check engine CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 2328 of 2438

FIXED DISPLACEMENT COMPRESSORÐMODEL 10PA17 INDEX
page page
Compressor ............................. 24
Compressor Clutch/Coil Assembly ............ 24
Compressor Front Shaft Seal ............... 27 Compressor High-Pressure Relief Valve
....... 30
Refrigerant System Diagnosis ............... 30
COMPRESSOR
COMPRESSOR NOISE
Excessive noise that occurs when the air condition-
ing is being used, can be caused by:
² Loose bolts
² Mounting brackets
² Loose clutch
² Excessive high refrigerant system operating pres-
sure Verify compressor drive belt condition, proper re-
frigerant charge and head pressure before compressor
repair is performed. For noise diagnostic procedures, refer to the Com-
pressor Noise and Compressor Clutch Diagnosis
chart in this section.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
The A/C compressor may be removed and posi-
tioned without discharging the refrigerant system.
Discharging is not necessary if removing the A/C
compressor clutch/coil assembly, engine, cylinder
head, or generator.
WARNING: REFRIGERANT PRESSURES REMAIN
HIGH EVEN THOUGH THE ENGINE MAY BE
TURNED OFF. BEFORE REMOVING A FULLY
CHARGED COMPRESSOR, REVIEW THE SAFETY
PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS SECTION IN THIS
GROUP. DO NOT TWIST OR KINK THE REFRIGER-
ANT LINES WHEN REMOVING A FULLY CHARGED
COMPRESSOR. SAFETY GLASSES MUST BE
WORN.
(1) Disconnect Negative battery cable.
(2) Loosen and remove drive belts (refer to Group
7, Cooling System) and disconnect compressor clutch
wire lead. (3) Remove refrigerant lines from compressor (if
necessary). (4) Remove compressor attaching nuts and bolts.
(5) Remove compressor. If refrigerant lines were
not removed, lift compressor/clutch assembly and tie
it to a suitable component. To install, reverse the preceding operation. If nec-
essary, refer to Charging Refrigerant System in the
Refrigerant Service Procedures section.
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL ASSEMBLY
CLUTCH INOPERATIVE
The air conditioning compressor clutch electrical
circuit is controlled by the engine controller. The
controller is located in the engine compartment out-
board of the battery. If the compressor clutch does not engage:
Verify refrigerant charge.
If the compressor clutch still does not engage check
for battery voltage at the low pressure or differential
pressure cut-off switch located on the expansion
valve. If voltage is not detected, refer to:
² Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams.
² The appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures
Manual for diagnostic information. If voltage is detected at the cut-off switch, recon-
nect switch. Then check for battery voltage between
the compressor clutch connector terminals. If voltage is detected, perform A/C Clutch Coil
Tests.
CLUTCH COIL TESTS
(1) Verify battery state of charge. (Test indicator
in battery should be green). (2) Connect an ammeter (0-10 ampere scale) in se-
ries with the clutch coil terminal. Use a volt meter
(0-20 volt scale) with clip leads measuring voltage
across the battery and A/C clutch. (3) With A/C control in A/C mode and blower at
low speed, start the engine and run at normal idle. (4) The A/C clutch should engage immediately and
the clutch voltage should be within two volts of the
battery voltage. If the A/C clutch does not engage,
test the fusible link. (5) The A/C clutch coil is acceptable if the current
draw is 2.0 to 3.7 amperes at 11.5-12.5 volts at clutch
coil. This is with the work area temperature at 21ÉC
(70ÉF). If voltage is more than 12.5 volts, add electri-
cal loads by turning on electrical accessories until
voltage reads below 12.5 volts. If coil current reads zero, the coil is open and
should be replaced. If the ammeter reading is 4 am-
peres or more, the coil is shorted and should be re-
placed. If the coil voltage is not within two volts of
the battery voltage, test clutch coil feed circuit for
excessive voltage drop.
24 - 24 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING Ä
Page 2331 of 2438

(7) Check bearing for roughness or excessive leak-
age of grease. Replace bearing as required.
INSTALLATION
(1) Align pin in back of field coil with hole in com-
pressor end housing, and position field coil into place.
Make sure that lead wires are properly routed, and
fasten with the wire clip retaining screw. (2) Install field coil retaining snap ring with Snap
Ring Pliers (C-4574). The bevel side of the snap ring
must be outward. Also both eyelets must be to the
right or left of the pin on the compressor. Press snap
ring to make sure it is properly seated in the groove.
CAUTION: If snap ring is not fully seated it will vi-
brate out, resulting in a clutch failure and severe
damage to the front face of the compressor.
(3) Install pulley assembly to compressor. If neces-
sary, tap gently with a block of wood on the friction
surface (Fig. 5).
CAUTION: Do not mar the pulley frictional surface.
(4) Install pulley assembly retaining snap ring
(bevel side outward) with Snap Ring Pliers (C-4574).
Press the snap ring to make sure it is properly
seated in the groove. (5) If the original front plate assembly and pulley
assembly are to be reused, the old shim(s) can be
used. If not, place a trial stack of shims, 2.54 mm
(0.10 in.) thick, on the shaft against the shoulder. (6) Install front plate assembly onto shaft.
(7) With the front plate assembly tight against the
shim(s), measure the air gap between front plate and
pulley face with feeler gauges. The air gap should be between 0.5 and 0.9 mm (.020 and .035 inch) If proper
air gap is not obtained, add or subtract shims until
desired air gap is obtained.
(8) Install compressor shaft bolt. Tighten to 17.5 62
N Im (155 620 in. lbs.).
Shims may compress after tightening shaft nut.
Check air gap in four or more places to verify if air
gap is still correct. Spin pulley for final check.
CLUTCH BREAK-IN
After a new clutch has been installed cycle the A/C
clutch 20 times (5 sec. on and 5 sec. off). During this
procedure, set the system to the A/C mode, engine rpm at
1500-2000, and high blower speed. This procedure (bur-
nishing) will seat the opposing friction surfaces and
provide a higher clutch torque capability.
COMPRESSOR FRONT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Using a refrigerant recovery machine, remove
the refrigerant from the system. (2) Remove A/C compressor.
(3) Remove compressor clutch/coil assembly.
(4) Remove compressor through-bolts (Fig. 1).
(5) Remove front cover by tapping on the outside
diameter of the cover with a plastic hammer (Fig. 2). (6) Remove steel valve plate gasket and O-ring seal
and discard (Fig. 3 and 4).
CAUTION:Never reuse cover O-rings or the steel
valve plate gaskets.
(7) Pry out the felt retainer and remove felt from
front cover (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5 Installing Pulley Assembly
Fig. 1 Compressor Through-Bolts
Ä HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 27
Page 2336 of 2438

FIXED DISPLACEMENT COMPRESSORÐMODEL TR105 INDEX
page page
Compressor ............................. 32
Compressor Clutch/Coil Assembly ............ 32
Compressor Shaft Bearing/Seal .............. 35 Refrigerant System Diagnosis
............... 36
Thermal Limiter Switch .................... 34
COMPRESSOR
Cleanliness is extremely important when disassem-
bly of the compressor is necessary. The surfaces
around the suction and discharge ports of the com-
pressor should be cleaned thoroughly before opening
the system at these points. If compressor is removed
from vehicle, apply tape to the opened ports to pre-
vent any contamination.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Loosen and remove drive belts (refer to Group
7, Cooling System). (3) Disconnect compressor clutch wire lead.
(4) Using a refrigerant recovery machine, remove
refrigerant from the A/C system. (5) Remove refrigerant lines from compressor.
(6) Remove compressor attaching bolts.
(7) Remove compressor.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the compressor on the mount and fit
drive belt. (2) Tighten the compressor attaching bolts to 41
N Im (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Adjust drive belt (see Group 7, Cooling Sys-
tem). (4) Install refrigerant hoses.
(5) Connect the clutch wire.
(6) Evacuate and charge the system.
(7) Connect the battery negative cable.
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL ASSEMBLY
CLUTCH INOPERATIVE
The air conditioning compressor clutch electrical
circuit is controlled by the engine controller. The
controller is located in the engine compartment out-
board of the battery. If the compressor clutch does not engage:
Verify refrigerant charge.
If the compressor clutch still does not engage check
for battery voltage at the low pressure or differential
pressure cut-off switch located on the expansion
valve. If voltage is not detected, refer to:
² Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams.
² The appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures
Manual for diagnostic information. If voltage is detected at the cut-off switch, recon-
nect switch. Then check for battery voltage between
the compressor clutch connector terminals. If voltage is detected, perform A/C Clutch Coil
Tests.
CLUTCH COIL TESTS
(1) Verify battery state of charge. (Test indicator
in battery should be green). (2) Connect an ammeter (0-10 ampere scale) in se-
ries with the clutch coil terminal. Use a volt meter
(0-20 volt scale) with clip leads measuring voltage
across the battery and A/C clutch. (3) With A/C control in A/C mode and blower at
low speed, start the engine and run at normal idle. (4) The A/C clutch should engage immediately and
the clutch voltage should be within two volts of the
battery voltage. If the A/C clutch does not engage,
test the fusible link. (5) The A/C clutch coil is acceptable if the current
draw is 2.0 to 3.7 amperes at 11.5-12.5 volts at clutch
coil. This is with the work area temperature at 21ÉC
(70ÉF). If voltage is more than 12.5 volts, add electri-
cal loads by turning on electrical accessories until
voltage reads below 12.5 volts. If coil current reads zero, the coil is open and
should be replaced. If the ammeter reading is 4 am-
peres or more, the coil is shorted and should be re-
placed. If the coil voltage is not within two volts of
the battery voltage, test clutch coil feed circuit for
excessive voltage drop.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the compressor from the mount.
(2) To prevent compressor shaft rotation, install 2
(6 mm) bolts, along with 2 wrenches, to the threaded
holes in the armature plate (Fig. 1). Remove com-
pressor shaft nut. (3) Tap the armature plate with a plastic and re-
move plate and shim(s).
CAUTION: Do not use screwdrivers between the ar-
mature plate assembly and rotor-pulley to remove
the armature plate. This may damage the armature
plate assembly.
24 - 32 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING Ä
Page 2338 of 2438

(8) With the front clutch plate assembly tight
against the shims, measure the air gap between ar-
mature plate and rotor-pulley face with feeler gauges
(Fig. 4). The air gap should be between 0.35 and 0.65
mm (0.013 and 0.025 inch). If proper air gap is not
obtained, add or subtract shims until desired air gap
is obtained.
(9) Install compressor shaft nut. Tighten nut to
17.5 N Im (155 in. lbs.) torque.
Shims may compress after tightening shaft bolt.
Check air gap in four or more places to verify if air
gap is still correct. Spin pulley for final check. (10) Install the compressor onto the mount.
CLUTCH/COIL BREAK-IN
After a new clutch/coil has been installed, cycle the
A/C clutch 20 times (5 sec. on and 5 sec. off). During
this procedure, run engine at 1500-2000 rpm and set
the A/C on the HIGH mode. This procedure (burnish-
ing) will seat the opposing friction surfaces and pro-
vide a higher clutch torque capability.
THERMAL LIMITER SWITCH
The Thermal Limiter Switch (Fig. 5) is bolted to
the side of the compressor case. It measures compres-
sor surface temperature and is used as a safety de-
vice to cut battery voltage to the compressor clutch
coil. This is performed if compressor case tempera-
ture is excessive. This switch is NOT USEDto cycle the clutch coil.
After the compressor has cooled to normal operating
temperature, the switch will reset.
DIAGNOSIS
The switch can remain bolted to the compressor for
testing. (1) Disconnect the wiring connectors from the ther-
mal limiter switch. (2) Using an ohmmeter, check for continuity be-
tween the two wiring leads. If continuity is not de-
tected, replace switch. Also check for possible
compressor overheating.
² Switch cut-out (no continuity) occurs at 125ÉC
6 3ÉC (255ÉF 637ÉF).
² Switch cuts back in (continuity) at 110ÉC 66ÉC
(230ÉF 642ÉF).
REMOVAL
The refrigerant system can remained fully charged
for thermal limiter switch replacement. After removing the thermal limiter switch, always
replace with a new unit. (1) Disconnect wiring connectors from switch.
(2) Remove the bolt retaining the switch holding
clamp and the switch to the side of the compressor
(Fig. 6). (3) Pry the switch from compressor case with a
screwdriver.
CLEANING
Remove silicone filler from the socket and thor-
oughly clean the socket with thinners.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place the new thermal limiter switch so that
the flat copper surface faces upward. (2) Apply the specified silicone filler (KE 347 RTV)
to the flat copper surface until the surface is evenly
covered. When silicone is applied, apply only from
tube and not by hand. (3) Install the thermal limiter switch into the
socket and secure it with the thermal protector (lim-
iting switch) fixing plate and bolt. Tighten the bolt
Fig. 4 Measuring Air Gap
Fig. 5 Thermal Limiter Switch
24 - 34 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING Ä
Page 2376 of 2438

NONÐCOMPUTER AIDED DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
Determine whether the operator complaint is due
to a system failure or improper operation of the ATC
system. The system will to go into a maximum heat
or cooling mode if the operator changes the tempera-
ture setting four or more degrees. Check the following:
² Coolant level
² Refrigerant charge
² Drive belt tension
² Radiator air flow
² Radiator fan operation
² Air suction of In-car Temperature Sensor/Aspirator
To check air suction of the Aspirator, place a small
piece of tissue paper over the Aspirator opening on
the instrument panel. This opening is located to the
right of the steering column. The tissue paper should
cling to the opening if system is functioning properly. Bring the engine to normal operating temperature
and proceed with Computer Aided Diagnostic Proce-
dures. Always test the entire system after each re-
pair has been performed.
COMPUTER AIDED DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
The ATC control has a computer capable of trou-
bleshooting the entire ATC system in approximately
60 seconds. The engine must be running and at nor-
mal operating temperature during the test to provide
hot coolant for the heater. During the ATC Diagnostic Test, the computer will
calibrate the Mode and Blend Door actuators.
CAUTION: Do not remove the actuators from the
heater-A/C unit assembly with power applied. Re-
moval should only be done with the Ignition OFF.
The actuators have no mechanical stops to limit the
travel. If the actuator rotates and is not connected
to the unit assembly, it will become un-calibrated.
The Diagnostic Test is capable of checking all elec-
trical signals between the ATC Control Module, ac-
tuators, sensors and blower control. The Diagnostic Test will display two types of Diag-
nostic trouble Codes (Fig. 21). The Diagnostic Trou-
ble Codes numbered 01 through 22, have been
detected during the Diagnostic Test. Diagnostic Trou-
ble Codes numbered 23 through 28, have been de-
tected during normal ATC operation. Diagnostic
Trouble Codes 23 through 28 would then be stored in
the ATC control computer and are only being re-
trieved during the Diagnostic Test.
For electrical pin numbers, refer to the wiring Pin
out charts on the following pages in this section. (1) Start vehicle and allow engine to warm up.
(2) For two seconds, depress the DEFROST,
FLOOR and MODE buttons at the same time. The
ATC control should begin to flash on and off. (3) During the Diagnostic Test perform the follow-
ing symptom tests: (a) Do all display symbols and indicators illumi-
nate ?
Fig. 19 Sun Sensor
Fig. 20 Sun Sensor Removal
Fig. 21 Automatic Temperature Control Diagnostic Trouble Codes
24 - 72 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING Ä
Page 2377 of 2438

(b) Does the blower motor operate at its highest
speed ? (c) Feel the outlet temperature. Does it get hot
and then cycle cold ? (d) Does the air flow switch from DEFROST out-
lets and then cycle to PANEL outlets?
If you can answer NO to any of these questions,
proceed to step 4, otherwise proceed to step 5. (4) If you answered NO to:
SYMPTOM A
The display symbols and indicators do not illumi-
nate. Diagnostic Trouble Codes are not displayed.
TEST
After self-diagnostic test is complete, select a mode
that will display the malfunction.
ACTION
If the ATC system operates properly, and the dis-
play does not, replace ATC control panel computer.
SYMPTOM B
The blower motor does not operate.
CAUTION: Stay clear of blower motor and power
module (PM) heat sink. Do not run system for more
than 10 minutes with PM removed from A/C unit.
TEST Check all power module and blower motor connec-
tions. Use a voltmeter to test for 12 volts (ignition)
at both ends of the fuse with ignition ON. If fuse is
good, test the green wire at the blower motor connec-
tor for 12 volts (ignition) to body ground. Turn ignition to the ON position.
With the blower motor still connected, check for 12
volts to body ground on the black/tan wire of the
blower motor two way connector. Check for 12 volts at the Power Module pin #4
(BK/TN). Check for continuity from the Power Module pin
#3 (BK) to chassis ground. Replace the Power Module.
ACTION If 12 volts is not detected, repair feed circuit. Refer
to the Front Wheel Drive Car-Wiring Diagrams Ser-
vice Manual. If 12 volts is not detected, repair wires of the
blower motor or replace the blower motor. If 12 volts is not present, repair wire from the
blower motor connector to the Power Module. If circuit is open, repair ground circuit of the Power
Module. Replace the Power Module (power transistor open).
SYMPTOM C
The outlet air temperature does not become hot
and then cycle to cold during self-test operation. Di-
agnostic Trouble Codes are not displayed.
TEST/ACTION
Make sure the blend-air door is properly attached
to the actuator. If cold air is not discharged from the outlets, check
the base A/C refrigerant system. Make sure heating operation works correctly, (wa-
ter level, thermostat, heater hoses, heater core, etc.).
SYMPTOM D
Air does not flow from DEFROST outlets and then
cycle to PANEL outlets during self-test operation.
TEST/ACTION Check linkages from the mode door actuator for
binding. Check for proper door travel in the unit.
(5) The computer will do one of two things:
² Will return to the control settings that were se-
lected before the Diagnostic Test was started. This
means the test is over. If Diagnostic Trouble Codes
did not occur, and answers to questions (a), (b), (c),
and (d) were YES, the entire system is operating cor-
rectly.
² The blower motor will stop and the computer will
flash a Diagnostic Trouble Code number from 01
through 28. Record the number and then depress the
PANEL button to advance to the next test. If the
ATC control flashes one or more codes 23 to 28, the
digits on the display will flash alternating Zeros. If
you do nothing, these codes will remain stored within
the ATC control computer. After all repairs have
been made erase fault codes. Refer to Erasing Diag-
nostic Trouble Codes 23 through 28 from ATC Con-
trol in this section. Repair all Diagnostic Trouble Codes in the order
that they have been indicated, and then retest the
system. If any blend door test fails, all remaining
blend door tests will be skipped. IF any mode door
tests fail, all remaining mode door tests will be
skipped. Diagnostic Test can be stopped at any time by de-
pressing any button other than PANEL.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DEFINITIONS
Non-computer aided diagnostics should be per-
formed first. Hood of vehicle should be closed during
the diagnostic test to keep engine heat from effecting
the ambient temperature sensor. Also refer to the wiring Pin out charts.
² DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE 1
Involves the wiring or the ATC control head.
² DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES 2, 13, 14, 15,
20, and 23
Ä HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 73
Page 2382 of 2438
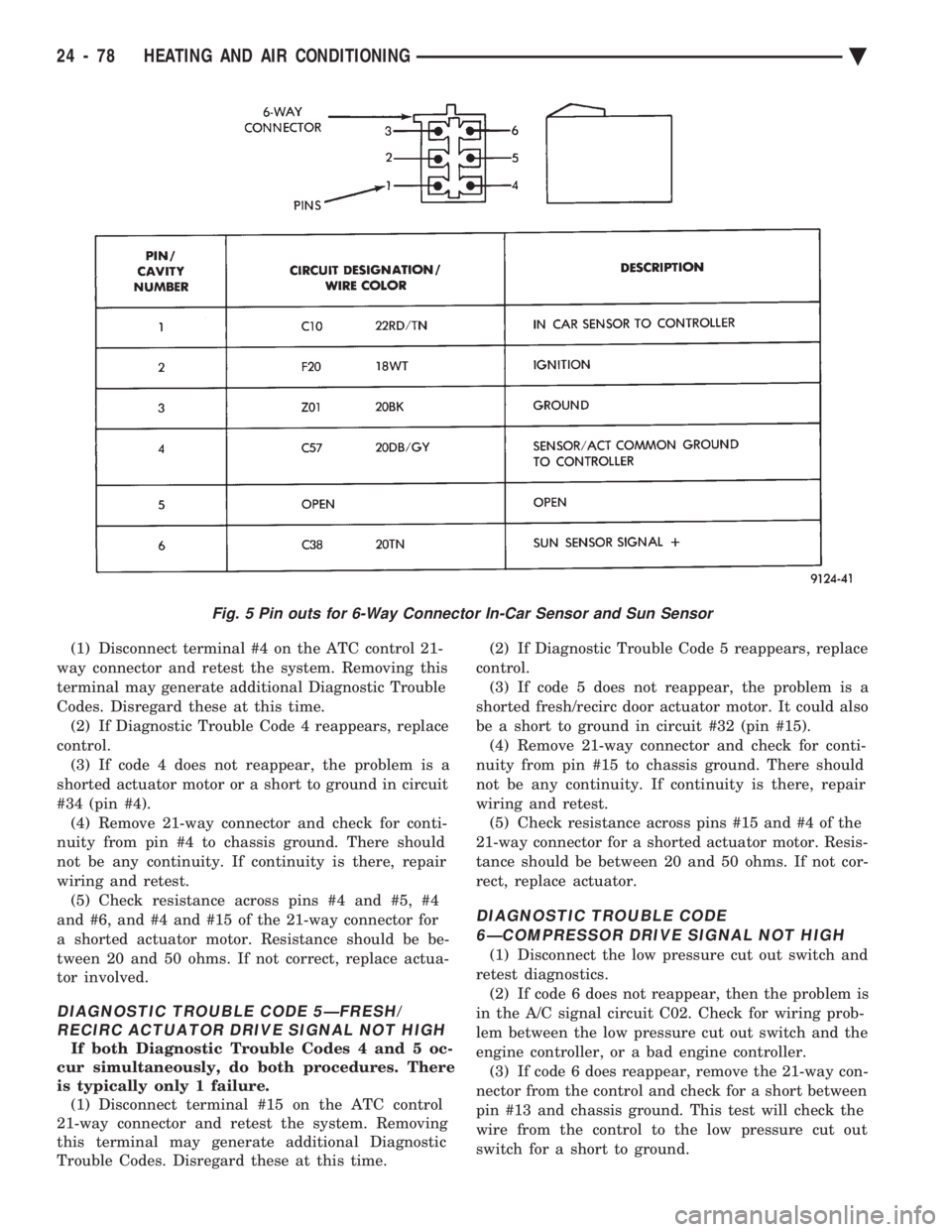
(1) Disconnect terminal #4 on the ATC control 21-
way connector and retest the system. Removing this
terminal may generate additional Diagnostic Trouble
Codes. Disregard these at this time. (2) If Diagnostic Trouble Code 4 reappears, replace
control. (3) If code 4 does not reappear, the problem is a
shorted actuator motor or a short to ground in circuit
#34 (pin #4). (4) Remove 21-way connector and check for conti-
nuity from pin #4 to chassis ground. There should
not be any continuity. If continuity is there, repair
wiring and retest. (5) Check resistance across pins #4 and #5, #4
and #6, and #4 and #15 of the 21-way connector for
a shorted actuator motor. Resistance should be be-
tween 20 and 50 ohms. If not correct, replace actua-
tor involved.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE 5ÐFRESH/ RECIRC ACTUATOR DRIVE SIGNAL NOT HIGH
If both Diagnostic Trouble Codes 4 and 5 oc-
cur simultaneously, do both procedures. There
is typically only 1 failure. (1) Disconnect terminal #15 on the ATC control
21-way connector and retest the system. Removing
this terminal may generate additional Diagnostic
Trouble Codes. Disregard these at this time. (2) If Diagnostic Trouble Code 5 reappears, replace
control. (3) If code 5 does not reappear, the problem is a
shorted fresh/recirc door actuator motor. It could also
be a short to ground in circuit #32 (pin #15). (4) Remove 21-way connector and check for conti-
nuity from pin #15 to chassis ground. There should
not be any continuity. If continuity is there, repair
wiring and retest. (5) Check resistance across pins #15 and #4 of the
21-way connector for a shorted actuator motor. Resis-
tance should be between 20 and 50 ohms. If not cor-
rect, replace actuator.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE 6ÐCOMPRESSOR DRIVE SIGNAL NOT HIGH
(1) Disconnect the low pressure cut out switch and
retest diagnostics. (2) If code 6 does not reappear, then the problem is
in the A/C signal circuit C02. Check for wiring prob-
lem between the low pressure cut out switch and the
engine controller, or a bad engine controller. (3) If code 6 does reappear, remove the 21-way con-
nector from the control and check for a short between
pin #13 and chassis ground. This test will check the
wire from the control to the low pressure cut out
switch for a short to ground.
Fig. 5 Pin outs for 6-Way Connector In-Car Sensor and Sun Sensor
24 - 78 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING Ä
Page 2405 of 2438

EXHAUST EMISSION CONTROLS INDEX
page page
Air Aspiration System ..................... 24
EGR Gas Flow Test ...................... 21
EGR System On-Board Diagnostics ........... 21
EGR Tube ServiceÐ2.2L and 2.5L TBI Engines . 22
EGR Tube ServiceÐ3.0L Engines ............ 22
EGR Tube ServiceÐ3.3L and 3.8L Engines .... 22
EGR Valve ServiceÐ2.2L and 2.5L TBI Engines . 22 EGR Valve ServiceÐ3.0L Engines
........... 22
EGR Valve ServiceÐ3.3L and 3.8L Engines .... 22
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System ...... 20
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System Test . . 21
Heated Inlet Air System ................... 17
Heated Oxygen Sensor (O
2Sensor) .......... 18
HEATED INLET AIR SYSTEM
2.5L MPI (Flexible Fuel AA-body), Turbo III, 3.0L,
3.3L and 3.8L engines do not use a heated inlet air
system. 2.2L and 2.5L TBI air cleaners have a heated air
assembly (Fig. 1). When ambient temperatures are
low, the assembly warms the air before it enters the
throttle body. The heated air assembly reduces hy-
drocarbon emissions, improves engine warm-up char-
acteristics and minimizes icing.
The heated air assembly contains a vacuum oper-
ated blend door. The blend door opens to either
heated air from a stove on the exhaust manifold or
ambient air (outside air). A vacuum diaphragm oper-
ates the door. A spring opposes the vacuum dia-
phragm. A temperature sensor controls the vacuum
diaphragm (Fig. 2). Adjustment of inlet air tempera-
ture occurs only at road load throttle positions or
when the intake manifold vacuum exceeds the vac-
uum diaphragm spring rate. Air flows through the outside air inlet when ambi-
ent air temperature is 8ÉC (15ÉF) or more above the
air temperature sensor control temperature. When ambient air temperature falls below the con-
trol temperature, air flows through both the ambient
and heated circuits. This occurs after the engine has
been started and the exhaust manifold starts to give
off heat. Colder ambient air cause greater air flow
through the heat stove on the exhaust manifold.
Warmer ambient air results in greater ambient air
flow through the air cleaner snorkel.
HEATED INLET AIR SYSTEM SERVICE
Heated air inlet system malfunctions may affect
driveability and vehicle exhaust emissions. Use the following procedure to determine if the
system functions properly. (1) Inspect the condition of the heat stove to air
cleaner flexible connector and all vacuum hoses. In-
spect them for proper attachment. Replace as neces-
sary. (2) With a cold engine and ambient temperature
less than 46ÉC (115ÉF.), the heat control door (valve
plate) should be in the up (heat on position).
(3) With the engine warmed up and running,
check the temperature of the air entering the snorkel
or passing the sensor. When the temperature of the
Fig. 1 Heated Air Inlet System
Fig. 2 Heated Air Temperature Sensor
Ä EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 17
Page 2406 of 2438

air entering the outer end of snorkel is 60ÉC (140ÉF.) or
higher, the door should be in the down (heat off)
position. (4) Remove the air cleaner from the engine and
allow it to cool down to 46ÉC (115ÉF). With 20 inches of
vacuum applied to the sensor, the door should be in the
up (heat on position). If the door does not rise to the
heat on position, check the vacuum diaphragm for
proper operation. (5) To test the diaphragm, apply 20 inches of vacuum
to it with vacuum pump tool number C-4207 or equiva-
lent (Fig. 3). The diaphragm should not bleed down
more than 10 inches of vacuum in 5 minutes. The door
should not lift off the bottom of the snorkel at less than
2 inches of vacuum. The door should be in the full up
position with no more than 4 inches of vacuum. (6) If the vacuum diaphragm does not perform ad-
equately, replace the heated air assembly.
(7) If the vacuum diaphragm performs adequately
but proper temperature is not maintained, replace the
sensor and repeat the temperature checks in steps 2
and 3.
HEATED AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR SER- VICE
REMOVAL
(1) Remove air cleaner housing from vehicle.
(2) Disconnect vacuum hoses from air temperature
sensor. Remove and discard retainer clips, new clips
are supplied with a new sensor (Fig. 4). (3) Remove and discard sensor and gasket.
INSTALLATION (1) Position gasket on the sensor. Install sensor (Fig.
5). (2) While supporting the sensor on outer diameter,
install new retainer clips securely. Ensure the gasket
compresses to form an air seal. Do not attempt to
adjust the sensor.
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (O2SENSOR)
The O2sensor threads into the exhaust manifold. It
provides an input voltage to the powertrain control
module (PCM). The input tells the PCM the oxygen
content of the exhaust gas (Fig. 6, 7, 8, 9, or 10). The
PCM uses this information to fine tune the air-fuel
ratio by adjusting injector pulse width. The O
2sensor produces voltages from 0 to 1 volt,
depending upon the oxygen content of the exhaust gas
in the exhaust manifold. When a large amount of
oxygen is present (caused by a lean air-fuel mixture),
the sensor produces a low voltage. When there is a
lesser amount of oxygen present (rich air-fuel mixture),
the sensor produces a higher voltage. By monitoring
the oxygen content and converting it to electrical
voltage, the sensor acts as a rich-lean switch.
Fig. 3 Testing Vacuum Diaphragm on Heated Air In- let Systems
Fig. 4 Removing Sensor Clips
Fig. 5 Air Temperature Sensor Installation
25 - 18 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 2409 of 2438

These systems do not allow EGR at idle. The 2.2L/
2.5L EGR systems operate at all temperatures. The
3.0L, 3.3L and 3.8L EGR systems do not operate
when coolant temperature is below 4.5ÉC (40É)F at
start-up. These systems activate when coolant tem-
perature reaches 77ÉC (170ÉF).
EGR SYSTEM ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
The powertrain control module (PCM) performs an
on-board diagnostic check of the EGR system on all
California vehicles with EGR systems. The diagnos-
tic system uses the Electric EGR Transducer (EET)
for the system tests. The diagnostic check activates only during selected
engine/driving conditions. When the conditions are
met, the PCM energizes the transducer solenoid to
disable the EGR. The PCM checks for a change in the oxygen sensor signal. If the air-fuel mixture goes
lean, the PCM will attempt to enrichen the mixture.
The PCM registers a fault if the EGR system has
failed or degraded. After registering a fault, the PCM
turns on the malfunction indicator lamp (instrument
panel Check Engine light). The malfunction indicator
lamp indicates the need for immediate service.
If a problem is indicated by the malfunction indicator
lamp and a diagnostic trouble code for the EGR system,
check for proper operation of the EGR system. Use the
System Test, EGR Gas Flow Test and EGR Diagnosis
Chart. If the EGR system tests properly, check the sys-
tem using the DRBII scan tool. Refer to On-Board Di-
agnosis in the General Diagnosis sections of Group 14.
Also, refer to the DRBII scan tool and the appropriate
Powertrain Diagnostics Procedure manual.
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM
TEST
WARNING: APPLY PARKING BRAKE AND/OR
BLOCK WHEELS BEFORE PERFORMING EGR SYS-
TEM TEST.
A failed or malfunctioning EGR system can cause
engine spark knock, sags or hesitation, rough idle,
and/or engine stalling. To ensure proper operation of
the EGR system, all passages and moving parts must
be free of deposits that could cause plugging or stick-
ing. Ensure system hoses do not leak. Replace leak-
ing components. Inspect hose connections between the throttle body,
intake manifold, EGR solenoid and transducer, and
EGR valve. Replace hardened, cracked, or melted
hoses. Repair or replace faulty connectors.
Check the EGR control system and EGR valve with
the engine fully warmed up and running (engine cool-
ant temperature over 150ÉF). With the transmission in
neutral and the throttle closed, allow the engine to idle
for 70 seconds. Abruptly accelerate the engine to ap-
proximately 2000 rpm, but not over 3000 rpm. The EGR
valve stem should move when accelerating the engine
(the relative position of the groove on the EGR valve
stem should change). Repeat the test several times to
confirm movement. If the EGR valve stem moves, the
control system is operating normally. If the control sys-
tem is not operating normally, refer to the EGR Diag-
nosis Chart to determine the cause.
EGR GAS FLOW TEST
The following procedure should be used to determine
if exhaust gas is flowing through the EGR system.
Connect a hand vacuum pump to the EGR valve
vacuum motor. With engine running at idle speed,
slowly apply vacuum. Engine speed should begin to
drop when applied vacuum reaches 2.0 to 3.5 inches.
Fig. 14 EGR MountingÐ3.3L and 3.8L Engines
Fig. 15 Electric EGR Transducer (EET) Assembly
Ä EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 21