sensor TOYOTA SIENNA 2007 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SIENNA, Model: TOYOTA SIENNA 2007Pages: 3000, PDF Size: 52.26 MB
Page 522 of 3000
ES–2162GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Turn the tester on.
(d) Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS /
ENHANCED OBD II / DATA LIST / PRIMARY /
COOLANT TEMP.
(e) Read the COOLANT TEMP twice, when the engine is
both cold and warmed up.
Standard:
With cold engine:
Same as ambient air temperature.
With warm engine:
Between 75
C and 95C (167F and 203F).
NG
OK
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Turn the tester on.
(d) Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS /
ENHANCED OBD II / DATA LIST / PRIMARY / MAF and
COOLANT TEMP.
(e) Allow the engine to idle until the COOLANT TEMP
reaches 75
C (167F) or more.
(f) Read the MAF with the engine in an idling condition and
at an engine speed of 2500 rpm.
Standard:
MAF while engine is idling:
Between 1.8 g/s and 4.7 g/s (shift position: N, A/
C: OFF).
MAF at engine speed of 2500 rpm:
Between 7.4 g/s and 18.9 g/s (shift position: N, A/
C: OFF).
NG
OK
21READ VALUE OF INTELLIGENT TESTER (COOLANT TEMP)
REPLACE ENGINE COOLANT
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
22READ VALUE OF INTELLIGENT TESTER (MASS AIR FLOW METER)
REPLACE MASS AIR FLOW METER
Page 527 of 3000
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–221
ESDESCRIPTION
A flat type knock sensor (non-resonant type) has a structure that can detect vibrations over a wide band of
frequencies: between approximately 6 kHz and 15 kHz.
Knock sensors are fitted onto the engine block to detect engine knocking.
The knock sensor contains a piezoelectric element which generates a voltage when the engine block
vibrates due to knocking. Any occurrence of engine knocking can be suppressed by delaying the ignition
timing.
HINT:
When any of DTCs P0327, P0328, P0332 and P0333 are set, the ECM enters fail-safe mode. During fail-
safe mode, the ignition timing is delayed to its maximum retardation. Fail-safe mode continues until the
ignition switch is turned off.
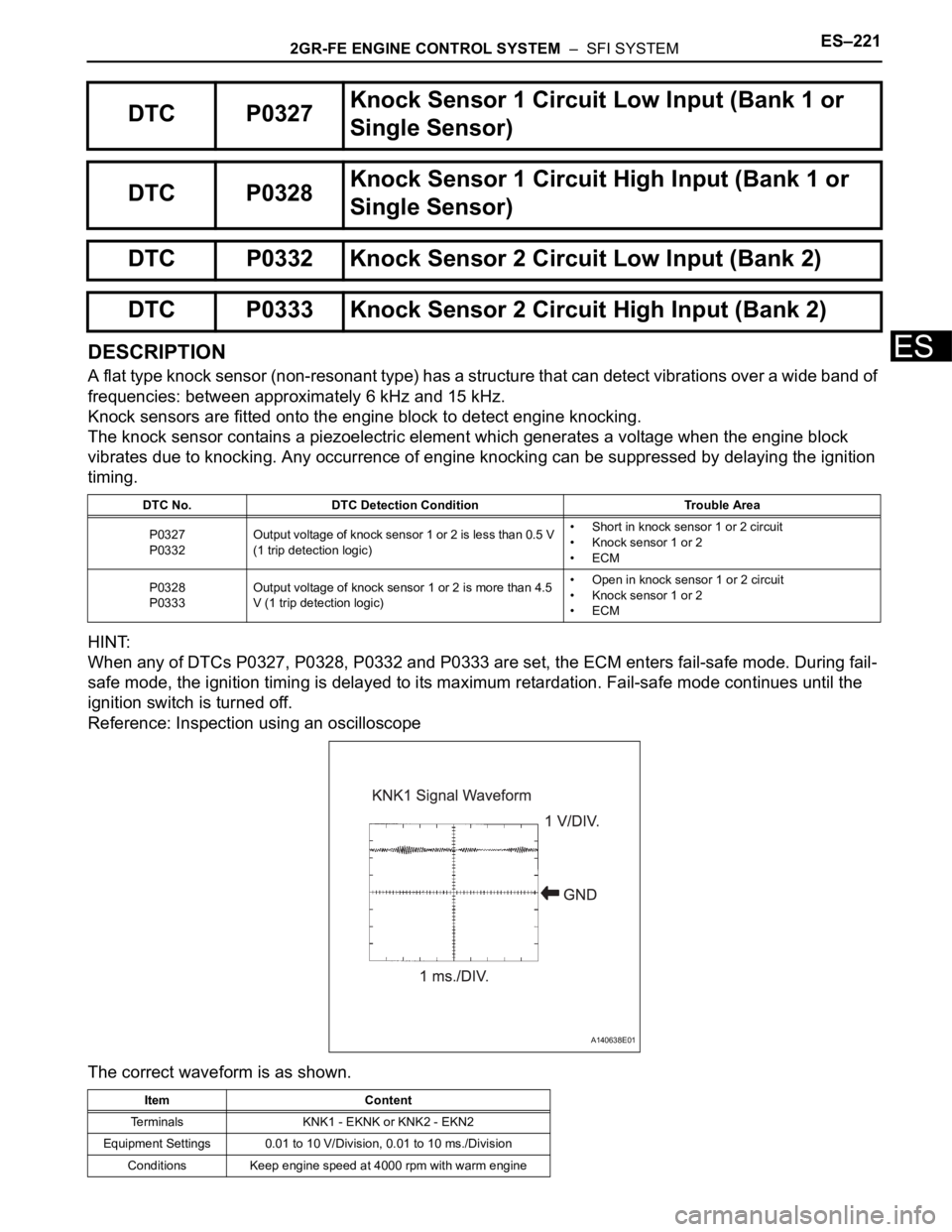
Reference: Inspection using an oscilloscope
The correct waveform is as shown.
DTC P0327Knock Sensor 1 Circuit Low Input (Bank 1 or
Single Sensor)
DTC P0328Knock Sensor 1 Circuit High Input (Bank 1 or
Single Sensor)
DTC P0332 Knock Sensor 2 Circuit Low Input (Bank 2)
DTC P0333 Knock Sensor 2 Circuit High Input (Bank 2)
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0327
P0332Output voltage of knock sensor 1 or 2 is less than 0.5 V
(1 trip detection logic)• Short in knock sensor 1 or 2 circuit
• Knock sensor 1 or 2
•ECM
P0328
P0333Output voltage of knock sensor 1 or 2 is more than 4.5
V (1 trip detection logic)• Open in knock sensor 1 or 2 circuit
• Knock sensor 1 or 2
•ECM
Item Content
Terminals KNK1 - EKNK or KNK2 - EKN2
Equipment Settings 0.01 to 10 V/Division, 0.01 to 10 ms./Division
Conditions Keep engine speed at 4000 rpm with warm engine
A140638E01
Page 528 of 3000

ES–2222GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The knock sensor, located on the cylinder block, detects spark knock. When a spark knock occurs, the
piezoelectric element of the sensor vibrates. When the ECM detects a voltage in this frequency range, it
retards the ignition timing to suppress the spark knock.
The ECM also senses background engine noise with the knock sensor and uses this noise to check for
faults in the sensor. If the knock sensor signal level is too low for more than 10 seconds, or if the knock
sensor output voltage is outside the normal range, the ECM interprets this as a fault in the knock sensor
and sets a DTC.
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
Knock Sensor Range Check (Low voltage) P0327 and P0332:
Knock Sensor Range Check (High voltage) P0328 and P0333:
Related DTCsP0327: Knock sensor (Bank 1) open/short (Low voltage)
P0328: Knock sensor (Bank 1) open/short (High voltage)
P0332: Knock sensor (Bank 2) open/short (Low voltage)
P0333: Knock sensor (Bank 2) open/short (High voltage)
Required Sensors / Components (Main) Knock sensor (Bank 1 and 2)
Required Sensors / Components (Related) -
Frequency of Operation Continuous
Duration 1 second
MIL Operation Immediate
Sequence of Operation None
The monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not
presentNone
Battery voltage 10.5 V or more
Time after engine start 5 seconds or more
Ignition switch ON
Starter OFF
Knock sensor voltage Less than 0.5 V
Knock sensor voltage More than 4.5 V
Page 529 of 3000
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–223
ES
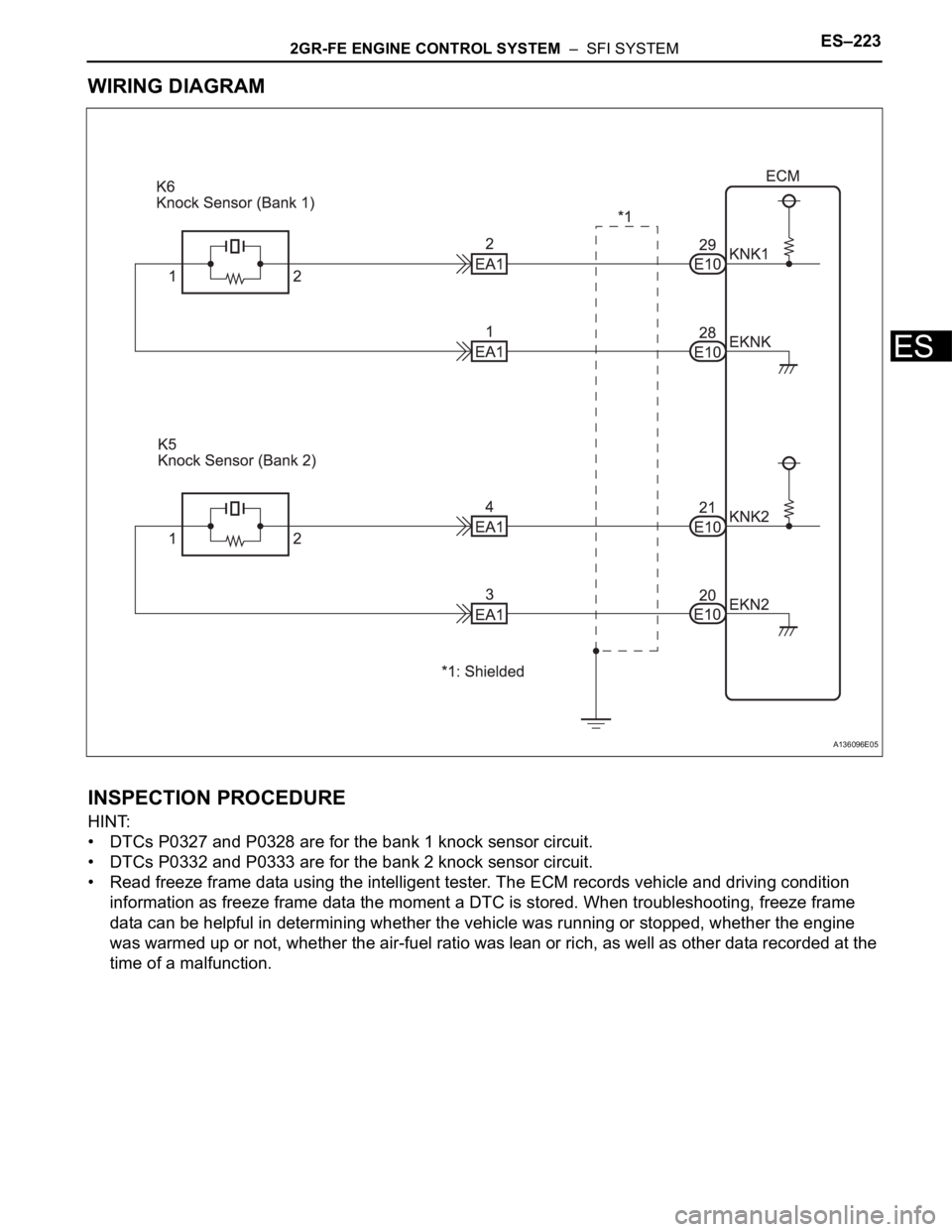
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
• DTCs P0327 and P0328 are for the bank 1 knock sensor circuit.
• DTCs P0332 and P0333 are for the bank 2 knock sensor circuit.
• Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition
information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame
data can be helpful in determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, whether the engine
was warmed up or not, whether the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, as well as other data recorded at the
time of a malfunction.
A136096E05
Page 530 of 3000
ES–2242GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
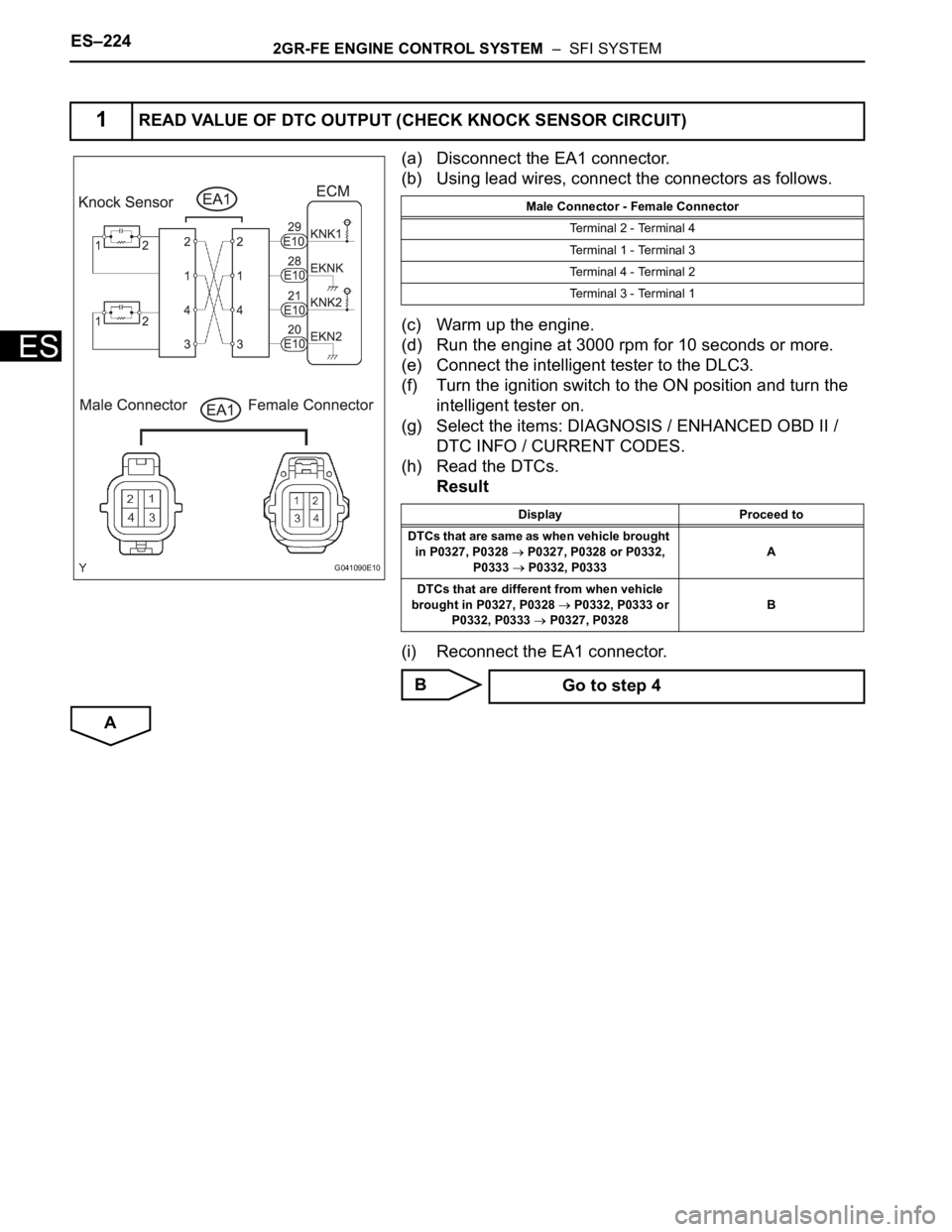
(a) Disconnect the EA1 connector.
(b) Using lead wires, connect the connectors as follows.
(c) Warm up the engine.
(d) Run the engine at 3000 rpm for 10 seconds or more.
(e) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(f) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position and turn the
intelligent tester on.
(g) Select the items: DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED OBD II /
DTC INFO / CURRENT CODES.
(h) Read the DTCs.
Result
(i) Reconnect the EA1 connector.
B
A
1READ VALUE OF DTC OUTPUT (CHECK KNOCK SENSOR CIRCUIT)
G041090E10
Male Connector - Female Connector
Terminal 2 - Terminal 4
Terminal 1 - Terminal 3
Terminal 4 - Terminal 2
Terminal 3 - Terminal 1
Display Proceed to
DTCs that are same as when vehicle brought
in P0327, P0328
P0327, P0328 or P0332,
P0333
P0332, P0333A
DTCs that are different from when vehicle
brought in P0327, P0328
P0332, P0333 or
P0332, P0333 P0327, P0328B
Go to step 4
Page 532 of 3000

ES–2262GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
OK
(a) Disconnect the EA1 connector.
(b) Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the
table below.
Standard resistance
(c) Reconnect the EA1 connector.
OK
NG
HINT:
• If DTC P0327 or P0328 has changed to P0332 or P0333,
check the knock sensor circuit on the right bank side.
• If DTC P0332 or P0333 has changed to P0327 or P0328,
check the knock sensor circuit on the left bank side.
(a) Disconnect the EA1 connector.
(b) Disconnect the K6 and K5 knock sensor connectors.
(c) Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the
table below.
Standard resistance:
Check for open
Check for short
(d) Reconnect the EA1 connector.
(e) Reconnect the knock sensor connector. CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEMS
4INSPECT KNOCK SENSOR
G042949E03
Tester Connection Specified Condition
EA1 male connector 1 - 2 120 to 280 k
EA1 male connector 3 - 4 120 to 280 k
CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEMS
5CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (EA1 CONNECTOR - KNOCK SENSOR)
A114618E08
Tester Connection Specified Condition
EA1 male connector 2 - K6-2 Below 1
EA1 male connector 1 - K6-1 Below 1
EA1 male connector 4 - K5-2 Below 1
EA1 male connector 3 - K5-1 Below 1
Tester Connection Specified Condition
EA1 male connector 2 or K6-2 - Body ground 10 k
or higher
EA1 male connector 1 or K6-1 - Body ground 10 k
or higher
EA1 male connector 4 or K5-2 - Body ground 10 k
or higher
EA1 male connector 3 or K5-1 - Body ground 10 k
or higher
Page 533 of 3000
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–227
ES
NG
OKREPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR
CONNECTOR (EA1 CONNECTOR - KNOCK
SENSOR)
REPLACE KNOCK SENSOR (See page ES-520)
Page 534 of 3000

ES–2282GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
DESCRIPTION
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor system consists of a CKP sensor plate and a pickup coil. The
sensor plate has 34 teeth and is installed on the crankshaft. The pickup coil is made of an iron core and a
magnet.
The sensor plate rotates as each tooth passes through the pickup coil, and a pulse signal is created. The
pickup coil generates 34 signals per engine revolution. Based on these signals, the ECM calculates the
crankshaft position and engine RPM. Using these calculations, the fuel injection time and ignition timing
are controlled.
Reference: Inspection using an oscilloscope
HINT:
• The correct waveform is shown in the illustration.
• VV1+ and VV2+ stand for the VVT sensor signal, and NE+ stands for the CKP sensor signal.
DTC P0335 Crankshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit
DTC P0339Crankshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit Inter-
mittent
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0335• No CKP sensor signal to ECM while cranking (1 trip
detection logic)
• No CKP sensor signal to ECM at engine speed of
600 rpm or more (1 trip detection logic)• Open or short in CKP sensor circuit
• CKP sensor
• Sensor plate (CKP sensor plate)
•ECM
P0339Under conditions (a), (b) and (c), no CKP sensor signal
to ECM for 0.05 seconds or more (1 trip detection
logic):
(a) Engine speed 1000 rpm or more
(b) Starter signal OFF
(c) 3 seconds or more have lapsed since starter signal
switched from ON to OFF• Open or short in CKP sensor circuit
• CKP sensor
• Sensor plate (CKP sensor plate)
•ECM
Item Content
Te r m i n a l sVV1+ - VV1-
VV2+ - VV2-
NE+ - NE-
Equipment Settings 5 V/Division, 20 ms./Division
Conditions Cranking or idling
A107148E09
Page 535 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–229
ES
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
If there is no signal from the CKP sensor despite the engine revolving, the ECM interprets this as a
malfunction of the sensor.
If the malfunction is not repaired successfully, a DTC is set 10 seconds after the engine is next started.
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
All:
Crankshaft Position Sensor Range Check during Cranking P0335:
Crankshaft Position Sensor Range Check during Engine Running P0335:
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
Crankshaft Position Sensor Range Check during Cranking P0335:
Crankshaft Position Sensor Range Check during Engine Running P0335:
COMPONENT OPERATING RANGE
Related DTCsP0335: Crankshaft position sensor range check during cranking
P0335: Crankshaft position sensor range check during engine running
Required Sensors / Components (Main) Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor
Required Sensors / Components (Related) -
Frequency of Operation Continuous
Duration 3 times
MIL Operation Immediate
Sequence of Operation None
The monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not
presentNone
Sta r t e r OF F
Ignition switch ON
Battery voltage 7 V or more
Minimum battery voltage while starter ON Less than 11 V
Number of VVT sensor signal pulse 6 times
CMP sensor circuit fail Not detected
Engine speed 600 rpm or more
Sta r t e r OF F
Time after starter from ON to OFF 3 seconds or more
Number of crankshaft position sensor signal pulse 132 or less, or 174 or more
CKP sensor signal No signal
CKP sensor• CKP sensor output voltage fluctuates while crankshaft is revolving
• 34 CKP sensor signals per crankshaft revolution
Page 537 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–231
ES
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
• If no problem is found by this diagnostic troubleshooting procedure, troubleshoot the engine
mechanical systems.
• Check the engine speed. The engine speed can be checked by using the intelligent tester. Perform the
following procedure:
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Start the engine.
(c) Turn the tester on.
(d) Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED OBD II / DATA LIST / PRIMARY /
ENGINE SPD.
The engine speed may be indicated as zero despite the engine revolving normally. This is caused
by a lack of NE signals from the Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor. Alternatively, the engine speed
may be indicated as lower than the actual engine speed, if the CKP sensor voltage output is
insufficient.
• Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition
information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame
data can be helpful in determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, whether the engine
was warmed up or not, whether the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, as well as other data recorded at the
time of a malfunction.
(a) Disconnect the C22 Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor
connector.
(b) Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the
table below.
Standard resistance
HINT:
Terms "cold" and "hot" refer to the temperature of the
coils. "Cold" means approximately -10 to 50
C (14 to
122
F). "Hot" means approximately 50 to 100C (122 to
212
F).
(c) Reconnect the CKP sensor connector.
NG
OK
1INSPECT CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (RESISTANCE)
A078431E26
Tester Connection Condition Specified Condition
1 - 2 Cold 1630 to 2740
1 - 2 Hot 2065 to 3225
REPLACE CRANKSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR (See page ES-514)