ECU SSANGYONG RODIUS 2012 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2012, Model line: RODIUS, Model: SSANGYONG RODIUS 2012Pages: 715, PDF Size: 79.36 MB
Page 346 of 715

15-210000-00
C. Learning Conditions
Idle MDP learning Drive MDP learning
Coolant temperatureover 60℃ over 60℃
Vehicle speedIdling over 50km/h (over 5 seconds)
Engine rpm2,000 to 2,500 rpm
Fuel temperature0 < Fuel temperature < 80℃
Learning2 times for each cylinder (every 5
seconds)2 times for each cylinder
(every 5 seconds)
If MDP learning is not properly performed, engine vibration and injection could be occurred.
MDP learning should be performed after replacing ECU, reprogramming and replacing injector. -
-
D. Injector characteristic curve for rail pressure
The fuel injection curve is also called injection characteristic curve as shown above. The amount of
injected fuel is proportional to the square root of injection period and rail pressure.
Page 348 of 715

15-230000-00
This is done periodically under certain operating conditions. When the resetting is finished, the new
minimum pulse value replaces the value obtained during the previous resetting. The first MDP value is
provided by the C3I. Each resetting then allows the closed loop of the MDP to be updated according to
the deviation of the injector.
B. Detection of leaks in the cylinders
The accelerometer is also used to detect any injector which may have stuck open. The detection
principle is based on monitoring the ratio. If there is a leak in the cylinder, the accumulated fuel self-
ignites as soon as the temperature and pressure conditions are favorable (high engine speed, high load
and small leak).
This combustion is set off at about 20 degrees before TDC and before main injection.
The ratio therefore increases considerably in the detection window. It is this increase which allows the
leaks to be detected. The threshold beyond which a fault is signaled is a percentage of the maximum
possible value of the ratio.
Because of the severity of the recovery process (engine shut-down), the etection must be extremely
robust.
An increase in the ratio can be the consequence of various causes:
Pilot injection too much
Main combustion offset
Fuel leak in the cylinder -
-
-
If the ratio becomes too high, the strategy initially restricts the pilot injection flow and retards the main
injection. If the ratio remains high despite these interventions, this shows that a real leak is present, a
fault is signaled and the engine is shut down.
C. Detection of an accelerometer fault
This strategy permits the detection of a fault in the sensor or in the wiring loom connecting the sensor to
the ECU.
It is based on detection of the combustion. When the engine is idling, the detection window is set too low
for the combustion caused by the main injection. If the ratio increases, this shows that the knock sensor
is working properly, but otherwise a fault is signaled to indicate a sensor failure. The recovery modes
associated with this fault consist of inhibition of the pilot injection and discharge through the injectors.
Page 349 of 715
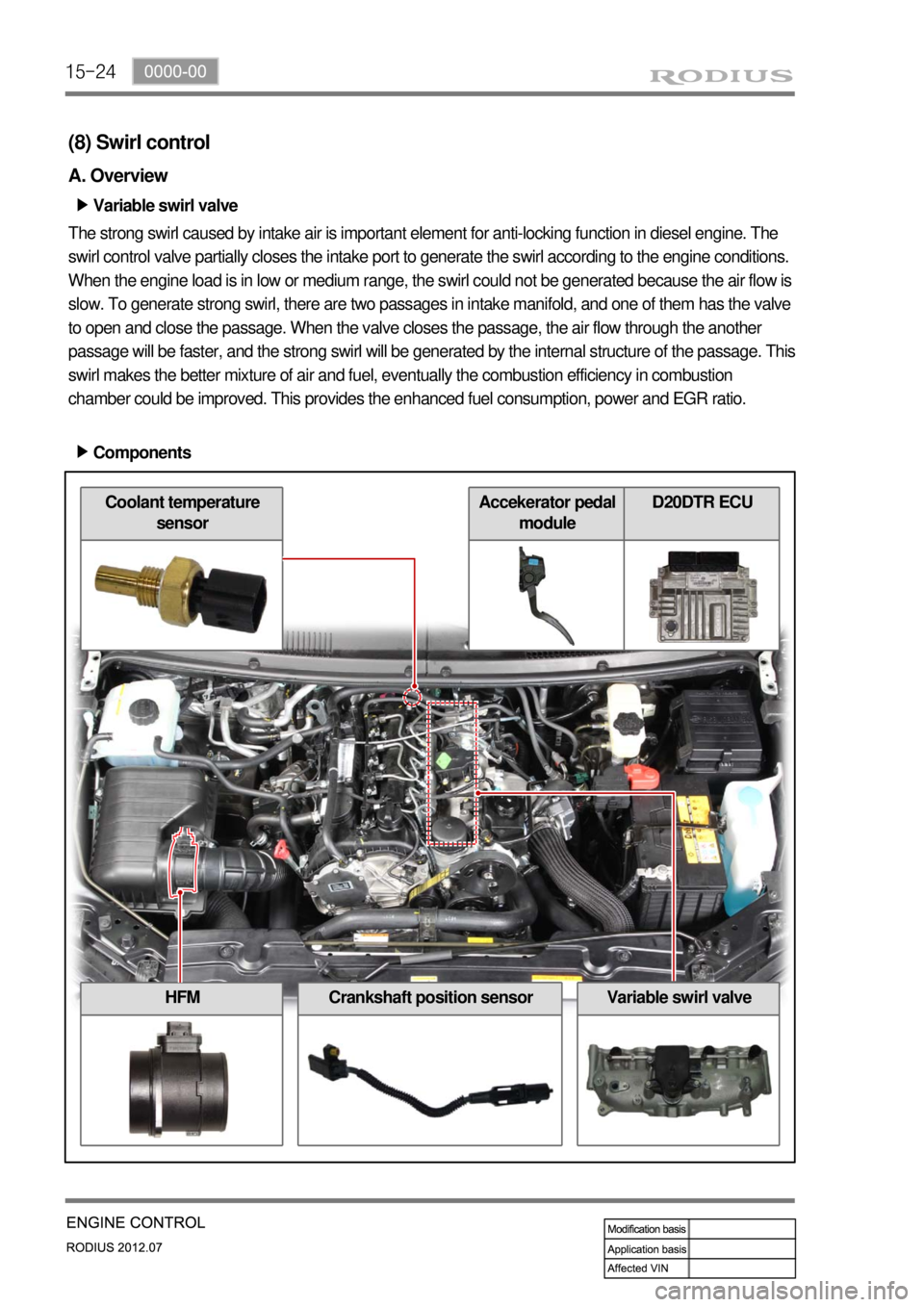
15-24
(8) Swirl control
A. Overview
Variable swirl valve â–¶
The strong swirl caused by intake air is important element for anti-locking function in diesel engine. The
swirl control valve partially closes the intake port to generate the swirl according to the engine conditions.
When the engine load is in low or medium range, the swirl could not be generated because the air flow is
slow. To generate strong swirl, there are two passages in intake manifold, and one of them has the valve
to open and close the passage. When the valve closes the passage, the air flow through the another
passage will be faster, and the strong swirl will be generated by the internal structure of the passage. This
swirl makes the better mixture of air and fuel, eventually the combustion efficiency in combustion
chamber could be improved. This provides the enhanced fuel consumption, power and EGR ratio.
Components â–¶
HFMCrankshaft position sensorVariable swirl valve
Coolant temperature
sensorAccekerator pedal
moduleD20DTR ECU
Page 353 of 715

15-28
Electric throttle
bodyAccelerator
pedal
moduleD20DTR
ECU
(9) EGR control
A. Overview
The EGR (Electric-Exhaust Gas Recirculation) valve reduces the NOx emission level by recirculating
some of the exhaust gas to the intake system.
To meet Euro-V regulation, the capacity and response rate of E-EGR valve in D20DTR engine have
been greatly improved. The EGR cooler with high capacity reduces the Nox, and the bypass valve
reduces the CO and HC due to EGR gas before warming up.
Also, the engine ECU adjusts the E-EGR opening by using the air mass signal through HFM sensor. If
the exhaust gas gets into the intake manifold when the EGR valve is open, the amount of fresh air
through HFM sensor should be decresed.
B. Components
E-EGR cooler
Coolant
temperature
sensorOxygen sensor
HFM (intake
air
temperature)
Crankshaft
position
sensorE-EGR valve
T-MAP
sensor
Page 355 of 715

15-30
D. Bypass control for EGR cooler
Cooler temperature â–¶
<007e008f008c00950047009b008f008c0047008a00960096009300880095009b0047009b008c00940097008c00990088009b009c0099008c00470090009a00470089008c00930096009e0047005e00570b4500530047009b008f008c0047008c009f008f00
88009c009a009b0047008e0088009a00470090009a00470089>ypassed the EGR cooler.
Exhaust gas temperature â–¶
<007e008f008c00950047009b008f008c0047008c009f008f0088009c009a009b0047008e0088009a0047009b008c00940097008c00990088009b009c0099008c00470090009a00470089008c00930096009e0047005a005700570b4500530047009b008f00
8c0047008c009f008f0088009c009a009b0047008e0088009a> is bypassed the EGR cooler.
Otherwise, PM could be increased due to too low exhaust gas temperature.
E. Control elements for EGR system
Accelerator pedal (engine load) - Indicates the driver's intention and engine load. If the load goes up,
the EGR ratio is decreased.
T-MAP (boost pressure map stored in ECU) - Compensates the difference in boost pressure by
adjusting EGR ratio.
Engine rpm - Used as the signal for determining EGR operating range.
Coolant temperature - When the coolant temperature is low, NOx is decreased but PM could be
increased. So, to reduce PM, decrease EGR ratio when the coolant temperature is low.
Intake air mass and temperature - HFM sensor measures the intake air mass to calculate the actual
EGR volume. If the air mass is larger than programmed value in map, EGR ratio will be higher.
EGR position sensor - Detects the actual opening angle of EGR valve and performs feedback
function according to PWM control by ECU.
Wide band oxygen sensor - Detects the oxygen volume in exhaust gas to check if the EGR ratio is
proper.
Electronic throttle body - Keeps EGR ratio to optimized level by controlling the throttle body in EGR
operating range (decreasing pressure in intake manifold). -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Page 357 of 715

15-32
(10) E-VGT control
A. Overview
E-VGT (Electric-Variable Geometry Turbine) turbocharger system in D20DTF engine uses the venturi
effect that controls the flow rate of exhaust gas by adjusting the passage in turbine housing. The newly
adopted DC motor actuator (E-actuator) controls the E-VGT system more precisely and faster. To get
the high operating power from turbine, the ECU reduces the exhaust gas passage In low speed range
and increases it in high speed range.
B. Components
HFM (intake air
temperature)
Front EGT
sensor
E-VGT actuatorAccelerator pedal
module
Crankshaft
position
sensorOxygen sensor
T-MAP sensor
Coolant
temperature
sensor
D20DTR ECU
Page 359 of 715

15-34
D. E-VGT system control
Turbocharger system operates the E-VGT actuator according to the signals for engine epm, accelerator
pedal position, atmospheric pressure, T-MAP, coolant temperature and intake air temperature.
Turbocharger actuator is performed PWM control by ECU.
In general, the boost pressure feedbacks the turbocharger operation and the boost temperature is used
for calculating the precise density.
E-VGT provides higher engine power with faster reaction speed compared to conventional VGT.
Operating wave Vane Control
Low
speed
rangeIn low speed range:
retract the vane to
increase boost
pressure. The vane
has low (-) duty, and
the unison ring
moves to retract the
vane in weak PWM
signal.
High
speed
rangeThe unison ring
moves to extend the
vane in strong PWM
signal. Maximum
pressure is 3 bar and
the system controls it
according to the input
signals.
Page 360 of 715

15-350000-00
HFM (intake air
temperature)CDPF
Electric throttle
bodyCoolant
temperature
sensorOxygen sensor
Injector (C3I)
E-EGR valve
(11) Wide band oxygen sensor control
A. Overview
For diesel engine, combustion is not performed at the optimum (theoretically correct) air-fuel ratio and
the oxygen concentration is thin in most cases. So the wide-band oxygen sensor is used for this kind of
engine, and this sensor is a little different from the one that used for gasoline engine. The combustion in
diesel engine is controlled by fuel injection volume. Therefore, the wide band oxygen sensor should be
used in diesel engine. This sensor measures the air-fuel ratio in very wide range, and is also called full
range oxygen sensor.
The wide band oxygen sensor measures the oxygen density in exhaust gas and sends it to ECU to
control the EGR more precisely. -
B. Components
D20DTR ECU
Page 363 of 715
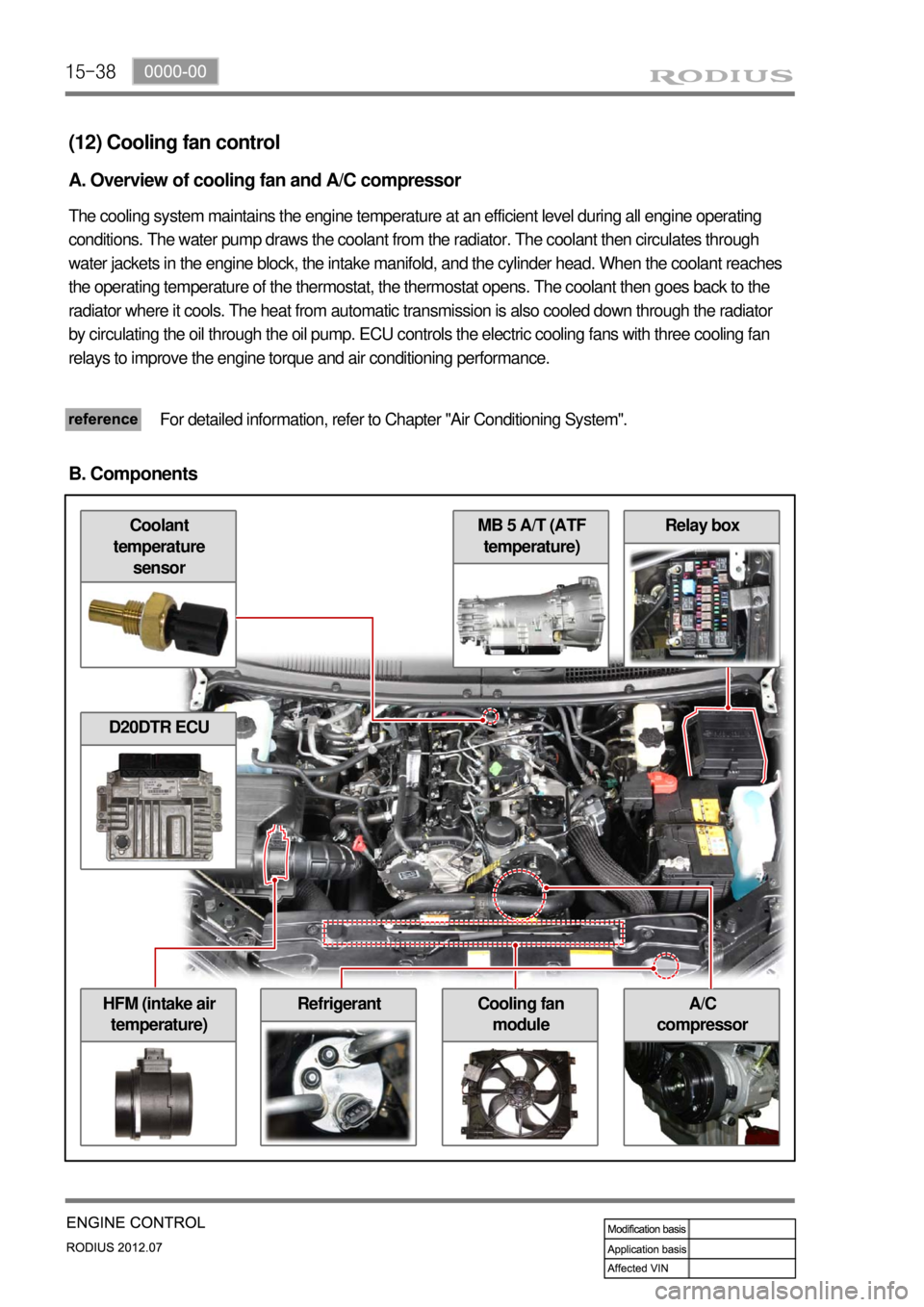
15-38
Relay box
A/C
compressorHFM (intake air
temperature)Cooling fan
module
MB 5 A/T (ATF
temperature)Coolant
temperature
sensor
(12) Cooling fan control
A. Overview of cooling fan and A/C compressor
The cooling system maintains the engine temperature at an efficient level during all engine operating
conditions. The water pump draws the coolant from the radiator. The coolant then circulates through
water jackets in the engine block, the intake manifold, and the cylinder head. When the coolant reaches
the operating temperature of the thermostat, the thermostat opens. The coolant then goes back to the
radiator where it cools. The heat from automatic transmission is also cooled down through the radiator
by circulating the oil through the oil pump. ECU controls the electric cooling fans with three cooling fan
relays to improve the engine torque and air conditioning performance.
For detailed information, refer to Chapter "Air Conditioning System".
B. Components
D20DTR ECU
Refrigerant
Page 365 of 715
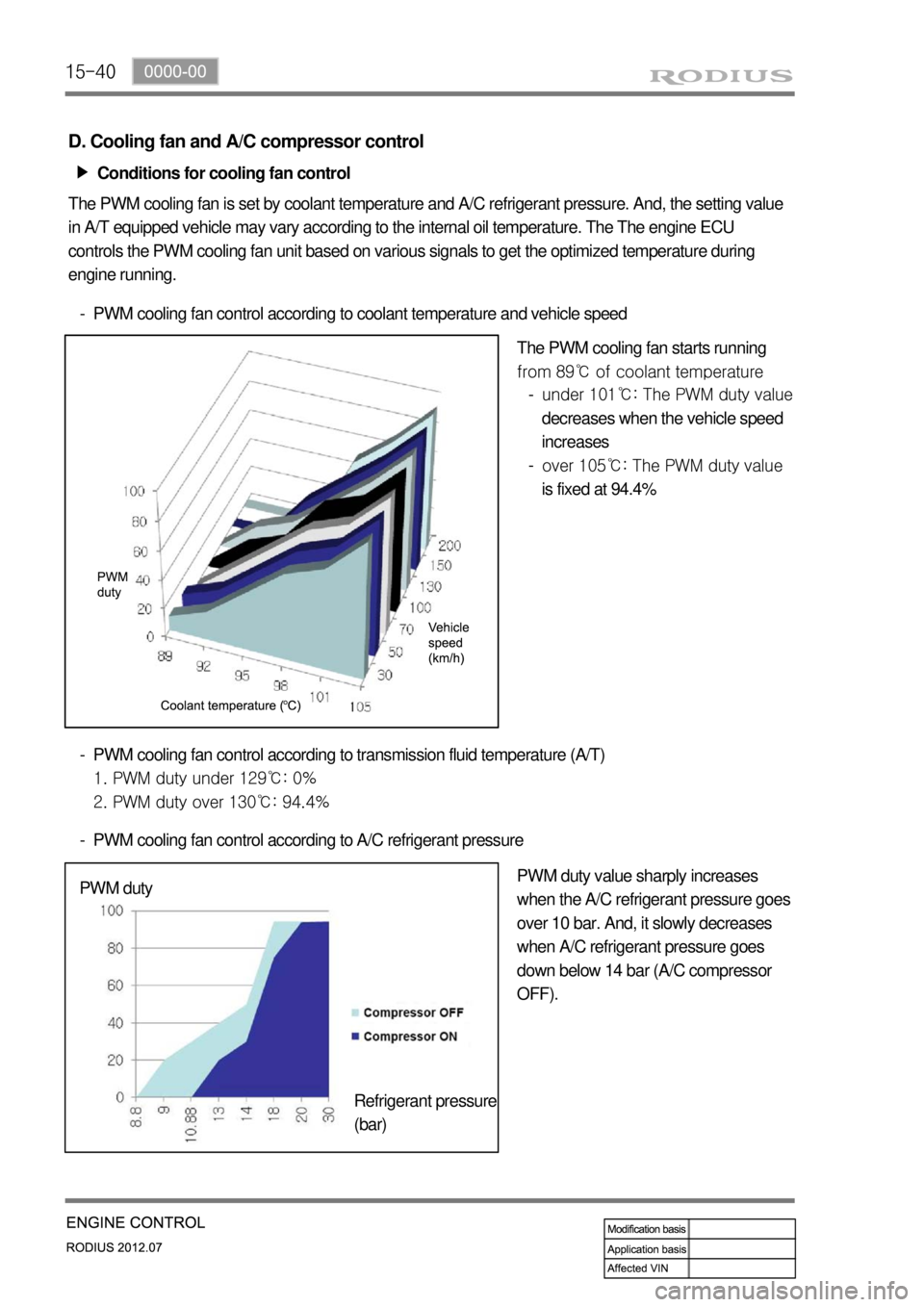
15-40
D. Cooling fan and A/C compressor control
Conditions for cooling fan control â–¶
The PWM cooling fan is set by coolant temperature and A/C refrigerant pressure. And, the setting value
in A/T equipped vehicle may vary according to the internal oil temperature. The The engine ECU
controls the PWM cooling fan unit based on various signals to get the optimized temperature during
engine running.
PWM cooling fan control according to coolant temperature and vehicle speed -
The PWM cooling fan starts running
from 89℃ of coolant temperature
PWM cooling fan control according to transmission fluid temperature (A/T)
1. PWM duty under 129℃: 0%
2. PWM duty over 130℃: 94.4% -
PWM cooling fan control according to A/C refrigerant pressure -
PWM duty value sharply increases
when the A/C refrigerant pressure goes
over 10 bar. And, it slowly decreases
when A/C refrigerant pressure goes
down below 14 bar (A/C compressor
OFF). PWM duty
Refrigerant pressure
(bar)under 101℃: The PWM duty value
decreases when the vehicle speed
increases
over 105℃: The PWM duty value
is fixed at 94.4% -
-