engine SSANGYONG TURISMO 2013 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 2013, Model line: TURISMO, Model: SSANGYONG TURISMO 2013Pages: 796, PDF Size: 78.99 MB
Page 373 of 796
15-450000-00
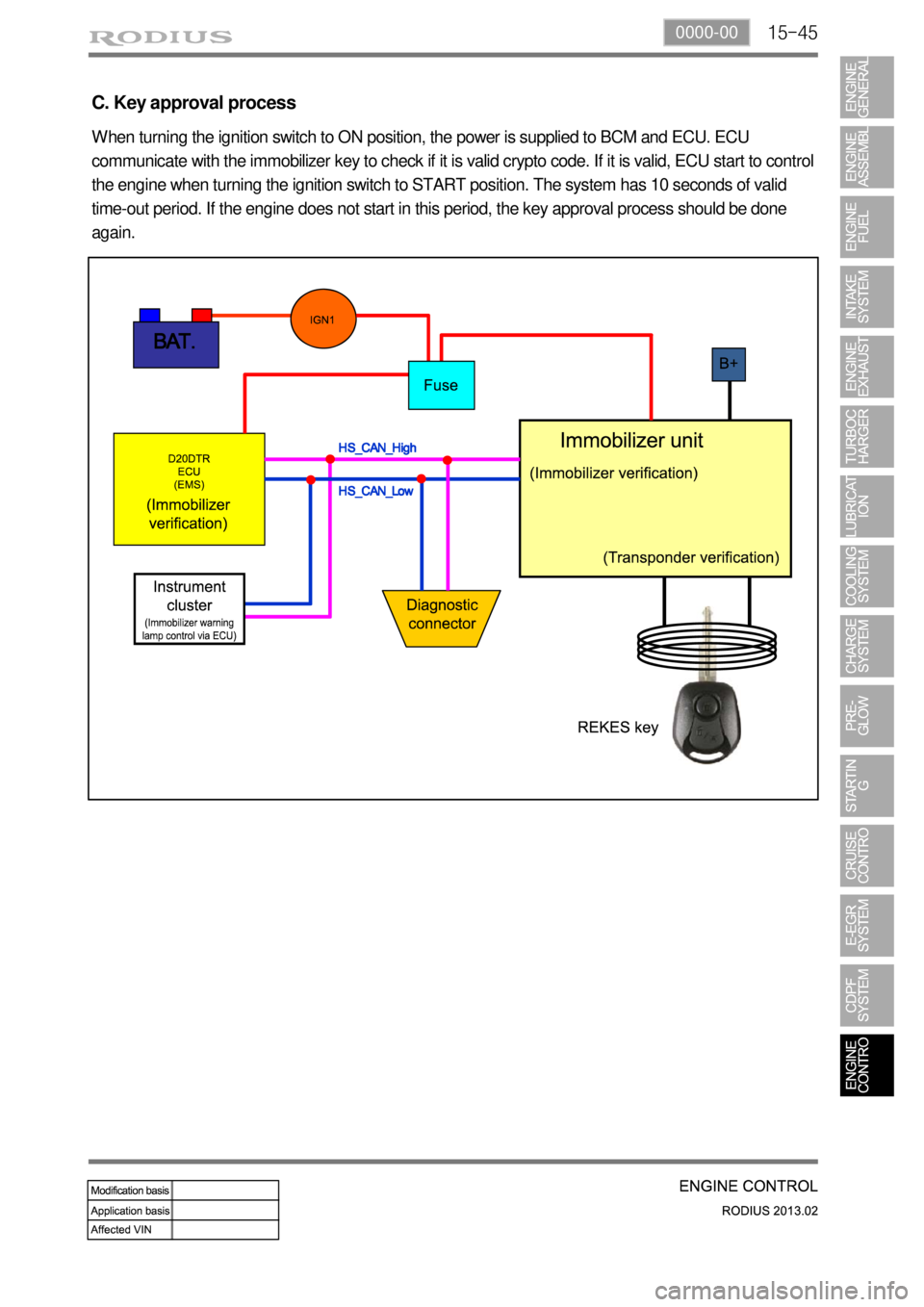
C. Key approval process
When turning the ignition switch to ON position, the power is supplied to BCM and ECU. ECU
communicate with the immobilizer key to check if it is valid crypto code. If it is valid, ECU start to control
the engine when turning the ignition switch to START position. The system has 10 seconds of valid
time-out period. If the engine does not start in this period, the key approval process should be done
again.
Page 374 of 796

15-46
(15) CDPF control
A. Overview
As the solution for environmental regulations and PM Particle Material) of diesel engine, the low
emission vehicle is getting popular. This vehicle is equipped with an extra filter to collect the soot and
burn it again so that the amount of PM in the exhaust gas passed through the DOC (Diesel Oxidation
Catalyst) is reduced. The CDPF (Catalyst & Diesel Particulate Filter) is an integrated filter including
DOC (Diesel Oxidation Catalyst) and DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter).
For details, refer to Chapter "CDPF".
B. Components
Oxygen sensorFront
EGT sensorCDPF
(DOC + DPF)Rear
EGT sensor
Differential pressure
sensorD20DTR ECUElectric throttle body
Page 376 of 796

15-48
Rear EGT sensor:
Measure DPF temp
Diff. pres. sensor:
Measure pressure
between front side and
rear side of CDPFElectronic throttle
body: Control intake
air mass
ECU (DCM 3.7)
Injector: Control post
injection
D. Operation process
When the differential pressure sensor detects the pressure difference between the front and the rear
side of CDPF, the sensor sends signal indicating the soot is accumulated and the post injection is
performed to raise the temperature of exhaust gas. The amount of fuel injected is determined
according to the temperature of exhaust gas detected by the rear temperature sensor. If the
tem
perature is below 600°C, the amount of fuel injected is increased to raise the temperature. If
the tem
perature is over 600°C, the amount of fuel injected is decreased or not controlled. When
the engine is running in low load range, the amount of post injection and the amount of intake air are
controlled. It is to raise the temperature by increasing the amount of fuel while decreasing the amount
of intake air.
Front EGT sensor:
Measure DOC temp
T-MAP sensor
Intake air
mass
Exceed PM
limitBooster
pressure/
temperaturePost injection
Control intake
air mass
Page 377 of 796

15-490000-00
E. Cautions
Use only specified Engine Oil (approved by MB Sheet 229.51) for CDPF. -
Use only specified engine oil (Low Ash Oil) ▶
The vehicle equipped with CDPF should use specific engine oil to improve the engine
performance and fuel economy, and ensure the service life of CDPF. -
Issue with normal engine oil ▶
Sulfur, one of the contents of engine oil is burned and generates soot that is not regenerated by
the DPF. This remains on the filter as ashes and keeps accumulating. Eventually, this ashes will
block the filter. -
Benefit for specified engine oil ▶
Minimized the sulfur content of engine oil which reduces the service life.
Improved fuel economy and emission level of CO2 with high performance and low viscosity.
Increased service life of engine oil with high resistance to temperature. -
-
-
Problems when using unspecified engine oil ▶
The service life of filter may be reduced by 30% or more by the ashes accumulated on the filter.
The fuel economy may be reduced because of engine rolling resistance, frequent regeneration of
DPF. -
-
These problems are also caused by oil with high sulfur content, such as tax exemption oil and
heating oil, etc. *
Page 380 of 796

01-50000-00
No. FUNCTION No. FUNCTION
1 HFM sensor 12 Intake manifold
2 Intake air duct 13 Connecting rod
3 Resonance flap 14 Exhaust manifold
4 Cylinder head cover 15 Crankshaft
5 Exhaust camshaft 16 Engine mounting
6 Intake camshaft 17 Starter
7 Cylinder head 18 Crankcase
8 Spark plug connector 19 Oil pump sprocket
9 Valve tappe
t20 Oil strainer
10 Injector 21 Oil pan
11 Exhaust valve 22 Drain plug
Front View ▶
Page 382 of 796

01-70000-00
2. DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
1) Cleanliness and Care
An automobile engine is a combination of many machined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces with
tolerances that are measured in the ten-thousandths of an inch. When any internal engine parts are
serviced, care and cleanliness are important. A liberal coating of engine oil should be applied to friction
areas during assembly, to protect and lubricate the surfaces on initial operation.
Proper cleaning and protection of machined surfaces and friction areas is part of the repair procedure.
This is considered standard shop practice even if not specifically stated.
Whenever valve train components are removed for service, they should be kept in order.
They should be installed in the same locations, and with the same mating surfaces, as when they were
removed. Battery cables should be disconnected before any major work is performed on the engine.
Failure to disconnect cables may result in damage to wire harness or other electrical parts.
2) On-Engine Service
Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit, or when a
tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals.
Disconnecting this cable will help prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle.
The ignition must also be in LOCK unless otherwise noted.
Notice Any time the air cleaner is removed, the intake opening -
Any time the air cleaner is removed, the intake opening should be covered. This will protect
against accidental entrance of foreign material, which could follow the intake passage into the
cylinder and cause extensive damage when the engine is started. -
Page 383 of 796

02-31113-01
1. SPECIFICATIONS
1) Engine Specifications
Page 388 of 796

03-32211-22
1. FUEL SYSTEM SPECIFICATION
Use Only Unleaded Fuel Rated at 89 Octane or Higher ▶
Fuel quality and additives contained in fuel have a significant effect on power output, drivability, and life
of the engine. Fuel with too low an octane number can cause engine knock.
Do Not Use Methanol ▶
Fuels containing methanol (wood alcohol) should not be used in vehicle.
This type of fuel can reduce vehicle performance and damage components of the fuel system.
Vehicle Fueling from Drums or Storage Containers ▶
For safety reasons (particularly when using noncommercial fueling systems) fuel containers, pumps
and hoses must be properly earthed. Static electricity build up can occur under certain atmospheric
and fuel flow conditions if unearthed hoses, particularly plastic, are fitted to the fuel-dispensing pump.
It is therefore recommended that earthed pumps with integrally earthed hoses be used, and that
storage containers be properly earthed during all noncommercial fueling operations.
Page 398 of 796

07-6
1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The cooling system maintains the engine temperature at an efficient level during all engine operating
conditions. When the engine is cold, the cooling system cools the engine slowly or not at all. This slo
w
cooling of the engine allows the engine to warm up quickly. The cooling system includes a radiator and
recovery subsystem, cooling fans, a thermostat and housing, a water pump, and a water pump drive
belt. The timing belt drives the water pump. All components must function properly for the cooling
system to operation. The water pump draws the coolant from the radiator.
The coolant then circulates through water jackets in the engine block, the intake manifold, and the
cylinder head. When the coolant reaches the operating temperature of the thermostat, the thermostat
opens. The coolant then goes back to the radiator where it cools. This system directs some coolant
through the hoses to the heat core. This provides for heating and defrosting. The coolant reservoir is
connected to the radiator to recover the coolant displaced by expansion from the high temperatures.
The coolant reservoir maintains the correct coolant level. The cooling system for this vehicle has no
radiator cap or filler neck. The coolant is added to the cooling system through the coolant reservoir.
Page 403 of 796

08-51452-01
1. CHARGING SYSTEM OPERATION
Alternators use a new type of regulator that incorporates a diode trio. A Delta stator, a rectifier bridge,
and a rotor with slip rings and brushes are electrically similar to earlier alternators.
A conventional pulley and fan are used. There is no test hole.
1) Charging Time Required
The time required to charge a battery will vary depending upon the following factors:
Size of Battery ▶
A Completely discharged large heavy-duty battery required more than twice the recharging
time as a completely discharged small passenger car battery. -
Temperature ▶
A longer time will be needed to charge any battery at -18°C (0°F) than at 27°C (80°F).
When a fast charger is connected to a cold battery, the current accepted by the battery will be
very low at first. The battery will accept a higher current rate as the battery warms. -
Charger Capacity ▶
A charger which can supply only 5 amperes will require a much longer charging period than a
charger that can supply 30 amperes or more. -
State-of-Charge ▶
A completely discharged battery requires more than twice as much charge as a one half
charged battery. Because the electrolyte is nearly pure water and a poor conductor in a
completely discharged battery, the current accepted by the battery is very low at first. Later, as
the charging current causes the electrolyte acid content to increase, the charging current will
likewise increase. -
2. STARTING SYSTEM OPERATION
The engine electrical system includes the battery, the ignition, the starter, the alternator, and all the
related wiring. Diagnostic tables will aid in troubleshooting system faults. When a fault is traced to a
particular component, refer to that component section of the service manual. The starting system
circuit consists of the battery, the starter motor, the ignition switch, and all the related electrical wiring.
All of these components are connected electrically.