sensor VOLKSWAGEN CORRADO 1993 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: VOLKSWAGEN, Model Year: 1993, Model line: CORRADO, Model: VOLKSWAGEN CORRADO 1993Pages: 920, PDF Size: 6.92 MB
Page 487 of 920
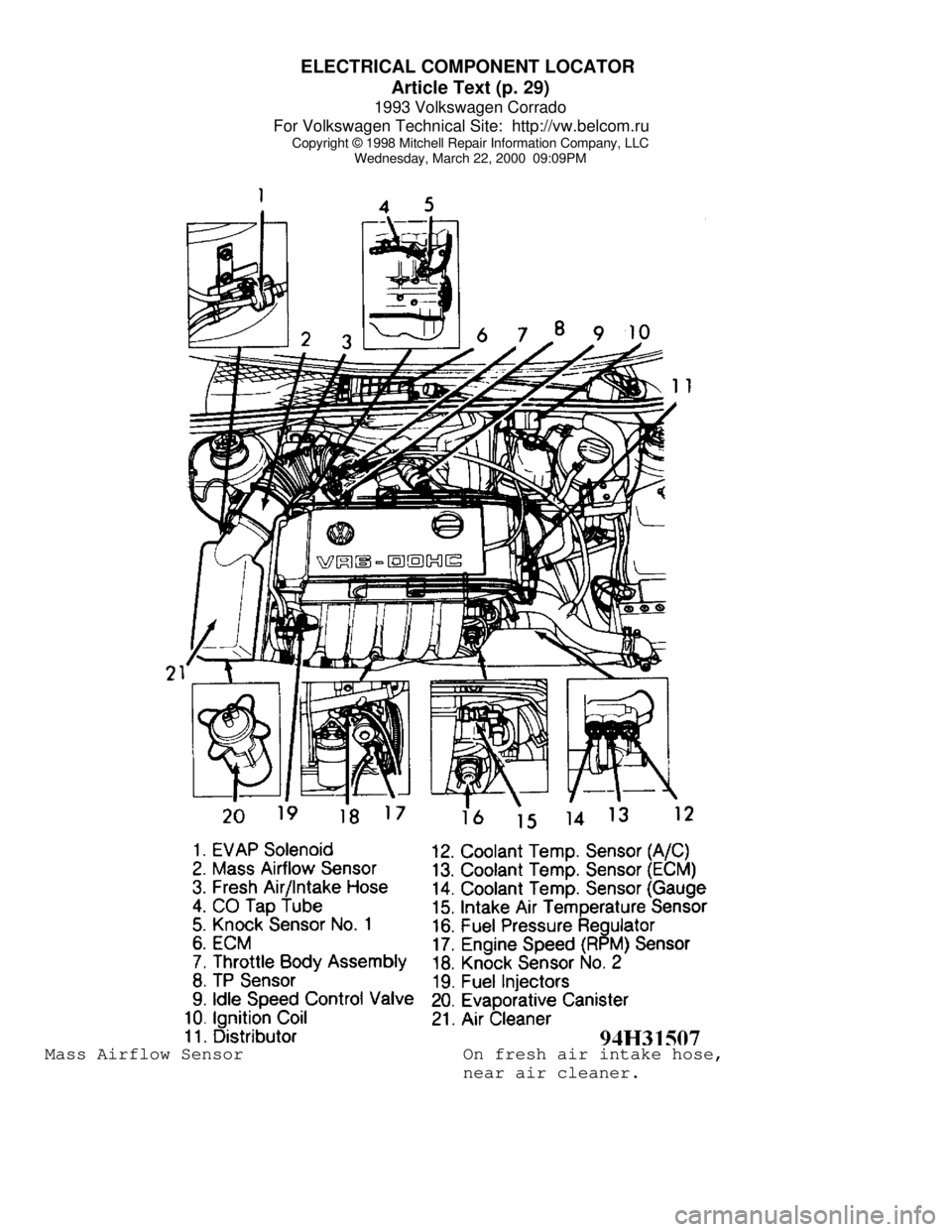
ELECTRICAL COMPONENT LOCATOR
Article Text (p. 29)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PMMass Airflow Sensor On fresh air intake hose,
near air cleaner.
Page 488 of 920
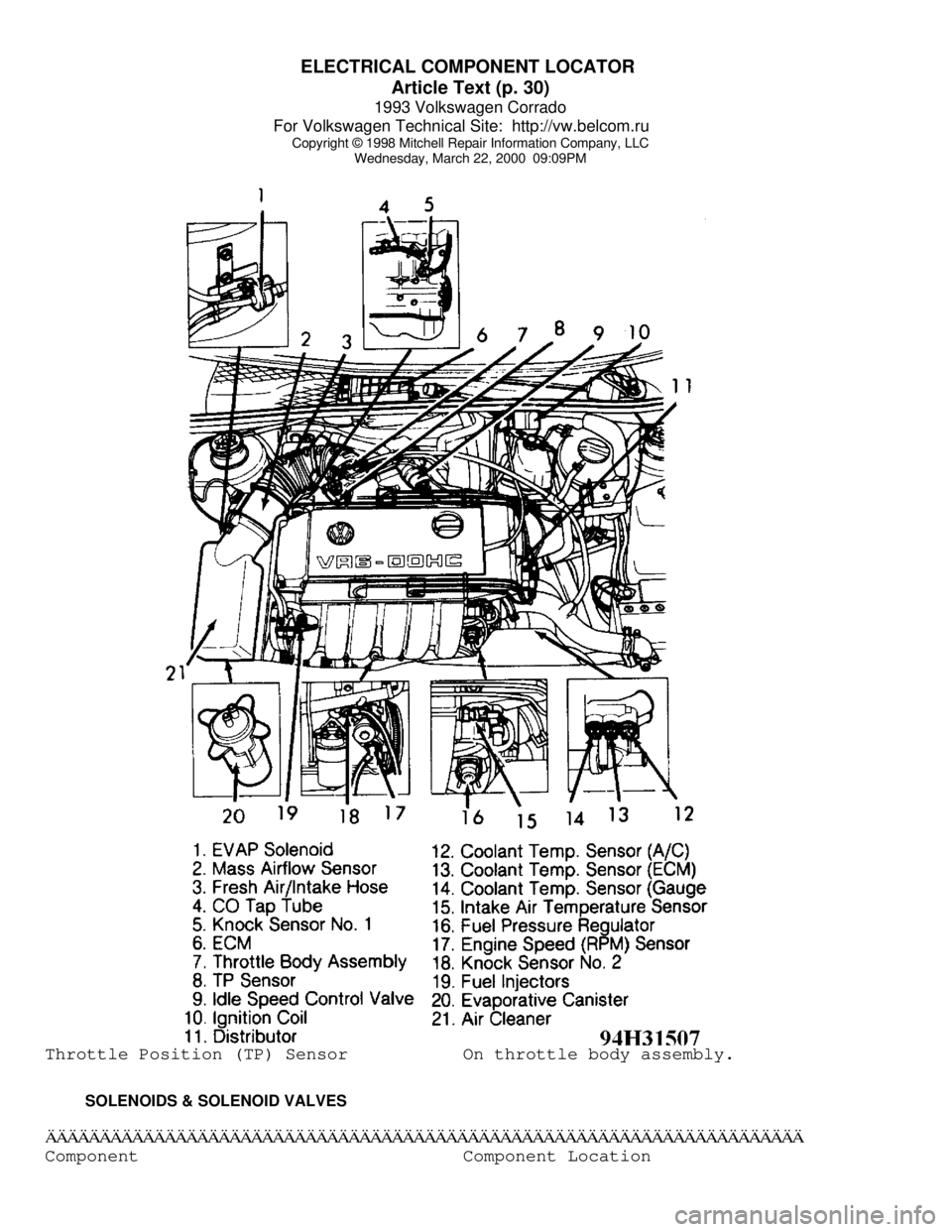
ELECTRICAL COMPONENT LOCATOR
Article Text (p. 30)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PMThrottle Position (TP) Sensor On throttle body assembly.
SOLENOIDS & SOLENOID VALVESÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄComponent Component Location
Page 489 of 920
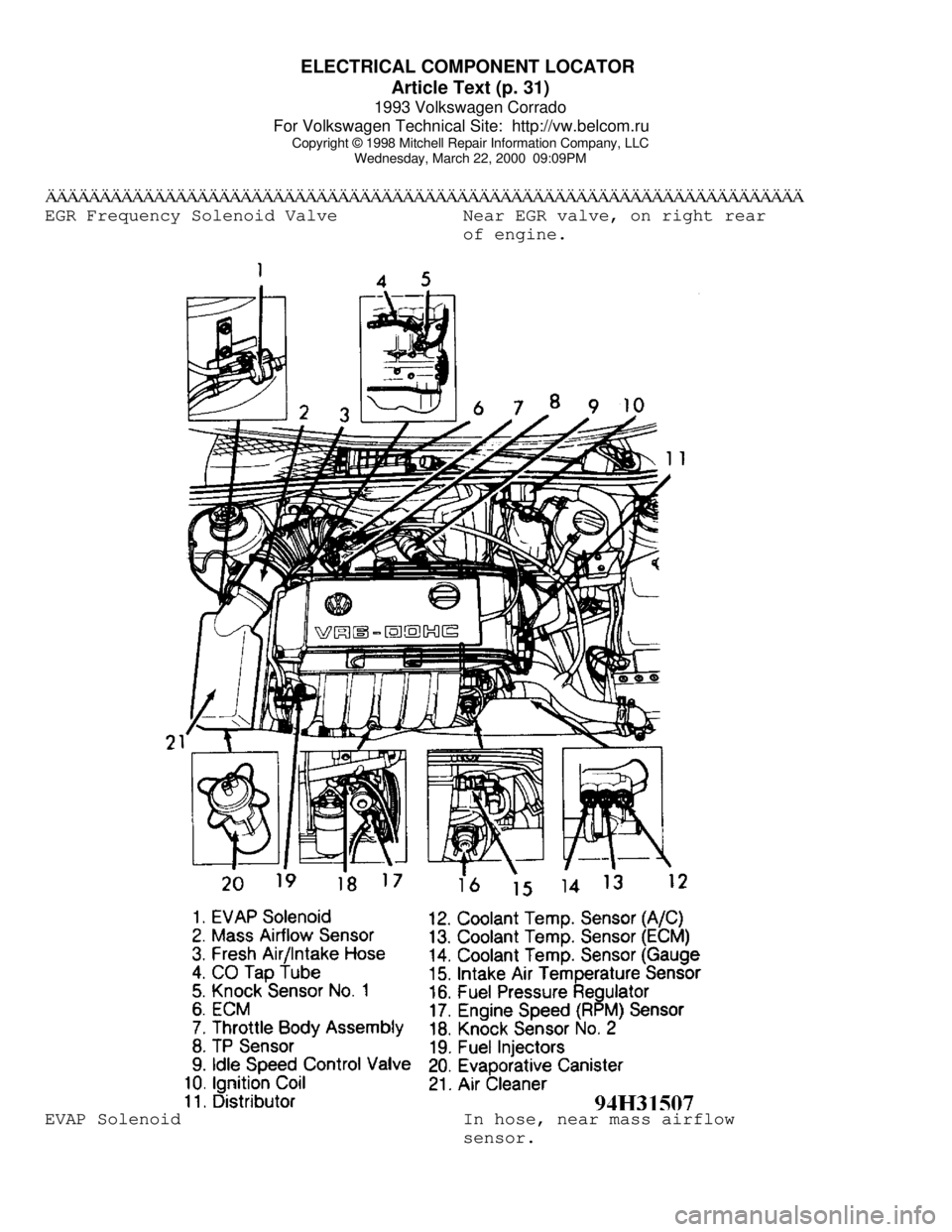
ELECTRICAL COMPONENT LOCATOR
Article Text (p. 31)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PMÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄEGR Frequency Solenoid Valve Near EGR valve, on right rear
of engine.EVAP Solenoid In hose, near mass airflow
sensor.
Page 494 of 920

D - ADJUSTMENTS
Article Text
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 08:59PM
ARTICLE BEGINNING
1993 ENGINE PERFORMANCE
On-Vehicle Adjustments
Corrado SLC
ENGINE MECHANICAL
Before performing any on-vehicle adjustments to fuel or
ignition systems, ensure engine mechanical condition is okay.
VALVE CLEARANCE
NOTE: All models use hydraulic lifters. No adjustments are
required.
IGNITION TIMING
NOTE: See ENTERING SELF-DIAGNOSTICS in the G - TESTS W/CODES
article in this section for additional scan tester
operating instructions.
VR6 IGNITION TIMING
1) Start and warm engine to normal operating temperature.
Ensure engine oil temperature is 176øF (80øC). Ensure A/C and
electrical loads are off, including cooling fan.
2) Connect engine analyzer to engine. Connect Scan Tester
(VAG 1551) to Data Link Connectors (DLC) located in center console, in
front of shift lever. Ensure no Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) are
stored.
3) Ensure throttle position sensor is properly adjusted.
Ensure idle air control valve is okay. Valve must vibrate or hum.
Connect CO tester using Adapter (VAG 1363/3) on CO tap tube. DO NOT
remove oxygen sensor. Ensure exhaust system has no leaks.
4) Start engine and let it run at closed throttle (less than
1500 RPM). Operate scan tester and observe display. Press "1" button
to select RAPID DATA TRANSFER function. Press "Q" button to enter
input. Press right arrow button.
5) Press "0" and "1" buttons to select ENGINE ELECTRONICS
function. Press "Q" button to enter input. Press right arrow button,
then "0" and "4" buttons to select BASIC SETTING function. Press "Q"
button to enter input.
6) Press "0" and "1" buttons to select INPUT DISPLAY GROUP
NUMBER 01. Press "Q" button to enter input. Scan tester will display
SYSTEM IN BASIC ADJUSTMENT 1 through 4. Briefly increase engine speed
and then let it run for 2 minutes at closed throttle. Scan tester
displays idle speed in field one and ignition timing in field four.
Check CO level on CO tester.
7) When radiator cooling fan stops running, end basic setting
Page 495 of 920

D - ADJUSTMENTS
Article Text (p. 2)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 08:59PM
function by pressing right arrow button. Press "0" and "6" for END
OUTPUT function. Press "Q" button to enter input.
8) If idle speed, CO level or ignition timing is incorrect,
turn ignition off. Check accelerator pedal and throttle cable for ease
of operation. Check dashpot adjustment. Check throttle position
sensor, idle air control valve, and EGR valve.
IDLE SPEED & MIXTURE
NOTE: Mixture adjustment is NOT a part of normal tune-up procedure
and should not be performed unless mixture control unit is
replaced or vehicle fails emissions testing.
NOTE: Ensure fuel system pressure is correct before attempting
idle speed or mixture adjustment.
VR6 IDLE SPEED & MIXTURE ADJUSTMENT
See VR6 IGNITION TIMING under IGNITION TIMING near the
beginning of this article.
THROTTLE BODY
THROTTLE BODY ADJUSTMENT
CAUTION: Throttle limiting (stop) screw is set by manufacturer and
should NOT be moved. If screw is accidentally turned,
perform throttle body adjustment.
If stop screw for basic throttle adjustment has been moved,
replace throttle body.
DASHPOT
Open and close throttle until dashpot piston contacts roller.
With throttle in this position, check gap between limiter (stop) screw
and throttle. Gap between limiter (stop) screw and throttle lever must
be 0.10-0.14" (2.5-3.5 mm).
IDLE & FULL THROTTLE SWITCHES
THROTTLE POSITION (TP) SENSOR ADJUSTMENT
1) Connect Scan Tester (VAG 1551) to Data Link Connectors
(DLC) located in center console, in front of shift lever. Turn
ignition on. Operate scan tester and select RAPID DATA TRANSFER,
ENGINE ELECTRONICS, then READ MEASURING VALUE BLOCK functions.
2) Press "0" and "3" buttons to select INSERT DISPLAY GROUP
NUMBER 03 function. Press "Q" button to enter input. Slowly open
throttle, while observing display in channel 3, until throttle is wide
open. Numerical value must increase uniformly over entire opening
Page 496 of 920

D - ADJUSTMENTS
Article Text (p. 3)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 08:59PM
range and without interruption.
3) Reading should be 5-19 at idle. Reading should be 94-100
at full throttle stop. If readings are correct, press right arrow
button. Press "0" and "6" to select ENDING OUTPUT function. Press "Q"
button to enter input. If readings are incorrect, check TP sensor
circuit or replace TP sensor as necessary.
END OF ARTICLE
Page 506 of 920

E - THEORY/OPERATION
Article Text
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PM
ARTICLE BEGINNING
1993 ENGINE PERFORMANCE
Volkswagen Theory & Operation - Motronic
Corrado SLC
INTRODUCTION
This article covers basic description and operation of engine
performance-related systems and components. Read this article before
diagnosing vehicles or systems with which you are not completely
familiar.
COMPUTERIZED ENGINE CONTROLS
ELECTRONIC CONTROL UNIT
The Motronic engine management system uses a single
Electronic Control Module (ECM) for fuel injection, idle speed
control, ignition, and emission controls. The Electronic Control
Module (ECM) continually corrects air/fuel mixture based on signals
from various signals. The ECM is located underneath center of
windshield cowl, directly behind engine compartment firewall.
NOTE: Components are grouped into 2 categories. The first category
covers INPUT DEVICES, which control or produce voltage
signals monitored by the control unit. The second category
covers OUTPUT SIGNALS, which are components controlled by
the control unit.
INPUT DEVICES
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Sensor is located on thermostat housing. As engine coolant
temperature increases, the resistance of the sensor decreases. Engine
coolant temperature sensor signals are used for control of ignition
timing, injector pulse width, and idle speed stabilization. In
addition, knock sensors, idle speed control, oxygen sensor and fuel
tank venting are activated based on coolant temperature.
Engine Speed (RPM)/Reference Sensor
Engine speed (RPM) and crankshaft position are registered by
a single sensor located on side of engine block. The sensor reads a
toothed wheel mounted on the crankshaft. The wheel has a 2-tooth gap
which is used as a reference point for crankshaft position. The engine
speed/reference signal is used to monitor engine RPM and to identify
TDC position of cylinder No. 1.
Hall Effect Sensor
See ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM under IGNITION SYSTEM in this
Page 507 of 920

E - THEORY/OPERATION
Article Text (p. 2)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PM
article.
NOTE: For component locations, see Fig. 1.Fig. 1: Motronic Component Locations (Corrado SLC)
Courtesy of Volkswagen United States, Inc.
Intake Air Temperature Sensor
Intake air temperature sensor is located on side of intake
manifold. The signal from this sensor is used for idle stabilization
and as a correction factor for ignition timing. If intake air
temperature sensor fails, the ECM uses a temperature of 68øF (20øC) as
a substitute value. If this happens, cold start problems could occur
at temperatures less than 32
øF (0øC).
Knock Sensor(s)
See IGNITION TIMING CONTROL under IGNITION SYSTEM in this
article.
Page 508 of 920

E - THEORY/OPERATION
Article Text (p. 3)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PM
Mass Airflow Sensor
A hot-wire air mass sensor is used to measure airflow into
the engine. The sensor is attached to air filter housing. The hot-wire
in sensor is kept at 356øF (180øC) above air temperature.
As airflow increases, the wire is cooled and the resistance
of the sensor changes. The resulting current change is converted to a
voltage signal and is used by the ECM to calculate the volume of air
taken in.
If a fault develops with mass airflow sensor signal, the
signal from throttle valve potentiometer is used as a substitute in
order for the car to be driveable.
Throttle Valve Potentiometer
Throttle valve potentiometer (throttle position sensor) is
connected to throttle valve shaft. It informs the ECM about the power
requested by the driver (throttle opening). Idle and full throttle
switches are NOT used in potentiometer. Idle speed and full throttle
applications are recognized by the ECM from the voltage output of the
potentiometer.
Throttle valve potentiometer signals are used for idle speed
stabilization, idle air volume control, fuel after-run shut-off, and
full throttle enrichment. The ECM uses mass airflow sensor signal and
engine RPM signals as substitute values if the potentiometer fails.
NOTE: On automatic transmission equipped vehicles, the throttle
valve potentiometer is combined in the housing with the
potentiometer for transmission control.
Oxygen (O2) Sensor
The heated oxygen sensor is made from zirconium dioxide,
while the inner and outer surfaces are coated with platinum. If fuel
mixture is lean (excess oxygen), the oxygen sensor will send a low
voltage signal (about 100 millivolts) to the ECM. If fuel mixture is
rich (lack of oxygen), the oxygen sensor will send a high voltage
signal (about 900 millivolts) to the ECM.
OUTPUT SIGNALS
NOTE: Vehicles are equipped with different combinations of
computer-controlled components. Not all components listed
below are used on every vehicle. For theory and operation on
each output component, refer to the system indicated after
component.
EGR Frequency Valve
See EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM under EMISSION
SYSTEMS in this article.
Fuel Evaporative (Frequency) Valve
See FUEL EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS SYSTEM under EMISSION SYSTEMS
in this article.
Page 510 of 920

E - THEORY/OPERATION
Article Text (p. 5)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PM
NOTE: Corrado SLC models are equipped with a Distributorless
Ignition System (DIS).
ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM
The electronic ignition system consists of ECM, power output
stage, ignition coil, distributor, mass airflow sensor, throttle valve
potentiometer, engine coolant temperature sensor, and Hall Effect
sensor.
Ignition system uses engine speed, engine load, and throttle
valve potentiometer signals to calculate ignition timing. Engine
coolant temperature signal is used to correct ignition timing when
engine is cold and to activate knock sensor circuit. See KNOCK
SENSOR(S) under IGNITION TIMING CONTROL in this article.
Hall Effect Sensor
On Corrado SLC, this sensor is mounted on end of camshaft
(near ignition coil). Sensor consists of a magnetic enclosure and
integrated semi-conductor circuit. A voltage signal is generated when
trigger wheel, turning at camshaft speed, interrupts magnetic field
created by the semi-conductor. Hall Effect sensor and engine
speed/reference signals are used to identify TDC position of cylinder
No. 1 for sequential fuel injection and spark knock regulation.
DISTRIBUTORLESS IGNITION SYSTEM (DIS)
Hall Effect Sensor
See HALL EFFECT SENSOR under ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM in
this article.
Ignition Coil & Output Stage
The distributorless (direct) ignition system consists of ECM,
power output stage, 3 double-ended ignition coils and secondary
ignition wires. The ECM operates each ignition coil through the power
output stage. The power output stage and heat sink are located behind
ignition coils. The ignition coils are located on left side of
cylinder head. When the power output stage fires an ignition coil, a
spark is supplied to 2 spark plugs at one time. One spark plug fires
during the compression stroke, and the other spark plug fires during
the exhaust stroke (waste spark).
IGNITION TIMING CONTROL
Knock Sensor(s)
The knock sensor(s) work(s) like a microphone to "listen" for
spark knock (detonation). When detonation occurs, ignition timing is
retarded until the knock is eliminated.
On Corrado SLC, 2 knock sensors are mounted on side of engine
block. Knock sensor I monitors cylinders No. 1, 3 and 5. Knock sensor
II monitors cylinders No. 2, 4 and 6.