height SUBARU TRIBECA 2009 1.G Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUBARU, Model Year: 2009, Model line: TRIBECA, Model: SUBARU TRIBECA 2009 1.GPages: 2453, PDF Size: 46.32 MB
Page 929 of 2453
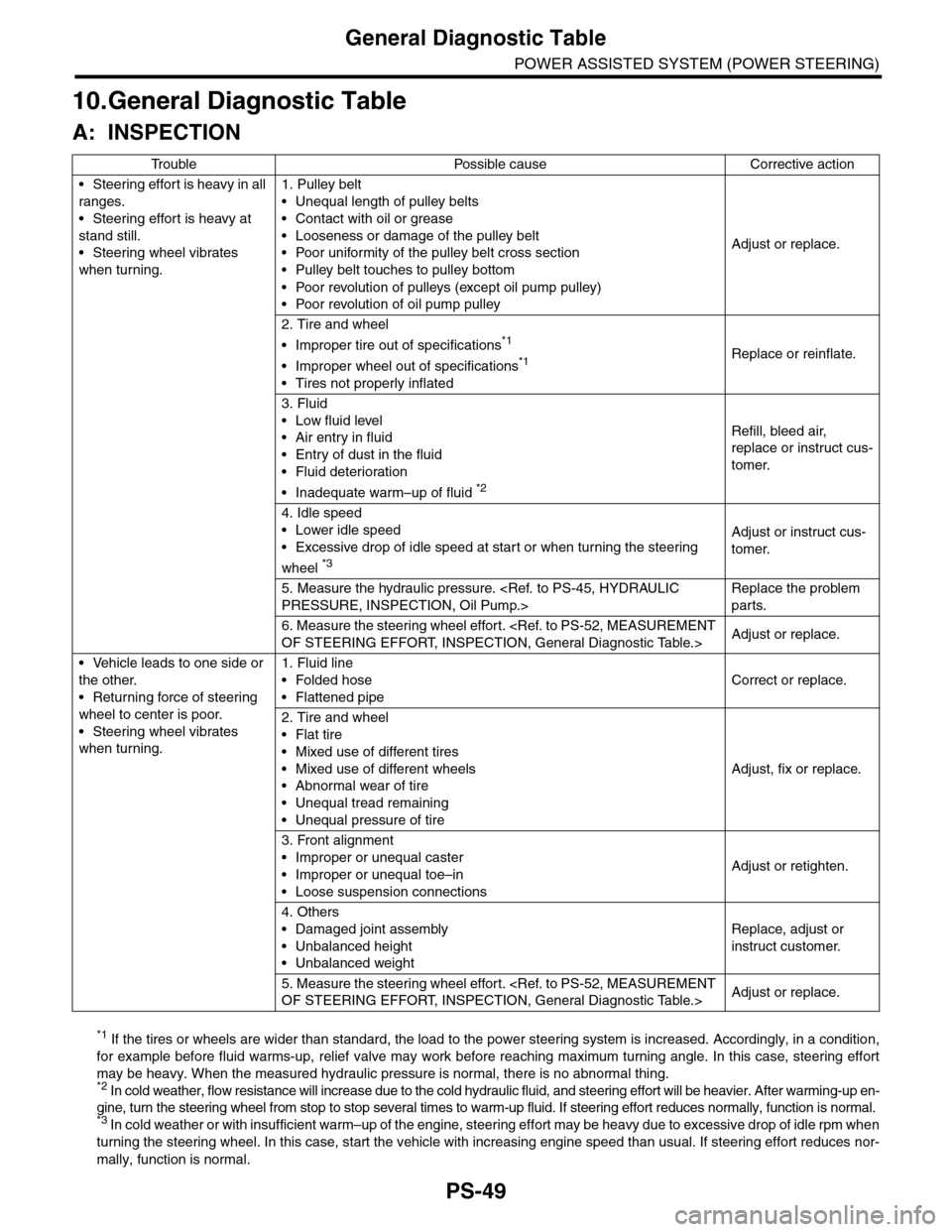
PS-49
General Diagnostic Table
POWER ASSISTED SYSTEM (POWER STEERING)
10.General Diagnostic Table
A: INSPECTION
*1 If the tires or wheels are wider than standard, the load to the power steering system is increased. Accordingly, in a condition,
for example before fluid warms-up, relief valve may work before reaching maximum turning angle. In this case, steering effort
may be heavy. When the measured hydraulic pressure is normal, there is no abnormal thing. *2 In cold weather, flow resistance will increase due to the cold hydraulic fluid, and steering effort will be heavier. After warming-up en-
gine, turn the steering wheel from stop to stop several times to warm-up fluid. If steering effort reduces normally, function is normal. *3 I n c o l d w e a t h e r o r w i t h i n s u f f i c i e n t w a r m – u p o f t h e e n g i n e , s t e e r i n g e f f o r t m a y b e h e a v y d u e t o e x c e s s i v e d r o p o f i d l e r p m w h en
turning the steering wheel. In this case, start the vehicle with increasing engine speed than usual. If steering effort reduces nor-
mally, function is normal.
Tr o u b l e P o s s i b l e c a u s e C o r r e c t i v e a c t i o n
•Steering effort is heavy in all
ranges.
•Steering effort is heavy at
stand still.
•Steering wheel vibrates
when turning.
1. Pulley belt
•Unequal length of pulley belts
•Contact with oil or grease
•Looseness or damage of the pulley belt
•Poor uniformity of the pulley belt cross section
•Pulley belt touches to pulley bottom
•Poor revolution of pulleys (except oil pump pulley)
•Poor revolution of oil pump pulley
Adjust or replace.
2. Tire and wheel
•Improper tire out of specifications*1
•Improper wheel out of specifications*1
•Tires not properly inflated
Replace or reinflate.
3. Fluid
•Low fluid level
•Air entry in fluid
•Entry of dust in the fluid
•Fluid deterioration
•Inadequate warm–up of fluid *2
Refill, bleed air,
replace or instruct cus-
tomer.
4. Idle speed
•Lower idle speed
•Excessive drop of idle speed at start or when turning the steering
wheel *3
Adjust or instruct cus-
tomer.
5. Measure the hydraulic pressure.
Replace the problem
parts.
6. Measure the steering wheel effort.
•Vehicle leads to one side or
the other.
•Returning force of steering
wheel to center is poor.
•Steering wheel vibrates
when turning.
1. Fluid line
•Folded hose
•Flattened pipe
Correct or replace.
2. Tire and wheel
•Flat tire
•Mixed use of different tires
•Mixed use of different wheels
•Abnormal wear of tire
•Unequal tread remaining
•Unequal pressure of tire
Adjust, fix or replace.
3. Front alignment
•Improper or unequal caster
•Improper or unequal toe–in
•Loose suspension connections
Adjust or retighten.
4. Others
•Damaged joint assembly
•Unbalanced height
•Unbalanced weight
Replace, adjust or
instruct customer.
5. Measure the steering wheel effort.
Page 935 of 2453
RS-2
General Description
REAR SUSPENSION
1. General Description
A: SPECIFICATION
NOTE:
•Front and rear toe–in and front camber can be
adjusted. Adjust if the toe–in or camber tolerance
exceeds specifications.
•Other items indicated in the specifications table
cannot be adjusted. If other items exceed specifica-
tions, check the suspension parts and connections
for deformation, and replace with new ones as re-
quired.
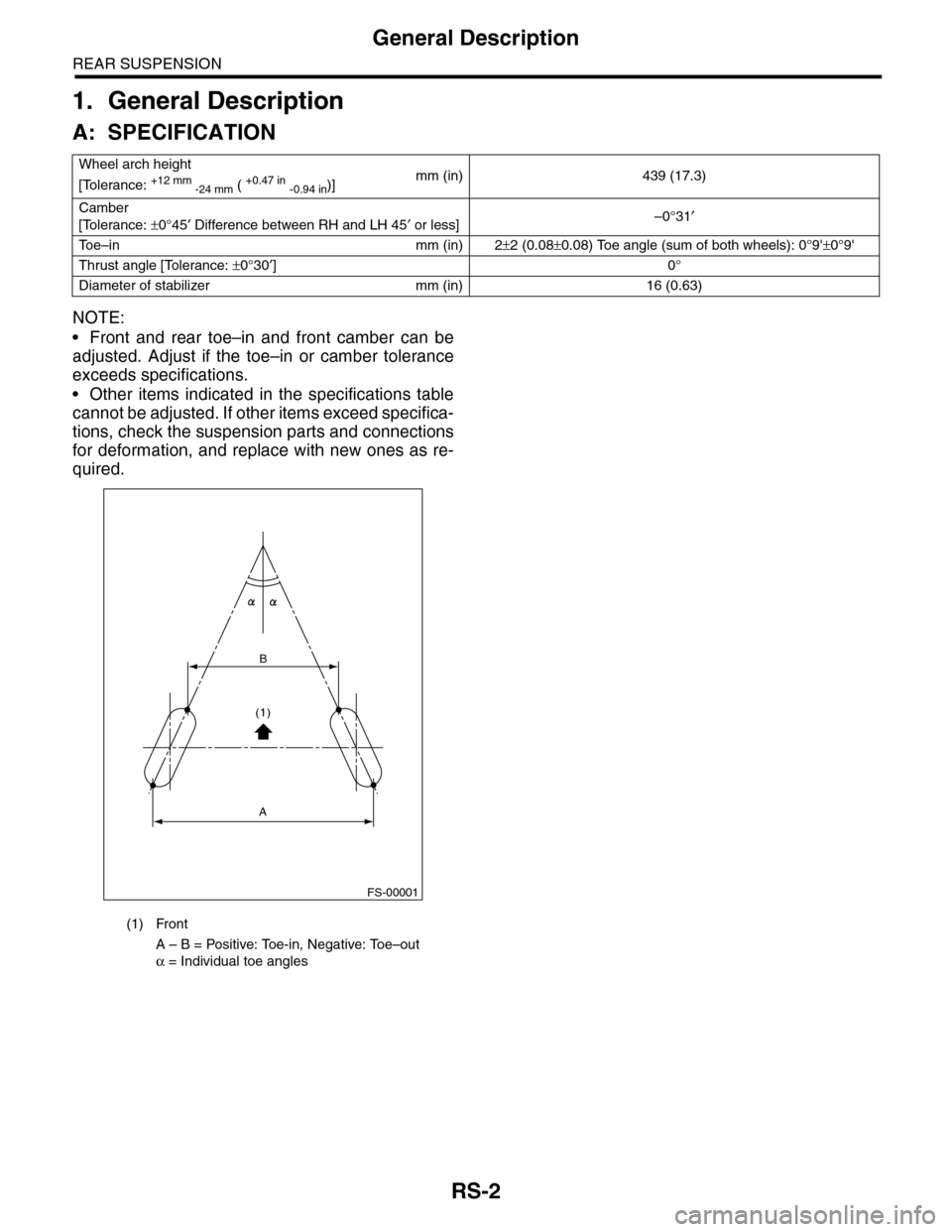
Wheel arch height
[Tolerance: +12 mm -24 mm ( +0.47 in -0.94 in)]mm (in) 439 (17.3)
Camber
[Tolerance: ±0°45′ Difference between RH and LH 45′ or less]–0°31′
To e – i n m m ( i n ) 2±2 (0.08±0.08) Toe angle (sum of both wheels): 0°9'±0°9'
Thrust angle [Tolerance: ±0°30′]0°
Diameter of stabilizer mm (in) 16 (0.63)
(1) Front
A – B = Positive: Toe-in, Negative: Toe–out
α = Individual toe angles
FS-00001
B
A
(1)
Page 950 of 2453

RS-17
General Diagnostic Table
REAR SUSPENSION
10.General Diagnostic Table
A: INSPECTION
1. IMPROPER VEHICLE POSTURE OR IMPROPER WHEEL ARCH HEIGHT
2. POOR RIDE COMFORT
1) Large rebound shock
2) Rocking of the vehicle continues too long after running over bump and hump.
3) Excessive shock in bumping
3. NOISE
Po ss ibl e c a us e C o r r e ct ive ac ti o n
(1) Permanent distortion or damaged coil spring Replace.
(2) Rough operation of damper strut or shock absorber Replace.
(3) Improper installation of strut or shock absorber Replace with proper parts.
(4) Installation of the wrong coil spring Replace with proper parts.
Po ss ibl e ca us e C or r e ct i ve a ct io n
(1) Damaged coil spring Replace.
(2) Overinflation of tires Adjust.
(3) Improper wheel arch height Adjust or replace the coil springs with new ones.
(4) Fault in operation of damper strut or shock absorber Replace.
(5) Damage or deformation of strut mount or shock absorber mount Replace.
(6) Unsuitable length (maximum or minimum) of damper strut or shock
absorber
Replace with appropriate parts.
(7) Deformation or loss of bushing Replace.
(8) Deformation or damage of helper in strut assembly or shock absorber Replace.
(9) Oil leakage from the damper strut or shock absorber Replace.
Po ss ibl e c a us e C o r r e ct ive ac ti o n
(1) Wear or damage of damper strut or shock absorber component parts Replace.
(2) Loosening of the suspension link installing bolt Tighten to the specified torque.
(3) Deformation or loss of bushing Replace.
(4) Unsuitable length (maximum or minimum) of damper strut or shock
absorber
Replace with appropriate parts.
(5) Damaged coil spring Replace.
(6) Wear or damage of the ball joint Replace.
(7) Deformation of the stabilizer clamp Replace.
Page 1121 of 2453
CO(H6DO)-2
General Description
COOLING
1. General Description
A: SPECIFICATION
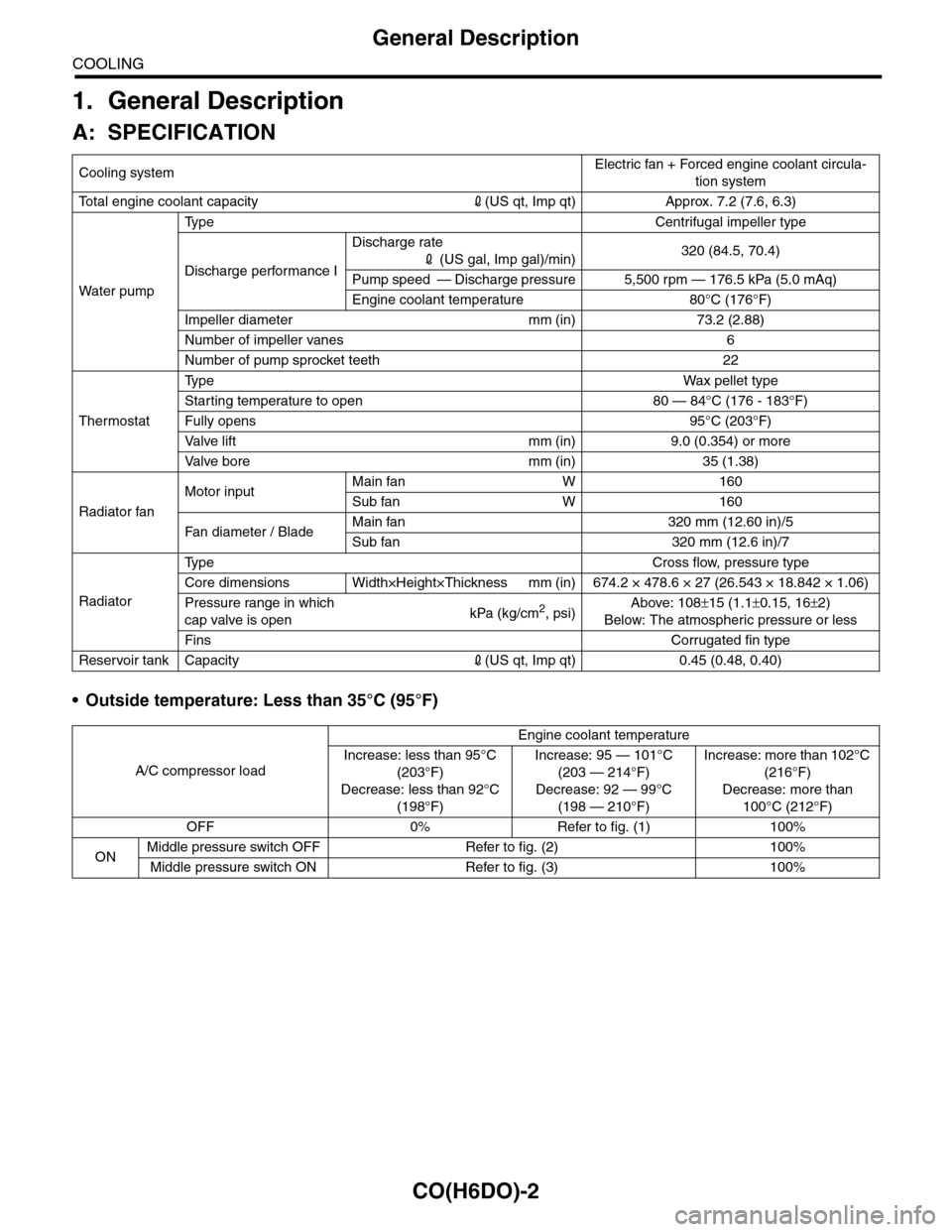
•Outside temperature: Less than 35°C (95°F)
Cooling systemElectric fan + Forced engine coolant circula-
tion system
To t a l e n g i n e c o o l a n t c a p a c i t y2(US qt, Imp qt) Approx. 7.2 (7.6, 6.3)
Wa t er p u mp
Ty p e C e n t r i f u g a l i m p e l l e r t y p e
Discharge performance I
Discharge rate
2 (US gal, Imp gal)/min)320 (84.5, 70.4)
Pump speed — Discharge pressure 5,500 rpm — 176.5 kPa (5.0 mAq)
Engine coolant temperature 80°C (176°F)
Impeller diameter mm (in) 73.2 (2.88)
Number of impeller vanes 6
Number of pump sprocket teeth 22
Thermostat
Ty p eWa x p el l et t yp e
Starting temperature to open 80 — 84°C (176 - 183°F)
Fully opens 95°C (203°F)
Va l ve l i f t m m ( i n ) 9 . 0 ( 0 . 3 5 4 ) o r m o r e
Va l ve b o r e m m ( i n ) 3 5 ( 1 . 3 8 )
Radiator fan
Motor inputMain fan W 160
Sub fan W 160
Fan di a me t er / B la deMain fan 320 mm (12.60 in)/5
Sub fan 320 mm (12.6 in)/7
Radiator
Ty p e C r o s s f l o w , p r e s s u r e t y p e
Core dimensions Width×Height×Thickness mm (in) 674.2 × 478.6 × 27 (26.543 × 18.842 × 1.06)
Pressure range in which
cap valve is openkPa (kg/cm2, psi)Above: 108±15 (1.1±0.15, 16±2)
Below: The atmospheric pressure or less
FinsCorrugated fin type
Reservoir tank Capacity2(US qt, Imp qt) 0.45 (0.48, 0.40)
A/C compressor load
Engine coolant temperature
Increase: less than 95°C
(203°F)
Decrease: less than 92°C
(198°F)
Increase: 95 — 101°C
(203 — 214°F)
Decrease: 92 — 99°C
(198 — 210°F)
Increase: more than 102°C
(216°F)
Decrease: more than
100°C (212°F)
OFF 0% Refer to fig. (1) 100%
ONMiddle pressure switch OFF Refer to fig. (2) 100%
Middle pressure switch ON Refer to fig. (3) 100%
Page 1131 of 2453
CO(H6DO)-12
Engine Coolant
COOLING
2. PROCEDURE TO ADJUST THE CON-
CENTRATION OF THE COOLANT
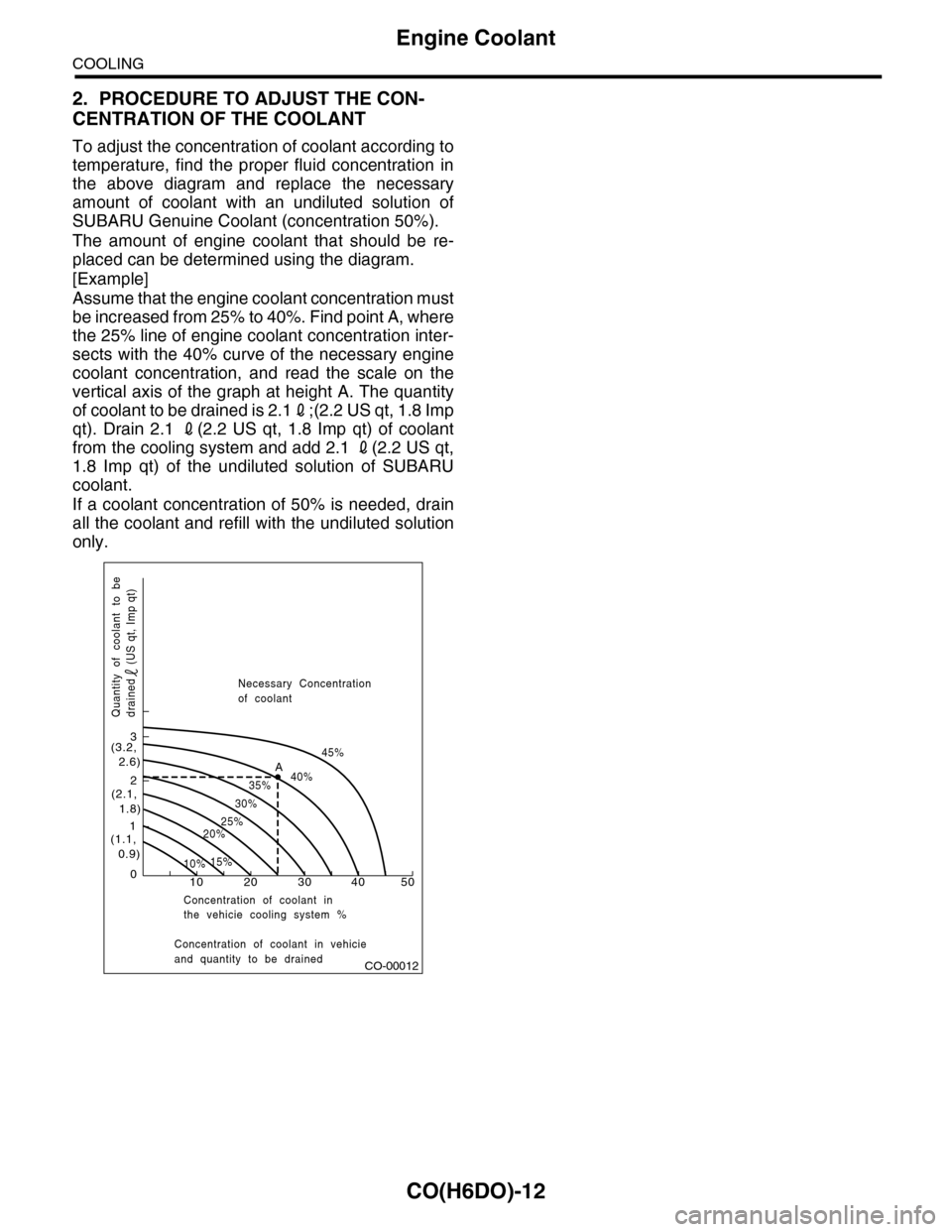
To adjust the concentration of coolant according to
temperature, find the proper fluid concentration in
the above diagram and replace the necessary
amount of coolant with an undiluted solution of
SUBARU Genuine Coolant (concentration 50%).
The amount of engine coolant that should be re-
placed can be determined using the diagram.
[Example]
Assume that the engine coolant concentration must
be increased from 25% to 40%. Find point A, where
the 25% line of engine coolant concentration inter-
sects with the 40% curve of the necessary engine
coolant concentration, and read the scale on the
vertical axis of the graph at height A. The quantity
of coolant to be drained is 2.12;(2.2 US qt, 1.8 Imp
qt). Drain 2.1 2(2.2 US qt, 1.8 Imp qt) of coolant
from the cooling system and add 2.1 2(2.2 US qt,
1.8 Imp qt) of the undiluted solution of SUBARU
coolant.
If a coolant concentration of 50% is needed, drain
all the coolant and refill with the undiluted solution
only.
CO-00012
100
1
2
3
(1.1, 0.9)
(2.1, 1.8)
(3.2, 2.6)
10%15%
25%20%
30%
35%40%
45%A
20 30 40 50
Concentration of coolant in vehicieand quantity to be drained
Quantity of coolant to bedrained (US qt, Imp qt)
Necessary Concentrationof coolant
Concentration of coolant inthe vehicie cooling system %
Page 1869 of 2453
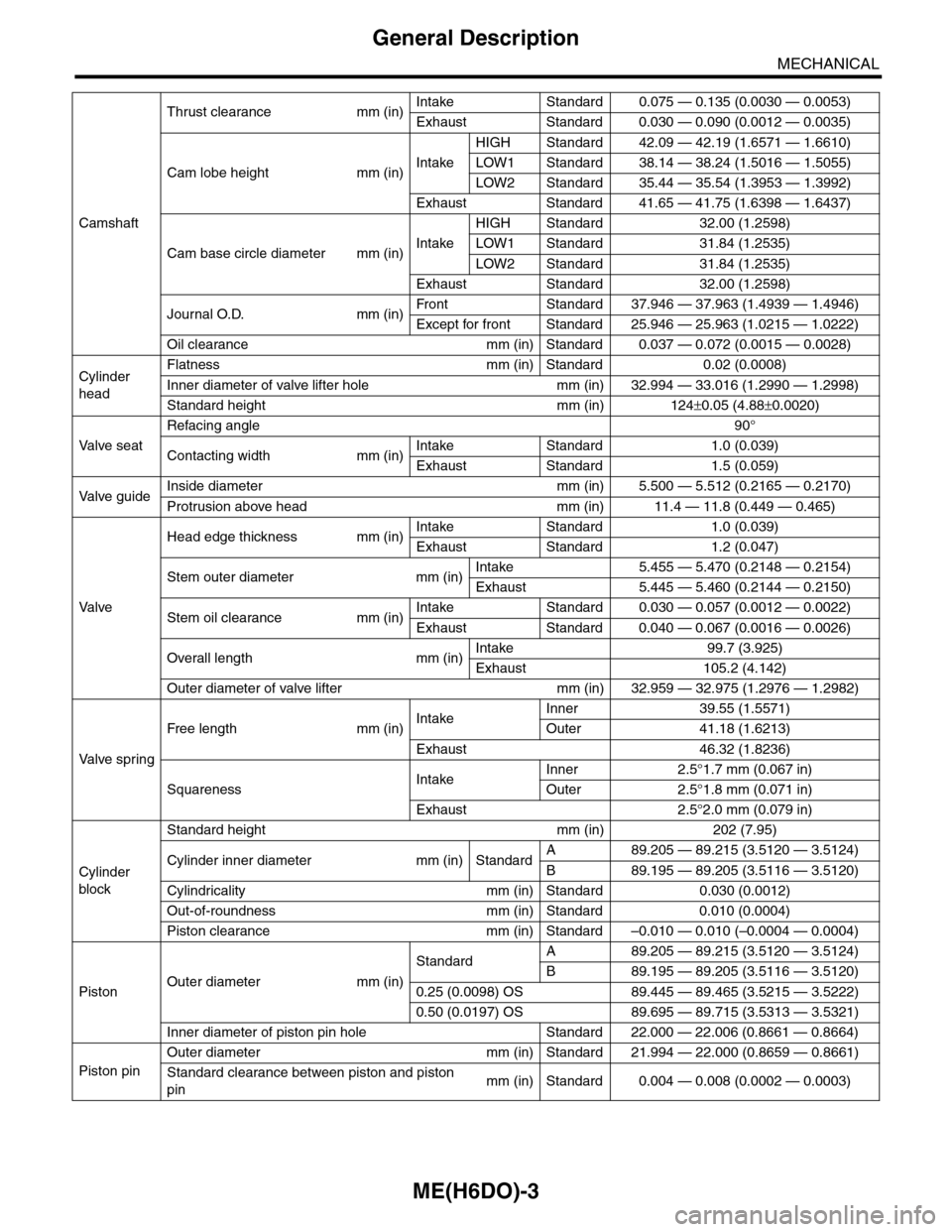
ME(H6DO)-3
General Description
MECHANICAL
Camshaft
Thrust clearance mm (in)Intake Standard 0.075 — 0.135 (0.0030 — 0.0053)
Exhaust Standard 0.030 — 0.090 (0.0012 — 0.0035)
Cam lobe height mm (in)Intake
HIGH Standard 42.09 — 42.19 (1.6571 — 1.6610)
LOW1 Standard 38.14 — 38.24 (1.5016 — 1.5055)
LOW2 Standard 35.44 — 35.54 (1.3953 — 1.3992)
Exhaust Standard 41.65 — 41.75 (1.6398 — 1.6437)
Cam base circle diameter mm (in)Intake
HIGH Standard 32.00 (1.2598)
LOW1 Standard 31.84 (1.2535)
LOW2 Standard 31.84 (1.2535)
Exhaust Standard 32.00 (1.2598)
Journal O.D. mm (in)Fr o nt S ta n da r d 3 7. 9 46 — 3 7 . 96 3 ( 1 . 49 3 9 — 1. 4 9 46 )
Except for front Standard 25.946 — 25.963 (1.0215 — 1.0222)
Oil clearance mm (in) Standard 0.037 — 0.072 (0.0015 — 0.0028)
Cylinder
head
Flatness mm (in) Standard 0.02 (0.0008)
Inner diameter of valve lifter hole mm (in) 32.994 — 33.016 (1.2990 — 1.2998)
Standard height mm (in) 124±0.05 (4.88±0.0020)
Va l ve s e a t
Refacing angle90°
Contacting width mm (in)Intake Standard 1.0 (0.039)
Exhaust Standard 1.5 (0.059)
Va l ve g u i d eInside diameter mm (in) 5.500 — 5.512 (0.2165 — 0.2170)
Protrusion above head mm (in) 11.4 — 11.8 (0.449 — 0.465)
Va l ve
Head edge thickness mm (in)Intake Standard 1.0 (0.039)
Exhaust Standard 1.2 (0.047)
Stem outer diameter mm (in)Intake 5.455 — 5.470 (0.2148 — 0.2154)
Exhaust 5.445 — 5.460 (0.2144 — 0.2150)
Stem oil clearance mm (in)Intake Standard 0.030 — 0.057 (0.0012 — 0.0022)
Exhaust Standard 0.040 — 0.067 (0.0016 — 0.0026)
Overall length mm (in)Intake 99.7 (3.925)
Exhaust 105.2 (4.142)
Outer diameter of valve lifter mm (in) 32.959 — 32.975 (1.2976 — 1.2982)
Va l ve s p r i n g
Free length mm (in)IntakeInner 39.55 (1.5571)
Outer 41.18 (1.6213)
Exhaust 46.32 (1.8236)
SquarenessIntakeInner 2.5°1.7 mm (0.067 in)
Outer 2.5°1.8 mm (0.071 in)
Exhaust 2.5°2.0 mm (0.079 in)
Cylinder
block
Standard height mm (in) 202 (7.95)
Cylinder inner diameter mm (in) StandardA89.205 — 89.215 (3.5120 — 3.5124)
B89.195 — 89.205 (3.5116 — 3.5120)
Cylindricality mm (in) Standard 0.030 (0.0012)
Out-of-roundness mm (in) Standard 0.010 (0.0004)
Piston clearance mm (in) Standard –0.010 — 0.010 (–0.0004 — 0.0004)
PistonOuter diameter mm (in)
StandardA89.205 — 89.215 (3.5120 — 3.5124)
B89.195 — 89.205 (3.5116 — 3.5120)
0.25 (0.0098) OS 89.445 — 89.465 (3.5215 — 3.5222)
0.50 (0.0197) OS 89.695 — 89.715 (3.5313 — 3.5321)
Inner diameter of piston pin hole Standard 22.000 — 22.006 (0.8661 — 0.8664)
Piston pin
Outer diameter mm (in) Standard 21.994 — 22.000 (0.8659 — 0.8661)
Standard clearance between piston and piston
pinmm (in) Standard 0.004 — 0.008 (0.0002 — 0.0003)
Page 1922 of 2453

ME(H6DO)-56
Camshaft
MECHANICAL
(6) Measure the widest point of the plastigauge
on each journal. If oil clearance exceeds the
standard, replace the camshaft. If necessary,
replace the camshaft caps and cylinder head as
a set.
Standard:
0.037 — 0.072 mm (0.0015 — 0.0028 in)
(7) Completely remove the plastigauge.
5) Check the cam face condition; remove the minor
faults by grinding with oil stone. Measure the cam
height H. If it exceeds the standard or offset wear
occurs, replace it.
Cam height H:
Standard
Intake
HIGH 42.09 — 42.19 mm (1.6571 — 1.6610
in)
LOW1 38.14 — 38.24 mm (1.5016 — 1.5055
in)
LOW2 35.44 — 35.54 mm (1.3953 — 1.3992
in)
Exhaust
41.65 — 41.75 mm (1.6398 — 1.6437 in)
Cam base circle diameter A:
Intake
HIGH 32.0 mm (1.2598 in)
LOW1 31.84 mm (1.2535 in)
LOW2 31.84 mm (1.2535 in)
Exhaust
32.0 mm (1.2598 in)
6) Measure the thrust clearance of camshaft with
dial gauge. If the clearance exceeds the standard
or offset wear occurs, replace the caps and cylinder
head as a set. If necessary replace the camshaft.
Standard
Intake
0.075 — 0.135 mm (0.0030 — 0.053 in)
Exhaust
0.030 — 0.090 mm (0.0012 — 0.035 in)
ME-00119
ME-00120
H
A
Page 1925 of 2453

ME(H6DO)-59
Cylinder Head
MECHANICAL
3) Measure the flatness of the cylinder head sur-
face that mates with crankcase using a straight
edge (A) and thickness gauge (B).
Flatness:
Standard
0.02 mm (0.0008 in)
Standard height of cylinder head:
124±0.05 mm (4.88±0.0020 in)
NOTE:
Uneven torque for the cylinder head nuts can
cause warping. When reinstalling, pay special at-
tention to the torque so as to tighten evenly.
2. VALVE SEAT
Inspect the intake and exhaust valve seats, and
correct the contact surfaces with a valve seat cutter
if they are defective or when valve guides are re-
placed.
Valve seat width W:
Intake
Standard
1.0 mm (0.039 in)
Exhaust
Standard
1.5 mm (0.059 in)
3. VALVE GUIDE
1) Check the clearance between valve guide and
stem. The clearance can be checked by measuring
respectively the outer diameter of valve stem and
inner diameter of valve guide with a micrometer.
Clearance between the valve guide and valve
stem:
Standard
Intake
0.030 — 0.057 mm (0.0012 — 0.0022 in)
Exhaust
0.040 — 0.067 mm (0.0016 — 0.0026 in)
2) If the clearance between valve guide and stem
exceeds the standard, replace the valve guide or
valve itself whichever shows greater amount of
wear or damaged and etc. See the following proce-
dure for valve guide replacement.
Valve guide inner diameter:
5.500 — 5.512 mm (0.2165 — 0.2170 in
Valve stem outer diameters:
Intake
5.455 — 5.470 mm (0.2148 — 0.2154 in)
Exhaust
5.445 — 5.460 mm (0.2144 — 0.2150 in)
(1) Place the cylinder head on ST1 with the
combustion chamber upward so that valve
guides fit the holes in ST1.
(2) Insert the ST2 into valve guide and press it
down to remove the valve guide.
ST1 18250AA010 CYLINDER HEAD TABLE
ST2 499765700 VALVE GUIDE REMOVER
(A)
(B)
ME-00551
ME-00127
WME-00553
Page 1937 of 2453
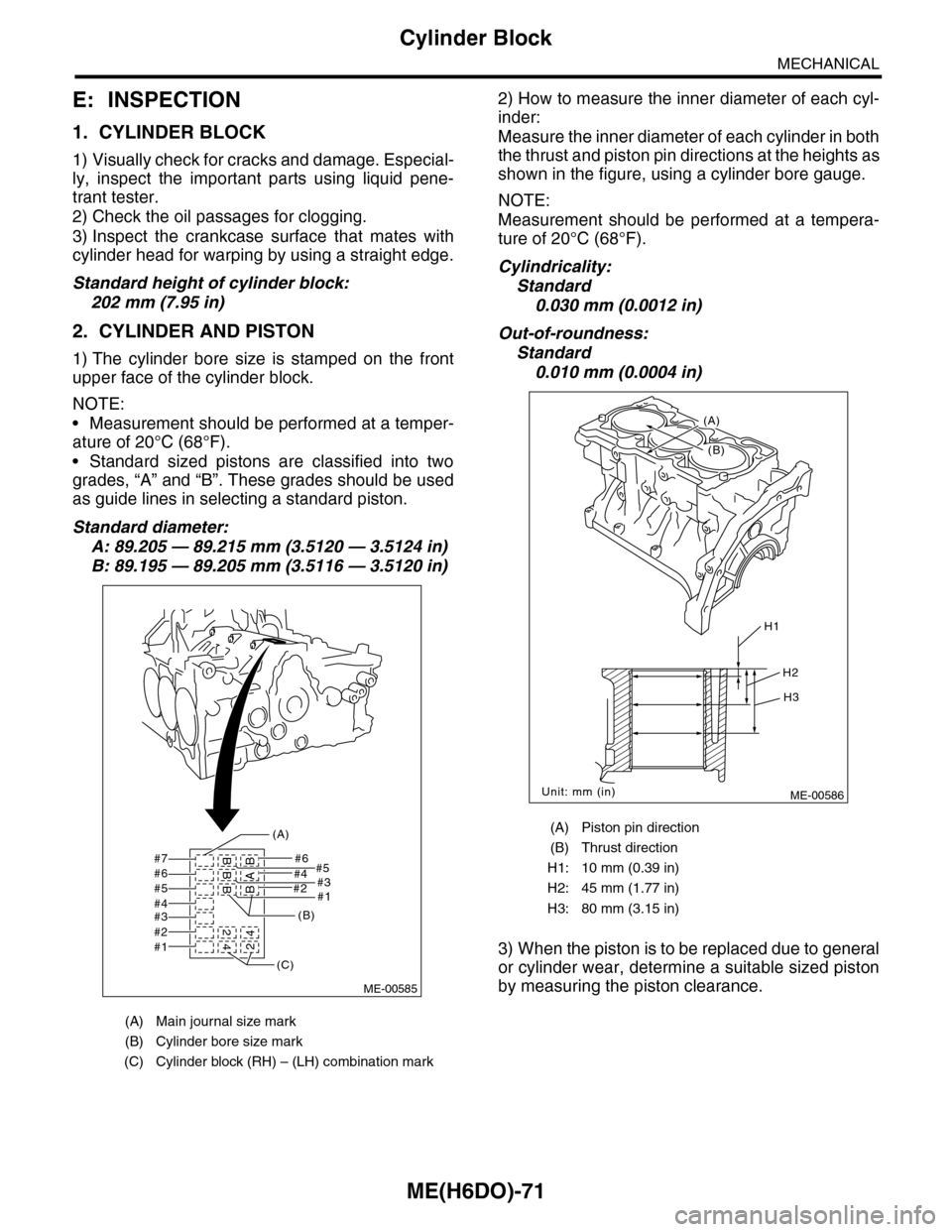
ME(H6DO)-71
Cylinder Block
MECHANICAL
E: INSPECTION
1. CYLINDER BLOCK
1) Visually check for cracks and damage. Especial-
ly, inspect the important parts using liquid pene-
trant tester.
2) Check the oil passages for clogging.
3) Inspect the crankcase surface that mates with
cylinder head for warping by using a straight edge.
Standard height of cylinder block:
202 mm (7.95 in)
2. CYLINDER AND PISTON
1) The cylinder bore size is stamped on the front
upper face of the cylinder block.
NOTE:
•Measurement should be performed at a temper-
ature of 20°C (68°F).
•Standard sized pistons are classified into two
grades, “A” and “B”. These grades should be used
as guide lines in selecting a standard piston.
Standard diameter:
A: 89.205 — 89.215 mm (3.5120 — 3.5124 in)
B: 89.195 — 89.205 mm (3.5116 — 3.5120 in)
2) How to measure the inner diameter of each cyl-
inder:
Measure the inner diameter of each cylinder in both
the thrust and piston pin directions at the heights as
shown in the figure, using a cylinder bore gauge.
NOTE:
Measurement should be performed at a tempera-
ture of 20°C (68°F).
Cylindricality:
Standard
0.030 mm (0.0012 in)
Out-of-roundness:
Standard
0.010 mm (0.0004 in)
3) When the piston is to be replaced due to general
or cylinder wear, determine a suitable sized piston
by measuring the piston clearance.
(A) Main journal size mark
(B) Cylinder bore size mark
(C) Cylinder block (RH) – (LH) combination mark
#7 #6#5
#2#1
#4#3#6#5#4#3#2#1
BBB 2
42BAB4
(A)
(B)
(C)
ME-00585
(A) Piston pin direction
(B) Thrust direction
H1: 10 mm (0.39 in)
H2: 45 mm (1.77 in)
H3: 80 mm (3.15 in)
ME-00586
H1
H2
H3
Unit: mm (in)
(B)
(A)
Page 1938 of 2453

ME(H6DO)-72
Cylinder Block
MECHANICAL
4) How to measure the outer diameter of each pis-
ton:
Measure the outer diameter of each piston at the
height as shown in the figure. (Thrust direction)
NOTE:
Measurement should be performed at a tempera-
ture of 20°C (68°F).
Piston grade point H:
37.3 mm (1.4865 in)
Piston outer diameter:
Standard
A: 89.205 — 89.215 mm (3.5120 — 3.5124
in)
B: 89.195 — 89.205 mm (3.5116 — 3.5120
in)
0.25 mm (0.0098 in) oversize
89.445 — 89.465 mm (3.5215 — 3.5222 in)
0.50 mm (0.0197 in) oversize
89.695 — 89.715 mm (3.5313 — 3.5321 in)
5) Calculate the clearance between cylinder and
piston.
NOTE:
Measurement should be performed at a tempera-
ture of 20°C (68°F).
20 Cylinder to piston clearance at 20°C (68°F):
Standard
–0.010 — 0.010 mm (–0.00039 — 0.00039 in)
6) Boring and honing:
(1) If the value of cylindricality, out-of-round-
ness, or cylinder-to-piston clearance measured
is out of standard or if there is any damage on
the cylinder wall, rebore it to use an oversize
piston.
CAUTION:
When any of the cylinders needs reboring, all
other cylinders must be bored at the same time,
and use oversize pistons. Do not perform bor-
ing on one cylinder only. Nor use an oversize
piston for one cylinder only.
(2) If the cylinder inner diameter exceeds
89.715 mm (3.5321 in) after boring and honing,
replace the crankcase.
NOTE:
Immediately after reboring, the cylinder diameter
may differ from its real diameter due to temperature
rise. Thus, pay attention to this when measuring
the cylinder diameter.
3. PISTON AND PISTON PIN
1) Check the pistons and piston pins for damage,
cracks and wear, and the piston ring grooves for
wear and damage. Replace if faulty.
2) Measure the piston-to-cylinder clearance at
each cylinder.
any of the clearances is not within standard, re-
place the piston or bore the cylinder to use an over-
size piston.
3) Make sure that the piston pin can be inserted
into the piston pin hole with a thumb at 20°C (68°F).
Replace if faulty.
Standard clearance between piston pin and
hole in piston:
Standard
0.004 — 0.008 mm (0.0002 — 0.0003 in)
ME-00172
H
ME-00173
ME-00174