charging SSANGYONG NEW ACTYON SPORTS 2013 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2013, Model line: NEW ACTYON SPORTS, Model: SSANGYONG NEW ACTYON SPORTS 2013Pages: 751, PDF Size: 72.63 MB
Page 132 of 751

06-18
Maximizes the intake air charging efficiency (Approx. 15%) -Optimizes the exhaust gas flow rate by controlling the vanes inside the turbine housing with the E-
Actuator. 1.
(2) E-VGT Actuator (Electric-Actuator)
Target temperature and airflow control -Enhanced emmission control: By temperature control with CDPF system 1.
(1) Performance (for EURO V)
Has a faster response time than the conventional vacuum actuator. 2.
Improved low speed torque, high speed power and fuel economy.
Improved acceleration performance with rapid response time of vane. -
-
2) Features
Features
BenefitsFolding and unfolding of the vane
is controlled electrically
Easy to get low speed air volume
Rapid response time
Electric control -
-
-
-
Improved low speed torque and
power
Reduced exhaust gas
Improved fuel consumption
Improved acceleration
performance -
-
-
-
Page 152 of 751
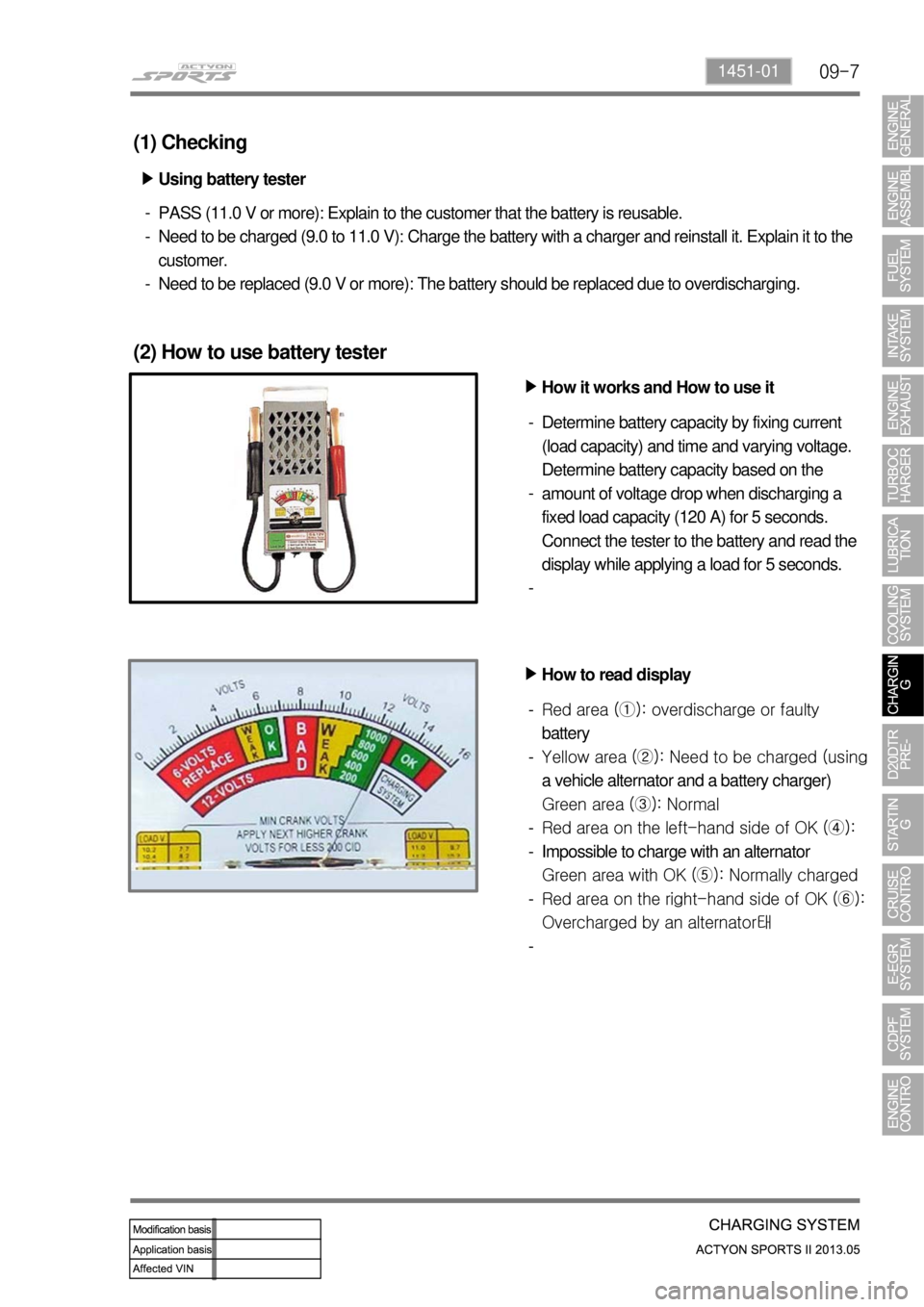
09-71451-01
(1) Checking
Using battery tester ▶
PASS (11.0 V or more): Explain to the customer that the battery is reusable.
Need to be charged (9.0 to 11.0 V): Charge the battery with a charger and reinstall it. Explain it to the
customer.
Need to be replaced (9.0 V or more): The battery should be replaced due to overdischarging. -
-
-
(2) How to use battery tester
How it works and How to use it ▶
Determine battery capacity by fixing current
(load capacity) and time and varying voltage.
Determine battery capacity based on the
amount of voltage drop when discharging a
fixed load capacity (120 A) for 5 seconds.
Connect the tester to the battery and read the
display while applying a load for 5 seconds. -
-
-
How to read display ▶
Red area (①): overdischarge or faulty
battery
Yellow area (②): Need to be charged (using
a vehicle alternator and a battery charger)
Green area (③): Normal
Red area on the left-hand side of OK (④):
Impossible to charge with an alternator
Green area with OK (⑤): Normally charged
Red area on the right-hand side of OK (⑥):
Overcharged by an alternator태 -
-
-
-
-
-
Page 156 of 751

09-111451-01
2. OPERATING PROCESS
1) Charging Flow
Page 157 of 751
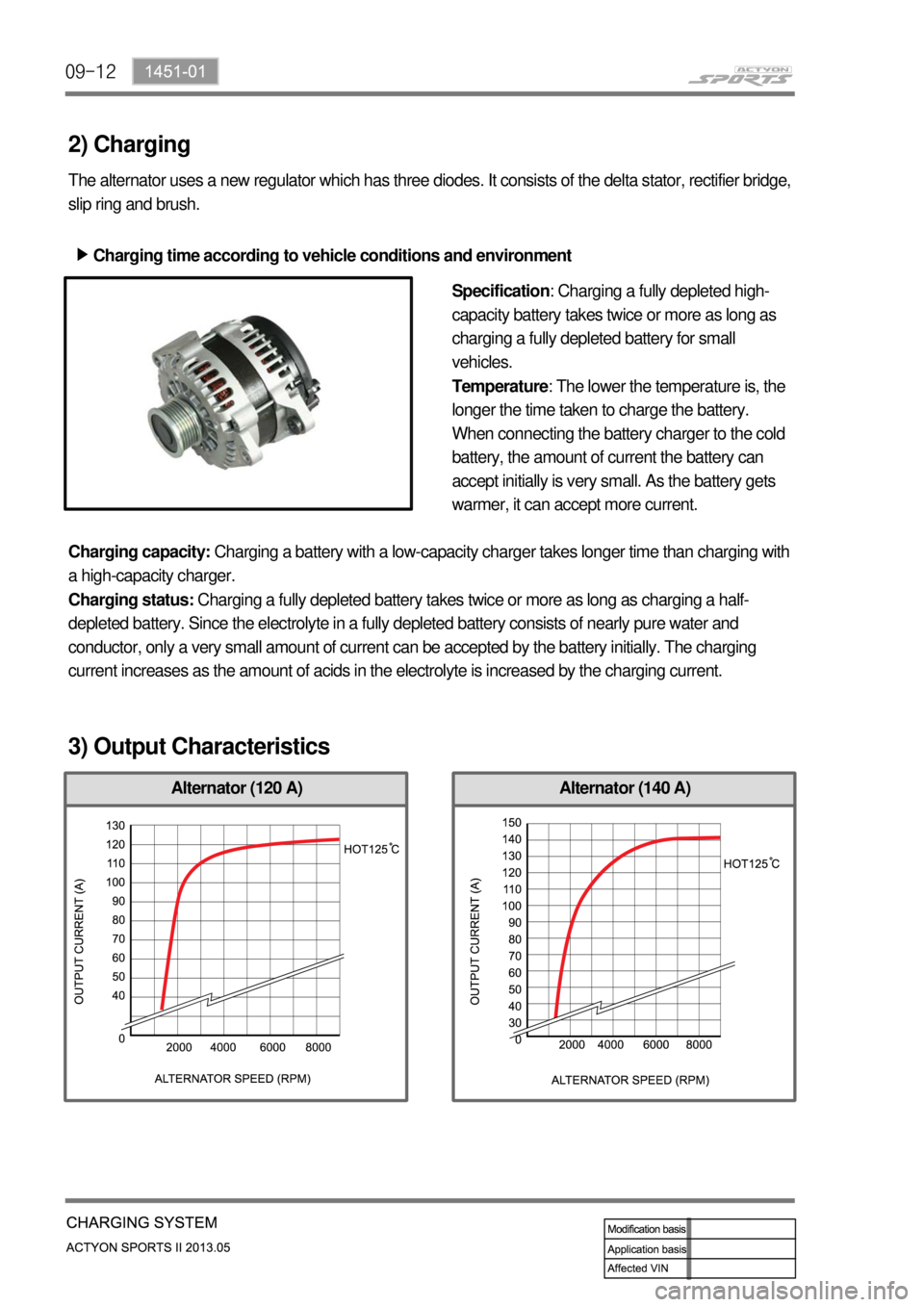
09-12
Alternator (140 A)Alternator (120 A)
2) Charging
The alternator uses a new regulator which has three diodes. It consists of the delta stator, rectifier bridge,
slip ring and brush.
Charging time according to vehicle conditions and environment ▶
Specification: Charging a fully depleted high-
capacity battery takes twice or more as long as
charging a fully depleted battery for small
vehicles.
Temperature: The lower the temperature is, the
longer the time taken to charge the battery.
When connecting the battery charger to the cold
battery, the amount of current the battery can
accept initially is very small. As the battery gets
warmer, it can accept more current.
Charging capacity: Charging a battery with a low-capacity charger takes longer time than charging with
a high-capacity charger.
Charging status: Charging a fully depleted battery takes twice or more as long as charging a half-
depleted battery. Since the electrolyte in a fully depleted battery consists of nearly pure water and
conductor, only a very small amount of current can be accepted by the battery initially. The charging
current increases as the amount of acids in the electrolyte is increased by the charging current.
3) Output Characteristics
Page 295 of 751

07-6
(2) Cold Cranking Amperage
The cold cranking amperage test is expressed at a battery temperature of -18°C(0°F).
The current rating is the minimum amperage, which must be maintained by the battery for 30 seconds at
the specified temperature, while meeting a minimum voltage requirement of 7.2 volts.
This rating is a measure of cold cranking capacity.
The battery is not designed to last indefinitely. However, with proper care, the battery will provide many
years of service. If the battery tests well, but fails to perform satisfactorily in service for no apparent
reason, the following factors may point to the cause of the trouble:
Vehicle accessories are left on overnight.
Slow average driving speeds are used for short periods.
The vehicle's electrical load is more than the generator output, particularly with the addition o
f
aftermarket equipment.
Defects in the charging system, such as electrical shorts, a slipping generator belt, a faulty generator,
or a faulty voltage regulator.
Battery abuse, including failure to keep the battery cable terminals clean and tight or a loose battery
hold-down clamp.
Mechanical problems in the electrical system, such as shorted or pinched wires. ·
·
·
·
·
·
3) Charging Time Required
The time required to charge a battery will vary depending upon the following factors:
Size of Battery - A Completely discharged large heavy-duty battery required more than twice the
recharging time as a completely discharged small passenger car battery. ▶
<007b008c00940097008c00990088009b009c0099008c00470054004700680047009300960095008e008c00990047009b00900094008c0047009e00900093009300470089008c00470095008c008c008b008c008b0047009b00960047008a008f0088009900
8e008c00470088009500a0004700890088009b009b008c0099>y at -18°C(0°F) than at
27°C(80°F).
When a fast charger is connected to a cold battery, the current accepted by the battery will be very
low at first.
The battery will accept a higher current rate as the battery warms. ▶
Charger Capacity - A charger which can supply only 5 amperes will require a much longer charging
period than a charger that can supply 30 amperes or more. ▶
State-of-Charge - A completely discharged battery requires more than twice as much charge as a
onehalf charged battery.
Because the electrolyte is nearly pure water and a poor conductor in a completely discharged
battery, the current accepted by the battery is very low at first. Later, as the charging current causes
the electrolyte acid content to increase, the charging current will likewise increase. ▶
Page 296 of 751

07-71452-01
4) Charging a Completely Discharged Battery (Off the Vehicle)
Unless this procedure is properly followed, a perfectly good battery may be needlessly replaced.
The following procedure should be used to recharge a completely discharged battery:
Measure the voltage at the battery terminals with an accurate voltmeter.
If the reading is below 10 volts, the charge current will be very low, and it could take some
time before the battery accepts the current in excess of a few milliamperes.
Refer to "Charging Time Required" in this section, which focuses on the factors affecting both the
charging time required. Such low current may not be detectable on ammeters available in the field.
Set the battery charger on the high setting. 1.
2.
Continue to charge the battery until the charge current is measurable. Battery chargers vary in the
amount of voltage and current provided. The time required for the battery to accept a measurable
charger current at various voltages may be as follows: 3.
If the charge current is not measurable at the end of the above charging times, the battery
should be replaced.
If the charge current is measurable during the charging time, the battery is good, and charging
should be completed in the normal manner. ·
·
If the charge current is still not measurable after using the charging time calculated by the above
method, the battery should be replaced. ·
It is important to remember that a completely discharged battery must be recharged for a sufficient
number of ampere hours (AH) to restore the battery to a usable state.
Page 297 of 751

07-8
5) Jump Starting Procedure
Position the vehicle with the charged battery so that the jumper cables will reach from the charged
battery to the battery that requires charging.
Turn off the ignition, all the lights, and all the electrical loads in both vehicles.
Leave the hazard flasher on if jump starting where there may be other traffic and any other lights
needed for the work area.
Apply the parking brake firmly in both vehicles. 1.
2.
3.
4.
Shift an automatic transmission to PARK. 5.
Clamp one end of the first jumper cable to the positive terminal on the booster battery. Make sure it
does not touch any other metal parts.
Clamp the other end of the same cable to the positive terminal on the discharged battery. Never
connect the other end to the negative terminal of the discharged battery. 6.
7.
Clamp one end of the second cable to the negative terminal of the booster battery.
Make the final connection to a solid engine ground, such as the engine lift bracket at least 450
millimeters (18 inches) from the discharged battery.
Start the engine of the vehicle with the good battery.
Run the engine at a moderate speed for several minutes.
Then start the engine of the vehicle with the discharged battery.
Remove the jumper cables by reversing the above sequence exactly, removing the negative cable
from the vehicle with the discharged battery first.
While removing each clamp, take care that it does not touch any other metal while the other end
remains attached. 8.
9.
10.
11.
12.In order to avoid damaging the vehicle make sure the cables are not on or near pulleys, fans, or
other parts that will move when the engine starts.
In order to avoid injury, do not use cables that have loose or missing insulation.
Page 298 of 751

07-91452-01
6) Alternator
Alternators are equipped with internal regulators.
Unlike three-wire generators, the alternator may be used with only two connections: battery positive and
an "D+" terminal to the charge indicator lamp.
As with other charging systems, the charge indicator lamp lights when the ignition switch is turned to
RUN, and goes out when the engine is running.
If the charge idicator is on with the engine running, a charging system defect is indicated. This indicato
r
light will glow at full brilliance for several kinds of defects as well as when the system voltage is too high
or too low.
The regulator voltage setting varies with temperature and limits the system voltage by controlling roto
r
field current.
Achieve correct average field current for proper system voltage control by varying the on-off time. At high
speeds, the on-time may be 10 percent and the off-time 90 percent.
At low speeds, with high electrical loads, the on-time may be 90 percent and the off-time 10 percent.
7) Charging System
Generators use a new type of regulator that incorporates a diode trio.
A Delta stator, a rectifier bridge, and a rotor with slip rings and brushes are electrically similar
to earlier generators.
A conventional pulley and fan are used.
There is no test hole.
8) Starter
Wound field starter motors have pole pieces, arranged around the armature, which are energized by
wound field coils.
Enclosed shift lever cranking motors have the shift lever mechanism and the solenoid plunger enclosed
in the drive housing, protecting them from exposure to dirt, icy conditions, and splashes.
In the basic circuit, solenoid windings are energized when the switch is closed.
The resulting plunger and shift lever movement causes the pinion to engage the engine flywheel ring
gear.
The solenoid main contacts close. Cranking then takes place.
When the engine starts, pinion overrun protects the armature from excessive speed until the switch is
opened, at which time the return spring causes the pinion to disengage.
To prevent excessive overrun, the switch should be released immediately after the engine starts.
Page 650 of 751

12-214610-01
1. SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The power steering has been designed to make the wheel move more easily than in a manual steering
system. The hydraulic power assists the process utilizing hydraulic fluid. The fluid increases pressure in
the power steering pump and aids the movement of the steering mechanism. The power steering
system consists of pump, oil reservoir, rack and gear box. The power steering pump is a vane type and
delivers hydraulic pressure to operate the power steering system. The pressure relief valve in the pump
controls the discharging pressure. The rotary valve in the rack and the pinion gear directs the oil from the
power steering pump to one side of the rack piston. The integrated rack piston converts the hydraulic
pressure to linear movement. The operating force of the rack moves the wheels through the tie rod, the
tie rod end and the steering knuckle. Even though the hydraulic pressure cannot be generated, a driver
can steer the vehicle without power assist but it needs very high steering force. In this case, the
operating force of the steering wheel is conveyed to the pinion, and the movement of the pinion moves
the rack through the pinion gear combined to the rack gear.