heating SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2000, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.GPages: 698, PDF Size: 16.01 MB
Page 3 of 698

TABLE OF CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION ENGINE0A6
General Information0A
General Information and Diagnosis6
0B6A1
Maintenance and Lubrication0B
Engine Mechanical6A1
6B
HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING
Engine Cooling6B
1A6C
Heater and Ventilation1A
Engine Fuel6C
1B6E1
Air Conditioning1B
Engine and Emission Control System6E1
6F1
STEERING, SUSPENSION, WHEELS
AND TIRESIgnition System6F1
36G
Cranking System6G
3A6H
Steering, Suspension, Wheels and Tires3
Charging System6H
3B6K
Front End Alignment3A
Exhaust System6K
3B1 6B
Manual Rack and Pinion3B TRANSMISSION, CLUTCH AND
DIFFERENTIAL
3C7A
Power Steering System3B1
3D7B
Steering Wheel and Column3C
Manual Transmission7A
3E7C
Front Suspension3D
Automatic Transmission7B
3F7D
Rear Suspension3E
Clutch7C
7F
Wheels and Tires3F
Transfer7D
4A
DRIVE SHAFT AND PROPELLER SHAFT
Differential (Rear)(4WD)7F
4B8
Front Drive Shaft 4A ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
8A
Propeller Shaft4B
Body Electrical System8
58G
BRAKE SYSTEM
Wiring Diagram8A5E
Brakes5
Immobilizer Control System (if equipped)8G
9
Antilock Brake System5E BODY SERVICE 9
RESTRAINT SYSTEM
10
Restraint System10
10B
Air Bag System (if equipped)10B
NOTE:
The screen toned Section 8A is in Wiring Diagram Manual mentioned in FOREWORD of this manual.
Page 39 of 698
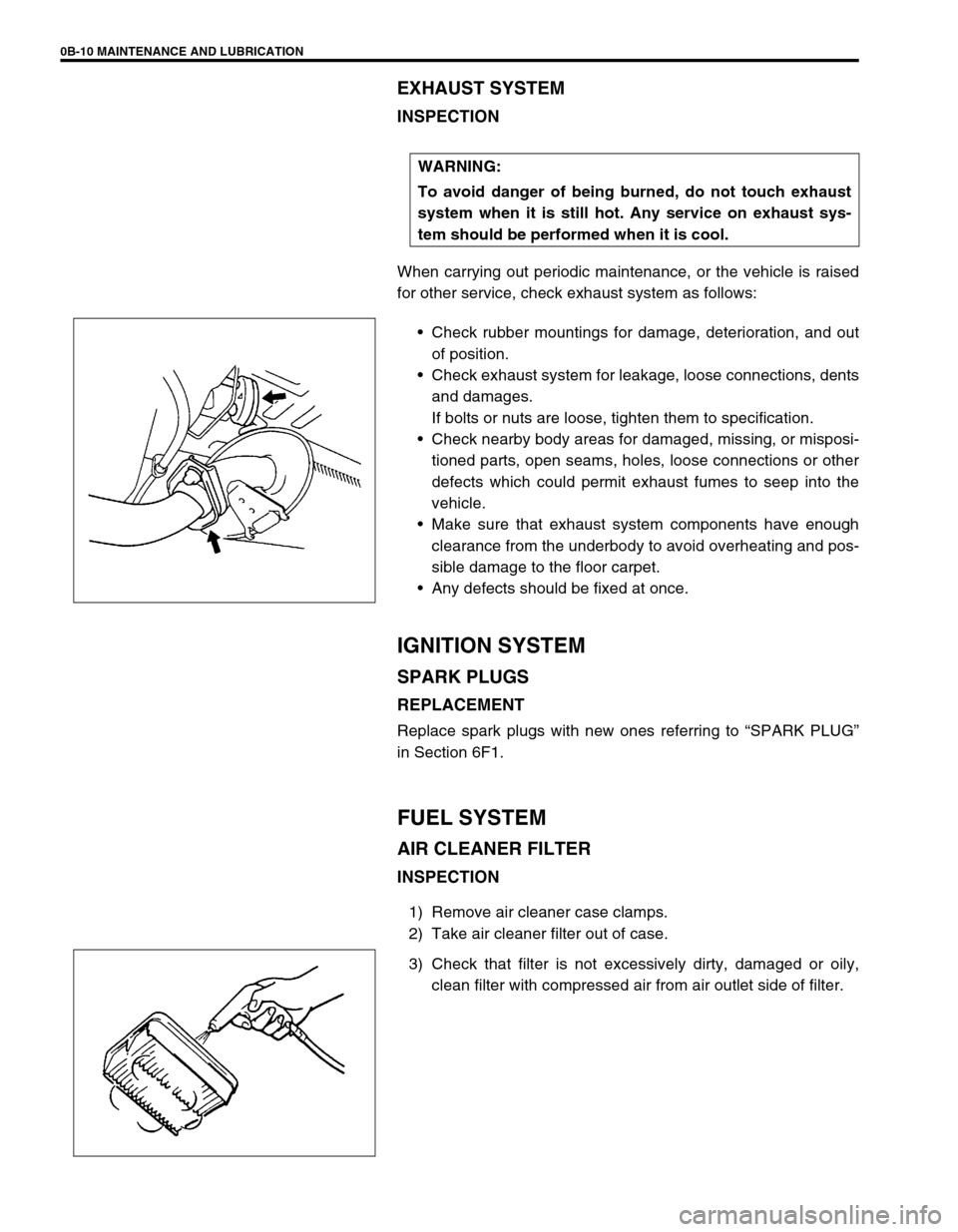
0B-10 MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION
EXHAUST SYSTEM
INSPECTION
When carrying out periodic maintenance, or the vehicle is raised
for other service, check exhaust system as follows:
Check rubber mountings for damage, deterioration, and out
of position.
Check exhaust system for leakage, loose connections, dents
and damages.
If bolts or nuts are loose, tighten them to specification.
Check nearby body areas for damaged, missing, or misposi-
tioned parts, open seams, holes, loose connections or other
defects which could permit exhaust fumes to seep into the
vehicle.
Make sure that exhaust system components have enough
clearance from the underbody to avoid overheating and pos-
sible damage to the floor carpet.
Any defects should be fixed at once.
IGNITION SYSTEM
SPARK PLUGS
REPLACEMENT
Replace spark plugs with new ones referring to “SPARK PLUG”
in Section 6F1.
FUEL SYSTEM
AIR CLEANER FILTER
INSPECTION
1) Remove air cleaner case clamps.
2) Take air cleaner filter out of case.
3) Check that filter is not excessively dirty, damaged or oily,
clean filter with compressed air from air outlet side of filter. WARNING:
To avoid danger of being burned, do not touch exhaust
system when it is still hot. Any service on exhaust sys-
tem should be performed when it is cool.
Page 250 of 698

WHEELS AND TIRES 3F-5
MAINTENANCE AND MINOR ADJUSTMENTS
WHEEL MAINTENANCE
Wheel repairs that use welding, heating, or peening are not approved. All damaged wheels should be replaced.
WHEEL ATTACHING STUDS
If a broken stud is found, see Section 3E (rear) or Section 3D (front) for Note and Replacement procedure.
MATCHED TIRES AND WHEELS
Tires and wheels are match mounted at the assembly plant.
This means that the radially stiffest part of the tire, or “high spot”,
is matched to the smallest radius or “low spot” of the wheel.
This is done to provide the smoothest possible ride.
The “high spot” of the tire is originally marked by paint dot (1) on
the outboard sidewall. This paint dot will eventually wash off the
tire.
The “ow spot” of the wheel is originally marked by paint dot (2) on
the wheel rim-flange. Properly assembled, the wheel rims’ paint
dot should be aligned with the tires’ paint dot as shown in left fig-
ure.
Whenever a tire is dismounted from its wheel, it should be
remounted so that the tire and wheel are matched. If the tire’s
paint dot cannot be located, a line should be scribed on the tire
and wheel before dismounting to assure that it is remounted in
the same position.
TIRE MAINTENANCE
TIRE PLACARD
The “Tire Placard” is located on the left door (right door for right-hand side steering vehicle) lock pillar and
should be referred to tire information.
The placard lists the maximum load, tire size and cold tire pressure where applicable.
NOTE:
Whether rim size and/or maximum load are listed or not depends on regulations of each country.
Page 390 of 698

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-21
P0340
(No.15)CMP SENSOR ECM changes injection control sys-
tem from sequential injection to simul-
taneous one.Hard starting
P0400 EGR VALVE–Hard starting/rough or incorrect
idle/ excessive fuel consumption/
hesitation/ poor acceleration/
surge/ detonation or spark knock/
engine stall
P0420 CATALYST––
P0443 PURGE CONTROL
VALVE–Rough or incorrect idle/ surge/
hard starting/ engine stall
P0480 RADIATOR FAN
CONTROL SYSTEM–Engine overheating
P0500
(No.16)VEHICLE SPEED
SENSORECM stops idle air control. Rough or incorrect idle
P0505 IDLE CONTROL
SYSTEM–Engine stall/ rough or incorrect idle
P0601
(No.71)ECM INTERNAL–Hard starting/ rough or incorrect
idle/ excessive fuel consumption/
detonation or spark knock/ hesita-
tion poor acceleration/
P1450
(No.29)BAROMETRIC
PRESSURE SEN-
SORECM controls actuators assuming
that barometric pressure is
100 kPa (760 mmHg).Hard starting/ rough or incorrect
idle DTC NO. TROUBLE AREA FAIL-SAFE OPERATION SYMPTOM
Page 396 of 698
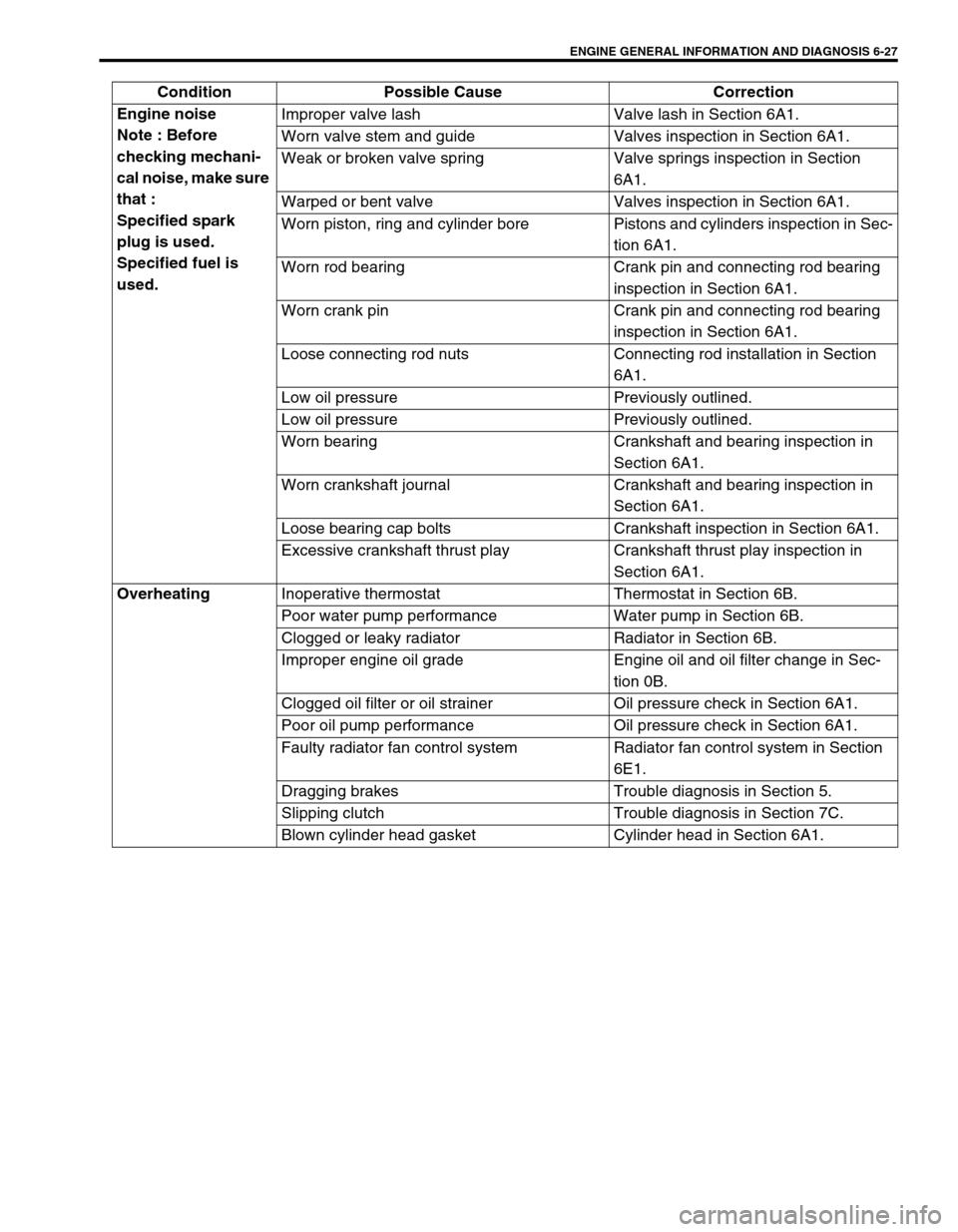
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-27
Engine noise
Note : Before
checking mechani-
cal noise, make sure
that :
Specified spark
plug is used.
Specified fuel is
used.Improper valve lash Valve lash in Section 6A1.
Worn valve stem and guide Valves inspection in Section 6A1.
Weak or broken valve spring Valve springs inspection in Section
6A1.
Warped or bent valve Valves inspection in Section 6A1.
Worn piston, ring and cylinder bore Pistons and cylinders inspection in Sec-
tion 6A1.
Worn rod bearing Crank pin and connecting rod bearing
inspection in Section 6A1.
Worn crank pin Crank pin and connecting rod bearing
inspection in Section 6A1.
Loose connecting rod nuts Connecting rod installation in Section
6A1.
Low oil pressure Previously outlined.
Low oil pressure Previously outlined.
Worn bearing Crankshaft and bearing inspection in
Section 6A1.
Worn crankshaft journal Crankshaft and bearing inspection in
Section 6A1.
Loose bearing cap bolts Crankshaft inspection in Section 6A1.
Excessive crankshaft thrust play Crankshaft thrust play inspection in
Section 6A1.
Overheating
Inoperative thermostat Thermostat in Section 6B.
Poor water pump performance Water pump in Section 6B.
Clogged or leaky radiator Radiator in Section 6B.
Improper engine oil grade Engine oil and oil filter change in Sec-
tion 0B.
Clogged oil filter or oil strainer Oil pressure check in Section 6A1.
Poor oil pump performance Oil pressure check in Section 6A1.
Faulty radiator fan control system Radiator fan control system in Section
6E1.
Dragging brakes Trouble diagnosis in Section 5.
Slipping clutch Trouble diagnosis in Section 7C.
Blown cylinder head gasket Cylinder head in Section 6A1. Condition Possible Cause Correction
Page 397 of 698
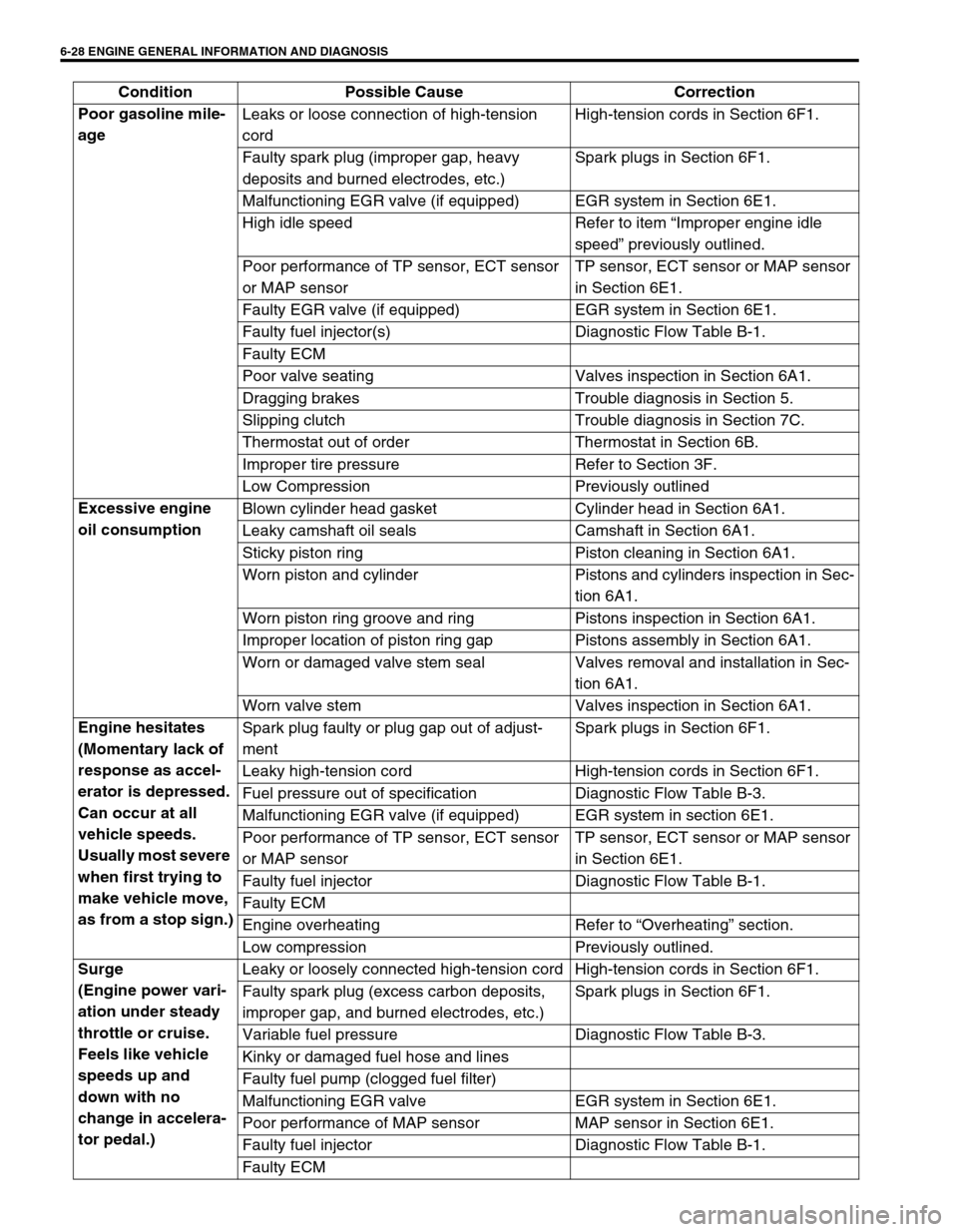
6-28 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
Poor gasoline mile-
age Leaks or loose connection of high-tension
cordHigh-tension cords in Section 6F1.
Faulty spark plug (improper gap, heavy
deposits and burned electrodes, etc.)Spark plugs in Section 6F1.
Malfunctioning EGR valve (if equipped) EGR system in Section 6E1.
High idle speed Refer to item “Improper engine idle
speed” previously outlined.
Poor performance of TP sensor, ECT sensor
or MAP sensorTP sensor, ECT sensor or MAP sensor
in Section 6E1.
Faulty EGR valve (if equipped) EGR system in Section 6E1.
Faulty fuel injector(s) Diagnostic Flow Table B-1.
Faulty ECM
Poor valve seating Valves inspection in Section 6A1.
Dragging brakes Trouble diagnosis in Section 5.
Slipping clutch Trouble diagnosis in Section 7C.
Thermostat out of order Thermostat in Section 6B.
Improper tire pressure Refer to Section 3F.
Low Compression Previously outlined
Excessive engine
oil consumption Blown cylinder head gasket Cylinder head in Section 6A1.
Leaky camshaft oil seals Camshaft in Section 6A1.
Sticky piston ring Piston cleaning in Section 6A1.
Worn piston and cylinder Pistons and cylinders inspection in Sec-
tion 6A1.
Worn piston ring groove and ring Pistons inspection in Section 6A1.
Improper location of piston ring gap Pistons assembly in Section 6A1.
Worn or damaged valve stem seal Valves removal and installation in Sec-
tion 6A1.
Worn valve stem Valves inspection in Section 6A1.
Engine hesitates
(Momentary lack of
response as accel-
erator is depressed.
Can occur at all
vehicle speeds.
Usually most severe
when first trying to
make vehicle move,
as from a stop sign.)Spark plug faulty or plug gap out of adjust-
mentSpark plugs in Section 6F1.
Leaky high-tension cord High-tension cords in Section 6F1.
Fuel pressure out of specification Diagnostic Flow Table B-3.
Malfunctioning EGR valve (if equipped) EGR system in section 6E1.
Poor performance of TP sensor, ECT sensor
or MAP sensorTP sensor, ECT sensor or MAP sensor
in Section 6E1.
Faulty fuel injector Diagnostic Flow Table B-1.
Faulty ECM
Engine overheating Refer to “Overheating” section.
Low compression Previously outlined.
Surge
(Engine power vari-
ation under steady
throttle or cruise.
Feels like vehicle
speeds up and
down with no
change in accelera-
tor pedal.)Leaky or loosely connected high-tension cord High-tension cords in Section 6F1.
Faulty spark plug (excess carbon deposits,
improper gap, and burned electrodes, etc.)Spark plugs in Section 6F1.
Variable fuel pressure Diagnostic Flow Table B-3.
Kinky or damaged fuel hose and lines
Faulty fuel pump (clogged fuel filter)
Malfunctioning EGR valve EGR system in Section 6E1.
Poor performance of MAP sensor MAP sensor in Section 6E1.
Faulty fuel injector Diagnostic Flow Table B-1.
Faulty ECM Condition Possible Cause Correction
Page 398 of 698
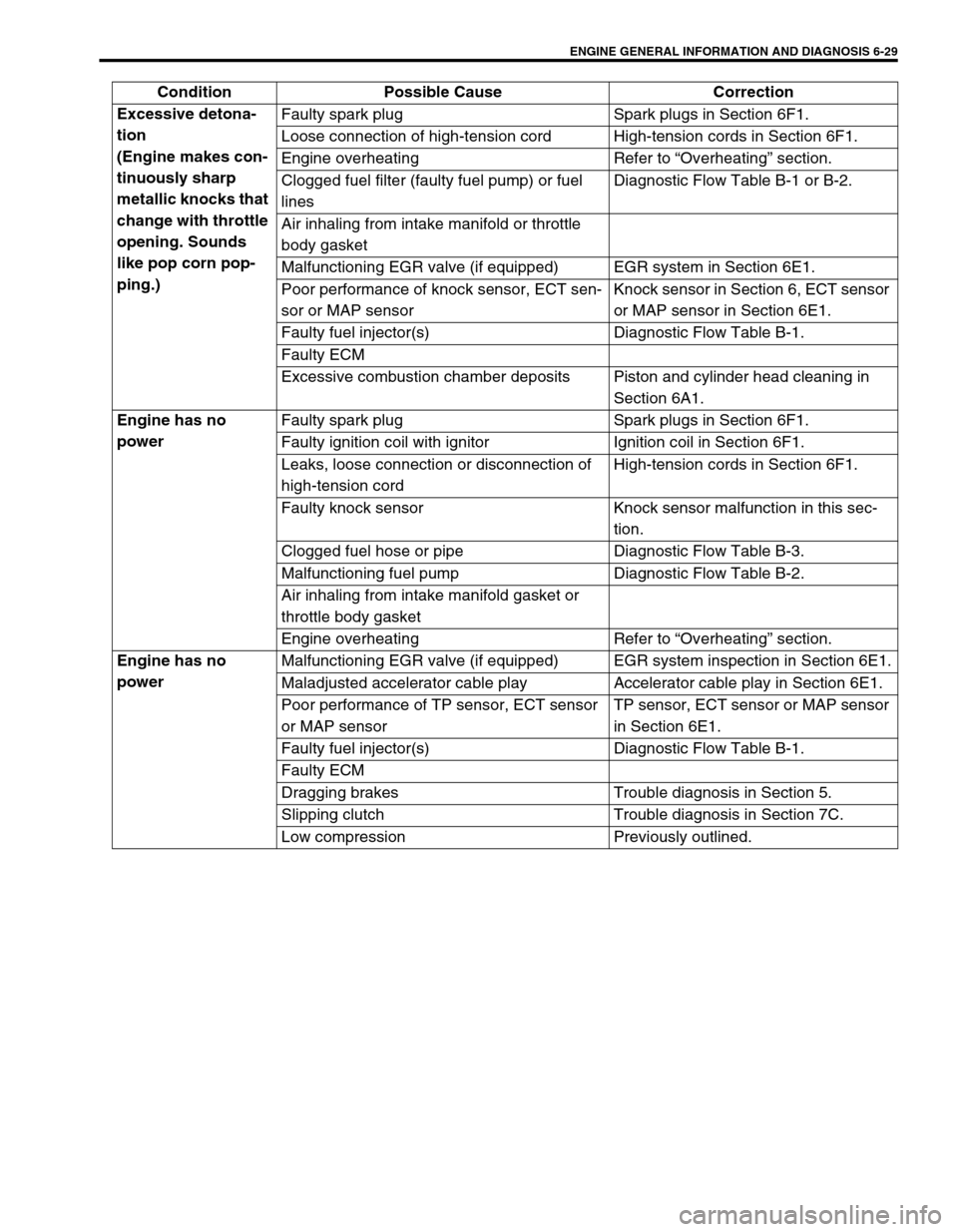
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-29
Excessive detona-
tion
(Engine makes con-
tinuously sharp
metallic knocks that
change with throttle
opening. Sounds
like pop corn pop-
ping.)Faulty spark plug Spark plugs in Section 6F1.
Loose connection of high-tension cord High-tension cords in Section 6F1.
Engine overheating Refer to “Overheating” section.
Clogged fuel filter (faulty fuel pump) or fuel
linesDiagnostic Flow Table B-1 or B-2.
Air inhaling from intake manifold or throttle
body gasket
Malfunctioning EGR valve (if equipped) EGR system in Section 6E1.
Poor performance of knock sensor, ECT sen-
sor or MAP sensorKnock sensor in Section 6, ECT sensor
or MAP sensor in Section 6E1.
Faulty fuel injector(s) Diagnostic Flow Table B-1.
Faulty ECM
Excessive combustion chamber deposits Piston and cylinder head cleaning in
Section 6A1.
Engine has no
powerFaulty spark plug Spark plugs in Section 6F1.
Faulty ignition coil with ignitor Ignition coil in Section 6F1.
Leaks, loose connection or disconnection of
high-tension cordHigh-tension cords in Section 6F1.
Faulty knock sensor Knock sensor malfunction in this sec-
tion.
Clogged fuel hose or pipe Diagnostic Flow Table B-3.
Malfunctioning fuel pump Diagnostic Flow Table B-2.
Air inhaling from intake manifold gasket or
throttle body gasket
Engine overheating Refer to “Overheating” section.
Engine has no
powerMalfunctioning EGR valve (if equipped) EGR system inspection in Section 6E1.
Maladjusted accelerator cable play Accelerator cable play in Section 6E1.
Poor performance of TP sensor, ECT sensor
or MAP sensorTP sensor, ECT sensor or MAP sensor
in Section 6E1.
Faulty fuel injector(s) Diagnostic Flow Table B-1.
Faulty ECM
Dragging brakes Trouble diagnosis in Section 5.
Slipping clutch Trouble diagnosis in Section 7C.
Low compression Previously outlined. Condition Possible Cause Correction
Page 399 of 698
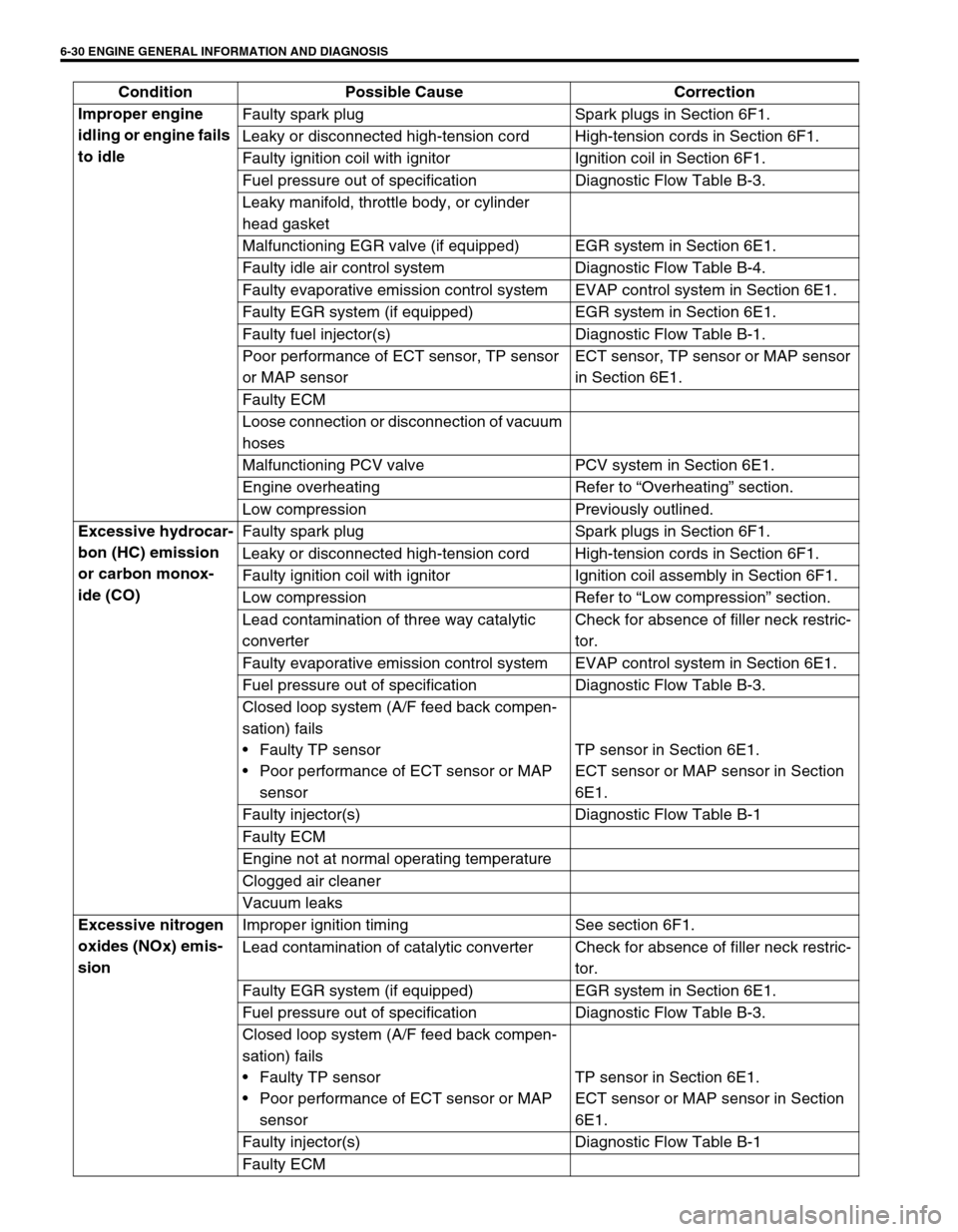
6-30 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
Improper engine
idling or engine fails
to idleFaulty spark plug Spark plugs in Section 6F1.
Leaky or disconnected high-tension cord High-tension cords in Section 6F1.
Faulty ignition coil with ignitor Ignition coil in Section 6F1.
Fuel pressure out of specification Diagnostic Flow Table B-3.
Leaky manifold, throttle body, or cylinder
head gasket
Malfunctioning EGR valve (if equipped) EGR system in Section 6E1.
Faulty idle air control system Diagnostic Flow Table B-4.
Faulty evaporative emission control system EVAP control system in Section 6E1.
Faulty EGR system (if equipped) EGR system in Section 6E1.
Faulty fuel injector(s) Diagnostic Flow Table B-1.
Poor performance of ECT sensor, TP sensor
or MAP sensorECT sensor, TP sensor or MAP sensor
in Section 6E1.
Faulty ECM
Loose connection or disconnection of vacuum
hoses
Malfunctioning PCV valve PCV system in Section 6E1.
Engine overheating Refer to “Overheating” section.
Low compression Previously outlined.
Excessive hydrocar-
bon (HC) emission
or carbon monox-
ide (CO)Faulty spark plug Spark plugs in Section 6F1.
Leaky or disconnected high-tension cord High-tension cords in Section 6F1.
Faulty ignition coil with ignitor Ignition coil assembly in Section 6F1.
Low compression Refer to “Low compression” section.
Lead contamination of three way catalytic
converterCheck for absence of filler neck restric-
tor.
Faulty evaporative emission control system EVAP control system in Section 6E1.
Fuel pressure out of specification Diagnostic Flow Table B-3.
Closed loop system (A/F feed back compen-
sation) fails
Faulty TP sensor
Poor performance of ECT sensor or MAP
sensorTP sensor in Section 6E1.
ECT sensor or MAP sensor in Section
6E1.
Faulty injector(s) Diagnostic Flow Table B-1
Faulty ECM
Engine not at normal operating temperature
Clogged air cleaner
Vacuum leaks
Excessive nitrogen
oxides (NOx) emis-
sionImproper ignition timing See section 6F1.
Lead contamination of catalytic converter Check for absence of filler neck restric-
tor.
Faulty EGR system (if equipped) EGR system in Section 6E1.
Fuel pressure out of specification Diagnostic Flow Table B-3.
Closed loop system (A/F feed back compen-
sation) fails
Faulty TP sensor
Poor performance of ECT sensor or MAP
sensorTP sensor in Section 6E1.
ECT sensor or MAP sensor in Section
6E1.
Faulty injector(s) Diagnostic Flow Table B-1
Faulty ECM Condition Possible Cause Correction
Page 426 of 698
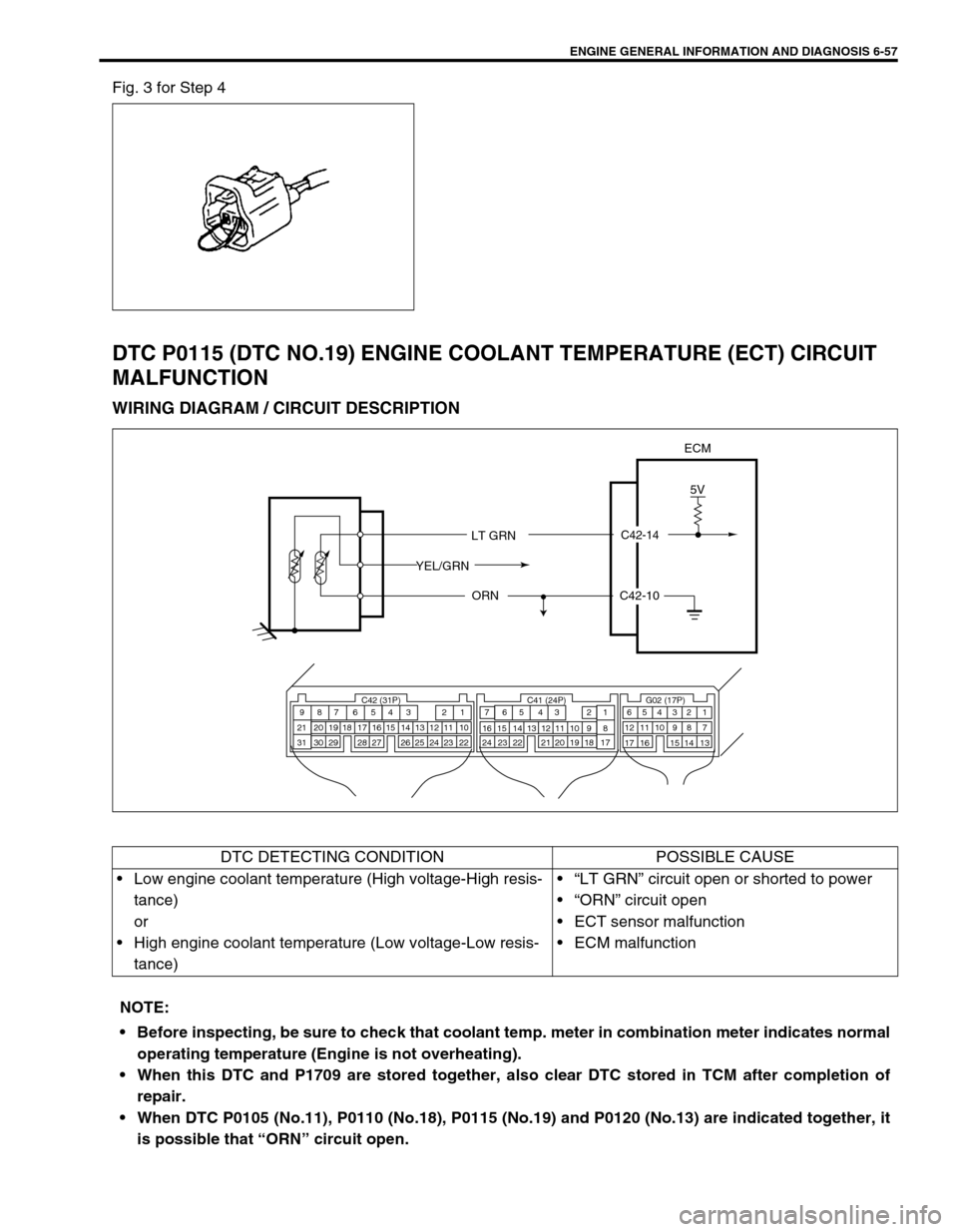
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-57
Fig. 3 for Step 4
DTC P0115 (DTC NO.19) ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT) CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION
WIRING DIAGRAM / CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
C42-14
5V
ECM
LT GRN
ORN
YEL/GRN
C42-10
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
Low engine coolant temperature (High voltage-High resis-
tance)
or
High engine coolant temperature (Low voltage-Low resis-
tance)“LT GRN” circuit open or shorted to power
“ORN” circuit open
ECT sensor malfunction
ECM malfunction
NOTE:
Before inspecting, be sure to check that coolant temp. meter in combination meter indicates normal
operating temperature (Engine is not overheating).
When this DTC and P1709 are stored together, also clear DTC stored in TCM after completion of
repair.
When DTC P0105 (No.11), P0110 (No.18), P0115 (No.19) and P0120 (No.13) are indicated together, it
is possible that “ORN” circuit open.
Page 451 of 698

6-82 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Clear DTC with ignition switch ON.
3) Check vehicle and environmental condition for :
–Altitude (barometric pressure) : 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmHg, 75 kPa or more)
–Ambient temp. : –10°C, 14°F or higher
–Intake air temp. : 70°C, 158°F or lower
–Engine coolant temp. : – 10 – 110°C, 14 – 230°F
4) Start engine and keep it at idle for 2 min. or more.
5) Check DTC in “DTC” mode and pending DTC in “ON BOARD TEST” or “PENDING DTC” mode.
6) If DTC is not detected at idle, consult usual driving based on information obtained in “Customer complaint
analysis” and “Freeze frame data check”.
INSPECTION
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
Engine under other than high revolution condition
Not on rough road
Engine speed changing rate (Below specified value)
Manifold absolute pressure changing rate (Below
specified value)
Throttle opening changing rate (Below specified
value)
Misfire rate per 200 or 1000 engine revolutions (how
much and how often crankshaft revolution speed
changes) is higher than specified valueEngine overheating
Vacuum leaks (air inhaling) from air intake system
Ignition system malfunction (spark plug(s), high-
tension cord(s), ignition coil assembly)
Fuel pressure out of specification
Fuel injector malfunction (clogged or leakage)
Engine compression out of specification
Valve lash (clearance) out of specification
Manifold absolute pressure sensor malfunction
Engine coolant temp. sensor malfunction
PCV valve malfunction
EVAP control system malfunction
EGR system malfunction
NOTE:
Among different types of random misfire, if misfire occurs at cylinders 1 and 4 or cylinders 3 and 2
simultaneously, it may not possible to reconfirm DTC by using the following DTC confirmation proce-
dure. When diagnosing the trouble of DTC P0300 (Random misfire detected) of the engine which is
apparently misfiring, even if DTC P0300 cannot be reconfirmed by using the following DTC confirma-
tion procedure, proceed to the following Diag. Flow Table.
WARNING:
When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic acci-
dent and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
Road test should be carried out with 2 persons, a driver and a tester.
CAUTION:
For iridium spark plugs, do not adjust air gap or clean.
Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” performed? Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE
DIAG. FLOW
TABLE”.