engine coolant CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 1844 of 2438

SYSTEM TESTS
Apply parking brake and/or block wheels be-
fore performing idle check or adjustment, or any
engine running tests.
OBTAINING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
(1) Connect DRBII scan tool to the data link connec-
tor (Fig. 1). (2) Start the engine if possible, cycle the trans mis-
sion selector and the A/Cswitch if applicable. Shut off
the engine. (3) Turn the ignition switch on, access Read Fault
Screen. Record all the fault messages shown on the
DRBII scan tool. Observe the malfunction indicator
lamp (check engine lamp on the instrument panel). The
lamp should light for 2 seconds then go out (bulb
check). Diagnostic trouble code erasure: access erase
diagnostic trouble code data.
STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs used by the powertrain control
module (PCM) have only two recognized states, HIGH
and LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize
the difference between a selected switch position ver-
sus an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective
switch. If the display changes, assume the entire
switch circuit to the PCM is functional. From the state
display screen access either State Display Inputs and
Outputs or State Display Sensors.
STATE DISPLAY INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and access
the State Display screen. Then access Inputs and
Outputs. The following is a list of the engine control
system functions accessible through the Inputs and
Outputs screen. Speed Control Resume
Brake Switch
Speed Control On/Off
Speed Control Set
A/C Switch Sense
S/C Vent Solenoid S/C Vacuum Solenoid
A/C Clutch Relay
Baro Read Solenoid
Wastegate Solenoid
Auto Shutdown Relay
Radiator Fan Relay
Purge Solenoid
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine Lamp)
STATE DISPLAY SENSORS
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the State Display screen. Then access Sensor
Display. The following is a list of the engine control
system functions accessible through the Sensor Dis-
play screen. Oxygen Sensor Signal
Coolant Temperature
Coolant Temp Sensor
Throttle Position
Minimum Throttle
Knock Sensor Signal
Battery Voltage
MAP Sensor Reading
Idle Air Control Motor Position
Adaptive Fuel Factor
Barometric Pressure
Min Airflow Idle Spd (speed)
Engine Speed
DIS Sensor Status
Fault #1 Key-On Info
Module Spark Advance
Cyl 1 Knock Retard
Cyl 2 Knock Retard
Cyl 3 Knock Retard
Cyl 4 Knock Retard
Boost Pressure Goal
Charge Temperature
Charge Temp Sensor
Speed Control Target
Fault #2 Key-on Info
Fault #3 Key-on Info
Speed Control Status
Charging System Goal
Theft Alarm Status
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DESCRIPTION (CON'T)
14 - 104 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1853 of 2438

3.0L MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTIONÐSYSTEM OPERATION INDEX
page page
Air Conditioning (A/C) Clutch Relay (AA, AG, AJ Body)ÐPCM Output .................... 118
Air Conditioning (A/C) Clutch Relay (AC Body) ÐPCM Output ........................ 118
Air Conditioning Switch Sense (AA, AG, AJ Body)ÐPCM Input ..................... 115
Air Conditioning Switch Sense (AC Body)ÐPCM Input ................................ 115
Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay and Fuel Pump RelayÐPCM Output .................... 119
Battery VoltageÐPCM Input ............... 115
Brake SwitchÐPCM Input ................. 115
CCD Bus .............................. 113
Data Link ConnectorÐPCM Output .......... 120
Distributor Pick-UpÐPCM Input ............. 115
Duty Cycle Evap Canister Purge Solenoid ÐPCM Output ........................ 119
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor ÐPCM Input ......................... 115
Fuel InjectorsÐPCM Output ............... 120
Fuel Pressure Regulator .................. 124
Fuel Supply Circuit ...................... 123
General Information ...................... 113 Generator FieldÐPCM Output
.............. 118
Heated Oxygen Sensor (O
2Sensor)
ÐPCM Input ......................... 116
Idle Air Control MotorÐPCM Output ......... 119
Ignition CoilÐPCM Output ................. 121
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine Lamp)ÐPCM Output ................... 120
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor ÐPCM Input ......................... 116
Modes of Operation ...................... 121
Park/Neutral SwitchÐPCM Input ............ 117
Part Throttle Unlock SolenoidÐPCM Output . . . 121
Powertrain Control Module ................. 113
Radiator Fan RelayÐPCM Output ........... 121
Speed Control SolenoidsÐPCM Output ....... 121
Speed ControlÐPCM Input ................ 117
System Diagnosis ....................... 113
TachometerÐPCM Output ................. 121
Throttle Body ........................... 123
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)ÐPCM Input .... 117
Transaxle Control ModuleÐPCM Output ...... 120
Vehicle Speed and Distance InputÐPCM Input . 118
Vehicle Speed SensorÐPCM Input .......... 118
GENERAL INFORMATION
The 3.0L engine uses a sequential Multi-Port Elec-
tronic Fuel Injection system (Fig. 1). The MPI system
is computer regulated and provides precise air/fuel
ratios for all driving conditions. The MPI system is operated by the powertrain con-
trol module (PCM). The PCM regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio,
emission control devices, cooling fan, charging sys-
tem, idle speed and speed control. Various sensors
provide the inputs necessary for the PCM to correctly
operate these systems. In addition to the sensors,
various switches also provide inputs to the PCM. All inputs to the PCM are converted into signals.
The PCM can adapt its programming to meet chang-
ing operating conditions. Fuel is injected into the intake port above the in-
take valve in precise metered amounts through elec-
trically operated injectors. The PCM fires the
injectors in a specific sequence. The PCM maintains
an air fuel ratio of 14.7 parts air to 1 part fuel by
constantly adjusting injector pulse width. Injector
pulse width is the length of time the injector is ener-
gized. The PCM adjusts injector pulse width by opening
and closing the ground path to the injector. Engine
RPM (speed) and manifold absolute pressure (air
density) are the primary inputs that determine injec-
tor pulse width.
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
The powertrain control module (PCM) tests many
of its own input and output circuits. If a fault is
found in a major system, the information is stored in
memory. Technicians can display fault information
through the malfunction indicator lamp (instrument
panel Check Engine lamp) or by connecting the
DRBII scan tool. For diagnostic trouble code informa-
tion, refer to the 3.0 Multi-Port Fuel InjectionÐOn-
Board Diagnostics section of this group.
CCD BUS
Various modules exchange information through a
communications port called the CCD Bus. The pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) transmits the malfunc-
tion indicator (instrument panel check engine lamp)
On/Off signal, engine RPM and vehicle load data on
the CCD Bus.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
The powertrain control module (PCM) is a digital
computer containing a microprocessor (Fig. 2). The
PCM receives input signals from various switches
and sensors that are referred to as PCM Inputs.
Based on these inputs, the PCM adjusts various en-
gine and vehicle operations through devices referred
to as PCM Outputs. PCM Inputs:
² Air Conditioning Controls
² Battery Voltage
² Brake Switch
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 113
Page 1854 of 2438
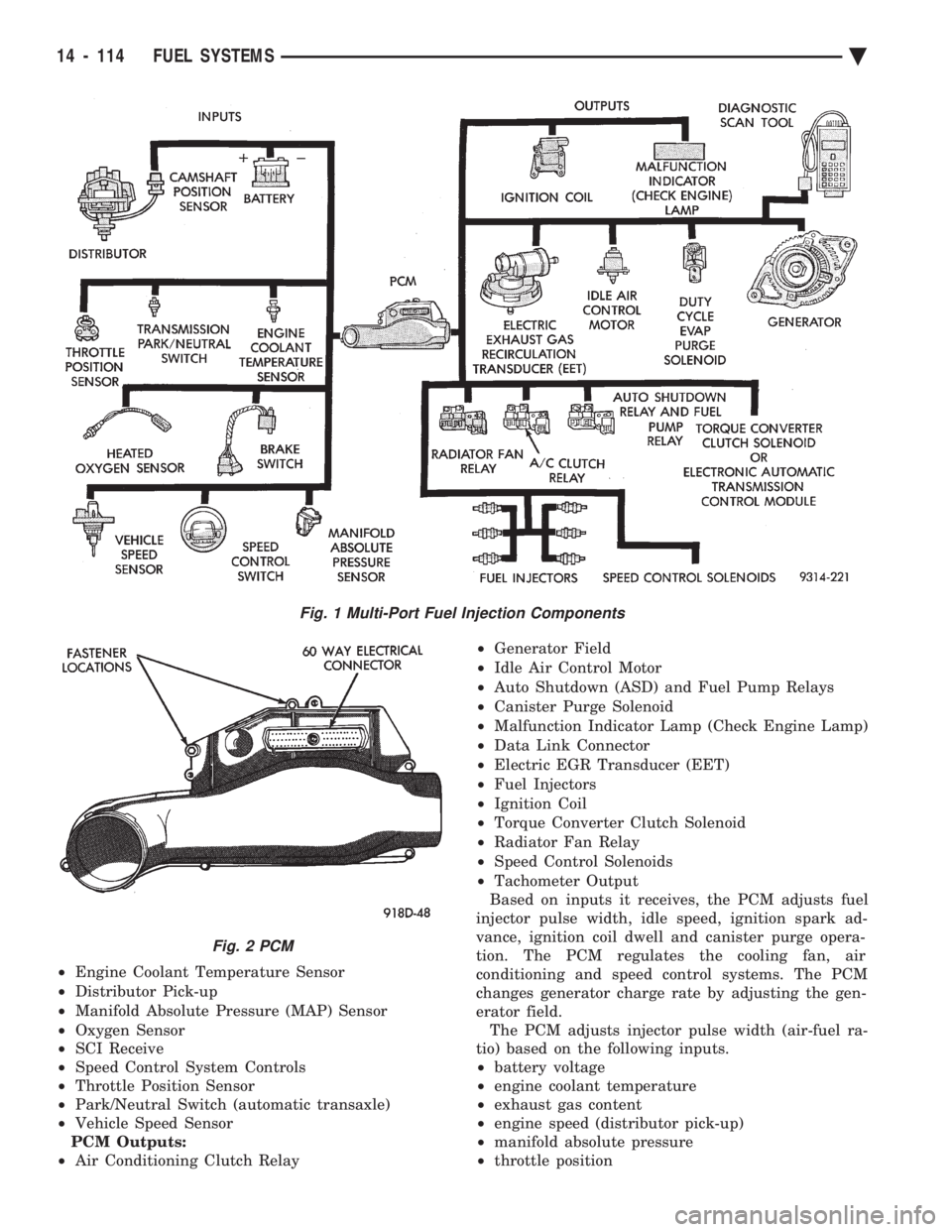
² Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
² Distributor Pick-up
² Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
² Oxygen Sensor
² SCI Receive
² Speed Control System Controls
² Throttle Position Sensor
² Park/Neutral Switch (automatic transaxle)
² Vehicle Speed Sensor
PCM Outputs:
² Air Conditioning Clutch Relay ²
Generator Field
² Idle Air Control Motor
² Auto Shutdown (ASD) and Fuel Pump Relays
² Canister Purge Solenoid
² Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine Lamp)
² Data Link Connector
² Electric EGR Transducer (EET)
² Fuel Injectors
² Ignition Coil
² Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
² Radiator Fan Relay
² Speed Control Solenoids
² Tachometer Output
Based on inputs it receives, the PCM adjusts fuel
injector pulse width, idle speed, ignition spark ad-
vance, ignition coil dwell and canister purge opera-
tion. The PCM regulates the cooling fan, air
conditioning and speed control systems. The PCM
changes generator charge rate by adjusting the gen-
erator field. The PCM adjusts injector pulse width (air-fuel ra-
tio) based on the following inputs.
² battery voltage
² engine coolant temperature
² exhaust gas content
² engine speed (distributor pick-up)
² manifold absolute pressure
² throttle position
Fig. 1 Multi-Port Fuel Injection Components
Fig. 2 PCM
14 - 114 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1855 of 2438

The PCM adjusts ignition timing based on the fol-
lowing inputs.
² engine coolant temperature
² engine speed (distributor pick-up)
² manifold absolute pressure
² throttle position
The Automatic Shut Down (ASD) and Fuel Pump
relays are mounted externally, but turned on and off
by the PCM through the same circuit. The distributor pick-up signal is sent to the PCM.
If the PCM does not receive a distributor signal
within approximately one second of engine cranking,
the ASD relay and fuel pump relay are deactivated.
When these relays are deactivated, power is shut off
to the fuel injector, ignition coil, oxygen sensor heat-
ing element and fuel pump. The PCM contains a voltage converter that
changes battery voltage to a regulated 8.0 volts. The
8.0 volts power the distributor pick-up and vehicle
speed sensor. The PCM also provides a 5.0 volts sup-
ply for the coolant temperature sensor, manifold ab-
solute pressure sensor and throttle position sensor.
AIR CONDITIONING SWITCH SENSE (AA, AG, AJ
BODY)ÐPCM INPUT
When the air conditioning or defrost switch is in
the ON position and the low pressure and high pres-
sure switches are closed, the PCM receives an input
for air conditioning. After receiving this input, the
PCM activates the A/C compressor clutch by ground-
ing the A/C clutch relay. The PCM also adjusts idle
speed to a scheduled RPM to compensate for in-
creased engine load.
AIR CONDITIONING SWITCH SENSE (AC
BODY)ÐPCM INPUT
When the air conditioning or defrost switch is in
the ON position and the low pressure, high pressure
and ambient temperature switches are closed, the
PCM receives an input for air conditioning. After re-
ceiving this input, the PCM activates the A/C com-
pressor clutch by grounding the A/C clutch relay.
The PCM also adjusts idle speed to a scheduled RPM
to compensate for increased engine load.
BATTERY VOLTAGEÐPCM INPUT
The PCM monitors the battery voltage input to de-
termine fuel injector pulse width and generator field
control. If battery voltage is low, the PCM will in-
crease injector pulse width.
BRAKE SWITCHÐPCM INPUT
When the brake switch is activated, the PCM re-
ceives an input indicating that the brakes are being
applied. After receiving this input the PCM main-
tains idle speed to a scheduled RPM through the idle
air control motor. The brake switch is mounted on
the brake pedal support bracket.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSORÐPCM
INPUT
The coolant temperature sensor is a variable resis-
tor with a range of -40É to 265É. The sensor is in-
stalled next to the thermostat housing. The PCM supplies 5.0 volts to the coolant temper-
ature sensor. The sensor provides an input voltage to
the PCM (Fig. 3). As coolant temperature varies, the
sensors resistance changes, resulting in a different
input voltage to the PCM. The PCM demands slightly richer air-fuel mixtures
and higher idle speeds until the engine reaches nor-
mal operating temperature. This sensor is also used for cooling fan control.
DISTRIBUTOR PICK-UPÐPCM INPUT
The distributor pick-up provides two inputs to the
PCM. From one input the PCM determines RPM (en-
gine speed). From the other input it derives crank-
shaft position. The PCM regulates injector
synchronization and adjusts ignition timing and en-
gine speed based on these inputs. The distributor pick-up contains two signal gener-
ators. The pick-up unit consists of 2 light emitting
diodes (LED), 2 photo diodes, and a separate timing
disk. The timing disk contains two sets of slots. Each
set of slots rotates between a light emitting diode
and a photo diode (Fig. 4). The inner set contains 6
large slots, one for each cylinder. The outer set con-
tains several smaller slots. The outer set of slots on the rotating disk repre-
sents 2 degrees of crankshaft rotation. Up to 1200
engine RPM, the PCM uses the input from the outer
set of slots to increase ignition timing accuracy. The outer set of slots contains a 10 degree flat spot
(Fig. 5). The flat spot tells the PCM that the next
piston at TDC will be number 6. The position of each
piston is referenced by one of the six inner slots (Fig.
5). As each slot on the timing disk passes between the
diodes, the beam from the light emitting diode is in-
Fig. 3 Coolant Temperature Sensor
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 115
Page 1859 of 2438

AUTO SHUTDOWN (ASD) RELAY AND FUEL PUMP
RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM operates the auto shutdown (ASD) relay
and fuel pump relay through one ground path. The
PCM operates the relays by switching the ground
path on and off. Both relays turn on and off at the
same time. The ASD relay connects battery voltage to the fuel
injector and ignition coil. The fuel pump relay con-
nects battery voltage to the fuel pump and oxygen
sensor heating element. The PCM turns the ground path off when the igni-
tion switch is in the Off position. Both relays are off.
When the ignition switch is in the On or Crank po-
sition, the PCM monitors the distributor pick-up sig-
nal to determine engine speed and ignition timing (coil dwell). If the PCM does not receive a distributor
signal when the ignition switch is in the Run posi-
tion, it will de-energize both relays. When the relays
are de-energized, battery voltage is not supplied to
the fuel injector, ignition coil, fuel pump and oxygen
sensor heating element. On AA body vehicles, the relays are located next to
the drivers side strut tower (Fig. 13). On AC, AG and AJ body vehicles, the relays are lo-
cated in the power distribution center (Fig. 12 or Fig.
14).
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTORÐPCM OUTPUT
The idle air control motor is mounted on the throt-
tle body and is controlled by the PCM (Fig. 10). The
PCM adjusts engine idle speed through the idle air
control motor to compensate for engine load or ambi-
ent conditions. The throttle body has an air bypass passage that
provides air for the engine at idle (the throttle blade
is closed). The idle air control motor pintle protrudes
into the air bypass passage and regulates air flow
through it. The PCM adjusts engine idle speed by moving the
idle air control motor pintle in and out of the bypass
passage. The adjustments are based on inputs the
PCM receives. The inputs are from the throttle posi-
tion sensor, engine speed sensor (distributor pick-up
coil), coolant temperature sensor, and various switch
operations (brake, park/neutral, air conditioning).
Deceleration die out is also prevented by increasing
airflow when the throttle is closed quickly after a
driving (speed) condition.
DUTY CYCLE EVAP CANISTER PURGE
SOLENOIDÐPCM OUTPUT
The duty cycle EVAP purge solenoid regulates the
rate of vapor flow from the EVAP canister to the
throttle body. The powertrain control module oper-
ates the solenoid. During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the so-
lenoid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged.
The PCM de-energizes the solenoid during open loop
operation. The engine enters closed loop operation after it
reaches a specified temperature and the time delay
ends. During closed loop operation, the PCM ener-
gizes and de-energizes the solenoid approximately 5
to 10 times per second, depending upon operating
conditions. The PCM varies the vapor flow rate by
changing solenoid pulse width. Pulse width is the
amount of time the solenoid energizes. A rubber boot covers the EVAP purge solenoid.
The solenoid and bracket attach to the EVAP canis-
ter mounting studs (Fig. 15). The top of the solenoid
has the word TOP on it. The solenoid will not oper-
ate unless it is installed correctly.
Fig. 13 Relay Identification (AA Body)
Fig. 14 Relay Identification (AG and AJ Body)
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 119
Page 1860 of 2438

MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (CHECK ENGINE
LAMP)ÐPCM OUTPUT
The malfunction indicator lamp (instrument panel
Check Engine lamp) comes on each time the ignition
key is turned ON and stays on for 3 seconds as a bulb
test. The malfunction indicator lamp warns the opera-
tor that the PCM has entered a Limp-in mode. During
Limp-in Mode, the PCM attempts to keep the system
operational. The malfunction indicator lamp signals
the need for immediate service. In limp-in mode, the
PCM compensates for the failure of certain components
that send incorrect signals. The PCM substitutes for
the incorrect signals with inputs from other sensors. Signals that can trigger the malfunction indi-
cator lamp (Check Engine Lamp).
² Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
² Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
² Throttle Position Sensor
² Battery Voltage Input
² An Emission Related System (California vehicles)
² Charging system
The malfunction indicator lamp displays diagnostic
trouble codes. Cycle the ignition switch on, off, on, off,
on, within five seconds to display any diagnostic
trouble codes stored in the PCM. Refer to the 3.0L
Multi-Port Fuel InjectionÐOn-Board Diagnostics sec-
tion of this Group for Diagnostic trouble code Descrip-
tions.
DATA LINK CONNECTORÐPCM OUTPUT
The data link connector provides the technician with
the means to connect the DRBII scan tool to diagnosis
the vehicle.
TRANSAXLE CONTROL MODULEÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies the following information to the
electronic automatic transaxle control module through
the CCD Bus:
² battery temperature ²
brake switch input
² engine coolant temperature
² manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
² speed control information
FUEL INJECTORSÐPCM OUTPUT
The fuel injectors are electrical solenoids (Fig. 16).
The injector contains a pintle that closes off an ori-
fice at the nozzle end. When electric current is sup-
plied to the injector, the armature and pintle move a
short distance against a spring, allowing fuel to flow
out the orifice. Because the fuel is under high pres-
sure, a fine spray is developed in the shape of a hol-
low cone. The spraying action atomizes the fuel,
adding it to the air entering the combustion cham-
ber.
The injectors are positioned in the intake manifold
with the nozzle ends directly above the intake valve
port (Fig. 16).
The fuel injectors are operated by the PCM. They
are energized in a sequential order during all engine
operating conditions except start up. The PCM ini-
Fig. 16 Fuel InjectorÐ3.0L Engine
Fig. 17 Fuel Injector Location
Fig. 15 EVAP Purge Solenoid
14 - 120 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1862 of 2438

The engine start-up (crank), engine warm-up, and
wide open throttle modes are OPEN LOOP modes. The
acceleration, deceleration, and cruise modes, with the
engine at operating temperature are CLOSED
LOOP modes (under most operating conditions).
IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE
When the multi-port fuel injection system is acti-
vated by the ignition switch, the following actions
occur:
² The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure from
the MAP sensor input to determine basic fuel strategy.
² The PCM monitors the coolant temperature sensor
and throttle position sensor input. The PCM modifies
fuel strategy based on these inputs. When the key is in the ON position and the engine is
not running (zero rpm), the auto shutdown (ASD) relay
and fuel pump relay are not energized. Therefore
battery voltage is not supplied to the fuel pump,
ignition coil, fuel injectors or oxygen sensor heating
element.
ENGINE START-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. The following actions
occur when the starter motor is engaged. If the PCM receives a distributor signal, it energizes
the auto shutdown (ASD) relay and fuel pump relay.
These relays supply battery voltage to the fuel pump,
fuel injectors, ignition coil, and oxygen sensor heating
element. If the PCM does not receive a distributor
input, the ASD relay and fuel pump relay will be
de-energized after approximately one second. The PCM energizes all six injectors until it deter-
mines crankshaft position from the distributor pick-up
signals. The PCM determines crankshaft position
within 2 engine revolutions. After determining crankshaft position, the PCM be-
gins energizing the injectors in sequence. The PCM
adjusts injector pulse width and controls injector syn-
chronization by turning the individual ground paths to
the injectors On and Off. When the engine idles within 664 RPM of its target
RPM, the PCM compares current MAP sensor value
with the atmospheric pressure value received during
the Ignition Switch On (zero RPM) mode. If the PCM
does not detect a minimum difference between the two
values, it sets a MAP fault into memory. Once the ASD and fuel pump relays have been
energized, the PCM:
² determines injector pulse width based on coolant
temperature, manifold absolute pressure (MAP) and
the number of engine revolutions since cranking was
initiated. ²
monitors the coolant temperature sensor, distribu-
tor pick-up, MAP sensor, and throttle position sensor
to determine correct ignition timing.
ENGINE WARM-UP MODE
This is a OPEN LOOP mode. The following inputs
are received by the PCM:
² engine coolant temperature
² crankshaft position (distributor pick-up)
² manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
² engine speed (distributor pick-up)
² throttle position
² A/C switch
² battery voltage
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off. The PCM adjusts engine idle speed by regulating
the idle air control motor and ignition timing.
CRUISE OR IDLE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature this
is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During cruising speed the
following inputs are received by the PCM:
² engine coolant temperature
² crankshaft position (distributor pick-up)
² manifold absolute pressure
² engine speed (distributor pick-up)
² throttle position
² exhaust gas oxygen content
² A/C control positions
² battery voltage
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off. The PCM adjusts engine idle speed and ignition
timing. The PCM controls the air/fuel ratio according
to the oxygen content in the exhaust gas.
ACCELERATION MODE This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. The PCM recog-
nizes an abrupt increase in throttle position or MAP
pressure as a demand for increased engine output
and vehicle acceleration. The PCM increases injector
pulse width in response to increased fuel demand.
DECELERATION MODE This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During decelera-
tion the following inputs are received by the PCM:
² engine coolant temperature
² crankshaft position (distributor pick-up)
² manifold absolute pressure
² engine speed (distributor pick-up)
² throttle position
² exhaust gas oxygen content
² A/C control positions
² battery voltage
14 - 122 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1863 of 2438

The PCM may receive a closed throttle input from
the throttle position sensor (TPS) when it senses an
abrupt decrease in manifold pressure. This indicates
a hard deceleration. The PCM may reduce injector
firing to once per engine revolution. This helps main-
tain better control of the air-fuel mixture. During a deceleration condition, the PCM grounds
the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) solenoid. When
the PCM grounds the solenoid, preventing EGR.
WIDE OPEN THROTTLE MODE This is an OPEN LOOP mode. During wide-open-
throttle operation, the following inputs are received
by the PCM:
² engine coolant temperature
² crankshaft position (distributor pick-up)
² manifold absolute pressure
² engine speed (distributor pick-up)
² throttle position
When the PCM senses wide open throttle condition
through the throttle position sensor (TPS) it will:
² Provide a ground for the electrical EGR transducer
(EET) solenoid. When the PCM grounds the solenoid,
the EGR system stops operating.
² De-energize the air conditioning relay. This dis-
ables the air conditioning system. The exhaust gas oxygen content input is not ac-
cepted by the PCM during wide open throttle opera- tion. The PCM will adjust injector pulse width to
supply a predetermined amount of additional fuel.
IGNITION SWITCH OFF MODE
When the ignition switch is turned to the OFF po-
sition, the following occurs:
² All outputs are turned off.
² No inputs are monitored.
² The PCM shuts down.
THROTTLE BODY
The throttle body assembly (Fig. 19) is located at
the left end of the air intake plenum. The throttle
body houses the throttle position sensor and the idle
air control motor. Air flow through the throttle body
is controlled by a cable operated throttle blade lo-
cated in the base of the throttle body.
FUEL SUPPLY CIRCUIT
Fuel is supplied to the fuel rail by an electric pump
mounted in the fuel tank. The pump inlet is fitted
with a strainer to prevent water and other contami-
nants from entering the fuel supply circuit. Fuel pressure is controlled to a preset level above
intake manifold pressure by a pressure regulator.
The pressure regulator is mounted on the fuel rail.
The regulator uses intake manifold pressure as a ref-
erence.
Fig. 19 Throttle Body
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 123
Page 1866 of 2438

(4) Verify vacuum connection at Purge Solenoid is
secure and not leaking (Fig. 3).
(5) Verify the electrical connector is attached to
the MAP sensor (Fig. 4). (6) Check MAP sensor hose at MAP Sensor Assem-
bly (Fig. 4), and at Vacuum Connection at Intake
Plenum Fitting.
(7) Check generator wiring connections. Ensure
the accessory drive belt has proper tension. (8) Verify hoses are securely attached to the vapor
canister (Fig. 5). (9) Verify the engine ground strap is attached at
the engine and dash panel (Fig. 6). (10) Ensure the heated oxygen sensor connector is
connected to the harness connector (Fig. 6). (11) Verify the distributor connector is connected
to the harness connector (Fig. 7). (12) Verify the coolant temperature sensor connec-
tor is connected to the harness connector (Fig. 8). (13) Check vacuum hose connection at fuel pres-
sure regulator and intake plenum connector (Fig. 8).
Fig. 3 Duty Cycle EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid
Fig. 4 Map Sensor Electrical and Vacuum Connections
Fig. 5 Vapor Canister
Fig. 6 Oxygen Sensor Connector
Fig. 7 Distributor Connector
14 - 126 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1874 of 2438

SYSTEM TESTS
WARNING: APPLY PARKING BRAKE AND/OR BLOCK
WHEELS BEFORE PERFORMING ANY TEST ON AN
OPERATING ENGINE.
OBTAINING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
(1) Connect DRBII scan tool to the data link connec-
tor located in the engine compartment near the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM). (2) Start the engine if possible, cycle the transaxle
selector and the A/Cswitch if applicable. Shut off the
engine. (3) Turn the ignition switch on, access Read Fault
Screen. Record all the fault messages shown on the
DRBII scan tool. Observe the malfunction indicator
lamp (Check Engine lamp on the instrument panel).
The lamp should light for 3 seconds then go out (bulb
check). Diagnostic trouble code erasure; access erase
diagnostic trouble code data
STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs used by the powertrain control
module (PCM) have only two recognized states, HIGH
and LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize
the difference between a selected switch position ver-
sus an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective
switch. If the change is displayed, it can be assumed
that the entire switch circuit to the PCM is functional.
From the state display screen access either State
Display Inputs and Outputs or State Display Sensors.
STATE DISPLAY INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle. Access
the State Display screen. Then access Inputs and
Outputs. The following is a list of the engine control
system functions accessible through the Inputs and
Outputs screen. Park/Neutral Switch
Speed Control Resume
Brake Switch
Speed Control On/Off
Speed Control Set
A/C Switch Sense
S/C Vent Solenoid
S/C Vacuum Solenoid
A/C Clutch Relay
EGR Solenoid
Auto Shutdown Relay
Radiator Fan Relay
Purge Solenoid
Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine Lamp)
STATE DISPLAY SENSORS
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the State Display screen. Then access Sensor
Display. The following is a list of the engine control
system functions accessible through the Sensor Dis-
play screen. Battery Temperature
Oxygen Sensor Signal
Engine Coolant Temperature
Engine Coolant Temp Sensor
Throttle Position
Minimum Throttle
Battery Voltage
MAP Sensor Reading
Idle Air Control Motor Position
Adaptive Fuel Factor
Barometric Pressure
Min Airflow Idle Speed
Engine Speed
Fault #1 Key-On Info
Module Spark Advance
Speed Control Target
Fault #2 Key-on Info
Fault #3 Key-on Info
Speed Control Status
Speed Control Switch Voltage
Charging System Goal
Theft Alarm Status
Map Sensor Voltage
Vehicle Speed
Oxygen Sensor State
MAP Gauge Reading
Throttle Opening (percentage)
Total Spark Advance
CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST MODE
The circuit actuation test mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices which the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) cannot internally rec-
ognize. The PCM can attempt to activate these
outputs and allow an observer to verify proper oper-
ation. Most of the tests provide an audible or visual
indication of device operation (click of relay contacts,
spray fuel, etc.). Except for intermittent conditions, if
a device functions properly during testing, assume
the device, its associated wiring, and driver circuit
working correctly.
OBTAINING CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the Actuators screen. The following is a list of
the engine control system functions accessible
through Actuators screens. Stop All Tests
Ignition Coil #1
Fuel Injector #1
Fuel Injector #2
Fuel Injector #3
14 - 134 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä