engine TOYOTA RAV4 2006 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2006, Model line: RAV4, Model: TOYOTA RAV4 2006Pages: 2000, PDF Size: 45.84 MB
Page 131 of 2000
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINEEG-69
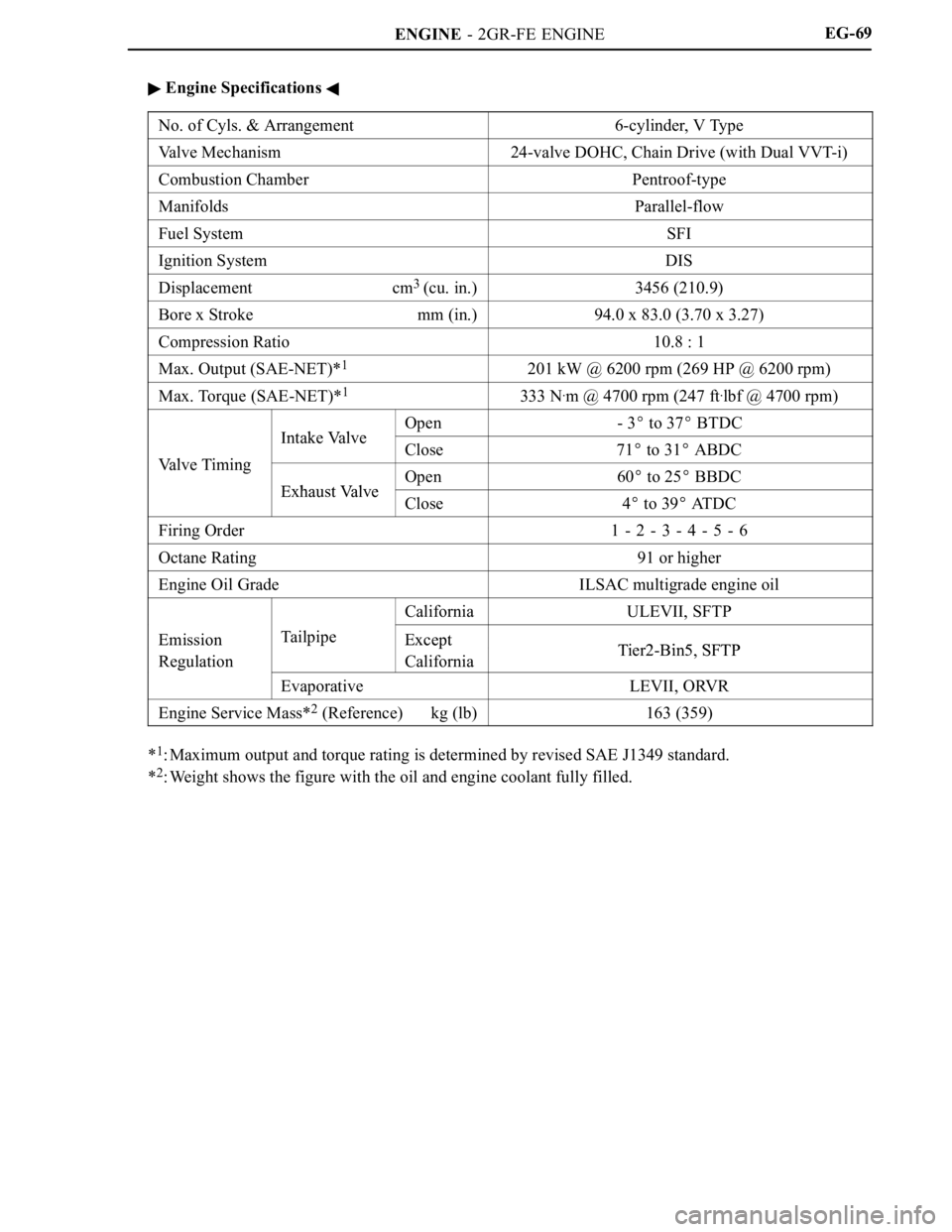
Engine Specifications
No. of Cyls. & Arrangement6-cylinder, V Type
Valve Mechanism24-valve DOHC, Chain Drive (with Dual VVT-i)
Combustion ChamberPentroof-type
ManifoldsParallel-flow
Fuel SystemSFI
Ignition SystemDIS
Displacement cm3
(cu. in.)3456 (210.9)
Bore x Stroke mm (in.)94.0 x 83.0 (3.70 x 3.27)
Compression Ratio10.8 : 1
Max. Output (SAE-NET)*1201 kW @ 6200 rpm (269 HP @ 6200 rpm)
Max. Torque (SAE-NET)*1333 N.m @ 4700 rpm (247 ft.lbf @ 4700 rpm)
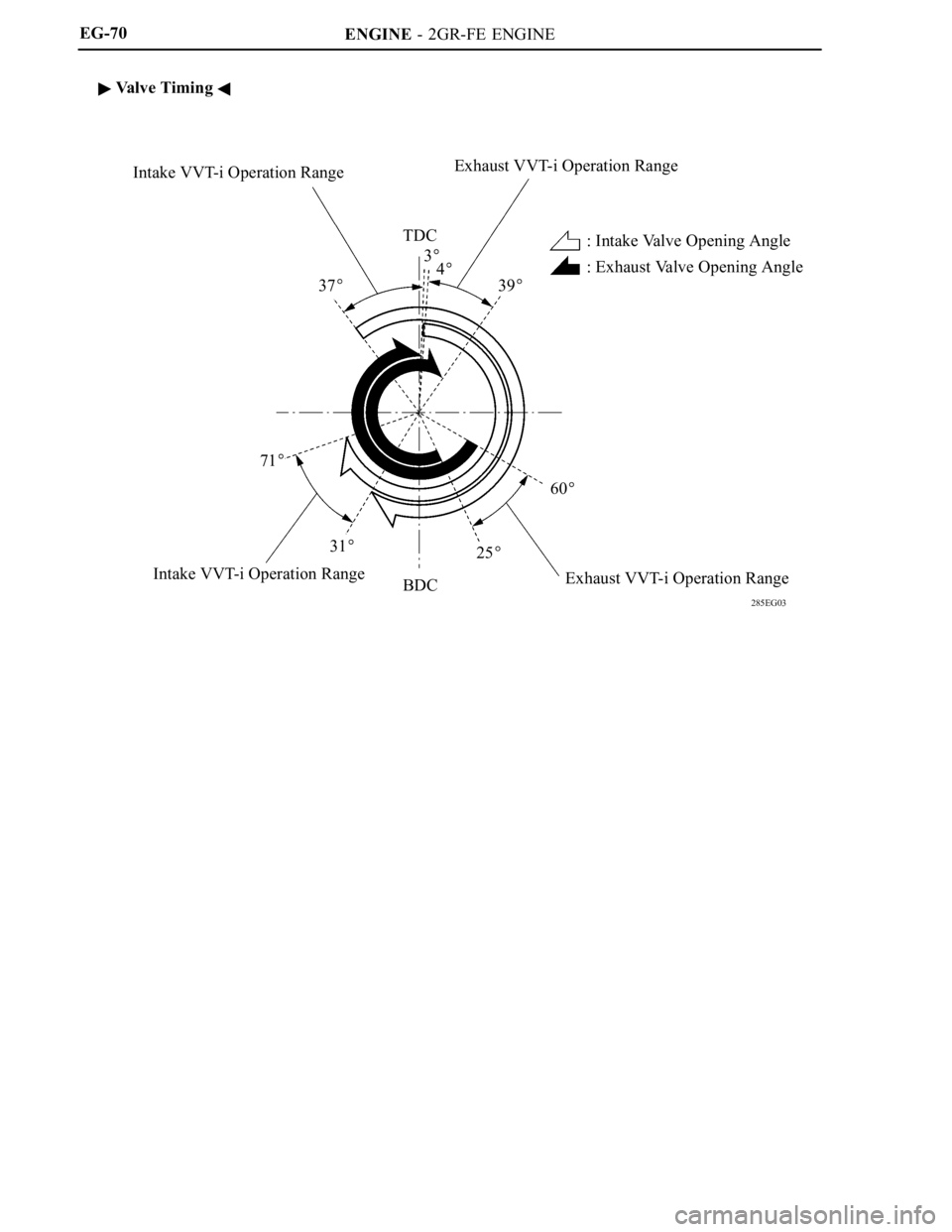
Intake ValveOpen-3 to 37 BTDC
Valve Timing
Intake ValveClose71 to 31 ABDCVa l v e T i m i n g
Exhaust ValveOpen60 to 25 BBDCExhaust ValveClose4 to 39 ATDC
Firing Order1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 6
Octane Rating91 or higher
Engine Oil GradeILSAC multigrade engine oil
CaliforniaULEVII, SFTP
EmissionTailpipeExceptTier2 Bin5 SFTPEmission
Regulation
ppExcept
CaliforniaTier2-Bin5, SFTPg
EvaporativeLEVII, ORVR
Engine Service Mass*2 (Reference) kg (lb)163 (359)
*1: Maximum output and torque rating is determined by revised SAE J1349 standard.
*
2: Weight shows the figure with the oil and engine coolant fully filled.
Page 132 of 2000
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
285EG03
: Exhaust Valve Opening Angle Intake VVT-i Operation RangeExhaust VVT-i Operation Range
TDC
374
39
71
31
BDC25
60
Intake VVT-i Operation Range
Exhaust VVT-i Operation Range: Intake Valve Opening Angle
3
EG-70
Valve Timing
Page 136 of 2000
CHASSIS - 4WD SYSTEMCH-69
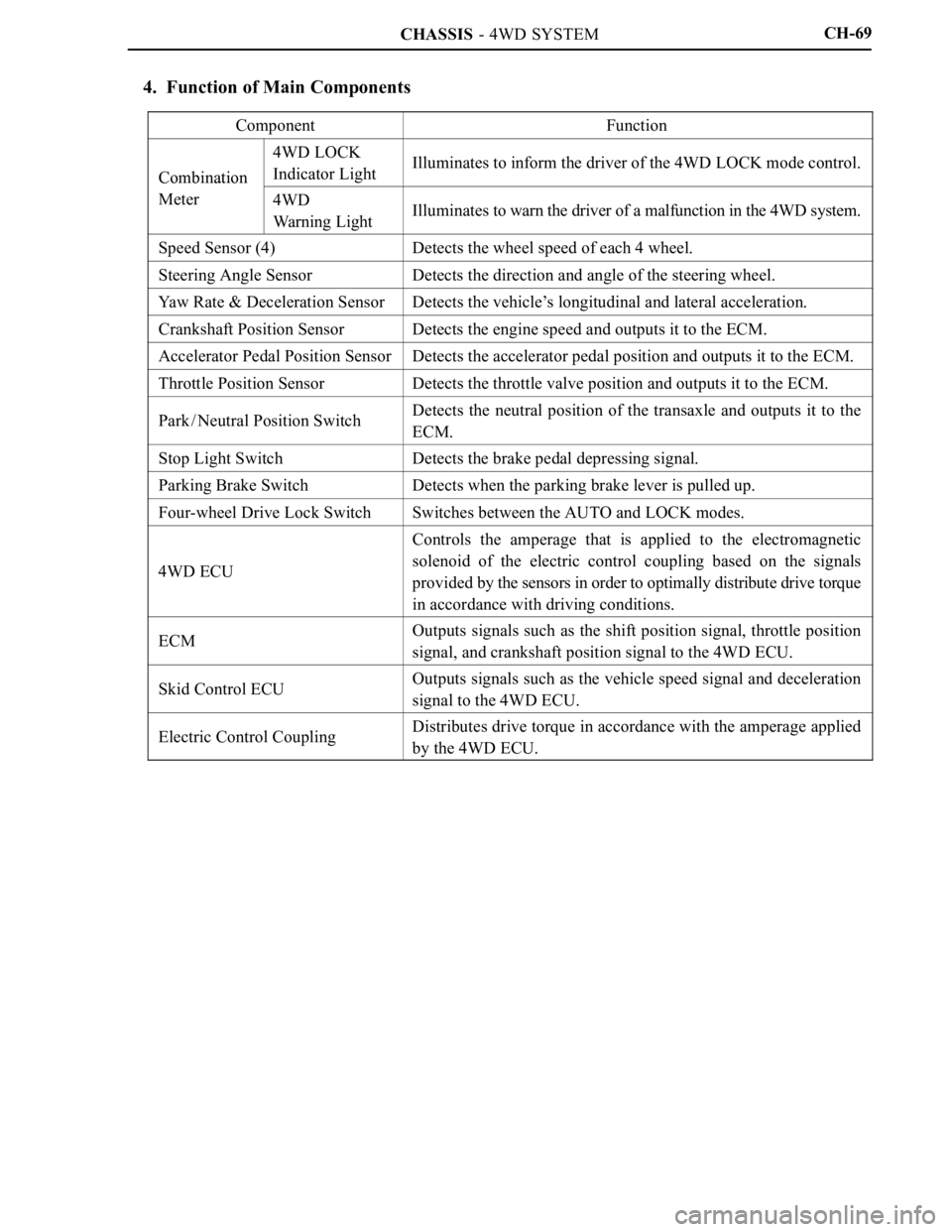
4. Function of Main Components
ComponentFunction
Combination
4WD LOCK
Indicator LightIlluminates to inform the driver of the 4WD LOCK mode control.Combination
Meter4WD
Warning LightIlluminates to warn the driver of a malfunction in the 4WD system.
Speed Sensor (4)Detects the wheel speed of each 4 wheel.
Steering Angle SensorDetects the direction and angle of the steering wheel.
Yaw Rate & Deceleration SensorDetects the vehicle’s longitudinal and lateral acceleration.
Crankshaft Position SensorDetects the engine speed and outputs it to the ECM.
Accelerator Pedal Position SensorDetects the accelerator pedal position and outputs it to the ECM.
Throttle Position SensorDetects the throttle valve position and outputs it to the ECM.
Park / Neutral Position SwitchDetects the neutral position of the transaxle and outputs it to the
ECM.
Stop Light SwitchDetects the brake pedal depressing signal.
Parking Brake SwitchDetects when the parking brake lever is pulled up.
Four-wheel Drive Lock SwitchSwitches between the AUTO and LOCK modes.
4WD ECU
Controls the amperage that is applied to the electromagnetic
solenoid of the electric control coupling based on the signals
provided by the sensors in order to optimally distribute drive torque
in accordance with driving conditions.
ECMOutputs signals such as the shift position signal, throttle position
signal, and crankshaft position signal to the 4WD ECU.
Skid Control ECUOutputs signals such as the vehicle speed signal and deceleration
signal to the 4WD ECU.
Electric Control CouplingDistributes drive torque in accordance with the amperage applied
by the 4WD ECU.
Page 137 of 2000

CHASSIS - 4WD SYSTEM
01NCH38Y
Torque Distribution
to Rear WheelsTorque Distribution
to Rear Wheels
Straightline Driving Low-Speed Cornering
01NCH39Y
Torque Distribution
to Rear WheelsTorque Distribution
to Rear Wheels
Steady Driving Straightline Acceleration
NOTICE
In the LOCK mode after the four-wheel drive lock switch is pressed, the system starts control upon
judging that the vehicle is operating in a stable manner. During this judgment, the 4WD LOCK
indicator light blinks.
CH-70
5. System Operation
Auto Mode
1) Starting Off
The system ensures start-off performance by optimally distributing the entire drive torque, which is
transmitted by the engine, to the front and rear wheels.
To prevent the tight corner braking phenomenon from occurring during low-speed cornering, the
system reduces the amount of torque distribution to the rear wheels.
2) Normal Driving
During normal driving, when the system judges that the vehicle is traveling steadily, it reduces the
amount of torque distribution to the rear wheels. This allows the vehicle to operate in conditions
similar to front-wheel-drive, which improves fuel economy.
To ensure excellent acceleration performance during straightline acceleration and excellent driving
stability during cornering, the system controls the amount of torque distribution to the rear wheels.
Lock Mode
When the vehicle is in a situation that poses difficulty for it to pull itself out, such as sand, the driver can
switch to LOCK mode by operating the four-wheel drive lock switch. Thus, this mode effects optimal
control in accordance with the driving conditions and transmits as much drive torque as possible to the rear
wheels, in a mode that is similar to the locked 4WD mode.
Page 138 of 2000

CHASSIS - 4WD SYSTEM
Service Tip
When the 4WD ECU judges that the vehicle has become stable, it cancels the stopping of the 4WD
control and transfers to AUTO control. If the 4WD warning light blinks, take the following actions
without turning the engine OFF:
Drop the vehicle speed until the light goes out
Stop the vehicle and stay there until the light goes out
CH-71
6. Diagnosis
When the 4WD ECU detects a malfunction, the 4WD ECU makes a diagnosis and memorizes the failed
section. Furthermore, the 4WD warning light in the combination meter illuminates to inform the driver.
At the same time, the DTCs (Diagnosis Trouble Codes) are stored in memory. The DTCs can be read by
connecting a hand-held tester, or by connecting the SST (09843-18040) to the TC and CG terminals of
DLC3 and observing the blinks of the 4WD warning light.
For details of the DTCs that are stored in 4WD ECU memory, see the 2006 RAV4 Repair Manual (Pub. No.
RM01M1U).
7. Fail-safe
When there is a possibility of causing damage to the drive system due to a malfunction in the 4WD system
or rough driving, the system illuminates or blinks the 4WD warning light to inform the driver, stops the 4WD
controls, and enables the vehicle to operate in the front-wheel-drive mode.
Malfunction
4WD Warning Light
4WD System MalfunctionIlluminate
Rough driving in 4WDPre-warning for stopping 4WD controlSlow blinkingRough driving in 4WDStopping 4WD controlFast blinking
Page 167 of 2000

IN–22INTRODUCTION – REPAIR INSTRUCTION
IN
VEHICLE LIFT AND SUPPORT
LOCATIONS
1. NOTICE ABOUT VEHICLE CONDITION WHEN
JACKING UP VEHICLE
(a) The vehicle must be unloaded before jacking up /
lifting up the vehicle. Never jack up / lift up a heavily
loaded vehicle.
(b) When removing heavy parts such as the engine and
transmission, the center of gravity of the vehicle
may shift. To stabilize the vehicle, place a balance
weight in a location where it will not roll or shift, or
use a mission jack to hold the jacking support.
2. NOTICE FOR USING 4 POST LIFT
(a) Follow the safety procedures outlined in the lift
instruction manual.
(b) Use precautionary measures to prevent the free
wheel beam from damaging tires or wheels.
(c) Use wheel chocks to secure the vehicle.
3. NOTICE FOR USING JACK AND SAFETY STAND
(a) Work on a level surface. Use wheel chocks at all
times.
(b) Use safety stands with rubber attachments as
shown in the illustration.
(c) Set the jack and safety stands to the specified
locations of the vehicle accurately.
(d) When jacking up the vehicle, first release the
parking brake and move the shift lever to N.
(e) When jacking up the entire vehicle:
• When jacking up the front wheels first, make sure
wheel chocks are behind the rear wheels.
• When jacking up the rear wheels first, make sure
wheel chocks are in front of the front wheels.
(f) When jacking up only the front or rear wheels of the
vehicle:
• Before jacking up the front wheels, place wheel
chocks on both sides of the rear wheels.
• Before jacking up the rear wheels, place wheel
chocks on both sides of the front wheels.
(g) When lowering a vehicle that only has its front or
rear wheels jacked up:
• Before lowering the front wheels, make sure
wheel chocks are in front of the rear wheels.
• Before lowering the rear wheels, make sure
wheel chocks are behind the front wheels.
D100922E01
Page 168 of 2000
INTRODUCTION – REPAIR INSTRUCTIONIN–23
IN
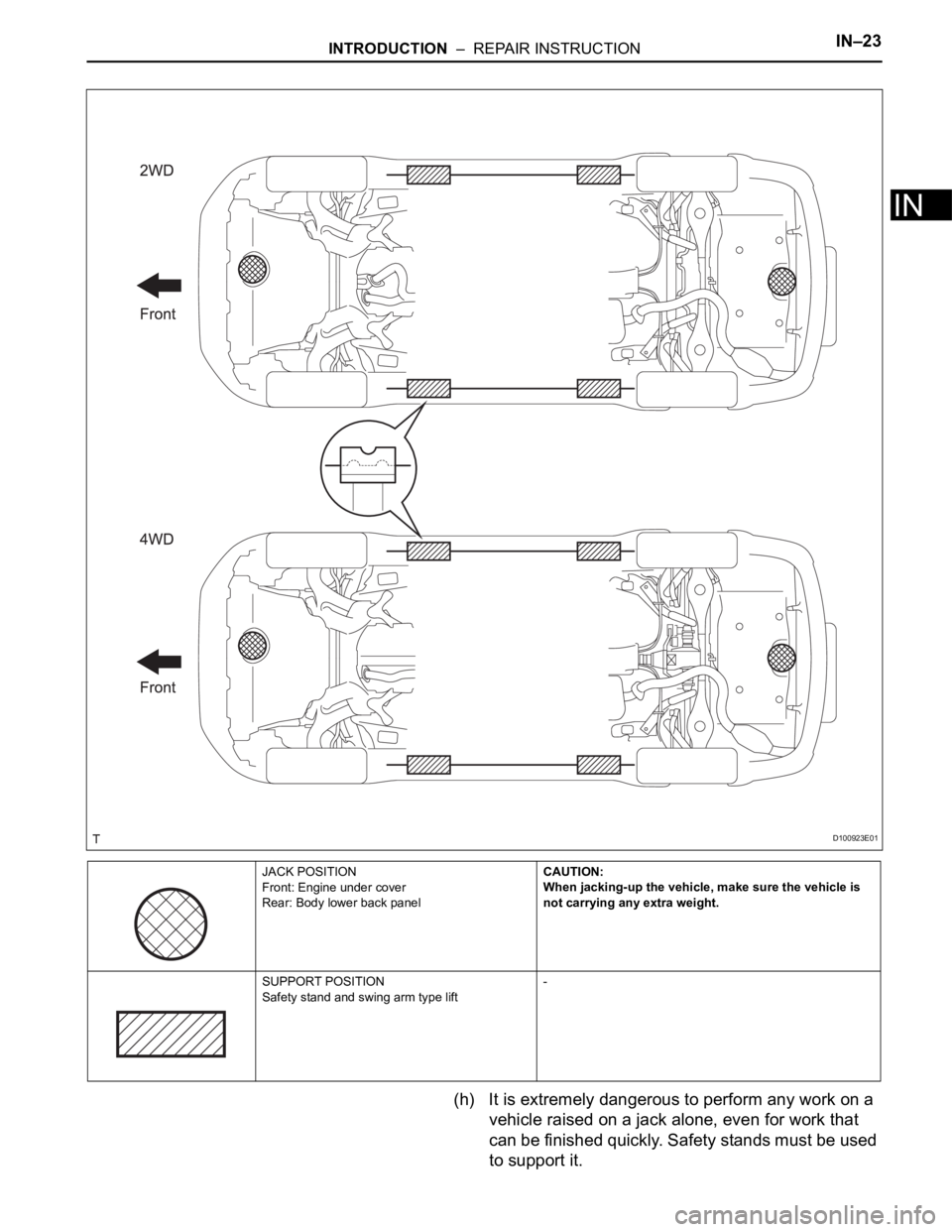
(h) It is extremely dangerous to perform any work on a
vehicle raised on a jack alone, even for work that
can be finished quickly. Safety stands must be used
to support it.
JACK POSITION
Front: Engine under cover
Rear: Body lower back panelCAUTION:
When jacking-up the vehicle, make sure the vehicle is
not carrying any extra weight.
SUPPORT POSITION
Safety stand and swing arm type lift-
D100923E01
Page 171 of 2000

PREPARATION – 2AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEMPP–3
PP
EQUIPMENT
Ohmmeter -
Service wire -
Torque wrench -
Page 179 of 2000

SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS – U151E AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONSS–47
SS
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
Automatic Transaxle Assembly
Part Tightened N*m kgf*cm ft*lbf
Park/neutral position switch Nut 6.9 70 61 in.*lbf
Bolt 5.4 55 48 in.*lbf
Control shaft lever x Control shaft 13 133 10
Shift control cable x Control shaft lever 15 153 11
Transaxle housing x Engine block Upper side bolt 64 653 47
Lower side bolt
A37 377 27
Lower side bolt
B46 470 34
Torque converter clutch x Drive plate 41 418 30
Flywheel housing under cover x Automatic transaxle 7.8 80 69 in.*lbf
Front engine mounting bracket x Transaxle 64 653 47
Rear engine mounting bracket x Transaxle 45 459 33
Engine mounting bracket LH x Transaxle 64 653 47
Oil filler tube x Transaxle
Oil filler tube x Front engine mounting bracket5.5 56 49 in.*lbf
Control cable bracket No. 1 x Transaxle 12 122 9
Control cable bracket No. 2 x Transaxle 12 122 9
Oil cooler inlet elbow x Transaxle 27 276 20
Oil cooler outlet elbow x Transaxle 27 276 20
Starter x Transaxle37 377 27
Starter wire x Starter9.8 100 88 in.*lbf
Speed sensor (NC) x Transaxle 11 112 8
Speed sensor (NT) x Transaxle 11 112 8
Drain plug x Oil pan47 479 35
Transmission wire x Transaxle 5.4 55 48 in.*lbf
ATF temperature sensor x Valve body 6.6 67 58 in.*lbf
Oil pan x Transaxle7.8 80 69 in.*lbf
Solenoid valve x Valve body SL2, DSL, S4 11 110 8
SL1, SL3 6.6 67 58 in.*lbf
Valve body x Transaxle11 11 2 8
Oil strainer x Valve body11 11 2 8
Floor shift assembly x Body12 122 9
Control cable clamp x Engine mounting insulator 12 122 9
Differential gear lube apply tube x Transaxle housing 9.8 100 87 in.*lbf
Front planetary gear lock nut 280 3,355 207
Brake apply tube clamp x Transaxle case 5.4 55 48 in.*lbf
Transaxle case No. 1 plug x Transaxle rear cover 7.4 75 65 in.*lbf
Transaxle rear cover x Transaxle case Bolt A 19 194 14
Other bolt 25 255 18
Parking lock pawl shaft x Transaxle case 9.8 100 87 in.*lbf
Oil pump assembly x Transaxle case 22 226 16
Transaxle housing x Transaxle case Bolt A 22 254 16
Bolt B 29 295 21
Bolt C 29 295 21
Bolt D 22 254 16
Automatic transmission case plug x Transaxle housing 7.4 75 65 in.*lbf
Automatic transmission case plug x Transaxle case 7.4 75 65 in.*lbf
Page 182 of 2000

MAINTENANCE – UNDER HOODMA–7
MA
GENERAL MAINTENANCE
(2006/01- )
1. GENERAL NOTES
• Maintenance requirements vary depending on the
country.
• Check the maintenance schedule in the owner's
manual supplement.
• Following the maintenance schedule is mandatory.
• Determine the appropriate time to service the vehicle
using either miles driven or time elapsed, whichever
reaches the specification first.
• Maintain similar intervals between periodic
maintenance, unless otherwise noted.
• Failing to check each vehicle part could lead to poor
engine performance and increase exhaust emissions.
2. WINDSHIELD WASHER FLUID
(a) Check that there is sufficient fluid in the tank.
3. ENGINE COOLANT LEVEL
(a) Check that the coolant level is between the "FULL"
and "LOW" lines on the see-through reservoir.
4. RADIATOR AND HOSES
(a) Check that the front of the radiator is clean and not
blocked by leaves, dirt or bugs.
(b) Check the hoses for cracks, kinks, rot or loose
connections.
5. BATTERY ELECTROLYTE LEVEL
(a) Check that the electrolyte level of all the battery
cells is between the upper and lower level lines on
the case.
HINT:
If the electrolyte level is difficult to see, lightly shake
the vehicle.
6. BRAKE FLUID LEVEL
(a) Check that the brake fluid levels are near the upper
level lines on the see-through reservoirs.
7. ENGINE DRIVE BELT
(a) Check the drive belt for fraying, cracks, wear or
oiliness.
8. ENGINE OIL LEVEL
(a) Check the level on the dipstick with the engine
stopped.
9. AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID LEVEL
10. EXHAUST SYSTEM
(a) Check for unusual exhaust sounds or abnormal
exhaust fumes. Inspect the cause and repair it.
Type See procedures
U151E See page AX-126
U151F See page AX-126