ECU SSANGYONG KORANDO 2012 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2012, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 2012Pages: 1082, PDF Size: 96.1 MB
Page 265 of 1082
13-71793-01
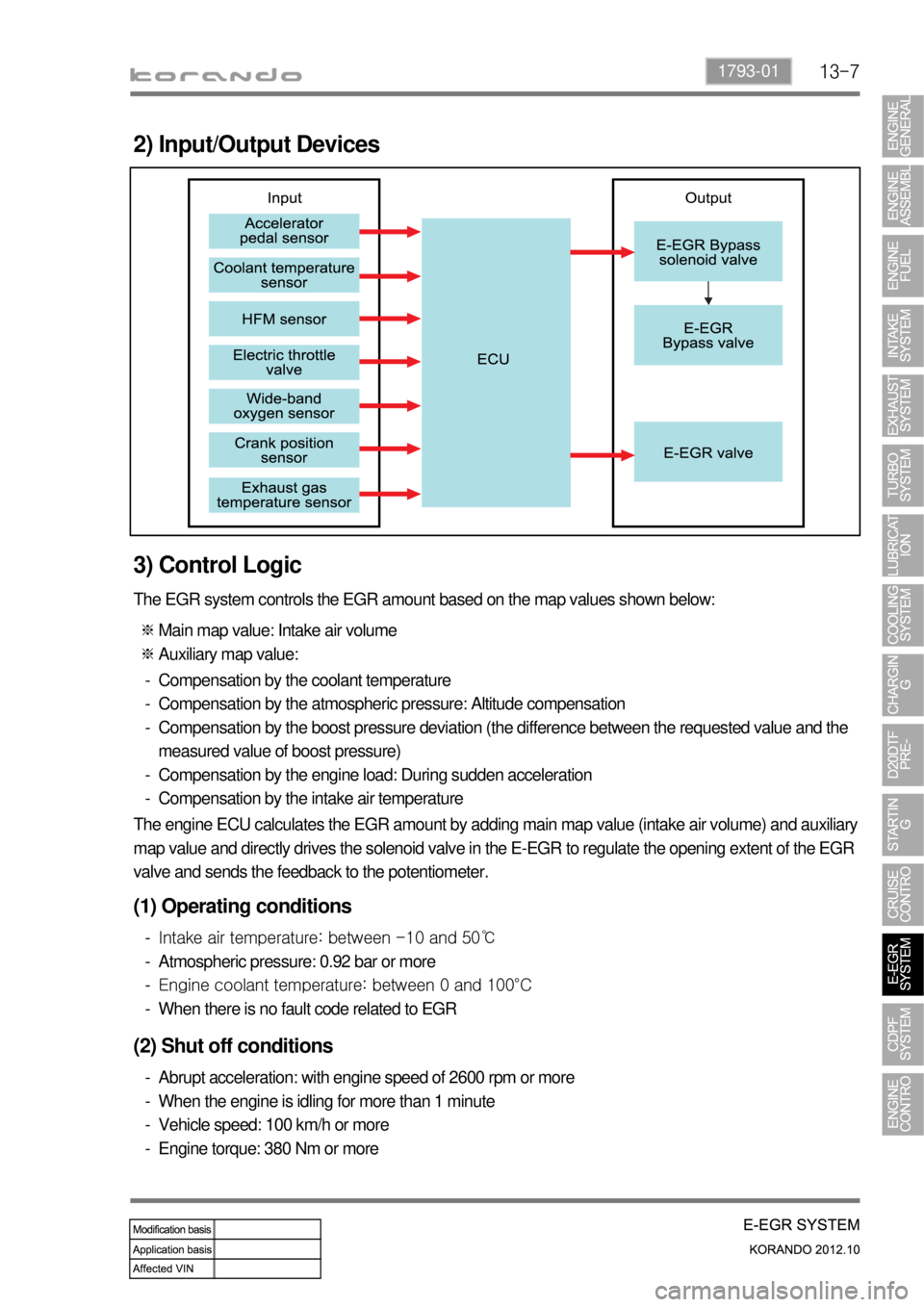
2) Input/Output Devices
3) Control Logic
The EGR system controls the EGR amount based on the map values shown below:
Main map value: Intake air volume
Auxiliary map value: ※
※
Compensation by the coolant temperature
Compensation by the atmospheric pressure: Altitude compensation
Compensation by the boost pressure deviation (the difference between the requested value and the
measured value of boost pressure)
Compensation by the engine load: During sudden acceleration
Compensation by the intake air temperature -
-
-
-
-
The engine ECU calculates the EGR amount by adding main map value (intake air volume) and auxiliary
map value and directly drives the solenoid valve in the E-EGR to regulate the opening extent of the EGR
valve and sends the feedback to the potentiometer.
(1) Operating conditions
Intake air temperature: between -10 and 50℃
Atmospheric pressure: 0.92 bar or more
Engine coolant temperature: between 0 and 100°C
When there is no fault code related to EGR -
-
-
-
(2) Shut off conditions
Abrupt acceleration: with engine speed of 2600 rpm or more
When the engine is idling for more than 1 minute
Vehicle speed: 100 km/h or more
Engine torque: 380 Nm or more -
-
-
-
Page 268 of 1082

14-51114-00
(3) Warning Lamp Related to CDPF
CDPF regeneration process (warning lamp NOT illuminated) ▶
Overload of CDPF (warning lamp blinking) ▶
The CDPF system enters the regeneration mode
when the driving distance becomes approx. 600
to 1,200 km (may differ by the driving condition
and driving style). Then, the engine ECU
performs the CDPF regeneration operation.
However, the driver is not informed with this
operation by any engine warning lamp or vehicle
signal, so he/she may not detect this operation.
The control logic at the post-injection dur-ing the
regeneration process is to increase the fuel
injection volume and control the intake air volume
(by the throttle body) in order to increase the
temperature of the exhaust gas. The driver may
not feel any particular difference from the vehicle.
If the CDPF cannot reach the regeneration
temperature due to low speed driving or other
reason during the regeneration process, the
soot is continuously accumulated in the
CDPF. When this condition continues and
the CDPF is overloaded with soot, the engine
warning lamp blinks to inform this situation to
the driver.
In order to solve this problem, drive the
vehicle at a speed of approx. 80 km/h for 15
to 20 minutes to perform the CDPF
regeneration process.
If the engine warning lamp on the instrument
cluster blinks, the CDPF is overloaded. In this
case, perform the step 2. 1.
2.
3.
Page 271 of 1082

14-8
Engine ECU (D20DTF)
Post-injectionDifferential pressure sensor
Calculates the amount of PM
collected by reading the pressure
difference between before and
after the CDPF.Electric throttle body
Regulates the rate of air
intake.
CDPF
(DOC + DPF)Front temperature
sensor
Protects the
turbocharger.Rear temperature
sensor
Measures the
temperature of fuel
combustion.
2. COMPONENT
Oxygen sensor
Page 274 of 1082

14-111114-00
ECU (DCM 3.7)
T-MAP sensorIntake air
volume
Detecting
excess of PM
amount limit
Boos
t
pressure
/
temperature
Front EGT sensor
Measures the temperature of
DOC.
The DOC performs the redox
reaction at between 300 and
500℃ and the front EGT
sensor monitors the
temperature of DOC.
Differential pressure sensor
Measures the pressure values
of before and after the CDPF.
The pressure difference
between before and after the
CDPF is measured by the
differential pressure sensor (If
PM is collected in the CDPF,
the pressure difference
between before and after the
CDPF exceeds the specified
value).
Rear EGT sensor
Measures the temperature of
DPF.
The DPF burns the soot with
hot exhaust gases
(regeneration) at around
600℃ and the rear EGT
sensor monitors the
temperature of DPF.
Injector (C3I)
Controls the post-injection.
Electric throttle body
Controls the intake air
volume.
HFM sensor
Page 275 of 1082

14-12
Collecting PM
→ Regeneration
The engine ECU detects the
amount of PM collected by the
information from the
temperature sensors and
differential pressure sensor.
When the soot is accumulated,
the engine ECU performs post-
injection to increase the
exhaust gas temperature and
burns the collected PM at
approx. 600°C.Oxidation (DOC)
When the exhaust gas enters
into the CDPF assembly, its
CO, HC and PM are reduced
by the redox reaction of the
DOC. The remaining PM is
filtered and collected in CDPF,
and the temperature of the
exhaust gas is increased to
between 450 and 500°C.
5. OPERATING PROCESS
[Configuration and principle of operation]
The exhaust gas
passed through the
exhaust manifold
enters into the CDPF
assembly (at approx
250℃).
Page 281 of 1082
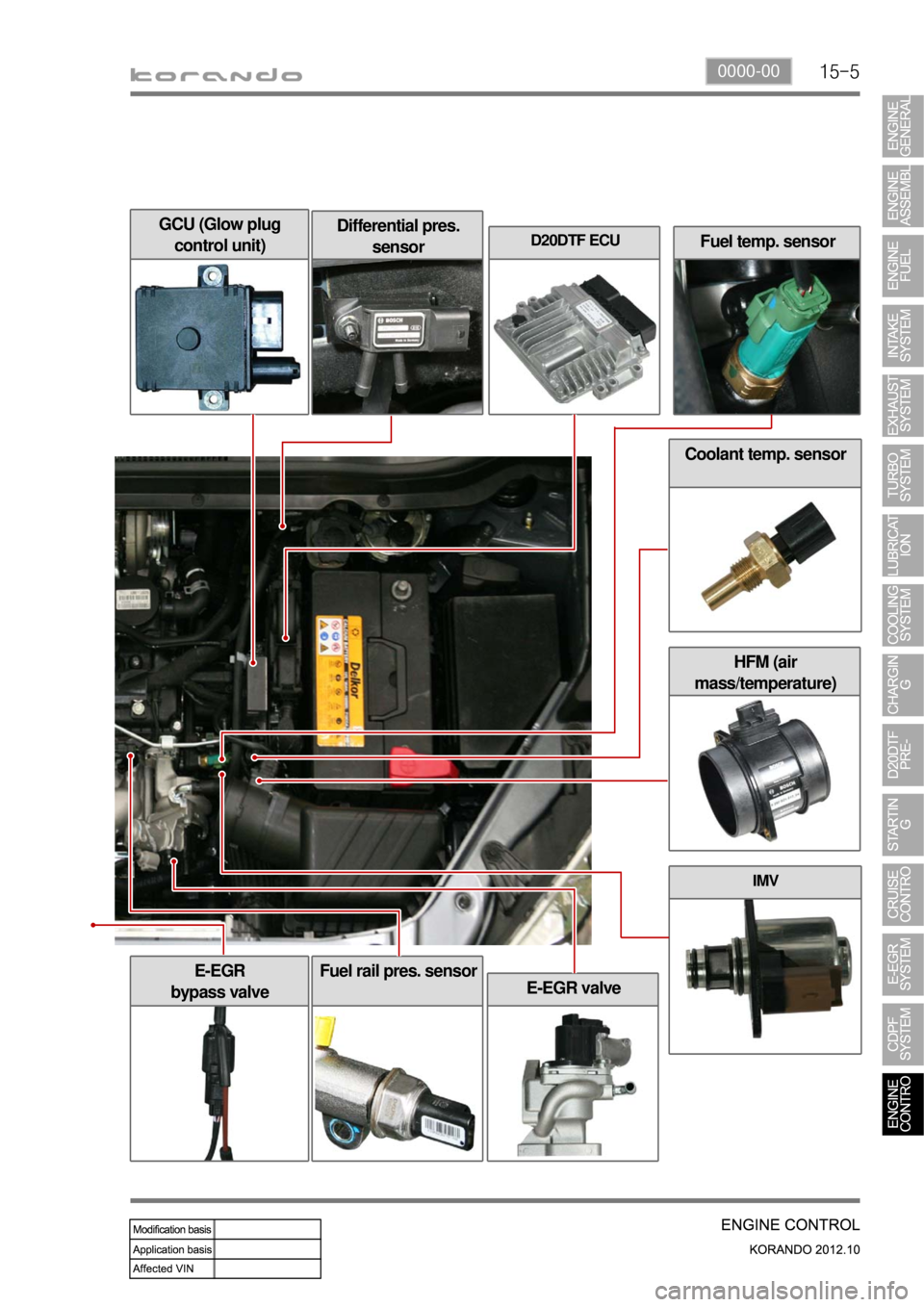
15-50000-00
HFM (air
mass/temperature)
Fuel temp. sensor
GCU (Glow plug
control unit)Differential pres.
sensorD20DTF ECU
Coolant temp. sensor
IMV
E-EGR
bypass valve
E-EGR valve
Fuel rail pres. sensor
Page 282 of 1082

15-6
2. SYSTEM OPERATION
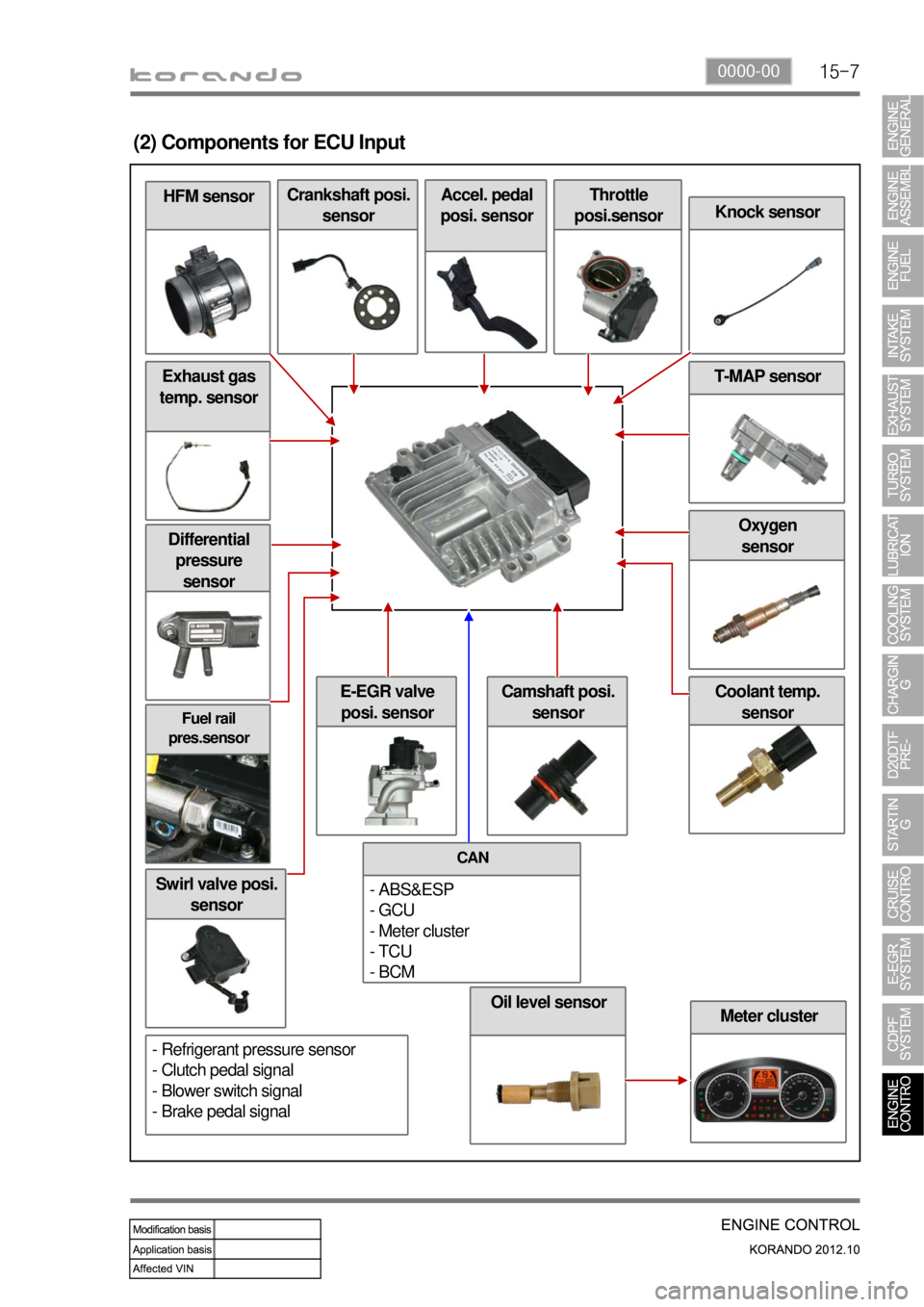
1) Input/Output of ECU
(1) ECU Block diagram
Page 283 of 1082
15-70000-00
Fuel rail
pres.sensor
Differential
pressure
sensor
Swirl valve posi.
sensor
Meter cluster
Coolant temp.
sensorE-EGR valve
posi. sensor
Oxygen
sensor
Exhaust gas
temp. sensor
HFM sensor
(2) Components for ECU Input
Crankshaft posi.
sensorAccel. pedal
posi. sensorThrottle
posi.sensor
Knock sensor
T-MAP sensor
Camshaft posi.
sensor
CAN
- ABS&ESP
- GCU
- Meter cluster
- TCU
- BCM
- Refrigerant pressure sensor
- Clutch pedal signal
- Blower switch signal
- Brake pedal signal
Oil level sensor
Page 284 of 1082

15-8
Engine room
relay box
E-EGR valve
Cooling fan
E-EGR cooler
bypass valveE-VGT
actuator
IMV
Throttle posi.
sensor
InjectorA/C
compressorStart motor
Variable swirl
valve
(3) Components for ECU Input
PTC heater
CAN
- Glow plug unit
- ABS & ESP unit
- BCM
- E-coupling unit
- EPS
- GCU
- Meter cluster
- SKM
- TCU
- Self diagnosis
Page 285 of 1082

15-90000-00
2) ECU Control
(1) Function
a. ECU Function
ECU receives and analyzes signals from various sensors and then modifies those signals into
permissible voltage levels and analyzes to control respective actuators.
ECU microprocessor calculates injection period and injection timing proper for engine piston speed and
crankshaft angle based on input data and stored specific map to control the engine power and emission
gas.
Output signal of the ECU microprocessor drives pressure control valve to control the rail pressure and
activates injector solenoid valve to control the fuel injection period and injection timing; so controls
various actuators in response to engine changes. Auxiliary function of ECU has adopted to reduce
emission gas, improve fuel economy and enhance safety, comforts and conveniences. For example,
there are EGR, booster pressure control, autocruise (export only) and immobilizer and adopted CAN
communication to exchange data among electrical systems (automatic T/M and brake system) in the
vehicle fluently. And Scanner can be used to diagnose vehicle status and defectives.
<00760097008c00990088009b00900095008e0047009b008c00940097008c00990088009b009c0099008c0047009900880095008e008c00470096008d0047006c006a007c00470090009a0047009500960099009400880093009300a000470054005b005700
47009b009600470052005f005c00b6006a004700880095008b> protected from factors like oil,
water and electromagnetism and there should be no mechanical shocks.
To control the fuel volume precisely under repeated injections, high current should be applied instantly
so there is injector drive circuit in the ECU to generate necessary current during injector drive stages.
Current control circuit divides current applying time (injection time) into full-in-current-phase and hold-
current-phase and then the injectors should work very correctly under every working condition.
b. Control Function
Controls by operating stages
To make optimum combustion under every operating stage, ECU should calculate proper injection
volume in each stage by considering various factors.
Starting injection volume control
During initial starting, injecting fuel volume will be calculated by function of temperature and engine
cranking speed. Starting injection continues from when the ignition switch is turned to ignition
position to till the engine reaches to allowable minimum speed.
Driving mode control
If the vehicle runs normally, fuel injection volume will be calculated by accelerator pedal travel and
engine rpm and the drive map will be used to match the drivers inputs with optimum engine power. -
-
-