check engine ACURA NSX 1997 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ACURA, Model Year: 1997, Model line: NSX, Model: ACURA NSX 1997Pages: 1503, PDF Size: 57.08 MB
Page 474 of 1503
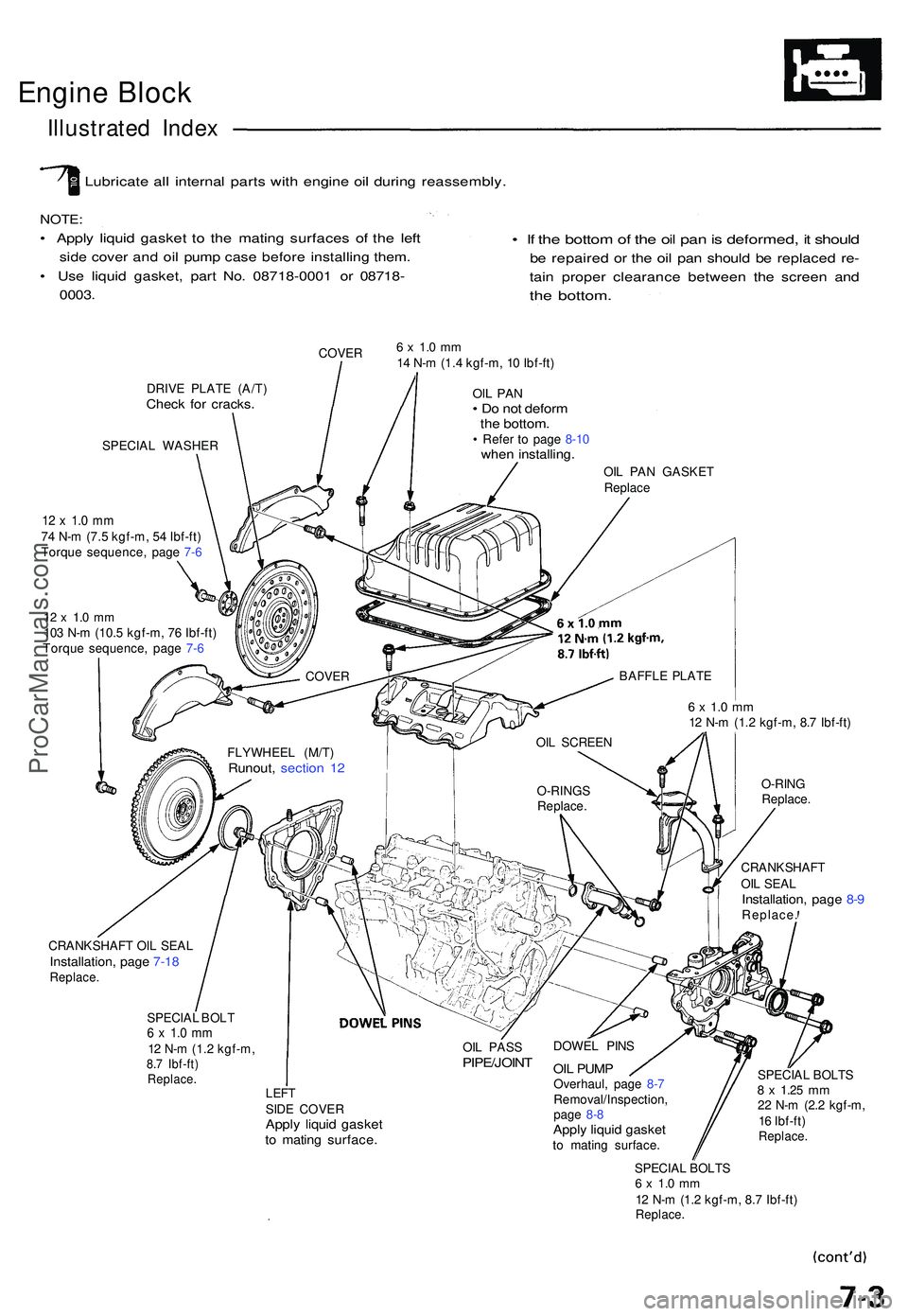
Engine Bloc k
Illustrate d Inde x
Lubricat e al l interna l part s wit h engin e oi l durin g reassembly .
NOTE:
• Appl y liqui d gaske t t o th e matin g surface s o f th e lef t
side cove r an d oi l pum p cas e befor e installin g them .
• Us e liqui d gasket , par t No . 0871 8-000 1 o r 0871 8-
0003 .
• I f th e botto m of th e oi l pa n is deformed , i t shoul d
be repaire d o r th e oi l pa n shoul d b e replace d re -
tain prope r clearanc e betwee n th e scree n an d
the bottom .
COVER
DRIV E PLAT E (A/T )
Check fo r cracks .
SPECIA L WASHER
12 x 1. 0 m m74 N- m (7. 5 kgf-m , 5 4 Ibf-ft )
Torqu e sequence , pag e 7- 6
12 x 1. 0 m m103 N- m (10. 5 kgf-m , 7 6 Ibf-ft )
Torqu e sequence , pag e 7- 6
6 x 1. 0 m m14 N- m (1. 4 kgf-m , 1 0 Ibf-ft )
OIL PA N• D o no t defor mthe bottom .• Refe r t o pag e 8-1 0whe n installing .
OIL PA N GASKE T
Replac e
6 x 1. 0 m m12 N- m (1. 2 kgf-m , 8. 7 Ibf-ft )
O-RIN G
Replace .
CRANKSHAF T
OI L SEA L
Installation , pag e 8- 9Replace .
CRANKSHAF T OI L SEA L
Installation , pag e 7-1 8Replace .
SPECIAL BOL T6 x 1. 0 m m12 N- m (1. 2 kgf-m ,8.7 Ibf-ft )Replace .
OIL PAS SPIPE/JOIN T
LEFTSIDE COVE RApply liqui d gaske tto matin g surface .
DOWEL PIN S
OIL PUM POverhaul , pag e 8- 7
Removal/Inspection ,
pag e 8- 8
Appl y liqui d gaske tto matin g surface . SPECIA
L BOLT S
8 x 1.2 5 mm22 N- m (2. 2 kgf-m ,
1 6 Ibf-ft )
Replace .
SPECIAL BOLT S6 x 1. 0 m m12 N- m (1. 2 kgf-m , 8. 7 Ibf-ft )Replace .
FLYWHEE L (M/T )Runout , sectio n 1 2
COVE R
OIL SCREE N
O-RING S
Replace .BAFFL
E PLAT E
ProCarManuals.com
Page 501 of 1503
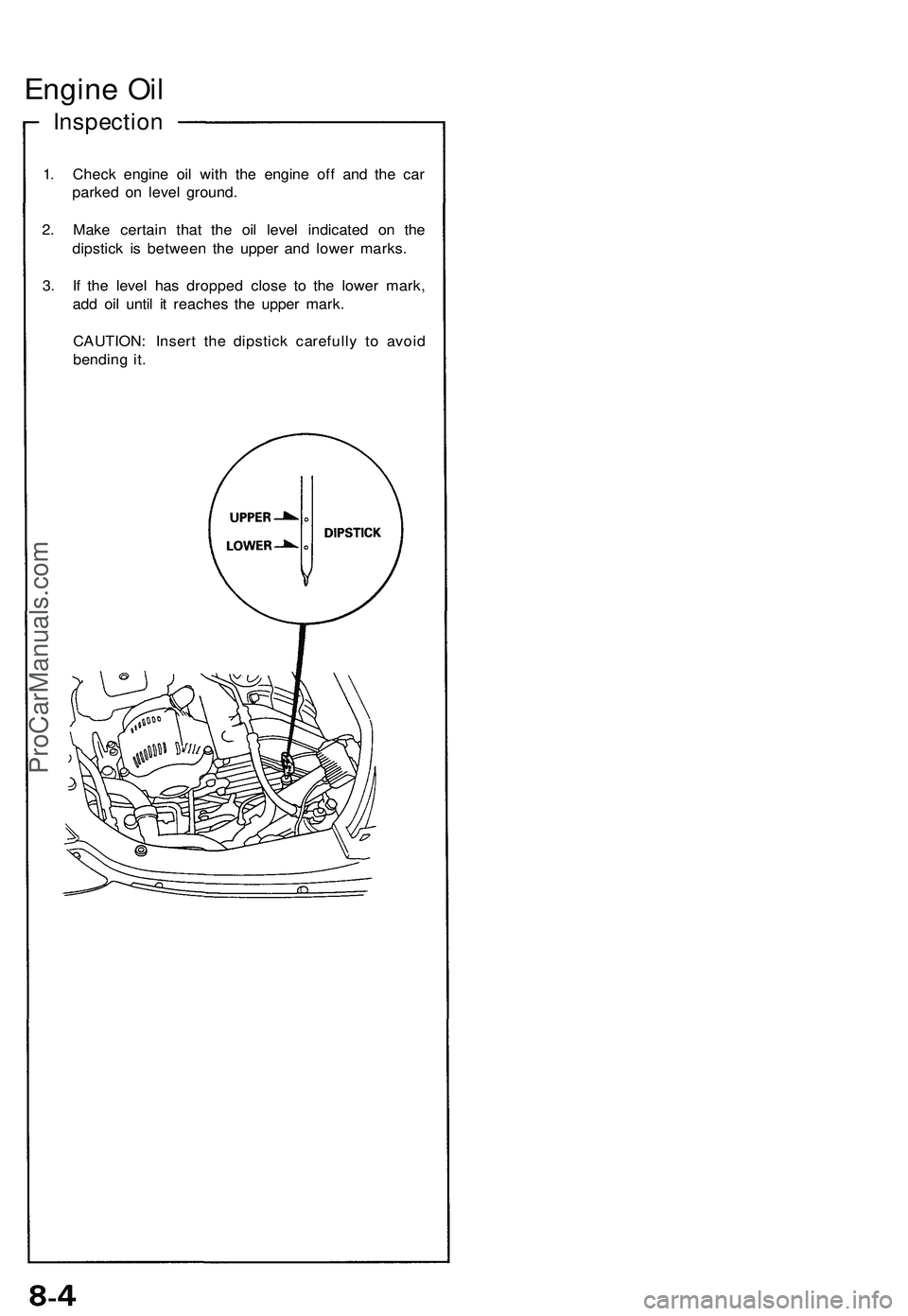
Engine Oil
Inspection
1. Check engine oil with the engine off and the car
parked on level ground.
2. Make certain that the oil level indicated on the
dipstick is between the upper and lower marks.
3. If the level has dropped close to the lower mark,
add oil until it reaches the upper mark.
CAUTION: Insert the dipstick carefully to avoid
bending it.ProCarManuals.com
Page 505 of 1503
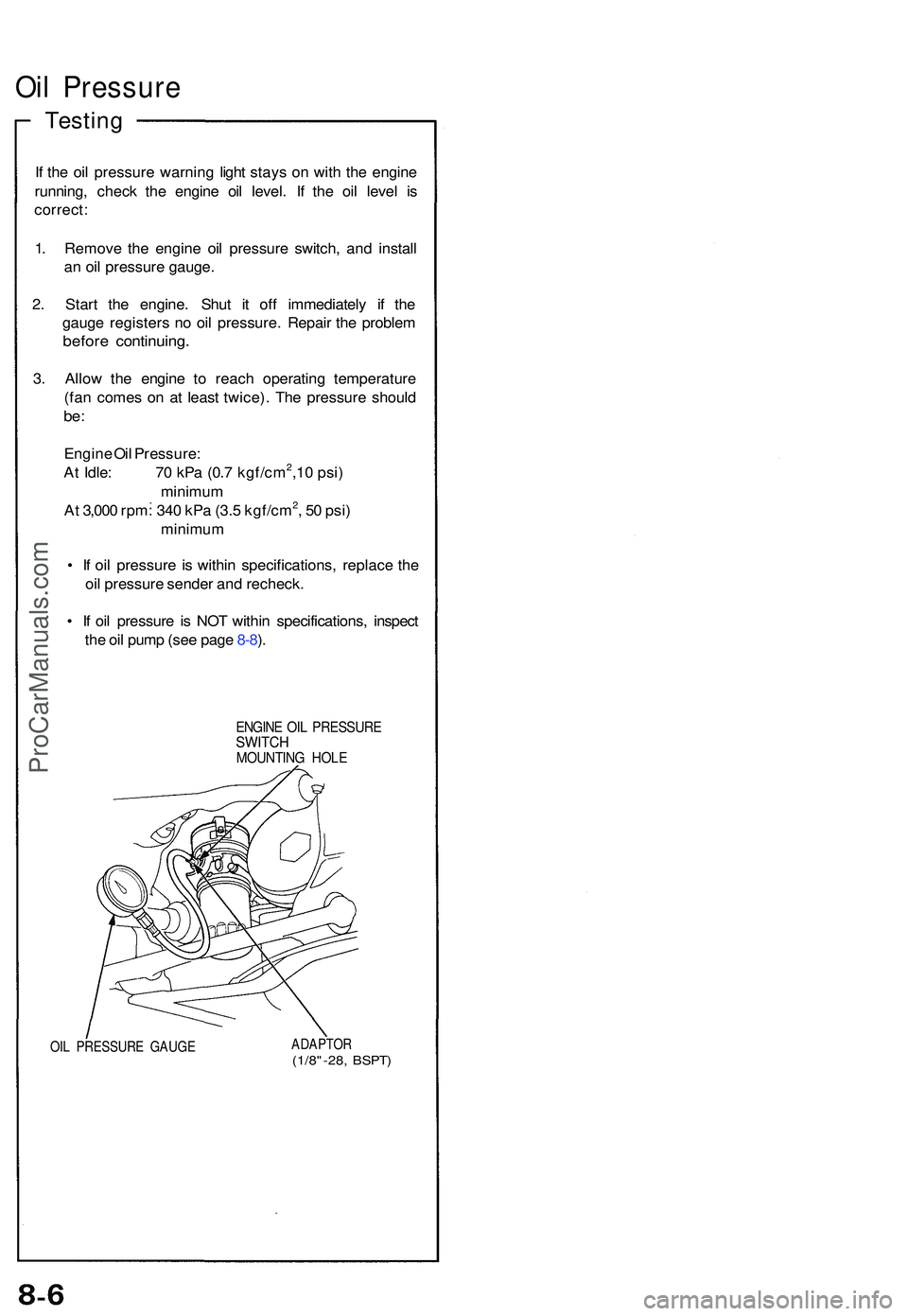
Oil Pressur e
Testing
If th e oi l pressur e warnin g ligh t stay s o n wit h th e engin e
running , chec k th e engin e oi l level . I f th e oi l leve l i s
correct :
1 . Remov e th e engine oil pressur e switch , an d instal l
a n oi l pressur e gauge .
2 . Star t th e engine . Shu t i t of f immediatel y i f th e
gaug e register s n o oi l pressure . Repai r th e proble m
before continuing .
3. Allo w th e engin e t o reac h operatin g temperatur e
(fa n come s o n a t leas t twice) . Th e pressur e shoul d
be:
Engin e Oi l Pressure :
A t Idle : 7 0 kP a (0. 7 kgf/cm2,1 0 psi )
minimu m
A t 3,00 0 rpm : 34 0 kP a (3. 5 kgf/cm
2, 5 0 psi )
minimu m
• I f oi l pressur e i s withi n specifications , replac e th e
oi l pressur e sende r an d recheck .
• I f oi l pressur e i s NO T withi n specifications , inspec t
th e oi l pum p (se e pag e 8-8 ).
ENGIN E OI L PRESSUR ESWITCHMOUNTIN G HOL E
OIL PRESSUR E GAUG EADAPTO R(1/8"-28, BSPT )
ProCarManuals.com
Page 523 of 1503
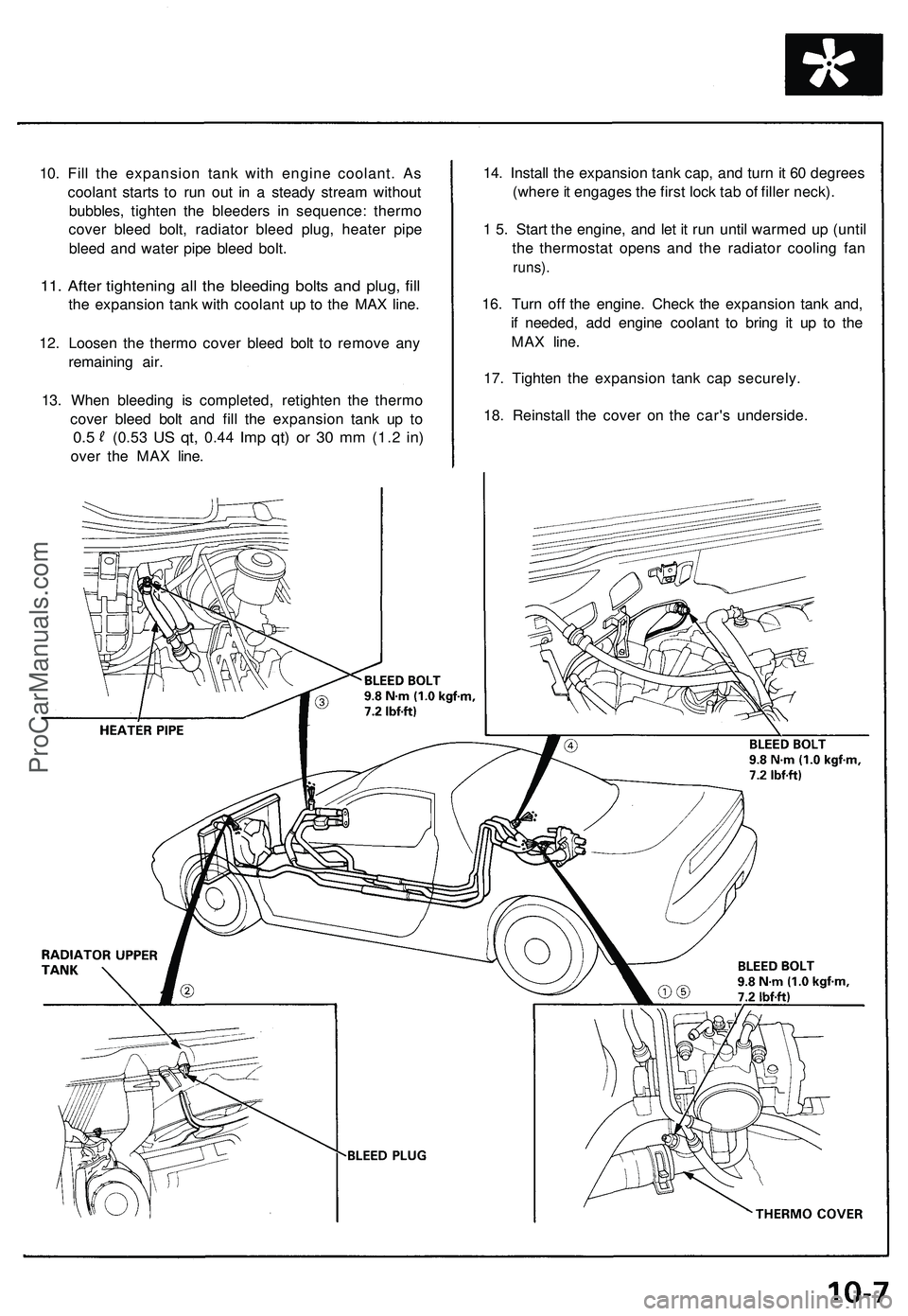
10. Fill the expansion tank with engine coolant. As
coolant starts to run out in a steady stream without
bubbles, tighten the bleeders in sequence: thermo
cover bleed bolt, radiator bleed plug, heater pipe
bleed and water pipe bleed bolt.
11. After tightening all the bleeding bolts and plug, fill
the expansion tank with coolant up to the MAX line.
12. Loosen the thermo cover bleed bolt to remove any
remaining air.
13. When bleeding is completed, retighten the thermo
cover bleed bolt and fill the expansion tank up to
0.5
(0.53
US qt,
0.44
Imp qt) or 30 mm
(1.2
in)
over the MAX line.
14. Install the expansion tank cap, and turn it 60 degrees
(where it engages the first lock tab of filler neck).
1 5. Start the engine, and let it run until warmed up (until
the thermostat opens and the radiator cooling fan
runs).
16. Turn off the engine. Check the expansion tank and,
if needed, add engine coolant to bring it up to the
MAX line.
17. Tighten the expansion tank cap securely.
18. Reinstall the cover on the car's underside.ProCarManuals.com
Page 584 of 1503
Troubleshooting
How to Read Flowcharts
A flowchart is designed to be used from start to final repair. It's like a map showing you the shortest distance. But beware:
if you go off the "map" anywhere but a "stop" symbol, you can easily get lost.
Describes the conditions or situation to start a troubleshooting flowchart.
Asks you to do something; perform a test, set up a condition etc.
Asks you about the result of an action, then sends you in the appropriate troubleshooting direction.
NOTE:
The term "Intermittent Failure" is used in these charts. It simply means a system may have had a failure, but it checks
out OK at this time. If the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) on the dash does not come on, check for poor connections
or loose wires at all connectors related to the circuit that you are troubleshooting (see illustration below).
Some of the troubleshooting flowcharts have you reset the Engine Control Module (ECM) and try to duplicate the
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC). If the problem is intermittent and you can't duplicate the code, do not continue through
the flowchart. To do so will only result in confusion and, possibly, a needlessly replaced ECM.
"Open" and "Short" are common electrical terms. An open is a break in a wire or at a connection. A short is an acci-
dental connection of a wire to ground or to another wire. In simple electronics, this usually means something won't
work at all. In complex electronics (like ECM's), this can sometimes mean something works, but not the way it's sup-
posed to.
TIGHT
LOOSE
The end of a series of actions and decisions, describes a final repair action and sometimes directs you to
an earlier part of the flowchart to confirm your repair.ProCarManuals.com
Page 586 of 1503
PGM-FI System
System Description (cont'd)
3. Fuel Cut-off Control
During deceleration with the throttle valve closed, current to the fuel injectors is cut off to improve fuel economy at
speeds over 1,500 rpm.
Fuel cut-off action also takes place when engine speed exceeds 8,300 rpm, regardless of the position of the throttle
valve, to protect the engine from over-revving.
4. A/C Compressor Clutch Relay
When the ECM receives a demand for cooling from the air conditioning system, it delays the compressor from being
energized, and enriches the mixture to assure smooth translation to the A/C mode.
5. Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Purge Control Solenoid Valve
When the engine coolant temperature is below 153°F (67°C), the ECM controls the EVAP purge control solenoid valve
which cuts vacuum to the EVAP purge control canister diaphragm.
6. Intake Air Bypass (IAB) Control Solenoid Valve
When the engine speed is below 4,800 rpm, the IAB control solenoid valve is activated by a signal from the ECM. Intake
air then flows through the smaller chamber, and high torque is delivered. To increase air flow at engine speeds higher
than 4,800 rpm, the solenoid valve is deactivated by the ECM, and the intake air flows through the larger chamber.
7. Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Control Solenoid Valve
When the EGR is required for control of oxides of nitrogen (NOx) emissions, the ECM supplies ground to the EGR
control solenoid valve which supplies regulated vacuum to the EGR valve.
ECM Fail-safe/Back-up Functions
1. Fail-Safe Function
When an abnormality occurs in a signal from a sensor, the ECM ignores that signal and assumes a pre-programmed
valve for that sensor that allows the engine to continue to run.
2. Back-up Function
When an abnormality occurs in the ECM itself, the fuel injectors are controlled by a back-up circuit independent of the
system in order to permit minimal driving.
3. Self-diagnosis Function [Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)]
When an abnormality occurs in a signal from a sensor, the ECM lights the MIL and stores the diagnostic trouble code
in erasable memory. When the ignition is initially turned on, the ECM supplies ground for the MIL for two seconds to
check the MIL bulb condition.
4. Two Trip Detection Method
To prevent false indications, the Two Trip Detection Method is used for the H02S, fuel metering-related, idle control
system, ECT sensor, EGR system self-diagnostic functions and EVAP control system. When an abnormality occurs,
the ECM stores it in its memory. When the same abnormality recurs after the ignition switch is turned OFF and ON (II)
again, the ECM informs the driver by lighting the MIL.
However, to ease troubleshooting, this function is cancelled when you short the service check connector. The MIL will
then blink immediately when an abnormality occurs.
5. Two (or three) Driving Cycle Detection Method
A "Driving Cycle" consists of starting the engine, beginning closed loop operation, and stopping the engine. If misfir-
ing that increases emissions or EVAP control system malfunction is detected during two consecutive driving cycles,
or TWC deterioration is detected during three consecutive driving cycles, the ECM turns the MIL on.
However,
to
ease
troubleshooting,
this
function
is
cancelled when
you
short
the
service check connector.
The MIL
will
then blink immediately when an abnormality occurs.ProCarManuals.com
Page 603 of 1503
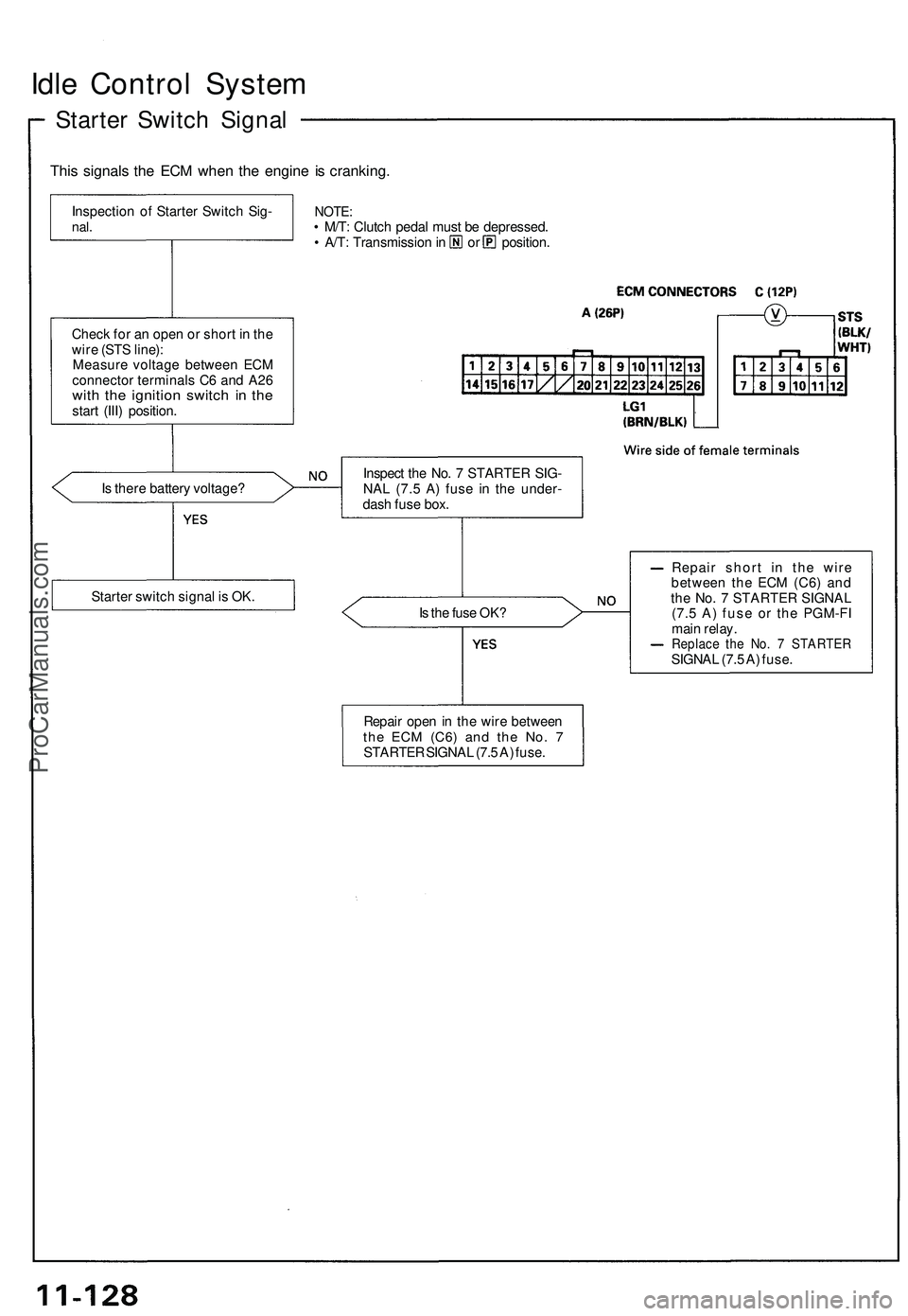
Idle Control System
Starter Switch Signal
This signals the ECM when the engine is cranking.
NOTE:
• M/T: Clutch pedal must be depressed.
• A/T: Transmission in or position.
Is there battery voltage?
Is the fuse OK?
Repair short in the wire
between the ECM (C6) and
the No. 7 STARTER SIGNAL
(7.5 A) fuse or the PGM-FI
main relay.
Replace the No. 7 STARTER
SIGNAL (7.5 A) fuse.
Inspection of Starter Switch Sig-
nal.
Check for an open or short in the
wire (STS line):
Measure voltage between ECM
connector terminals C6 and A26
with the ignition switch in the
start (III) position.
Starter switch signal is OK.
Repair open in the wire between
the ECM
(C6)
and the No. 7
STARTER SIGNAL (7.5 A) fuse.
Inspect the No. 7 STARTER SIG-
NAL (7.5 A) fuse in the under-
dash fuse box.ProCarManuals.com
Page 617 of 1503
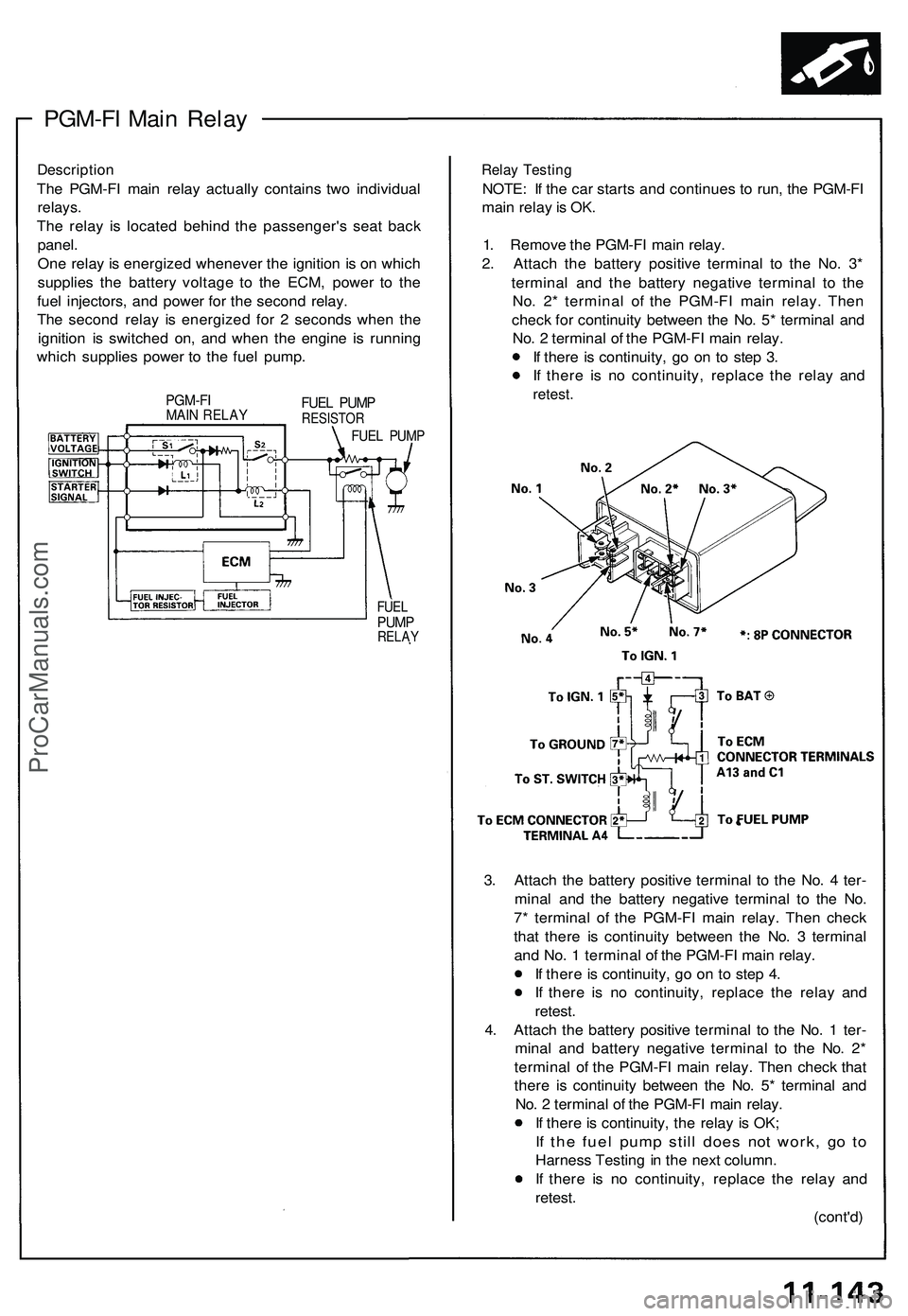
PGM-FI Main Relay
Description
The PGM-FI main relay actually contains two individual
relays.
The relay is located behind the passenger's seat back
panel.
One relay is energized whenever the ignition is on which
supplies the battery voltage to the ECM, power to the
fuel injectors, and power for the second relay.
The second relay is energized for 2 seconds when the
ignition is switched on, and when the engine is running
which supplies power to the fuel pump.
PGM-FI
MAIN RELAY
FUEL PUMP
RESISTOR
FUEL PUMP
FUEL
PUMP
RELAY
Relay Testing
NOTE: If the car starts and continues to run, the PGM-FI
main relay is OK.
1. Remove the PGM-FI main relay.
2. Attach the battery positive terminal to the No. 3*
terminal and the battery negative terminal to the
No. 2* terminal of the PGM-FI main relay. Then
check for continuity between the No. 5* terminal and
No. 2 terminal of the PGM-FI main relay.
If there is continuity, go on to step 3.
If there is no continuity, replace the relay and
retest.
3. Attach the battery positive terminal to the No. 4 ter-
minal and the battery negative terminal to the No.
7* terminal of the PGM-FI main relay. Then check
that there is continuity between the No. 3 terminal
and No. 1 terminal of the PGM-FI main relay.
If there is continuity, go on to step 4.
If there is no continuity, replace the relay and
retest.
4. Attach the battery positive terminal to the No. 1 ter-
minal and battery negative terminal to the No. 2*
terminal of the PGM-FI main relay. Then check that
there is continuity between the No. 5* terminal and
No. 2 terminal of the PGM-FI main relay.
If there is continuity, the relay is OK;
If the fuel pump still does not work, go to
Harness Testing in the next column.
If there is no continuity, replace the relay and
retest.
(cont'd)ProCarManuals.com
Page 628 of 1503
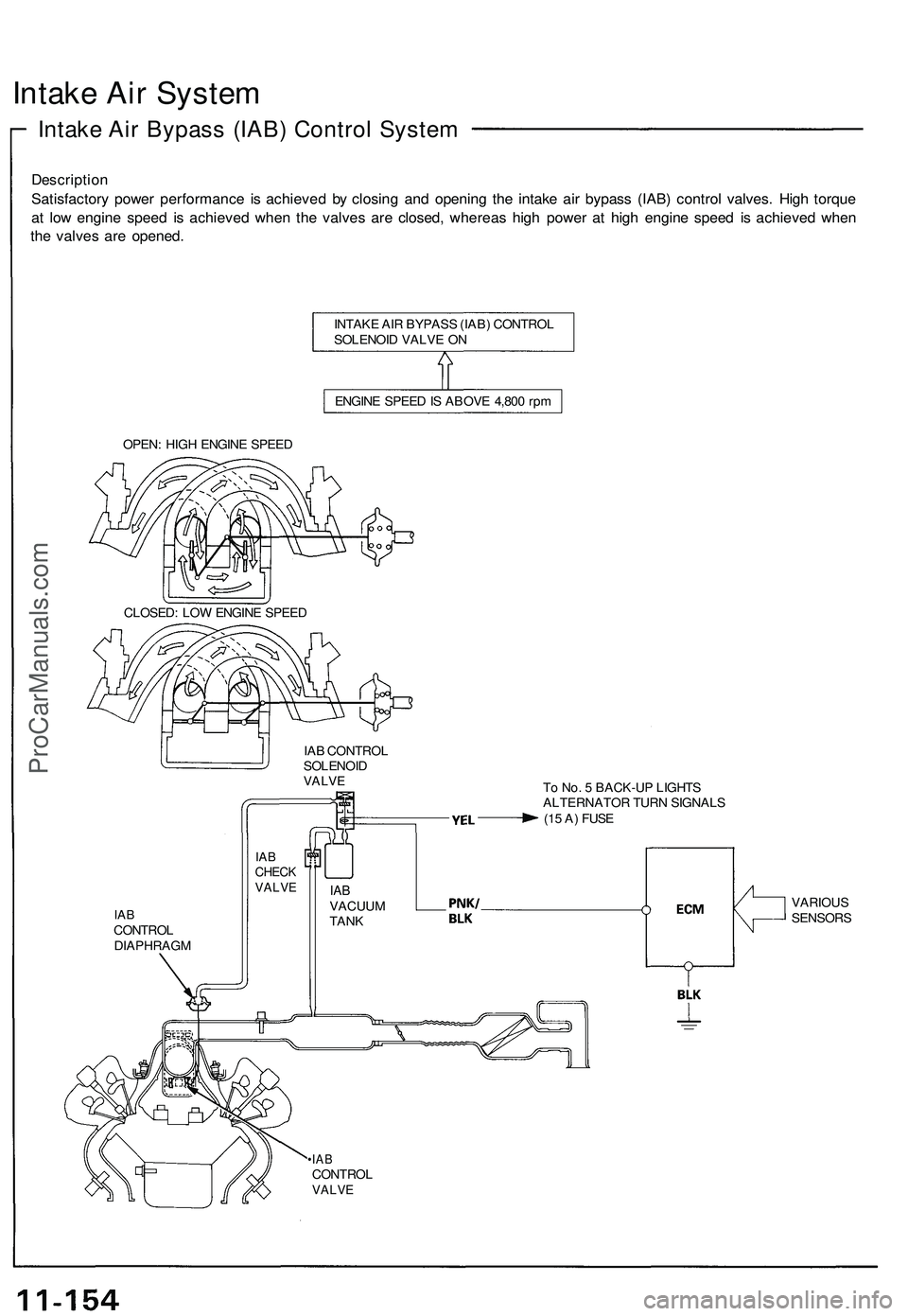
Intake Air System
Intake Air Bypass (IAB) Control System
Description
Satisfactory power performance is achieved by closing and opening the intake air bypass (IAB) control valves. High torque
at low engine speed is achieved when the valves are closed, whereas high power at high engine speed is achieved when
the valves are opened.
INTAKE AIR BYPASS (IAB) CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE ON
ENGINE SPEED IS ABOVE 4,800 rpm
OPEN: HIGH ENGINE SPEED
CLOSED: LOW ENGINE SPEED
IAB CONTROL
SOLENOID
VALVE
To No. 5 BACK-UP LIGHTS
ALTERNATOR TURN SIGNALS
(15 A) FUSE
IAB
CONTROL
DIAPHRAGM
•IAB
CONTROL
VALVE
IAB
CHECK
VALVE
IAB
VACUUM
TANK
VARIOUS
SENSORSProCarManuals.com
Page 635 of 1503
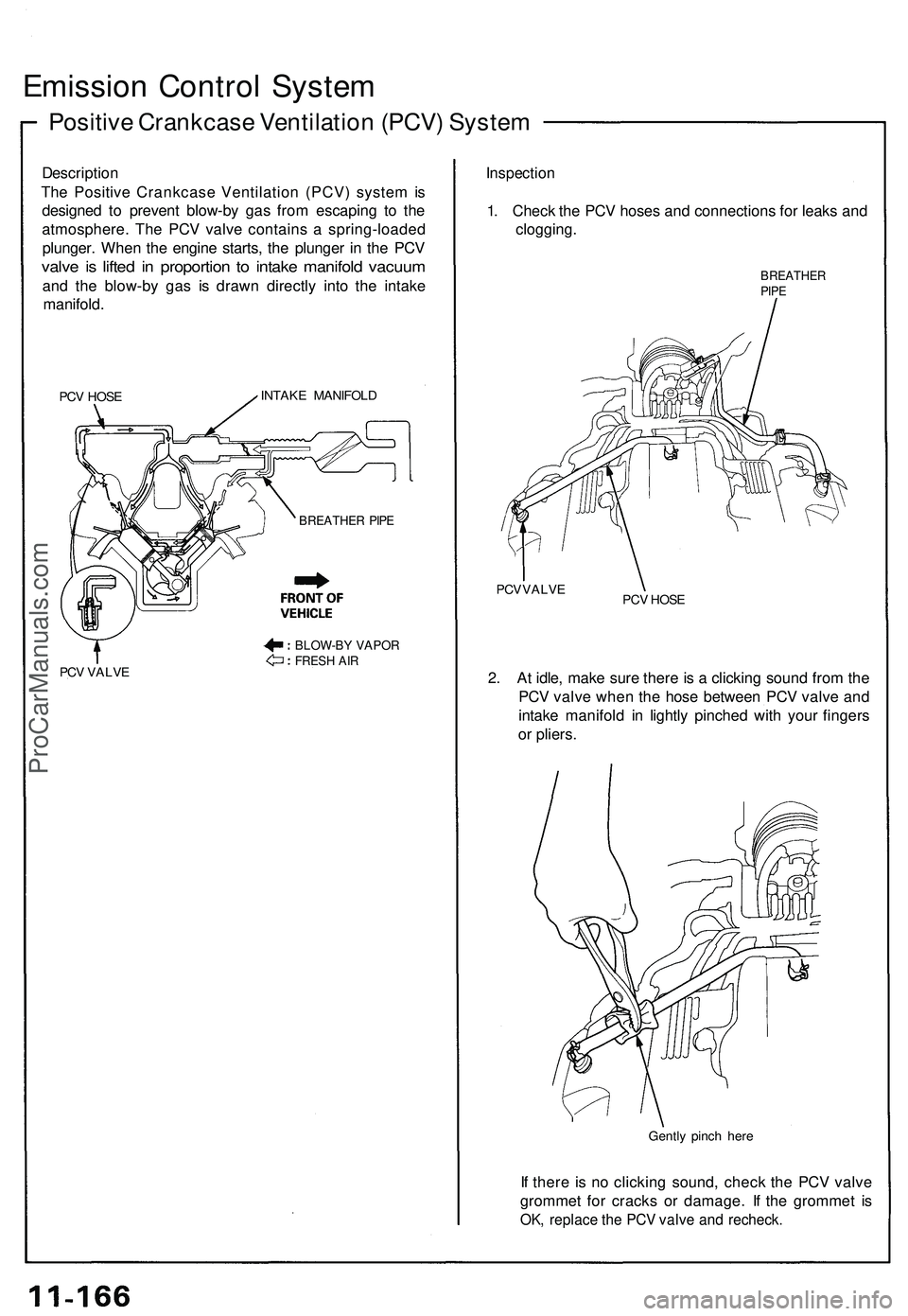
Emission Control System
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) System
Description
The Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system is
designed to prevent blow-by gas from escaping to the
atmosphere. The PCV valve contains a spring-loaded
plunger. When the engine starts, the plunger in the PCV
valve is lifted in proportion to intake manifold vacuum
and the blow-by gas is drawn directly into the intake
manifold.
PCV HOSE
INTAKE MANIFOLD
PCV VALVE
Inspection
1. Check the PCV hoses and connections for leaks and
clogging.
BREATHER
PIPE
PCV VALVE
PCV HOSE
2. At idle, make sure there is a clicking sound from the
PCV valve when the hose between PCV valve and
intake manifold in lightly pinched with your fingers
or pliers.
Gently pinch here
If there is no clicking sound, check the PCV valve
grommet for cracks or damage. If the grommet is
OK, replace the PCV valve and recheck.
BLOW-BY VAPOR
FRESH AIR
BREATHER PIPEProCarManuals.com