warning SKODA YETI 2015 1.G / 5L Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SKODA, Model Year: 2015, Model line: YETI, Model: SKODA YETI 2015 1.G / 5LPages: 232, PDF Size: 30.84 MB
Page 121 of 232
Deactivating/activating›Press the symbol button » Fig. 133 .
When system is deactivated, the warning light in the button illuminates.
If the system is turned off, it will be automatically reactivated after turning the
ignition off and on.
Note
If the system is deactivated when the engine is turned off automatically, then
the automatic start process takes place.
Information messages
The warning symbols are shown in the instrument cluster display.
Start engine manually!START MANUALLY
If for example the driver's seat belt is stored, the engine must be started man-
ually.
On vehicles with the starter button the ignition is turned off by the first press
of the start button, only after pressing for the second time is the start process
initiated.
Error: Start-StopERROR START-STOP
A system error is present. Seek help from a specialist garage.
Brakes and parking
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Information on braking
119
Handbrake
120
Parking
121WARNING■ Greater physical effort is required for braking when the engine is switch-
ed off – risk of accident!■
During the braking procedure on a vehicle with manual transmission,
when the vehicle is in gear and at low revs, press the clutch pedal. Other-
wise, the functionality of the brake system may be impaired – risk of acci-
dent!
■
When leaving the vehicle never leave persons leave unattended in the
vehicle who could release the brake. The vehicle could then start to move –
risk of accident!
■
Observe the recommendations on the new brake pads » page 125, New
brake pads .
CAUTION
Never let the brakes slip with light pressure on the pedal if braking is not nec-
essary. This causes the brakes to overheat and can also result in a longer brak-
ing distance and excessive wear.
Information on braking
Read and observe
and on page 119 first.
Wear-and-tear
The wear of the brake pads is dependent on the operating conditions and driv-
ing style.
The brake pads wear more quickly if a lot of journeys are completed in towns
and over short distances or if a very sporty style of driving is adopted.
If operated under severe conditions , the thickness of the brake pads must be
checked by a specialist garage between service appointments as well.
Wet roads or road salt
The performance of the brakes can be delayed as the brake discs and brake
pads may be moist or have a coating of ice or layer of salt on them in winter.
The brakes are cleaned and dried by applying the brakes several times »
.
Corrosion
Corrosion on the brake discs and dirt on the bake pads occur if the vehicle has
been parked for a long period and if you do not make much use of the braking
system. The brakes are cleaned by applying the brakes several times »
.
119Starting-off and Driving
Page 122 of 232
Long or steep slopes
Before travelling a long distance with a steep gradient, reduce speed and shift
into the next lowest gear. As a result, the braking effect of the engine will be
used, reducing the load on the brakes. Any additional braking should be com-
pleted intermittently, not continuously.
Emergency brake display
If the brakes are applied in full and the vehicle systems evaluate the situation
as dangerous for the traffic following behind, the brake light flashes automati-
cally.
After the speed was reduced below around 10 km/h or the vehicle was stop-
ped, the brake light stops flashing and the hazard warning light system
switches on. The hazard warning light system is switched off automatically af-
ter accelerating or driving off again.
Faults in the brake surface
If it is found that the braking distance has suddenly become longer and that
the brake pedal can be depressed further, the brake system may be faulty.
Visit a specialist garage immediately and adjust your style of driving appropri-
ately, as you will not know the exact extent of the damage.
Low brake fluid level
An insufficient level of brake fluid may result in problems in the brake system.
The level of the brake fluid is monitored electronically » page 33,
Brake sys-
tem .
Brake booster
The brake booster increases the pressure generated with the brake pedal. The
brake booster only operates when the engine is running.WARNINGOnly apply the brakes for the purpose of drying and cleaning the brake
discs if the traffic conditions permit this. Do not place any other road users
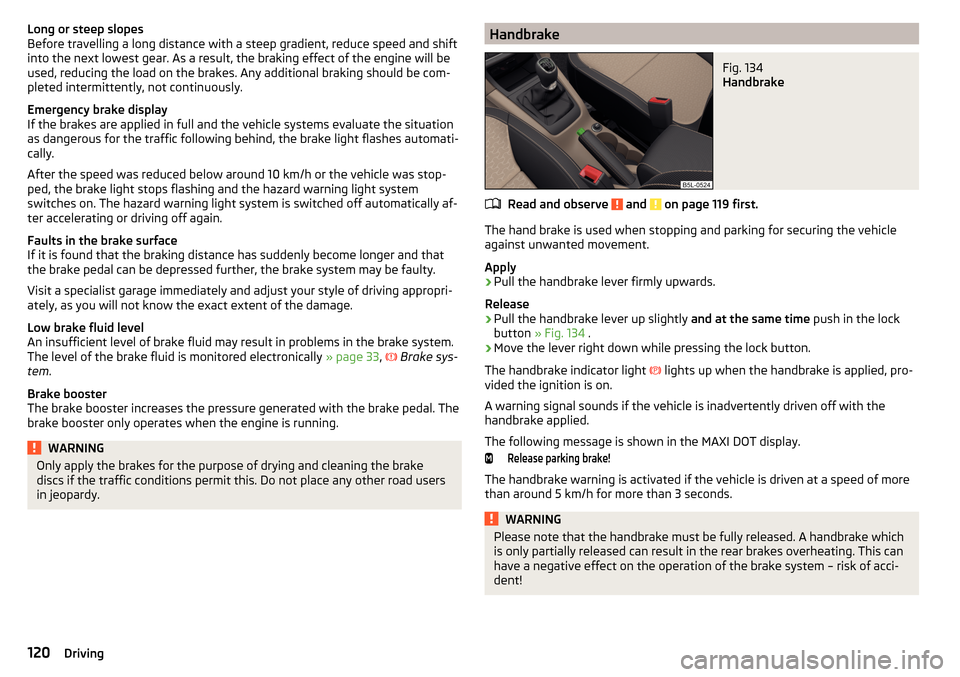
in jeopardy.HandbrakeFig. 134
Handbrake
Read and observe and on page 119 first.
The hand brake is used when stopping and parking for securing the vehicle
against unwanted movement.
Apply
›
Pull the handbrake lever firmly upwards.
Release
›
Pull the handbrake lever up slightly and at the same time push in the lock
button » Fig. 134 .
›
Move the lever right down while pressing the lock button.
The handbrake indicator light lights up when the handbrake is applied, pro-
vided the ignition is on.
A warning signal sounds if the vehicle is inadvertently driven off with the
handbrake applied.
The following message is shown in the MAXI DOT display.
Release parking brake!
The handbrake warning is activated if the vehicle is driven at a speed of more
than around 5 km/h for more than 3 seconds.
WARNINGPlease note that the handbrake must be fully released. A handbrake which
is only partially released can result in the rear brakes overheating. This can
have a negative effect on the operation of the brake system – risk of acci-
dent!120Driving
Page 123 of 232
ParkingRead and observe
and on page 119 first.
When stopping and parking, look for a place with a suitable surface » .
Only carry out the activities while parking in the specified order.
›
Bring the vehicle to a stop and depress the brake pedal.
›
Firmly apply the handbrake.
›
On vehicles with automatic transmission place the selector lever in the P po-
sition.
›
Switch off the engine.
›
For vehicles with Manual transmission select the 1st gear or the Reverse
gear R .
›
Release the brake pedal.
WARNINGThe exhaust system components can become very hot. Therefore, never
stop the vehicle at places where the underside of your vehicle can come in-
to contact with flammable materials such as dry grass, undergrowth,
leaves, spilled fuel or such like. - Risk of fire and serious injury can occur!
Manual gear changing and pedals
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Manual gear changing
121
Pedals
121
Manual gear changing
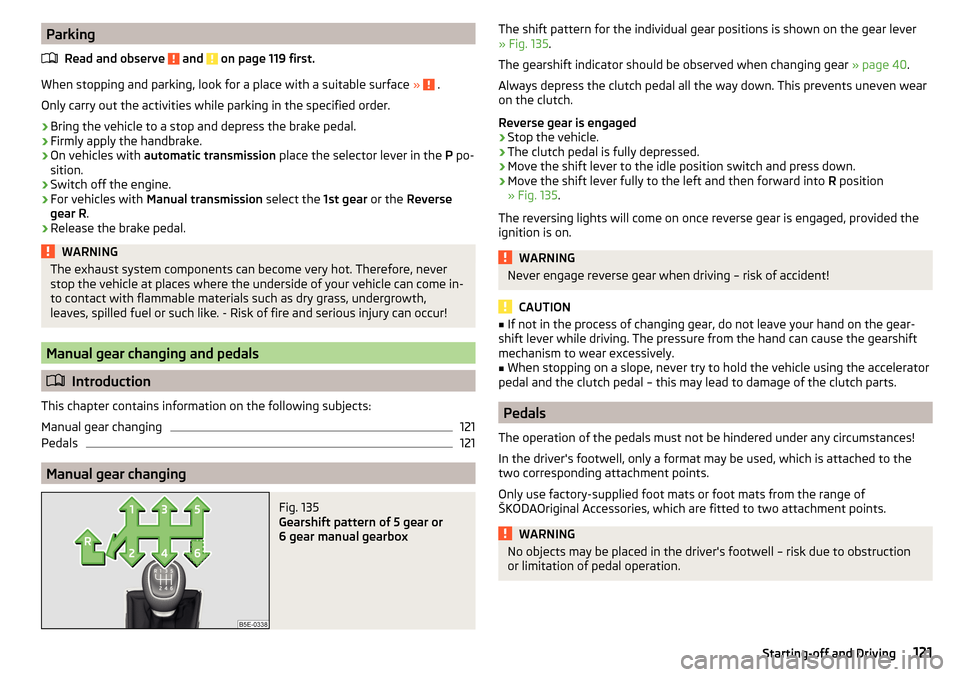
Fig. 135
Gearshift pattern of 5 gear or
6 gear manual gearbox
The shift pattern for the individual gear positions is shown on the gear lever » Fig. 135 .
The gearshift indicator should be observed when changing gear » page 40.
Always depress the clutch pedal all the way down. This prevents uneven wear
on the clutch.
Reverse gear is engaged›
Stop the vehicle.
›
The clutch pedal is fully depressed.
›
Move the shift lever to the idle position switch and press down.
›
Move the shift lever fully to the left and then forward into R position
» Fig. 135 .
The reversing lights will come on once reverse gear is engaged, provided the
ignition is on.
WARNINGNever engage reverse gear when driving – risk of accident!
CAUTION
■ If not in the process of changing gear, do not leave your hand on the gear-
shift lever while driving. The pressure from the hand can cause the gearshift
mechanism to wear excessively.■
When stopping on a slope, never try to hold the vehicle using the accelerator
pedal and the clutch pedal – this may lead to damage of the clutch parts.
Pedals
The operation of the pedals must not be hindered under any circumstances!
In the driver's footwell, only a format may be used, which is attached to the
two corresponding attachment points.
Only use factory-supplied foot mats or foot mats from the range of
ŠKODAOriginal Accessories, which are fitted to two attachment points.
WARNINGNo objects may be placed in the driver's footwell – risk due to obstruction
or limitation of pedal operation.121Starting-off and Driving
Page 124 of 232
Automatic transmission
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Modes and use of selector lever
122
Selector lever lock
123
Manual shifting of gears (Tiptronic)
123
Starting-off and driving
124
The automatic transmission performs automatic gear changes.
The modes of the automatic transmission can be adjusted by the driver by
means of the selector lever.
WARNING■ No throttle when it is set before starting the mode for moving forward
with the selector lever - there is a risk of accident!■
Never move the selector lever to mode R or P when driving – risk of an
accident!
■
If the vehicle is in the mode selected D, S , R or Tiptronic and the engine
stops when at idle speed, then the brake pedal must be pressed. Even
when the engine is idling, the power transmission is never completely in-
terrupted – the vehicle creeps.
■
When leaving the vehicle, the selector lever is always to put in the P
mode. Otherwise, the vehicle could be set in motion - risk of accident!
CAUTION
■ If the selector lever is moved to mode N while driving, the accelerator pedal
must be released and you will need to wait until the engine has reached its
idling speed before moving the selector lever to a forward driving mode again.■
When the outdoor temperature is below -10 ° C, the selector lever when
starting must always be in P mode.
■
When stopping on a slope, never try to hold the vehicle using the accelerator
pedal – this may lead to gear damage.
Note
After the ignition is switched off, the ignition key can only be withdrawn if the
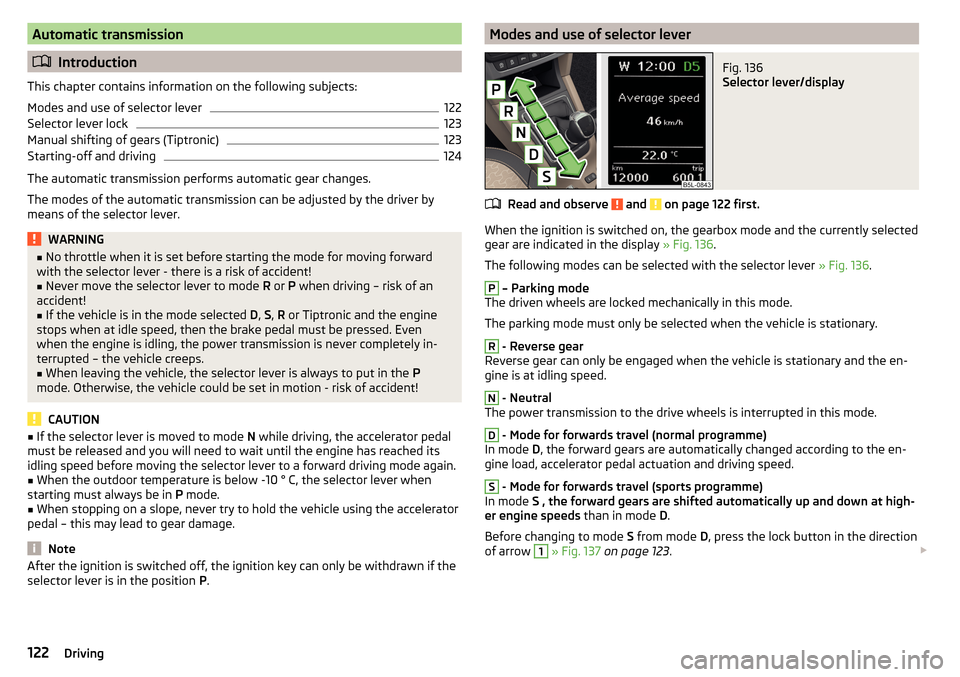
selector lever is in the position P.Modes and use of selector leverFig. 136
Selector lever/display
Read and observe and on page 122 first.
When the ignition is switched on, the gearbox mode and the currently selected
gear are indicated in the display » Fig. 136.
The following modes can be selected with the selector lever » Fig. 136.
P
– Parking mode
The driven wheels are locked mechanically in this mode.
The parking mode must only be selected when the vehicle is stationary.
R
- Reverse gear
Reverse gear can only be engaged when the vehicle is stationary and the en-
gine is at idling speed.
N
- Neutral
The power transmission to the drive wheels is interrupted in this mode.
D
- Mode for forwards travel (normal programme)
In mode D, the forward gears are automatically changed according to the en-
gine load, accelerator pedal actuation and driving speed.
S
- Mode for forwards travel (sports programme)
In mode S , the forward gears are shifted automatically up and down at high-
er engine speeds than in mode D.
Before changing to mode S from mode D, press the lock button in the direction
of arrow
1
» Fig. 137 on page 123 .
122Driving
Page 125 of 232

Fault in the automatic gearbox
A fault in the automatic gearbox can, for example, be noticeable by the follow-
ing.
▶ Only certain gears are selected.
▶ The reverse gear R cannot be used.
▶ Shifting gears in Tiptronic mode is not possible.
CAUTION
If an error occurs on the automatic transmission the help of a specialist firm
should be sought immediately - there is a risk of damaging the vehicle.
Selector lever lock
Fig. 137
Shift lock button
Read and observe and on page 122 first.
The selector lever is locked in mode P and N to prevent that the forward driv-
ing is selected accidentally, thereby setting the vehicle in motion.
The selector lever is locked only when the vehicle is stationary and at speeds
up to 5 km/h.
The selector lever lock is indicated by the illumination of the warning light
.
The selector lever is not locked when quickly moving across the position N
(e.g. from R to D). This, for example, helps to rock out a vehicle that is stuck,
e.g. in a bank of snow. The selector lever lock will engage if the lever is in posi-
tion N for more than approx. 2 seconds without the brake pedal being de-
pressed.
Releasing selector lever from mode P or N (selector lever lock)
›
Press the brake pedal and the lock button at the same time in the direction
of
1
» Fig. 137 .
Just depress the brake pedal, if you would like to change from the mode N to
D .
Defective selector lever lock
If the selector lever lock is defective or its power supply is interrupted (e.g. dis-
charged vehicle battery, faulty fuse), the selector lever can no longer be moved
out of position P in the normal manner and the vehicle can no longer be driven.
The selector lever must be unlocked specially » page 195.
Note
If you want to move the selector lever from mode P to mode D or vice versa,
move the selector lever quickly. This prevents that you accidentally select
mode R or N.
Manual shifting of gears (Tiptronic)
Fig. 138
Selector lever
Read and observe and on page 122 first.
Tiptronic mode makes it possible to manually shift gears on the selector lever.
This mode can be selected both while stopping and while driving.
The currently selected gear is indicated in the display » Fig. 136 on page 122 .
The gearshift indicator should be observed when changing gear » page 40.
Switching to manual shifting
›
Push the gear selector from mode D towards the right, or left in a right-hand
drive vehicle.
Shifting up gears
›
Push the selector lever forwards
+
» Fig. 138 .
Shifting down gears
›
Push the selector lever backwards
-
» Fig. 138 .
123Starting-off and Driving
Page 126 of 232
Note■It may be beneficial, for example, when travelling downhill, to use manual
shifting of gears. Shifting to a lower gear reduces the load on the brakes and
hence the wear of the brakes » page 119, Information on braking .■
When accelerating, the gearbox automatically shifts up into the higher gear
just before the maximum permissible engine speed is reached.
■
If a lower gear is selected, the gearbox does not shift down until there is no
risk of the engine overrevving.
Starting-off and driving
Read and observe
and on page 122 first.
Starting off
›
Start the engine.
›
Firmly depress and hold the brake pedal.
›
Press the lock button in the direction of
1
» Fig. 137 on page 123 and hold.
›
Move the selector lever into the desired position » page 122 and then release
the lock button.
›
Release the brake pedal and accelerate.
Stopping (while the car is moving)
›
Depress the brake pedal and bring the vehicle to a stop.
›
Keep holding the brake pedal until driving is resumed.
The selector lever position N does not have to be selected when stopping for a
short time, such as at a cross roads.
Kickdown
The kickdown function allows you to achieve the maximum acceleration of
your vehicle while driving.
When the accelerator pedal is fully depressed, the kickdown function is activa-
ted in any forward driving mode.
The gearbox shifts down one or more gears depending on the vehicle speed
and engine speed, and the vehicle accelerates.
The gearbox does not shift up into the highest gear until the engine has
reached its maximum revolutions for this gear range.
Driving in Neutral (Coasting) 1)›In the MAXI DOT display in the menu
Settings
activate the menu item
Coasting
» page 44
.
›
Move the selector lever into the position D.
›
Remove your foot from the accelerator pedal (the speed is higher than 20
km/h).
The vehicle moves without the braking effect of the engine.
The gear is automatically inserted again by depressing either the accelerator
or brake pedal.
WARNINGRapid acceleration, particularly on slippery roads, can lead to loss of control
of the vehicle – risk of accident!
Running-in and economical driving
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Running-in
124
Tips for economical driving
125
The fuel consumption, degree of pollution and vehicle wear depend on driving
style, road condition, weather conditions and the like.
Running-in
Driving in the engine
The engine has to be run in during the first 1 500 kilometres. During this peri-
od, the driving style decides on the quality of the driving-in process.
During the first 1 000 km we recommend not driving faster than 3/4 of the
maximum permissible engine speed, not to drive at full throttle and to dis-
pense with the trailer.
In the area of 1,000 to 1,500 kilometres the engine load can be increased up
to the maximum permitted engine speed.
1)
This function is only valid for some engines.
124Driving
Page 128 of 232

WARNING■Always adjust your driving to the current terrain and weather conditions.
Excessive speed or incorrect driving manoeuvres can cause damage to the
vehicle and lead to serious injuries.■
Combustible objects such as dry leaves or twigs caught under the base of
the vehicle could ignite on hot vehicle parts - risk of fire!
CAUTION
■ Pay attention to the ground clearance of the vehicle! When driving over ob-
jects which are larger than the ground clearance, the vehicle can get damaged.■
Any objects that get trapped under the vehicle floor must be removed as
soon as possible. These objects can damage the fuel lines, the brake system,
seals and other parts of the vehicle.
■
Drive slowly in unknown terrain and watch out for unexpected obstacles,
such as potholes, rocks, stumps, etc.
■
Check up on confusing sections of unpaved roads before travelling on them
and consider whether such travelling is possible without risk.
Driving through water
Fig. 139
Maximum permissible water lev-
el when driving through water
The following must be observed to avoid damage to the vehicle when driving
through bodies of water (e.g. flooded roads).
›
Therefore determine the depth of the water before driving through bodies of
water.
The water level must not reach above the web of the lower beam » Fig. 139.
›
Do not drive any faster than at a walking speed.
At a higher speed, a water wave can form in front of the vehicle which can
cause water to penetrate into the air induction system of the engine or into
other parts of the vehicle.
› Never stop in the water, do not reverse and do not switch the engine off.
CAUTION
■
Should water penetrate into the intake system of the engine, there is a
threat of serious damage being incurred by the engine parts!■
When driving through water, some vehicle parts such as chassis, electrics or
transmission can be severely damaged.
■
Oncoming vehicles can generate water waves which can exceed the permis-
sible water level for your vehicle.
■
Potholes, mud or rocks can be hidden under the water, making it difficult or
impossible to drive through the body of water.
■
Do not drive through salt water, as the salt can cause corrosion. An vehicle
coming into contact with salt water is to be thoroughly rinsed with fresh wa-
ter.
126Driving
Page 129 of 232
Assist systems
General information
Introduction
WARNINGThe following general information regarding the use of assistance systems
must be observed.■
The assistance systems only serve to support and do not relieve the driv-
er of the responsibility for driving the vehicle.
■
The increased safety provision, as well as the increased occupant protec-
tion provided by the assistance systems must not tempt you to take risks -
risk of accident!
■
Adjust the speed and driving style to the current visibility, weather, road
and traffic conditions.
■
The assistance systems have physical and system-related limitations. For
this reason, the driver may experience some undesired or delayed system
responses in certain situations. You should therefore always be alert and
ready to intervene!
■
Only activate, deactivate or set the assistance systems so that you have
the car fully under control in every traffic situation - risk of accident!
Braking and stabilisation systems
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Stability Control (ESC)
127
Anti-lock braking system (ABS)
127
Traction control (TCS)
128
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)
128
Driver Steering Recommendation (DSR)
128
Brake Assist (HBA)
128
Hill Start Assist (HHC)
128
Trailer stabilization system (TSA)
129
This chapter describes the functions of the brake and stabilization systems.
The error display is in Chapter » page 32, Warning lights .
The brake and stabilization systems are automatically activated each time the
ignition is switched on, unless otherwise indicated.WARNINGThe general information relating to the use of assistance systems must be
observed » page 127, in section Introduction .
Stability Control (ESC)
Fig. 140
Press the ESC system: Activat-
ing/deactivating TCS
Read and observe on page 127 first.
The ESC improves vehicle stability in dynamic driving situations, such as when
the vehicle starts to skid.
The ESC monitors whether the desired direction of the current vehicle motion
is occurring. In case of any deviation (e.g. over steer), the ESC automatically
brakes individual wheels to maintain the desired direction.
During an intervention of the system, the indicator light
flashes in the in-
strument cluster.
The ESC system cannot be deactivated. The
» Fig. 140 button can only be
used to deactivate the TCS » page 128.
The warning light
lights up in the instrument cluster when the ASR is deacti-
vated.
Anti-lock braking system (ABS)
Read and observe
on page 127 first.
ABS prevents the wheels locking when braking. Thus helping the driver to
maintain control of the vehicle.
127Assist systems
Page 130 of 232

The intervention of the ABS is noticeable from the pulsating movements of
the brake pedal which is accompanied by noises.
When the ABS system is active, do not brake periodically or reduce the pres- sure on the brake pedal.
Traction control (TCS)
Fig. 141
Button for the TCS system: TCS
disable / enable (vehicle without
ESC)
Read and observe on page 127 first.
TCS prevents the spinning of the wheels of the driven axle. TCS reduces the
drive power transmitted to the wheels in the case of slipping wheels. Thus, for
example, driving on road surfaces with low grip is made easier.
If your vehicle is fitted with the ESC system, the ASR is integrated into the ESC
system » page 127 .
During a TCS intervention, the indicator light flashes in the instrument clus-
ter.
The TCS should normally always be enabled. The system should be deactivated
only in the following situations, for example. ▶ When driving with snow chains.
▶ When driving in deep snow or on a very loose surface.
▶ When it is necessary to “rock” a car free when it has become stuck.
The ASR can be deactivated via the
» Fig. 141 symbol button.
The warning light lights up in the instrument cluster when the ASR is deacti-
vated.
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)
Read and observe
on page 127 first.
EDL prevents the turning of the respective wheel of the driven axle. EDL
brakes the spinning wheel, if necessary, and transmits the driving force to the
other driving wheel. Driving becomes easier on road surfaces with different
traction under each wheel of the driven axle.
EDL switches off automatically to avoid excessive heat generation on the
brake of the wheel being braked. Once the brakes have cooled down, there is
an automatic re-activation of EDL.
Driver Steering Recommendation (DSR)
Read and observe
on page 127 first.
In critical situations, the DSR provides the driver with a steering recommenda-
tion in order to stabilise the vehicle. The DSR is activated, for example, on the
right and left vehicle side when braking sharply on different road surfaces.
Brake Assist (HBA)
Read and observe
on page 127 first.
The HBA increases the braking effect and helps to reduce the braking dis-
tance.
The HBA is activated by very quick operation of the brake pedal. In order to
achieve the shortest possible braking distance, the brake pedal must be ap-
plied firmly until the vehicle has come to a standstill.
The HBA function is automatically deactivated when the brake pedal is re-
leased.
Hill Start Assist (HHC)
Read and observe
on page 127 first.
When driving on slopes, HHC allows you to move your foot from the brake ped-
al to the accelerator pedal without having to use the handbrake.
The system holds the brake pressure produced by the activation of the brake pedal for approx. 2 seconds after the brake pedal is released.
128Driving
Page 131 of 232

The HHC is active from a 5% slope if the driver's door is closed. HHC is only ev-
er active on slopes when in forward or reverse start off.
Trailer stabilization system (TSA)
Read and observe
on page 127 first.
The TSA helps the combination stable in situations where the trailer sways
and then the whole trailer combination.
TSA brakes the individual wheels of the towing vehicle in order to damp the
rocking motion of the entire vehicle combination.
The following conditions are required for the correct TSA function. The trailer was shipped from the factory or purchased from the ŠKODA
genuine accessories.
The trailer is electrically connected to the towing vehicle via the trailer
socket.
The TCS is activated.
The speed is higher than approx. 60 km/h.
Further information » page 141, Hitch and trailer .
OFF ROAD-mode
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Operation
129
Hill Descent Assistant
130
TCSOFF ROAD
130
EDS OFF ROAD
130
ABS OFF ROAD
130
Start-Off Assistant
131
The OFF ROAD mode includes several features that help to overcome difficult
navigable routes when travelling on non-paved roads.
But even with OFF ROAD mode activated, your vehicle is never a true SUV.
WARNING■ The general information relating to the use of assistance systems must
be observed » page 127, in section Introduction .■
A lack of fuel can cause irregular engine running or cause the engine to
shut down. This would lead the OFF ROAD mode to lose its effectiveness -
risk of accident!
CAUTION
■ The OFF ROAD mode is not designed for the use on common roads.■All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres approved by the manufac-
turer to ensure theOFF ROAD mode operates correctly.
Operation
Fig. 142
OFF ROAD button
Read and observe and on page 129 first.
We recommend that you activate the OFF ROAD mode for every trip on non- paved roads.
Activating
›
Press the symbol button
» Fig. 142 .
The symbol in the button comes on.
Deactivate
›
Press the symbol key
» Fig. 142 or turn the ignition off.
The symbol in the button is no longer illuminated.
129Assist systems