heater SSANGYONG KORANDO 2013 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2013, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 2013Pages: 1336, PDF Size: 92.18 MB
Page 194 of 1336
0000-00
4. CODING
1) Engine Variant Coding
Description Selection Coding
Additional heater
NOPTC auxiliary heater is the standard equipment in
this vehicle.
Select "YES". YES
Gear box 5-speed M/T M/T : 6-speed M/T
A/T : 6-speed A/T (DSI 6AT)
6-speed M/T
5-speed A/T (DC 5 AT)
7-speed A/T (DC 7 AT)
6-speed A/T (DC 6 AT)
Immobilizer
NOImmobilizer is the standard equipment in this
behicle.
Select "YES". YES
FAN 2 relays Select "2 relays".
FAN
Not defind
Engine level control
NOEngine level control system is not available in this
vehicle.
Select "NO". YES
SKM key NO with Smart key : Select "YES".
YES
Glow plug
Relay (K-Line)AQGS is the standard equipment in this vehicle.
Select "AQGS".
AQGS (CAN)
A/C NO Select the appropriate system.
YES
Not defind
Vehicle speed
sensorCAN with ABS or ESP : Select "CAN".
WIRE
Cruise control NO with cruise control system : Select "YES".
YES
G-sensor NO with 2WD ABS and non-ABS : Select "NO"
with 4WD ABS and ESP : Select "YES"
YES
Page 227 of 1336
0000-00
1. SPECIFICATION
Description Specification
Fuel Diesel
Fuel filterTypeFuel heater + priming pump + water separator
integrated type
Filter type Changeable filter element type
every 40,000 km
every 45,000 km
Water accumulating capacity 200 cc
Heater capacity 250W 13.5V
Injector System pressure 1800 bar
High pressure fuel
pumpType Eccentric cam/Plunger type
Operating type Gear driven type
Normal operating temperature
Operating pressure 1800 bar
Operating temperature
Low pressure fuel
pumpType Vane type
Gear ratio (pump/engine) 0.5 : 1
Pressure 6 bar
Fuel tankCapacity 57 L
Material Plastic
Fuel sender Dual sender type
Change intervalEU
GEN
Page 247 of 1336

0000-00
(2) Di engine and its expected problems and remedies can be caused by
water in fuel
System supplement against paraffin separation
In case of Diesel fuel, paraffin, one of the elements, can be separated from fuel during winter and then
can stick on the fuel filter blocking fuel flow and causing difficult starting finally. Oil companies supply
summer fuel and winter fuel by differentiating mixing ratio of kerosene and other elements by region and
season. However, above phenomenon can be happened if stations have poor facilities or sell improper
fuel for the season. In case of DI engine, purity of fuel is very important factor to keep internal
preciseness of HP pump and injector.
Accordingly, more dense mesh than conventional fuel filter is used. To prevent fuel filter internal clogging
due to paraffin separation, SYMC is using fuel line that high pressure and temperature fuel injected by
injector returns through fuel filter to have an effect of built-in heater (see fuel system).
System supplement and remedy against water in fuel
As mentioned above, some gas stations supply fuel with excessive than specified water. In the
conventional IDI engine, excessive water in the fuel only causes dropping engine power or engine
hunting. However, fuel system in the DI engine consists of precise components so water in the fuel can
cause malfunctions of HP pump due to poor lubrication of pump caused by poor coating film during high
speed pumping and bacterization (under long period parking). To prevent problems can be caused by
excessive water in fuel, water separator is installed inside of fuel filter. When fuel is passing filter, water
that has relatively bigger specific gravity is accumulated on the bottom of the filter.
Water drain from water separator
If water in the separator on the fuel filter exceeds a certain level, it will be supplied to HP pump with fuel,
so the engine ECU turns on warning lamp on the meter cluster and buzzer if water level is higher than a
certain level.
Due to engine layout, a customer cannot easily drain water from fuel filter directly, so if a customer
checks in to change engine oil, be sure to perform water drain from fuel filter.
Water separator
Page 252 of 1336
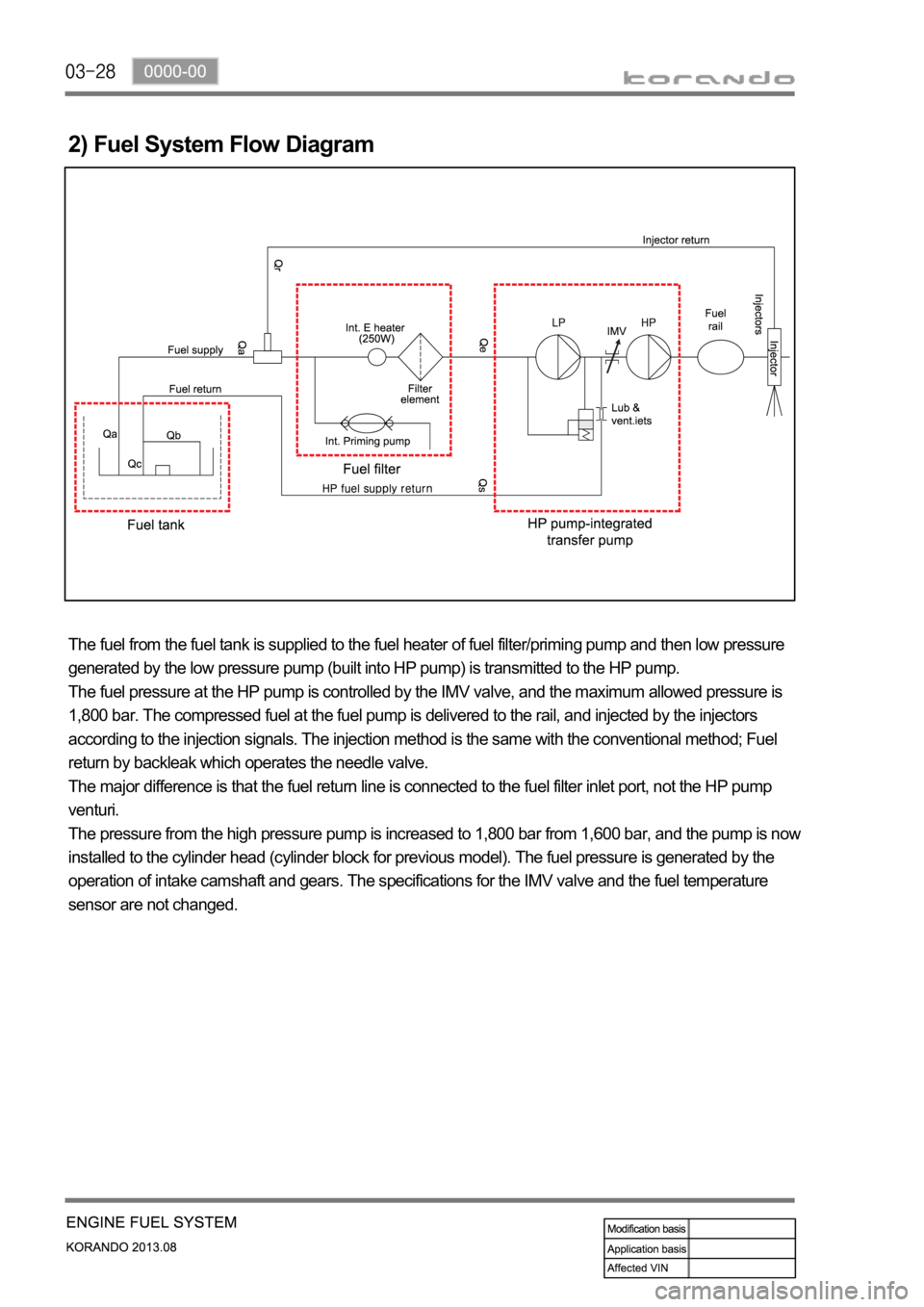
2) Fuel System Flow Diagram
The fuel from the fuel tank is supplied to the fuel heater of fuel filter/priming pump and then low pressure
generated by the low pressure pump (built into HP pump) is transmitted to the HP pump.
The fuel pressure at the HP pump is controlled by the IMV valve, and the maximum allowed pressure is
1,800 bar. The compressed fuel at the fuel pump is delivered to the rail, and injected by the injectors
according to the injection signals. The injection method is the same with the conventional method; Fuel
return by backleak which operates the needle valve.
The major difference is that the fuel return line is connected to the fuel filter inlet port, not the HP pump
venturi.
The pressure from the high pressure pump is increased to 1,800 bar from 1,600 bar, and the pump is now
installed to the cylinder head (cylinder block for previous model). The fuel pressure is generated by the
operation of intake camshaft and gears. The specifications for the IMV valve and the fuel temperature
sensor are not changed.
Page 299 of 1336
2. INSPECTION
Possible Cause Action
Coolant level
is too low- Leak from the radiator
- Leak from the auxiliary reservoir
- Leak from the heater core- Replace the radiator
- Replace the auxiliary reservoir
- Replace the heater
- Leak from the coolant hose connections
- Damaged coolant hose- Reconnect the hose or replace
the clamp
- Replace the hose
- Leak from the water pump gasket
- Leak from the water pump internal seal- Replace the gasket
- Replace the water pump
- Leak from the water inlet cap
- Leak from the thermostat housing- Replace the water inlet cap
gasket
- Replace the thermostat sealing
- Incorrect tightening torque of the
cylinder head bolts
- Damaged cylinder head gasket- Tighten the bolts to the specified
torque
- Replace the cylinder head
gasket
Coolant
temperature is
too high- Coolant leakage (Coolant level is low)
- Improper coolant mixture ratio
- Kinked coolant hose- Add coolant
- Check the coolant concentration
(Anti-freeze)
- Repair or replace the hose
- Defective thermostat
- Defective water pump
- Defective radiator
- Defective auxiliary reservoir or tank cap- Replace the thermostat
- Replace the water pump
- Replace the radiator
- Replace the auxiliary reservoir
or tank cap
- Cracks on the cylinder block or cylinder
head
- Clogged coolant passages in the
cylinder block or cylinder head- Replace cylinder block or
cylinder head
- Clean the coolant passage
- Clogged radiator core - Clean the radiator core
- Improper operation of cooling fan - Replace the cooling fan or repair
the related circuit
- Defective temperature sensor or faulty
wiring- Replace the sensor or repair the
related wiring
Coolant
temperature is
too low- Thermostat is stuck open - Replace the thermostat
- Improper operation of cooling fan - Replace the cooling fan or repair
the related circuit
- Defective temperature sensor or faulty
wiring- Replace the sensor or repair the
related wiring
Page 322 of 1336

1413-00
1. OVERVIEW
The pre-heating system for D20DTF engine has the glow plug to the cylinder head (combustion
chamber), and improves the cold start performance and reduces the emission level.
The pre-heating resistor (air heater) is used to heat the intake air.
This enables the diesel fuel to be ignited in low temperature condition.
The ECU receives the information such as, engine rpm, coolant temperature, engine torque, etc.,
through CAN communication during pre-heating process; and the pre-heating control unit controls the
pre-heating, heating during cranking and post-heating by the PWM control.
Glow plugGlow plug control unit
(GCU)
Glow indicatorEngine ECU (D20DTF)
Page 379 of 1336
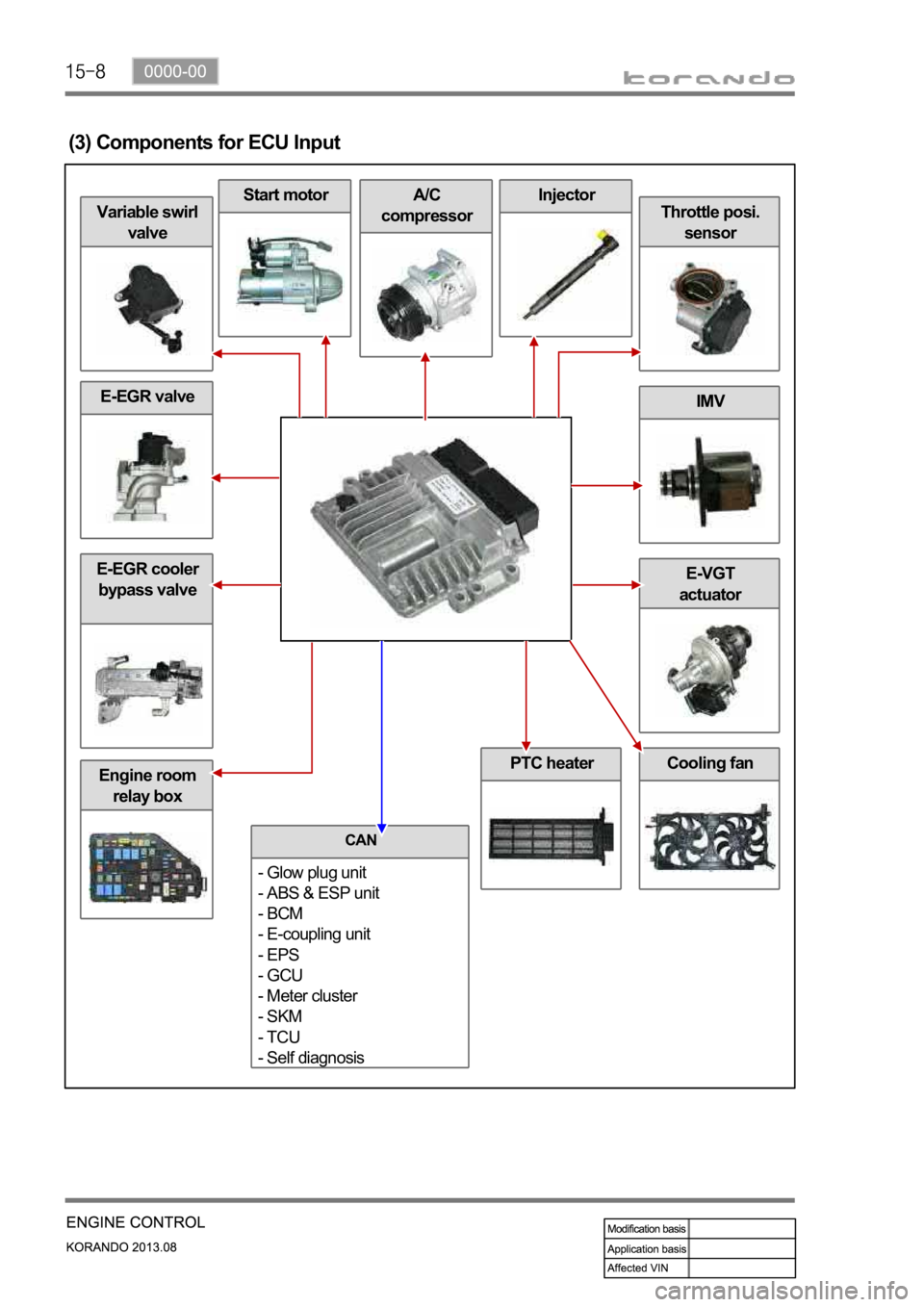
Engine room
relay box
E-EGR valve
Cooling fan
E-EGR cooler
bypass valveE-VGT
actuator
IMV
Throttle posi.
sensor
InjectorA/C
compressorStart motor
Variable swirl
valve
(3) Components for ECU Input
PTC heater
CAN
- Glow plug unit
- ABS & ESP unit
- BCM
- E-coupling unit
- EPS
- GCU
- Meter cluster
- SKM
- TCU
- Self diagnosis
Page 408 of 1336
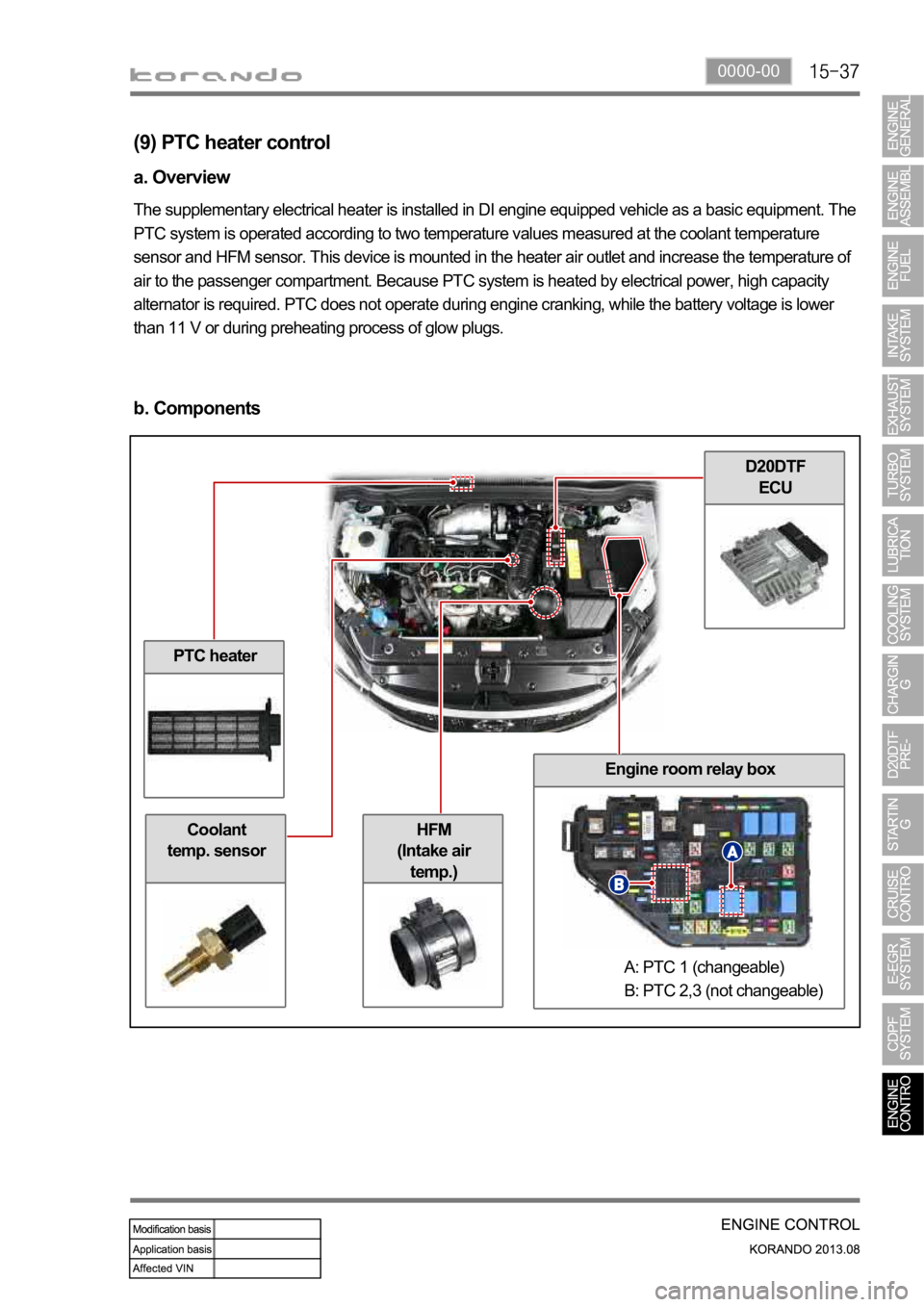
0000-00
PTC heater
Coolant
temp. sensor
D20DTF
ECU
Engine room relay box
HFM
(Intake air
temp.)
(9) PTC heater control
a. Overview
The supplementary electrical heater is installed in DI engine equipped vehicle as a basic equipment. The
PTC system is operated according to two temperature values measured at the coolant temperature
sensor and HFM sensor. This device is mounted in the heater air outlet and increase the temperature of
air to the passenger compartment. Because PTC system is heated by electrical power, high capacity
alternator is required. PTC does not operate during engine cranking, while the battery voltage is lower
than 11 V or during preheating process of glow plugs.
b. Components
A: PTC 1 (changeable)
B: PTC 2,3 (not changeable)
Page 409 of 1336

c. Operation process
The ceramic PTC has a feature that the resistance goes up very high at a certain temperature. There
are three circuits in PTC heater. Only one circuit is connected when PTC1 relay is ON, and two circuits
are connected when PTC2 relay is ON.
Page 410 of 1336

0000-00
d. Control conditions
Operation Operating condition PTC Heater
HI
(PTC2)
PTC HI ON
LO
(PTC1)
PTC LO ON
Stop- A/C blower switch OFF
- Defective ambient air temperature sensor
(including open or short circuit)
- Engine cranking
- Low battery voltage (below 11V)
- During pre-glow process (glow indicator ON)
Operation diagram for PTC heater LO (step 2)