differential ACURA NSX 1997 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ACURA, Model Year: 1997, Model line: NSX, Model: ACURA NSX 1997Pages: 1503, PDF Size: 57.08 MB
Page 17 of 1503
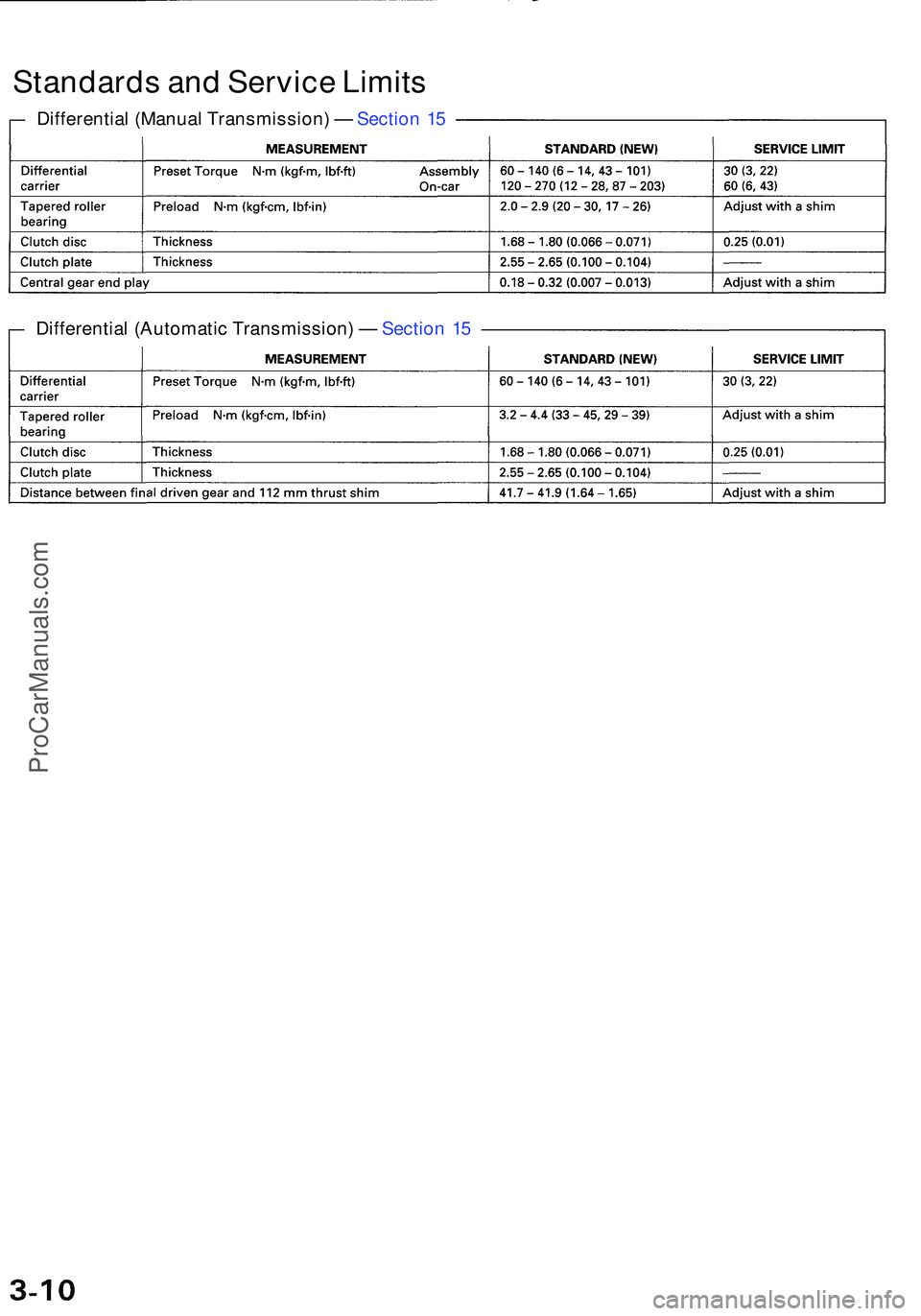
Differential (Automati c Transmission ) — Sectio n 1 5
Standard s an d Servic e Limit s
Differentia l (Manua l Transmission ) — Sectio n 1 5
ProCarManuals.com
Page 661 of 1503
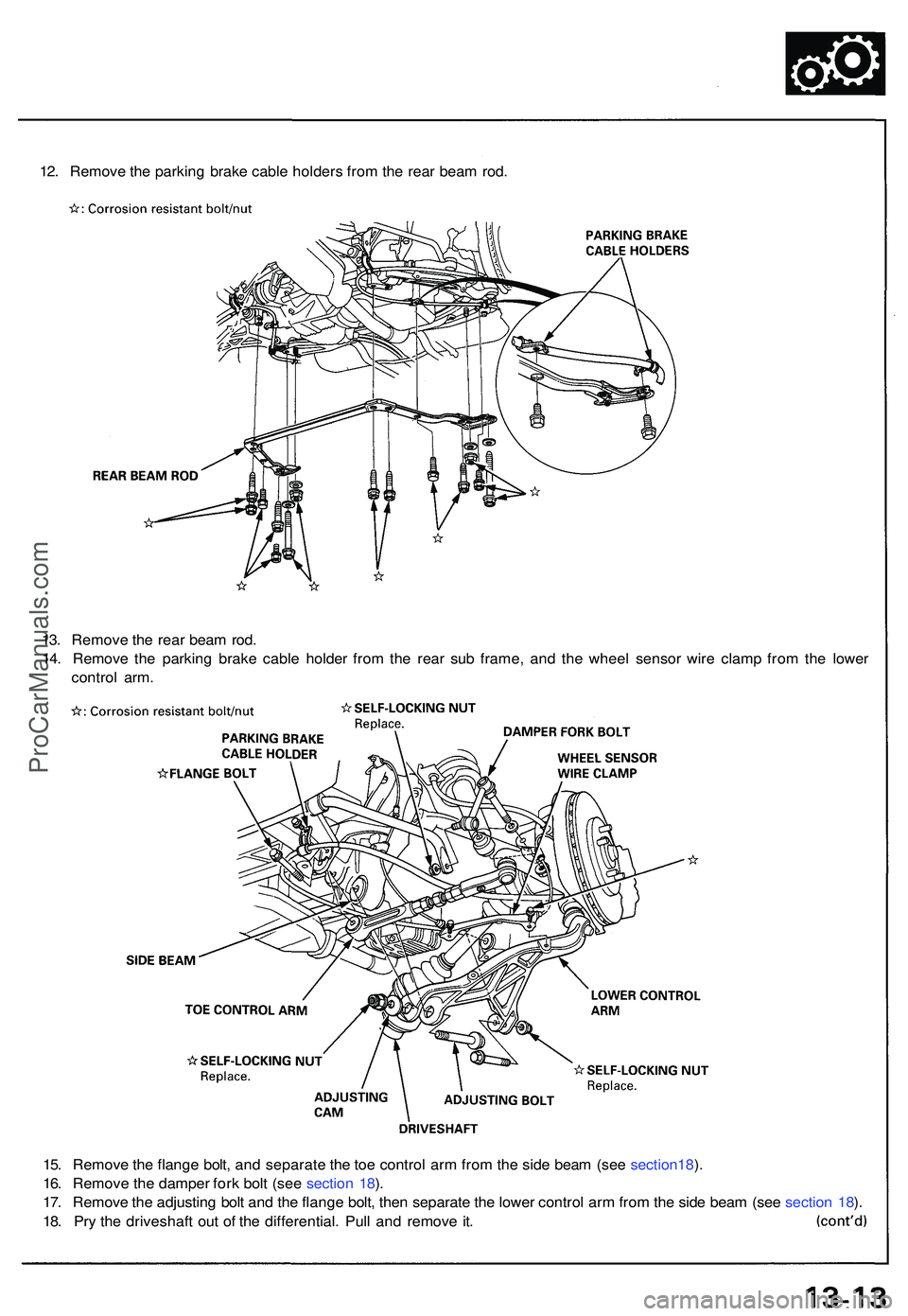
12. Remov e th e parkin g brak e cabl e holder s fro m th e rea r bea m rod .
13 . Remov e th e rea r bea m rod .
14 . Remov e th e parkin g brak e cabl e holde r fro m th e rea r su b frame , an d th e whee l senso r wir e clam p fro m th e lowe r
contro l arm .
15 . Remov e th e flang e bolt , an d separat e th e to e contro l ar m fro m th e sid e bea m (se e section18 ).
16 . Remov e th e dampe r for k bol t (se e sectio n 18 ).
17 . Remov e th e adjustin g bol t an d th e flang e bolt , the n separat e th e lowe r contro l ar m fro m th e sid e bea m (se e sectio n 18 ).
18 . Pr y th e driveshaf t ou t o f th e differential . Pul l an d remov e it .
ProCarManuals.com
Page 662 of 1503
Transmission Assembl y
Removal (cont'd )
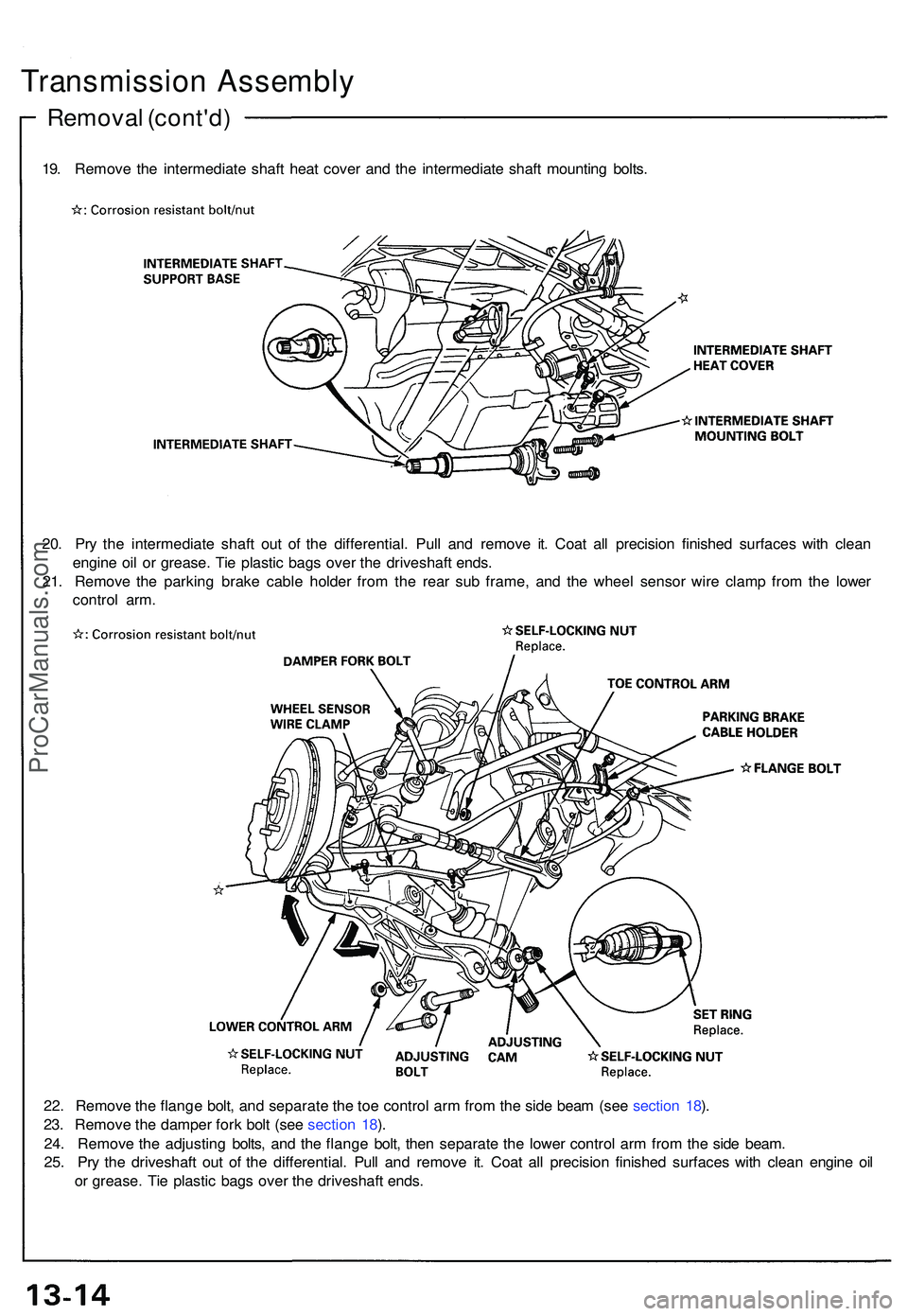
19. Remov e th e intermediat e shaf t hea t cove r an d th e intermediat e shaf t mountin g bolts .
20 . Pr y th e intermediat e shaf t ou t o f th e differential . Pul l an d remov e it . Coa t al l precisio n finishe d surface s wit h clea n
engin e oi l o r grease . Ti e plasti c bag s ove r th e driveshaf t ends .
21 . Remov e th e parkin g brak e cabl e holde r fro m th e rea r su b frame , an d th e whee l senso r wir e clam p fro m th e lowe r
contro l arm .
22 . Remov e th e flang e bolt , an d separat e th e to e contro l ar m fro m th e sid e bea m (se e sectio n 18 ).
23 . Remov e th e damper fork bol t (se e sectio n 18 ).
24 . Remov e th e adjustin g bolts , an d th e flang e bolt , the n separat e th e lowe r contro l ar m fro m th e sid e beam .
25 . Pr y th e driveshaf t ou t o f th e differential . Pul l an d remov e it . Coa t al l precisio n finishe d surfaces with clea n engin e oi l
o r grease . Ti e plasti c bag s ove r th e driveshaf t ends .
ProCarManuals.com
Page 673 of 1503
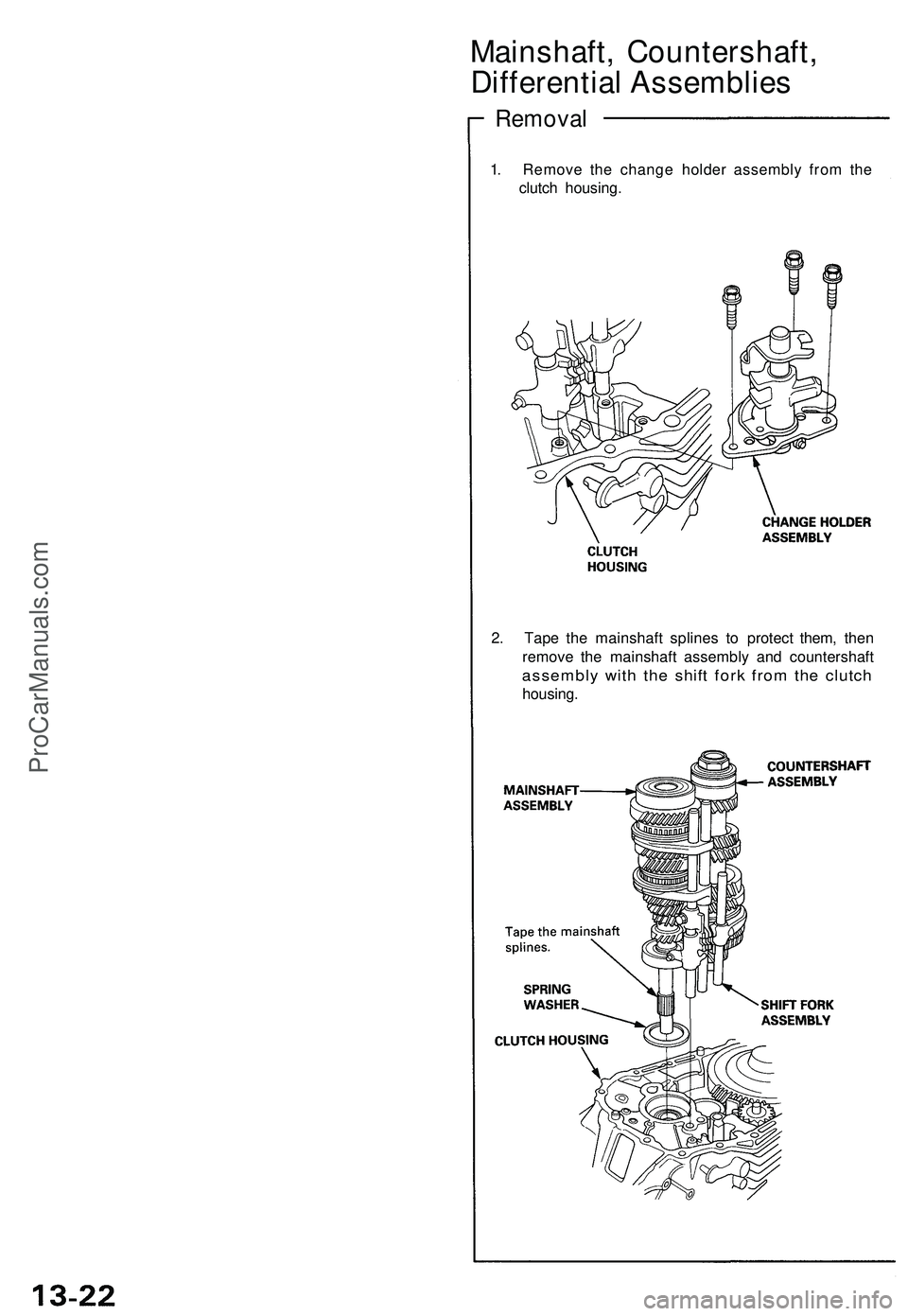
Mainshaft, Countershaft,
Differential Assemblies
Removal
1. Remove the change holder assembly from the
clutch housing.
2. Tape the mainshaft splines to protect them, then
remove the mainshaft assembly and countershaft
assembly with the shift fork from the clutch
housing.ProCarManuals.com
Page 674 of 1503
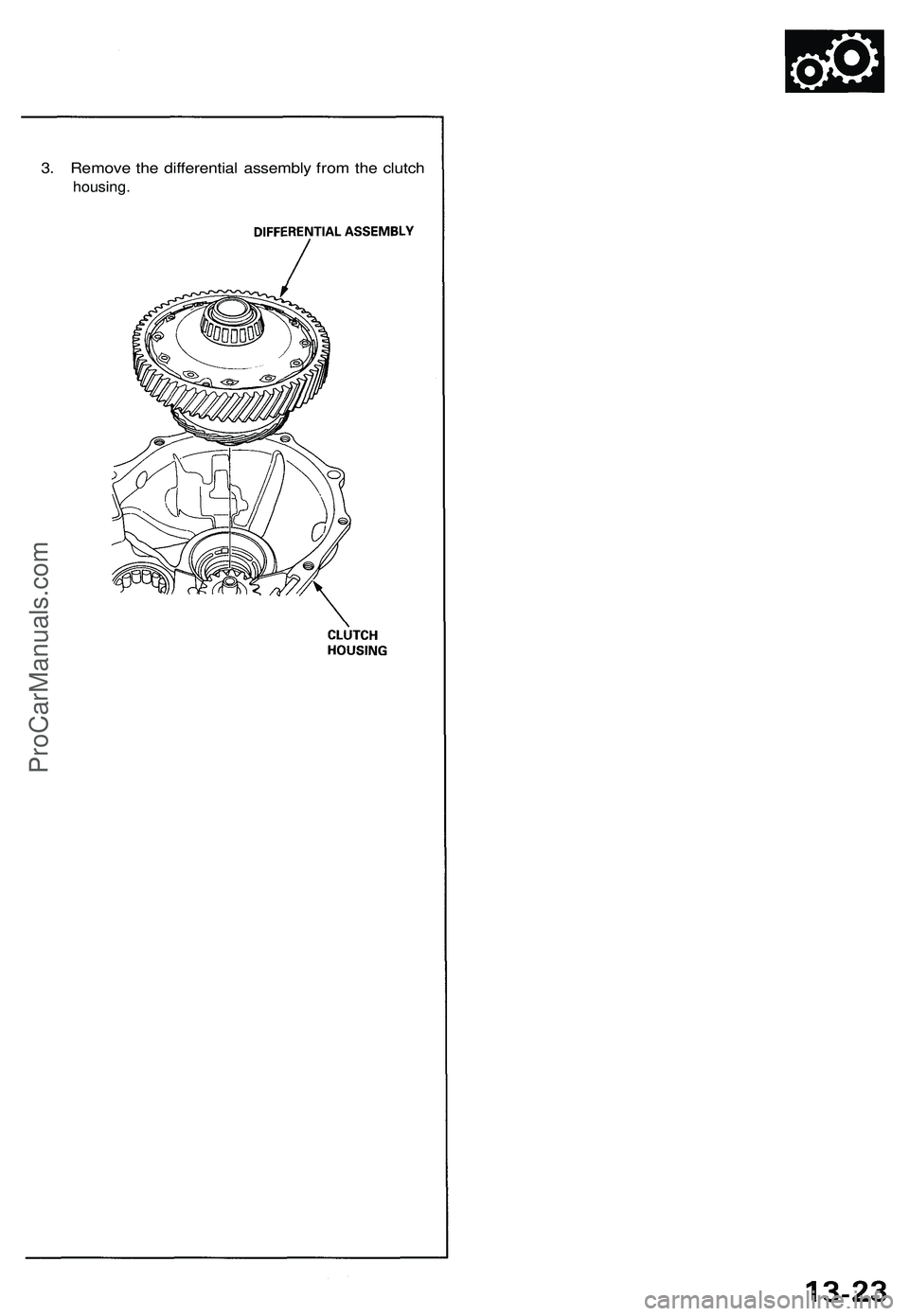
3. Remove the differential assembly from the clutch
housing.ProCarManuals.com
Page 702 of 1503
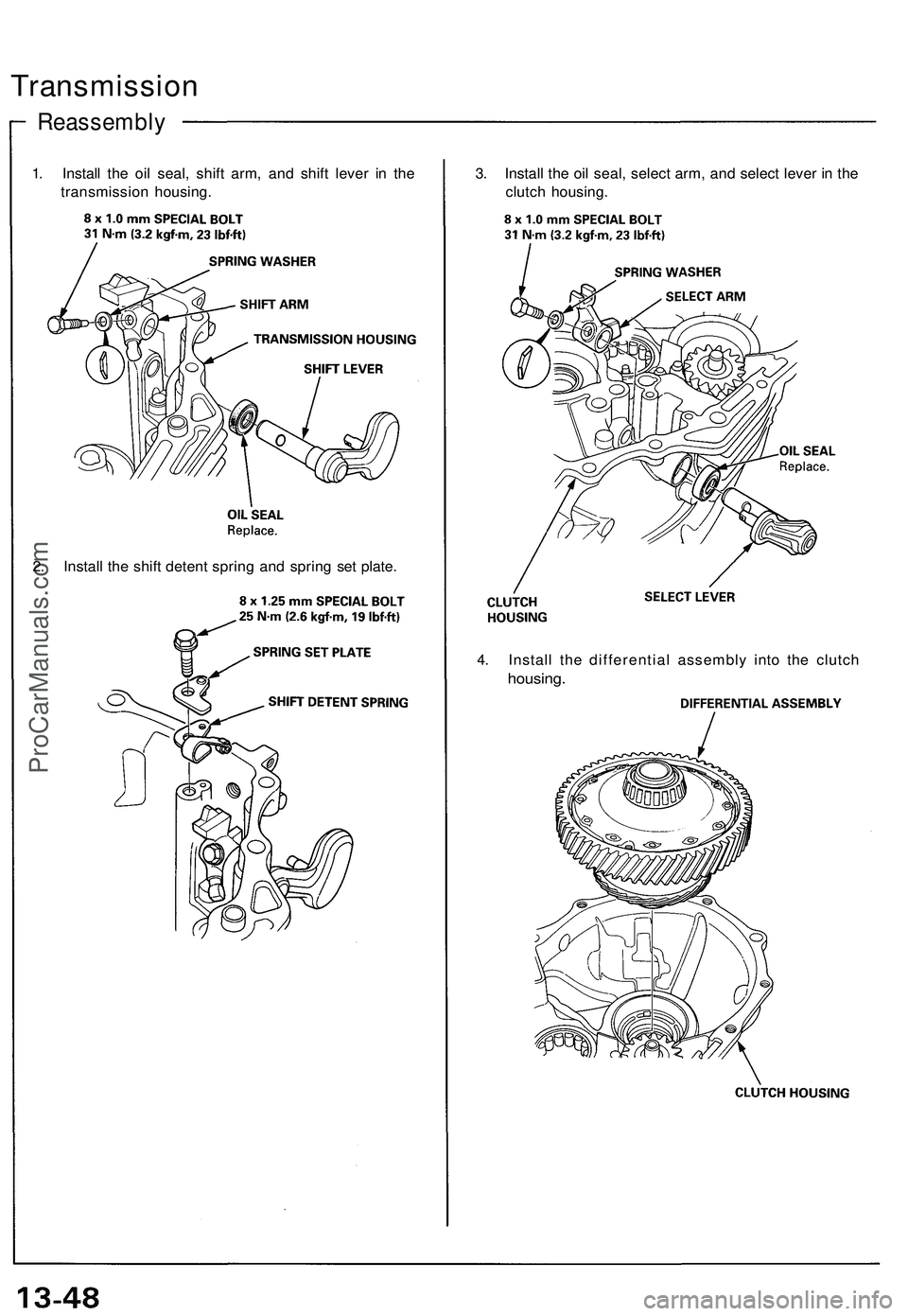
Transmission
Reassembly
1. Install the oil seal, shift arm, and shift lever in the
transmission housing.
3. Install the oil seal, select arm, and select lever in the
clutch housing.
2. Install the shift detent spring and spring set plate.
4. Install the differential assembly into the clutch
housing.ProCarManuals.com
Page 713 of 1503

Description
The automatic transmission is a combination of a 3-element torque converter and a triple-shaft electronically controlled
automatic transmission which provides 4 speeds forward and 1 speed reverse. The entire unit is positioned in line with the
engine.
Torque Converter, Gears, and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump, turbine, and stator, assembled in a single unit.
They are connected to the engine crankshaft so they turn together as a unit as the engine turns.
Around the outside of the torque converter is a ring gear which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being
started. The entire torque converter assembly serves as a flywheel while transmitting power to the transmission main-
shaft. The transmission has three parallel shafts: the mainshaft, the countershaft, and the secondary shaft. The mainshaft
is in line with the engine crankshaft.
The mainshaft includes the 1st and 4th clutches, and gears for 3rd, 4th, reverse, and 1st (3rd gear is integral with the main-
shaft, while reverse gear is integral with 4th gear).
The countershaft includes the 1st-hold and 3rd clutches, and gears for 2nd, 3rd, 4th, reverse, 1st, and parking.
The secondary shaft includes the 2nd clutch and gears for 2nd and 3rd.
The 4th and reverse gears can be locked to the countershaft at its center, providing 4th gear or reverse, depending on
which way the selector is moved.
The gears on the mainshaft and secondary shaft are in constant mesh with those on the countershaft.
When certain combinations of gears in the transmission are engaged by clutches, power is transmitted from the mainshaft
to the countershaft to provide positions.
Electronic Control
The electronic control system consists of the Transmission Control Module (TCM), sensors, a linear solenoid, a shift switch,
and 4 solenoid valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all conditions.
The TCM is located on the insulator center bulkhead, behind the driver's seat.
Hydraulic Control
The valve bodies include the main valve body, secondary valve body, servo body, regulator valve body, throttle valve
body, lock-up valve body, and the 2nd accumulator body.
They are bolted to the torque converter housing as an assembly.
The main valve body contains the manual valve, 1-2 shift valve, 2-3 shift valve, 3-4 shift valve, relief valve, one-way relief
valve, and oil pump gears.
The secondary valve body contains the 3-2 kick-down valve, clutch pressure control (CPC) valve, 2nd orifice control valve, 3rd
orifice control valve, modulator valve, 4th exhaust valve, servo control valve, 2nd exhaust valve, and 4-3 kick-down valve.
The servo body contains the accumulator pistons and servo valve. The throttle valve body includes the throttle valve B
which is bolted to the servo body.
The regulator valve body contains the pressure regulator valve, lock-up control valve, and cooler relief valve. Fluid from
the regulator passes through the manual valve to the various control valves.
The lock-up valve body contains the lock-up timing B valve and lock-up shift valve. The 2nd accumulator body contains
the accumulator pistons and limited slip differential relief valve.
The torque converter check valve is located in the torque converter housing, under the main valve body.
The 1st, 1st-hold, 3rd, and 4th clutches receive fluid from their respective feed pipes and the 2nd clutch receives fluid from
the internal hydraulic circuit.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input from various sensors located throughout the vehicle determines which shift control solenoid valve the TCM will acti-
vate. Activating a shift control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This pressurizes
a line to one of the clutches, engaging that clutch and its corresponding gear.
Lock-up Mechanism
In position and position in 2nd, 3rd, and 4th, pressurized fluid is drained from the back of the torque converter
through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held against the torque converter cover. As this takes place, the
mainshaft rotates at the same speed as the engine crankshaft. Together with hydraulic control, the TCM optimizes the tim-
ing of the lock-up mechanism.
The lock-up valves control the range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B, and throttle valve B.
When lock-up control solenoid valves A and B activate, modulator pressure changes. The lock-up control solenoid valves
A and B are mounted on the torque converter housing, and are controlled by the TCM.
(cont'd)ProCarManuals.com
Page 715 of 1503
![ACURA NSX 1997 Service Repair Manual
TORQUE CONVERTER
LOCK-UP CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE
ASSEMBLY
4TH CLUTCH
1ST CLUTCH
1ST-HOLD CLUTCH
ATF COOLER
DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
[LIMITED SLIP DIFFERENTIAL (LSD)]
2ND CLUTCH
3RD CLUTCHProCa ACURA NSX 1997 Service Repair Manual
TORQUE CONVERTER
LOCK-UP CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE
ASSEMBLY
4TH CLUTCH
1ST CLUTCH
1ST-HOLD CLUTCH
ATF COOLER
DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
[LIMITED SLIP DIFFERENTIAL (LSD)]
2ND CLUTCH
3RD CLUTCHProCa](/img/32/56989/w960_56989-714.png)
TORQUE CONVERTER
LOCK-UP CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE
ASSEMBLY
4TH CLUTCH
1ST CLUTCH
1ST-HOLD CLUTCH
ATF COOLER
DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
[LIMITED SLIP DIFFERENTIAL (LSD)]
2ND CLUTCH
3RD CLUTCHProCarManuals.com
Page 735 of 1503
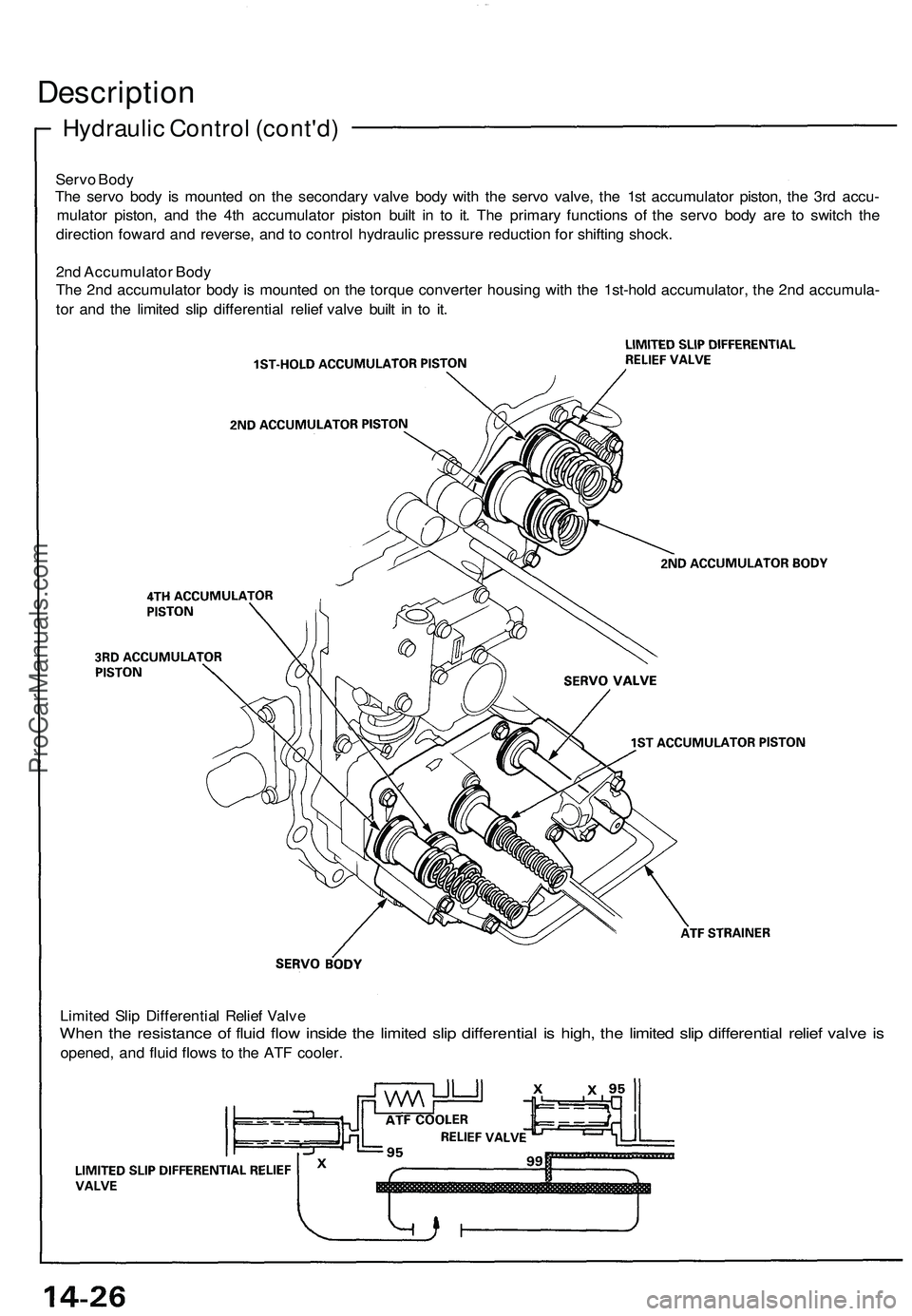
Hydraulic Control (cont'd)
Description
Servo Body
The servo body is mounted on the secondary valve body with the servo valve, the 1st accumulator piston, the 3rd accu-
mulator piston, and the 4th accumulator piston built in to it. The primary functions of the servo body are to switch the
direction foward and reverse, and to control hydraulic pressure reduction for shifting shock.
2nd Accumulator Body
The 2nd accumulator body is mounted on the torque converter housing with the 1st-hold accumulator, the 2nd accumula-
tor and the limited slip differential relief valve built in to it.
Limited Slip Differential Relief Valve
When the resistance of fluid flow inside the limited slip differential is high, the limited slip differential relief valve is
opened, and fluid flows to the ATF cooler.ProCarManuals.com
Page 780 of 1503
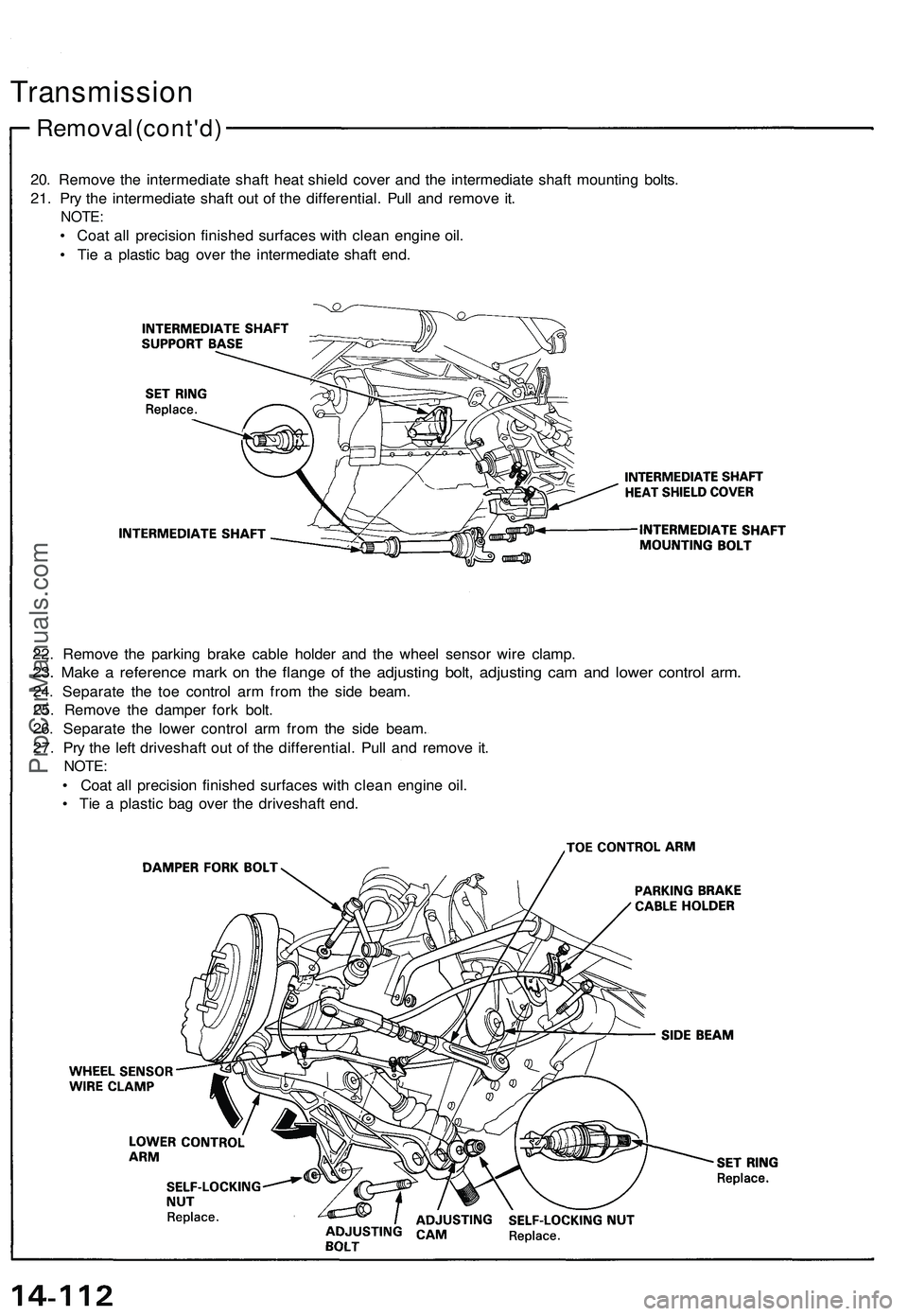
20. Remove the intermediate shaft heat shield cover and the intermediate shaft mounting bolts.
21. Pry the intermediate shaft out of the differential. Pull and remove it.
NOTE:
• Coat all precision finished surfaces with clean engine oil.
• Tie a plastic bag over the intermediate shaft end.
Removal (cont'd)
Transmission
22. Remove the parking brake cable holder and the wheel sensor wire clamp.
23. Make a reference mark on the flange of the adjusting bolt, adjusting cam and lower control arm.
24. Separate the toe control arm from the side beam.
25. Remove the damper fork bolt.
26. Separate the lower control arm from the side beam.
27. Pry the left driveshaft out of the differential. Pull and remove it.
NOTE:
• Coat all precision finished surfaces with clean engine oil.
• Tie a plastic bag over the driveshaft end.ProCarManuals.com