sensor TOYOTA SIENNA 2007 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SIENNA, Model: TOYOTA SIENNA 2007Pages: 3000, PDF Size: 52.26 MB
Page 461 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–155
ESHINT:
• When any of these DTCs are set, check the throttle valve opening angle by selecting the following
menu items on the intelligent tester: DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED OBD II / DATA LIST / ETCS /
THROTTLE POS AND THROTTLE POS #2.
• THROTTLE POS denotes the VTA1 signal (expressed in percentages), and THROTTLE POS #2
denotes the VTA2 signal (expressed in voltages).
Reference (Normal Condition)
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The ECM uses the Throttle Position (TP) sensor to monitor the throttle valve opening angle. There are
several checks that the ECM performs to confirm the proper operation of the TP sensor.
• A specific voltage difference is expected between the sensor terminals, VTA1 and VTA2, for each
throttle valve opening angle. If the difference between VTA1 and VTA2 is incorrect, the ECM interprets
this as a malfunction in the sensor, and sets a DTC.
• VTA1 and VTA2 each have a specific voltage range. If VTA1 or VTA2 is outside the normal operating
range, the ECM interprets this as a malfunction in the sensor, and sets a DTC.
• VTA1 and VTA2 should never be close to the same voltage level. If VTA1 is within 0.02 V of VTA2, the
ECM determines that there is a short circuit in the sensor, and sets a DTC.
If the malfunction is not repaired successfully, a DTC is set 2 seconds after the engine is next started.
MONITOR STRATEGY
P0222Output voltage of VTA2 is 1.75 V or less for 2 seconds
(1 trip detection logic)• TP sensor (built into throttle body)
• Short in VTA2 circuit
• Open in VC circuit
•ECM
P0223Output voltage of VTA2 is 4.8 V or more, and VTA1 is
between 0.2 V and 2.02 V, for 2 seconds (1 trip
detection logic)• TP sensor (built into throttle body)
• Open in VTA2 circuit
• Open in E2 circuit
• Short between VC and VTA2 circuits
•ECM
P2135Either condition (a) or (b) is met (1 trip detection logic):
(a) Difference between output voltages of VTA1 and
VTA2 is 0.02 V or less for 0.5 seconds or more
(b) Output voltage of VTA1 is 0.2 V or less, and VTA2 is
0.5 V or less, for 0.4 seconds or more• Short between VTA1 and VTA2 circuits
• TP sensor (built into throttle body)
•ECM
Tester Display Accelerator Pedal Fully Released Accelerator Pedal Fully Depressed
THROTTLE POS 10 to 24% 64 to 96%
THROTTLE POS #2 2.1 to 3.1 V 4.5 to 5.0 V
Related DTCsP0120: Throttle position sensor 1 range check (Fluctuating)
P0122: Throttle position sensor 1 range check (Low voltage)
P0123: Throttle position sensor 1 range check (High voltage)
P0220: Throttle position sensor 2 range check (Fluctuating)
P0222: Throttle position sensor 2 range check (Low voltage)
P0223: Throttle position sensor 2 range check (High voltage)
P2135: Throttle position sensor range check (Correlation)
Required Sensors / Components (Main) Throttle position sensor
Required Sensors / Components (Related) -
Frequency of Operation Continuous
Duration2 seconds: P0120, P0122, P0123, P0220, P0222 and P0223 (Accelerator pedal ON)
10 seconds: P0120, P0122, P0123, P0220, P0222 and P0223 (Accelerator pedal
OFF)
0.5 seconds: P2135
MIL Operation Immediate
Sequence of Operation NoneDTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
Page 464 of 3000
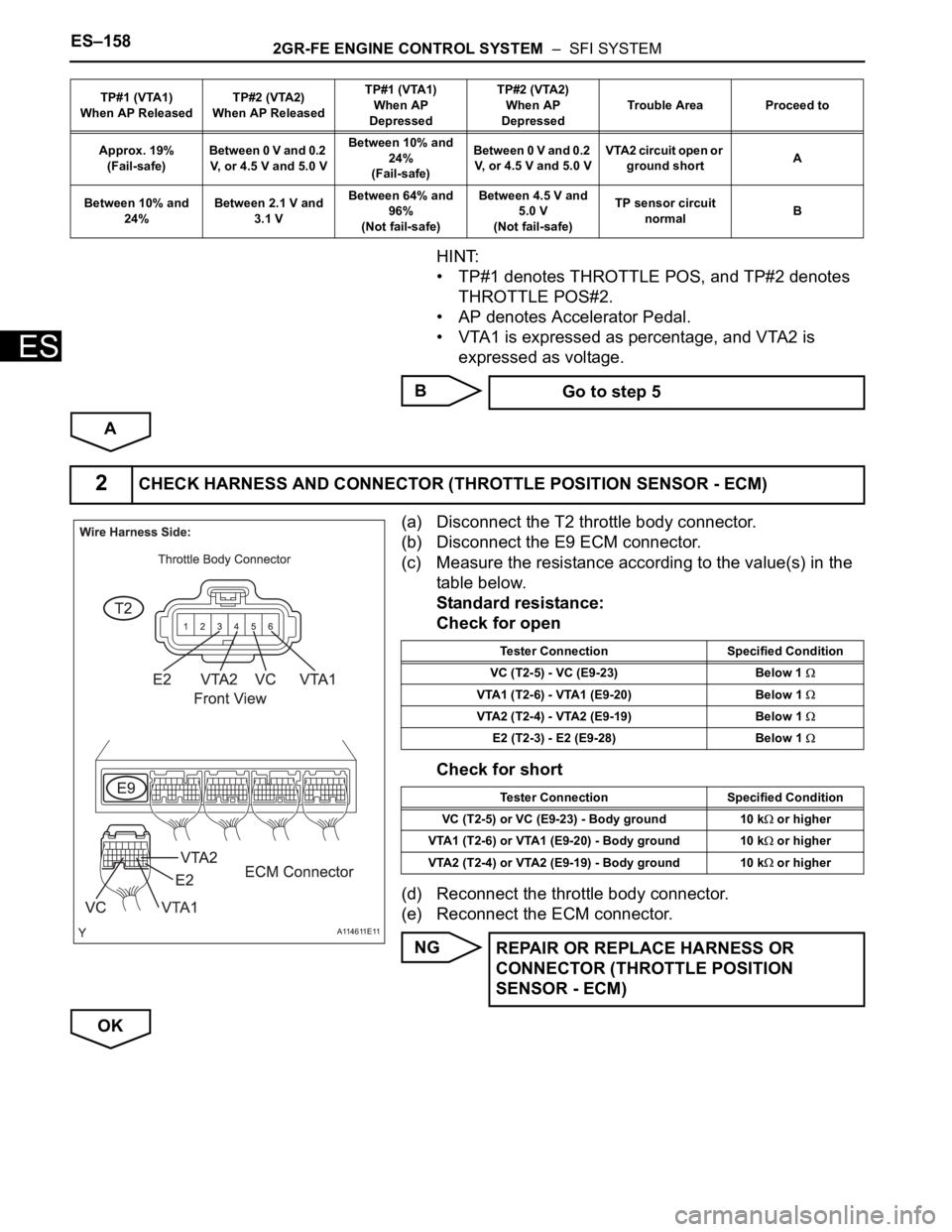
ES–1582GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
HINT:
• TP#1 denotes THROTTLE POS, and TP#2 denotes
THROTTLE POS#2.
• AP denotes Accelerator Pedal.
• VTA1 is expressed as percentage, and VTA2 is
expressed as voltage.
B
A
(a) Disconnect the T2 throttle body connector.
(b) Disconnect the E9 ECM connector.
(c) Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the
table below.
Standard resistance:
Check for open
Check for short
(d) Reconnect the throttle body connector.
(e) Reconnect the ECM connector.
NG
OK
Approx. 19%
(Fail-safe)Between 0 V and 0.2
V, or 4.5 V and 5.0 VBetween 10% and
24%
(Fail-safe)B e t w e e n 0 V a n d 0 . 2
V, or 4.5 V and 5.0 VVTA2 circuit open or
ground shortA
Between 10% and
24%Between 2.1 V and
3.1 VBetween 64% and
96%
(Not fail-safe)Between 4.5 V and
5.0 V
(Not fail-safe)TP sensor circuit
normalB TP#1 (VTA1)
When AP ReleasedTP#2 (VTA2)
When AP ReleasedTP#1 (VTA1)
When AP
DepressedTP#2 (VTA2)
When AP
DepressedTrouble Area Proceed to
Go to step 5
2CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR - ECM)
A114611E11
Tester Connection Specified Condition
VC (T2-5) - VC (E9-23) Below 1
VTA1 (T2-6) - VTA1 (E9-20) Below 1
VTA2 (T2-4) - VTA2 (E9-19) Below 1
E2 (T2-3) - E2 (E9-28) Below 1
Tester Connection Specified Condition
VC (T2-5) or VC (E9-23) - Body ground 10 k
or higher
VTA1 (T2-6) or VTA1 (E9-20) - Body ground 10 k
or higher
VTA2 (T2-4) or VTA2 (E9-19) - Body ground 10 k
or higher
REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR
CONNECTOR (THROTTLE POSITION
SENSOR - ECM)
Page 465 of 3000
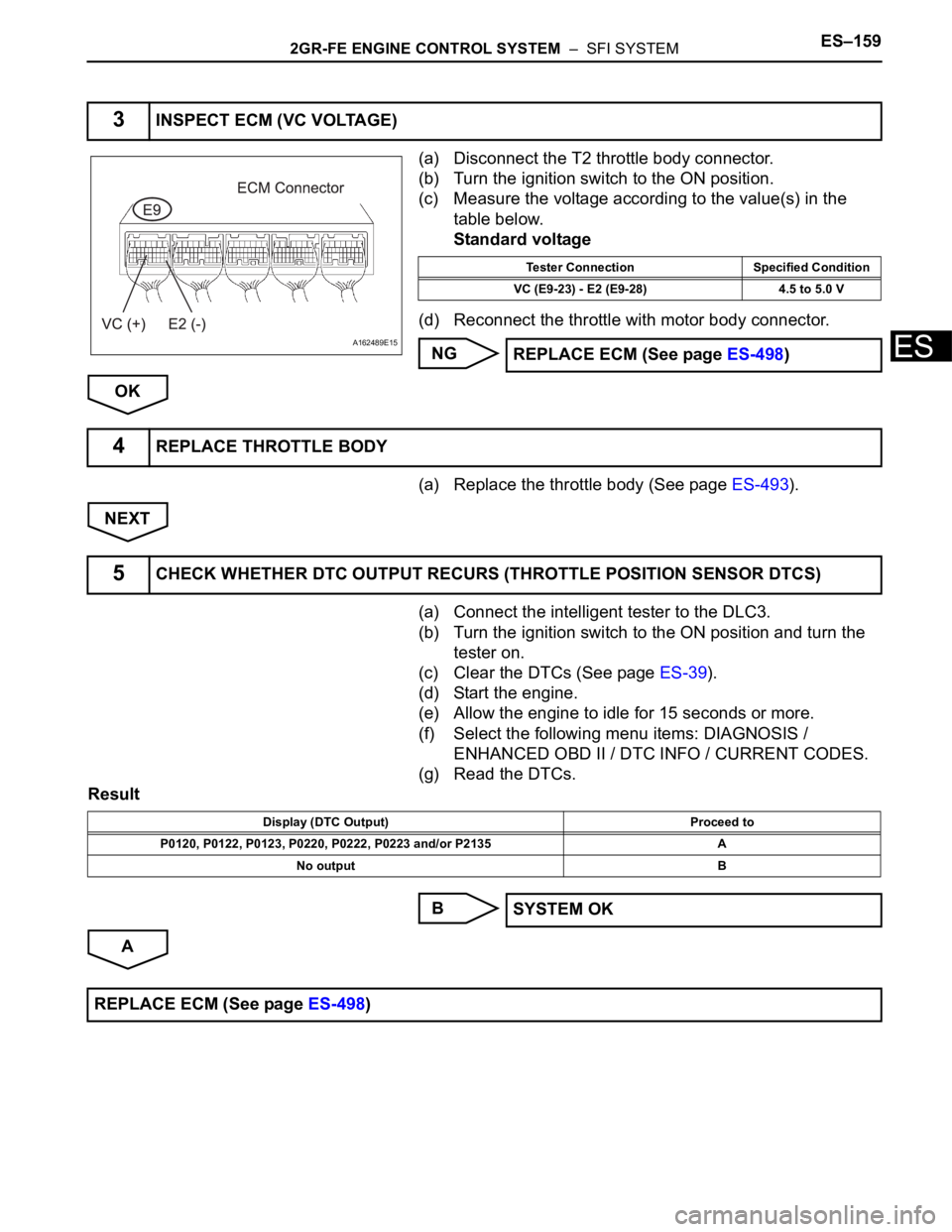
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–159
ES
(a) Disconnect the T2 throttle body connector.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the
table below.
Standard voltage
(d) Reconnect the throttle with motor body connector.
NG
OK
(a) Replace the throttle body (See page ES-493).
NEXT
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position and turn the
tester on.
(c) Clear the DTCs (See page ES-39).
(d) Start the engine.
(e) Allow the engine to idle for 15 seconds or more.
(f) Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS /
ENHANCED OBD II / DTC INFO / CURRENT CODES.
(g) Read the DTCs.
Result
B
A
3INSPECT ECM (VC VOLTAGE)
A162489E15
Tester Connection Specified Condition
VC (E9-23) - E2 (E9-28) 4.5 to 5.0 V
REPLACE ECM (See page ES-498)
4REPLACE THROTTLE BODY
5CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR DTCS)
Display (DTC Output) Proceed to
P0120, P0122, P0123, P0220, P0222, P0223 and/or P2135 A
No output B
SYSTEM OK
REPLACE ECM (See page ES-498)
Page 466 of 3000

ES–1602GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
HINT:
This DTC relates to the Throttle Position (TP) sensor.
DESCRIPTION
Refer to DTC P0120 (See page ES-145).
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The ECM uses the TP sensor to monitor the throttle valve opening angle.
This sensor transmits two signals: VTA1 and VTA2. VTA1 is used to detect the throttle opening angle and
VTA2 is used to detect malfunctions in VTA1. The ECM performs several checks to confirm the proper
operation of the TP sensor and VTA1.
For each throttle opening angle, a specific voltage difference is expected between the outputs of VTA1
and VTA2. If the voltage output difference between the two signals deviates from the normal operating
range, the ECM interprets this as a malfunction of the TP sensor. The ECM illuminates the MIL and sets
the DTC.
If the malfunction is not repaired successfully, the DTC is set 2 seconds after the engine is next started.
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
DTC P0121Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "A"
Circuit Range / Performance Problem
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0121Difference between VTA1 and VTA2 voltages less than
0.8 V, or more than 1.6 V for 2 seconds (1 trip detection
logic)TP sensor (built into throttle body)
Related DTCs P0121: TP sensor rationality
Required Sensors / Components (Main) TP sensor
Required Sensors / Components (Related) -
Frequency of Operation Continuous
Duration Within 2 seconds
MIL Operation Immediate
Sequence of Operation None
This monitor will not run whenever these DTCs are not
presentNone
Either of the following conditions is met: Condition 1 or 2
1. Ignition switch ON
2. Electric throttle motor power ON
TP sensor malfunction (P0120, P0122, P0123, P0220,
P0222, P0223, P2135)Not detected
Difference of TP sensor voltage between VTA1 and
VTA2 x 0.8Less than 0.8 V, or more than 1.6 V
Page 468 of 3000

ES–1622GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
DESCRIPTION
Refer to DTC P0115 (See page ES-133).
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The resistance of the ECT sensor varies in proportion to the actual ECT. The ECM supplies a constant
voltage to the sensor and monitors the signal output voltage of the sensor. The signal voltage output
varies according to the changing resistance of the sensor. After the engine is started, the ECT is
monitored through this signal. If the ECT sensor indicates that the engine is not yet warm enough for
closed-loop fuel control, despite a specified period of time having elapsed since the engine was started,
the ECM interprets this as a malfunction in the sensor or cooling system and sets the DTC.
Example:
The ECT is 0
C (32F) at engine start. After 5 minutes running time, the ECT sensor still indicates that the
engine is not warm enough to begin closed-loop fuel (air-fuel ratio feedback) control. The ECM interprets
this as a malfunction in the sensor or cooling system and sets the DTC.
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P0115 (See page ES-134).
DTC P0125Insufficient Coolant Temperature for Closed
Loop Fuel Control
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0125Engine coolant temperature (ECT) does not reach
closed-loop enabling temperature for 20 minutes (this
period varies with engine start ECT)• Cooling system
• Engine coolant temperature sensor
• Thermostat
Related DTCs P0125: Insufficient engine coolant temperature for closed-loop fuel control
Required Sensors / Components (Main) Thermostat, cooling system
Required Sensors / Components (Related) Engine coolant temperature sensor and mass air flow meter
Frequency of Operation Continuous
Duration78 seconds: Engine coolant temperature at engine start -8.34
C (17F) or more
131.3 seconds: Engine coolant temperature at engine start -19.45 to -8.34C (-3 to
17
F)
20 minutes: Engine coolant temperature at engine start less than -19.45
C (-3F)
MIL Operation 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
The monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not
presentP0100, P0101, P0102, P0103 (MAF) sensor, P0110, P0111, P0112, P0113 (IAT
sensor), P0115, P0116, P0117, P0118 (ECT sensor)
Fuel cut OFF
Engine Running
Time until actual engine coolant temperature reaches
closed-loop fuel control enabling temperature78 seconds or more: Engine coolant temperature at engine start -8.34
C (17F) or
more
131.3 seconds or more: Engine coolant temperature at engine start -19.45 to -8.34
C
(-3 to 17
F)
20 minutes or more: Engine coolant temperature at engine start less than -19.45C (-
3
F)
Page 469 of 3000
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–163
ES
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
• If any of DTCs P0115, P0116, P0117 or P0118 are set simultaneously with DTC P0125, the Engine
Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor may have an open or a short circuit. Troubleshoot those DTCs first.
• Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition
information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame
data can be helpful in determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, whether the engine
was warmed up or not, whether the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, as well as other data recorded at the
time of a malfunction.
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Turn the tester on.
(d) Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS /
ENHANCED OBD II / DTC INFO / CURRENT CODES.
(e) Read the DTCs.
Result
HINT:
If any DTCs other than P0125 are output, troubleshoot
those DTCs first.
B
A
(a) Remove the thermostat (See page CO-16).
(b) Check the valve opening temperature of the thermostat
(See page CO-17).
Standard:
80 to 84
C (176 to 183F)
HINT:
In addition to the above check, confirm that the valve is
completely closed when the temperature is below the
standard.
(c) Reinstall the thermostat (See page CO-17).
NG
OK
1CHECK ANY OTHER DTCS OUTPUT (IN ADDITION TO DTC P0125)
Display (DTC Output) Proceed to
P0125 A
P0125 and other DTCs B
GO TO DTC CHART (See page ES-56)
2INSPECT THERMOSTAT
REPLACE THERMOSTAT (See page CO-16)
Page 470 of 3000

ES–1642GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
(a) Check for defects in the cooling system that might cause
the system to be too cold, such as abnormal radiator fan
operation or any modifications.
NG
OK
3CHECK COOLING SYSTEM
REPAIR OR REPLACE COOLING SYSTEM
REPLACE ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR (See page ES-516)
Page 471 of 3000
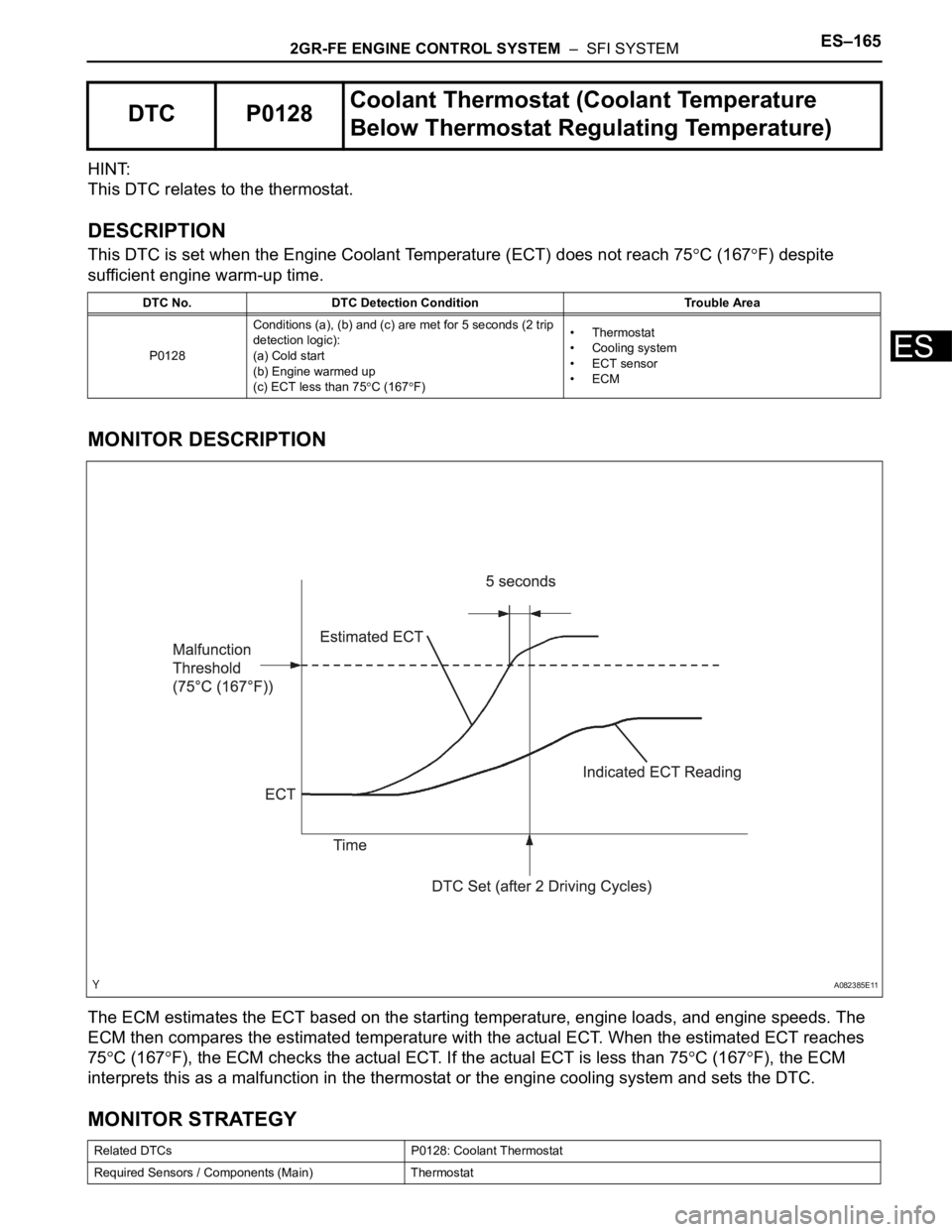
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–165
ES
HINT:
This DTC relates to the thermostat.
DESCRIPTION
This DTC is set when the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) does not reach 75C (167F) despite
sufficient engine warm-up time.
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The ECM estimates the ECT based on the starting temperature, engine loads, and engine speeds. The
ECM then compares the estimated temperature with the actual ECT. When the estimated ECT reaches
75
C (167F), the ECM checks the actual ECT. If the actual ECT is less than 75C (167F), the ECM
interprets this as a malfunction in the thermostat or the engine cooling system and sets the DTC.
MONITOR STRATEGY
DTC P0128Coolant Thermostat (Coolant Temperature
Below Thermostat Regulating Temperature)
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0128Conditions (a), (b) and (c) are met for 5 seconds (2 trip
detection logic):
(a) Cold start
(b) Engine warmed up
(c) ECT less than 75
C (167F)•Thermostat
• Cooling system
• ECT sensor
•ECM
Related DTCs P0128: Coolant Thermostat
Required Sensors / Components (Main) Thermostat
A082385E11
Page 472 of 3000

ES–1662GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition
information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data
can be helpful in determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, whether the engine was
warmed up or not, whether the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, as well as other data recorded at the time of
a malfunction.
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Turn the tester on.
(d) Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS /
ENHANCED OBD II / DTC INFO / CURRENT CODES.
(e) Read the DTCs.
Required Sensors / Components (Related)Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor, Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor,
Vehicle speed sensor
Frequency of Operation Once per driving cycle
Duration 900 seconds
MIL Operation 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
The monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not
presentP0010, P0020 (VVT VSV 1, 2), P0011, P0012 (VVT System 1-Advance, Retard),
P0021, P0022 (VVT System 2-Adavance, Retard), P0031, P0032, P0051, P0052 (A/
F Sensor Heater Sensor 1), P0100, P0101, P0102, P0103 (MAF Sensor), P0110,
P0112, P0113 (IAT Sensor), P0115, P0116, P0117, P0118 (ECT Sensor), P0125
(Insufficient ECT for Closed Loop), P0136, P0156 (O2 Sensor 2), P0171, P0172
(Fuel System), P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0305, P0306 (Misfire),
P0335 (CKP Sensor), P0340 (CMP sensor), P0345 (VVT sensor), P0351, P0352,
P0353, P0354, P0355, P0356 (Ignitor), P0500 (VSS), P2196, P2198(A/F Sensor
(Rationality)), P2A00, P2A03 (A/F Sensor (Slow Response))
Battery voltage 11 V or more
Either of following conditions is met: Condition 1 or 2
1. All of following conditions are met: Conditions (a), (b) and (c)
(a) ECT at engine start - IAT at engine start -15 to 7
C (5 to 45F)
(b) ECT at engine start -10 to 56
C (14 to 133F)
(c) IAT at engine start -10 to 56
C (14 to 133F)
2. All of following conditions are met: Conditions (d), (e) and (f)
(d) ECT at engine start - IAT at engine start More than 7
C (45F)
(e) ECT at engine start 56
C (133F) or less
(f) IAT at engine start -10
C (14F) or more
Accumulated time that vehicle speed is 80 mph (128
km/h) or moreLess than 20 seconds
Duration that all of the following conditions 1 and 2 are
met5 seconds or more
1. Estimated ECT 75
C (167F) or more
2. ECT sensor output Less than 75
C (167F)
1CHECK ANY OTHER DTCS OUTPUT (IN ADDITION TO DTC P0128)
Page 474 of 3000

ES–1682GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
HINT:
Sensor 2 refers to the sensor mounted behind the Three-Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) and located far
from the engine assembly.
DESCRIPTION
A three-way catalytic converter (TWC) is used in order to convert the carbon monoxide (CO), hydro
carbon (HC), and nitrogen oxides (HOx) into less harmful substances. To allow the TWC to function
effectively, it is necessary to keep the air-fuel ratio of the engine near the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio. For
helping the ECM to deliver accurate air-fuel ratio control, a Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor becomes used.
The HO2 sensor is located behind the TWC, and detects the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas.
Since the sensor is integrated with the heater that heats the sensing portion, it is possible to detect the
oxygen concentration even when the intake air volume is low (the exhaust gas temperature is low).
When the air-fuel ratio becomes lean, the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas becomes rich. The
HO2 sensor informs the ECM that the post-TWC air-fuel ratio is lean (low voltage, i.e. less than 0.45 V).
Conversely, when the air-fuel ratio is richer than the stoichiometric air-fuel level, the oxygen concentration
in the exhaust gas becomes lean. The HO2 sensor informs the ECM that the post-TWC air-fuel ratio is
rich (high voltage, i.e. more than 0.45 V). The HO2 sensor has the property of changing its output voltage
drastically when the air-fuel ratio is close to the stoichiometric level.
The ECM uses the supplementary information from the HO2 sensor to determine whether the air-fuel ratio
after the TWC is rich or lean, and adjusts the fuel injection time accordingly. Thus, if the HO2 sensor is
working improperly due to internal malfunctions, the ECM is unable to compensate for deviations in the
primary air-fuel ratio control.
DTC P0136Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1
Sensor 2)
DTC P0137Oxygen Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1
Sensor 2)
DTC P0138Oxygen Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1
Sensor 2)
DTC P0156Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2
Sensor 2)
DTC P0157Oxygen Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2
Sensor 2)
DTC P0158Oxygen Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2
Sensor 2)