service CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 333 of 2438

MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH
CONTENTS
page page
CLEANING PRECAUTIONS ................. 6
CLUTCH CABLE MECHANISM .............. 1
CLUTCH CABLE REPLACEMENT ............ 2
CLUTCH CHATTER COMPLAINTS ........... 1
CLUTCH DISC REPLACEMENT ............. 5
CLUTCH PEDAL NOISE/POP ............... 2 CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH
......... 4
EXCESSIVE CLUTCH SPIN TIME/CLASH INTO REVERSE COMPLAINTS ............ 1
GENERAL INFORMATION .................. 1
RELEASE BEARING AND FORK ............. 6
GENERAL INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references may be made to
a particular vehicle by letter or number designation.
A chart showing the breakdown of these designations
is included in the Introduction Section at the front of
this service manual. The clutch used in all models are a single, dry disc
type with no adjustment for wear being provided in
the clutch itself. The clutch pedal is connected to the release shaft
through a cable and lever. The upper end of the clutch pedal pivots in the
pedal bracket on two nylon bushings. These bushings
do not require periodic lubrication.
CLUTCH CHATTER COMPLAINTS
For all clutch chatter complaints, do the following:
(1) Check for loose, misaligned, or broken engine
and transmission mounts. If present, they should be
corrected at this time. Test vehicle for chatter. If
chatter is gone, there is no need to go any further. If
chatter persists: (2) Check to see if clutch cable routing is correct
and operates smoothly. (3) Check for loose connections in drive train. Cor-
rect any problems and determine if clutch chatter
complaints has been satisfied. If not, (4) Remove transaxle. See Group 21, Manual Tran-
saxle, for procedure. (5) Check to see if the release bearing is sticky or
binding. Replace bearing, if needed. (6) Check linkage for excessive wear on bushings.
Replace all worn parts. A small amount of bearing
grease between the release shaft bushings and the
shaft is beneficial, but not required. (7) Check flywheel and clutch pressure plate for
contamination (dirt, oil) or scored. Replace flywheel
and/or pressure plate, if required. (8) Check to see if the clutch disc hub splines are
damaged. Replace with new disc. (9) Check input shaft splines for damage. Replace
if necessary. (10) Check for uneven wear on clutch fingers.
EXCESSIVE CLUTCH SPIN TIME/CLASH INTO
REVERSE COMPLAINTS
For all excessive clutch spin time/clash into reverse
complaints, do the following: (1) Depress clutch pedal to floor and hold. After
three seconds, shift to reverse. If clash is present,
clutch has excessive spin time. (2) Remove transaxle. See Group 21, Manual Tran-
saxle, for procedure. (3) Check the input shaft spline, clutch disc splines
and release bearing for dry rust. If present, clean
rust off and apply a light coat of bearing grease to
the input shaft splines. Apply grease on the input
shaft splines only where the clutch disc slides. (4) Check to see if the clutch disc hub splines are
damaged, replace with new disc if required. (5) Check the input shaft for damaged splines. Re-
place as necessary. (6) Check for excessive clutch disc runout or
warpage. (7) Install clutch assembly and transaxle.
CLUTCH CABLE MECHANISM
The manual transaxle clutch release system has a
unique self-adjusting mechanism to compensate for
clutch disc wear. This adjuster mechanism is located
within the clutch pedal. The preload spring main-
tains tension on the cable. This tension keeps the
clutch release bearing continuously loaded against
the fingers of the clutch cover assembly. When the pedal is depressed, teeth on the adjuster
and the positioner engage and pull the release cable.
A spring located behind the adjuster ensures proper
tooth engagement. When the pedal is released, the adjuster contacts
the bumper. This separates the adjuster and posi-
tioner teeth, allowing the preload spring to function.
Ä MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH 6 - 1
Page 339 of 2438
hicle is steam cleaned. The facing of the disc will
absorb moisture. The force exerted by the pressure
plate will bond the facings to flywheel and/or, pres-
sure plate, if vehicle is allowed to stand for some
time before use. If this condition occurs, it will re- quire replacement of disc assembly, flywheel, and/or
clutch assembly. After cleaning, drive the vehicle to
its normal clutch operating temperature. This will
dry off disc assembly, pressure plate, and flywheel.
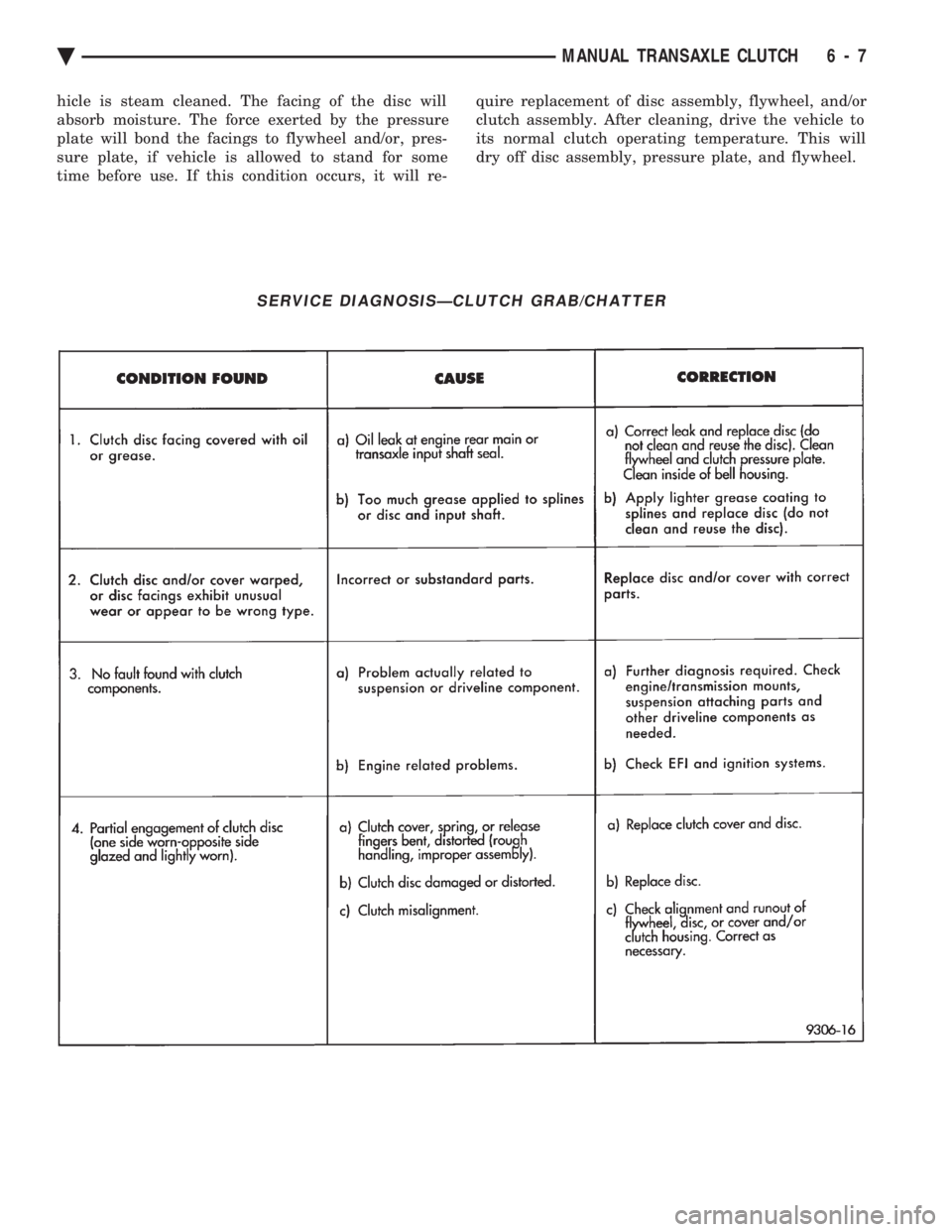
SERVICE DIAGNOSISÐCLUTCH GRAB/CHATTER
Ä MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH 6 - 7
Page 340 of 2438

SERVICE DIAGNOSISÐCLUTCH SLIPS
6 - 8 MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH Ä
Page 341 of 2438
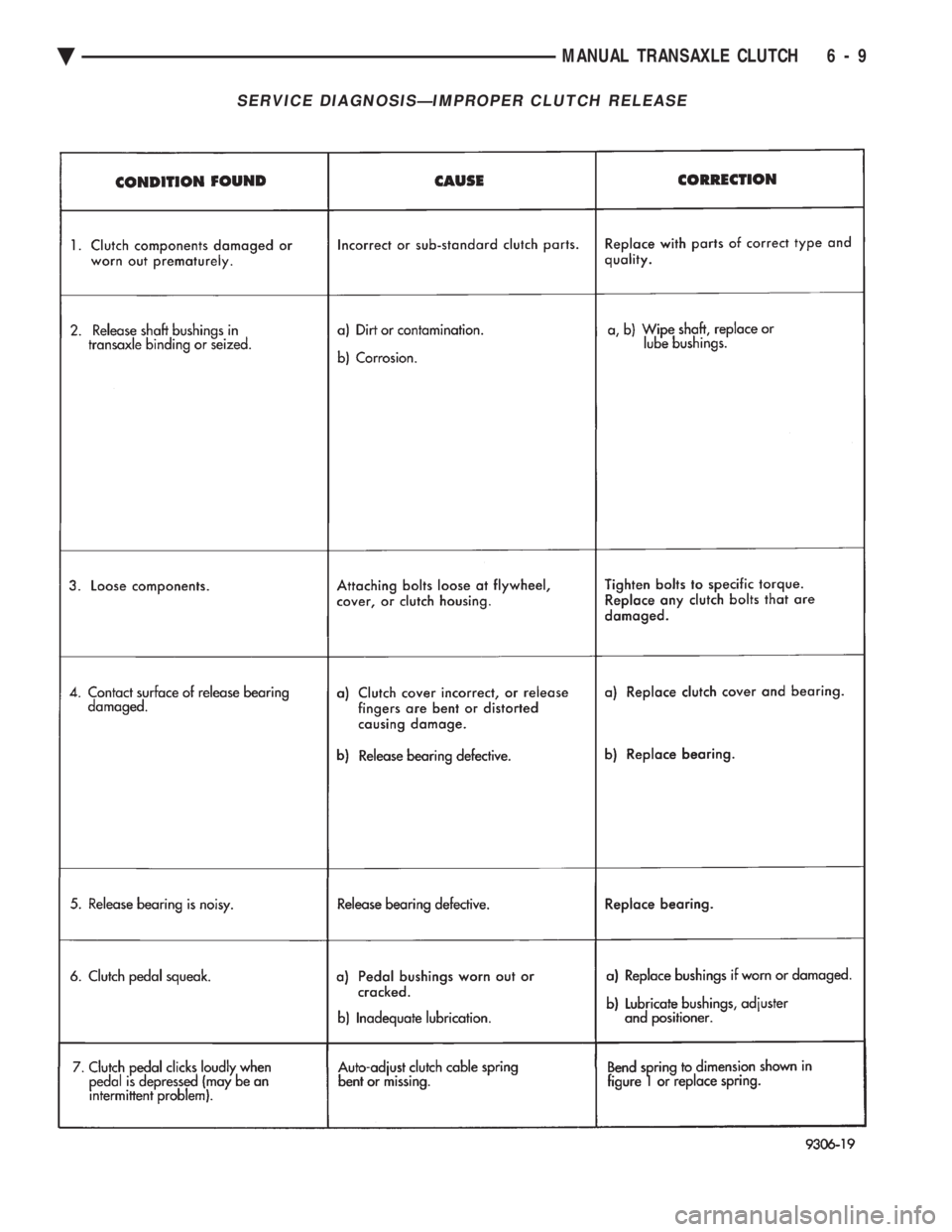
SERVICE DIAGNOSISÐIMPROPER CLUTCH RELEASE
Ä MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH 6 - 9
Page 342 of 2438
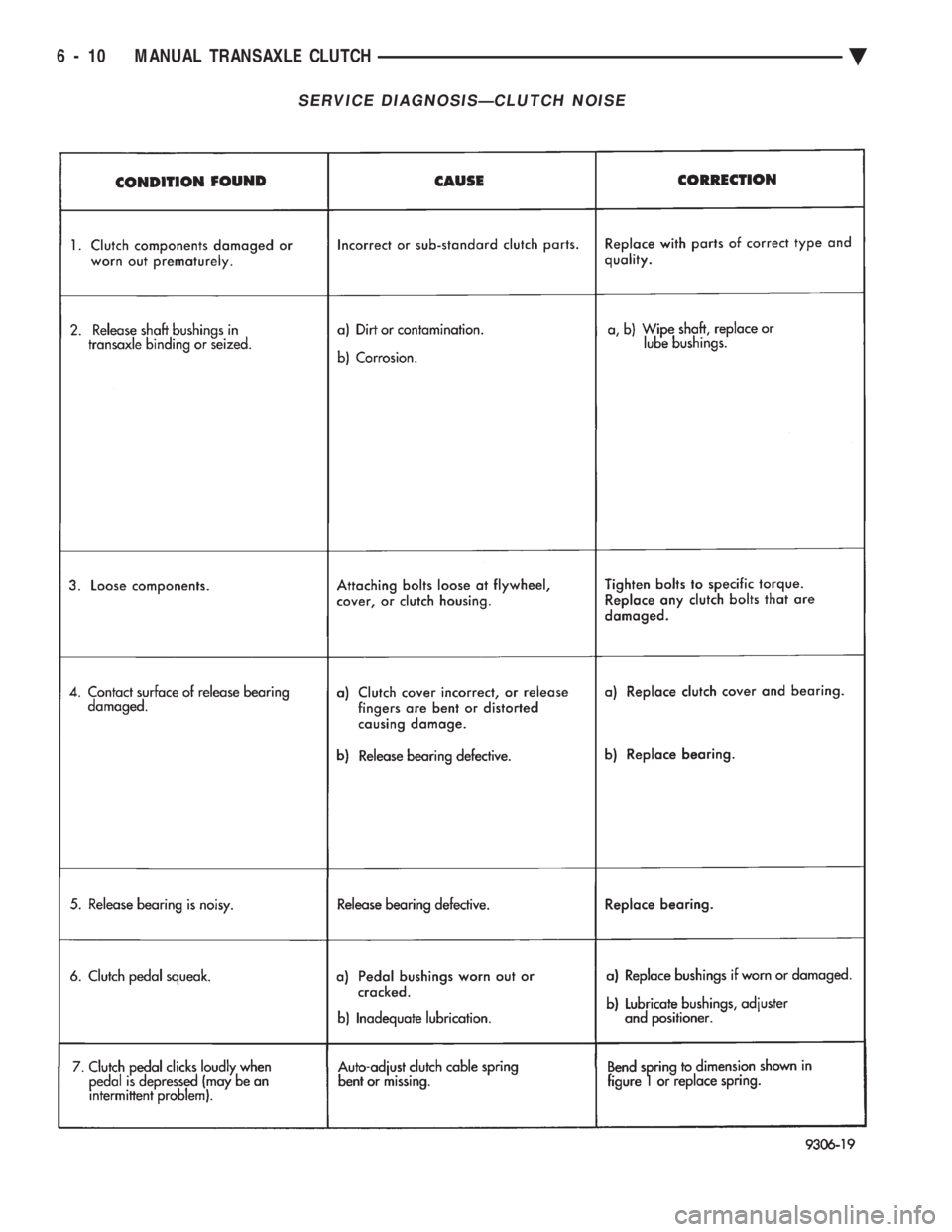
SERVICE DIAGNOSISÐCLUTCH NOISE
6 - 10 MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH Ä
Page 343 of 2438

COOLING SYSTEM
CONTENTS
page page
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS ............... 24
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER ................. 28
GENERAL INFORMATION .................. 1 SERVICE PROCEDURES
.................. 10
SPECIFICATIONS ....................... 29
GENERAL INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references may be made to
a particular vehicle by letter or number designation.
A chart showing the breakdown of these designations
is included in the Introduction Section at the front of
this service manual.
COOLING SYSTEM
The cooling system consists of an engine cooling
module, thermostat, coolant, a water pump to circu-
late the coolant. The engine cooling module may con-
sist of a radiator, electric fan motor, shroud, radiator
pressure cap, coolant reserve system, transmission oil
cooler, hoses, clamps, air condition condenser, trans-
mission oil lines and charge air cooler.
² When Engine is cold: Thermostat is closed, cooling
system has no flow through the radiator. The coolant
bypass flows through the engine only. ²
When Engine is warm: Thermostat is open, cooling
system has bypass flow and coolant flow through ra-
diator. Its primary purpose is to maintain engine temper-
ature in a range that will provide satisfactory engine
performance and emission levels under all expected
driving conditions. It also provides hot water (cool-
ant) for heater performance and cooling for auto-
matic transmission oil. It does this by transferring
heat from engine metal to coolant, moving this
heated coolant to the radiator, and then transferring
this heat to the ambient air. Coolant flow circuits for 2.2L and 2.5L engine
equipped vehicles are shown in (Fig 1). Turbocharged
equipped engines coolant routing and plumbing are
shown in (Fig 2). The 3.0L engine coolant routing is
shown in (Fig 3). The 3.3L and 3.8L engine coolant
routing is shown in (Fig 5).
Fig. 1 Cooling System OperationÐ2.2/2.5L Engines
Ä COOLING SYSTEM 7 - 1
Page 352 of 2438
SERVICE PROCEDURES INDEX
page page
Automatic Transmission Oil Coolers .......... 23
Coolant ................................ 14
Coolant Recovery System (CRS) ............. 17
Cooling System Drain, Clean, Flush and Refill . . 15
Electric Fan Motor ........................ 22
Engine Thermostats ....................... 13
Fan Shroud ............................. 23 Fans
.................................. 21
Radiator Hoses .......................... 21
Radiator Pressure Cap .................... 18
Radiators ............................... 18
Testing System for Leaks .................. 17
Water Pumps ........................... 10
WATER PUMPS
A quick test to tell whether or not the pump is
working is to see if the heater warms properly. A
defective pump will not be able to circulate heated
coolant through the long heater hose. The water pump on all models can be replaced
without discharging the air conditioning system.
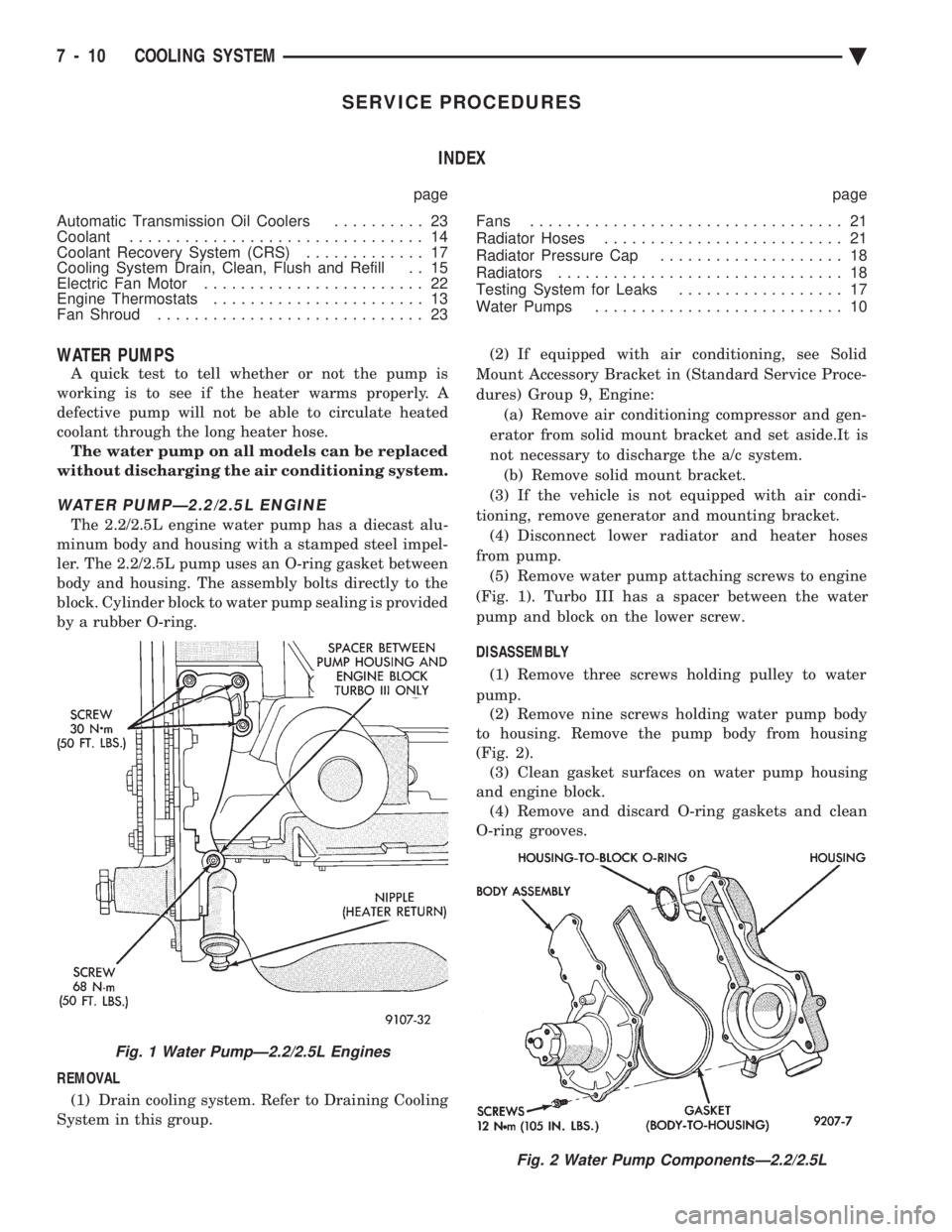
WATER PUMPÐ2.2/2.5L ENGINE
The 2.2/2.5L engine water pump has a diecast alu-
minum body and housing with a stamped steel impel-
ler. The 2.2/2.5L pump uses an O-ring gasket between
body and housing. The assembly bolts directly to the
block. Cylinder block to water pump sealing is provided
by a rubber O-ring.
REMOVAL (1) Drain cooling system. Refer to Draining Cooling
System in this group. (2) If equipped with air conditioning, see Solid
Mount Accessory Bracket in (Standard Service Proce-
dures) Group 9, Engine: (a) Remove air conditioning compressor and gen-
erator from solid mount bracket and set aside.It is
not necessary to discharge the a/c system. (b) Remove solid mount bracket.
(3) If the vehicle is not equipped with air condi-
tioning, remove generator and mounting bracket. (4) Disconnect lower radiator and heater hoses
from pump. (5) Remove water pump attaching screws to engine
(Fig. 1). Turbo III has a spacer between the water
pump and block on the lower screw.
DISASSEMBLY (1) Remove three screws holding pulley to water
pump. (2) Remove nine screws holding water pump body
to housing. Remove the pump body from housing
(Fig. 2). (3) Clean gasket surfaces on water pump housing
and engine block. (4) Remove and discard O-ring gaskets and clean
O-ring grooves.
Fig. 2 Water Pump ComponentsÐ2.2/2.5L
Fig. 1 Water PumpÐ2.2/2.5L Engines
7 - 10 COOLING SYSTEM Ä
Page 353 of 2438
INSPECTION Replace water pump body assembly if it has any of
these defects: (1) Cracks or damage on the body.
(2) Water leaks from the shaft seal, evident by
coolant traces below the vent hole. (3) Loose or rough turning bearing.
(4) Impeller rubs either the pump body or the hous-
ing.
ASSEMBLY
Body assembly and housing are serviced as separate
components. (1) Install new O-ring gasket in body O-ring groove.
(2) Assemble pump body to housing and tighten nine
screws to 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.) (Fig. 2).
(3) Rotate pump by hand to check for freedom of
movement. (4) Position water pump pulley to water pump.In-
stall three screws and tighten to 30 N Im (250 in. lbs.).
(5) Position new O-ring in housing to block O-ring
groove.
INSTALLATION (1) On Turbo III engines install the coolant deflector
into the block before installing pump on engine (Fig. 3).
Install spacer between the pump and block for
Turbo III only before tightening pump to speci-
fications. Tighten three top screws (Fig. 1) to 28 N Im
(250 in. lbs.) and lower screw to 68 N Im (50 ft. lbs.).
(2) Install bypass/heater hose and lower radiator
hose. (3) Install generator and air conditioning compres-
sor bracket(s). For solid mount bracket see standard
service procedures in Group 9 Engine. (4) Install generator and air conditioning compres-
sor. (5) Refill cooling system. See
Refilling Cooling
System. (6) Install drive belt, See Accessory Drive Belts,
this Group.
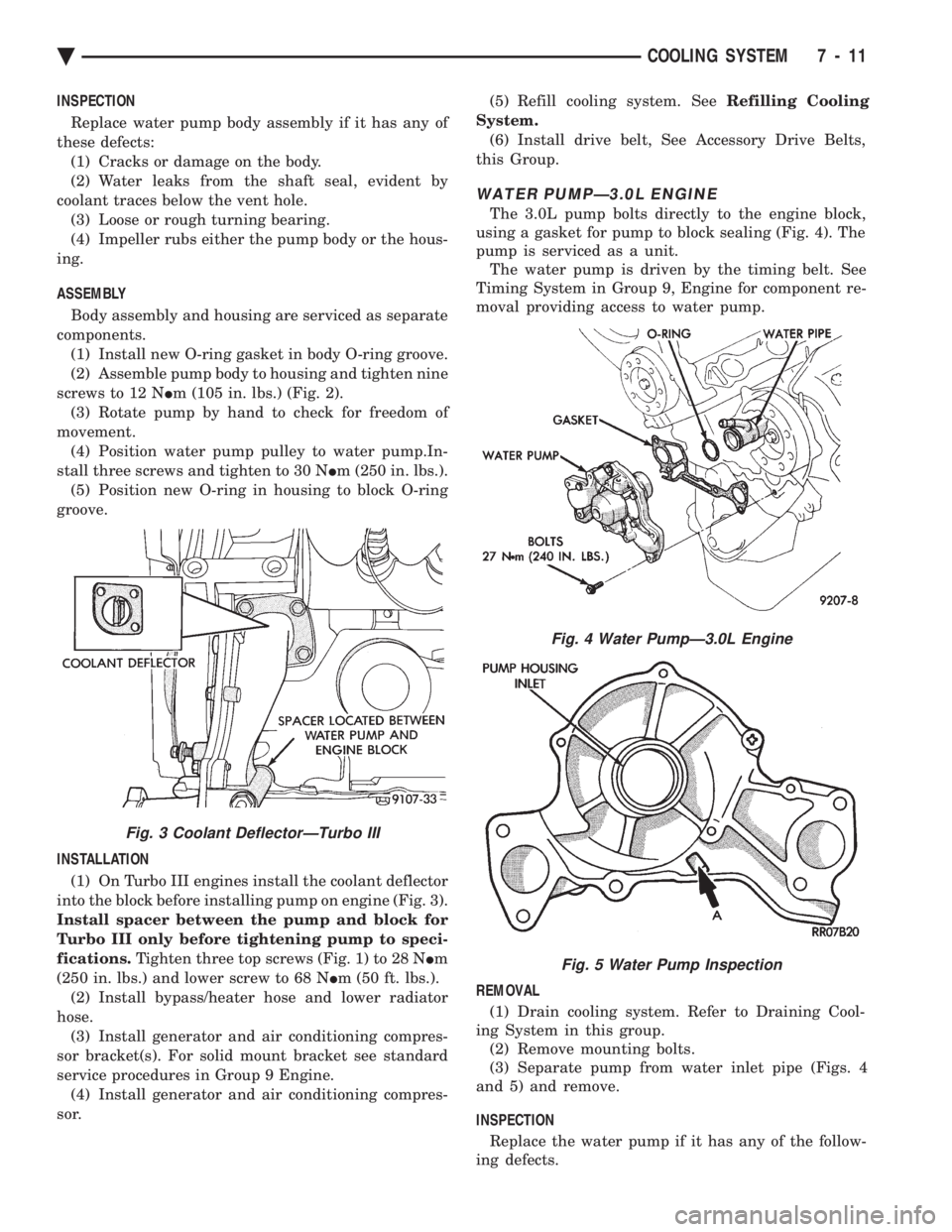
WATER PUMPÐ3.0L ENGINE
The 3.0L pump bolts directly to the engine block,
using a gasket for pump to block sealing (Fig. 4). The
pump is serviced as a unit. The water pump is driven by the timing belt. See
Timing System in Group 9, Engine for component re-
moval providing access to water pump.
REMOVAL (1) Drain cooling system. Refer to Draining Cool-
ing System in this group. (2) Remove mounting bolts.
(3) Separate pump from water inlet pipe (Figs. 4
and 5) and remove.
INSPECTION Replace the water pump if it has any of the follow-
ing defects.
Fig. 4 Water PumpÐ3.0L Engine
Fig. 5 Water Pump Inspection
Fig. 3 Coolant DeflectorÐTurbo III
Ä COOLING SYSTEM 7 - 11
Page 357 of 2438

-37ÉC (-35ÉF) to -59ÉC (-50ÉF). If it looses color or
becomes contaminated, drain, flush, and replace with
fresh properly mixed solution.
SERVICE
Coolant should be changed at 52,500 miles or three
years, whichever occurs first, then every two years or
30,000 miles.
ROUTINE LEVEL CHECK
Do not remove radiator cap for routine coolant
level inspections. The coolant reserve system provides a quick visual
method for determining the coolant level without re-
moving the radiator cap. Simply observe, with the
engine idling and warmed up to normal operating
temperature, that the level of the coolant in the reserve
tank (Figs. 5 and 6) is between the minimum and
maximum marks.
ADDING ADDITIONAL COOLANT
The radiator cap should not be removed. When
additional coolant is needed to maintain this level, it
should be added to the coolant reserve tank. Use only
50/50 concentration of ethylene glycol type antifreeze
and water.
SERVICE COOLANT LEVEL
The cooling system is closed and designed to main-
tain coolant level to the top of the radiator. When servicing requires a coolant level check in the
radiator, the engine must be offand notunder pres-
sure. Drain several ounces of coolant from the radiator
drain cock while observing the Coolant Recovery Sys-
tem (CRS) Tank. Coolant level in the CRS tank should
drop slightly. Then remove the radiator cap. The radia-
tor should be full to the top. If not, and the coolant level
in the CRS tank is at the MIN mark there is a air leak
in the CRS system. Check hose or hose connections to
the CRS tank, radiator filler neck or the pressure cap
seal to the radiator filler neck for leaks.
LOW COOLANT LEVEL AERATION
Low coolant level in a cross flow radiator will equal-
ize in both tanks with engine off. With engine at
running operating temperature the high pressure inlet
tank runs full and the low pressure outlet tank drops.
If this level drops below the top of the transmission oil
cooler, air will be sucked into the water pump:
² Transmission oil will become hotter.
² High reading shown on the temperature gauge.
² Air in the coolant will also cause loss of flow through
the heater.
² Exhaust gas leaks into the coolant can also cause the
same problems.
DEAERATION
Air can only be removed from the system by gather-
ing under the pressure cap. On the next heat up it will
be pushed past the pressure cap into the CRS tank by
thermal expansion of the coolant. It then escapes to the
atmosphere in the CRS tank and is replaced with solid
coolant on cool down.
COOLING SYSTEM DRAIN, CLEAN, FLUSH AND
REFILL
Drain, flush, and fill the cooling system at the
mileage or time intervals specified in the Maintenance
Schedule in this Group. If the solution is dirty or rusty
or contains a considerable amount of sediment, clean
and flush with a reliable cooling system cleaner. Care
should be taken in disposing of the used engine coolant
from your vehicle. Check governmental regulations for
disposal of used engine coolant.
DRAINING
To drain cooling system move temperature selector
for heater to full heat with engine running (to provide
vacuum for actuation). Without removing radiator
pressure cap and with system not under pres-
sure, Shut engine off and open draincock. The coolant
reserve tank (Fig. 5) should empty first, then remove
radiator pressure cap. (if not, see Testing Cooling
System for leaks). To vent 2.2/2.5L engines remove the
plug above thermostat housing (Fig. 1). For Turbo III
engines remove coolant temperature sensor in the
thermostat housing (Fig. 2). For 3.3L /3.8L engine
remove the engine temperature sending unit (Fig. 3).
Removal of a plug or other component is required
because the thermostat has no air vent and prevents
air flow through it. This allows the coolant to drain
from the engine block.
Fig. 1 Thermostat Housing Drain/Fill PlugÐ2.2/2.5L Engines
Ä COOLING SYSTEM 7 - 15
Page 359 of 2438

TESTING SYSTEM FOR LEAKS
With engine not running, wipe the radiator filler
neck sealing seat clean. The radiator should be full. Attach a radiator pressure tester to the radiator, as
shown in (Fig. 4) and apply 104 kPa (15 psi) pres-
sure. If the pressure drops more than 2 psi in 2 min-
utes inspect all points for external leaks. All hoses, radiator and heater, should be moved
while at 15 psi since some leaks occur while driving
due to engine rock, etc.
If there are no external leaks after the gauge dial
shows a drop in pressure, detach the tester. Start en-
gine and run the engine to normal operating temper-
ature in order to open the thermostat and allow the
coolant to expand. Re-attach the tester. If the needle
on the dial fluctuates it indicates a combustion leak,
usually a head gasket leak.
WARNING: WITH TOOL IN PLACE PRESSURE
BUILDS UP FAST. ANY EXCESSIVE AMOUNT OF
PRESSURE BUILT UP BY CONTINUOUS ENGINE
OPERATION MUST BE RELEASED TO A SAFE
PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRESSURE TO
EXCEED 138 KPA (20 PSI).
If the needle on the dial does not fluctuate, race
the engine a few times. If an abnormal amount of
coolant or steam is emitted from the tail pipe, it may
indicate a faulty head gasket, cracked engine block
or cylinder head. There may be internal leaks which can be deter-
mined by removing the oil dip-stick. If water glob-
ules appear intermixed with the oil it will indicate a internal leak in the engine. If there is an internal
leak, the engine must be disassembled for repair.
COOLANT RECOVERY SYSTEM (CRS)
This system works in conjunction with the radiator
pressure cap to utilize thermal expansion and con-
traction of the coolant to keep the coolant free of
trapped air. It provides a volume for expansion and
contraction, provides a convenient and safe method
for checking coolant level and adjusting level at at-
mospheric pressure without removing the radiator
pressure cap. It also provides some reserve coolant to
cover minor leaks and evaporation or boiling losses.
All vehicles are equipped with this system (Figs. 5
and 6).
See Coolant Level Check Service, Deaeration and
Pressure Cap sections for operation and service. Ve-
hicles equipped with the electric monitor system use
a level sensor in the CRS tank, see Group 8E Elec-
trical for service.
Fig. 4 Pressure Testing Cooling System
Fig. 5 Coolant Recovery System Typical
Fig. 6 Coolant Recovery SystemÐAC-AY Models
Ä COOLING SYSTEM 7 - 17