ignition SSANGYONG RODIUS 2012 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2012, Model line: RODIUS, Model: SSANGYONG RODIUS 2012Pages: 715, PDF Size: 79.36 MB
Page 336 of 715

15-110000-00
2) ECU Control
(1) Function
a. ECU Function
ECU receives and analyzes signals from various sensors and then modifies those signals into
permissible voltage levels and analyzes to control respective actuators.
ECU microprocessor calculates injection period and injection timing proper for engine piston speed and
crankshaft angle based on input data and stored specific map to control the engine power and emission
gas.
Output signal of the ECU microprocessor drives pressure control valve to control the rail pressure and
activates injector solenoid valve to control the fuel injection period and injection timing; so controls
various actuators in response to engine changes. Auxiliary function of ECU has adopted to reduce
emission gas, improve fuel economy and enhance safety, comforts and conveniences. For example,
there are EGR, booster pressure control, autocruise (export only) and immobilizer and adopted CAN
communication to exchange data among electrical systems (automatic T/M and brake system) in the
vehicle fluently. And Scanner can be used to diagnose vehicle status and defectives.
<00760097008c00990088009b00900095008e0047009b008c00940097008c00990088009b009c0099008c0047009900880095008e008c00470096008d0047006c006a007c00470090009a0047009500960099009400880093009300a000470054005b005700
47009b009600470052005f005c00b6006a004700880095008b> protected from factors like oil,
water and electromagnetism and there should be no mechanical shocks.
To control the fuel volume precisely under repeated injections, high current should be applied instantly
so there is injector drive circuit in the ECU to generate necessary current during injector drive stages.
Current control circuit divides current applying time (injection time) into full-in-current-phase and hold-
current-phase and then the injectors should work very correctly under every working condition.
b. Control Function
Controls by operating stages
To make optimum combustion under every operating stage, ECU should calculate proper injection
volume in each stage by considering various factors.
Starting injection volume control
During initial starting, injecting fuel volume will be calculated by function of temperature and engine
cranking speed. Starting injection continues from when the ignition switch is turned to ignition
position to till the engine reaches to allowable minimum speed.
Driving mode control
If the vehicle runs normally, fuel injection volume will be calculated by accelerator pedal travel and
engine rpm and the drive map will be used to match the drivers inputs with optimum engine power. -
-
-
Page 338 of 715
15-130000-00
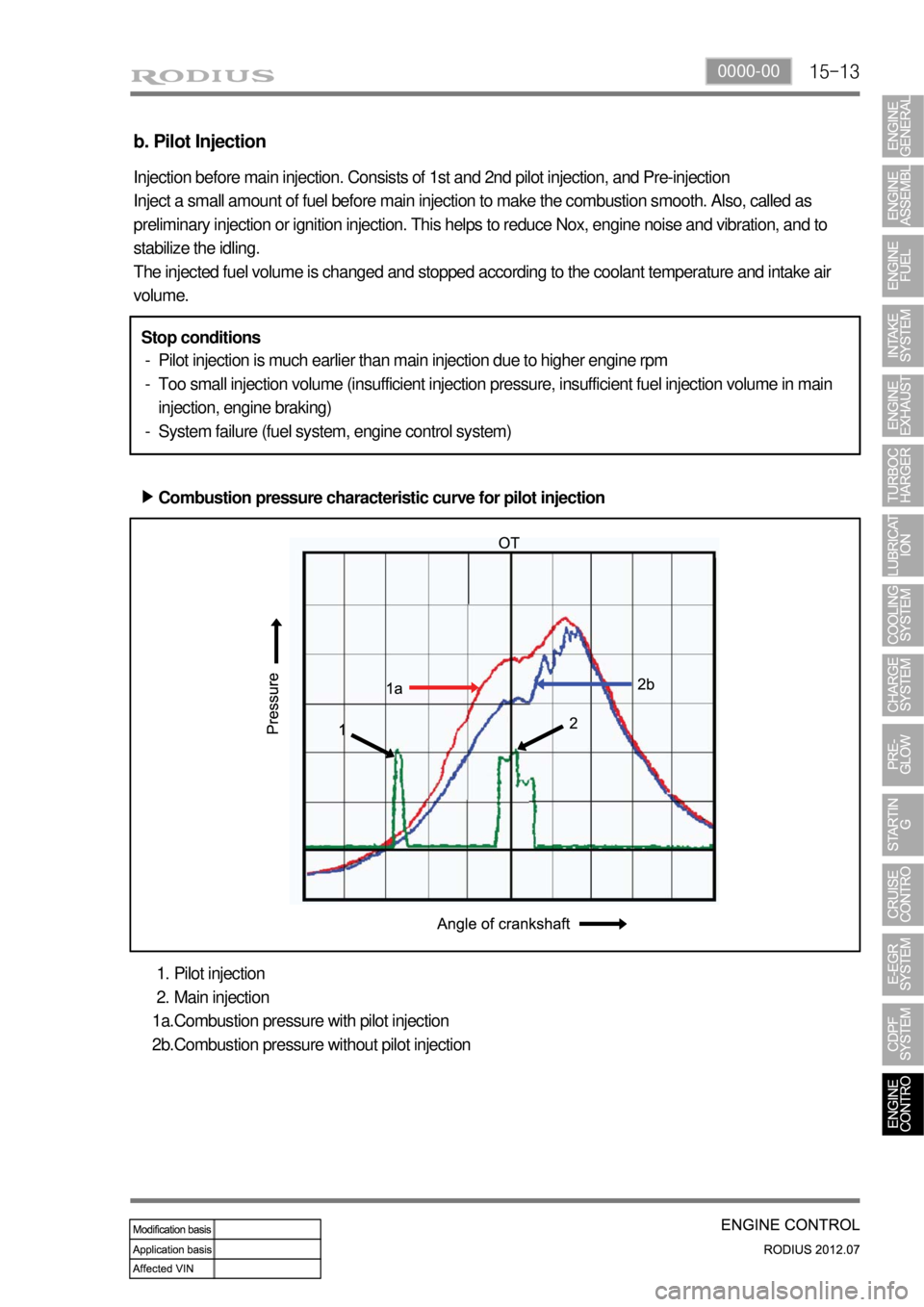
b. Pilot Injection
Injection before main injection. Consists of 1st and 2nd pilot injection, and Pre-injection
Inject a small amount of fuel before main injection to make the combustion smooth. Also, called as
preliminary injection or ignition injection. This helps to reduce Nox, engine noise and vibration, and to
stabilize the idling.
The injected fuel volume is changed and stopped according to the coolant temperature and intake air
volume.
Pilot injection is much earlier than main injection due to higher engine rpm
Too small injection volume (insufficient injection pressure, insufficient fuel injection volume in main
injection, engine braking)
System failure (fuel system, engine control system) -
-
-
Pilot injection
Main injection
Combustion pressure with pilot injection
Combustion pressure without pilot injection 1.
2.
1a.
2b. Stop conditions
Combustion pressure characteristic curve for pilot injection ▶
Page 340 of 715

15-150000-00
(3) Fuel Pressure Control
Fuel pressure is controlled by IMV opening according to the calculated value by ECU.
Pressure in the fuel rail is determined according to engine speed and load on the engine. ▶
When engine speed and load are high
The degree of turbulence is very great and the fuel can be injected at very high pressure in order to
optimize combustion.
When engine speed and load are low
The degree of turbulence is low. If injection pressure is too high, the nozzle's penetration will be
excessive and part of the fuel will be sprayed directly onto the sides of the cylinder, causing
incomplete combustion. So there occurs smoke and damages engine durability. -
-
Fuel pressure is corrected according to air temperature, coolant temperature and atmospheric pressure
and to take account of the added ignition time caused by cold running or by high altitude driving. A
special pressure demand is necessary in order to obtain the additional flow required during starts. This
demand is determined according to injected fuel and coolant temperature.
Open loop determines the current which needs to be sent to the actuator in order to obtain the
flow demanded by the ECU. ▶
Closed loop will correct the current value depending on the difference between the pressure
demand and the pressure measured. ▶
If the pressure is lower than the demand, current is reduced so that the fuel sent to the high pressure
pump is increased.
If the pressure is higher than the demand, current is increased so that the fuel sent to the high
pressure pump is reduced. -
-Fuel Pressure ▶
Page 344 of 715

15-190000-00
F. Pilot Flow Control
The pilot flow represents the amount of fuel injected into the cylinder during the pilot injection. This
amount is determined according to the engine speed and the total flow.
A first correction is made according to the air and water temperature.
This correction allows the pilot flow to be adapted to the operating temperature of the engine. When
the engine is warm, the ignition time decreases because the end-of-compression temperature is
higher. The pilot flow can therefore be reduced because there is obviously less combustion noise
when the engine is warm.
A second correction is made according to the atmospheric pressure. -
-
During starting, the pilot flow is determined on the basis of the engine speed and the coolant
temperature.
G. Cylinder Balancing Strategy
Balancing of the point to point flows ▶
The pulse of each injector is corrected according to the difference in instantaneous speed measured
between 2 successive injectors.
The instantaneous speeds on two successive injections are first calculated.
The difference between these two instantaneous speeds is then calculated.
Finally, the time to be added to the main injection pulse for the different injectors is determined.
For each injector, this time is calculated according to the initial offset of the injector and the
instantaneous speed difference.
Detection of an injector which has stuck closed ▶
The cylinder balancing strategy also allows the detection of an injector which has stuck closed. The
difference in instantaneous speed between 2 successive injections then exceeds a predefined threshold.
In this case, a fault is signaled by the system.
Page 352 of 715

15-270000-00
Load Engine speedSwirl
valveAmount of
swirlRemarks
Low speed,
Low loadbelow 3,000 rpm Closed HeavyIncreased EGR ratio, better air-fuel
mixture (reduce exhaust gas))
High speed,
High loadover 3,000 rpm Open LightIncrease charge efficiency, higher
engine power
The variable swirl valve actuator operates when
turning the ignition switch ON/OFF position to
open/close the swirl valve. In this period, the soot
will be removed and the learning for swirl valve
position is performed.
Swirl: This is the twisted (radial) air flow along the cylinder wall during the intake stroke. This
stabilizes the combustion even in lean air-fuel mixture condition.
Swirl valve
E. Features
Swirl and air intake efficiency
To generate the swirl, the intake port should be serpentine design. This makes the resistance in air
flow. The resistance in air flow in engine high speed decreases the intake efficiency. Eventually, the
engine power is also decreased, Thus, the swirl operation is deactivated in high speed range to
increase the intake efficiency.
Relationship between swirl and EGR
To reduce Nox, it is essential to increase EGR ratio. However, if EGR ratio is too high, the PM also
could be very higher. And, the exhaust gas should be evenly mixed with newly aspired air. Otherwise,
PM and CO are dramatically increased in highly concentrated exhaust gas range and EGR ratio
could not be increased beyond a certain limit. If the swirl valve operates in this moment, the limit of
EGR ratio will be higher. -
-
F. Relationship between swirl and fuel injection pressur
The injector for DI engine uses the multi hole design. For this vehicle, there are 8 holes in injector. If the
swirl is too strong, the injection angles might be overlapped and may cause the increased PM and
insufficient engine power. Also, if the injection pressure is too high during strong swirl, the injection
angles might be overlapped. Therefore, the system may decreases the fuel injection pressure when the
swirl is too strong.
Page 369 of 715

15-44
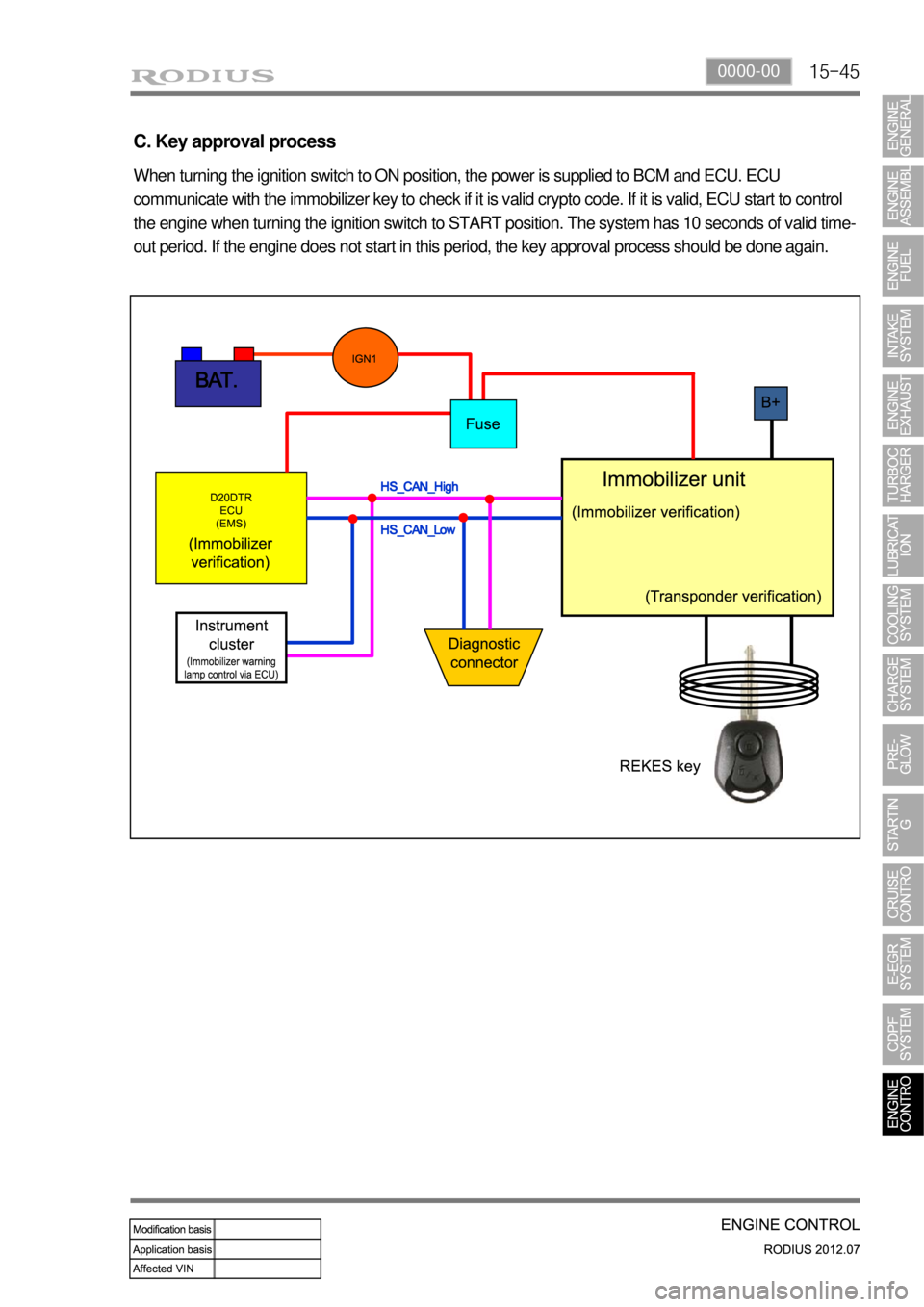
(14) Immobilizer control
A. Overview
The Immobilizer System provides an additional theft deterrent to the vehicle in which it is installed and
prevents it from being started by unauthorized persons. The transponder integrated in the key and the
engine control unit have the same code. When the ignition key with the integrated transponder is turned
to the ON position, the ECU (Engine Control Unit) checks the crypto code of the key and, if correct,
allows the vehicle to start the engine.
B. Components
Basic components (ignition key system) ▶
D20DTR ECUImmobilizer antennaIndicator/Warning Lamp
Start motorImmobilizer key
Page 370 of 715
15-450000-00
C. Key approval process
When turning the ignition switch to ON position, the power is supplied to BCM and ECU. ECU
communicate with the immobilizer key to check if it is valid crypto code. If it is valid, ECU start to control
the engine when turning the ignition switch to START position. The system has 10 seconds of valid time-
out period. If the engine does not start in this period, the key approval process should be done again.
Page 379 of 715

01-70000-00
2. DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
1) Cleanliness and Care
An automobile engine is a combination of many machined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces
with tolerances that are measured in the ten-thousanths of an inch. When any internal engine
parts are serviced, care and cleanliness are important. A liberal coating of enigne oil should be
applied to friction areas during assembly, to protect and lubricate the surfaces on initial operation.
Proper cleaning and protection of machined surfaces and friction areas is part of the repair
procedure. This is considered standard shop practice even if not specifically stated.
Whenever valve train components are removed for service, they should be kept in order.
They should be installed in the same locations, and with the same mating surfaces, as when they
were removed. Battery cables should be disconnected before any major work is performed on the
engine. Failure to disconnect cables may result in damage to wire harness or other electrical
parts.
2) On-Engine Service
Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit, or
when a tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals.
Disconnecting this cable will help prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle.
The ignition must also be in LOCK unless otherwise noted.
Notice Any time the air cleaner is removed, the intake opening -
Any time the air cleaner is removed, the intake opening should be covered. This will protect
against accidental entrance of foreign material, which could follow the intake passage into
the cylinder and cause extensive damage when the engine is started.g -
Page 402 of 715

08-51452-01
1. CHARGING SYSTEM OPERATION
Alternators use a new type of regulator that incorpo-rates a diode trio. A Delta stator, a rectifier
bridge, and a rotor with slip rings and brushes are electrically similar to earlier alternators.
A conventional pulley and fan are used. There is no test hole.
1) Charging Time Required
The time required to charge a battery will vary depending upon the following factors:
Size of Battery ▶
A Completely discharged large heavy-duty battery required more than twice the
recharging time as a completely discharged small passenger car battery. -
Temperature ▶
A longer time will be needed to charge any battery at -18°C (0°F) than at 27°C (80°F).
When a fast charger is connected to a cold battery, the current accepted by the battery
will be very low at first. The battery will accept a higher current rate as the battery warms. -
Charger Capacity ▶
A charger which can supply only 5 amperes will require a much longer charging period
than a charger that can supply 30 amperes or more. -
State-of-Charge ▶
A completely discharged battery requires more than twice as much charge as a onehalf
charged battery. Because the electrolyte is nearly pure water and a poor conductor in a
completely discharged battery, the current accepted by the battery is very low at first.
Later, as the charging current causes the electrolyte acid content to increase, the charging
current will likewise increase. -
2. STARTING SYSTEM OPERATION
The engine electrical system includes the battery, the ignition, the starter, the alternator, and all
the related wiring. Diagnostic tables will aid in troubleshooting system faults. When a fault is
traced to a particular component, refer to that component section of the service manual. The
starting system circuit consists of the battery, the starter motor, the ignition switch, and all the
related electrical wiring. All of these components are connected electrically.
Page 403 of 715

08-6
3. IGNITION SYSTEM OPERATION
This ignition system does not use a conventional distributor and coil. It uses a crankshaft position
sensor input to the Engine Control Module (ECM).
The ECM then determines Electronic Spark Timing (EST) and triggers the electronic ignition
system ignition coil.
This type of distributorless ignition system uses a "waste spark" method of spark distribution.
Each cylinder is paired with the cylinder that is opposite it (2.3L DOHC: 2 - 3 or 1 - 4, 3.2L
DOHC: 1 - 6 or 2 - 5 or 3 - 4).
The spark occurs simultaneously in the cylinder coming up on the compression stroke and in the
cylinder coming up on the exhaust stroke.
The cylinder on the exhaust stroke requires very little of the available energy to fire the spark plug.
The remaining energy is available to the spark plug in the cylinder on the compression stroke.
These systems use the EST signal from the ECM to control the EST.
The ECM uses the following information: Engine load (mass air flow sensor, manifold air pressure
sensor).
Engine coolant temperature.
Intake air temperature.
Crankshaft position.
Engine speed (rpm).
1) Electronic Ignition System Ignition Coil
The Electronic Ignition (EI) system ignition coil is located on the cylinder head cover.
The double ended coils re ceive the signal for the ECM which controls the spark advance.
Each EI system ignition coil provides the high voltage to two spark plugs simultaneously;
3.2L DOHC
T1/1: cylinder 2 and 5
T1/2: cylinder 3 and 4
T1/3: cylinder 1 and 6
The EI system ignition coil is not serviceable and must be replaced as an assembly.