Ignition system SUZUKI JIMNY 2005 3.G Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: JIMNY, Model: SUZUKI JIMNY 2005 3.GPages: 687, PDF Size: 13.38 MB
Page 359 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6-2 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC) table ......... 6-16
Fail-safe table............................................ 6-19
Visual inspection ....................................... 6-20
Engine basic inspection ............................ 6-21
Engine diagnosis table .............................. 6-23
Scan Tool Data ............................................. 6-28
Scan tool data definitions .......................... 6-30
Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits ................ 6-33
Component Location ..................................... 6-42
Table A-1 Malfunction Indicator Lamp Circuit
Check - Lamp Does Not Come “ON” at Ignition
Switch ON (But Engine at Stop).................... 6-43
Table A-2 Malfunction Indicator Lamp Circuit
Check - Lamp Remains “ON” after Engine
Starts............................................................. 6-44
Table A-3 Malfunction Indicator Lamp Circuit
Check - Mil Flashes at Ignition Switch ON .... 6-45
Table A-4 Malfunction Indicator Lamp Circuit
Check - MIL Does Not Flash, Just Remains
ON or Just Remains OFF Even with Grounding
Diagnosis Switch Terminal............................ 6-45
Table A-5 ECM Power and Ground Circuit
Check - MIL Doesn’t Light at Ignition Switch
ON and Engine Doesn’t Start Though It Is
Cranked Up ................................................... 6-46
DTC P0105 (DTC No.11) Manifold Absolute
Pressure (MAP) Circuit Malfunction .............. 6-48
DTC P0110 (DTC No.18) Intake Air Temp.
(IAT) Circuit Malfunction ............................... 6-51
DTC P0115 (DTC No.19) Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT) Circuit Malfunction ........ 6-53
DTC P0120 (DTC No.13) Throttle Position
Circuit Malfunction ........................................ 6-55
DTC P0121 Throttle Position Circuit Range /
Performance Problem ................................... 6-57
DTC P0130 (DTC No.14) Heated Oxygen
Sensor (HO2S) Circuit Malfunction
(Sensor-1) ..................................................... 6-59
DTC P0133 Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S)
Circuit Slow Response (Sensor-1) ................ 6-61
DTC P0135 (DTC No.14) Heated Oxygen
Sensor (HO2S) Heater Circuit Malfunction
(Sensor-1) ..................................................... 6-62
DTC P0136 Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S)
Circuit Malfunction (Sensor-2) ...................... 6-64
DTC P0141 Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S)
Heater Circuit Malfunction (Sensor-2)........... 6-66
DTC P0171 Fuel System Too Lean .............. 6-68
DTC P0172 Fuel System Too Rich ............... 6-68
DTC P0300 Random Misfire Detected
(Misfire Detected at 2 or More Cylinders) ..... 6-72DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected ........ 6-72
DTC P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected ........ 6-72
DTC P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected ........ 6-72
DTC P0304 Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected ........ 6-72
DTC P0325 (DTC No.17) Knock Sensor Circuit
Malfunction .................................................... 6-77
DTC P0335 (DTC No.23) Crankshaft Position
(CKP) Sensor Circuit Malfunction .................. 6-79
DTC P0340 (DTC No.15) Camshaft Position
(CMP) Sensor Circuit Malfunction ................. 6-82
DTC P0400 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow
Malfunction .................................................... 6-85
DTC P0420 Catalyst System Efficiency below
Threshold ....................................................... 6-88
DTC P0443 Purge Control Valve Circuit
Malfunction .................................................... 6-91
DTC P0481 A/C Condenser Fan Control
Circuit Malfunction ......................................... 6-92
DTC P0500 (DTC No.16) Vehicle Speed
Sensor (VSS) Malfunction ............................. 6-94
DTC P0505 Idle Control System
Malfunction .................................................... 6-96
DTC P0601 Internal Control Module Memory
Check Sum Error (DTC No.71) ...................... 6-98
DTC P1450 Barometric Pressure Sensor
Low / High Input ............................................. 6-99
DTC P1451 Barometric Pressure Sensor
Performance Problem .................................... 6-99
DTC P1500 Engine Starter Signal Circuit
Malfunction .................................................. 6-101
DTC P1510 ECM Back-up Power Supply
Malfunction .................................................. 6-103
DTC P1570 (DTC No.21) ABS Signal Circuit
Malfunction .................................................. 6-104
DTC P1600 Serial Communication Problem
Between ECM and TCM .............................. 6-105
DTC P1717 A/T Drive Range (Park / Neutral
Position) Signal Circuit Malfunction ............. 6-107
Table B-1 Fuel Injector Circuit Check ..........6-109
Table B-2 Fuel Pump and Its Circuit
Check........................................................... 6-110
Table B-3 Fuel Pressure Check................... 6-112
Table B-4 Idle Air Control System Check ....6-114
Table B-5 A/C Signal Circuits Check
(Vehicle with A/C) ........................................ 6-117
Table B-6 Electric Load Signal Circuit
Check........................................................... 6-119
TAble B-7 A/C Condenser Fan Control
System Check.............................................. 6-121
Special Tool ................................................... 6-123
Page 362 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-5
Fuel pressure relief procedure
After making sure that engine is cold, release fuel pressure as fol-
lows.
1) Place transmission gear shift lever in “Neutral” (Shift selector
lever to “P” range for A/T model), set parking brake, and
block drive wheels.
2) Remove relay box cover.
3) Disconnect fuel pump relay (1) from its connector.
4) Remove fuel filler cap to release fuel vapor pressure in fuel
tank and then reinstall it.
5) Start engine and run it till it stops for lack of fuel. Repeat
cranking engine 2-3 times for about 3 seconds each time to
dissipate fuel pressure in lines. Fuel connections are now
safe for servicing.
6) Upon completion of servicing, connect fuel pump relay (1) to
its connector.
Fuel leakage check procedure
After performing any service on fuel system, check to make sure
that there are no fuel leakages as follows.
1) Turn ON ignition switch for 3 seconds (to operate fuel pump)
and then turn it OFF.
Repeat this (ON and OFF) 3 or 4 times and apply fuel pres-
sure to fuel line. (till fuel pressure is felt by hand placed on
fuel feed hose.)
2) In this state, check to see that there are no fuel leakages
from any part of fuel system. CAUTION:
This work must not be done when engine is hot. If done
so, it may cause adverse effect to catalyst.
Page 363 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6-6 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
Engine Diagnosis
General Description
This vehicle is equipped with an engine and emission control system which are under control of ECM.
The engine and emission control system in this vehicle are controlled by ECM. ECM has an On-Board Diagnos-
tic system which detects a malfunction in this system and abnormality of those parts that influence the engine
exhaust emission. When diagnosing engine troubles, be sure to have full understanding of the outline of “On-
Board Diagnostic System” and each item in “Precaution in Diagnosing Trouble” and execute diagnosis accord-
ing to “ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC FLOW TABLE”.
There is a close relationship between the engine mechanical, engine cooling system, ignition system, exhaust
system, etc. and the engine and emission control system in their structure and operation. In case of an engine
trouble, even when the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) doesn’t turn ON, it should be diagnosed according to
this flow table.
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle with
Immobilizer Indicator Lamp)
ECM in this vehicle has following functions.
When the ignition switch is turned ON with the engine at a
stop, malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) (1) turns ON to check
the bulb of the malfunction indicator lamp (1).
When ECM detects a malfunction which gives an adverse
effect to vehicle emission while the engine is running, it
makes the malfunction indicator lamp (1) in the meter cluster
of the instrument panel turn ON or flash (flashing only when
detecting a misfire which can cause damage to the catalyst)
and stores the malfunction area in its memory.
(If it detects that continuously 3 driving cycles are normal
after detecting a malfunction, however, it makes MIL (1) turn
OFF although DTC stored in its memory will remain.)
As a condition for detecting a malfunction in some areas in
the system being monitored by ECM and turning ON the
malfunction indicator lamp (1) due to that malfunction, 2 driv-
ing cycle detection logic is adopted to prevent erroneous
detection.
When a malfunction is detected, engine and driving condi-
tions then are stored in ECM memory as freeze frame data.
(For the details, refer to description on Freeze frame data.)
It is possible to communicate by using not only SUZUKI scan
tool (2) but also generic scan tool. (Diagnostic information
can be accessed by using a scan tool.)
WARM-UP CYCLE
A warm-up cycle means sufficient vehicle operation such that the
coolant temperature has risen by at least 22 °C (40 °F) from
engine starting and reaches a minimum temperature of 70 °C
(160 °F).
Page 366 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-9
On-Board Diagnostic System (Vehicle without
Immobilizer Indicator Lamp)
ECM diagnosis troubles which may occur in the area including
the following parts when the ignition switch is ON and the engine
is running, and indicates the result by turning on or flashing mal-
function indicator lamp (1).
Heated oxygen sensor (if equipped)
ECT sensor
TP sensor
IAT sensor
MAP sensor
CMP sensor
CKP sensor
Knock sensor
VSS
CPU (Central Processing Unit) of ECM
ECM and malfunction indicator lamp (1) operate as follows.
Malfunction indicator lamp (1) lights when the ignition switch
is turned ON (but the engine at stop) with the diagnosis
switch terminal ungrounded regardless of the condition of
Engine and Emission Control system. This is only to check
the malfunction indicator lamp (1) bulb and its circuit.
If the above areas of Engine and Emission Control system is
free from any trouble after the engine start (while engine is
running), malfunction indicator lamp (1) turns OFF.
When ECM detects a trouble which has occurred in the
above areas, it makes malfunction indicator lamp (1) turn ON
while the engine is running to warn the driver of such occur-
rence of trouble and at the same time it stores the trouble
area in ECM back-up memory. (The memory is kept as it is
even if the trouble was only temporary and disappeared
immediately. And it is not erased unless the power to ECM is
shut off for specified time below.)
ECM also indicates trouble area in memory by means of
flashing of malfunction indicator lamp (1) at the time of
inspection. (i.e. when connecting diagnosis switch terminal
(2) and ground terminal (4) of monitor connector (3) with a
service wire (5) and ignition switch is turned ON.)
NOTE:
When a trouble occurs in the above areas and disap-
pears soon while the diagnosis switch terminal is
ungrounded and the engine is running, malfunction
indicator lamp (1) lights and remains ON as long as the
trouble exists but it turns OFF when the normal condi-
tion is restored.
Time required to erase diagnostic trouble code mem-
ory thoroughly varies depending on ambient tempera-
ture as follows.
Page 378 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-21
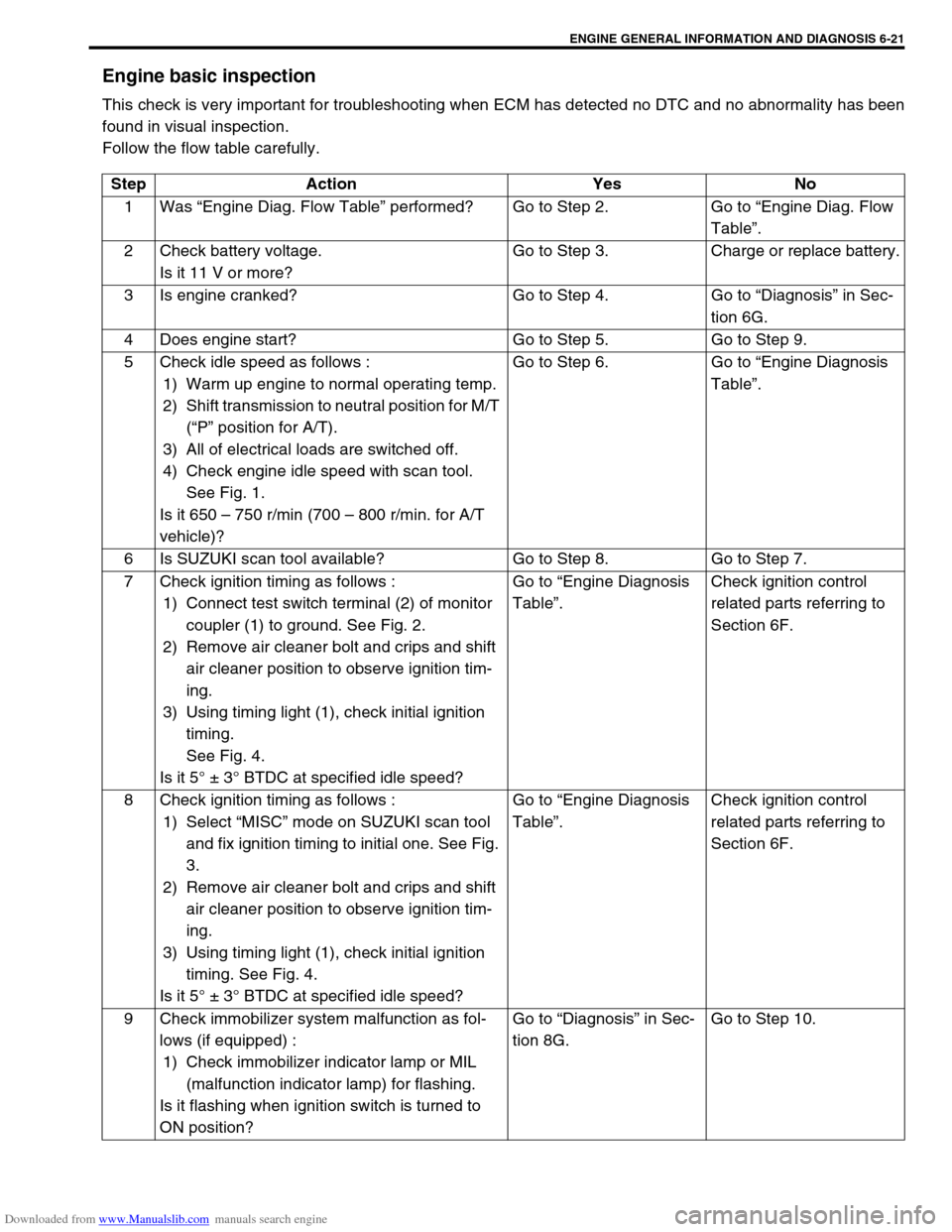
Engine basic inspection
This check is very important for troubleshooting when ECM has detected no DTC and no abnormality has been
found in visual inspection.
Follow the flow table carefully.
Step Action Yes No
1Was “Engine Diag. Flow Table” performed? Go to Step 2. Go to “Engine Diag. Flow
Table”.
2 Check battery voltage.
Is it 11 V or more?Go to Step 3. Charge or replace battery.
3 Is engine cranked? Go to Step 4. Go to “Diagnosis” in Sec-
tion 6G.
4 Does engine start? Go to Step 5. Go to Step 9.
5 Check idle speed as follows :
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temp.
2) Shift transmission to neutral position for M/T
(“P” position for A/T).
3) All of electrical loads are switched off.
4) Check engine idle speed with scan tool.
See Fig. 1.
Is it 650 – 750 r/min (700 – 800 r/min. for A/T
vehicle)?Go to Step 6. Go to “Engine Diagnosis
Table”.
6 Is SUZUKI scan tool available? Go to Step 8. Go to Step 7.
7 Check ignition timing as follows :
1) Connect test switch terminal (2) of monitor
coupler (1) to ground. See Fig. 2.
2) Remove air cleaner bolt and crips and shift
air cleaner position to observe ignition tim-
ing.
3) Using timing light (1), check initial ignition
timing.
See Fig. 4.
Is it 5° ± 3° BTDC at specified idle speed?Go to “Engine Diagnosis
Table”.Check ignition control
related parts referring to
Section 6F.
8 Check ignition timing as follows :
1) Select “MISC” mode on SUZUKI scan tool
and fix ignition timing to initial one. See Fig.
3.
2) Remove air cleaner bolt and crips and shift
air cleaner position to observe ignition tim-
ing.
3) Using timing light (1), check initial ignition
timing. See Fig. 4.
Is it 5° ± 3° BTDC at specified idle speed?Go to “Engine Diagnosis
Table”.Check ignition control
related parts referring to
Section 6F.
9 Check immobilizer system malfunction as fol-
lows (if equipped) :
1) Check immobilizer indicator lamp or MIL
(malfunction indicator lamp) for flashing.
Is it flashing when ignition switch is turned to
ON position?Go to “Diagnosis” in Sec-
tion 8G.Go to Step 10.
Page 380 of 687
![SUZUKI JIMNY 2005 3.G Service Repair Manual Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-23
[D] Fig. 4 for Step 7 or 8 / [E] Fig. 5 for Step 10 / [F] Fig. 6 for Step 13
Engine diagnosis tab SUZUKI JIMNY 2005 3.G Service Repair Manual Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-23
[D] Fig. 4 for Step 7 or 8 / [E] Fig. 5 for Step 10 / [F] Fig. 6 for Step 13
Engine diagnosis tab](/img/20/7588/w960_7588-379.png)
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-23
[D] Fig. 4 for Step 7 or 8 / [E] Fig. 5 for Step 10 / [F] Fig. 6 for Step 13
Engine diagnosis table
Perform troubleshooting referring to following table when ECM has no DTC and no abnormality found in visual
inspection and engine basic inspection previously.
Condition Possible Cause Reference Item
Hard Starting
(Engine cranks OK)Faulty ignition coil Ignition coil assembly in Section 6F.
Faulty CMP sensing rotor or CKP sensing
rotorCMP sensing rotor or CKP sensing
rotor inspection in Section 6E.
Faulty idle air control system Diagnostic Flow Table B-4
Faulty ECT sensor, TP sensor, CKP sen-
sor, CMP sensor or MAP sensorECT sensor, TP sensor, CKP sensor,
CMP sensor or MAP sensor in Sec-
tion 6E.
Fuel pressure out of specification Diagnostic Flow Table B-3
Faulty fuel injector Diagnostic Flow Table B-1
Faulty ECM Inspection of ECM and its circuit in
this section.
Malfunctioning PCV system PCV system in Section 6E.
Low compression Compression check in Section 6A1.
Improper valve lash Valve lash in Section 6A1.
Improper valve timing Timing chain and chain tensioner in
Section 6A1.
Compression leak from valve seat Valves and cylinder head in Section
6A1.
Sticky valve stem Valves and cylinder head in Section
6A1.
Weak or damaged valve springs Valves and cylinder head in Section
6A1.
Compression leak at cylinder head gasket Valves and cylinder head in Section
6A1.
Sticking or damaged piston ring Pistons, piston rings, connecting rods
and cylinders in Section 6A1.
Worn piston, ring or cylinder Pistons, piston rings, connecting rods
and cylinders in Section 6A1.
Page 381 of 687
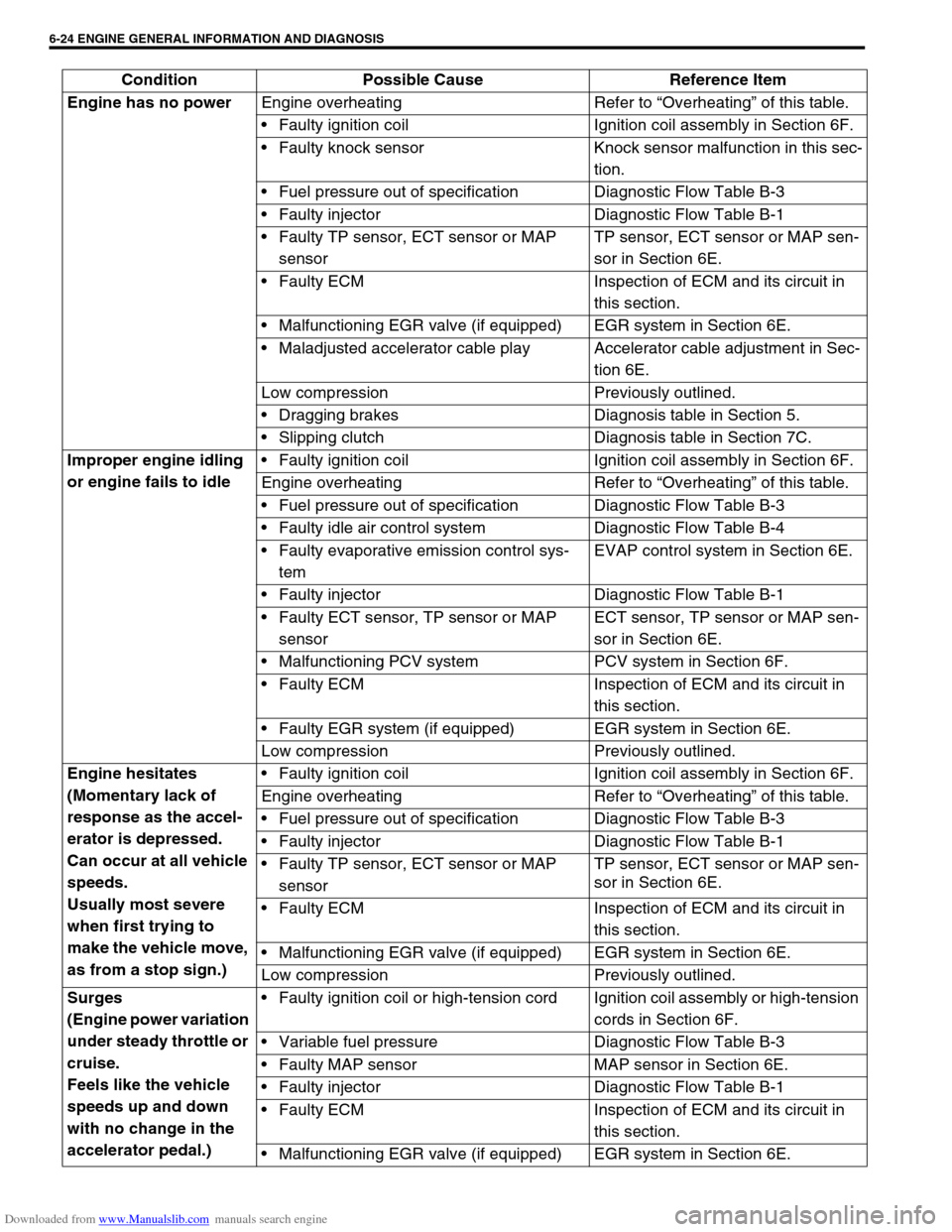
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6-24 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
Engine has no power
Engine overheating Refer to “Overheating” of this table.
Faulty ignition coil Ignition coil assembly in Section 6F.
Faulty knock sensor Knock sensor malfunction in this sec-
tion.
Fuel pressure out of specification Diagnostic Flow Table B-3
Faulty injector Diagnostic Flow Table B-1
Faulty TP sensor, ECT sensor or MAP
sensorTP sensor, ECT sensor or MAP sen-
sor in Section 6E.
Faulty ECM Inspection of ECM and its circuit in
this section.
Malfunctioning EGR valve (if equipped) EGR system in Section 6E.
Maladjusted accelerator cable play Accelerator cable adjustment in Sec-
tion 6E.
Low compression Previously outlined.
Dragging brakes Diagnosis table in Section 5.
Slipping clutch Diagnosis table in Section 7C.
Improper engine idling
or engine fails to idleFaulty ignition coil Ignition coil assembly in Section 6F.
Engine overheating Refer to “Overheating” of this table.
Fuel pressure out of specification Diagnostic Flow Table B-3
Faulty idle air control system Diagnostic Flow Table B-4
Faulty evaporative emission control sys-
temEVAP control system in Section 6E.
Faulty injector Diagnostic Flow Table B-1
Faulty ECT sensor, TP sensor or MAP
sensorECT sensor, TP sensor or MAP sen-
sor in Section 6E.
Malfunctioning PCV system PCV system in Section 6F.
Faulty ECM Inspection of ECM and its circuit in
this section.
Faulty EGR system (if equipped) EGR system in Section 6E.
Low compression Previously outlined.
Engine hesitates
(Momentary lack of
response as the accel-
erator is depressed.
Can occur at all vehicle
speeds.
Usually most severe
when first trying to
make the vehicle move,
as from a stop sign.)Faulty ignition coil Ignition coil assembly in Section 6F.
Engine overheating Refer to “Overheating” of this table.
Fuel pressure out of specification Diagnostic Flow Table B-3
Faulty injector Diagnostic Flow Table B-1
Faulty TP sensor, ECT sensor or MAP
sensorTP sensor, ECT sensor or MAP sen-
sor in Section 6E.
Faulty ECM Inspection of ECM and its circuit in
this section.
Malfunctioning EGR valve (if equipped) EGR system in Section 6E.
Low compression Previously outlined.
Surges
(Engine power variation
under steady throttle or
cruise.
Feels like the vehicle
speeds up and down
with no change in the
accelerator pedal.)Faulty ignition coil or high-tension cord Ignition coil assembly or high-tension
cords in Section 6F.
Variable fuel pressure Diagnostic Flow Table B-3
Faulty MAP sensor MAP sensor in Section 6E.
Faulty injector Diagnostic Flow Table B-1
Faulty ECM Inspection of ECM and its circuit in
this section.
Malfunctioning EGR valve (if equipped) EGR system in Section 6E. Condition Possible Cause Reference Item
Page 382 of 687
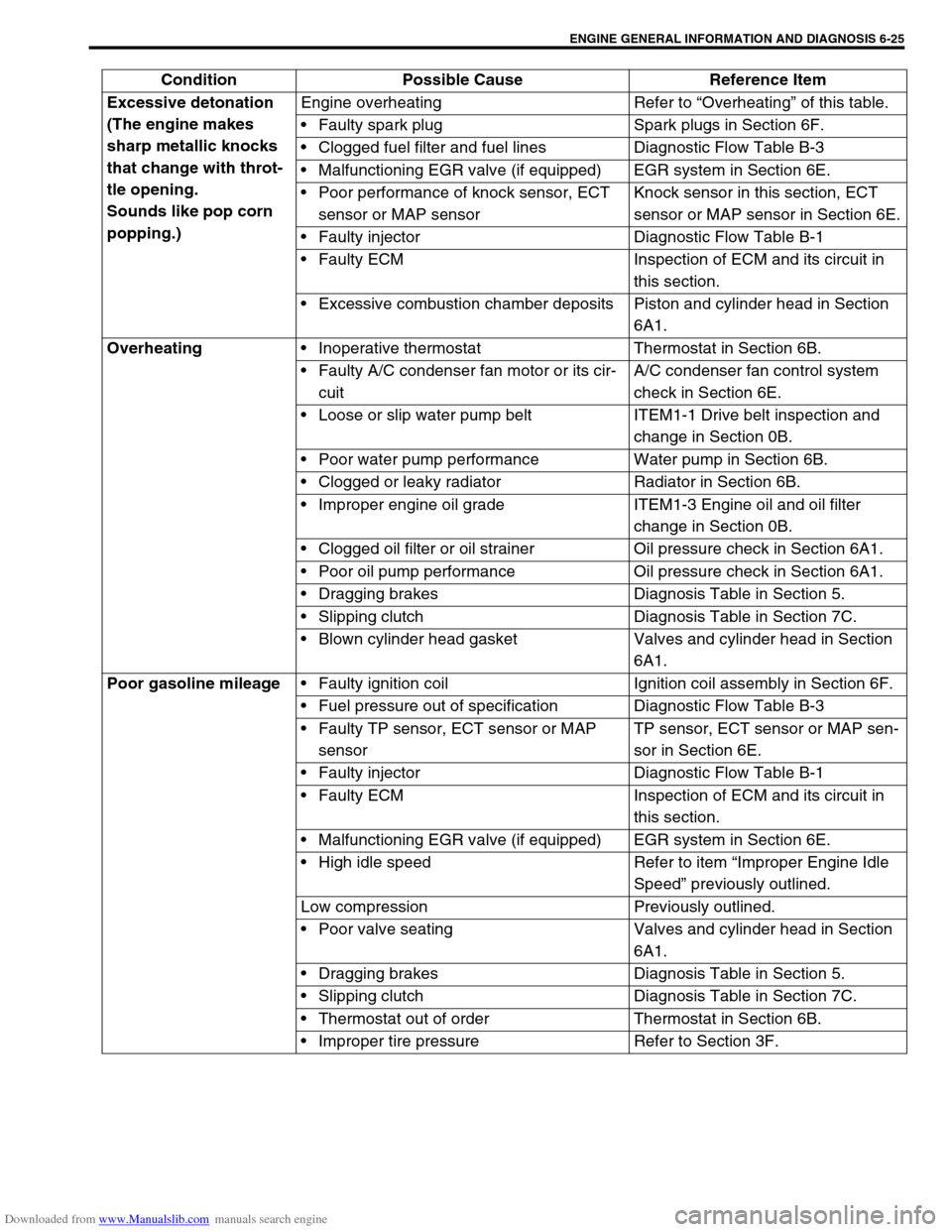
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-25
Excessive detonation
(The engine makes
sharp metallic knocks
that change with throt-
tle opening.
Sounds like pop corn
popping.)Engine overheating Refer to “Overheating” of this table.
Faulty spark plug Spark plugs in Section 6F.
Clogged fuel filter and fuel lines Diagnostic Flow Table B-3
Malfunctioning EGR valve (if equipped) EGR system in Section 6E.
Poor performance of knock sensor, ECT
sensor or MAP sensorKnock sensor in this section, ECT
sensor or MAP sensor in Section 6E.
Faulty injector Diagnostic Flow Table B-1
Faulty ECM Inspection of ECM and its circuit in
this section.
Excessive combustion chamber deposits Piston and cylinder head in Section
6A1.
Overheating
Inoperative thermostat Thermostat in Section 6B.
Faulty A/C condenser fan motor or its cir-
cuitA/C condenser fan control system
check in Section 6E.
Loose or slip water pump belt ITEM1-1 Drive belt inspection and
change in Section 0B.
Poor water pump performance Water pump in Section 6B.
Clogged or leaky radiator Radiator in Section 6B.
Improper engine oil grade ITEM1-3 Engine oil and oil filter
change in Section 0B.
Clogged oil filter or oil strainer Oil pressure check in Section 6A1.
Poor oil pump performance Oil pressure check in Section 6A1.
Dragging brakes Diagnosis Table in Section 5.
Slipping clutch Diagnosis Table in Section 7C.
Blown cylinder head gasket Valves and cylinder head in Section
6A1.
Poor gasoline mileage
Faulty ignition coil Ignition coil assembly in Section 6F.
Fuel pressure out of specification Diagnostic Flow Table B-3
Faulty TP sensor, ECT sensor or MAP
sensorTP sensor, ECT sensor or MAP sen-
sor in Section 6E.
Faulty injector Diagnostic Flow Table B-1
Faulty ECM Inspection of ECM and its circuit in
this section.
Malfunctioning EGR valve (if equipped) EGR system in Section 6E.
High idle speed Refer to item “Improper Engine Idle
Speed” previously outlined.
Low compression Previously outlined.
Poor valve seating Valves and cylinder head in Section
6A1.
Dragging brakes Diagnosis Table in Section 5.
Slipping clutch Diagnosis Table in Section 7C.
Thermostat out of order Thermostat in Section 6B.
Improper tire pressure Refer to Section 3F. Condition Possible Cause Reference Item
Page 384 of 687
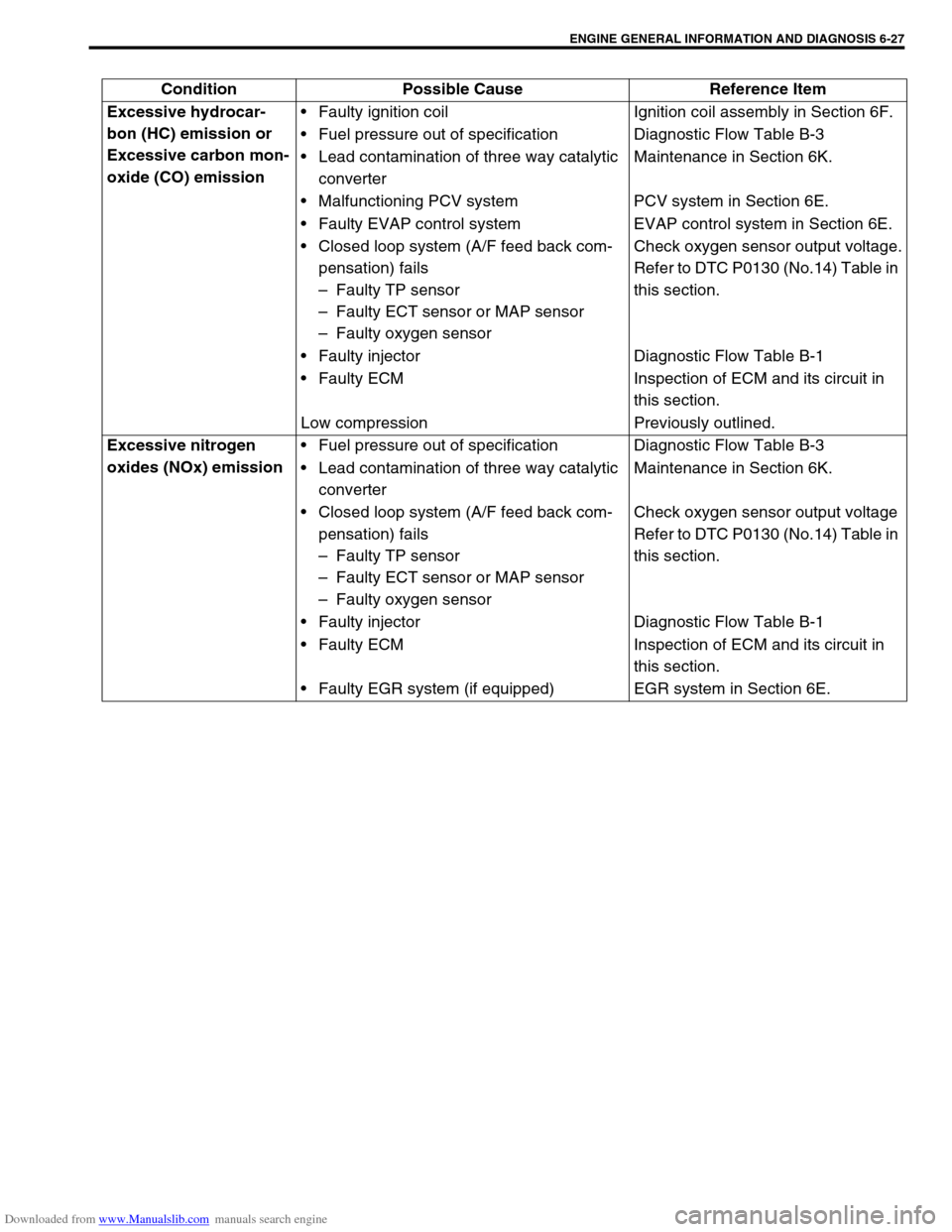
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-27
Condition Possible Cause Reference Item
Excessive hydrocar-
bon (HC) emission or
Excessive carbon mon-
oxide (CO) emissionFaulty ignition coil Ignition coil assembly in Section 6F.
Fuel pressure out of specification Diagnostic Flow Table B-3
Lead contamination of three way catalytic
converterMaintenance in Section 6K.
Malfunctioning PCV system PCV system in Section 6E.
Faulty EVAP control system EVAP control system in Section 6E.
Closed loop system (A/F feed back com-
pensation) fails
–Faulty TP sensor
–Faulty ECT sensor or MAP sensor
–Faulty oxygen sensorCheck oxygen sensor output voltage.
Refer to DTC P0130 (No.14) Table in
this section.
Faulty injector Diagnostic Flow Table B-1
Faulty ECM Inspection of ECM and its circuit in
this section.
Low compression Previously outlined.
Excessive nitrogen
oxides (NOx) emissionFuel pressure out of specification Diagnostic Flow Table B-3
Lead contamination of three way catalytic
converterMaintenance in Section 6K.
Closed loop system (A/F feed back com-
pensation) fails
–Faulty TP sensor
–Faulty ECT sensor or MAP sensor
–Faulty oxygen sensorCheck oxygen sensor output voltage
Refer to DTC P0130 (No.14) Table in
this section.
Faulty injector Diagnostic Flow Table B-1
Faulty ECM Inspection of ECM and its circuit in
this section.
Faulty EGR system (if equipped) EGR system in Section 6E.
Page 385 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6-28 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
Scan Tool Data
As the data values given below are standard values estimated on the basis of values obtained from the normally
operating vehicles by using a scan tool, use them as reference values. Even when the vehicle is in good condi-
tion, there may be cases where the checked value does not fall within each specified data range. Therefore,
judgment as abnormal should not be made by checking with these data alone.
Also, conditions in the below table that can be checked by the scan tool are those detected by ECM and output
from ECM as commands and there may be cases where the engine or actuator is not operating (in the condi-
tion) as indicated by the scan tool. Be sure to use the timing light to check the ignition timing.
NOTE:
With the generic scan tool, only star (
✱
✱✱ ✱) marked data in the table below can be read.
The triangle (
∆
∆∆ ∆) marked data in the table below can not be read for vehicle without immobilizer indi-
cator lamp at combination meter.
When checking the data with the engine running at idle or racing, be sure to shift M/T gear to the
neutral gear position and A/T gear to the “Park” position and pull the parking brake fully. Also, if
nothing or “no load” is indicated, turn OFF A/C, all electric loads, P/S and all the other necessary
switches.
SCAN TOOL DATA CONDITION REFERENCE VALUES
✱
✱✱ ✱FUEL SYSTEM B1 (FUEL
SYSTEM STATUS)At specified idle speed after warming up CLOSED (closed loop)
✱
✱✱ ✱
CALC LOAD
(CALCULATED LOAD
VALUE)At specified idle speed with no load after
warming up3 – 9 %
At 2500 r/min with no load after warming up 12 – 17 %
✱
✱✱ ✱COOLANT TEMP.
(ENGINE COOLANT
TEMP.)At specified idle speed after warming up 80 – 100 °C, 176 – 212 °F
✱
✱✱ ✱SHORT FT B1 (SHORT
TERM FUEL TRIM)At specified idle speed after warming up– 20 – +20 %
✱
✱✱ ✱LONG FT B1 (LONG TERM
FUEL TRIM)At specified idle speed after warming up– 15 – +15 %
✱
✱✱ ✱MAP (INTAKE MANIFOLD
ABSOLUTE PRESSURE)At specified idle speed with no load after30 – 37 kPa,
220 – 340 mmHg
✱
✱✱ ✱
ENGINE SPEED At idling with no load after warming upDesired idle speed
±50 r/min
✱
✱✱ ✱VEHICLE SPEED At stop 0 km/h, 0 MPH
✱
✱✱ ✱IGNITION ADVANCE
(IGNITION TIMING
ADVANCE FOR NO.1 CYL-
INDER)At specified idle speed with no load after
warming up5 – 16° BTDC
✱
✱✱ ✱
INTAKE AIR TEMP. At specified idle speed after warming upAmbient temp. :
+15 °C (59 °F)
–5 °C (23 °F)
✱
✱✱ ✱MAF (MASS AIR FLOW
RATE)At specified idle speed with no load after
warming up1 – 4 gm/sec
✱
✱✱ ✱
THROTTLE POS
(THROTTLE POSITION)Ignition switch
ON / engine
stoppedThrottle valve fully closed 7 – 18 %
Throttle valve fully open 70 – 90 %
✱
✱✱ ✱O2S B1 S1 (HEATED OXY-
GEN SENSOR-1)At specified idle speed after warming up 0.01 – 0.95 V