YAMAHA WR 450F 2005 Owners Manual
Manufacturer: YAMAHA, Model Year: 2005, Model line: WR 450F, Model: YAMAHA WR 450F 2005Pages: 758, PDF Size: 17.3 MB
Page 391 of 758

ENG
4 - 45
ZYLINDER UND KOLBEN
ZYLINDER UND KOLBEN
Arbeitsumfang:
1 Zylinder demontieren
2 Kolben demontieren
ArbeitsumfangReihen-
folgeBauteil Anz. Bemerkungen
ZYLINDER UND KOLBEN DEMONTIE-
REN
Vorbereitungsarbeiten Zylinderkopf Siehe unter “ZYLINDERKOPF”.
1 Zylinder-Schraube 1
2 Zylinder 1
3 Dichtung 1
4Paßhülse 2
5Paßhülse/O-Ring 1/1
6 Kolbenbolzen-Sicherungsring 2
Spezialwerkzeug verwenden.
Siehe unter “DEMONTAGE-EINZELHEITEN”. 7 Kolbenbolzen 1
8 Kolben 1
9 Kolbenringsatz 1
2
1
CYLINDRE ET PISTON
CYLINDRE ET PISTON
Organisation de la dépose:1 Dépose du cylindre2 Dépose du piston
Organisation de la dépose Ordre Nom de la pièce QtéRemarques
DEPOSE DES CYLINDRES ET DES PIS-
TONS
Préparation à la dépose Culasse Se reporter à la section “CULASSE”.
1 Boulon (cylindre) 1
2 Cylindre 1
3 Joint 1
4Goujon 2
5 Goujon /joint torique 1/1
6 Agrafe d’axe de piston 2
Utiliser l’outil spécial.
Se reporter à “POINTS DE DEPOSE”. 7 Axe de piston 1
8 Piston 1
9 Segments de piston 1
2
1
CILINDRO Y PISTÓN
CILINDRO Y PISTÓN
Extensión del desmontaje:1 Desmontaje del cilindro2 Desmontaje del pistón
Extensión del desmontaje Orden Nombre de la pieza Ctd. Observaciones
DESMONTAJE DEL CILINDRO Y EL
PISTÓN
Preparación para el desmontaje Culata Consulte el apartado “CULATA”.
1 Tornillo (cilindro) 1
2 Cilindro 1
3Junta 1
4 Clavija de centrado 2
5 Clavija de centrado/junta tórica 1/1
6 Clip del pasador de pistón2
Utilice la herramienta especial.
Consulte el apartado “PUNTOS DE DESMONTAJE”. 7 Pasador del pistón1
8Pistón1
9 Conjunto de aros de pistón1
2
1
CYLINDRE ET PISTON
ZYLINDER UND KOLBEN
CILINDRO Y PISTÓN
Page 392 of 758
4 - 46
ENGCYLINDER AND PISTON
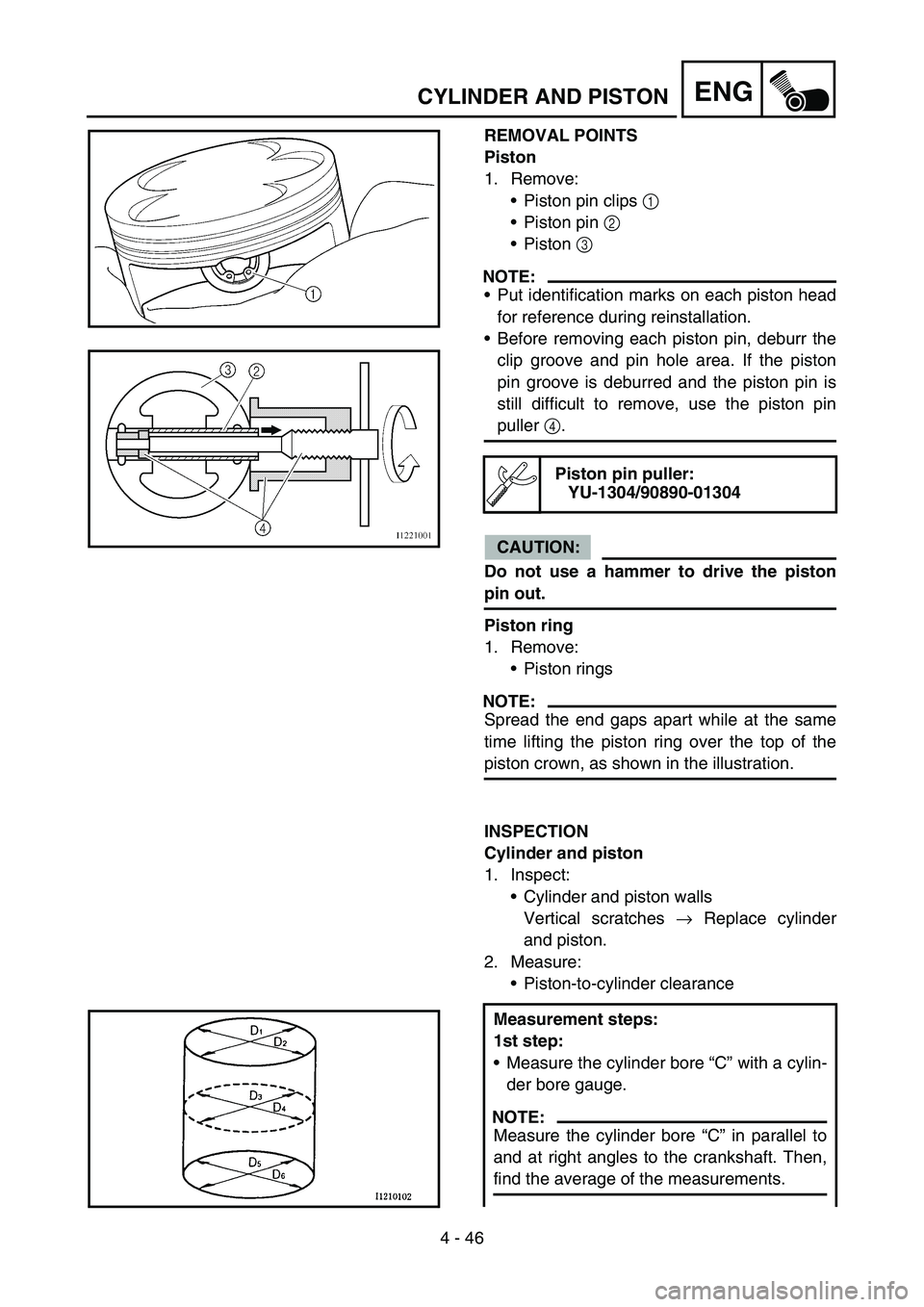
REMOVAL POINTS
Piston
1. Remove:
Piston pin clips 1
Piston pin 2
Piston 3
NOTE:
Put identification marks on each piston head
for reference during reinstallation.
Before removing each piston pin, deburr the
clip groove and pin hole area. If the piston
pin groove is deburred and the piston pin is
still difficult to remove, use the piston pin
puller 4.
CAUTION:
Do not use a hammer to drive the piston
pin out.
Piston ring
1. Remove:
Piston rings
NOTE:
Spread the end gaps apart while at the same
time lifting the piston ring over the top of the
piston crown, as shown in the illustration.
INSPECTION
Cylinder and piston
1. Inspect:
Cylinder and piston walls
Vertical scratches → Replace cylinder
and piston.
2. Measure:
Piston-to-cylinder clearance
Piston pin puller:
YU-1304/90890-01304
Measurement steps:
1st step:
Measure the cylinder bore “C” with a cylin-
der bore gauge.
NOTE:
Measure the cylinder bore “C” in parallel to
and at right angles to the crankshaft. Then,
find the average of the measurements.
Page 393 of 758

ENG
4 - 46
DEMONTAGE-EINZELHEITEN
Kolben
1. Demontieren:
Kolbenbolzen-Sicherungs-
ringe
1
Kolbenbolzen
2
Kolben
3
HINWEIS:
Die Kolbenböden für den späteren
Wiedereinbau markieren.
Vor dem Ausbau des Kolbenbol-
zens den Bereich der Sicherungs-
ring-Nut und des
Kolbenbolzenauges entgraten.
Läßt sich der Kolbenbolzen auch
danach nur schwer lösen, den Kol-
benbolzen-Abzieher
4 verwen-
den.
ACHTUNG:
Den Kolbenbolzen unter keinen
Umständen mit einem Hammer
austreiben.
Kolbenringe
1. Demontieren:
Kolbenringe
HINWEIS:
Wie in der Abbildung gezeigt, die
Ringenden spreizen und dabei den
Kolbenring hochschieben.
KONTROLLE
Zylinder und Kolben
1. Kontrollieren:
Zylinder und Kolbenhemd
In Laufrichtung riefig
→ Zylin-
der und Kolben erneuern.
2. Messen:
Kolben-Laufspiel
Kolbenbolzen-Abzieher:
YU-1304/90890-01304
Arbeitsvorgang:
1. Schritt:
Die Zylinderbohrung “C” mit
einer Innenmeßschraube mes-
sen.
HINWEIS:
Die Zylinderbohrung “C” sowohl
parallel als auch im rechten Win-
kel zur Kurbelwelle messen.
Anschließend den Durchschnitt
der gemessenen Werte ermitteln.
POINTS DE DEPOSE
Piston
1. Déposer:
Agrafes d’axes de pistons 1
Axe de piston 2
Piston 3
N.B.:
Placer des repères d’identification sur
chaque tête de piston comme référence
pour la repose.
Avant de retirer chaque axe de piston,
ébavurer la gorge de l’agrafe et le
pourtour du trou de l’axe. Si la gorge
de l’axe de piston est ébavurée et que
l’axe du piston reste difficile à déga-
ger, utiliser l’extracteur d’axe de pis-
ton 4.
ATTENTION:
Ne pas employer de marteau pour
chasser l’axe de piston.
Segment de piston
1. Déposer:
Segments de piston
N.B.:
Ecarter les coupes du segment tout en
soulevant le segment de piston par des-
sus la calotte du piston, comme illustré.
CONTROLE
Cylindre et piston
1. Contrôler:
Parois du cylindre et du piston
Rayures verticales → Remplacer
le cylindre et le piston.
2. Mesurer:
Jeu entre piston et cylindre
Extracteur d’axe de piston:
YU-1304/90890-01304
Etapes de la mesure:
1ère étape:
Mesurer l’alésage de cylindre “C”
à l’aide d’un comparateur à cadran
pour cylindre.
N.B.:
Mesurer l’alésage du cylindre “C”
parallèlement et perpendiculairement
à l’arbre à cames. Calculer ensuite la
moyenne de ces mesures.
PUNTOS DE DESMONTAJE
Pistón
1. Extraer:
Clips del pasador de pistón 1
Pasador del pistón2
Pistón 3
NOTA:
Haga marcas de identificación en cada
cabeza de pistón como referencia para
el posterior montaje.
Antes de extraer el pasador de pistón,
desbarbe el surco del clip y la zona del
orificio del pasador. Si el surco del
pasador del pistón está desbarbado
pero sigue siendo difícil extraer el
pasador, utilice el extractor del pasa-
dor de pistón 4.
ATENCION:
No utilice un martillo para extraer el
pasador del pistón.
Aro de pistón
1. Extraer:
Aros del pistón
NOTA:
Separe los extremos levantando al
mismo tiempo el aro por encima de la
corona del pistón como se muestra en la
ilustración.
COMPROBACIÓN
Cilindro y pistón
1. Comprobar:
Cilindro y paredes del pistón
Rayaduras verticales → Cambiar
el cilindro y el pistón.
2. Medir:
Holgura entre pistón y cilindro
Extractor de pasador de
pistón:
YU-1304/90890-01304
Procedimiento de medición:
1er paso:
Mida el diámetro del cilindro “C”
con un medidor de diámetro de
cilindros.
NOTA:
Mida el diámetro del cilindro “C”
paralelo y perpendicular al cigüeñal.
Seguidamente calcule el promedio de
las mediciones.
CYLINDRE ET PISTON
ZYLINDER UND KOLBEN
CILINDRO Y PISTÓN
Page 394 of 758

4 - 47
ENGCYLINDER AND PISTON
Cylinder bore “C”95.00 ~ 95.01 mm
(3.7402 ~ 3.7406 in)
Taper limit “T”0.05 mm (0.002 in)
Out of round “R”0.05 mm (0.002 in)
“C” = Maximum D
“T” = (Maximum D
1 or D2)
– (Maximum D
5 or D6)
“R” = (Maximum D
1, D3 or D5)
– (Minimum D2, D4 or D6)
If out of specification, replace the cylinder,
and replace the piston and piston rings as
set.
2nd step:
Measure the piston skirt diameter “P” with
a micrometer.
a
8 mm (0.315 in) from the piston bottom edge
Piston size “P”
Standard94.945 ~ 94.960 mm
(3.738 ~ 3.739 in)
If out of specification, replace the piston
and piston rings as a set.
3rd step:
Calculate the piston-to-cylinder clearance
with following formula:
Piston-to-cylinder clearance =
Cylinder bore “C” –
Piston skirt diameter “P”
Piston-to-cylinder clearance:
0.040 ~ 0.065 mm
(0.0016 ~ 0.0026 in)
If out of specification, replace the cylinder,
and replace the piston and piston rings as
set.
Page 395 of 758

ENG
4 - 47
Zylinderboh-
rung “C”95,00–95,01 mm
(3,7402–
3,7406 in)
Max. Konizität
“T”0,05 mm
(0,002 in)
Max. Ovalität
“R”0,05 mm
(0,002 in)
“C” = größtes Maß unter D
“T” = (größtes Maß unter D
1
und D2) – (größtes Maß unter D5
und D6)
“R” = (größtes Maß unter D
1, D3
und D5) – (kleinstes Maß unter
D2, D4 und D6)
Falls nicht nach Vorgabe, Zylin-
der sowie Kolben und Kolben-
ringe erneuern.
2. Schritt:
Den Kolbenschaft-Durchmes-
ser “P” mit einer Bügelmeß-
schraube messen.
a8 mm (0,315 in) oberhalb der
Unterkante
Kolbengröße
“P”
Sollwert94,945–
94,960 mm
(3,738–3,739 in)
Falls nicht nach Vorgabe, Kol-
ben samt Kolbenringen erneu-
ern.
3. Schritt:
Das Kolben-Laufspiel nach fol-
gender Formel ermitteln:
Kolben-Laufspiel =
Zylinderbohrung “C” -
Kolbenschaft-Durchmes-
ser “P”
Kolben-Laufspiel:
0,040–0,065 mm
(0,0016–0,0026 in)
0,1 mm (0,004 in)
Falls nicht nach Vorgabe, Zylin-
der sowie Kolben und Kolben-
ringe erneuern.
Alésage de cylin-
dre “C”95,00 à 95,01 mm
(3,7402 à 3,7406 in)
Limite de coni-
cité “T”0,05 mm (0,002 in)
Ovalisation “R”0,05 mm (0,002 in)
“C” = D maximum
“T” = (D
1 ou D2 maximum)
– (D5 ou D6 maximum)
“R” = (D
1, D3 ou D5 maximum) – (D2, D4 ou D6 minimum)
Si le résultat est hors spécifica-
tions, remplacer le cylindre et rem-
placer ensemble le piston et les
segments de piston.
2ème étape:
Mesurer le diamètre “P” de la jupe
de piston à l’aide d’un palmer.
a
8 mm (0,315 in) depuis le bord infé-
rieur du piston
Taille du piston
“P”
Standard94,945 à
94,960 mm
(3,738 à 3,739 in)
Si hors spécifications, remplacer
ensemble le piston et les segments
de piston.
3ème étape:
Calculer le jeu entre piston et
cylindre au moyen de la formule
suivante:
Jeu entre piston et cylindre =
Alésage de cylindre “C” –
Diamètre de la jupe de piston
“P”
Jeu entre piston et cylindre:
0,040 à 0,065 mm
(0,0016 à 0,0026 in)
0,1 mm (0,004 in)
Si le résultat est hors spécifica-
tions, remplacer le cylindre et rem-
placer ensemble le piston et les
segments de piston.
Diámetro del
cilindro “C”95,00 ~ 95,01 mm
(3,7402 ~ 3,7406 in)
Límite de conici-
dad “T”0,05 mm (0,002 in)
Ovalización “R”0,05 mm (0,002 in)
“C” = Máximo D
“T” = (Máximo D
1 o D2)
– (máximo D5 o D6)
“R” = (máximo D
1, D3 o D5) – (mínimo D2, D4 o D6)
Si está fuera del valor especificado,
cambie el cilindro y cambie el con-
junto de pistón y aros.
2º paso:
Mida el diámetro de la superficie
lateral del pistón “P” con un micró-
metro.
a
8 mm (0,315 in) desde el borde infe-
rior del pistón
Tamaño del pis-
tón “P”
Estándar94,945 ~
94,960 mm
(3,738 ~ 3,739 in)
Si está fuera del valor especificado
cambie el conjunto de pistón y
aros.
3er paso:
Calcule la holgura de pistón a
cilindro con la fórmula siguiente:
Holgura entre pistón y cilindro =
Diámetro del cilindro “C” –
Diámetro de la superficie late-
ral del pistón “P”
Holgura entre pistón y
cilindro:
0,040 ~ 0,065 mm
(0,0016 ~ 0,0026 in)
0,1 mm (0,004 in)
Si está fuera del valor especificado,
cambie el conjunto de cilindro, pis-
tón y aros.
CYLINDRE ET PISTON
ZYLINDER UND KOLBEN
CILINDRO Y PISTÓN
Page 396 of 758

4 - 48
ENGCYLINDER AND PISTON
Piston ring
1. Measure:
Ring side clearance
Use a feeler gauge 1.
Out of specification → Replace the piston
and rings as a set.
NOTE:
Clean carbon from the piston ring grooves and
rings before measuring the side clearance.
2. Position:
Piston ring
(in cylinder)
NOTE:
Insert a ring into the cylinder and push it
approximately 10 mm (0.39 in) into the cylin-
der. Push the ring with the piston crown so that
the ring will be at a right angle to the cylinder
bore.
a10 mm (0.39 in)
Side clearance:
Standard
Top ring0.030 ~ 0.065 mm
(0.0012 ~ 0.0026 in)0.12 mm
(0.005 in)
2nd ring0.020 ~ 0.055 mm
(0.0008 ~ 0.0022 in)0.12 mm
(0.005 in)
3. Measure:
Ring end gap
Out of specification → Replace.
NOTE:
You cannot measure the end gap on the
expander spacer of the oil control ring. If the oil
control ring rails show excessive gap, replace
all three rings.
End gap:
Standard
Top ring0.20 ~ 0.30 mm
(0.008 ~ 0.012 in)0.55 mm
(0.022 in)
2nd ring0.35 ~ 0.50 mm
(0.014 ~ 0.020 in)0.85 mm
(0.033 in)
Oil ring0.20 ~ 0.50 mm
(0.01 ~ 0.02 in)—
Page 397 of 758

ENG
4 - 48
Kolbenringe
1. Messen:
Ringnutspiel
Eine Fühlerlehre
1 verwen-
den.
Nicht nach Vorgabe
→ Kolben
samt Kolbenringen erneuern.
HINWEIS:
Vor der Messung des Ringnutspiels
müssen die Ölkohleablagerungen
von den Kolbenringen und Ringnuten
entfernt werden.
2. Anordnen:
Kolbenringe
(im Zylinder)
HINWEIS:
Den Kolbenring ca.10 mm (0,39 in) in
den Zylinder einschieben. Den Kol-
benring mit dem Kolbenboden in die
Zylinderbohrung schieben, so daß
der Ring rechtwinklig im Zylinder
sitzt.
a10 mm (0,39 in)
Ringnutspiel:
Sollwert
1. Kom-
pressi-
onsring
(Topring)0,030–0,065 mm
(0,0012–
0,0026 in)0,12 mm
(0,005 in)
2. Kom-
pressi-
onsring
0,020–0,055 mm
(0,0008–
0,0022 in)0,12 mm
(0,005 in)
3. Messen:
Kolbenring-Stoß
Nicht nach Vorgabe
→ Erneu-
ern.
HINWEIS:
Der Stoß der Ölabstreifring-Expan-
derfeder kann nicht gemessen wer-
den. Wenn der Stoß der
Ölabstreifschneiden nicht im Sollbe-
reich liegt, müssen alle Kolbenringe
erneuert werden.
Ringstoß:
Sollwert
1. Kom-
pressi-
onsring
(Topring)0,20–0,30 mm
(0,008–0,012 in)0,55 mm
(0,022 in)
2. Kom-
pressi-
onsring0,35–0,50 mm
(0,014–0,020 in)0,85 mm
(0,033 in)
Ölab-
streifring0,20–0,50 mm
(0,01–0,02 in)—
Segment de piston
1. Mesurer:
Jeu latéral du segment
Utiliser une jauge d’épaisseur à
lames 1.
Hors spécifications → Remplacer
ensemble le piston et les seg-
ments de piston.
N.B.:
Eliminer les dépôts de calamine des gor-
ges des segments de piston et des seg-
ments avant de mesurer le jeu latéral.
2. Position:
Segment de piston
(dans le cylindre)
N.B.:
Insérer un segment dans le cylindre et
l’enfoncer d’environ 10 mm (0,39 in).
Enfoncer le segment à l’aide de la calotte
de piston de manière que le segment
fasse un angle droit avec l’alésage du
cylindre.
a
10 mm (0,39 in)
Jeu latéral:
Standard
Segment
de feu
0,030 à 0,065 mm
(0,0012 à
0,0026 in)0,12 mm
(0,005 in)
Segment
d’étan-
chéité0,020 à 0,055 mm
(0,0008 à
0,0022 in)0,12 mm
(0,005 in)
3. Mesurer:
Coupe de segment
Hors spécifications → Rempla-
cer.
N.B.:
Il n’est pas possible de mesurer la coupe
de la bague extensible du segment
racleur d’huile. Si les rails du segment
racleur d’huile présentent un jeu exces-
sif, remplacer les trois segments.
Coupe:
Standard
Segment
de feu
0,20 à 0,30 mm
(0,008 à 0,012 in)0,55 mm
(0,022 in)
Segment
d’étan-
chéité0,35 à 0,50 mm
(0,014 à 0,020 in)0,85 mm
(0,033 in)
Segment
racleur
d’huile0,20 à 0,50 mm
(0,01 à 0,02 in)—
Aro de pistón
1. Medir:
Holgura lateral del aro
Utilice una galga palpadora 1.
Fuera del valor especificado →
Cambiar el conjunto de pistón y
aros.
NOTA:
Limpie el carbón de los surcos de los
aros antes de medir la holgura lateral.
2. Situar:
Aro de pistón
(en cilindro)
NOTA:
Introduzca un aro en el cilindro y empú-
jelo aproximadamente 10 mm (0,39 in)
en el interior. Empuje el aro con la
corona del pistón de forma que el aro se
sitúe perpendicular al diámetro del cilin-
dro.
a
10 mm (0,39 in)
Holgura lateral:
Estándar
Aro supe-
rior
0,030 ~ 0,065 mm
(0,0012 ~
0,0026 in) 0,12 mm
(0,005 in)
2º aro0,020 ~ 0,055 mm
(0,0008 ~
0,0022 in) 0,12 mm
(0,005 in)
3. Medir:
Distancia entre extremos de aro
de pistón
Fuera del valor especificado →
Cambiar.
NOTA:
No se puede medir la distancia entre
extremos de aro de pistón en el espacia-
dor expansor del aro de engrase. Si los
surcos del aro de engrase tienen una hol-
gura excesiva, cambie los tres aros.
Distancia entre extremos de
aro de pistón:
Estándar
Aro supe-
rior
0,20 ~ 0,30 mm
(0,008 ~ 0,012 in)0,55 mm
(0,022 in)
2º aro0,35 ~ 0,50 mm
(0,014 ~ 0,020 in)0,85 mm
(0,033 in)
Aro de
engrase0,20 ~ 0,50 mm
(0,01 ~ 0,02 in)—
CYLINDRE ET PISTON
ZYLINDER UND KOLBEN
CILINDRO Y PISTÓN
Page 398 of 758

4 - 49
ENGCYLINDER AND PISTON
Piston pin
1. Inspect:
Piston pin
Blue discoloration/grooves → Replace,
then inspect the lubrication system.
2. Measure:
Piston pin-to-piston clearance
ASSEMBLY AND INSTALLATION
Piston
1. Install:
Piston rings
Onto the piston.
NOTE:
Be sure to install the piston rings so that the
manufacturer’s marks or numbers are
located on the upper side of the rings.
Lubricate the piston and piston rings liberally
with engine oil. Measurement steps:
Measure the outside diameter (piston pin)
a.
If out of specification, replace the piston
pin.
Outside diameter (piston pin):
17.991 ~ 18.000 mm
(0.7083 ~ 0.7087 in)
Measure the inside diameter (piston) b.
Inside diameter (piston):
18.004 ~ 18.015 mm
(0.7088 ~ 0.7093 in)
Calculate the piston pin-to-piston clear-
ance with the following formula.
Piston pin-to-piston clearance =
Inside diameter (piston)
b –
Outside diameter (piston pin)
a
If out of specification, replace the piston.
Piston pin-to-piston clearance:
0.004 ~ 0.024 mm
(0.00016 ~ 0.00094 in)
Page 399 of 758

ENG
4 - 49
Kolbenbolzen
1. Kontrollieren:
Kolbenbolzen
Blaubrüchig/riefig
→ Kolben-
bolzen erneuern und Schmier-
system kontrollieren.
2. Messen:
Kolbenbolzen-Spiel
ZUSAMMENBAU UND MONTAGE
Kolben
1. Montieren:
Kolbenringe
(auf den Kolben)
HINWEIS:
Die Kolbenringe so einbauen, daß
die Herstellerangaben nach oben
gerichtet sind.
Den Kolben und die Kolbenringe
großzügig mit Motoröl bestreichen. Arbeitsvorgang:
Den Kolbenbolzen-Durchmes-
ser
a messen.
Falls nicht nach Vorgabe, den
Kolbenbolzen erneuern.
Kolbenbolzen-Durch-
messer:
17,991-18,000 mm
(0,7083–0,7087 in)
Den Kolbenbolzenaugen-Durch-
messer
b messen.
Kolbenbolzenaugen-
Durchmesser:
18,004–18,015 mm
(0,7088–0,7093 in)
Das Kolben-Laufspiel nach fol-
gender Formel ermitteln:
Kolbenbolzen-Spiel =
Kolbenbolzenaugen-
Durchmesser b –
Kolbenbolzen-Durchmesser a
Falls nicht nach Vorgabe, den
Kolben erneuern.
Kolbenbolzen-Spiel:
0,004–0,024 mm
(0,00016–0,00094 in)
0,07 mm (0,003 in)
Axe de piston
1. Contrôler:
Axe de piston
Décoloration bleue/rainures →
Remplacer, puis contrôler le sys-
tème de lubrification.
2. Mesurer:
Jeu entre axe de piston et piston
ASSEMBLAGE ET MONTAGE
Piston
1. Monter:
Segments de piston
Sur le piston.
N.B.:
Veiller à monter les segments de pis-
ton en plaçant les repères ou numéros
du fabricant du côté supérieur des seg-
ments.
Lubrifier généreusement le piston et
les segments à l’aide d’huile moteur. Etapes de la mesure:
Mesurer le diamètre extérieur (axe
de piston) a.
Si hors spécifications, remplacer
l’axe de piston.
Diamètre extérieur (axe de
piston):
17,991 à 18,000 mm
(0,7083 à 0,7087 in)
Mesurer le diamètre intérieur (pis-
ton) b.
Diamètre intérieur (pis-
ton):
18,004 à 18,015 mm
(0,7088 à 0,7093 in)
Calculer le jeu entre axe de piston
et piston au moyen de la formule
suivante.
Jeu entre axe de piston et piston =
Diamètre intérieur (piston) b –
Diamètre extérieur (axe de
piston) a
Si hors spécifications, remplacer le
piston.
Jeu entre axe de piston et
piston:
0,004 à 0,024 mm
(0,00016 à 0,00094 in)
0,07 mm (0,003 in)
Pasador del pistón
1. Comprobar:
Pasador del pistón
Decoloración azul/estrías →
Cambiar y luego comprobar el
sistema de engrase.
2. Medir:
Holgura entre pasador y pistón
MONTAJE E INSTALACIÓN
Pistón
1. Instalar:
Aros de pistón
En el pistón.
NOTA:
Verifique que los aros de pistón que-
den colocados con las marcas o núme-
ros del fabricante en la parte superior
de los aros.
Engrase el pistón y los aros con aceite
de motor abundante. Procedimiento de medición:
Mida el diámetro exterior (pasador
del pistón) a.
Si está fuera del valor especificado
cambie el pasador de pistón.
Diámetro exterior (pasa-
dor de pistón):
17,991 ~ 18,000 mm
(0,7083 ~ 0,7087 in)
Mida el diámetro interior (pistón)
b.
Diámetro interior (pistón):
18,004 ~ 18,015 mm
(0,7088 ~ 0,7093 in)
Calcule la holgura de pasador a
pistón con la fórmula siguiente:
Holgura entre pasador y pistón =
Diámetro interior (pistón) b –
Diámetro exterior (pasador de
pistón) a
Si está fuera del valor especificado
cambie el pistón.
Holgura entre pasador y
pistón:
0,004 ~ 0,024 mm
(0,00016 ~ 0,00094 in)
0,07 mm (0,003 in)
CYLINDRE ET PISTON
ZYLINDER UND KOLBEN
CILINDRO Y PISTÓN
Page 400 of 758

4 - 50
ENGCYLINDER AND PISTON
2. Position:
Top ring
2nd ring
Oil ring
Offset the piston ring end gaps as shown.
aTop ring end
b2nd ring end
cOil ring end (upper)
dOil ring
eOil ring end (lower)
45
135 135
a
b ced
3. Install:
Piston 1
Piston pin 2
Piston pin clips 3
NOTE:
Apply engine oil onto the piston pin and pis-
ton.
Be sure that the arrow mark
a on the piston
points to the exhaust side of the engine.
Before installing the piston pin clip, cover the
crankcase with a clean rag to prevent the
piston pin clip from falling into the crankcase.
Install the piston pin clips with their ends fac-
ing downward.
4. Lubricate:
Piston
Piston rings
Cylinder
NOTE:
Apply a liberal coating of engine oil.
Cylinder
1. Install:
Dowel pins
O-ring
Gasket 1
Cylinder 2
NOTE:
Install the cylinder with one hand while com-
pressing the piston rings with the other hand.
CAUTION:
Pass the timing chain
3 through the tim-
ing chain cavity.
Be careful not to damage the timing chain
guide
4 during installation.
2. Install:
Bolt (cylinder)
3New
New
New
T R..10 Nm (1.0 m · kg, 7.2 ft · lb)