fuel system SSANGYONG KORANDO 2012 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2012, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 2012Pages: 1082, PDF Size: 96.1 MB
Page 354 of 1082

02-8
Fuel and engine oil system ▶
The engine oil and fuel damages the painted surfaces and rubber material of the vehicle.
Disconnect the negative cable from the battery before servicing the fuel system, and prepare the
service plug grip.
When working with the fuel or oil systems in enclosed area, always keep the working area well-
ventilated and never allow anybody to smoke.
Do not allow the gasoline to contact to rubber or leather parts.
Carefully separate the pipe between high pressure fuel pump and fuel injector so that any fuel can
be spilled out.
Fully release the pressure from the fuel system before removing any parts of fuel system.
To release the fuel pressure in high pressure line, let the engine fully cool down.
Gaskets and seals on the fuel and oil systems should be replaced with new ones. All bolts and nuts
should be tightened as specified.
Prolonged exposure to the engine oil make cause a skin cancer or an irritation.
Used engine cotains the hazardous material that may cause the skin cancer. Do not allow the used
engine to make contact with your skin.
Make sure to wear the protection gloves and goggle when handling the engine oil. If contact
happens, rinse affected areas immediately with plenty of water. Do not wash it with gasoline or
solvent. If irritation persists, consult a doctor.
Improperly disposed engine oil can pollute the environment. Dispose the used engine oil and oil
filter in accordance with local environmental regulations.
Make sure to check the connections for leak after installation. -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Electric devices ▶
To prevent any damage to electric systems, make sure to disconnect the negative (-) cable from the
battery and place the ignition switch to OFF position before servicing.
Use only the specified parts with same ratings when replacing the electric devices. Check the
grounds and connections for looseness. -
- Extraordinary care should be taken when servicing the electric systems. Currently, the engine uses a lot
of electric devices. Short circuit and poor contact may cause the low engine performance, incomplete
combustion and other abnormalities.
Page 365 of 1082

02-191211-01
4) Intake/Exhaust Valve Assembly (Installed on Cylinder Head)
(1) Features
Automatic adustment of valve clearance by hydraulic pressure system (Maintenance Free)_Hydraulic
lash
Decreased valve operating noise
Decreased friction loss by introducing the roller type finger follower
Valave installation angle: 17°
Decreased running amount by compact design (increased valve following movement in high speed
and improved fuel economy by decreased friction loss) -
-
-
-
-
(2) Layout and components
Intake camshaft assemblyExhaust camshaft assembly
Valve stem seal
Valve upper
spring seat
Valve guide
Hydraulic lash
adjuster
Exhaust valve assembly
Valve spring
Finger follower
Intake valve assembly
Page 393 of 1082

03-32221-01
1. SPECIFICATION
Unit Specification
Fuel systemFuel Unleaded gasoline
Fuel injection MPI (Muilt Point Injecter) type
Fuel supply Returnless Fuel System
Fuel tankCapacity 57 L
Material Plastic
Fuel sender Dual sender type
Fuel filter Service interval Change every 100,000 km
Fuel pump Pressure 3.8 bar
InjectorColor Black
Capacity 187.2 g/min
Page 394 of 1082

03-4
2. SYSTEM LAYOUT
Fuel tank assy
Fuel tank strap assy
Heat shield assy
Sub sender assy
Main fuel pump assy
Fuel filler assy
Fuel filler cap assy
Feed tube assy
Return tube assy 1.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.Suction tube assy
Harness wiring assy
Fuel pump plate cover
O-ring
clamp
Nut
Nut
Screw 11.
12.
13.
14.
20.
21.
22.
23.
Page 396 of 1082

03-6
Returnless Type
1. OVERVIEW
The fuel system is a returnless type that the fuel pressure regulator is mounted inside the fuel tank.
The engine ECU controls the fuel injection in each injector electronically.
According to the engine loads, the engine ECU draws or cuts off the evaporated gas in canister into the
combustion chamber. The fuel system consists of fuel tank, fuel lines, fuel pump and fuel pressure
regulator.
Fuel supply line to
sub tank
Fuel return lineFuel supply line
Maintain 3.8 bar
Page 406 of 1082

05-71745-01
1. OVERVIEW
This system purifies the exhaust gas generated by the combustion in the engine to reduce the pollutants
and noise during that arise during combustion.
Harmful materials produced in the combustion process is treated and reduced in the exhaust system.
Harmful materials discharged from the crankcase and fuel tank is drawn into the intake system again to
reduce discharge amount of harmful materials.
Emission aftertreatment system ▶
Catalytic Converter & O2 Sensor
The catalytic converter is a monolith type purification system composed of cordierite which purifies
exhaust gas through the small holes of active monolith catalyst from the exhaust manifold. As exhaus
t
gas passes through the small holes in the layer in the middle, its CO and HC are reduced by
oxidization reaction and its NOx is reduced by reduction reaction to Pt, Ph and Pd. The oxygen
sensor sends signals for feedback and determination of catalyst condition. For detailed description,
see the corresponding section. -
The fuel evaporative gas is a gas evaporated to the atmosphere in the section between the fuel tank and
fuel line, and its main component is hydrocarbon (HC). The fuel evaporative gas is temporarily stored in
the canister, and it is drawn to the engine through the throttle body when the purge control solenoid valve
is open according to the engine operating condition.
Gas in the combustion chamber is sealed by the piston. However, gas is leaked through the gap
between the cylinder and piston and drawn into the crankcase during the compression and explosion
strokes. This gas is blow-by gas and its main components are hydrocarbon and carbon monoxide. If this
gas is drawn into the crankcase, the system can be corroded and oil can be deteriorated. Also, if this
gas is discharged into the air, it can pollute the environment. To prevent these, the blow-by gas
reduction system (also called as crankcase ventilation system) draws the blow-by gas from the
crankcase to the combustion chamber for combustion.
Purge Canister Control ▶
Blow-by gas control system (crankcase ventilation system) ▶
Page 413 of 1082

06-51443-01
1. OVERVIEW
The ignition system is to supply high voltage generated from the ignition coil to the spark plug. The
G20DF engine is equipped with the independent type direct ignition system that the ignition coil is
installed in each cylinder.
The basic ignition timing in each cylinder is determined by the signals from camshaft position sensor and
crankshaft position sensor.
This ignition system controls the electronic ignition timing received from the engine ECU. To control the
ignition timing precisely, the ECU use the information below:
Engine load
Coolant temperature
Intake air temperature
Engine rpm
Camshaft position sensor (CPS)
Crankshaft position sensor (CKS) -
-
-
-
-
-
If the signal from the camshaft position sensor is not delivered to the engine ECU, the ignition coil and
fuel system cannot be operated.
Page 465 of 1082

12-118530-00
5) ECO Cruise Control
The ECO cruise control system has nearly same functions with the auto cruise control system. It is an
automatic speed control system that maintains a desired driving speed without using the accelerator
pedal.
ECO cruise driving mode
The engine ECU controls the sharp acceleration and deceleration to improve the fuel economy.
The ECO cruise system is ready when pushing down the cruise control lever. At this moment, the
ECO indicator on the instrument cluster comes on.
The ECO cruise system operates when pulling up the cruise control lever.
To cancel the ECO cruise driving, push doen the cruise control lever. At this moment, the ECO
indicator on the instrument cluster goes off and the auto cruise starts to operate. -
-
-
-
Control leverECO indicator
ON Blinking
Push down the lever O
Push down it again O
Page 474 of 1082

15-91490-00
3. ECU CONTROL
1) Functions
ECU receives and analyzes signals from various sensors and then modifies those signals into
permissible voltage levels and analyzes to control respective actuators.
ECU microprocessor calculates injection period and injection timing proper for engine piston speed and
crankshaft angle based on input data and stored specific map to control the engine power and emission
gas.
Output signal of the ECU microprocessor activates the injector solenoid valve to control the fuel injection
period and injection timing; so controls various actuators in response to engine changes.
Auxiliary function of ECU has adopted to reduce emission gas, improve fuel economy and enhance
safety, comforts and conveniences. For example, there are autocruise and immobilizer and adopted
CAN communication to exchange data among electrical systems (automatic T/M and brake system) in
the vehicle fluently. And the diagnostic tool can be used to diagnose vehicle status and defectives.
<00760097008c00990088009b00900095008e0047009b008c00940097008c00990088009b009c0099008c0047009900880095008e008c00470096008d0047006c006a007c00470090009a0047009500960099009400880093009300a000470054005b005700
47009b009600470052005f005c00b6006a004700880095008b> protected from factors like oil,
water and electromagnetism and there should be no mechanical shocks.
2) Control Functions
Controls by operating stages:
To make optimum combustion under every operating stage, ECU should calculate proper injection
volume in each stage by considering various factors.
Starting injection volume control:
During initial starting, injecting fuel volume will be calculated by function of temperature and engine
cranking speed. Starting injection continues from when the ignition switch is turned to ignition
position to till the engine reaches to allowable minimum speed.
Driving mode control:
If the vehicle runs normally, fuel injection volume will be calculated by accelerator pedal travel and
engine rpm and the drive map will be used to match the drivers inputs with optimum engine power. -
-
-
Page 494 of 1082
01-6
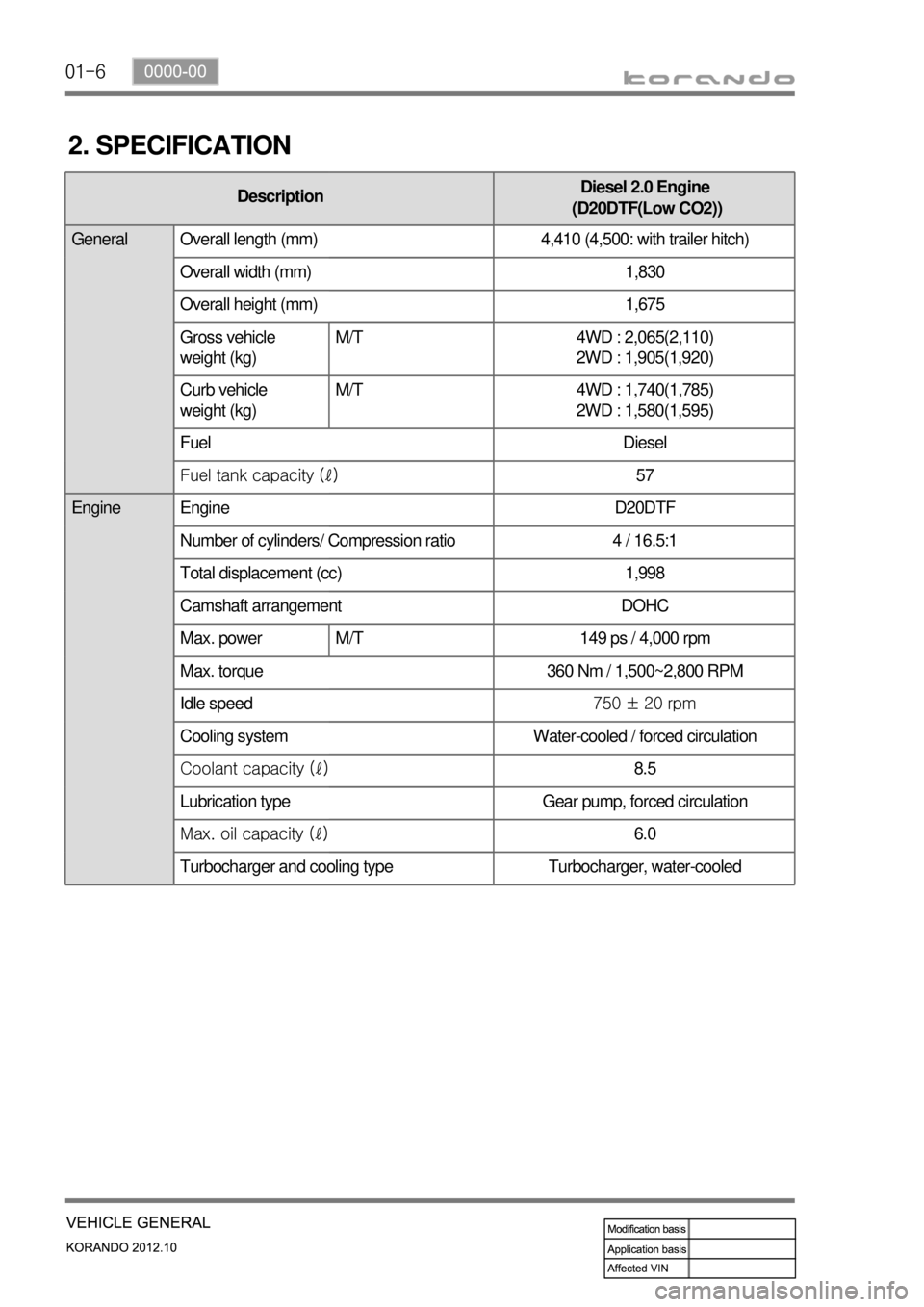
2. SPECIFICATION
DescriptionDiesel 2.0 Engine
(D20DTF(Low CO2))
General Overall length (mm) 4,410 (4,500: with trailer hitch)
Overall width (mm) 1,830
Overall height (mm) 1,675
Gross vehicle
weight (kg)M/T 4WD : 2,065(2,110)
2WD : 1,905(1,920)
Curb vehicle
weight (kg)M/T 4WD : 1,740(1,785)
2WD : 1,580(1,595)
Fuel Diesel
Fuel tank capacity (ℓ)57
Engine Engine D20DTF
Number of cylinders/ Compression ratio 4 / 16.5:1
Total displacement (cc) 1,998
Camshaft arrangement DOHC
Max. power M/T 149 ps / 4,000 rpm
Max. torque 360 Nm / 1,500~2,800 RPM
Idle speed750 ± 20 rpm
Cooling system Water-cooled / forced circulation
Coolant capacity (ℓ)8.5
Lubrication type Gear pump, forced circulation
Max. oil capacity (ℓ)6.0
Turbocharger and cooling type Turbocharger, water-cooled