wiring diagram SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2000, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.GPages: 698, PDF Size: 16.01 MB
Page 472 of 698
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-103
DTC P0500 (DTC NO.16) VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR (VSS) MALFUNCTION
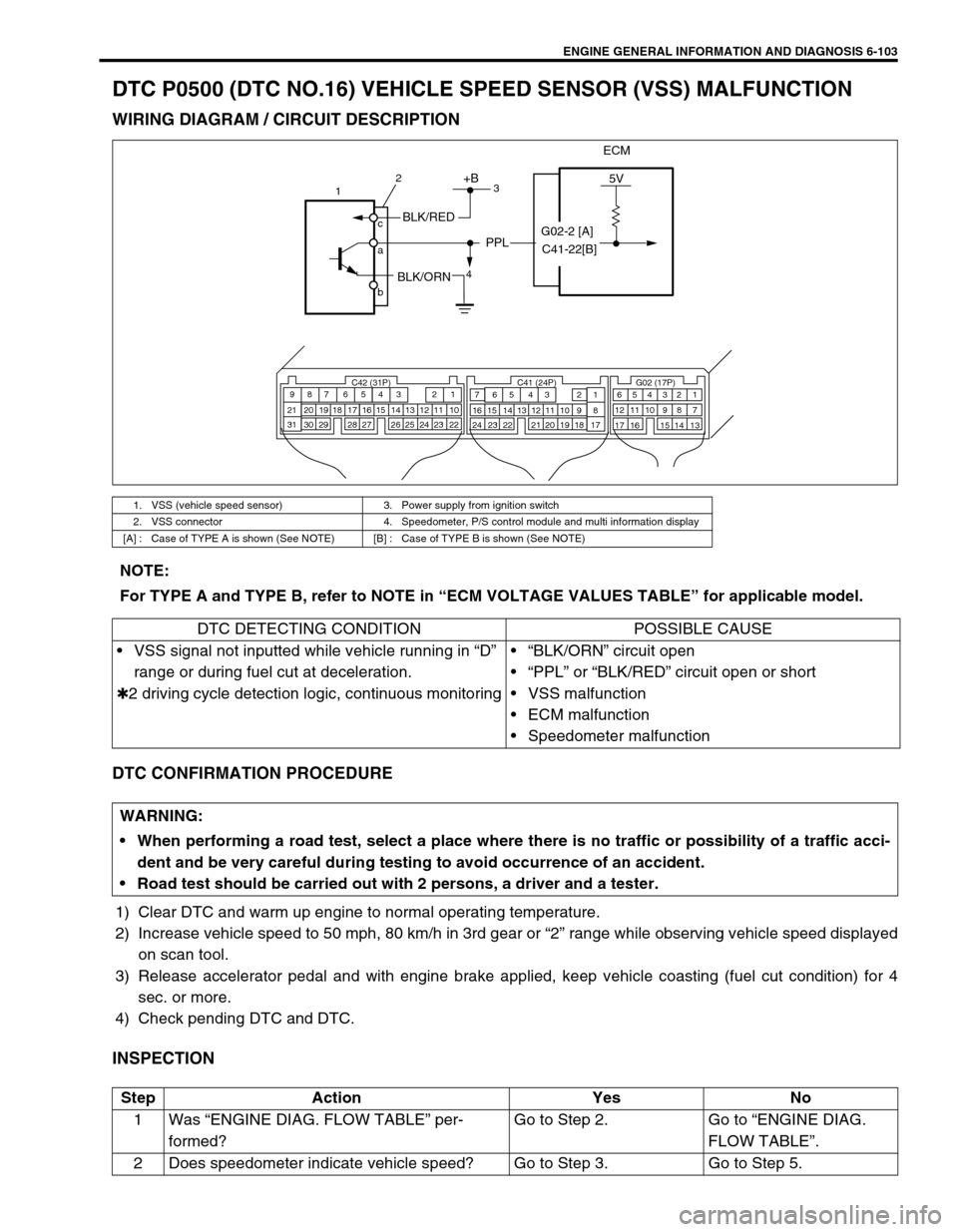
WIRING DIAGRAM / CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Clear DTC and warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
2) Increase vehicle speed to 50 mph, 80 km/h in 3rd gear or “2” range while observing vehicle speed displayed
on scan tool.
3) Release accelerator pedal and with engine brake applied, keep vehicle coasting (fuel cut condition) for 4
sec. or more.
4) Check pending DTC and DTC.
INSPECTION
1. VSS (vehicle speed sensor) 3. Power supply from ignition switch
2. VSS connector 4. Speedometer, P/S control module and multi information display
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE) [B] : Case of TYPE B is shown (See NOTE)
ECM
5V+B
BLK/RED
BLK/ORN
PPL
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
1
4 c
a
b2
3
G02-2 [A]
C41-22[B]
NOTE:
For TYPE A and TYPE B, refer to NOTE in “ECM VOLTAGE VALUES TABLE” for applicable model.
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
VSS signal not inputted while vehicle running in “D”
range or during fuel cut at deceleration.
✱2 driving cycle detection logic, continuous monitoring“BLK/ORN” circuit open
“PPL” or “BLK/RED” circuit open or short
VSS malfunction
ECM malfunction
Speedometer malfunction
WARNING:
When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic acci-
dent and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
Road test should be carried out with 2 persons, a driver and a tester.
Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” per-
formed?Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Does speedometer indicate vehicle speed? Go to Step 3. Go to Step 5.
Page 477 of 698
6-108 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
DTC P1450 BAROMETRIC PRESSURE SENSOR LOW/HIGH INPUT
DTC P1451 BAROMETRIC PRESSURE SENSOR PERFORMANCE PROBLEM
WIRING DIAGRAM / CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Barometric pressure sensor is installed in ECM.
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Clear DTC with ignition switch ON.
3) Turn ignition switch ON for 2 sec., crank engine for 2 sec. and run it at idle for 1 min.
4) Check pending DTC in “ON BOARD TEST” or “PENDING DTC” mode and DTC in “DTC” mode.
INSPECTION
DTC P1450 :
Substitute a known-good ECM and recheck.
DTC P1451 :
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
DTC P1450 :
Barometric pressure : Sensor voltage is 4.7 V or higher, or
1.6 V or lowerECM (barometric pressure sensor) malfunc-
tion
DTC P1451 :
Vehicle stopped
Engine cranking
Difference between barometric pressure and intake mani-
fold absolute pressure is 26 kPa, 200 mmHg or more
Difference between intake manifold absolute pressure at
engine start and the pressure after engine start is 1.3 kPa,
10 mmHg or less.
✱2 driving cycle detection logic, monitoring once/1 driving.Manifold absolute pressure sensor and its
circuit malfunction
ECM (barometric pressure sensor) malfunc-
tion
NOTE:
Note that atmospheric pressure varies depending on weather conditions as well as altitude.
Take that into consideration when performing these check.
Step Action Yes No
1 Check Barometric Pressure Valve.
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition
switch OFF.
2) Turn ignition switch ON and select “DATA
LIST” mode on scan tool.
3) Check manifold absolute pressure. See Fig.
1.
Is it barometric pressure (approx. 100 kPa, 760
mmHg) at sea level?Substitute a known-good
ECM and recheck.Go to Step 2.
Page 480 of 698
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-111
DTC P1510 ECM BACK-UP POWER SUPPLY MALFUNCTION
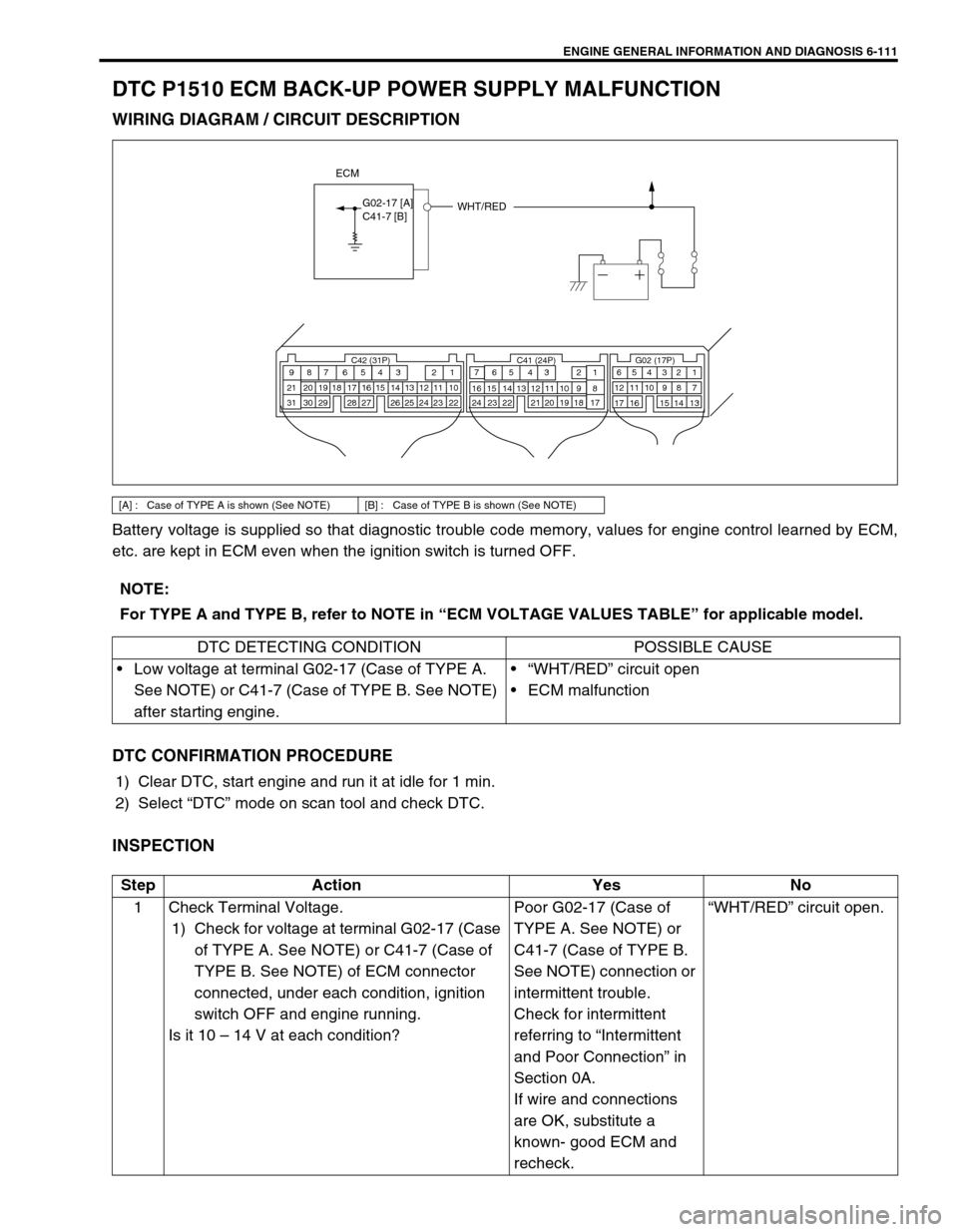
WIRING DIAGRAM / CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Battery voltage is supplied so that diagnostic trouble code memory, values for engine control learned by ECM,
etc. are kept in ECM even when the ignition switch is turned OFF.
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Clear DTC, start engine and run it at idle for 1 min.
2) Select “DTC” mode on scan tool and check DTC.
INSPECTION
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE) [B] : Case of TYPE B is shown (See NOTE)
WHT/RED
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
ECM
G02-17 [A]C41-7 [B]
NOTE:
For TYPE A and TYPE B, refer to NOTE in “ECM VOLTAGE VALUES TABLE” for applicable model.
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
Low voltage at terminal G02-17 (Case of TYPE A.
See NOTE) or C41-7 (Case of TYPE B. See NOTE)
after starting engine.“WHT/RED” circuit open
ECM malfunction
Step Action Yes No
1 Check Terminal Voltage.
1) Check for voltage at terminal G02-17 (Case
of TYPE A. See NOTE) or C41-7 (Case of
TYPE B. See NOTE) of ECM connector
connected, under each condition, ignition
switch OFF and engine running.
Is it 10 – 14 V at each condition?Poor G02-17 (Case of
TYPE A. See NOTE) or
C41-7 (Case of TYPE B.
See NOTE) connection or
intermittent trouble.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection” in
Section 0A.
If wire and connections
are OK, substitute a
known- good ECM and
recheck.“WHT/RED” circuit open.
Page 481 of 698
6-112 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
DTC P1600 SERIAL COMMUNICATION PROBLEM BETWEEN ECM AND TCM
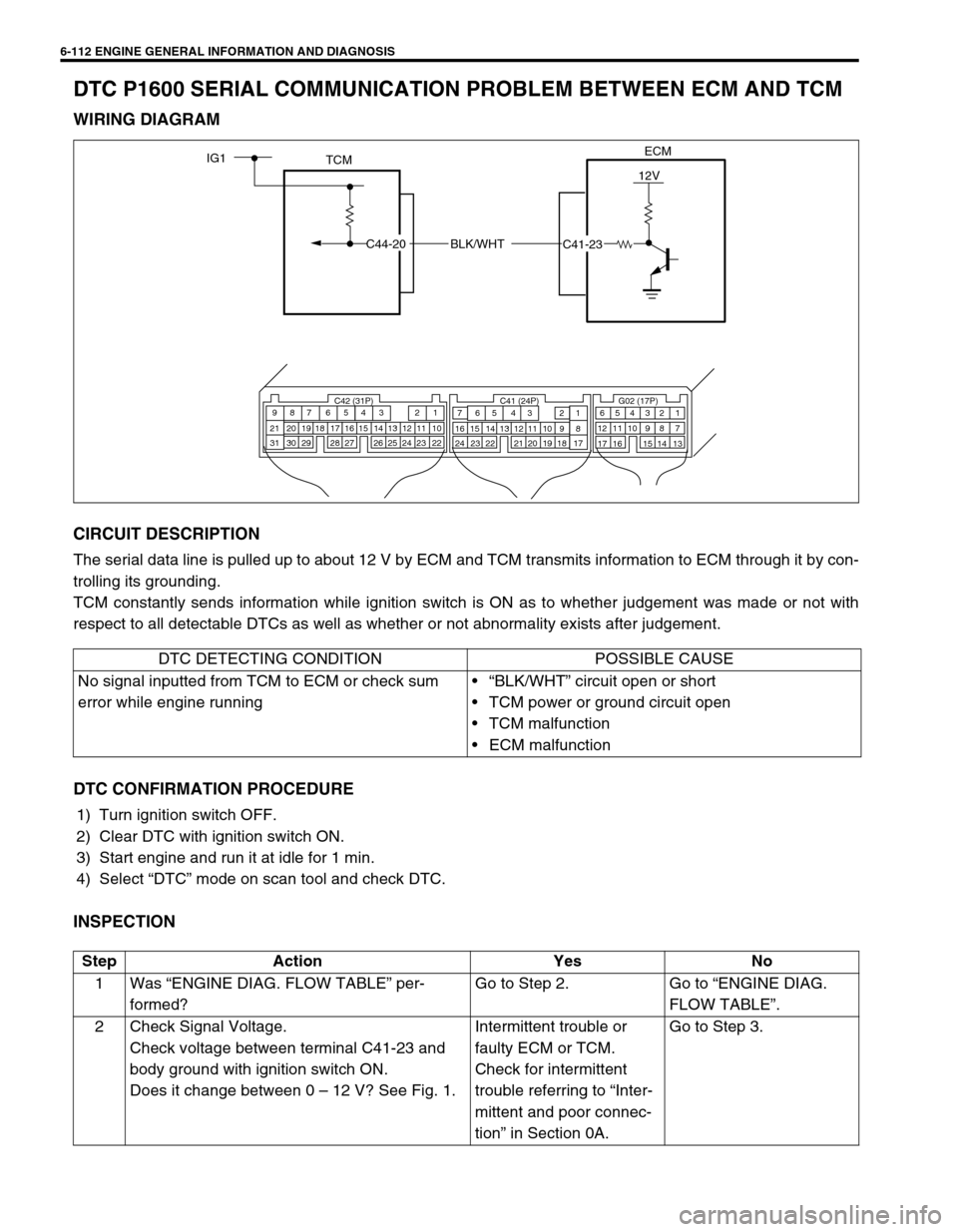
WIRING DIAGRAM
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The serial data line is pulled up to about 12 V by ECM and TCM transmits information to ECM through it by con-
trolling its grounding.
TCM constantly sends information while ignition switch is ON as to whether judgement was made or not with
respect to all detectable DTCs as well as whether or not abnormality exists after judgement.
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Clear DTC with ignition switch ON.
3) Start engine and run it at idle for 1 min.
4) Select “DTC” mode on scan tool and check DTC.
INSPECTION
ECM
TCMIG1
BLK/WHT
12V
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
C44-20
C41-23
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
No signal inputted from TCM to ECM or check sum
error while engine running“BLK/WHT” circuit open or short
TCM power or ground circuit open
TCM malfunction
ECM malfunction
Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” per-
formed?Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Check Signal Voltage.
Check voltage between terminal C41-23 and
body ground with ignition switch ON.
Does it change between 0 – 12 V? See Fig. 1.Intermittent trouble or
faulty ECM or TCM.
Check for intermittent
trouble referring to “Inter-
mittent and poor connec-
tion” in Section 0A.Go to Step 3.
Page 483 of 698
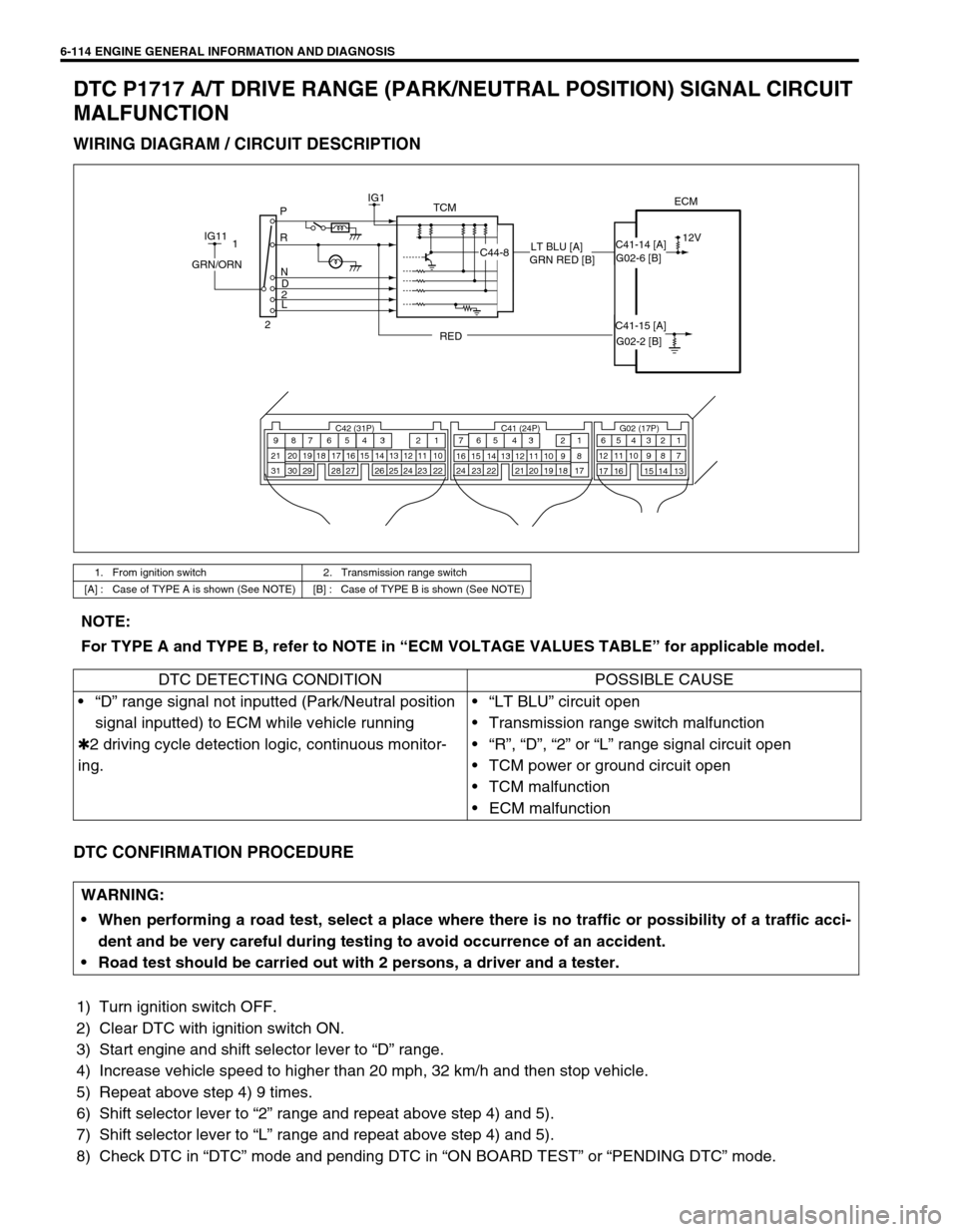
6-114 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
DTC P1717 A/T DRIVE RANGE (PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION) SIGNAL CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION
WIRING DIAGRAM / CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Clear DTC with ignition switch ON.
3) Start engine and shift selector lever to “D” range.
4) Increase vehicle speed to higher than 20 mph, 32 km/h and then stop vehicle.
5) Repeat above step 4) 9 times.
6) Shift selector lever to “2” range and repeat above step 4) and 5).
7) Shift selector lever to “L” range and repeat above step 4) and 5).
8) Check DTC in “DTC” mode and pending DTC in “ON BOARD TEST” or “PENDING DTC” mode.
1. From ignition switch 2. Transmission range switch
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE) [B] : Case of TYPE B is shown (See NOTE)
TCMECMIG1
12V P
R
N
D
2
L
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
IG11
C44-8
REDGRN/ORN1
2G02-6 [B] C41-14 [A]
C41-15 [A]
G02-2 [B] GRN RED [B]LT BLU [A]
NOTE:
For TYPE A and TYPE B, refer to NOTE in “ECM VOLTAGE VALUES TABLE” for applicable model.
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
“D” range signal not inputted (Park/Neutral position
signal inputted) to ECM while vehicle running
✱2 driving cycle detection logic, continuous monitor-
ing.“LT BLU” circuit open
Transmission range switch malfunction
“R”, “D”, “2” or “L” range signal circuit open
TCM power or ground circuit open
TCM malfunction
ECM malfunction
WARNING:
When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic acci-
dent and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
Road test should be carried out with 2 persons, a driver and a tester.
Page 486 of 698
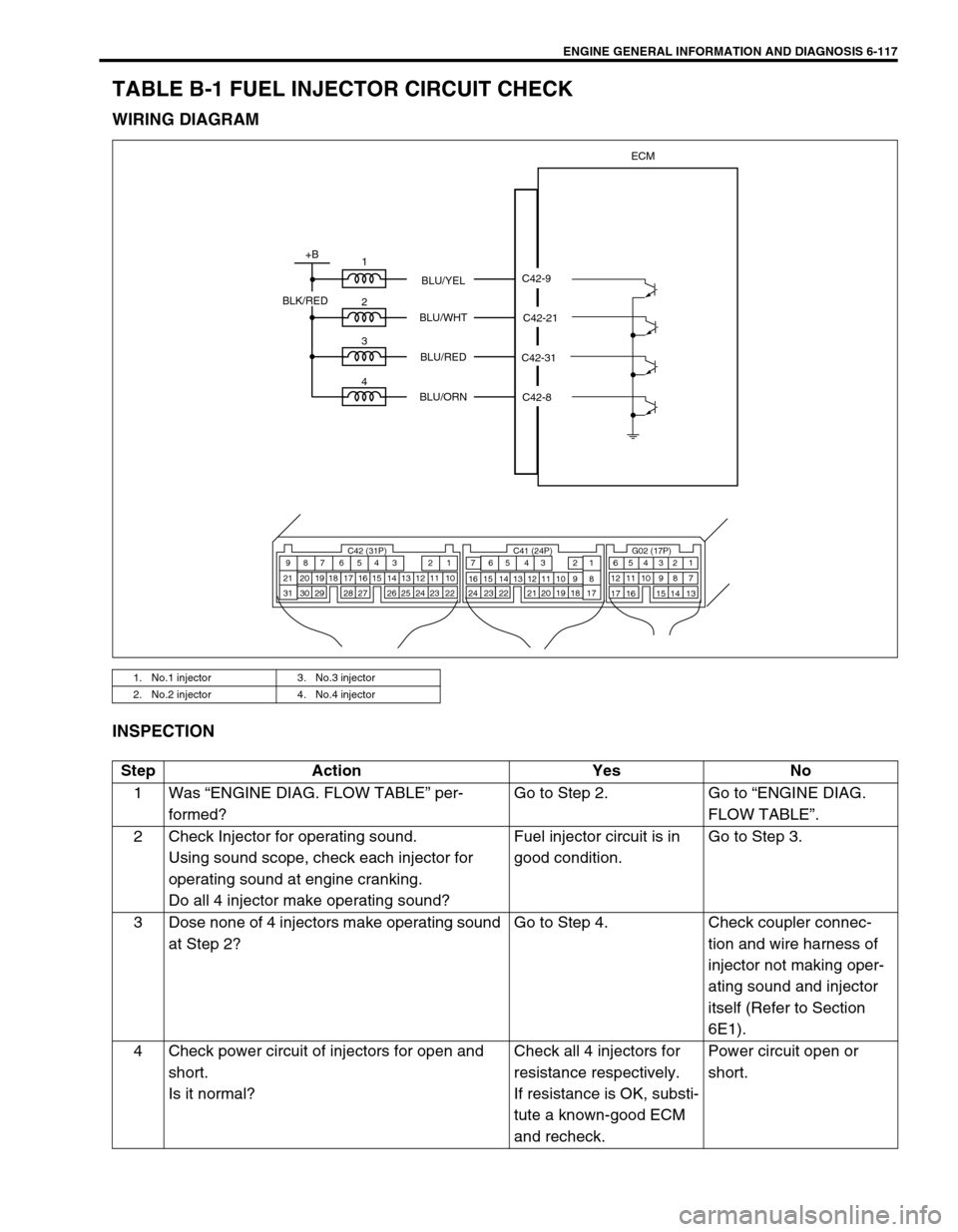
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-117
TABLE B-1 FUEL INJECTOR CIRCUIT CHECK
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION
1. No.1 injector 3. No.3 injector
2. No.2 injector 4. No.4 injector
ECM
1
2
3
4
+B
C42-9
C42-21
C42-8 C42-31 BLU/YEL
BLU/WHT
BLU/RED
BLU/ORN
BLK/RED
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” per-
formed?Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Check Injector for operating sound.
Using sound scope, check each injector for
operating sound at engine cranking.
Do all 4 injector make operating sound?Fuel injector circuit is in
good condition.Go to Step 3.
3 Dose none of 4 injectors make operating sound
at Step 2?Go to Step 4. Check coupler connec-
tion and wire harness of
injector not making oper-
ating sound and injector
itself (Refer to Section
6E1).
4 Check power circuit of injectors for open and
short.
Is it normal?Check all 4 injectors for
resistance respectively.
If resistance is OK, substi-
tute a known-good ECM
and recheck.Power circuit open or
short.
Page 489 of 698
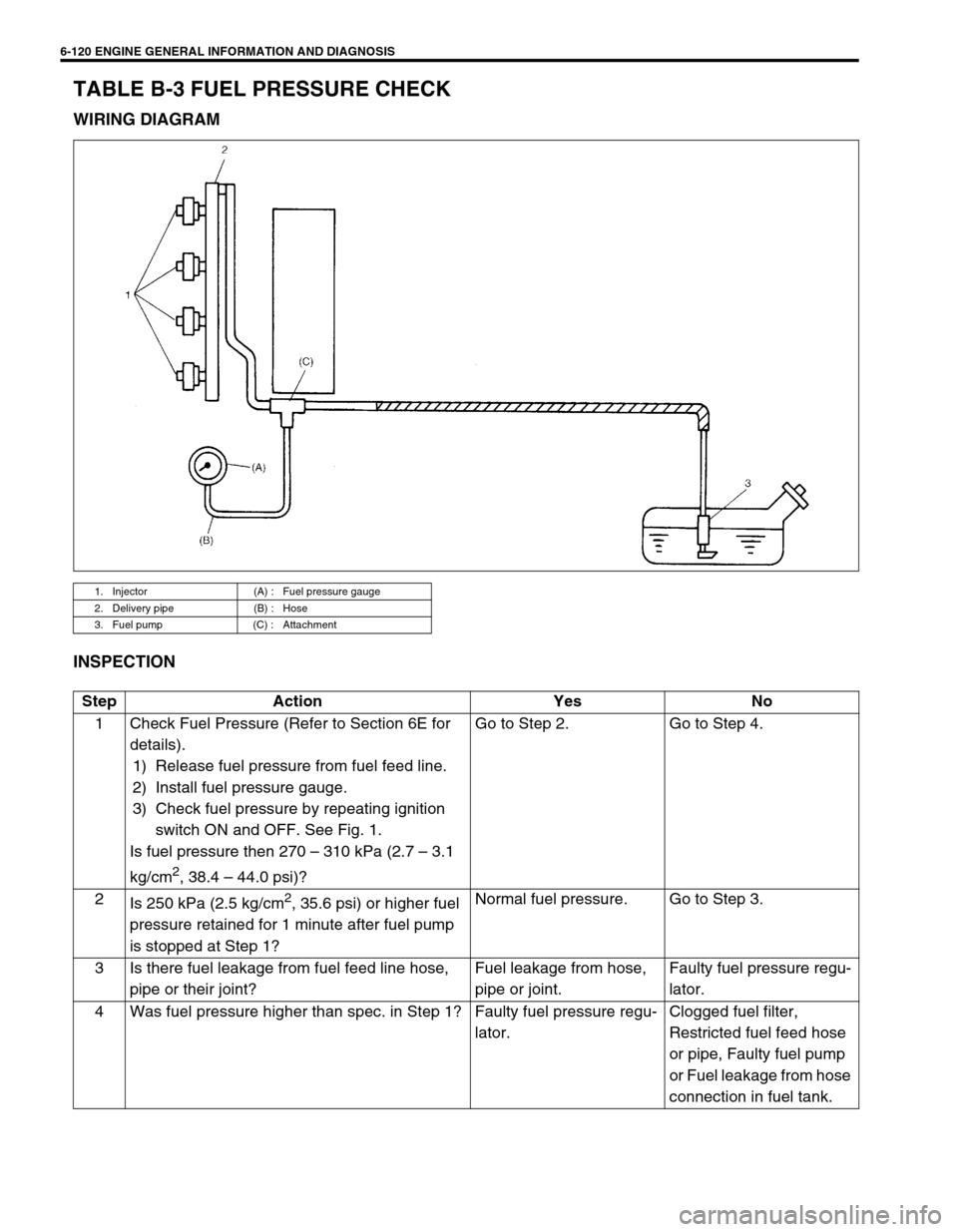
6-120 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
TABLE B-3 FUEL PRESSURE CHECK
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION
1. Injector (A) : Fuel pressure gauge
2. Delivery pipe (B) : Hose
3. Fuel pump (C) : Attachment
Step Action Yes No
1 Check Fuel Pressure (Refer to Section 6E for
details).
1) Release fuel pressure from fuel feed line.
2) Install fuel pressure gauge.
3) Check fuel pressure by repeating ignition
switch ON and OFF. See Fig. 1.
Is fuel pressure then 270 – 310 kPa (2.7 – 3.1
kg/cm
2, 38.4 – 44.0 psi)?Go to Step 2. Go to Step 4.
2
Is 250 kPa (2.5 kg/cm
2, 35.6 psi) or higher fuel
pressure retained for 1 minute after fuel pump
is stopped at Step 1?Normal fuel pressure. Go to Step 3.
3 Is there fuel leakage from fuel feed line hose,
pipe or their joint?Fuel leakage from hose,
pipe or joint.Faulty fuel pressure regu-
lator.
4 Was fuel pressure higher than spec. in Step 1? Faulty fuel pressure regu-
lator.Clogged fuel filter,
Restricted fuel feed hose
or pipe, Faulty fuel pump
or Fuel leakage from hose
connection in fuel tank.
Page 622 of 698

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 6E1-1
6F1
6F2
6G
6H
6E1
7A
7A1
7B1
7C1
7D
7E
7F
8A
8B
8C
8D
8E
9
10
10A
10B
SECTION 6E1
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION ............................ 6E1-2
AIR INTAKE SYSTEM ............................... 6E1-5
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM ....................... 6E1-6
FUEL PUMP ........................................... 6E1-6
ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM .......... 6E1-7
ENGINE & EMISSION CONTROL
INPUT/OUTPUT TABLE ........................ 6E1-8
ECM INPUT/OUTPUT CIRCUIT
DIAGRAM............................................... 6E1-9
ECM TERMINAL ARRANGEMENT
TABLE .................................................. 6E1-13
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE .............................. 6E1-15
ACCELERATOR CABLE
ADJUSTMENT ..................................... 6E1-15
IDLE SPEED/IDLE AIR CONTROL
(IAC) DUTY INSPECTION ................... 6E1-15
IDLE MIXTURE INSPECTION /
ADJUSTMENT (VEHICLE WITHOUT
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR) ............. 6E1-17
AIR INTAKE SYSTEM ............................. 6E1-18
THROTTLE BODY ............................... 6E1-18IDLE AIR CONTROL VALVE (IAC
VALVE) ................................................ 6E1-20
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM ..................... 6E1-21
FUEL PRESSURE INSPECTION ........ 6E1-21
FUEL PUMP WITH PRESSURE
REGULATOR ....................................... 6E1-22
FUEL INJECTOR ................................. 6E1-23
ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM ....... 6E1-27
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE
(ECM) ................................................... 6E1-27
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE
SENSOR (MAP SENSOR)................... 6E1-27
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TP
SENSOR) ............................................. 6E1-28
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR (IAT SENSOR) ..................... 6E1-29
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR (ECT SENSOR) ................... 6E1-30
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HO2S-1
AND HO2S-2) ...................................... 6E1-31
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR ....... 6E1-32 WARNING:
For vehicles equipped with Supplemental Restraint (Air Bag) System :
Service on and around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed only by an
authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer to “Air Bag System Components and Wiring Location View” under
“General Description” in air bag system section in order to confirm whether you are performing ser-
vice on or near the air bag system components or wiring. Please observe all WARNINGS and “Ser-
vice Precautions” under “On-Vehicle Service” in air bag system section before performing service
on or around the air bag system components or wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could result in
unintentional activation of the system or could render the system inoperative. Either of these two
conditions may result in severe injury.
Technical service work must be started at least 90 seconds after the ignition switch is turned to the
“LOCK” position and the negative cable is disconnected from the battery. Otherwise, the system
may be activated by reserve energy in the Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM).
NOTE:
Whether the following system (parts) are used in the particular vehicle or not depends on vehicle
specifications. Be sure to bear this in mind when performing service work.
EGR valve
Heated oxygen sensor(s) or CO adjusting resistor
Three way catalytic converter
Immobilizer indicator lamp
Knock sensor
Page 665 of 698

IGNITION SYSTEM (ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM 6F1-3
SYSTEM WIRING DIAGRAM
DIAGNOSIS
1. Ignition switch 7. No.1 spark plug
2. Main relay 8. No.2 spark plug
3. Ignition coil assembly for No.1 and No.4 spark plugs 9. No.3 spark plug
4. Ignition coil assembly for No.2 and No.3 spark plugs 10. No.4 spark plug
5. CMP sensor 11. Sensed information (MAP sensor, ECT sensor, IAT sensor, TP sensor, Knock sensor (if
equipped), VSS, Park/Neutral position signal, Electric load signal, Engine start signal, Test switch
terminal (Vehicle without immobilizer indicator lamp))
6. CKP sensor
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Engine cranks, but will
not start or hard to
start (No spark)Blown fuse for ignition coil Replace.
Loose connection or disconnection of lead wire
or high-tension cord(s)Connect securely.
Faulty high-tension cord(s) Replace.
Faulty spark plug(s) Adjust, clean or replace.
Faulty ignition coil Replace ignition coil assembly.
Faulty CKP sensor or CKP sensor plate Clean, tighten or replace.
Faulty ECM Replace.
Poor fuel economy or
engine performanceIncorrect ignition timing Check related sensors and CKP
sensor plate.
Faulty spark plug(s) or high-tension cord(s) Adjust, clean or replace.
Faulty ignition coil assembly Replace.
Faulty CKP sensor or CKP sensor plate Clean, tighten or replace.
Faulty ECM Replace.