service CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 237 of 2438

ABS BRAKING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
WARNING: SOME OPERATIONS IN THIS SECTION
REQUIRE THAT HYDRAULIC TUBES, HOSES AND
FITTINGS BE DISCONNECTED FOR INSPECTION
OR TESTING PURPOSES. THIS BRAKE SYSTEM
USES A HYDRAULIC ACCUMULATOR THAT, WHEN
FULLY CHARGED, CONTAINS BRAKE FLUID AT
HIGH PRESSURE. BEFORE DISCONNECTING ANY
HYDRAULIC TUBE, HOSE OR FITTING. BE SURE
THAT THE ACCUMULATOR IS FULLY DE-PRES-
SURIZED AS DESCRIBED IN THIS SECTION. FAIL-
URE TO DE-PRESSURIZE THE ACCUMULATOR
MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR DAM-
AGE TO PAINTED SURFACES.
CAUTION: Certain components of the Anti-Lock
Brake System (ABS) are not intended to be serviced
individually. Attempting to remove or disconnect
certain system components, may result in personal
injury and/or improper system operation. Only
those components with approved removal, service
and installation procedures described in this man-
ual should be serviced.
GENERAL INFORMATION
This section contains information necessary to di-
agnosis mechanical conditions that can affect opera-
tion of the Bendix Anti-Lock 10 Brake System.
Specifically, this section should be used to help diag-
nose mechanical conditions that result in any of the
following:
CAUTION: Review this entire section before per-
forming any mechanical work on a vehicle equipped
with the Bendix Anti-Lock 10 brake system. For in-
formation on precautions pertaining to potential
component damage, vehicle damage and personal
injury.
(1) Anti-Lock warning lamp illuminated
(2) BRAKE warning lamp on
(3) Lack of Power Assist or Excessive Pedal Travel
(4) Brakes Lock on Hard Application
Diagnosis of conditions that are obviously mechan-
ical in nature. Such as brake noise, brake pulsation,
or vehicle vibration during normal braking. Should
be directed to Group 5 Brakes in the service manual.
This also pertains to problems involving the parking
brake system.
Fig. 13 Hold Pressure - Hydraulic Control
Ä ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 87
Page 238 of 2438

In order to effectively diagnose an Anti-Lock Brake
System (ABS) condition. It is important to read Sec-
tion 1 of this manual, Anti-Lock Brake System De-
scription. This section will give you information on
the function of the ABS components. Then follow the
diagnostic procedures outlined in this section. Many conditions that generate customer com-
plaints of the ABS system may be normal operating
conditions. These conditions though are judged to be
a problem due to unfamiliarity with the ABS system.
These conditions can be recognized without perform-
ing extensive diagnostic work, given adequate under-
standing of operating principles and performance
characteristics of the ABS system. See Section 1 of
this manual to familiarize yourself with the operat-
ing principles of the ABS system.
DEFINITIONS
Several abbreviations are used in this manual.
They are presented here for reference.
² CABÐController Anti-Lock Brake
² ABSÐAnti-Lock Brake System
² PSIÐPounds per Square Inch (pressure)
² WSSÐWheel Speed Sensor
ABS CONTROLLER ANTI-LOCK BRAKE (CAB) SER-
VICE PRECAUTIONS
The ABS system uses an electronic control module,
the (CAB). This module is designed to withstand nor-
mal current draws associated with vehicle operation.
However care must be taken to avoid overloading the
(CAB) circuits. In testing for open or short circuits, do
not ground or apply voltage to any of the circuits unless
instructed to do so by the appropriate diagnostic pro-
cedure. These circuits should only be tested using a
high impedance multi-meter, special tools or the DRB
II tester as described in this section. Power should
never be removed or applied to any control module with
the ignition in the ON position. Before removing or
connecting battery cables, fuses, or connectors, always
turn the ignition to the OFF position.
ABS SYSTEM GENERAL SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
TEST DRIVING ABS COMPLAINT VEHICLES
Most ABS complaints will require a test drive as a
part of the diagnostic procedure. The purpose of the
test drive is to duplicate the condition. Before test driving a brake complaint vehicle,
especially if the Red Brake Warning Lamp is on.
Test the brake function at low speed to be sure
that the car will stop normally. Remember that
conditions that result in illumination of the Red
Fig. 14 Decay Pressure - Hydraulic Control
5 - 88 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 239 of 2438

Brake Warning Lamp may indicate reduced
braking ability. The following procedure should
be used to test drive an ABS complaint:(1) Ignition on. Turn the ignition to the ON position
without starting the car and wait until the Red Brake
Warning Lamp and Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp
turn off. This will allow the pump to charge the
accumulator to operating pressure. If the warning
lamp(s) do not turn off, go to step 3. (2) Ignition off for 15 seconds.
(3) Start car. Wait for displays to return to normal
operating mode before proceeding. (4) With Shift lever in PARK, slowly depress brake
pedal and release. (5) Drive vehicle a short distance. During this test
drive, be sure that the vehicle achieves at least 20 mph.
Then brake to at least one complete stop and accelerate
slowly back up to at least 20 mph. (6) If a functional problem with the A.B.S. system is
determined while test driving a vehicle. Refer to the
Bendix Anti-Lock 10 Diagnostics Manual for required
test procedures and proper use of the DRB II tester.
CAUTION: The following are general precautions that
should be observed when servicing and diagnosing
the ABS system and/or other vehicle systems. Failure
to observe these precautions may result in ABS
system damage.
(1) If welding work is to be performed on the vehicle
using an arc welder, the (CAB) should be disconnected
before the welding operation begins. (2) The (CAB) and hydraulic assembly 10 way con-
nectors should never be connected or disconnected with
the ignition on. (3) Some components of the ABS system are not
serviced separately and must be serviced as complete
assemblies. Do not disassemble any component which
is designated as non-serviceable. (4) Always de-pressurize the Hydraulic Accu-
mulator when performing any work that re-
quires disconnecting any hydraulic tube, flex
hose or fitting. The ABS system uses brake fluid
at high pressure. Failure to de-pressurize the
accumulator may result in personal injury
and/or damage to painted surfaces. Brake fluid will damage painted surfaces. If brake
fluid is spilled on any painted surfaces, wash off with
water immediately.
DE-PRESSURIZING HYDRAULIC ACCUMULA- TOR
The ABS pump/motor assembly keeps the hydraulic
accumulator charged between approximately 11,032
and 13,790 kPa (1600 and 2000 psi) anytime key is in the ON position. The pump/motor assembly
cannot run if the ignition is off or either battery ca-
ble is disconnected. Unless otherwise specified, the hydraulic accumu-
lator should be de-pressurized before disassembling
any portion of the hydraulic system. The following
procedure should be used to de-pressurize the hy-
draulic accumulator: (1) With ignition off, or either battery cable discon-
nected, pump the brake pedal a minimum of 40 times
using approximately 50 pounds of pedal force. A no-
ticeable change in pedal feel will occur when the ac-
cumulator becomes discharged. (2) When a definite increase in pedal effort is felt,
pump the pedal a few additional times. This will in-
sure removal of all hydraulic pressure from the
brake system.
WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CABLES
Proper installation of wheel speed sensor cables is
critical to continued ABS system operation. Be sure
that cables are installed and routed properly. Failure
to install cables in their retainers, as shown in Sec-
tion 3 of this manual. May result in contact with
moving parts or over extension of cables, resulting in
an open circuit.
MECHANICAL DIAGNOSTICS AND SERVICE
PROCEDURES
SPECIAL SERVICE TOOLS
Some diagnostic procedures in this section require
the use of special service tools. Each of these tools is
described below.
DRB II DIAGNOSTIC TESTER
Some of the diagnostic procedures that are ex-
plained in this section require the use of the DRB II
DIAGNOSTICS TESTER to insure that proper diag-
nostics are performed. Refer to those sections for
proper testing procedures and the DRB II manual for
its proper operational information.
MST-6163 PRESSURE TESTER
Some diagnostic procedures in this manual require
the use of the MST-6163 pressure gauge and adaptor
(Fig. 2). Pressure Gauge, Special Tool MST-6163 is
required to measure accumulator pressure during
certain phases of ABS operation. The pressure gauge
and adaptor should be installed as follows: (1) De-pressurize the accumulator by pumping the
brake pedal a minimum of 40 times with the ignition
off. The procedure is fully explained under De-Pres-
surizing Hydraulic Accumulator which is described
earlier in this System Diagnosis Section.
Ä ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 89
Page 242 of 2438

(11) Remove all special tools previously installed,
from the ABS hydraulic assembly. (12) Install accumulator port plug into hydraulic
assembly. Torque accumulator port plug to 12 N Im(9
ft. lbs.). (13) Install high pressure brake hose from the
pump motor assembly into hydraulic fitting on ABS
hydraulic assembly. Torque high pressure brake hose
tube nut to 16 N Im (145 in. lbs.).
(14) Turn ignition switch to the run position to en-
ergize the pump/motor assembly and pressurize hy-
draulic system. Check for leakage at the hydraulic
assembly to hydraulic bladder accumulator fitting. (15) Again de-pressurize accumulator by pumping
brake pedal a minimum of 40 times. Use procedure
described in De-Pressurizing Hydraulic Accumulator
in this section of the service manual. (16) Then check the brake fluid level in the hy-
draulic assembly reservoir. If brake fluid level is low,
fill reservoir to proper level with Mopar tbrake fluid
or equivalent conforming to DOT 3 requirements.
INTERMITTENT FAULTS
As with almost any electronic system, intermittent
faults in the ABS system may be difficult to accu-
rately diagnose. Most intermittent faults are caused by faulty elec-
trical connections or wiring. When an intermittent
fault is encountered, check suspect circuits for: (1) Poor mating of electrical connector halves, or
electrical terminals not fully seated in the connector
body. (2) Improperly formed or damaged electrical termi-
nals. All connector terminals in a suspect circuit
should be carefully reformed to increase contact ten-
sion. (3) Poor terminal to wire connection. This requires
removing the terminal from the connector body and
inspecting for proper terminal to wire connection. If a visual check does not find the cause of the
problem, operate the vehicle in an attempt to dupli-
cate the condition and record the Fault Code. Most failures of the ABS system will disable the
Anti-Lock function for the entire ignition cycle even
if the fault clears before ignition key-off. There are
some failure conditions however, which will allow
ABS operation to resume during the ignition cycle in
which a failure occurred. If the failure conditions are
no longer present. The following conditions may result in intermittent
illumination of the Red Brake Warning Lamp and/or
Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp. All other failures
will cause the lamp(s) to remain on until the ignition
switch is turned off. Circuits and or components in-
volving these inputs to the (CAB) should be investi-
gated if a complaint of intermittent warning system
operation is encountered. ²
Low system voltage. If low system voltage is de-
tected by the (CAB), the (CAB) will turn on the Am-
ber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp until normal system
voltage is achieved. Once normal voltage is seen at
the (CAB), normal operation resumes.
² Low Brake Fluid. A low brake fluid condition will
cause the Red Brake Warning Lamp to illuminate.
When the fluid sensor again indicates an acceptable
fluid level, the Red Brake Warning Lamp will go out.
This condition may exist during hard cornering or
while the vehicle is on a grade. If the vehicle is in
motion above 3 M.P.H. the Amber Anti-Lock Warn-
ing Lamp will also be turned on.
² Low Accumulator Pressure. Low Accumulator
Pressure will cause both the Red Brake Warning and
Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamps to illuminate.
Once normal operating pressure is achieved, the
lamps will extinguish and the system will return to
normal operation. Additionally, any condition that results in an inter-
ruption of power to the (CAB) or hydraulic assembly.
May cause the Red Brake Warning and Amber Anti-
Lock Warning Lamps to illuminate intermittently. All the conditions (or faults) mentioned above, can
store a fault code in the (CAB) module.
ABS BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES
SYSTEM SELF DIAGNOSIS
The ABS system is equipped with a diagnostic ca-
pability that may be used to assist in isolation of
ABS faults. The features of the diagnostics system
are described below.
CONTROLLER ANTI-LOCK BRAKE (CAB)
Fault codes are kept in a Non-Volatile memory un-
til either erased by the technician using the DRB II
or erased automatically after 50 ignition cycles (key
ON-OFF cycles). The only fault that will not be
erased after 50 (KEY CYCLES) is the (CAB) fault.
The (CAB) fault can only be erased by using the
DRB II diagnostic tester. More than one fault can be
stored at a time. The number of key cycles since the
most recent fault was stored is also displayed. Most
functions of the (CAB) and (ABS) system can be ac-
cessed by the technician for testing and diagnostic
purposes by using the DRB II Diagnostic Tester.
START-UP CYCLE
The START-UP CYCLE takes place immediately
after the ignition switch is turned on. It is an elec-
trical check of basic electrical functions such as the
System Relay and Anti-Lock Warning Lamp Relay.
During this check, the Amber Anti-Lock Warning
Lamp is turned on, then turned off at the end of the
test. The test takes approximatel y1-2seconds to
complete.
5 - 92 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 243 of 2438

DRIVE-OFF CYCLE
The DRIVE-OFF CYCLE takes place when the ve-
hicle reaches about 3 miles per hour the first time af-
ter an ignition reset. During this test, the modulator
solenoid valves are activated briefly to test their
function. The DRIVE-OFF CYCLE will be bypassed
if you drive-off with the service brake pedal de-
pressed.
LATCHING VERSUS NON-LATCHING FAULTS
Some faults detected by the (CAB) are latching.
The fault is latched and (ABS) function is disabled
until the ignition switch is reset (turned OFF/ON).
Thus (ABS) function is disabled even if the original
fault has disappeared during the ignition cycle in
which it occurred. Other faults are non-latching; any
warning lights that are turned on are only on as long
as the fault condition exists. As soon as the condition
goes away. The Amber Anti-Lock Warning Light is
turned off. Although a fault code will be set in most
cases. (Example:low accumulator fault will not be
stored for a time of 2 minutes after the fault is de-
tected).
BENDIX ABS SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS
The Bendix Anti-Lock 10 Brake System diagnos-
tics. Beyond the basic mechanical diagnostics, sys-
tems and components covered earlier in this section,
is accomplished by using the DRB II diagnostic
tester. See testing procedures outlined in the Bendix
Anti-Lock 10 Diagnostics Manual for the 1993 M.Y. Please reference the above mentioned manual. For
any further diagnostic service procedures that are re-
quired on the Bendix Anti-Lock 10 Brake System, re-
quiring the use of the DRB II diagnostic tester.
ON CAR HYDRAULIC ABS COMPONENT SERVICE
WARNING: FAILURE TO FULLY DE-PRESSURIZE
THE HYDRAULIC ACCUMULATOR BEFORE PER-
FORMING HYDRAULIC SYSTEM SERVICE OPERA-
TIONS. COULD RESULT IN INJURY TO SERVICE
PERSONNEL AND OR DAMAGE TO PAINTED SUR-
FACES. SEE SECTION 2 FOR ADDITIONAL WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS.
GENERAL SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
The following are general precautions that should
be observed when servicing the Anti-Lock Brake Sys-
tem and/or other vehicle systems. Failure to observe
these precautions may result in Anti-Lock brake sys-
tem damage. If welding work is to be performed on the vehicle,
using an electric arc welder, the (CAB) connector
should be disconnected during the welding operation. The (CAB) or hydraulic assembly connector should
never be connected or disconnected with the ignition
switch in the ONposition.
Many components of the Anti-Lock brake system are
not serviceable and must be replaced as an assembly.
Do not attempt to disassemble any component
that is not designed to be a serviced component.
DE-PRESSURIZING HYDRAULIC ACCUMULA- TOR
The pump/motor assembly will keep the hydraulic
accumulator charged to approximately 11,032 and
13,790 kPa (1600 and 2000 psi) any time that the
ignition is in the ON position. The pump/motor assem-
bly cannot run if the ignition is off or if either battery
cable is disconnected. Unless otherwise specified, the hydraulic accumula-
tor should be de-pressurized before disassembling any
portion of the hydraulic system. The following proce-
dure should be used to relieve the pressure in the
hydraulic accumulator: (1) With ignition off, or either battery cable discon-
nected, pump the brake pedal a minimum of 40 times,
using approximately 222 N (50 lbs.) pedal force. A
noticeable change in pedal feel will occur, when the
accumulator is discharged. (2) When a definite increase in pedal effort is felt,
pump pedal a few additional times. This will insure
removal of all hydraulic pressure from the brake sys-
tem.
CHECKING BRAKE FLUID LEVEL
CAUTION: Use only brake fluid conforming to DOT 3
specifications such as Mopar Tor Equivalent. Do not
use any fluid in the brake hydraulic system, which
contains a petroleum base. Do not use a container
which has been used for petroleum based fluids or a
container that is wet with water. Petroleum based
fluids will cause swelling and distortion of rubber
parts in the hydraulic brake system and water will mix
with brake fluid, lowering the fluid boiling point. Keep
all brake fluid containers tightly capped to prevent
contamination.
The hydraulic assembly is equipped with a plastic
fluid reservoir, with a filter/strainer located in the filler
neck of each reservoir section. The Anti-Lock brake system requires that the hy-
draulic accumulator be de-pressurized when checking
the fluid level. To check the brake fluid level, the
following procedure should be used: (1) With the ignition off, de-pressurize the hydraulic
accumulator by applying the brake pedal approxi-
mately 40 times, using a pedal force of approximately
220 N (50 lbs.). A noticeable change in pedal feel will
occur when the accumulator is de-
Ä ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 93
Page 246 of 2438

PUMP/MOTOR SERVICE (FIG. 4)
REMOVE (1) Fully de-pressurize the hydraulic accumulator
by pumping the pedal a minimum of 40 times. Use
the procedure described in De-Pressurizing Hydraulic
Accumulator listed earlier in this section.
WARNING: FAILURE TO DE-PRESSURIZE HYDRAU-
LIC ACCUMULATOR, BEFORE PERFORMING THIS
OPERATION, MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY
AND/OR DAMAGE TO PAINTED SURFACES.
(2) Remove the fresh air intake ducts from the en-
gine induction system. (3) Loosen the low pressure hose clamp (Fig. 5) at
the hydraulic assembly. (4) Disconnect any routing clips which attach the
high and low pressure fluid lines to the body or com-
ponents of the vehicle (Fig. 5). (5) Unclip the pump/motor assembly wiring har-
ness electrical connector from the left side engine
mount (Fig. 5). Disconnect the pump/motor assembly
wiring harness from the underhood wiring harness. (6) Loosen the high pressure hose tube nut at the
hydraulic assembly fitting (Fig. 5). (7) Remove the high and low pressure hose assem-
bly (Fig. 5) from the hydraulic assembly. Cap all
open ports on reservoir and hydraulic assembly to
prevent brake fluid from leaking out. (8) Remove the pump/motor assembly front heat
shield to mounting bracket attaching bolt, from front
of pump/motor bracket (Fig. 5). (9) Remove front heat shield from the pump/motor
assembly. (10) Lift pump/motor assembly from mounting
bracket and remove assembly from the vehicle.
INSTALL
CAUTION:Be sure all high and low pressure hose
routing clips. Are securely fastened to the vehicle
body or component they were removed from when
hose assembly is reinstalled (Fig. 5).
(1) Install pump/motor assembly in reverse order of
removal. (2) Tighten the pump/motor assembly fluid lines to
the torque values shown below.
² Low pressure hose clamp. 1 N Im (10 in. lbs.)
² High pressure hose fitting to pump/motor assembly.
16 N Im (145 in. lbs.) Fig. 5.
Note: It is not necessary to bleed the founda-
tion brakes of the vehicle when the pump/motor
assembly and high and low pressure fluid hoses
are serviced. Any other service to the brake
system unless stated otherwise will require
bleeding of the complete brake system.
BRAKE FLUID PRESSURE AND RETURN HOSES (FIG. 6)
REMOVE
(1) Remove the pump/motor assembly from its
mounting bracket, see Pump/Motor Service. (2) Cut the 4 tie straps that secure the high and low
pressure hoses and pump/motor assembly wiring har-
ness together Fig. 6. (3) Remove the banjo bolt and spray shield from the
pump/motor assembly Fig. 6.
Fig. 4 Pump/Motor Assembly MountingFig. 5 Brake Tube and Hose Routing
5 - 96 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 247 of 2438
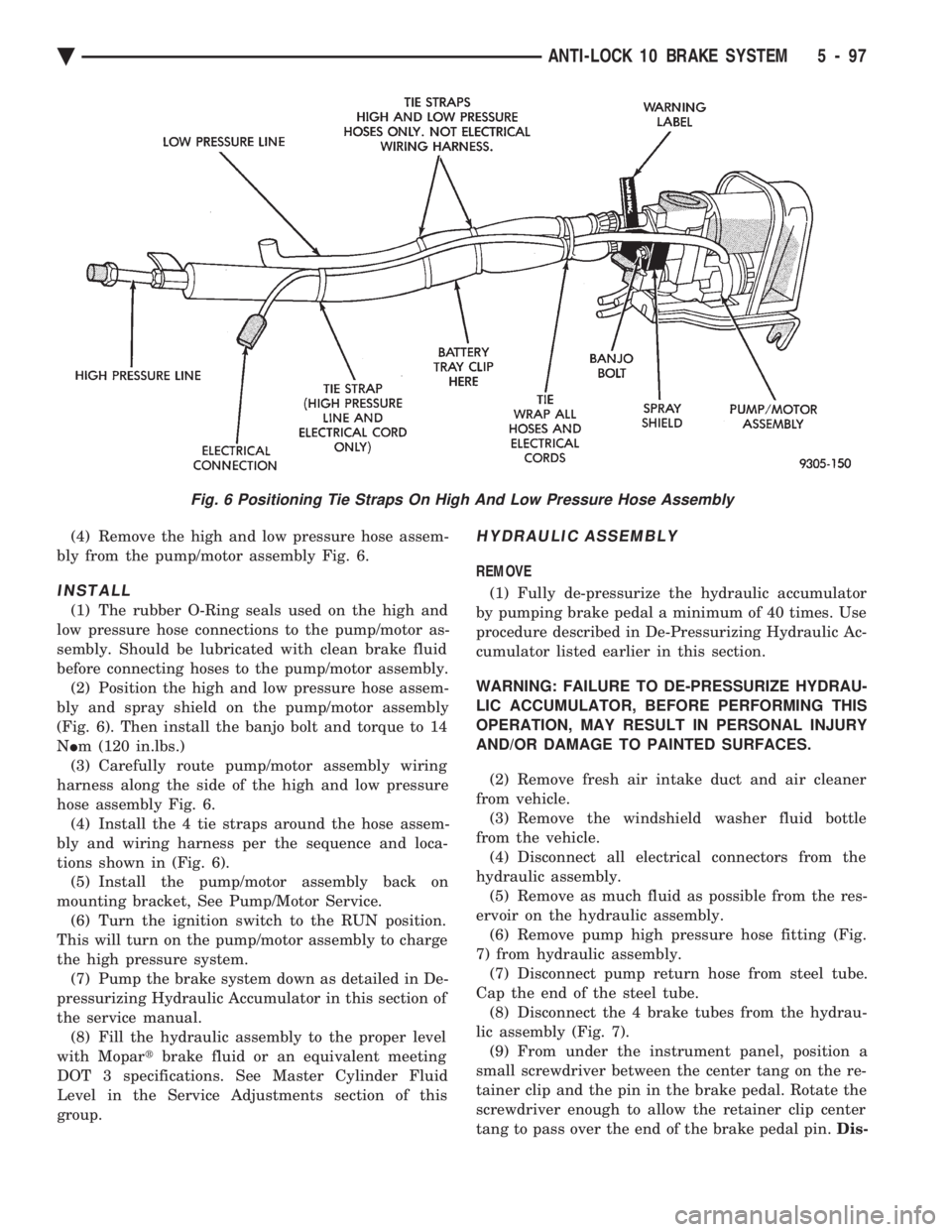
(4) Remove the high and low pressure hose assem-
bly from the pump/motor assembly Fig. 6.
INSTALL
(1) The rubber O-Ring seals used on the high and
low pressure hose connections to the pump/motor as-
sembly. Should be lubricated with clean brake fluid
before connecting hoses to the pump/motor assembly. (2) Position the high and low pressure hose assem-
bly and spray shield on the pump/motor assembly
(Fig. 6). Then install the banjo bolt and torque to 14
N Im (120 in.lbs.)
(3) Carefully route pump/motor assembly wiring
harness along the side of the high and low pressure
hose assembly Fig. 6. (4) Install the 4 tie straps around the hose assem-
bly and wiring harness per the sequence and loca-
tions shown in (Fig. 6). (5) Install the pump/motor assembly back on
mounting bracket, See Pump/Motor Service. (6) Turn the ignition switch to the RUN position.
This will turn on the pump/motor assembly to charge
the high pressure system. (7) Pump the brake system down as detailed in De-
pressurizing Hydraulic Accumulator in this section of
the service manual. (8) Fill the hydraulic assembly to the proper level
with Mopar tbrake fluid or an equivalent meeting
DOT 3 specifications. See Master Cylinder Fluid
Level in the Service Adjustments section of this
group.
HYDRAULIC ASSEMBLY
REMOVE
(1) Fully de-pressurize the hydraulic accumulator
by pumping brake pedal a minimum of 40 times. Use
procedure described in De-Pressurizing Hydraulic Ac-
cumulator listed earlier in this section.
WARNING: FAILURE TO DE-PRESSURIZE HYDRAU-
LIC ACCUMULATOR, BEFORE PERFORMING THIS
OPERATION, MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY
AND/OR DAMAGE TO PAINTED SURFACES.
(2) Remove fresh air intake duct and air cleaner
from vehicle. (3) Remove the windshield washer fluid bottle
from the vehicle. (4) Disconnect all electrical connectors from the
hydraulic assembly. (5) Remove as much fluid as possible from the res-
ervoir on the hydraulic assembly. (6) Remove pump high pressure hose fitting (Fig.
7) from hydraulic assembly. (7) Disconnect pump return hose from steel tube.
Cap the end of the steel tube. (8) Disconnect the 4 brake tubes from the hydrau-
lic assembly (Fig. 7). (9) From under the instrument panel, position a
small screwdriver between the center tang on the re-
tainer clip and the pin in the brake pedal. Rotate the
screwdriver enough to allow the retainer clip center
tang to pass over the end of the brake pedal pin. Dis-
Fig. 6 Positioning Tie Straps On High And Low Pressure Hose Assembly
Ä ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 97
Page 249 of 2438

(7) Install high pressure hose to hydraulic assem-
bly (Fig. 7). Tighten the hose, to hydraulic assembly
fitting to 16 N Im (145 in. lbs)
(8) Fill hydraulic assembly brake fluid reservoir to
top of screen on the reservoir filter/strainer Fig. 9.
(9) Connect all electrical connectors to the hydrau-
lic assembly. (10) Bleed the entire brake system, see Bleeding
Brake System in this section of the Service Manual. (11) Replace all fresh air intake ducts, air cleaner
and washer bottle. (12) Check that the brake fluid in the hydraulic
assembly is at the correct level before moving vehicle
(Fig. 9). (See Checking Brake Fluid Level in this sec-
tion of the service manual).
BRAKE FLUID RESERVOIR
REMOVE
(1) Fully de-pressurize the hydraulic accumulator
by pumping brake pedal a minimum of 40 times. Use
procedure described in De-Pressurizing Hydraulic Ac-
cumulator listed earlier in this section.
WARNING: FAILURE TO DE-PRESSURIZE HYDRAU-
LIC ACCUMULATOR, BEFORE PERFORMING THIS
OPERATION, MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY
AND/OR DAMAGE TO PAINTED SURFACES.
(2) Remove as much brake fluid as possible from
the fluid reservoir, using a syringe or equivalent
method. (3) Using Oil Filter Band Wrench, Special Tool
C-4065 or equivalent loosen bladder accumulator. Then remove the bladder accumulator and brake
fluid spray shield from the hydraulic assembly (Fig.
10). Remove high pressure banjo fitting from hydrau-
lic assembly.
(4) Using needle nose pliers, remove the three
fluid reservoir retaining pins from the hydraulic as-
sembly (Fig. 11). Compress the barb on the opposite
side of retaining pin to prevent pin from breaking.
(5) Remove reservoir from hydraulic assembly by
CAREFULLY prying between reservoir and hydrau-
Fig. 9 ABS Fill Level On Filter/Strainer
Fig. 10 Removing Bladder Accumulator
Fig. 11 Remove Reservoir Retaining Pins
Ä ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 99
Page 252 of 2438
WARNING: FAILURE TO DE-PRESSURIZE HYDRAU-
LIC ASSEMBLY/ACCUMULATOR PRIOR PERFORM-
ING THIS OPERATION. MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL
INJURY AND/OR DAMAGE TO PAINTED SURFACES
OF THE VEHICLE.
(2) Using Oil Filter Band Wrench, Special Tool
C-4065 or equivalent loosen bladder accumulator.
Then remove the bladder accumulator and brake
fluid shield from the hydraulic assembly (Fig. 17).
INSTALL
(1) Install the brake fluid spray shield onto the hy-
draulic accumulator (Fig. 1). (2) Install the bladder accumulator onto the hy-
draulic assembly by hand. Be sure that the O-Ring
on the bladder accumulator is fully seated into the
hydraulic assembly. (3) Using Oil Filter Band Wrench, Special Tool
C-4065 or equivalent, (Fig. 17) torque the bladder ac-
cumulator to 48 N Im (35 ft. lbs.)
(4) Turn ignition switch to the run position to en-
ergize the pump/motor assembly and pressurize hy-
draulic system. Check for leakage at the hydraulic
assembly to hydraulic bladder accumulator fitting. (5) Again de-pressurize accumulator by pumping
brake pedal a minimum of 40 times. Use procedure
described in De-Pressurizing Hydraulic Accumulator
in this section of the service manual. (6) Then check the brake fluid level in the hydrau-
lic assembly reservoir. If brake fluid level is low, fill
reservoir to proper level (Fig. 15) with Mopar tbrake
fluid or equivalent conforming to DOT 3 require-
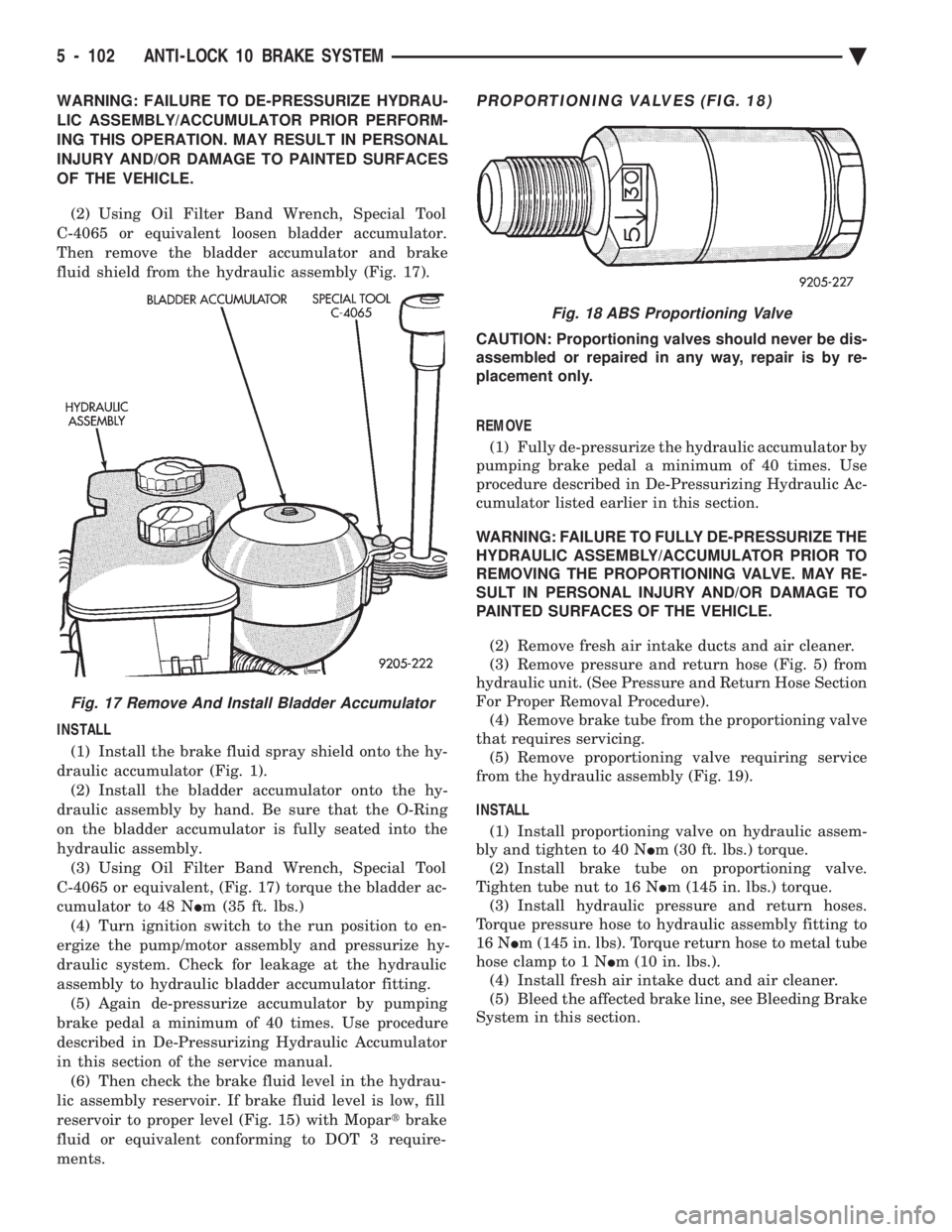
ments.PROPORTIONING VALVES (FIG. 18)
CAUTION: Proportioning valves should never be dis-
assembled or repaired in any way, repair is by re-
placement only.
REMOVE (1) Fully de-pressurize the hydraulic accumulator by
pumping brake pedal a minimum of 40 times. Use
procedure described in De-Pressurizing Hydraulic Ac-
cumulator listed earlier in this section.
WARNING: FAILURE TO FULLY DE-PRESSURIZE THE
HYDRAULIC ASSEMBLY/ACCUMULATOR PRIOR TO
REMOVING THE PROPORTIONING VALVE. MAY RE-
SULT IN PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR DAMAGE TO
PAINTED SURFACES OF THE VEHICLE.
(2) Remove fresh air intake ducts and air cleaner.
(3) Remove pressure and return hose (Fig. 5) from
hydraulic unit. (See Pressure and Return Hose Section
For Proper Removal Procedure). (4) Remove brake tube from the proportioning valve
that requires servicing. (5) Remove proportioning valve requiring service
from the hydraulic assembly (Fig. 19).
INSTALL (1) Install proportioning valve on hydraulic assem-
bly and tighten to 40 N Im (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install brake tube on proportioning valve.
Tighten tube nut to 16 N Im (145 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install hydraulic pressure and return hoses.
Torque pressure hose to hydraulic assembly fitting to
16 N Im (145 in. lbs). Torque return hose to metal tube
hose clamp to 1 N Im (10 in. lbs.).
(4) Install fresh air intake duct and air cleaner.
(5) Bleed the affected brake line, see Bleeding Brake
System in this section.
Fig. 17 Remove And Install Bladder Accumulator
Fig. 18 ABS Proportioning Valve
5 - 102 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 260 of 2438

(7) Using needle nose pliers, install the 3 brake fluid
reservoir to hydraulic assembly retaining pins (Fig.
14). Be sure retaining pins are fully installed with
barbs extending out past reservoir on opposite
side. (8) Install high pressure hose banjo fitting onto
hydraulic assembly and install banjo fitting attaching
bolt. Torque banjo fitting to hydraulic assembly banjo
bolt to 13 N Im (10 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install brake fluid spray shield onto hydraulic
assembly. Install bladder accumulator into hydraulic
assembly by hand (using care not to cross thread
accumulator) until O-ring seal is fully seated into
hydraulic assembly. (10) Using Oil Filter Band Wrench, Special Tool
C-4065 or equivalent, (Fig. 12) torque bladder accumu-
lator to 48 N Im (35 ft. lbs.).
(11) Fill hydraulic assembly fluid reservoir to the top
of the screen on the filter rainer. Use only fresh clean
brake fluid conforming to DOT 3 requirements, such as
Mopar tor equivalent.
(12) Bleed the brake hydraulic system using proce-
dure shown in Bleeding Brake System in this section of
the service manual.
DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SWITCH
REMOVE
WARNING: FAILURE TO FULLY DE-PRESSURIZE THE
HYDRAULIC BLADDER ACCUMULATOR PRIOR TO
REMOVING DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SWITCH.
WILL RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR DAM-
AGE TO PAINTED SURFACES OF THE VEHICLE.
To remove the differential pressure switch (Fig. 18),
from the hydraulic assembly, removal of the hydraulic
assembly from the vehicle is notrequired. (1) De-pressurize hydraulic bladder accumulator on
hydraulic assembly by pumping the brake pedal a
minimum of 40 times. Refer to the procedure as de-
scribed in De-Pressurizing Hydraulic Accumulator
listed earlier in this section. (2) Disconnect the hydraulic assembly wiring har-
ness connector from the primary pressure transducer
(Fig. 19).
(3) Disconnect differential pressure switch wiring
harness connector from hydraulic assembly wiring
harness (Fig. 19). Do not attempt to remove wiring
harness from differential pressure switch. (4) Raise vehicle on a frame contact type hoist. See
Hoisting in the Lubrication And Maintenance section
of this manual, for the required lifting procedure to be
used for this vehicle. (5) Using a long extension and Socket, Special Tool
6684 loosen and remove differential pressure switch
from bottom of hydraulic assembly (Fig. 20)
Fig. 18 Differential Pressure Switch Location
Fig. 19 Primary Pressure Transducer And Differen- tial Pressure Switch Wiring Harness Connectors
Fig. 17 Primary Pressure Transducer Removal And Replacement
5 - 110 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä