SAAB 9-3 2001 Owners Manual
Manufacturer: SAAB, Model Year: 2001, Model line: 9-3, Model: SAAB 9-3 2001Pages: 260, PDF Size: 12.01 MB
Page 221 of 260
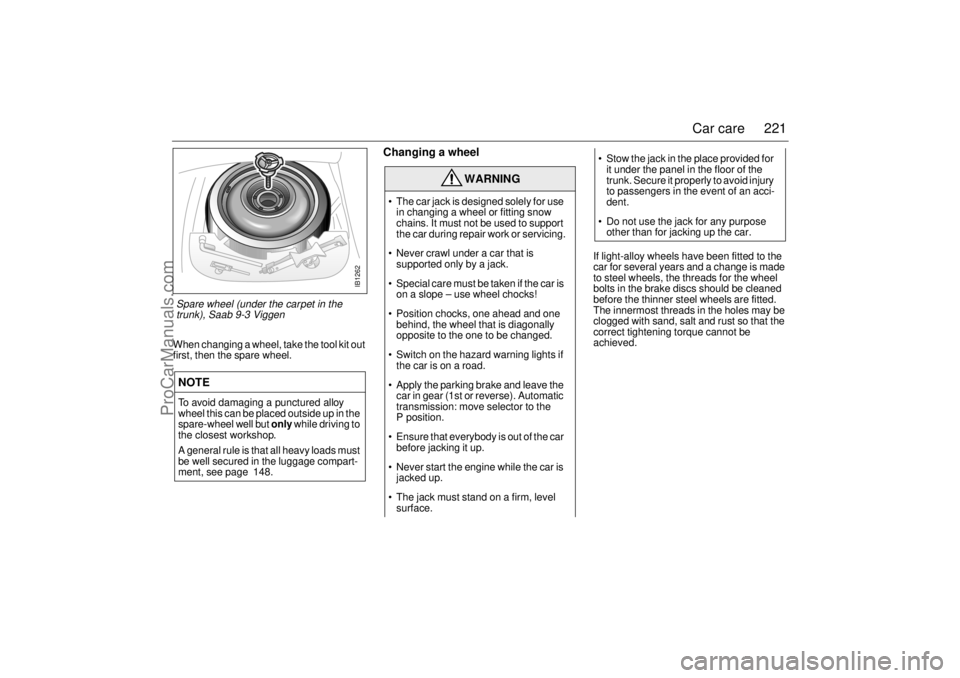
221 Car care
When changing a wheel, take the tool kit out
first, then the spare wheel.
Changing a wheel
If light-alloy wheels have been fitted to the
car for several years and a change is made
to steel wheels, the threads for the wheel
bolts in the brake discs should be cleaned
before the thinner steel wheels are fitted.
The innermost threads in the holes may be
clogged with sand, salt and rust so that the
correct tightening torque cannot be
achieved.
NOTETo avoid damaging a punctured alloy
wheel this can be placed outside up in the
spare-wheel well but only while driving to
the closest workshop.
A general rule is that all heavy loads must
be well secured in the luggage compart-
ment, see page 148.
WARNING
The car jack is designed solely for use
in changing a wheel or fitting snow
chains. It must not be used to support
the car during repair work or servicing.
Never crawl under a car that is
supported only by a jack.
Special care must be taken if the car is
on a slope – use wheel chocks!
Position chocks, one ahead and one
behind, the wheel that is diagonally
opposite to the one to be changed.
Switch on the hazard warning lights if
the car is on a road.
Apply the parking brake and leave the
car in gear (1st or reverse). Automatic
transmission: move selector to the
P position.
Ensure that everybody is out of the car
before jacking it up.
Never start the engine while the car is
jacked up.
The jack must stand on a firm, level
surface.
Stow the jack in the place provided for
it under the panel in the floor of the
trunk. Secure it properly to avoid injury
to passengers in the event of an acci-
dent.
Do not use the jack for any purpose
other than for jacking up the car.
IB1261IB1262
Spare wheel (under the carpet in the
trunk), Saab 9-3 Viggen
ProCarManuals.com
Page 222 of 260
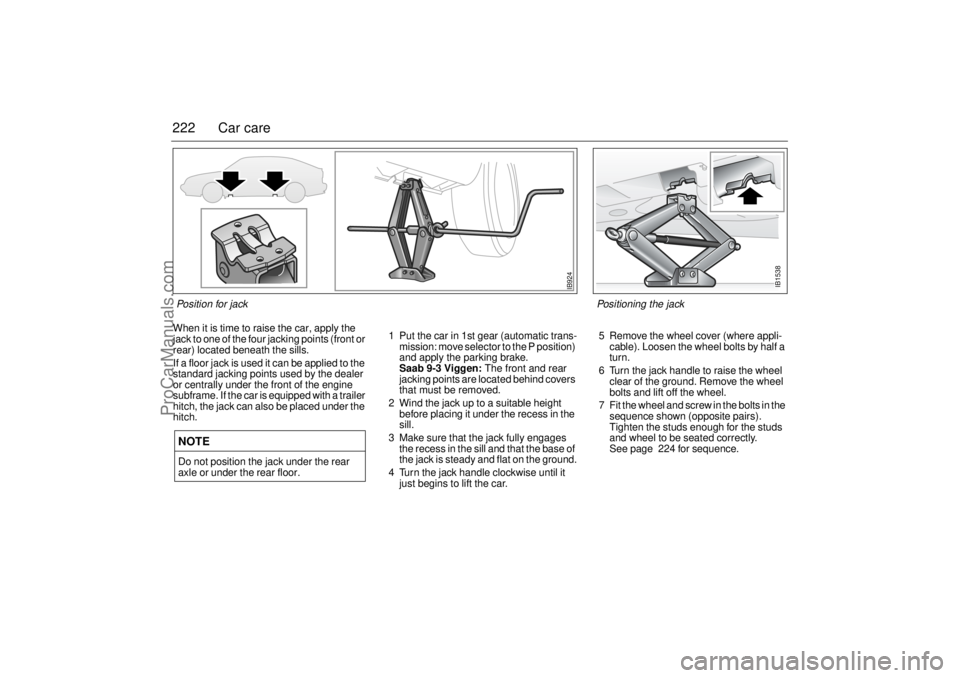
222 Car careWhen it is time to raise the car, apply the
jack to one of the four jacking points (front or
rear) located beneath the sills.
If a floor jack is used it can be applied to the
standard jacking points used by the dealer
or centrally under the front of the engine
subframe. If the car is equipped with a trailer
hitch, the jack can also be placed under the
hitch. 1 Put the car in 1st gear (automatic trans-
mission: move selector to the P position)
and apply the parking brake.
Saab 9-3 Viggen: The front and rear
jacking points are located behind covers
that must be removed.
2 Wind the jack up to a suitable height
before placing it under the recess in the
sill.
3 Make sure that the jack fully engages
the recess in the sill and that the base of
the jack is steady and flat on the ground.
4 Turn the jack handle clockwise until it
just begins to lift the car. 5 Remove the wheel cover (where appli-
cable). Loosen the wheel bolts by half a
turn.
6 Turn the jack handle to raise the wheel
clear of the ground. Remove the wheel
bolts and lift off the wheel.
7 Fit the wheel and screw in the bolts in the
sequence shown (opposite pairs).
Tighten the studs enough for the studs
and wheel to be seated correctly.
See page 224 for sequence.NOTEDo not position the jack under the rear
axle or under the rear floor.
IB924
Pos i ti o n for j ack
IB1538
Positioning the jack
ProCarManuals.com
Page 223 of 260
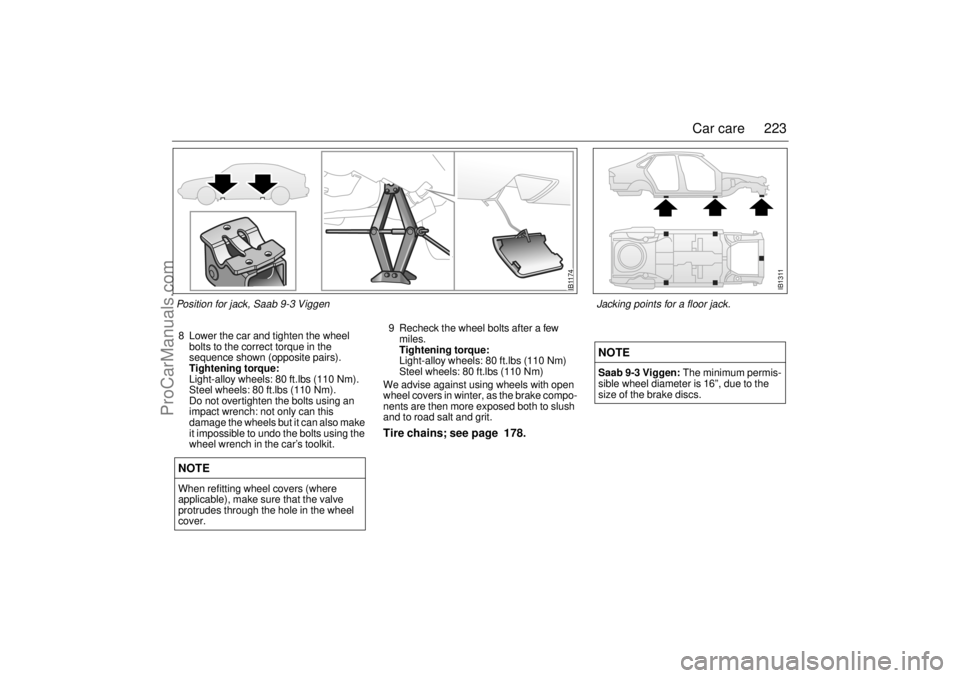
223 Car care
8 Lower the car and tighten the wheel
bolts to the correct torque in the
sequence shown (opposite pairs).
Tightening torque:
Light-alloy wheels: 80 ft.lbs (110 Nm).
Steel wheels: 80 ft.lbs (110 Nm).
Do not overtighten the bolts using an
impact wrench: not only can this
damage the wheels but it can also make
it impossible to undo the bolts using the
wheel wrench in the car’s toolkit.9 Recheck the wheel bolts after a few
miles.
Tightening torque:
Light-alloy wheels: 80 ft.lbs (110 Nm)
Steel wheels: 80 ft.lbs (110 Nm)
We advise against using wheels with open
wheel covers in winter, as the brake compo-
nents are then more exposed both to slush
and to road salt and grit.
Tire chains; see page 178.
NOTE
When refitting wheel covers (where
applicable), make sure that the valve
protrudes through the hole in the wheel
cover.
NOTESaab 9-3 Viggen: The minimum permis-
sible wheel diameter is 16”, due to the
size of the brake discs.
IB1174
Position for jack, Saab 9-3 Viggen
IB1311
Jacking points for a floor jack.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 224 of 260
224 Car care
Flat spottingAll tires get hot, especially on long journeys
or when the car is driven hard. After the car
has been parked with hot tires and the tires
have cooled down, a flat spot can form in the
tire, where it is in contact with the ground.
The same can occur if the car has not been
moved for a long time.
Flat spots can cause vibration that can be
felt through the steering wheel, similar to
that experienced when the wheels need bal-
ancing. Flat spots of this type disappear
once the tires get hot again, usually after
10–15 miles (20–25 km) of driving at cruis-
ing speed.
Safety beltsA check should be made periodically to
ensure that the safety belts are working
properly.
Hold the diagonal strap and pull it sharply.
The safety belt should lock and it should
not be possible to withdraw it further.
A sharp tug on the belt should cause the
inertia reel to lock. Check the floor anchor-
age points for corrosion damage. If a belt is
worn or has any fraying edges, it should be
replaced.
Safety belts must not come into contact with
substances such as polishes, oil or chemi-
cals. If the belts get dirty, wash them with
warm water and a detergent or have them
replaced.
WARNING
Safety belts and belt pretensioners that
were in use in a serious collision must be
replaced even if they are not visibly
damaged.
No attempt must be made to repair, or
modify the function of, safety belts.
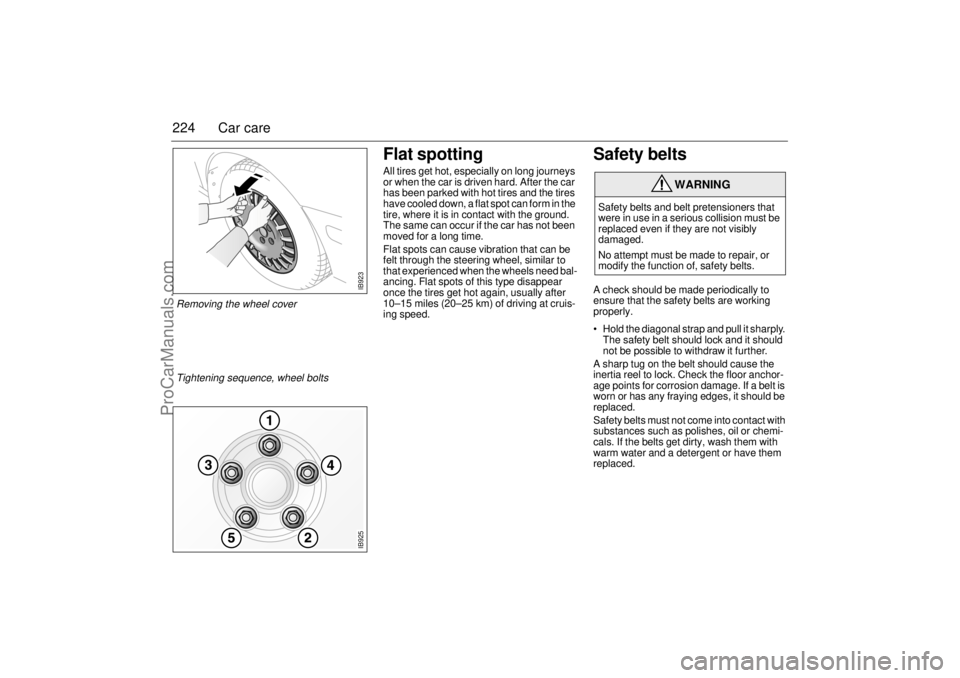
IB923
Removing the wheel cover
IB925
Tightening sequence, wheel bolts
ProCarManuals.com
Page 225 of 260

225 Car care
Upholstery and trimTo remove fluff or hairs from the seat uphol-
stery or headlining, use a moist, lint-free
cloth or a special lint remover (brush or
roller). Remove any dirty marks using a
cloth moistened with lukewarm soapy
water.
When using a stain remover, always work
from the outside towards the center to avoid
leaving a ring. If a soiled ring or spot should
remain, it can usually be removed using
lukewarm soapy water or water alone.
Wet patches left by spilled soft drinks or thin
oil must be wiped off immediately using an
absorbent material, such as paper toweling,
and treated with stain remover.
Isopropyl alcohol is recommended for
removing grease or oil stains, and a
semi-stiff brush may also be used.
Cleaning and caring for leather
upholsteryThe principal reason for treating leather
upholstery is to maintain its elegant appear-
ance and to provide it with a protective film.
Discoloration caused by dust and wear
mainly affects the lighter shades, although
this is not detrimental to the leather –
indeed, the patina resulting from use is often
considered desirable in leather. But if the
leather is allowed to become too grubby, it
can start to look shabby.
It is a good idea to clean and recondition the
leather twice a year – in conjunction with a
general spring-cleaning of the car – after the
winter and in the autumn, for instance. In
hot, dry climates, the leather will need to be
treated more frequently.
Moisten a soft cloth in a mild soap solution.
Carefully apply this damp (not wet) cloth to
the leather, working in light, circular move-
ments until the leather is clean. Repeat the
procedure using clean water and then leave
the leather to dry thoroughly. Finally, treat
the leather with a conditioner.Apply the leather conditioner using a soft
cloth and the same circular movements as
described above. After it has dried, polish
the leather with a soft, dry cloth. Follow the
directions given above. Do not use hot
water, unknown abrasive polishes, sol-
vents, sprays or soaps that might scratch
the leather. Look after the leather as
described and it will stay clean and attrac-
tive for many years.
Textile carpetingVacuum clean the carpeting regularly. Car-
pets can also be cleaned using a brush, or
carpet shampoo applied with a sponge. Do
not use vacuum cleaners outdoors unless
they are properly grounded.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 226 of 260

226 Car careEngine bayClean the engine compartment using an
engine detergent and rinse with hot water.
Cover the headlights. If using a high-pres-
sure washer do not aim the spray nozzle on
the:
Radiator
Throttle cable
Throttle housing
Other engine controls
The alternator
Ignition system and other electrical com-
ponents
Avoid spraying the hood liner, as this can
become heavy and hang down and touch
the engine when the hood is closed.
Additional care should be taken if using a
high-pressure washer. Hold the nozzle at
right angles to the area to be cleaned. This
is particularly important when spraying
labels.
Do not use gasoline as a cleaning agent or
solvent when carrying out repairs or mainte-
nance. Saab recommends the use of envi-
ronmentally safe degreasing agents.
WashingThe bodywork must be washed frequently.
When the car is new, the body should be
washed by hand using plain cold water and
a clean, soft brush, or in a brushless car-
wash that uses mild detergent. Automatic
carwashes with brushes should be avoided
when the car is new. Do not use automatic
car washes for the first five or six months,
before the paintwork has hardened prop-
erly. Thereafter, use a high quality car wash
soap added to lukewarm water.
Do not use a pressure washer at close
range on stone chip damage, scratches or
other damage to the paintwork. The paint
can otherwise start to flake.
Remove any bird droppings without delay,
as these can discolor the paintwork and
prove difficult to polish out.
Use a soft cloth moistened with methyl alco-
hol to remove splashes of tar or asphalt. Do
not use strong cleaners, as these can dry
out the paintwork. The underside of the car also needs wash-
ing regularly, and this should be done very
thoroughly at the end of winter. Clean the
underside of the car by hand if the car is usu-
ally washed in an automatic car wash with-
out special facilities for underbody cleaning.
Never wash or leave the car to dry in the
sun, but wipe it dry with a chamois leather
immediately after washing to avoid smears
and streaks.
Clean the window glass inside and out using
a high quality window cleaner. This is partic-
ularly important when the car is new, as
upholstery and trim have a tendency to
sweat a little at first.
Keep the glass well cleaned, as this helps to
prevent misting.NOTEAvoid using any alcohol-based cleaners
on the front and rear light clusters, as
these can cause cracking of the lenses.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 227 of 260

227 Car care
Waxing and polishingDo not wax a new car during the first three
or four months. In fact, there is no need to
polish the car before the paintwork has
started to go dull through oxidation. Other
than in exceptional cases, do not use abra-
sive polishes containing a cutting agent on
a new car. Always wash the car thoroughly
before waxing or polishing.
Touching up the paintDamaged paintwork should be treated as
soon as it is discovered: the longer it is left,
the greater the risk of corrosion. The
anti-perforation warranty does not cover
corrosion resulting from untreated defects.
Paintwork damage sustained in a collision is
usually extensive and can only be properly
restored by professionals.
However, you can repair small scratches
and stone-chip damage yourself. The nec-
essary tools and materials, such as primer,
touch-up paint and brushes, are available
from your Saab dealer.
In the case of minor flaws in the paintwork,
where the metal has not been exposed and
an undamaged layer of paint remains,
touch-up paint can usually be applied
directly, after any dirt has been scraped
away using a pointed knife.
If corrosion has already set in, e.g. as a
result of stone-chip damage, use a pointed
knife to scrape off all surface rust. If possi-
ble, the damaged area should be taken
back to the bare metal. The metal should
then be primed with two thin coats of primer
applied by brush.
After the primer has dried, apply several thin
layers of topcoat enamel until the surface of
the repaired area is flush with the surround-
ing paintwork.
Stir both primer and touch-up enamel thor-
oughly before use and allow each coat to
dry before applying the next.
NOTE Try your brakes on leaving a car wash.
Wet brake discs reduce the braking
effect.
Turn off the radio before entering an
automatic car wash so the power
antenna mast does not get damaged.
Clean the rod of the electrically pow-
ered antenna about once a month with
a clean, dry rag.
IMPORTANT! Use no oil, nor any sili-
cone-based cleaning product.
Fixed antennas must be removed
when going through an automatic car
wash.
Saab 9-3 Viggen, Coupé and
5-door: If you wash the car in an auto-
matic car wash, you must first remove
the roof-mounted antenna, otherwise
it will be damaged.
On Covertible models with OnStar,
fold down the cellular antenna
mounted on the windshield before
entering a car wash to avoid damage
to the antenna or convertible top.
IB1271
Removing the roof-mounted antenna,
Saab 9-3 Viggen Coupé and 5-door
ProCarManuals.com
Page 228 of 260

228 Car careTwo-coat enamelAs the name implies, two-coat enamel is
applied in two operations. The first coat, the
base color, contains the pigment, metal
flakes and binder. The second coat consists
of a clear enamel, which provides the final
gloss for the paintwork and protects the
base from moisture and environmental con-
taminants.
Touch-up stone-chip damage as follows:
1 Thoroughly clean the damaged area.
2 Then apply the primer, base color, and
finally, the enamel. To achieve the best
finish, apply two or three coats of primer.
Anti-corrosion
treatmentThe entire car is corrosion-protected at the
factory in different stages by an electrolytic
immersion coating and a polyester-based
protective coating to protect against corro-
sion caused by stones flung up by the
wheels. A thin penetrating anti-rust oil is
also applied in cavities and body members.
In addition to conventional anti-corrosion
treatment like painting, underbody treat-
ment and cavity treatment, most of the body
panel surfaces are galvanized. These
include the hood, the doors and the under-
body.
The anti-corrosion treatment on the under-
side of the car and inside the wheel arches
is particularly exposed to constant wear and
possible damage, the degree of which will
obviously depend on driving conditions.
IB1334
Surface-treatment composition 1 Body panel
2 Zinc (certain parts) 7.5 µm
3 Phosphate coating
4 Cathodic ED 28 µm
5 Intermediate coat 35 µm
6 Metallic base/solid base15 µm
7 Clear enamel 40 µm
ProCarManuals.com
Page 229 of 260

229 Car care
What causes rust?Steel body panels of automobiles are sub-
ject to rusting whenever air and moisture
manage to penetrate the protective finish.
Body panels may rust through if the process
is unchecked. Rusting can occur wherever
water is trapped or where the car’s panels
are continuously damp.
Damage to paint and undercoating by
stones, gravel and minor accidents immedi-
ately exposes metal to air and moisture.
Road salts used for de-icing will collect on
the bottom of the car and promote rusting.
Areas of the country with high humidity have
a greater potential for rust problems, espe-
cially where salt is used on roads or there is
moist sea air. Industrial pollution (fallout)
may also damage paint and promote rust-
ing.
Preventive maintenanceThe following procedures are necessary to
help protect against rusting. Refer also to
the terms and conditions of the Performa-
tion Limited Warranty described in the war-
ranty booklet.
1Wash the car frequently, and wax at
least twice a year. Under adverse con-
ditions, where there is a rapid buildup of
dirt, sand or road salt, wash your car at
least once a week. After extreme expo-
sure to salted snow or slush, evidenced
by a white film on the car, wash the car
immediately. Frequent washing will pre-
vent paint damage from acid rain and
other airborne contaminants such as
tree sap and bird droppings. If any of
these contaminants are noticed on the
car the finish should be washed immedi-
ately.
Begin washing by rinsing the entire car
with water to loosen and flush off heavy
concentrations of dirt (include the
underbody).
Sponge the car with a solution of either
a good quality car soap or mild general
purpose (dish washing) detergent and
water.
Rinse car thoroughly with clean water.
After washing, check and clear all
drains in doors and body panels.
Wipe the car dry, preferably using a
chamois.2Clean the underside of the car during
the winter. Use high pressure water to
clean the car’s underside (floor panels,
wheel wells) at least at mid- winter and
in the spring.
3Inspect the car frequently for leaks or
damage, and arrange for needed
repairs promptly. After washing or after
heavy rain, check for leaks. When wash-
ing the car inspect body surfaces for
paint damage. While checking for leaks,
lift the floor mats and check underneath
them. Water can collect in these areas
and remain for prolonged periods. Dry
any wet areas including the floor mats.
Have leaks repaired as soon as possi-
ble.
Use touch-up paint to repair small
scratches or minor finish damage. Areas
where metal is exposed will rust quickly
and MUST be repaired immediately by
touch-up or professional repainting.
Rust must be removed, the bare metal
primed and painted. Major body
damage should be repaired immediately
and new panels or exposed areas
should be undercoated with anti- corro-
sion material.
Repairs of this type are the owner’s
responsibility and are not covered under
warranty.
IB926
Drainage holes in doors
ProCarManuals.com
Page 230 of 260

230 Car careInspect the undercoating and touch up if
necessary. Pay particular attention to the
fenders and wheel housings, which are
exposed to abrasion by flying gravel, etc. If
the composition has worn or flaked off, the
steel must be thoroughly cleaned and dried
before a fresh coat is applied. The cleaning
is best done with a scraper and a steel wire
brush, followed by washing with solvent.
Apply the new coating thinly, otherwise it
may run off or fall off when dry.
Recovery and/or
recycling of automotive
materialsA typical car consists of metals (65–75%),
plastics (10–15%), rubber (5%) and small
quantities of glass, wood, paper and tex-
tiles.
Some of these materials can be recycled,
while others can be recovered in chemical
processes for reuse in new products or as a
source of energy.
While the Saab 9-3 was still at the draw-
ing-board stage, Saab engineers were
giving serious consideration to how the
maximum quantity of materials could be
reclaimed from the car on its eventual
scrapping. To facilitate sorting, plastic parts,
for instance, have been marked to identify
the precise nature of the plastic.Approximately 90% of the materials in the
car can be recycled or recovered, where
facilities exist.
Before the car is scrapped, all the oils and
other fluids that could pollute the environ-
ment should be recovered from the car. It
may be of interest in this context to learn that
the refrigerant used in the Saab 9-3’s A/C
and ACC systems (R134a) contains neither
CFCs nor any other chlorine compounds
ProCarManuals.com