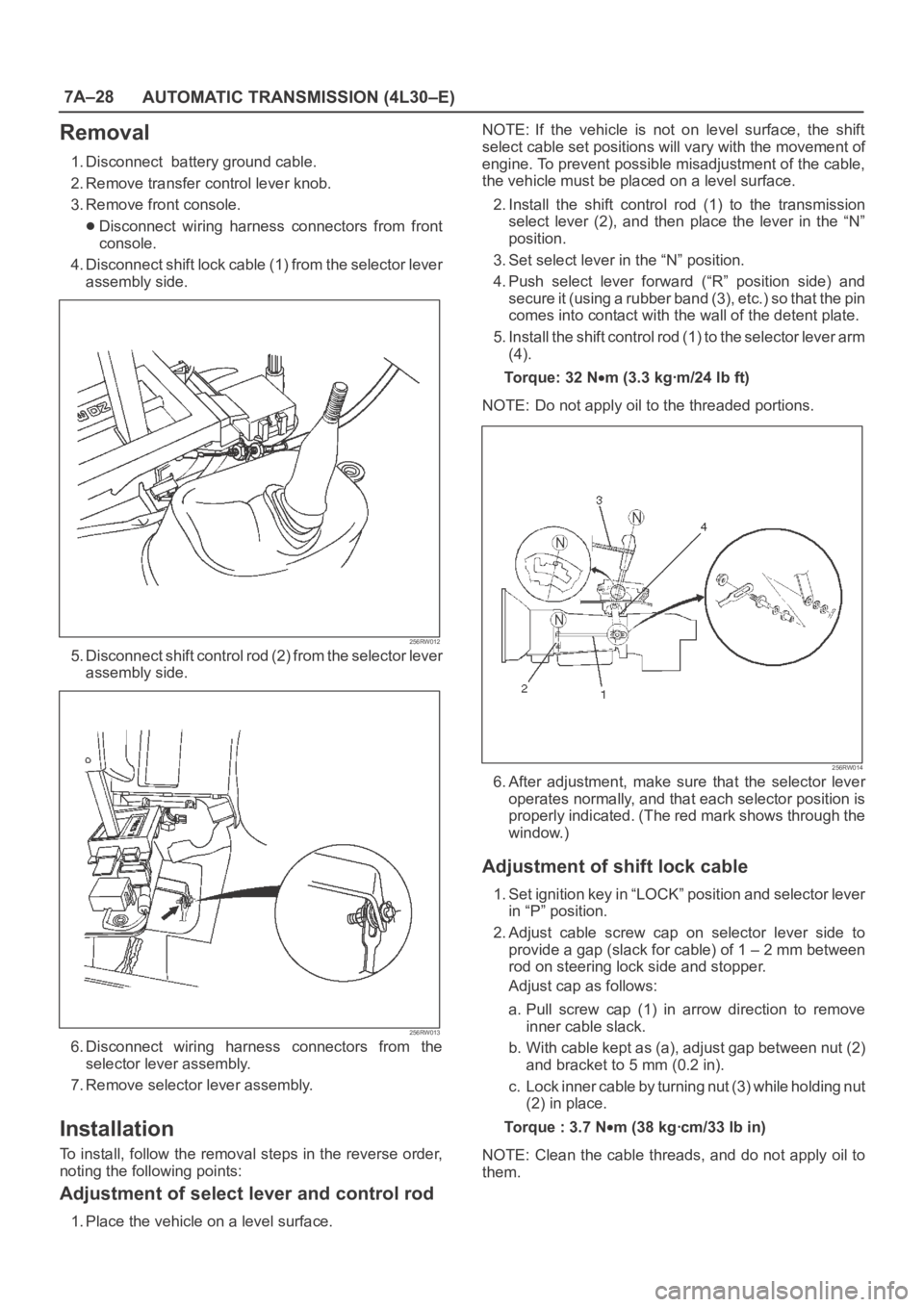
7A–28
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Removal
1. Disconnect battery ground cable.
2. Remove transfer control lever knob.
3. Remove front console.
Disconnect wiring harness connectors from front
console.
4. Disconnect shift lock cable (1) from the selector lever
assembly side.
256RW012
5. Disconnect shift control rod (2) from the selector lever
assembly side.
256RW013
6. Disconnect wiring harness connectors from the
selector lever assembly.
7. Remove selector lever assembly.
Installation
To install, follow the removal steps in the reverse order,
noting the following points:
Adjustment of select lever and control rod
1. Place the vehicle on a level surface.NOTE: If the vehicle is not on level surface, the shift
select cable set positions will vary with the movement of
engine. To prevent possible misadjustment of the cable,
the vehicle must be placed on a level surface.
2. Install the shift control rod (1) to the transmission
select lever (2), and then place the lever in the “N”
position.
3. Set select lever in the “N” position.
4. Push select lever forward (“R” position side) and
s e c u r e i t ( u s i n g a r u b b e r b a n d ( 3 ) , e t c . ) s o t h a t t h e p i n
comes into contact with the wall of the detent plate.
5. Install the shift control rod (1) to the selector lever arm
(4).
To r q u e : 3 2 N
m (3.3 kgꞏm/24 lb ft)
NOTE: Do not apply oil to the threaded portions.
256RW014
6. After adjustment, make sure that the selector lever
operates normally, and that each selector position is
properly indicated. (The red mark shows through the
window.)
Adjustment of shift lock cable
1. Set ignition key in “LOCK” position and selector lever
in “P” position.
2. Adjust cable screw cap on selector lever side to
provide a gap (slack for cable) of 1 – 2 mm between
rod on steering lock side and stopper.
Adjust cap as follows:
a. Pull screw cap (1) in arrow direction to remove
inner cable slack.
b. With cable kept as (a), adjust gap between nut (2)
and bracket to 5 mm (0.2 in).
c. Lock inner cable by turning nut (3) while holding nut
(2) in place.
Torque : 3.7 N
m (38 kgꞏcm/33 lb in)
NOTE: Clean the cable threads, and do not apply oil to
them.
Page 2183 of 6000

7A–29 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
256RW015
3. Check the shift lock operation:
a. Selector lever should not move out of “P” position
with ignition key in “Lock” position.
b. Selector lever can be moved out of “P” position with
ignition key in “ON” position only when brake pedal
is depressed.
c. Ignition key can be turned to “LOCK” position only
when selector lever is in “P” position (key can be
pulled out).
If (a) and (c) fail, readjust cable. If (b) fails, readjust
connector wiring and brake pedal switch.
Mode Switch
Removal
1. Place selector lever in neutral.
2. Disconnect battery ground cable.
3. Remove mode switch cover (1).
4. Disconnect selector lever (2) from the mode switch.
5. Disconnect transmission harness from the mode
switch connector (3).
6. Remove bracket with mode switch connector from
the transmission case.
7. Remove mode switch connector (3) from the bracket
(4).
8. Remove two mode switch bolts and nut then remove
mode switch (5).
210RW008
Installation
To install, follow the removal steps in the reverse order,
noting the following points;
1. Torque
Mode switch bolt: 13 N
m(1.3kgꞏm/113lbin)
Selector lever nut: 23 N
m (2.3 kgꞏm/17 lb ft)
2. Mode switch setting procedure
Perform either of the following adjustment
procedures:
Procedure 1
a. Place selector lever in neutral.
b. Remove selector lever from the mode switch.
c. Remove the mode switch cover.
d. Loosen the two 10 mm screws.
e. Rotate the mode switch until the slot in the mode
switch housing aligns with the selector shaft
bushing, and insert a 3/32 in. (2.4 mm) drill bit or
punch (1) into the slot.
f. Tighten the screws to 13 Nꞏm (1.3 kgꞏm/113 lb in).
g. After completing adjustment, snap the mode
switch cover into place.
h. Reinstall the selector lever.
Page 2254 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–9
Winter Drive Mode
1.Operation
The winter switch will operate when switched on after
all of the following conditions are present:
a. The gear select position is “D”, “N”, “R” and “P”
range.
b. Vehicle speed is 7 mph (11 km/h) or less.
c. Transmission oil temperature is 120
C (248F) or
less.
d. Kickdown switch is off.
e. Accelerator opening is at 8% or less.
2.Cancel Release
1. Cancellation by driver
a. Turning off the winter drive mode switch
b. Shifting select position to “3”, “2”, or “L” (Winter
drive mode is not canceled by selecting “D”, “N”,
“R”, or “P”)
c. Ignition key is turned off.
2. Automatic cancellation
a. When vehicle runs at 21mph (34 km/h) or more
for 1 second or more
b. When transmission oil temperature reaches
140
C (284F) or above
NOTE: The mode returns to normal drive mode or power
drive mode after the winter drive mode is canceled.
Backup Mode
If a major system failure occurs which could affect safety
or damage the transmission under normal vehicle
operation, the diagnostic system detects the fault and
overrides the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
The “CHECK TRANS” light flashes to alert the driver, and
the transmission must be manually shifted as follows:
Select lever position
Gear Ratio Selected
D4 (Fourth)
Manual 34 (Fourth)
Manual 23 (Third)
Manual L1 (First)
RReverse
Shifts are firmer to prevent clutch slip and consequent
wear. The fault should be corrected as soon as possible.
Page 2256 of 6000
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–11
Diagnosis
Electronic Diagnosis
How To Diagnose The Problem
1. To avoid incorrect diagnostics, this book needs to be
followed accurately. Unless stated, do not jump
directly to a section that could contain the solution.
Some important information may be missed.
2. The sections in CAPITALS and bold are the main
sections that can be found in the contents.
3. The GOTO “SECTION” means to continue to check
going to the “section”.
4. The GOTHROUGH “SECTION” means to go
through the “section” and then to go back to the place
the GOTHROUGH was written.
5. BASIC ELECTRIC CIRCUITS:
You should understand the basic theory of electricity.
This includes the meaning of voltage, amps, ohms,
and what happens in a circuit with an open or shorted
wire. You should also be able to read and understand
wiring diagrams.
Check Trans Indicator
Find CHECK TRANS indicator and verify if it is
A. Flashing: GOTO DIAGNOSTIC CHECK.
B. Staying on: GOTHROUGH CHECK TRANS
CHECK.
C. Is never ON when the ignition key is turned on:
GOTHROUGH CHECK TRANS CHECK
D. Is ON during 2 to 3 seconds at ignition but OFF after:
Normal operation. No DTC or malfunction.
821RW261
Diagnostic Check
This test determines if the transmission or its inputs,
outputs, connections, or sensors are failing.
1. Connect the Tech2: GOTHROUGH Te c h 2 O B D I I
CONNECTION.
2. Turn on the ignition but not the engine.3. Push “F2” on Tech2 to see the Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC):
4. Do you have a DTC?
YES: write down all code numbers and do the DTC
CHECK
NO: the DTC can not help you finding the problem.
1. GOTHROUGH “CHECK TRANS” CHECK
2. IF it is flashing and the flash is 0.2 seconds ON
and 0.2 seconds OFF, this means that you should
have a DTC stored. Please recheck GOTO
DIAGNOSTIC CHECK and if you find the same
problem, replace the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM).
Normal
C07RW047
Abnormal
C07RW048
Page 2257 of 6000
7A1–12
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
“Check Trans” Check
1. Indicator it is ON during 2 to 3 seconds at ignition (or
when the engine is cranked) but it is OFF after the
engine starts. The indicator is working normally
GOTO DIAGNOSTIC CHECK.
821RW261
Normal
C07RW047
2. Indicator it is flashing and the flash is 0.2 seconds ON
and 0.2 seconds OFF always when ignition is on
(engine cranked or not). This means that there is a
malfunction. GOTO DIAGNOSTICAbnormal
C07RW048
3. Indicator it is staying ON always when Ignition is ON.
1. This means that connection between the lamp
and the PCM is shorted to ground.
2. Verify if instrument panel terminal 3 of connector
I–9 is shorted to ground.
3. Verify if the PCM connector J1 (RED) terminal
A14 is shorted to ground.
4. Verify that the instrument panel terminal 15 of
connector I–9 is connected to battery.
5. IF problem solved: GOTO CHECK TRANS
INDICATOR.
NO:Replace Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
4. Indicator it is staying OFF with the ignition ON (engine
OFF).
1. This means that connection between the lamp
and the PCM is shorted to battery or opened.
2. Verify if instrument panel terminal 3 of connector
I–9 is shorted to battery or open.
3. Verify if the PCM connector J1 (RED) terminal
A14 is shorted to battery or open.
4. Verify that the instrument panel terminal 15 of
connector I–9 is connected to battery. If not,
check the fuses and the connections voltage.
5. IF problem solved: GOTO CHECK TRANS
INDICATOR.
NO: Replace Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
Page 2259 of 6000
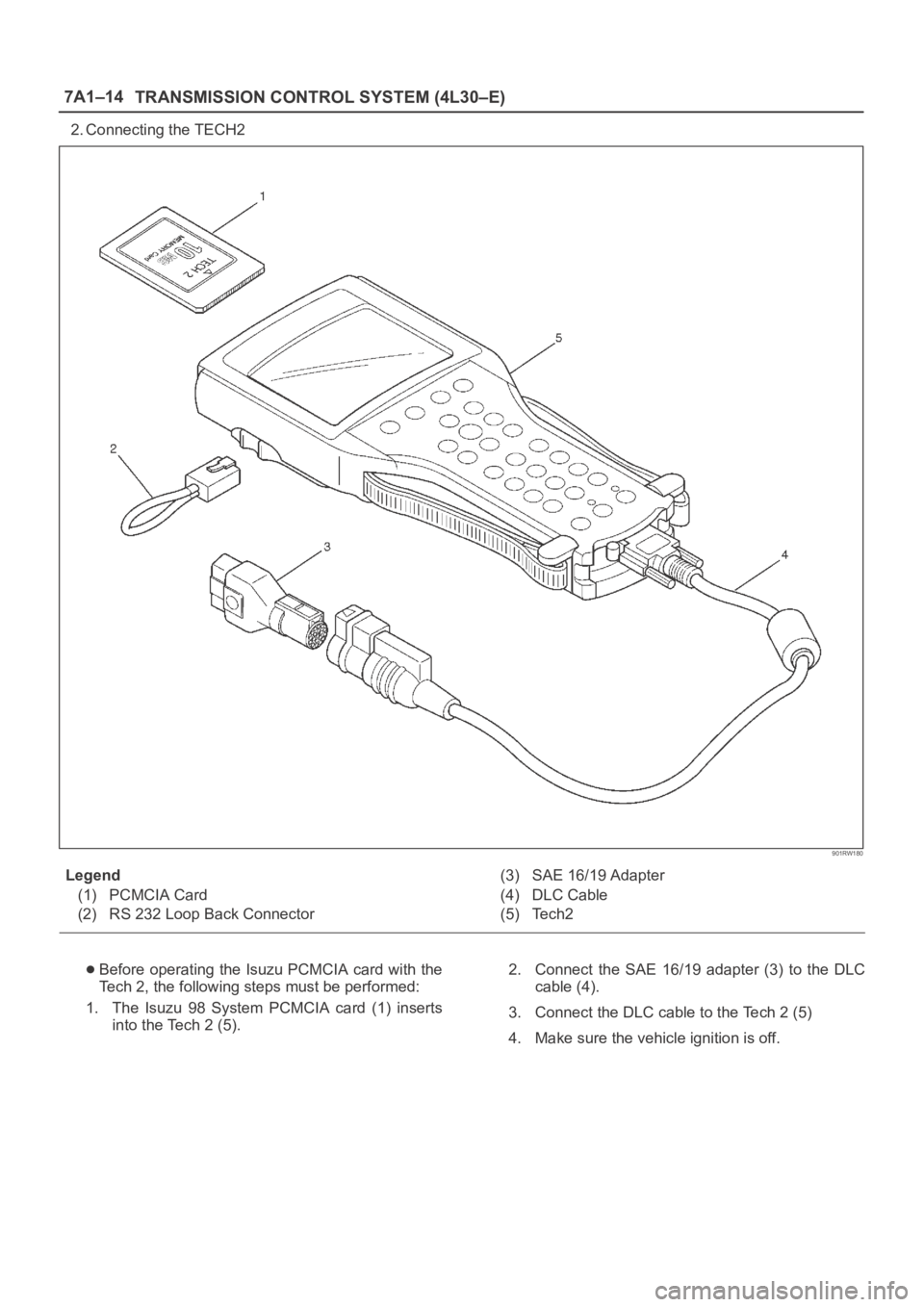
7A1–14
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
2. Connecting the TECH2
901RW180
Legend
(1) PCMCIA Card
(2) RS 232 Loop Back Connector(3) SAE 16/19 Adapter
(4) DLC Cable
(5) Tech2
Before operating the Isuzu PCMCIA card with the
Tech 2, the following steps must be performed:
1. The Isuzu 98 System PCMCIA card (1) inserts
into the Tech 2 (5).2. Connect the SAE 16/19 adapter (3) to the DLC
cable (4).
3. Connect the DLC cable to the Tech 2 (5)
4. Make sure the vehicle ignition is off.
Page 2260 of 6000
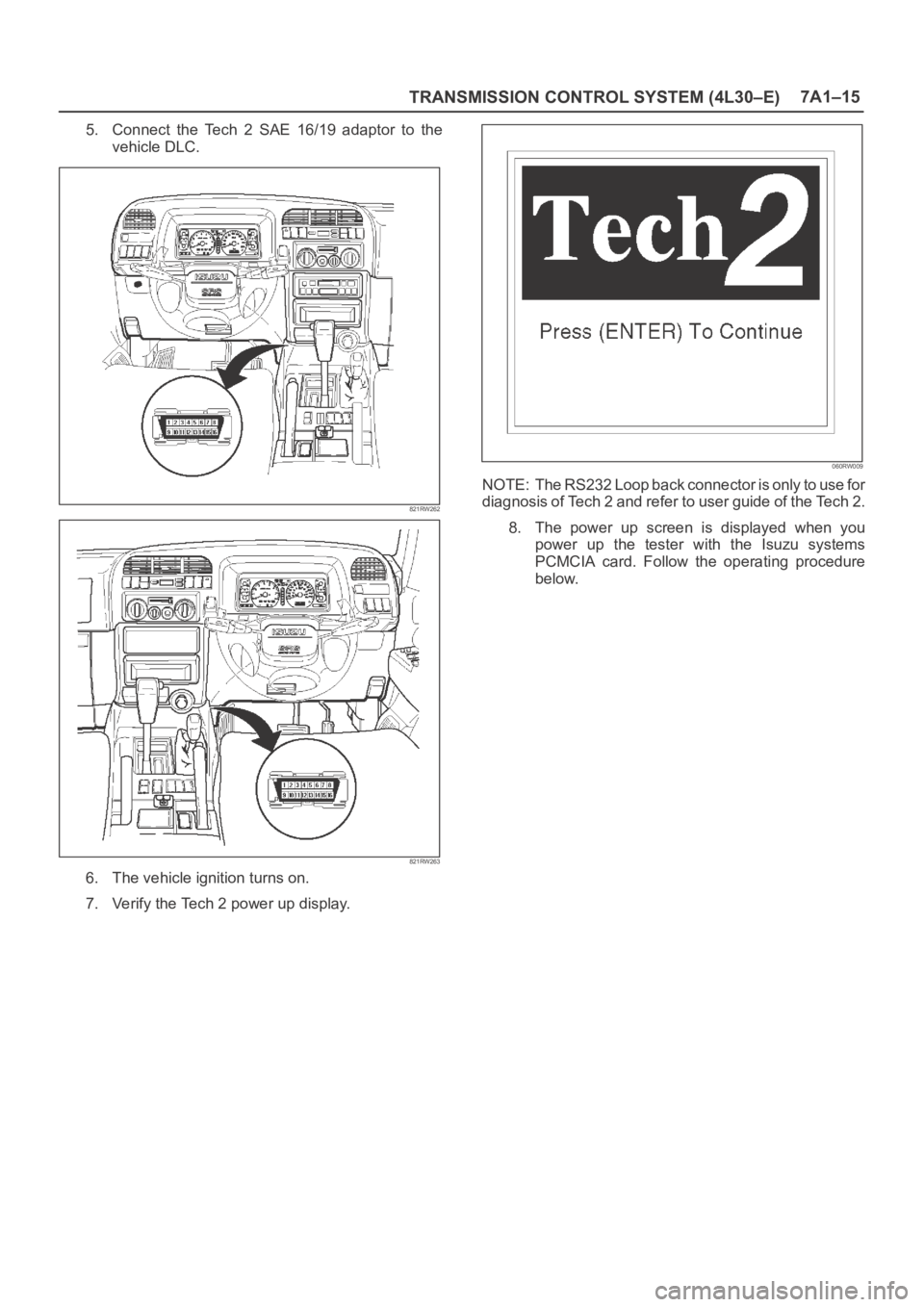
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–15
5. Connect the Tech 2 SAE 16/19 adaptor to the
vehicle DLC.
821RW262
821RW263
6. The vehicle ignition turns on.
7. Verify the Tech 2 power up display.
060RW009
NOTE: The RS232 Loop back connector is only to use for
diagnosis of Tech 2 and refer to user guide of the Tech 2.
8. The power up screen is displayed when you
power up the tester with the Isuzu systems
PCMCIA card. Follow the operating procedure
below.