turn signal SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2000, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.GPages: 698, PDF Size: 16.01 MB
Page 458 of 698
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-89
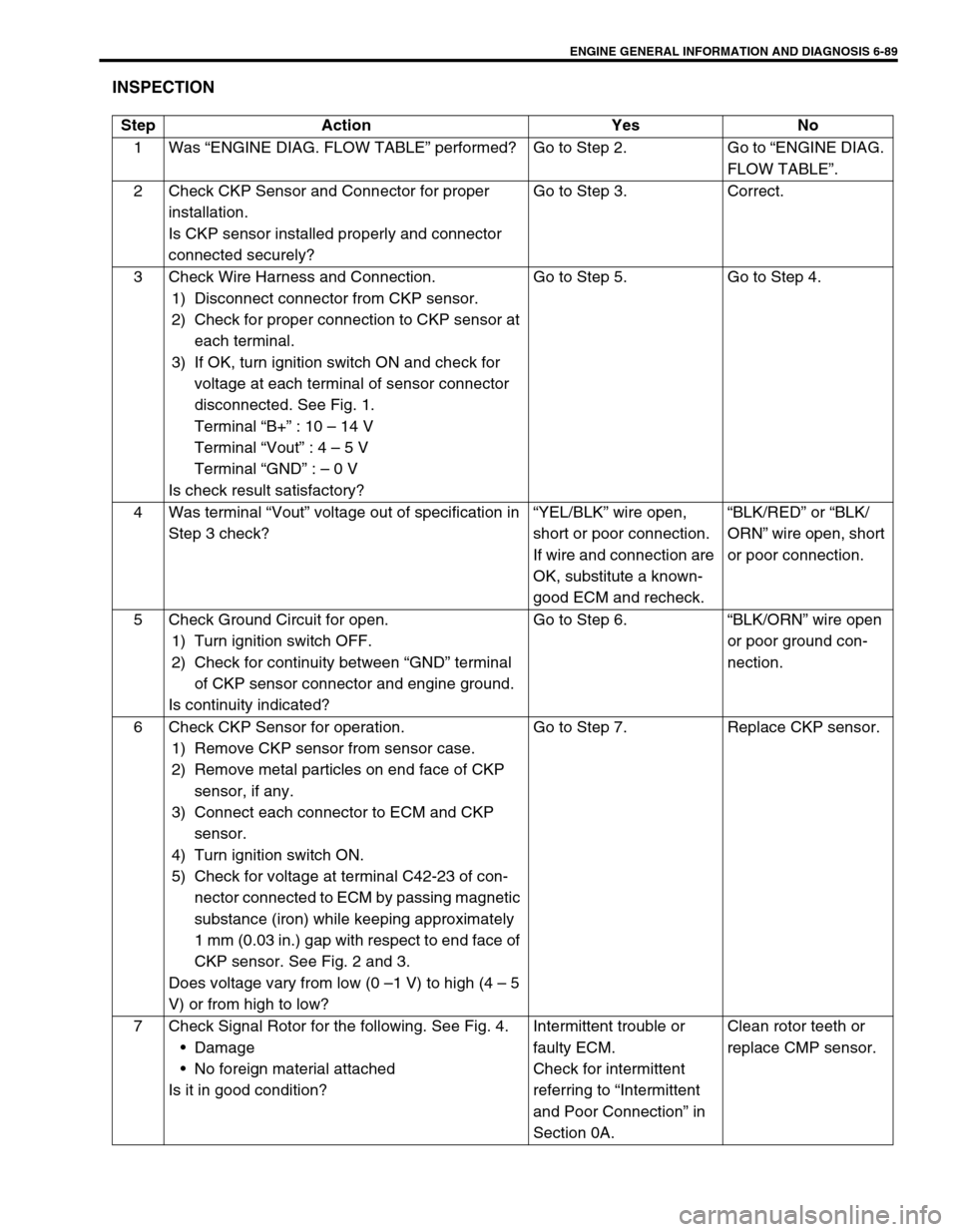
INSPECTION
Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” performed? Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Check CKP Sensor and Connector for proper
installation.
Is CKP sensor installed properly and connector
connected securely?Go to Step 3. Correct.
3 Check Wire Harness and Connection.
1) Disconnect connector from CKP sensor.
2) Check for proper connection to CKP sensor at
each terminal.
3) If OK, turn ignition switch ON and check for
voltage at each terminal of sensor connector
disconnected. See Fig. 1.
Terminal “B+” : 10 – 14 V
Terminal “Vout” : 4 – 5 V
Terminal “GND” : – 0 V
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 5. Go to Step 4.
4 Was terminal “Vout” voltage out of specification in
Step 3 check?“YEL/BLK” wire open,
short or poor connection.
If wire and connection are
OK, substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.“BLK/RED” or “BLK/
ORN” wire open, short
or poor connection.
5 Check Ground Circuit for open.
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Check for continuity between “GND” terminal
of CKP sensor connector and engine ground.
Is continuity indicated?Go to Step 6.“BLK/ORN” wire open
or poor ground con-
nection.
6 Check CKP Sensor for operation.
1) Remove CKP sensor from sensor case.
2) Remove metal particles on end face of CKP
sensor, if any.
3) Connect each connector to ECM and CKP
sensor.
4) Turn ignition switch ON.
5) Check for voltage at terminal C42-23 of con-
nector connected to ECM by passing magnetic
substance (iron) while keeping approximately
1 mm (0.03 in.) gap with respect to end face of
CKP sensor. See Fig. 2 and 3.
Does voltage vary from low (0 –1 V) to high (4 – 5
V) or from high to low?Go to Step 7. Replace CKP sensor.
7 Check Signal Rotor for the following. See Fig. 4.
Damage
No foreign material attached
Is it in good condition?Intermittent trouble or
faulty ECM.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection” in
Section 0A.Clean rotor teeth or
replace CMP sensor.
Page 461 of 698
6-92 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
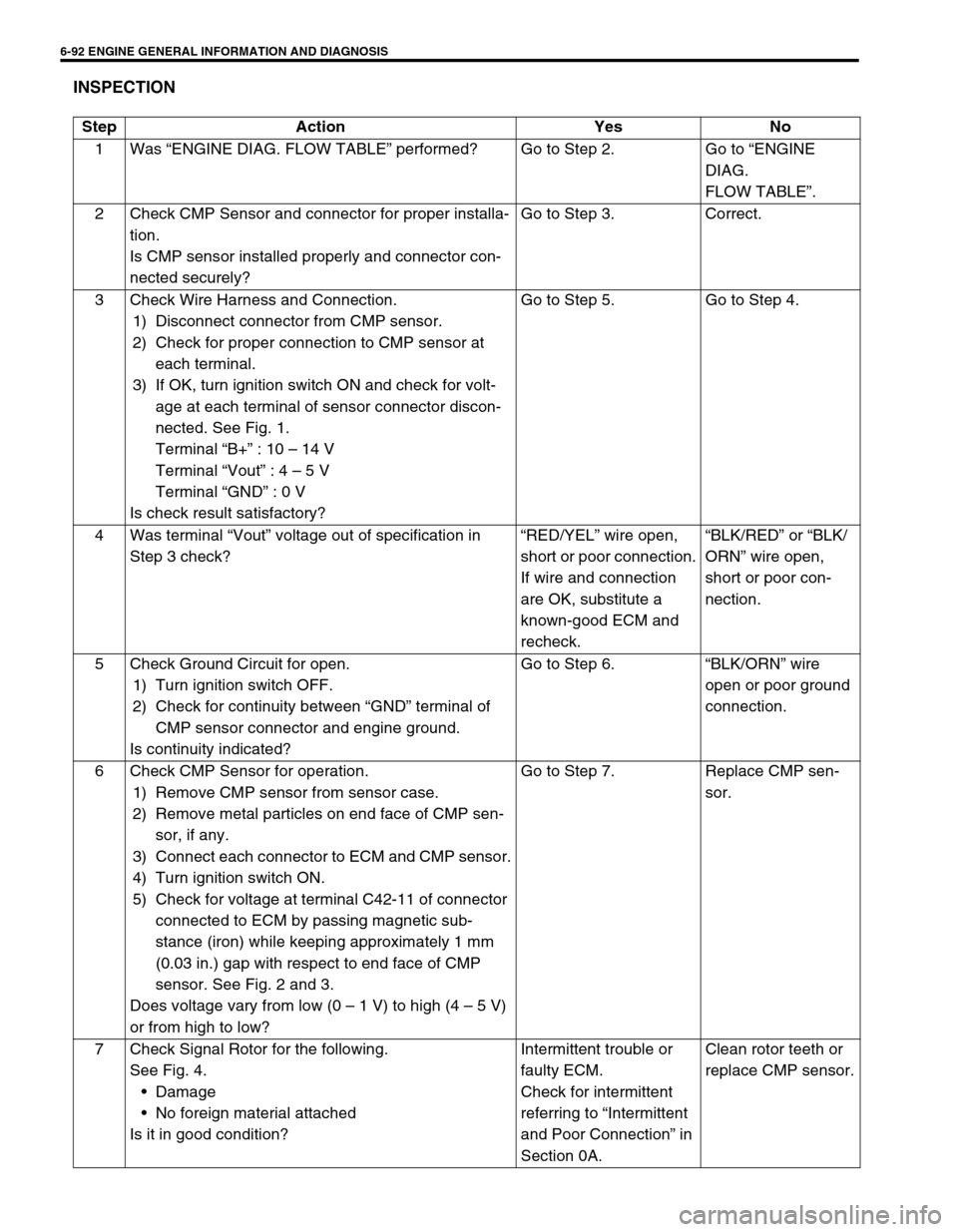
INSPECTION
Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” performed? Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE
DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Check CMP Sensor and connector for proper installa-
tion.
Is CMP sensor installed properly and connector con-
nected securely?Go to Step 3. Correct.
3 Check Wire Harness and Connection.
1) Disconnect connector from CMP sensor.
2) Check for proper connection to CMP sensor at
each terminal.
3) If OK, turn ignition switch ON and check for volt-
age at each terminal of sensor connector discon-
nected. See Fig. 1.
Terminal “B+” : 10 – 14 V
Terminal “Vout” : 4 – 5 V
Terminal “GND” : 0 V
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 5. Go to Step 4.
4Was terminal “Vout” voltage out of specification in
Step 3 check?“RED/YEL” wire open,
short or poor connection.
If wire and connection
are OK, substitute a
known-good ECM and
recheck.“BLK/RED” or “BLK/
ORN” wire open,
short or poor con-
nection.
5 Check Ground Circuit for open.
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Check for continuity between “GND” terminal of
CMP sensor connector and engine ground.
Is continuity indicated?Go to Step 6.“BLK/ORN” wire
open or poor ground
connection.
6 Check CMP Sensor for operation.
1) Remove CMP sensor from sensor case.
2) Remove metal particles on end face of CMP sen-
sor, if any.
3) Connect each connector to ECM and CMP sensor.
4) Turn ignition switch ON.
5) Check for voltage at terminal C42-11 of connector
connected to ECM by passing magnetic sub-
stance (iron) while keeping approximately 1 mm
(0.03 in.) gap with respect to end face of CMP
sensor. See Fig. 2 and 3.
Does voltage vary from low (0 – 1 V) to high (4 – 5 V)
or from high to low?Go to Step 7. Replace CMP sen-
sor.
7 Check Signal Rotor for the following.
See Fig. 4.
Damage
No foreign material attached
Is it in good condition?Intermittent trouble or
faulty ECM.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection” in
Section 0A.Clean rotor teeth or
replace CMP sensor.
Page 473 of 698
6-104 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
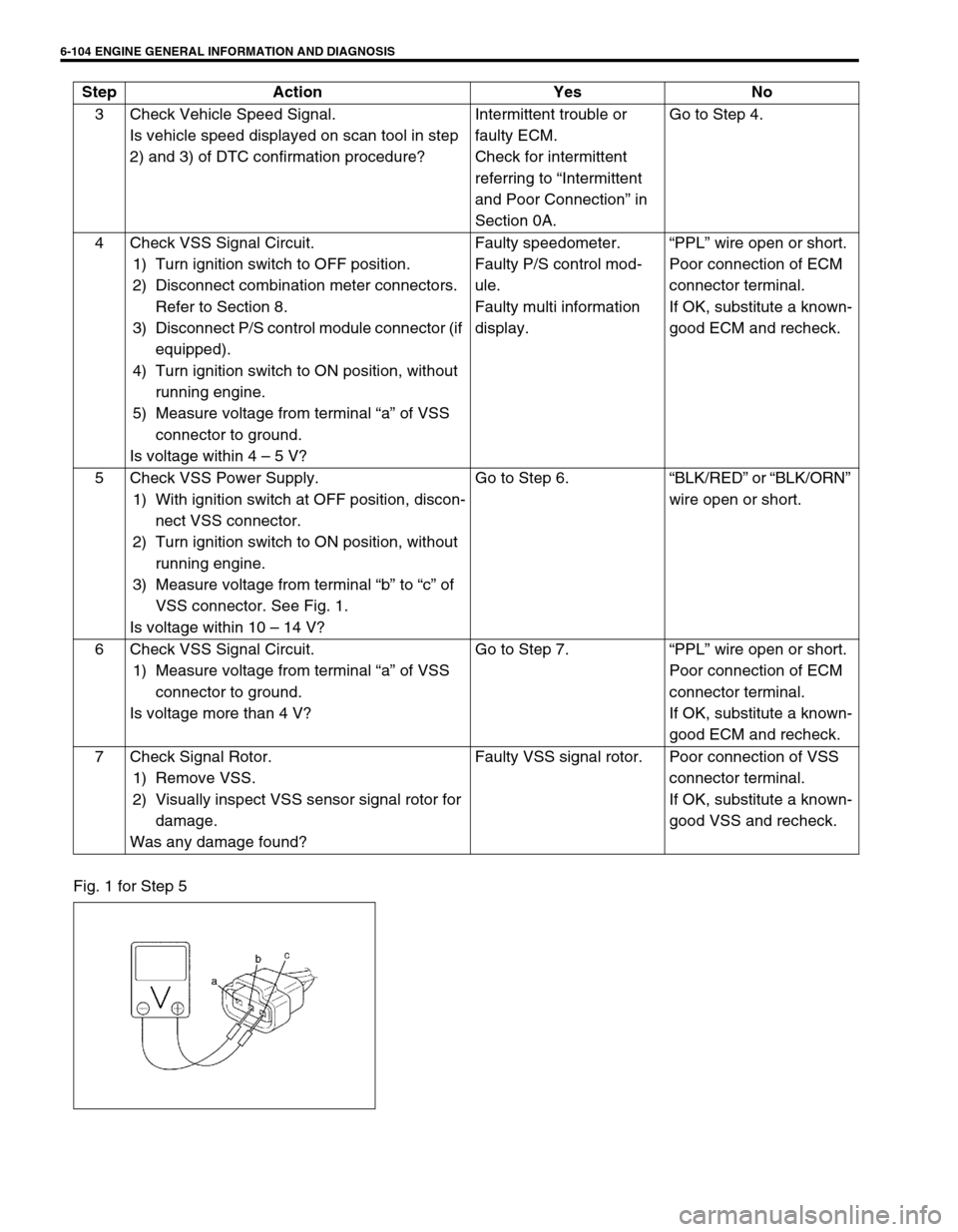
Fig. 1 for Step 53 Check Vehicle Speed Signal.
Is vehicle speed displayed on scan tool in step
2) and 3) of DTC confirmation procedure?Intermittent trouble or
faulty ECM.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection” in
Section 0A.Go to Step 4.
4 Check VSS Signal Circuit.
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Disconnect combination meter connectors.
Refer to Section 8.
3) Disconnect P/S control module connector (if
equipped).
4) Turn ignition switch to ON position, without
running engine.
5) Measure voltage from terminal “a” of VSS
connector to ground.
Is voltage within 4 – 5 V?Faulty speedometer.
Faulty P/S control mod-
ule.
Faulty multi information
display.“PPL” wire open or short.
Poor connection of ECM
connector terminal.
If OK, substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
5 Check VSS Power Supply.
1) With ignition switch at OFF position, discon-
nect VSS connector.
2) Turn ignition switch to ON position, without
running engine.
3) Measure voltage from terminal “b” to “c” of
VSS connector. See Fig. 1.
Is voltage within 10 – 14 V?Go to Step 6.“BLK/RED” or “BLK/ORN”
wire open or short.
6 Check VSS Signal Circuit.
1) Measure voltage from terminal “a” of VSS
connector to ground.
Is voltage more than 4 V?Go to Step 7.“PPL” wire open or short.
Poor connection of ECM
connector terminal.
If OK, substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
7 Check Signal Rotor.
1) Remove VSS.
2) Visually inspect VSS sensor signal rotor for
damage.
Was any damage found?Faulty VSS signal rotor. Poor connection of VSS
connector terminal.
If OK, substitute a known-
good VSS and recheck. Step Action Yes No
Page 474 of 698
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-105
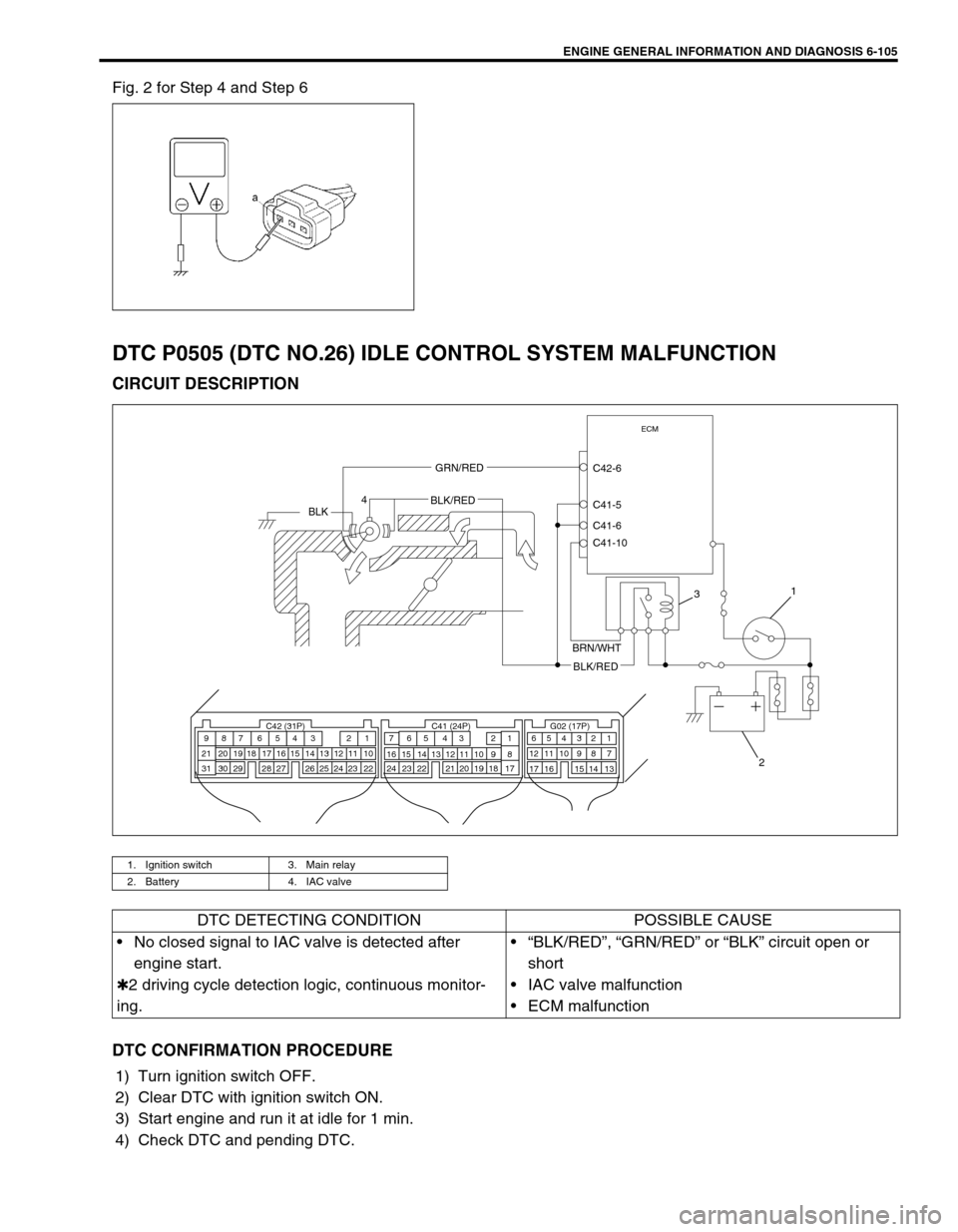
Fig. 2 for Step 4 and Step 6
DTC P0505 (DTC NO.26) IDLE CONTROL SYSTEM MALFUNCTION
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Clear DTC with ignition switch ON.
3) Start engine and run it at idle for 1 min.
4) Check DTC and pending DTC.
1. Ignition switch 3. Main relay
2. Battery 4. IAC valve
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
2
13 4
ECM
C42-6
C41-5
C41-6
C41-10GRN/RED
BLKBLK/RED
BRN/WHT
BLK/RED
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
No closed signal to IAC valve is detected after
engine start.
✱2 driving cycle detection logic, continuous monitor-
ing.“BLK/RED”, “GRN/RED” or “BLK” circuit open or
short
IAC valve malfunction
ECM malfunction
Page 479 of 698
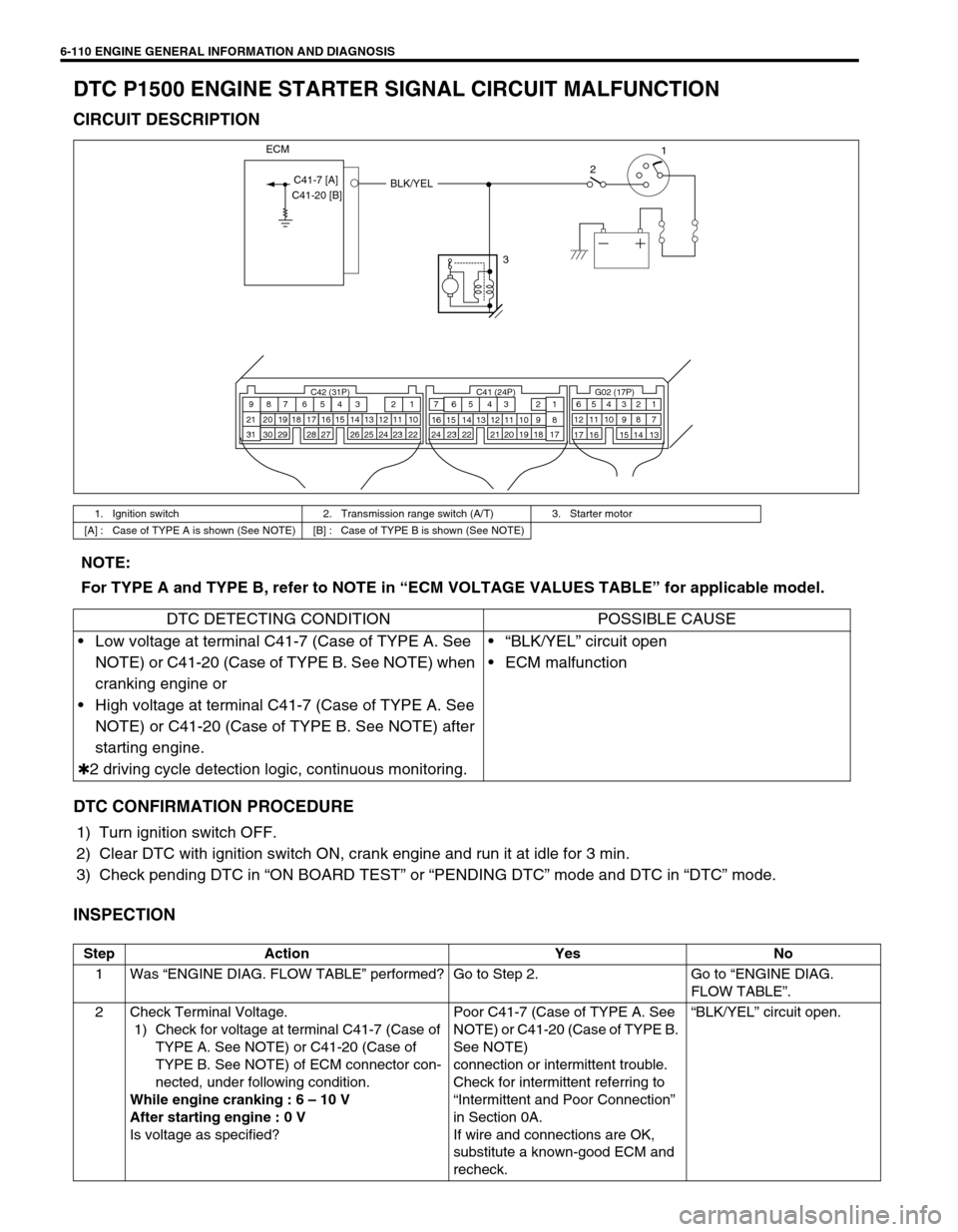
6-110 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
DTC P1500 ENGINE STARTER SIGNAL CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Clear DTC with ignition switch ON, crank engine and run it at idle for 3 min.
3) Check pending DTC in “ON BOARD TEST” or “PENDING DTC” mode and DTC in “DTC” mode.
INSPECTION
1. Ignition switch 2. Transmission range switch (A/T) 3. Starter motor
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE) [B] : Case of TYPE B is shown (See NOTE)
321
BLK/YEL
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
ECM
C41-7 [A]
C41-20 [B]
NOTE:
For TYPE A and TYPE B, refer to NOTE in “ECM VOLTAGE VALUES TABLE” for applicable model.
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
Low voltage at terminal C41-7 (Case of TYPE A. See
NOTE) or C41-20 (Case of TYPE B. See NOTE) when
cranking engine or
High voltage at terminal C41-7 (Case of TYPE A. See
NOTE) or C41-20 (Case of TYPE B. See NOTE) after
starting engine.
✱2 driving cycle detection logic, continuous monitoring.“BLK/YEL” circuit open
ECM malfunction
Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” performed? Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Check Terminal Voltage.
1) Check for voltage at terminal C41-7 (Case of
TYPE A. See NOTE) or C41-20 (Case of
TYPE B. See NOTE) of ECM connector con-
nected, under following condition.
While engine cranking : 6 – 10 V
After starting engine : 0 V
Is voltage as specified?Poor C41-7 (Case of TYPE A. See
NOTE) or C41-20 (Case of TYPE B.
See NOTE)
connection or intermittent trouble.
Check for intermittent referring to
“Intermittent and Poor Connection”
in Section 0A.
If wire and connections are OK,
substitute a known-good ECM and
recheck.“BLK/YEL” circuit open.
Page 481 of 698
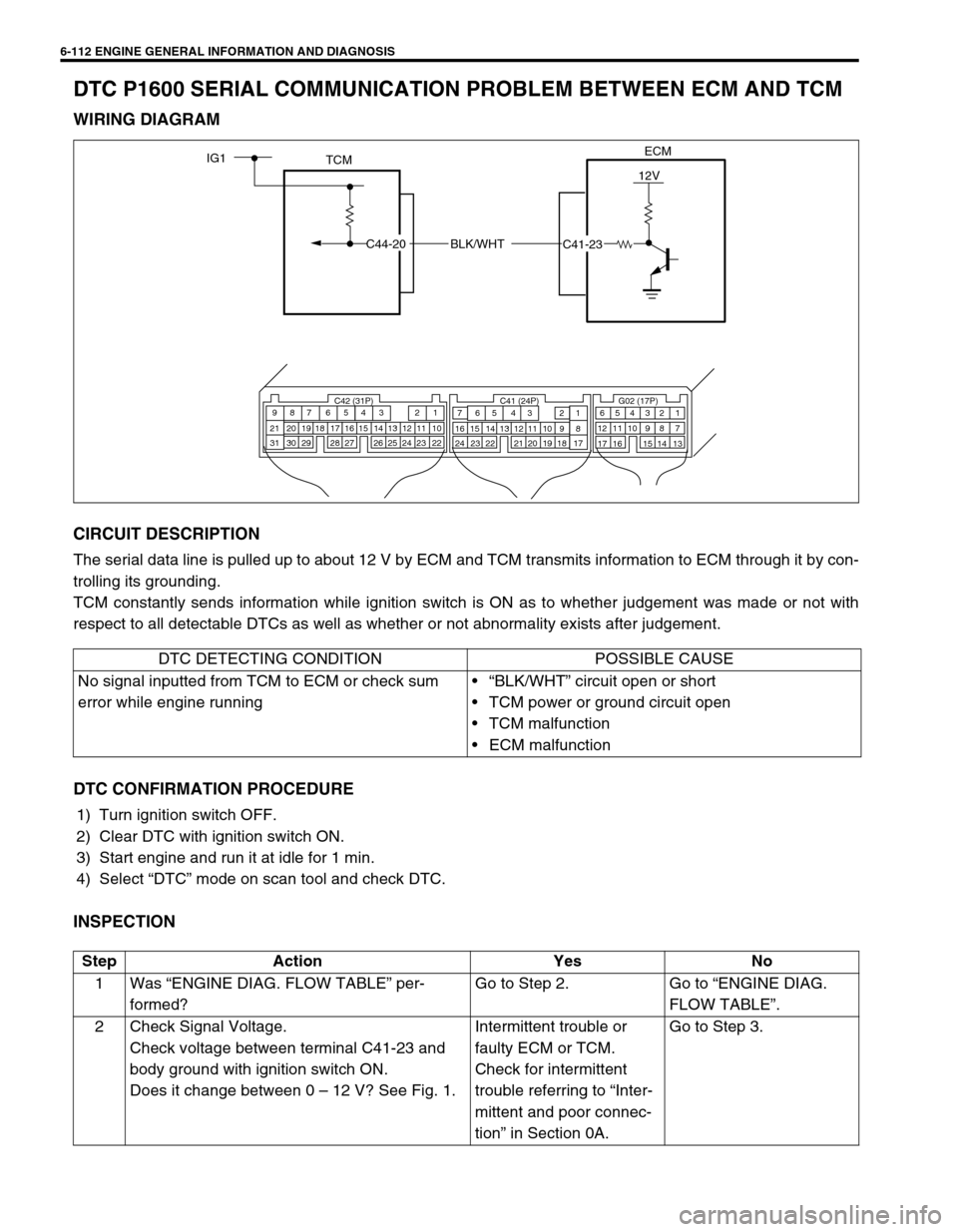
6-112 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
DTC P1600 SERIAL COMMUNICATION PROBLEM BETWEEN ECM AND TCM
WIRING DIAGRAM
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The serial data line is pulled up to about 12 V by ECM and TCM transmits information to ECM through it by con-
trolling its grounding.
TCM constantly sends information while ignition switch is ON as to whether judgement was made or not with
respect to all detectable DTCs as well as whether or not abnormality exists after judgement.
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Clear DTC with ignition switch ON.
3) Start engine and run it at idle for 1 min.
4) Select “DTC” mode on scan tool and check DTC.
INSPECTION
ECM
TCMIG1
BLK/WHT
12V
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
C44-20
C41-23
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
No signal inputted from TCM to ECM or check sum
error while engine running“BLK/WHT” circuit open or short
TCM power or ground circuit open
TCM malfunction
ECM malfunction
Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” per-
formed?Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Check Signal Voltage.
Check voltage between terminal C41-23 and
body ground with ignition switch ON.
Does it change between 0 – 12 V? See Fig. 1.Intermittent trouble or
faulty ECM or TCM.
Check for intermittent
trouble referring to “Inter-
mittent and poor connec-
tion” in Section 0A.Go to Step 3.
Page 483 of 698
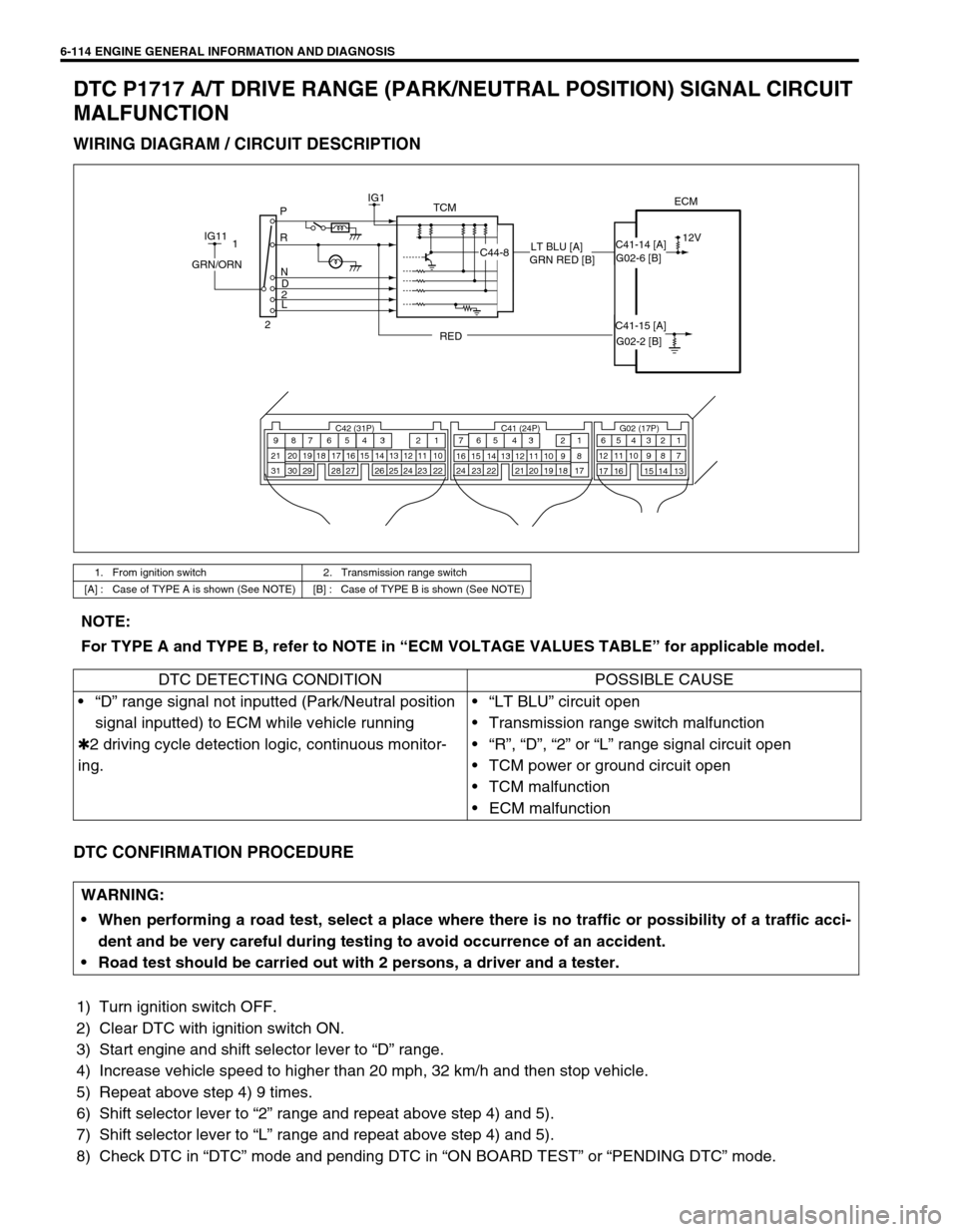
6-114 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
DTC P1717 A/T DRIVE RANGE (PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION) SIGNAL CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION
WIRING DIAGRAM / CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Clear DTC with ignition switch ON.
3) Start engine and shift selector lever to “D” range.
4) Increase vehicle speed to higher than 20 mph, 32 km/h and then stop vehicle.
5) Repeat above step 4) 9 times.
6) Shift selector lever to “2” range and repeat above step 4) and 5).
7) Shift selector lever to “L” range and repeat above step 4) and 5).
8) Check DTC in “DTC” mode and pending DTC in “ON BOARD TEST” or “PENDING DTC” mode.
1. From ignition switch 2. Transmission range switch
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE) [B] : Case of TYPE B is shown (See NOTE)
TCMECMIG1
12V P
R
N
D
2
L
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
IG11
C44-8
REDGRN/ORN1
2G02-6 [B] C41-14 [A]
C41-15 [A]
G02-2 [B] GRN RED [B]LT BLU [A]
NOTE:
For TYPE A and TYPE B, refer to NOTE in “ECM VOLTAGE VALUES TABLE” for applicable model.
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
“D” range signal not inputted (Park/Neutral position
signal inputted) to ECM while vehicle running
✱2 driving cycle detection logic, continuous monitor-
ing.“LT BLU” circuit open
Transmission range switch malfunction
“R”, “D”, “2” or “L” range signal circuit open
TCM power or ground circuit open
TCM malfunction
ECM malfunction
WARNING:
When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic acci-
dent and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
Road test should be carried out with 2 persons, a driver and a tester.
Page 484 of 698
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-115
INSPECTION
Fig. 1 for Step 3Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” per-
formed?Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Is SUZUKI scan tool available? Go to Step 3. Go to Step 4.
3 Check PNP Signal (“D” range signal).
1) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to DLC with igni-
tion switch OFF. See Fig. 1.
2) Turn ignition switch ON and check PNP sig-
nal (“P/N” or “D” range) on display when
shifting selector lever to each range.
Is “D” range on display (Is 0 – 1 V indicated) no
matter which of “R”, “D”, “2” and “L” range posi-
tions selector lever may be at? See Table 1.Intermittent trouble or
faulty ECM. Check for
intermittent referring to
“Intermittent and poor
connection” in Section 0A.Go to Step 5.
4 Check PNP Signal (“D” range signal).
1) Turn ignition switch ON.
2) Check voltage at terminal C41-14 (Case of
TYPE A. See NOTE) or G02-6 (Case of
TYPE B. See NOTE) of ECM connector
connected. See Fig. 2.
Is “D” range on display (Is 0 – 1 V indicated) no
matter which of “R”, “D”, “2” and “L” range posi-
tions selector lever may be at? See Table 1.Intermittent trouble or
faulty ECM. Check for
intermittent referring to
“Intermittent and poor
connection” in Section 0A.Go to Step 5.
5Is “P/N range on display (Is 10 – 14 V indicated)
when selector lever is at one of “R”, “D”, “2” and
“L” range positions only?Check transmission range
switch and circuits refer-
ring to section 7B.Go to Step 6.
6 Check PNP Signal Circuit.
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Disconnect TCM connectors.
3) Check for proper connection to TCM at ter-
minal C44-8.
4) If OK, then check voltage at terminal
C44-8 in TCM connector disconnected, with
ignition switch ON.
Is it 10 – 14 V? See Fig. 3“GRN/ORN” circuit open,
poor transmission range
switch connector connec-
tion, select cable malad-
justed, transmission
range sensor malad-
justed or transmission
range sensor malfunction.
If all above are OK, sub-
stitute a known-good
TCM and recheck.“LT BLU” (Case of TYPE
A. See NOTE) or “GRN
RED” (Case of TYPE B.
See NOTE) circuit open or
poor C41-14 (Case of
TYPE A. See NOTE) or
G02-6 (Case of TYPE B.
See NOTE) connection.
If wire and connection are
OK, substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
Page 492 of 698
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-123
Fig. 1 for Step 105 Check A/C (input) signal circuit referring to Step
1 of Table B-5 A/C Signal Circuit Check, if
equipped. (A/C signal can be also checked by
using SUZUKI scan tool.)
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 6. Repair or replace A/C sig-
nal circuit or A/C system.
6 Check IAC system referring to Step 2 of DTC
P0505 Diag. Flow Table.
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 7. Go to Step 3 of DTC
P0505 Diag. Flow Table.
7 Was IAC duty less than about 3% (or more than
about 97% for OFF duty meter) in Step 1 of this
table?Check abnormal air inhal-
ing from air intake system,
PCV valve and EVAP
canister purge control
system.Check TP sensor (closed
throttle position) and ECT
sensor for performance.
If sensors are OK, substi-
tute a known-good ECM.
8 Is SUZUKI scan Tool available? Go to Step 9. Go to Step 10.
9 Check PNP signal (“D” range signal).
1) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to DLC with igni-
tion switch OFF.
2) Turn ignition switch ON and check PNP sig-
nal (“P/N” and “D” range) on display when
shifting selector lever to each range. See
Table 1.
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 11. Repair or replace.
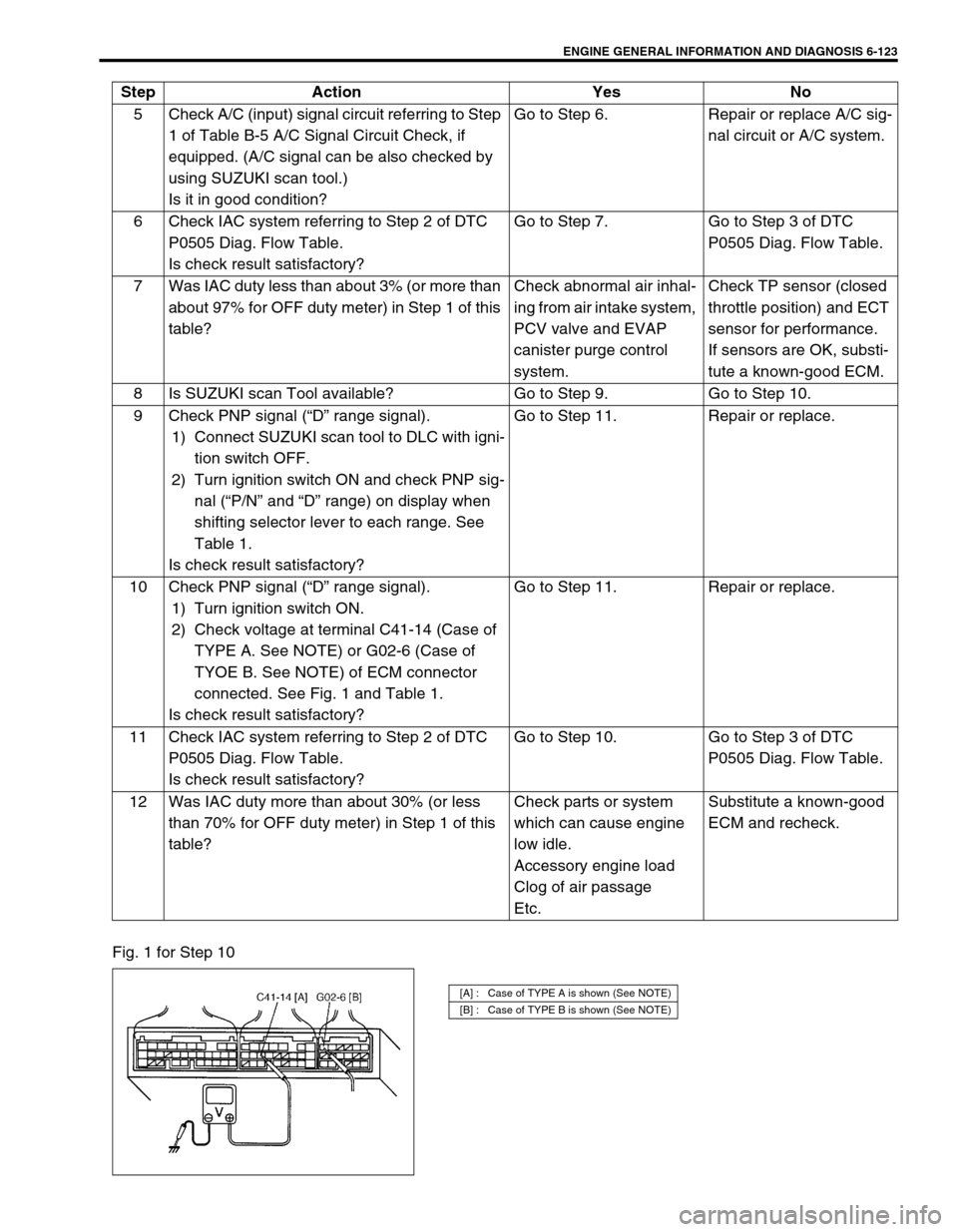
10 Check PNP signal (“D” range signal).
1) Turn ignition switch ON.
2) Check voltage at terminal C41-14 (Case of
TYPE A. See NOTE) or G02-6 (Case of
TYOE B. See NOTE) of ECM connector
connected. See Fig. 1 and Table 1.
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 11. Repair or replace.
11 Check IAC system referring to Step 2 of DTC
P0505 Diag. Flow Table.
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 10. Go to Step 3 of DTC
P0505 Diag. Flow Table.
12 Was IAC duty more than about 30% (or less
than 70% for OFF duty meter) in Step 1 of this
table?Check parts or system
which can cause engine
low idle.
Accessory engine load
Clog of air passage
Etc.Substitute a known-good
ECM and recheck. Step Action Yes No
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE)
[B] : Case of TYPE B is shown (See NOTE)
Page 495 of 698
![SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service User Guide 6-126 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
TABLE B-6 ELECTRIC LOAD SIGNAL CIRCUIT CHECK
INSPECTION
1. Blower fan motor 3. Rear defogger 5. To A/C switch
2. Blower fan switch 4. Position lamp
[A] : SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service User Guide 6-126 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
TABLE B-6 ELECTRIC LOAD SIGNAL CIRCUIT CHECK
INSPECTION
1. Blower fan motor 3. Rear defogger 5. To A/C switch
2. Blower fan switch 4. Position lamp
[A] :](/img/20/7606/w960_7606-494.png)
6-126 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
TABLE B-6 ELECTRIC LOAD SIGNAL CIRCUIT CHECK
INSPECTION
1. Blower fan motor 3. Rear defogger 5. To A/C switch
2. Blower fan switch 4. Position lamp
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE) [B] : Case of TYPE B is shown (See NOTE)
IG2
M
ECM
PNK/BLUG02-13
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
RED/BLK [A]
IG11
+BB
43 25 1
C42-17 [A]
C41-17 [B] RED/YEL [B]
NOTE:
For TYPE A and TYPE B, refer to NOTE in “ECM VOLTAGE VALUES TABLE” for applicable model.
Step Action Yes No
1 Is SUZUKI scan tool available? Go to Step 2. Go to Step 3.
2 Check Electric Load Signal Circuit.
1) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to DLC with igni-
tion switch OFF.
2) Start engine and select “DATA LIST” mode
on scan tool.
3) Check electric load signal under following
each condition. See Fig. 1 and Table 1.
Is check result satisfactory?Electric load signal circuit
is in good condition.“RED/BLK” (Case of
TYPE A. See NOTE) or
C41-17 (Case of TYPE B.
See NOTE) and/or “PNK/
BLU” circuit open or short,
Electric load diodes mal-
function or Each electric
load circuit malfunction.
3 Check Electric Load Signal Circuit.
1) Turn ignition switch ON.
2) Check voltage at each terminals C42-17
(Case of TYPE A. See NOTE) or C41-17
(Case of TYPE B. See NOTE) and G02-13
of ECM connector connected, under above
each condition. See Fig. 2 and Table 1.
Is each voltage as specified?Electric load signal circuit
is in good condition.“RED/BLK” (Case of
TYPE A. See NOTE) or
C41-17 (Case of TYPE B.
See NOTE) and/or “PNK/
BLU” circuit open or short,
Electric load diodes mal-
function or Each electric
load circuit malfunction.