warning CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Manual Online
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 321 of 2438

(4) If equipped, remove the 2 bolts (Fig. 4) attaching
speed control vacuum reservoir to battery tray. Then
remove vacuum reservoir (Fig. 4) from the battery tray.
Vacuum lines (Fig. 4) do not need to be removed
from vacuum reservoir. (5) Remove the 4 bolts attaching battery tray (Fig.
5) to frame rail and fender shield of the vehicle.
Then remove battery tray.
(6) Remove battery acid shield, (Fig. 6) from the
ABS modulator assembly.
(7) Remove the 6 tube nuts (Fig. 7), attaching hy-
draulic brake line tube bundle to modulator assem-
bly, thread savers and proportioning valves. Then
remove the 6 hydraulic brake lines as an assembly,
from the modulator assembly. (8) Remove electrical connector from the brake
pressure differential warning switch on hydraulic
junction block (Fig. 8). (9) Remove the primary and secondary hydraulic
brake tubes (Fig. 9) going from the master cylinder
to the junction block, from both master cylinder and
junction block. (10) Remove the brake hydraulic tube going to the
vehicle's left front wheel from the junction block. (11) Remove the 6 hydraulic brake tubes at the hy-
draulic junction block, coming from the antilock mod-
ulator assembly.
Fig. 5 Battery Tray And Attaching Bolts
Fig. 6 ABS Modulator Assembly Acid Shield
Fig. 2 Battery Heat Shield And Hold Down Clamp
Fig. 3 Battery Tray Shield
Fig. 4 Speed Control System Vacuum Reservoir
Ä ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 35
Page 336 of 2438

CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH
The clutch pedal position switch functions as a
safety interlock device. It prevents possible engine
cranking with the clutch engaged. The clutch pedal position switch is wired in series
between the starter relay coil and the ignition
switch. The clutch pedal position switch is mounted to a
bracket located next to the clutch pedal. The switch
is held in place by four plastic wing tabs. The clutch pedal position switch has an adjustable
striker plate. The striker plate is located on the left
side of the clutch pedal (Fig. 3).
DIAGNOSIS
Disconnect clutch pedal position switch harness
from instrument panel wiring harness. Using a ohm
meter, check for continuity between the two termi-
nals in the connector on the switch harness. There
should be no continuity between the terminals when
the switch is in its neutral (fully extended) position.
When the switch is depressed more than 1.25 mm
(0.050) the ohm meter should show continuity. If all ohm meter readings are correct and the
switch does not operate correctly, adjustment is re-
quired. Refer to Switch Adjustment Procedure to ad-
just switch.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect electrical harness to switch connec-
tor. (2) Depress wing tabs on switch and push switch out
of mounting bracket. Then slide wires through slot in
bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Slide switch wires through slot in switch bracket.
(2) Line up switch tab with slot in switch bracket
and push switch into position. Do not pull on the switch
wires to seat switch into bracket, switch damage may
occur. (3) After installation, the switch must be adjusted
and checked for proper operation. Refer to Switch
Adjustment Procedure.
ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
When performing switch adjustment, the floor mat
should be removed before beginning adjustment proce-
dures. (1) Set the park brake.
(2) Disconnect clutch cable at the transaxle end of
the cable. (3) Depress clutch pedal, loosen adjusting nut and
slide the striker plate forward to fully compress the
clutch pedal position switch plunger. (4) Tighten adjusting nut to 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.).
(5) Reconnect clutch cable.
The clutch pedal position switch is now ad-
justed. A final check is required to insure that the
switch is ``made'' below the clutch release point. (1) With the park brake set and the vehicle IN
NEUTRAL turn the key to the start position. The
vehicle should not crank. If the vehicle cranks do
not continue with this test. Recheck the switch and
switch adjustment to determine the cause. If the ve-
hicle does not crank proceed to step 2. (2) With the park brake set and the vehicle IN
GEAR turn the key to the start position.
WARNING: BEFORE PERFORMING STEP THREE BE
SURE THAT THE AREA IN FRONT OF THE VEHICLE
IS CLEAR OF OBSTRUCTIONS AND PEOPLE. VE-
HICLE MAY MOVE WHEN PERFORMING THIS TEST.
(3) Slowly depress the clutch pedal and feel for any
vehicle motion when the starter is energized. If there is
no motion the switch is properly adjusted. If motion is
felt, repeat the adjustment procedure.
Fig. 3 Clutch Pedal Position Switch and Components
6 - 4 MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH Ä
Page 359 of 2438

TESTING SYSTEM FOR LEAKS
With engine not running, wipe the radiator filler
neck sealing seat clean. The radiator should be full. Attach a radiator pressure tester to the radiator, as
shown in (Fig. 4) and apply 104 kPa (15 psi) pres-
sure. If the pressure drops more than 2 psi in 2 min-
utes inspect all points for external leaks. All hoses, radiator and heater, should be moved
while at 15 psi since some leaks occur while driving
due to engine rock, etc.
If there are no external leaks after the gauge dial
shows a drop in pressure, detach the tester. Start en-
gine and run the engine to normal operating temper-
ature in order to open the thermostat and allow the
coolant to expand. Re-attach the tester. If the needle
on the dial fluctuates it indicates a combustion leak,
usually a head gasket leak.
WARNING: WITH TOOL IN PLACE PRESSURE
BUILDS UP FAST. ANY EXCESSIVE AMOUNT OF
PRESSURE BUILT UP BY CONTINUOUS ENGINE
OPERATION MUST BE RELEASED TO A SAFE
PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRESSURE TO
EXCEED 138 KPA (20 PSI).
If the needle on the dial does not fluctuate, race
the engine a few times. If an abnormal amount of
coolant or steam is emitted from the tail pipe, it may
indicate a faulty head gasket, cracked engine block
or cylinder head. There may be internal leaks which can be deter-
mined by removing the oil dip-stick. If water glob-
ules appear intermixed with the oil it will indicate a internal leak in the engine. If there is an internal
leak, the engine must be disassembled for repair.
COOLANT RECOVERY SYSTEM (CRS)
This system works in conjunction with the radiator
pressure cap to utilize thermal expansion and con-
traction of the coolant to keep the coolant free of
trapped air. It provides a volume for expansion and
contraction, provides a convenient and safe method
for checking coolant level and adjusting level at at-
mospheric pressure without removing the radiator
pressure cap. It also provides some reserve coolant to
cover minor leaks and evaporation or boiling losses.
All vehicles are equipped with this system (Figs. 5
and 6).
See Coolant Level Check Service, Deaeration and
Pressure Cap sections for operation and service. Ve-
hicles equipped with the electric monitor system use
a level sensor in the CRS tank, see Group 8E Elec-
trical for service.
Fig. 4 Pressure Testing Cooling System
Fig. 5 Coolant Recovery System Typical
Fig. 6 Coolant Recovery SystemÐAC-AY Models
Ä COOLING SYSTEM 7 - 17
Page 360 of 2438

RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP
Radiators are equipped with a pressure cap which
releases pressure at some point within a range of
97-124 kPa (14-18 psi) (Fig. 7). The system will operate at higher than atmospheric
pressure which raises the coolant boiling point allow-
ing increased radiator cooling capacity. There is also a vent valve in the center of the cap that
allows a small coolant flow to the CRS tank. If valve is
stuck shut, the radiator hoses will be collapsed
on cool down. Clean the vent valve (Fig. 7) to
ensure proper sealing when boiling point is
reached.
There is also a gasket in the cap to seal to the top of
the filler neck so that vacuum can be maintained for
drawing coolant back into the radiator from the coolant
reserve system tank.
RADIATOR CAP TO FILLER NECK SEAL PRES- SURE RELIEF CHECK
The pressure cap upper gasket (seal) pressure relief
can be checked by removing the overflow hose at the
radiator filler neck nipple (Fig. 7). Attach the Radiator
Pressure Tool to the filler neck nipple and pump air
into the radiator. Pressure cap upper gasket should
relieve at 69-124 kPa (10-18 psi) and hold pressure at
55 kPa (8 psi) minimum.
WARNING: THE WARNING WORDS DO NOT OPEN
HOT ON THE RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP IS A
SAFETY PRECAUTION. WHEN HOT, PRESSURE
BUILDS UP IN COOLING SYSTEM. TO PREVENT
SCALDING OR INJURY, THE RADIATOR CAP
SHOULD NOT BE REMOVED WHILE THE SYSTEM IS
HOT AND/OR UNDER PRESSURE.
There is no need to remove the radiator cap at any
time except for the following purposes:
(1) Check and adjust antifreeze freeze point.
(2) Refill system with new antifreeze.
(3) Conducting service procedures.
(4) Checking for vacuum leaks.
WARNING: IF VEHICLE HAS BEEN RUN RECENTLY,
WAIT 15 MINUTES BEFORE REMOVING CAP. THEN PLACE A SHOP TOWEL OVER THE CAP AND WITH-
OUT PUSHING DOWN ROTATE IT COUNTER-
CLOCKWISE TO THE FIRST STOP. ALLOW FLUIDS
TO ESCAPE THROUGH THE OVERFLOW TUBE AND
WHEN THE SYSTEM STOPS PUSHING COOLANT
AND STEAM INTO THE CRS TANK AND PRESSURE
DROPS PUSH DOWN AND REMOVE THE CAP COM-
PLETELY. SQUEEZING THE RADIATOR INLET HOSE
WITH A SHOP TOWEL (TO CHECK PRESSURE) BE-
FORE AND AFTER TURNING TO THE FIRST STOP IS
RECOMMENDED.
PRESSURE TESTING RADIATOR CAPS
Dip the pressure cap in water, clean any deposits off
the vent valve or its seat and apply cap to end of
Radiator Pressure Tool. Working the plunger, bring the
pressure to 104 kPa (15 psi) on the gauge. If the
pressure cap fails to hold pressure of at least 97 kPa
(14 psi) replace cap. See CAUTION
If the pressure cap tests properly while positioned on
Radiator Pressure Tool, but will not hold pressure or
vacuum when positioned on the radiator. Inspect the
radiator filler neck and cap top gasket for irregularities
that may prevent the cap from sealing properly.
CAUTION: Radiator Pressure Tool is very sensitive to
small air leaks which will not cause cooling system
problems. A pressure cap that does not have a
history of coolant loss should not be replaced just
because it leaks slowly when tested with this tool.
Add water to the tool. Turn tool upside down and
recheck pressure cap to confirm that cap is bad.
INSPECTION
Hold the cap in hand, right side up(Fig. 7). The
vent valve at the bottom of the cap should open. If the
rubber gasket has swollen and prevents the valve from
opening, replace the cap. Hold the cleaned cap in hand upside down.If any
light can be seen between vent valve and rubber
gasket, replace cap. Do not use a replacement cap
that has a spring to hold the vent shut. Replacement cap must be of the type designed for
coolant reserve systems. This design assures coolant
return to radiator.
RADIATORS
The radiators are crossflow types (horizontal tubes)
with design features that provide greater strength as
well as sufficient heat transfer capabilities to keep the
engine satisfactorily cooled.
CAUTION: Plastic tanks, while stronger then brass
are subject to damage by impact, such as wrenches.
Fig. 7 Radiator Pressure Cap Filler Neck
7 - 18 COOLING SYSTEM Ä
Page 361 of 2438

RADIATOR DRAINCOCK SERVICE
REMOVAL (1) Turn the drain cock stem counterclockwise to
unscrew the stem. When the stem is unscrewed to
the end of the threads, pull the stem (Fig. 10) from
the radiator tank.
INSTALLATION (1) Push the draincock assembly body into the
tank opening until it snaps into place. (2) Tighten the draincock stem by turning clock-
wise to 2.0-2.7 N Im (18-25 in. lbs.) torque.
RADIATOR COOLANT FLOW CHECK
To determine whether coolant is flowing through
the cooling system, use the following procedure: (1) If engine is cold, idle engine until normal oper-
ating temperature is reached. Then feel the upper ra-
diator hose. If it is hot, coolant is circulating.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE RADIATOR PRES-
SURE CAP WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM
COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
Fig. 9 Cooling ModuleÐTypical
Fig. 8 Pressure Testing Radiator Cap
Fig. 10 Draincock AssemblyÐTypical
Ä COOLING SYSTEM 7 - 19
Page 362 of 2438

(2) Remove radiator pressure cap when engine is
cold, Idle engine until thermostat opens, you should
observe coolant flow while looking down the filler
neck. Once flow is detected install radiator pressure
cap.
RADIATOR
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK PLUG OR THE RADIATOR DRAINCOCK
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
(2) Drain cooling system. Refer to Draining Cool-
ing System of this section. (3) Remove hose clamps and hoses from the radia-
tor (Fig. 11). Remove coolant reserve system tank to
filler neck tube. (4) Remove automatic transmission hoses, if
equipped. (5) Remove fan and fan support assembly by dis-
connecting fan motor electrical connector. Remove
fan shroud retaining clips, located on the top and
bottom of the shroud for AA, AG, AJ and AP vehi-
cles. AC/AY vehicle retainer clips are located on the
top only. Lift shroud up and out of bottom shroud at-
tachment clips separating shroud from radiator. Fan
damage should always be avoided. (6) Remove upper radiator mounting screws. Dis-
connect the engine block heater wire if equipped. (7) Remove the air conditioning condenser attaching
screws located at the top front of the radiator,if
equipped. Radiator can now be lifted free from engine compart-
ment. Care should be taken not to damage radia-
tor cooling fins or water tubes during removal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Slide radiator down into position behind radiator
support (yoke). (2) Attach air conditioning condenser to radiator, if
equipped, with a force of approximately 10 lbs. to seat
the radiator assembly lower rubber isolators in the
mount holes provided. (3) Tighten radiator mounting screws to 11.9N Im
(105 in. lbs.). (4) Connect automatic transmission hoses, if
equipped. Tighten hose clamps to 4 N Im (35 in. lbs.).
(5) Slide fan shroud, fan and motor down into clips
on lower radiator flange. Replace shroud retaining
clips. (6) Install upper and lower radiator hoses (including
coolant reserve hose). (7) Connect fan motor electrical connection and con-
nect negative battery cable. (8) Fill cooling system with coolant. Refer to Refill-
ing Cooling Systems. in this group.
(9) Operate engine until it reaches normal operating
temperature. Check cooling system and automatic
transmission for correct fluid levels.
Fig. 11 Cooling ModulesÐAll Models
7 - 20 COOLING SYSTEM Ä
Page 375 of 2438

BATTERY TEST PROCEDURES ON-VEHICLE INDEX
page page
Battery Charging .......................... 7
Battery Load Test ......................... 6
Battery Open Circuit Voltage Test ............. 4
Causes of Battery Discharging ............... 4 General Information
........................ 3
State of Charge Tests ...................... 4
Test Indicator ............................ 3
GENERAL INFORMATION
The battery stores, stabilizes, and produces electri-
cal current to operate various electrical systems in
the vehicle. The determination of whether a battery
is good or bad is made by the battery's ability to ac-
cept a charge. It also must produce high amperage
current output over an extended period to be able to
start the vehicle. The capability of the battery to
store electrical current comes from a chemical reac-
tion. This reaction takes place between the sulfuric
acid solution electrolyte and the lead +/- plates in
each cell of the battery. As the battery discharges,
the plates react with the acid from the electrolyte.
When the charging system charges the battery, the
water is converted to sulfuric acid in the battery. The
amount of acid, specific gravity in the electrolyte can
be measured with a hydrometer. The factory in-
stalled battery is equipped with a built in hydrome-
ter as a test indicator (Figs. 3, 4 and 5) to help in
determining the battery's state of charge. The factory
installed battery also is sealed. Water cannot and
should not be added.
The battery is vented to release gases that is cre-
ated when the battery is being charged and dis-
charged. The battery top, posts, and terminals should
be cleaned when other under hood maintenance is
performed (Fig. 3).
WARNING: DO NOT ASSIST BOOST, CHARGE, ADD
WATER, OR LOAD TEST BATTERY WHEN ELEC- TROLYTE LEVEL IS BELOW THE TOP OF THE
PLATES. PERSONAL INJURY MAY OCCUR.
When the electrolyte level is below the top of the
plates a yellow or bright color indicator in sight glass
(Figs. 4 and 5), the battery must be replaced. Refer
to Test Indicator. The battery must be completely
charged with a green color in sight glass. The top,
posts, and terminals should be properly cleaned be-
fore diagnostic procedures are performed. Also refer
to Group 8B, Battery/Starter/Generator Service.
TEST INDICATOR
The test indicator a hydrometer is viewed through
a sight glass, it is built into the top of battery case
(Figs. 3, 4 and 5). This provides visual information
for battery testing. The test indicator sight glass is to
be used with diagnostic procedures described in this
Group.
Fig. 3 Battery Construction and Test Indicator
Fig. 4 Built in Test Indicator
Fig. 5 Test Indicator Sight Glass
Ä BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS 8A - 3
Page 376 of 2438

It is important when using the Test Indicator that
the battery be level and have a clean top to see the
correct indications. A light may be required to view
the Indicator.
WARNING: DO NOT USE OPEN FLAME NEAR BAT-
TERY BECAUSE OF EXPLOSIVE GASES AT FORM
ABOVE BATTERY.
STATE OF CHARGE TESTS
USING TEST INDICATOR
The built in test hydrometer (Figs. 3, 4 and 5) mea-
sures the specific gravity of the electrolyte. Specific
Gravity (SG) of the electrolyte will show state of
charge voltage. The test indicator WILL NOT show
cranking capacity of the battery. Refer to Battery
Load. Look into the sight glass (Figs. 4 and 5) and
note the color of the indicator (Fig. 5). Refer to the
following description of colors:
² GREEN = 75 to 100 degree state of charge
The battery is adequately charged for further test-
ing and may be returned to use. If the vehicle will
not crank for a maximum 15 seconds, refer to Bat-
tery Load Test in this Group for more information.
² BLACK OR DAR K=0to75degree state of
charge The battery is INADEQUATELY charged and
must be charged until green dot is visible, (12.4 volts
or greater) before the battery is tested or returned to
use. Refer to Causes of Battery Discharging.
² YELLOW OR BRIGHT COLOR = Battery must
be replace
WARNING: DO NOT CHARGE, ASSIST BOOST,
LOAD TEST, OR ADD WATER TO THE BATTERY
WHEN YELLOW OR BRIGHT COLOR DOT IS VISI-
BLE. PERSONAL INJURY MAY OCCUR.
A yellow or bright color dot shows electrolyte level
in battery is below the test indicator (Fig. 5). Water
cannot be added to a maintenance free battery. The
battery must be replaced. A low electrolyte level may
be caused by an over charging condition. Refer to
Generator Test Procedures on Vehicle.
CAUSES OF BATTERY DISCHARGING
It is normal to have a small 5 to 30 milliamperes
continuous electrical draw from the battery. This
draw will take place with the ignition in the OFF po-
sition, and the courtesy, dome, storage compart-
ments, and engine compartment lights OFF. The
continuous draw is due to various electronic features
or accessories that require electrical current with the
ignition OFF to function properly. When a vehicle is
not used over an extended period approximately 20
days the Main Fusible Link Connector (Fig. 6)
should be disconnected. This is located near the bat- tery on the engine wiring harness. Disconnection of
this connector will help prevent battery discharging.
Refer to Fig. 7 for Battery Diagnostics.
ABNORMAL BATTERY DISCHARGING
(1) Corroded battery posts, cables or terminals.
(2) Loose or worn generator drive belt.
(3) Electrical loads that exceed the output of the
charging system due to equipment or accessories in-
stalled after delivery. (4) Slow driving speeds in heavy traffic conditions
or prolonged idling with high-amperage electrical
systems in use. (5) Defective electrical circuit or component caus-
ing excess Ignition Off Draw (IOD). Refer to Ignition
OFF Draw (IOD). (6) Defective charging system.
(7) Defective battery.
BATTERY OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE TEST
An open circuit voltage, no load test will show the
state of charge in a battery. Also, if it will pass a
load test of 50 percent of the battery cold crank rat-
ing. Refer to Battery Load Test. If a battery has an
open circuit voltage reading of 12.4 volts or greater,
and will not pass a load test, it is defective and re-
placement would be required. To test open circuit
voltage, perform the following operation: (1) Remove both battery cables, negative first. If
the battery has been boosted, charged, or loaded just
prior to this operation, allow the battery a few min-
utes to stabilize. (2) Using a voltmeter connected to the battery
posts and measure the open circuit voltage (Fig. 8).
Fig. 6 Main Fusible Link Connector
8A - 4 BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS Ä
Page 378 of 2438
This voltage reading will show the battery state of
charge. It will not reveal battery cranking capacity
(Fig. 8).
BATTERY LOAD TEST
A fully charged battery must have reserve crank-
ing capacity. This will enable the starter motor and
ignition system enough power to start the engine
over a broad range of ambient temperatures. A bat-
tery load test will verify the actual cranking perfor-
mance based on the cold crank rating of the battery.
WARNING: IF BATTERY SHOWS SIGNS OF FREEZ-
ING, LEAKING, LOOSE POSTS, OR EXCESSIVELY
LOW ELECTROLYTE LEVEL, DO NOT TEST. ACID
BURNS OR AN EXPLOSIVE CONDITION MAY RE-
SULT. (1) Remove both battery cables, negative first. Bat-
tery top, cables and posts should be clean. If green
dot is not visible in indicator, charge the battery. Re-
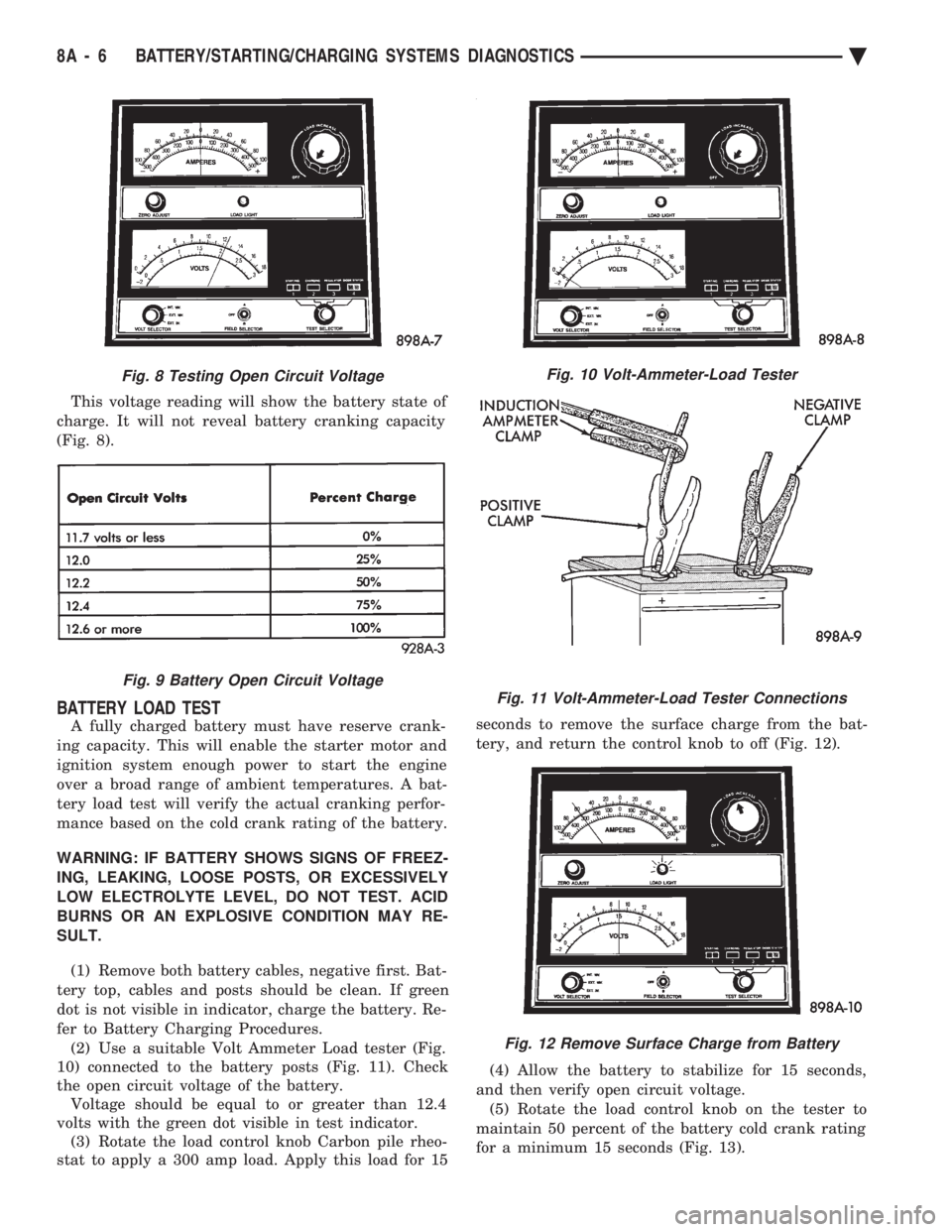
fer to Battery Charging Procedures. (2) Use a suitable Volt Ammeter Load tester (Fig.
10) connected to the battery posts (Fig. 11). Check
the open circuit voltage of the battery. Voltage should be equal to or greater than 12.4
volts with the green dot visible in test indicator. (3) Rotate the load control knob Carbon pile rheo-
stat to apply a 300 amp load. Apply this load for 15 seconds to remove the surface charge from the bat-
tery, and return the control knob to off (Fig. 12).
(4) Allow the battery to stabilize for 15 seconds,
and then verify open circuit voltage. (5) Rotate the load control knob on the tester to
maintain 50 percent of the battery cold crank rating
for a minimum 15 seconds (Fig. 13).
Fig. 8 Testing Open Circuit Voltage
Fig. 9 Battery Open Circuit Voltage
Fig. 10 Volt-Ammeter-Load Tester
Fig. 11 Volt-Ammeter-Load Tester Connections
Fig. 12 Remove Surface Charge from Battery
8A - 6 BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS Ä
Page 379 of 2438

After 15 seconds, record the loaded voltage reading
and return the load control to the off position. (6) Voltage drop will vary according to battery
temperature at the time of the load test. Battery
temperature can be estimated by the temperature of
exposure over the preceding several hours. If the bat-
tery has been charged, boosted, or loaded a few min-
utes prior to the test, the battery would be slightly
warmer. Refer to Fig. 14 for proper loaded voltage
reading.
(7) If battery passes load test, it is in good condi-
tion and further tests are not necessary. If it fails
load test, it should be replaced.
BATTERY CHARGING
A battery is considered fully charged when it will
meet all the following requirements:
² It has an open circuit voltage charge of at least
12.4 volts (Fig. 9)
² It passes the 15 second load test (Fig. 14)
² The built in test indicator dot is GREEN (Fig. 5)
² The battery cannot be refilled with water. It must
be replaced WARNING: DO NOT CHARGE A BATTERY THAT
HAS EXCESSIVELY LOW ELECTROLYTE LEVEL.
BATTERY MAY SPARK INTERNALLY AND EX-
PLODE. EXPLOSIVE GASES FORM OVER THE BATTERY.
DO NOT SMOKE, USE FLAME, OR CREATE
SPARKS NEAR BATTERY. DO NOT ASSIST BOOST OR CHARGE A FROZEN
BATTERY. BATTERY CASING MAY FRACTURE. BATTERY ACID IS POISON, AND MAY CAUSE SE-
VERE BURNS AND THE BATTERY CONTAIN SUL-
FURIC ACID. AVOID CONTACT WITH SKIN, EYES,
OR CLOTHING. IN THE EVENT OF CONTACT,
FLUSH WITH WATER AND CALL PHYSICIAN IMME-
DIATELY. KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.
CAUTION: Disconnect the battery negative cable
first (Fig. 15) before charging battery to avoid dam-
age to electrical systems. Do not exceed 16.0 volts
while charging battery. Refer to the instructions
supplied with charging equipment
Battery electrolyte will bubble inside the battery
case while being charged properly. If the electrolyte
boils violently, or is discharged from the vent holes
while charging, immediately reduce charging rate or
turn off charger. Evaluate battery condition. Battery
damage may occur if charging is excessive. Some battery chargers are equipped with polarity
sensing devices to protect the charger or battery from
being damaged if improperly connected. If the bat-
tery state of charge is too low for the polarity sensor
to detect, the sensor must be bypassed for charger to
operate. Refer to operating instructions provided
with battery charger being used.
CAUTION: Charge battery until test indicator ap-
pears green. Do not overcharge.
It may be necessary to jiggle the battery or vehicle
to bring the green dot (in the test indicator) into
view. After the battery has been charged to 12.4 volts or
greater, perform a load test to decide cranking capac-
Fig. 13 Load 50 Percent Cold Crank Rating
Fig. 14 Load Test Temperature
Fig. 15 Disconnect Negative Battery Cable
Ä BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS 8A - 7