TOYOTA SIENNA 2007 Service Manual PDF
Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SIENNA, Model: TOYOTA SIENNA 2007Pages: 3000, PDF Size: 52.26 MB
Page 61 of 3000
INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMSIN–31
IN
ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT INSPECTION
PROCEDURE
1. BASIC INSPECTION
(a) WHEN MEASURING RESISTANCE OF
ELECTRONIC PARTS
(1) Unless otherwise stated, all resistance
measurements should be made at an ambient
temperature of 20
C (68F). Resistance
measurements may be inaccurate if measured
at high temperatures, i.e. immediately after the
vehicle has been running. Measurements should
be made after the engine has cooled down.
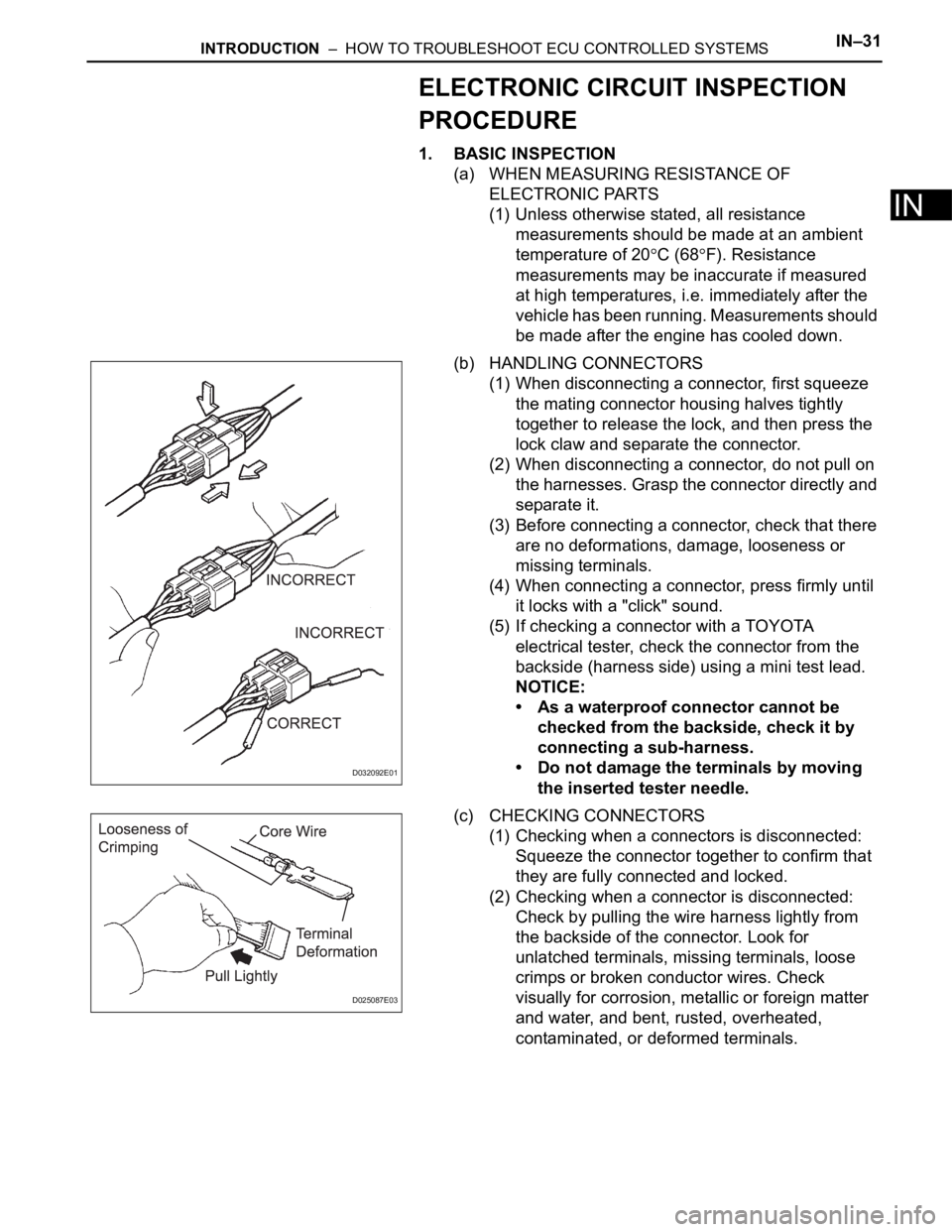
(b) HANDLING CONNECTORS
(1) When disconnecting a connector, first squeeze
the mating connector housing halves tightly
together to release the lock, and then press the
lock claw and separate the connector.
(2) When disconnecting a connector, do not pull on
the harnesses. Grasp the connector directly and
separate it.
(3) Before connecting a connector, check that there
are no deformations, damage, looseness or
missing terminals.
(4) When connecting a connector, press firmly until
it locks with a "click" sound.
(5) If checking a connector with a TOYOTA
electrical tester, check the connector from the
backside (harness side) using a mini test lead.
NOTICE:
• As a waterproof connector cannot be
checked from the backside, check it by
connecting a sub-harness.
• Do not damage the terminals by moving
the inserted tester needle.
(c) CHECKING CONNECTORS
(1) Checking when a connectors is disconnected:
Squeeze the connector together to confirm that
they are fully connected and locked.
(2) Checking when a connector is disconnected:
Check by pulling the wire harness lightly from
the backside of the connector. Look for
unlatched terminals, missing terminals, loose
crimps or broken conductor wires. Check
visually for corrosion, metallic or foreign matter
and water, and bent, rusted, overheated,
contaminated, or deformed terminals.
D032092E01
D025087E03
Page 62 of 3000
IN–32INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
IN
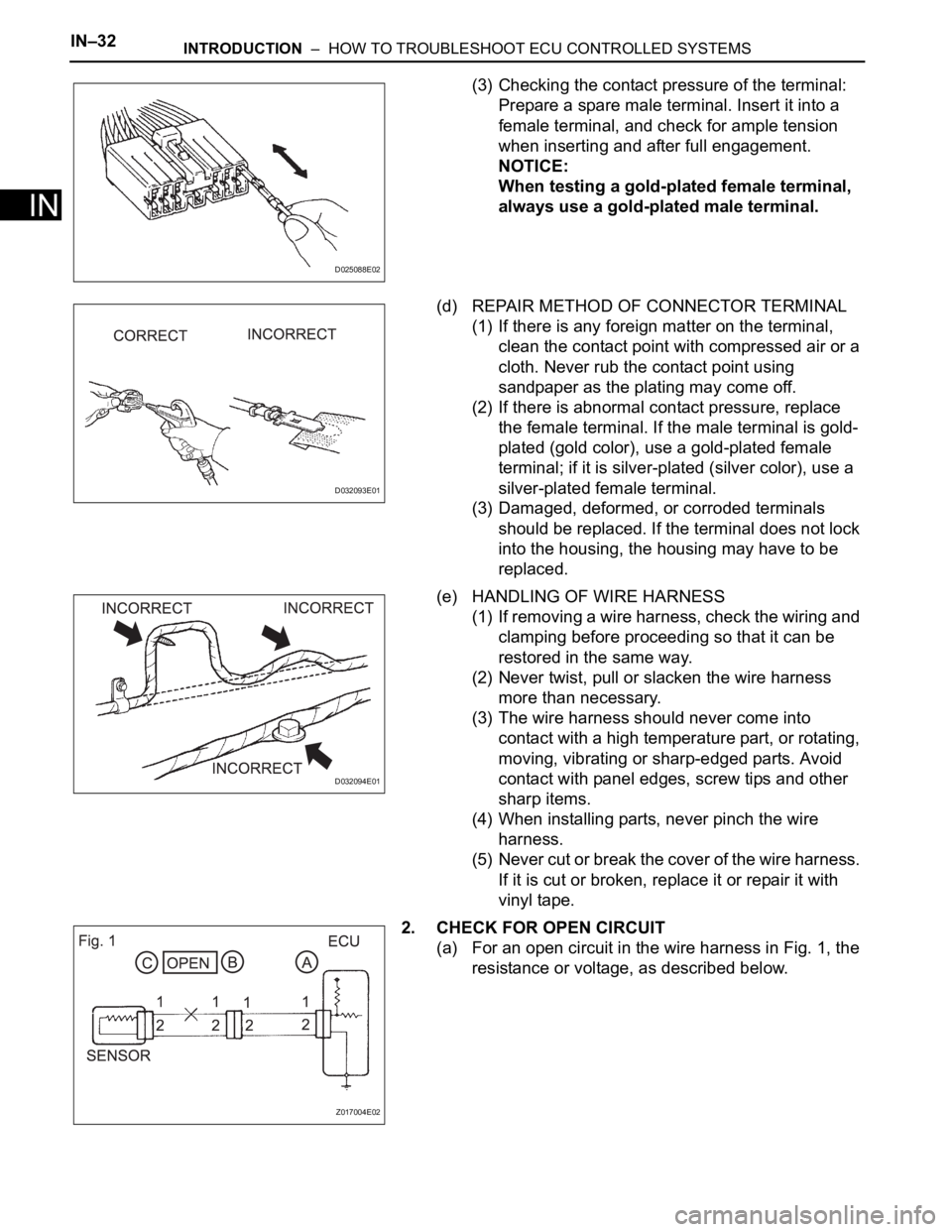
(3) Checking the contact pressure of the terminal:
Prepare a spare male terminal. Insert it into a
female terminal, and check for ample tension
when inserting and after full engagement.
NOTICE:
When testing a gold-plated female terminal,
always use a gold-plated male terminal.
(d) REPAIR METHOD OF CONNECTOR TERMINAL
(1) If there is any foreign matter on the terminal,
clean the contact point with compressed air or a
cloth. Never rub the contact point using
sandpaper as the plating may come off.
(2) If there is abnormal contact pressure, replace
the female terminal. If the male terminal is gold-
plated (gold color), use a gold-plated female
terminal; if it is silver-plated (silver color), use a
silver-plated female terminal.
(3) Damaged, deformed, or corroded terminals
should be replaced. If the terminal does not lock
into the housing, the housing may have to be
replaced.
(e) HANDLING OF WIRE HARNESS
(1) If removing a wire harness, check the wiring and
clamping before proceeding so that it can be
restored in the same way.
(2) Never twist, pull or slacken the wire harness
more than necessary.
(3) The wire harness should never come into
contact with a high temperature part, or rotating,
moving, vibrating or sharp-edged parts. Avoid
contact with panel edges, screw tips and other
sharp items.
(4) When installing parts, never pinch the wire
harness.
(5) Never cut or break the cover of the wire harness.
If it is cut or broken, replace it or repair it with
vinyl tape.
2. CHECK FOR OPEN CIRCUIT
(a) For an open circuit in the wire harness in Fig. 1, the
resistance or voltage, as described below.
D025088E02
D032093E01
D032094E01
Z017004E02
Page 63 of 3000
INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMSIN–33
IN
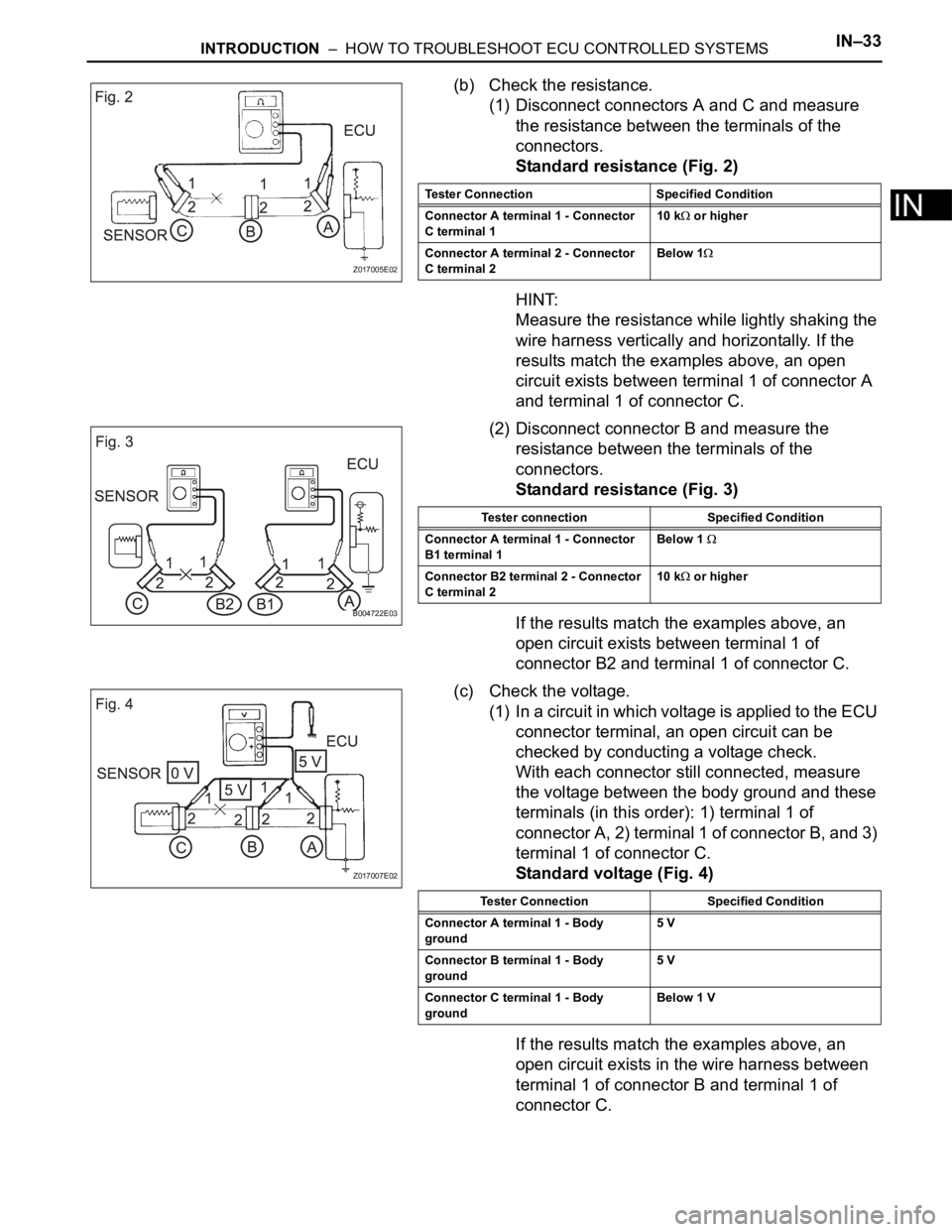
(b) Check the resistance.
(1) Disconnect connectors A and C and measure
the resistance between the terminals of the
connectors.
Standard resistance (Fig. 2)
HINT:
Measure the resistance while lightly shaking the
wire harness vertically and horizontally. If the
results match the examples above, an open
circuit exists between terminal 1 of connector A
and terminal 1 of connector C.
(2) Disconnect connector B and measure the
resistance between the terminals of the
connectors.
Standard resistance (Fig. 3)
If the results match the examples above, an
open circuit exists between terminal 1 of
connector B2 and terminal 1 of connector C.
(c) Check the voltage.
(1) In a circuit in which voltage is applied to the ECU
connector terminal, an open circuit can be
checked by conducting a voltage check.
With each connector still connected, measure
the voltage between the body ground and these
terminals (in this order): 1) terminal 1 of
connector A, 2) terminal 1 of connector B, and 3)
terminal 1 of connector C.
Standard voltage (Fig. 4)
If the results match the examples above, an
open circuit exists in the wire harness between
terminal 1 of connector B and terminal 1 of
connector C.
Z017005E02
Tester Connection Specified Condition
Connector A terminal 1 - Connector
C terminal 110 k
or higher
Connector A terminal 2 - Connector
C terminal 2Below 1
B004722E03
Tester connection Specified Condition
Connector A terminal 1 - Connector
B1 terminal 1Below 1
Connector B2 terminal 2 - Connector
C terminal 210 k or higher
Z017007E02
Tester Connection Specified Condition
Connector A terminal 1 - Body
ground5 V
Connector B terminal 1 - Body
ground5 V
Connector C terminal 1 - Body
groundBelow 1 V
Page 64 of 3000
IN–34INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
IN
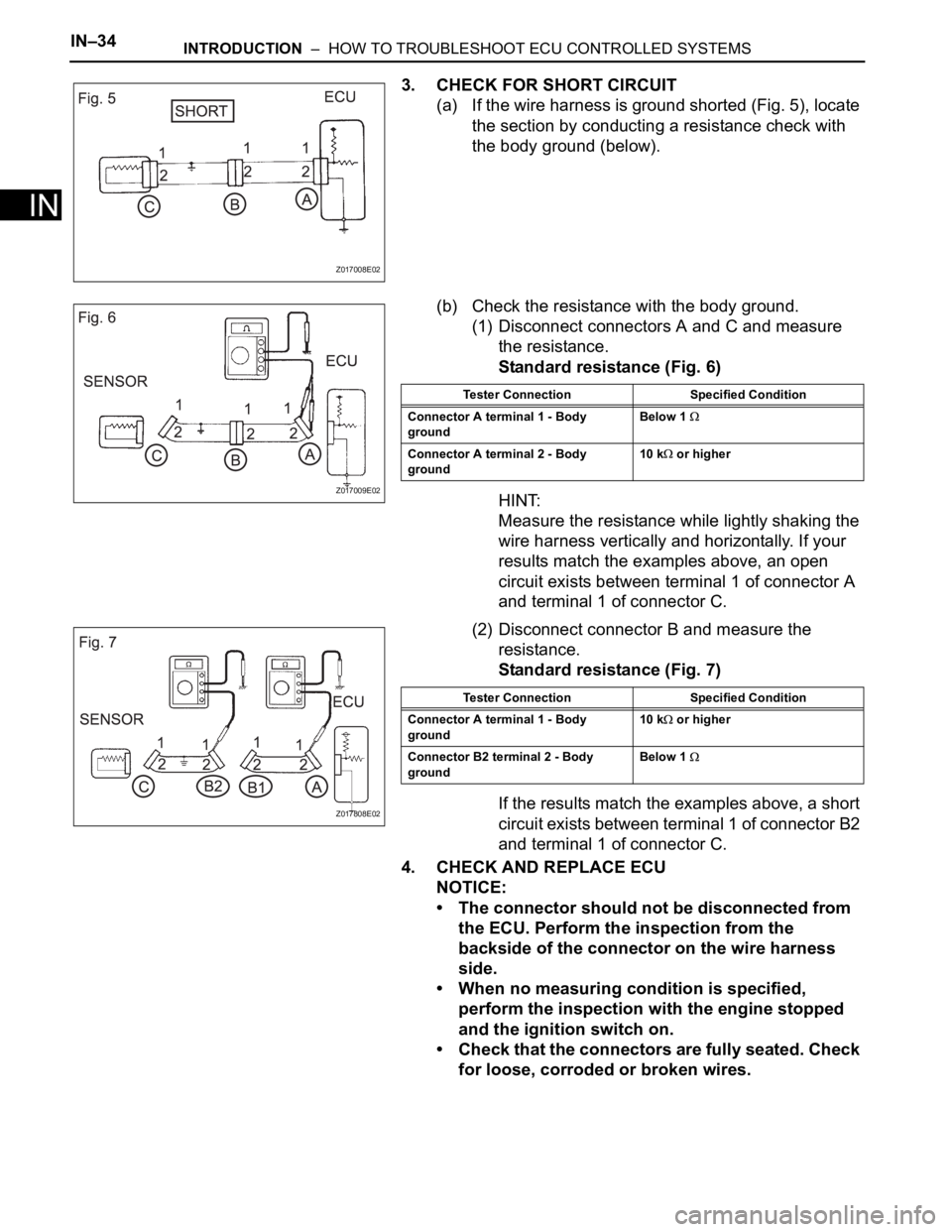
3. CHECK FOR SHORT CIRCUIT
(a) If the wire harness is ground shorted (Fig. 5), locate
the section by conducting a resistance check with
the body ground (below).
(b) Check the resistance with the body ground.
(1) Disconnect connectors A and C and measure
the resistance.
Standard resistance (Fig. 6)
HINT:
Measure the resistance while lightly shaking the
wire harness vertically and horizontally. If your
results match the examples above, an open
circuit exists between terminal 1 of connector A
and terminal 1 of connector C.
(2) Disconnect connector B and measure the
resistance.
Standard resistance (Fig. 7)
If the results match the examples above, a short
circuit exists between terminal 1 of connector B2
and terminal 1 of connector C.
4. CHECK AND REPLACE ECU
NOTICE:
• The connector should not be disconnected from
the ECU. Perform the inspection from the
backside of the connector on the wire harness
side.
• When no measuring condition is specified,
perform the inspection with the engine stopped
and the ignition switch on.
• Check that the connectors are fully seated. Check
for loose, corroded or broken wires.
Z017008E02
Z017009E02
Tester Connection Specified Condition
Connector A terminal 1 - Body
groundBelow 1
Connector A terminal 2 - Body
ground10 k or higher
Z017808E02
Tester Connection Specified Condition
Connector A terminal 1 - Body
ground10 k
or higher
Connector B2 terminal 2 - Body
ground Below 1
Page 65 of 3000
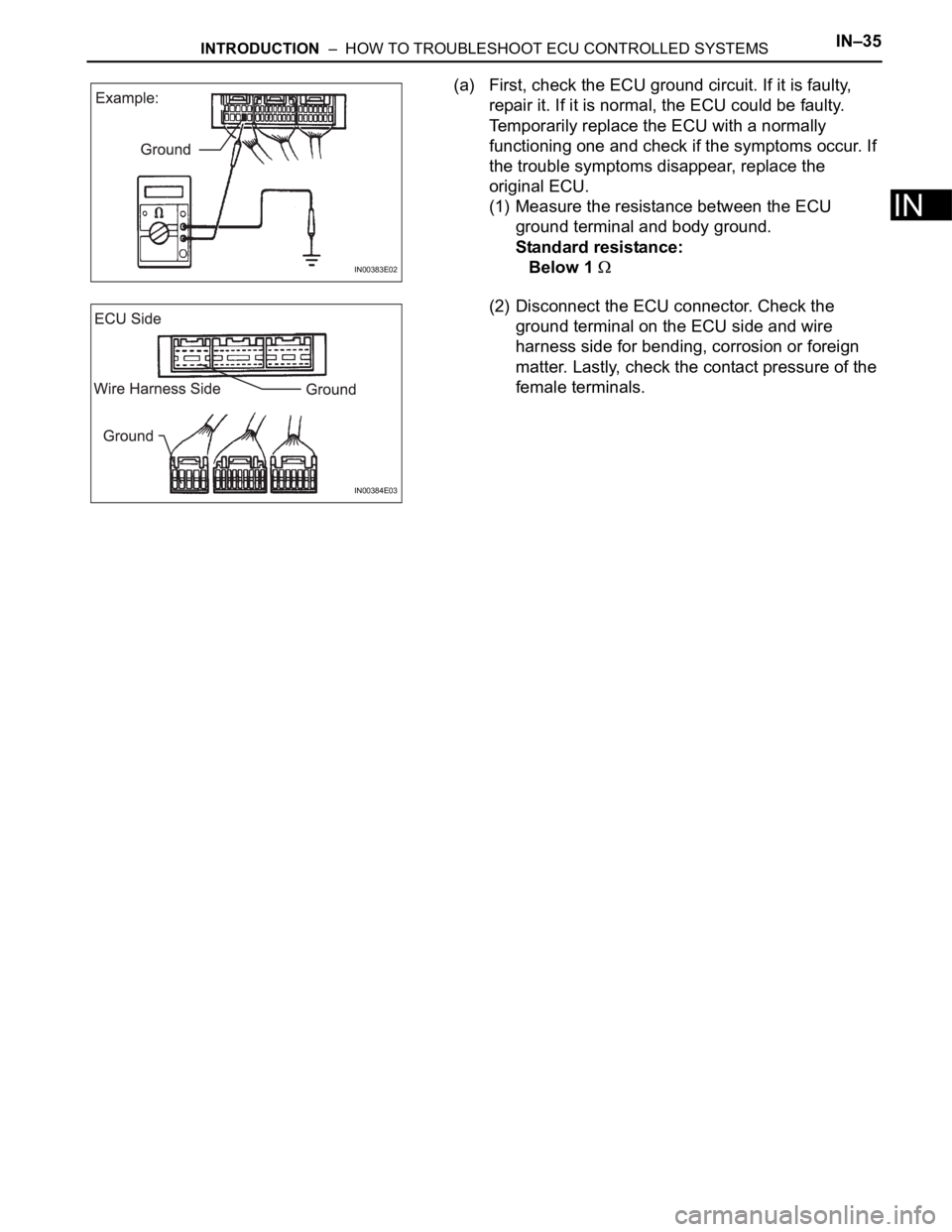
INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMSIN–35
IN
(a) First, check the ECU ground circuit. If it is faulty,
repair it. If it is normal, the ECU could be faulty.
Temporarily replace the ECU with a normally
functioning one and check if the symptoms occur. If
the trouble symptoms disappear, replace the
original ECU.
(1) Measure the resistance between the ECU
ground terminal and body ground.
Standard resistance:
Below 1
(2) Disconnect the ECU connector. Check the
ground terminal on the ECU side and wire
harness side for bending, corrosion or foreign
matter. Lastly, check the contact pressure of the
female terminals.
IN00383E02
IN00384E03
Page 66 of 3000

IN–36INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
IN
HOW TO PROCEED WITH
TROUBLESHOOTING
1. OPERATION FLOW
HINT:
Perform troubleshooting in accordance with the
procedures below. The following is an outline of basic
troubleshooting procedures. Confirm the troubleshooting
procedures for the circuit you are working on before
beginning troubleshooting.
NEXT
(a) Ask the customer about the conditions and environment
when the problem occurred.
NEXT
Standard voltage:
11 to 14 V
If the voltage is below 11 V, recharge or replace the
battery before proceeding.
NEXT
(a) Visually check the wire harnesses, connectors and fuses
for open and short circuits.
(b) Warm up the engine to the normal operating
temperature.
(c) Confirm the problem symptoms and conditions, and
check for DTCs
Result
B
A
1VEHICLE BROUGHT TO WORKSHOP
2CUSTOMER PROBLEM ANALYSIS
3INSPECT BATTERY VOLTAGE
4SYMPTOM CONFIRMATION AND DTC (AND FREEZE FRAME DATA) CHECK
Result Proceed to
DTC is output A
DTC is not output B
Go to step 6
Page 67 of 3000

INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMSIN–37
IN
(a) Check the results obtained in step 4. Then find the
output DTC in the DTC chart. Look at the "Trouble Area"
column for a list of potentially malfunctioning circuits and
/ or parts.
NEXT
(a) Check the results obtained in step 4. Then find the
problem symptoms in the problem symptoms table. Look
at the "Suspected Area" column for a list of potentially
malfunctioning circuits and / or parts.
NEXT
(a) Identify the malfunctioning circuit or part.
NEXT
(a) Adjust, repair or replace the malfunctioning circuit or
parts.
NEXT
(a) After the adjustment, repairs or replacement, confirm
that the malfunction no longer exists. If the malfunction
does not reoccur, perform a confirmation test under the
same conditions and in the same environment as when
the malfunction occurred the first time.
NEXT
2. CUSTOMER PROBLEM ANALYSIS
5DTC CHART
Go to step 7
6PROBLEM SYMPTOMS CHART
7CIRCUIT INSPECTION OR PARTS INSPECTION
8ADJUST, REPAIR OR REPLACE
9CONFIRMATION TEST
END
Page 68 of 3000

IN–38INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
IN
HINT:
• In troubleshooting, confirm that the problem symptoms
have been accurately identified. Preconceptions should be
discarded in order to make an accurate judgment. To
clearly understand what the problem symptoms are, it is
extremely important to ask the customer about the
problem and the conditions at the time the malfunction
occurred.
• Gather as much information as possible for reference.
Past problems that seem unrelated may also help in some
cases.
• The following 5 items are important points in the problem
analysis:
3. SYMPTOM CONFIRMATION AND DIAGNOSTIC
TROUBLE CODE
HINT:
The diagnostic system in the SIENNA has various
functions.
• The first function is the Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) check. A DTC is a code stored in the ECU
memory whenever a malfunction in the signal circuits
to the ECU occurs. In a DTC check, a previous
malfunction's DTC can be checked by a technician
during troubleshooting.
• Another function is the Input Signal Check, which
checks if the signals from various switches are sent to
the ECU correctly.
By using these functions, the problem areas can be
narrowed down and troubleshooting is more effective.
Diagnostic functions are incorporated in the following
system in the SIENNA.
What Vehicle model, system name
When Date, time, occurrence frequency
Where Road conditions
Under what conditions? Running conditions, driving conditions, weather conditions
How did it happen? Problem symptoms
SystemSYMPTOM CONFIRMATION AND DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
DTC Check
(Normal Mode)DTC Check
(Check Mode)Sensor Check/
Test Mode
(Input Signal
Check)Data List Active Test
2GR-FE SFI System
X
U151E Automatic Transaxle SystemX
U151F Automatic Transaxle SystemX
Tire pressure warning systemXX
Anti-lock Brake System
X
Vehicle Stability Control SystemX
Air Conditioning System (for Manual Air
Conditioning System)XXXXX
Air Conditioning System (for Automatic Air
Conditioning System)
XX
Airbag SystemXX
Occupant Classification System
XXX
Page 69 of 3000
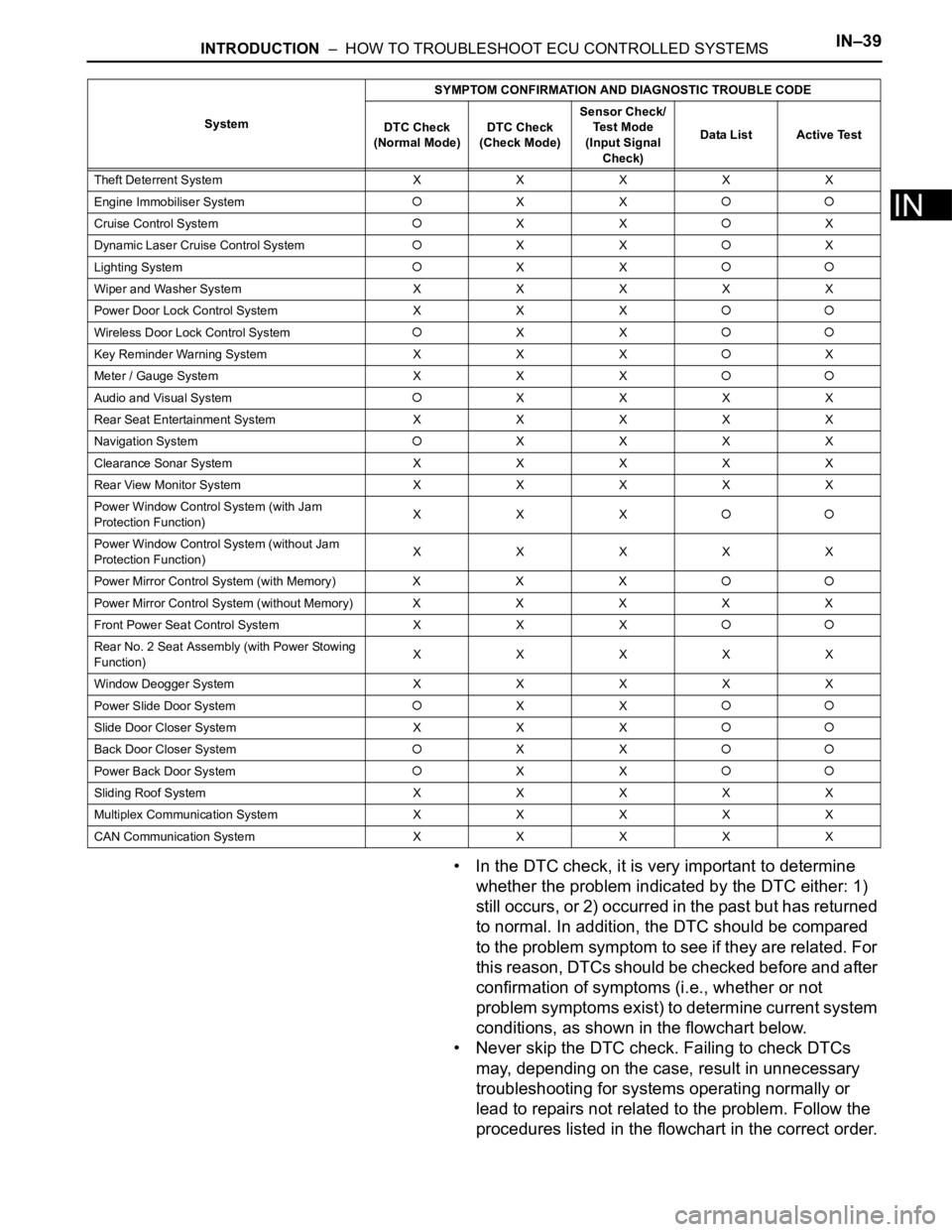

INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMSIN–39
IN
• In the DTC check, it is very important to determine
whether the problem indicated by the DTC either: 1)
still occurs, or 2) occurred in the past but has returned
to normal. In addition, the DTC should be compared
to the problem symptom to see if they are related. For
this reason, DTCs should be checked before and after
confirmation of symptoms (i.e., whether or not
problem symptoms exist) to determine current system
conditions, as shown in the flowchart below.
• Never skip the DTC check. Failing to check DTCs
may, depending on the case, result in unnecessary
troubleshooting for systems operating normally or
lead to repairs not related to the problem. Follow the
procedures listed in the flowchart in the correct order.
Theft Deterrent System XXXXX
Engine Immobiliser System
XX
Cruise Control SystemXXX
Dynamic Laser Cruise Control System
XXX
Lighting System
XX
Wiper and Washer SystemXXXXX
Power Door Lock Control System X X X
Wireless Door Lock Control SystemXX
Key Reminder Warning System X X XX
Meter / Gauge System X X X
Audio and Visual SystemXXXX
Rear Seat Entertainment System XXXXX
Navigation System
XXXX
Clearance Sonar SystemXXXXX
Rear View Monitor System XXXXX
Power Window Control System (with Jam
Protection Function)XXX
Power Window Control System (without Jam
Protection Function)XXXXX
Power Mirror Control System (with Memory) X X X
Power Mirror Control System (without Memory)XXXXX
Front Power Seat Control System X X X
Rear No. 2 Seat Assembly (with Power Stowing
Function)XXXXX
Window Deogger SystemXXXXX
Power Slide Door System
XX
Slide Door Closer System X X X
Back Door Closer SystemXX
Power Back Door SystemXX
Sliding Roof System XXXXX
Multiplex Communication System XXXXX
CAN Communication System XXXXXSystemSYMPTOM CONFIRMATION AND DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
DTC Check
(Normal Mode)DTC Check
(Check Mode)Sensor Check/
Test Mode
(Input Signal
Check)Data List Active Test
Page 70 of 3000

IN–40INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
IN
• The following flowchart shows how to proceed with
troubleshooting using the DTC check. Directions from
the flowchart will indicate how to proceed either to
DTC troubleshooting or to the troubleshooting of each
problem symptom.
NEXT
NEXT
Result
B
A
NEXT
Result
B
A
Result
1DTC CHECK
2MAKE A NOTE OF DTCS DISPLAYED AND THEN CLEAR MEMORY
3SYMPTOM CONFIRMATION
Result Proceed to
No symptoms exist A
Symptoms exist B
Go to step 5
4SIMULATION TEST USING SYMPTOM SIMULATION METHODS
5DTC CHECK
Result Proceed to
DTC is not output A
DTC is output B
TROUBLESHOOTING OF PROBLEM
INDICATED BY DTC
6SYMPTOM CONFIRMATION
Result Proceed to
No symptoms exist A
Symptoms exist B