ABS CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 2 of 2438

WIRING DIAGRAMS AA-BODY
INDEX
Wiring Diagram Name Sheet Number
Anti-Lock Brake System.................41, 42, 43, 44
ABS Pump Motor Relay.......................41
ABS System Relay..........................43
Brake Switch..............................44
Controller.....................41, 42, 43, 44, 114
Data Link Connector.........................44Wiring Diagram Name Sheet Number
Diode-Warning Lamp.........................43
Hydraulic Modulator.........................41
Ignition Switch.............................44
Park Brake Switch...........................44
Wheel Sensors.............................42
ÄWIRING DIAGRAMS AA-BODY 8W - 1
Page 9 of 2438

WIRING DIAGRAMS AJ BODY
ALPHABETICAL INDEX
Wiring Diagram Name Sheet Number
Anti-Lock Brake System.................68, 69, 70, 71
ABS Controller..................68, 69, 70, 71, 170
ABS Hydraulic Modulator......................68
ABS Pump Motor Relay.......................68
ABS System Relay..........................69
ABS Warning Lamp Diode......................69
ABS Warning Switch Lamp Switch................70Wiring Diagram Name Sheet Number
Brake Switch..............................70
Data Link Connector.........................70
Left Front Wheel Sensor.......................71
Left Rear Wheel Sensor.......................71
Park Brake Switch...........................70
Right Front Wheel Sensor......................71
Right Rear Wheel Sensor......................71
8W - 8 WIRING DIAGRAMS AJ BODYÄ
Page 29 of 2438

FOREWORD
The information contained in this Service Manual has been prepared for the professional automotive
technician involved in daily repair operations. Information describing the operation and use of standard and
optional equipment is included in the Owner's Manual provided with the vehicle.
These diagrams contain the latest information at the time of publication and incorporate the wiring schematic
for the basic vehicle and available optional equipment.
The diagrams are grouped by body type and sales division. The body codes are explained in the General
Information section. (ExampleÐAP-D, P=Shadow, Sundance). To locate a system or component refer to the black
index tabs on the next page. The tab will assist you in locating the desired area of the manual.
An alphabetical index is provided at the beginning of each section to help you in locating a system or
component. All diagrams are identified by SHEET NUMBER which is found in the lower right- or left-hand corner
of the page.
A Service Manual Comment form is included at the rear of this manual. Use the form to provide Chrysler
Corporation with your comments and suggestions.
Chrysler Corporation reserves the right to change testing procedures, specifications, diagnosis, repair
methods, or vehicle wiring at any time without prior notice or incurring obligation.
NOTE: The acronyms, terminology and nomenclature used to identify emissions related components in this
manual may have changed from prior publications. These new terms are in compliance with S.A.E.
recommended practice J1930. This terminology standard (J1930) is required to comply with the 1993
California Air Research Board (CARB) requirements.
FOR INFORMATION NOT CONTAINED IN THIS MANUAL, REFER TO THE FRONT WHEEL
DRIVE PASSENGER VEHICLES ENGINEÐCHASSISÐBODY OR ELECTRICALÐFUELÐEMISSIONS
SERVICE MANUALS.
NEXT PAGE ©
Page 35 of 2438

COMPONENT AND SYSTEM INDEX
Name Group-page Name Group-page
BRAKES ..................................5-1
BENDIX ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM ...........5-12
ABS BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES.......5-24
ABS SYSTEM SELF DIAGNOSIS................ 5-24
BENDIX ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTICS....5-25
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE CAB............. 5-24
LATCHING VERSUS NON-LATCHING ABS FAULTS.......5-25
START-UP CYCLE........................ 5-24
ABS COMPUTER SYSTEM SERVICE PRECAUTIONS....5-23
ABS GENERAL SERVICE PRECAUTIONS........... 5-23
ABS BRAKE SYSTEM ON VEHICLE SERVICE.........5-23
TEST DRIVING ABS COMPLAINT VEHICLES.......... 5-23
WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CABLES............... 5-23
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS..........5-16
BUILD/DECAY VALVES..................... 5-16
FLUID SUMPS.......................... 5-17
HYDRAULIC SPRING ACCUMULATOR.............5-17
MODULATOR ASSEMBLY.................... 5-16
PRESSURE DIFFERENTIAL SWITCH..............5-17
PROPORTIONING VALVES................... 5-17
PUMP/MOTOR ASSEMBLY...................5-17
SHUTTLE ORIFICE........................ 5-16
WHEEL SPEED SENSORS....................5-18
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM DEFINITIONS..........5-14
ANTILOCK BRAKES OPERATION AND PERFORMANCE. . . 5-15
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM OPERATION............ 5-15
PEDAL FEEL........................... 5-15
TIRE NOISE & MARKS.....................5-15
ANTILOCK SYSTEM RELAYS AND WARNING LAMPS. . . 5-19
ANTILOCK WARNING LAMP DIODE..............5-20
Antilock Warning Lamp Off................... 5-20
Antilock Warning Lamp On...................5-20
PUMP/MOTOR RELAY...................... 5-20
SYSTEM RELAY......................... 5-19
BENDIX ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTICS. . . 5-22
DEFINITIONS........................... 5-23
GENERAL INFORMATION....................5-22
BLEEDING BENDIX ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM......5-25
BENDIX ANTILOCK 4 MODULATOR ASSEMBLY BLEEDING
PROCEDURE
......................... 5-26
HYDRAULIC BRAKE TUBE ASSEMBLY (JUNCTION BLOCK
TO MODULATOR ASSEMBLY)
................ 5-34
INSTALL............................ 5-36
REMOVE............................5-34
MASTER CYLINDER AND POWER BOOSTER.........5-38
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION................. 5-38
MODULATOR ASSEMBLY CIRCUIT BLEEDING PROCEDURE
AND SEQUENCE
....................... 5-26
1 MODULATOR PRIMARY CHECK VALVE CIRCUIT........5-26
2 MODULATOR SECONDARY CHECK VALVE CIRCUIT......5-26
3 MODULATOR ASSEMBLY PRIMARY SUMP CIRCUIT......5-27
4 MODULATOR ASSEMBLY PRIMARY ACCUMULATOR CIRCUIT. 5-27
5 MODULATOR ASSEMBLY SECONDARY SUMP CIRCUIT....5-28
6 MODULATOR ASSEMBLY SECONDARY ACCUMULATOR
CIRCUIT
........................... 5-29
MODULATOR ASSEMBLY (FIG. 1)...............5-30
INSTALL............................ 5-32
REMOVE............................5-30
PROPORTIONING VALVES (FIG. 1)...............5-38
INSTALL............................ 5-39
REMOVAL...........................5-38
PUMP/MOTOR SERVICE....................5-29
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE CAB.............5-18
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE (INPUTS)..........5-19
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE (OUTPUTS).........5-19
DIAGNOSTIC CONNECTOR.................... 5-19
ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS..................5-41
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE CAB.............5-41
INSTALL............................ 5-42
REMOVE............................5-41
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (FIG. 9)...........5-43
INSTALLATION......................... 5-44
REMOVAL........................... 5-43
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (FIGS. 10 AND 11)......5-44
INSTALLATION......................... 5-44
REMOVAL........................... 5-44
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION OF SYSTEM RELAY.........5-42
INSTALL............................ 5-43
REMOVE............................5-43
REMOVE/INSTALL PUMP MOTOR RELAY...........5-43
WHEEL SPEED SENSORS.................... 5-43
INSPECTION.......................... 5-43
GENERAL INFORMATION....................5-12
HYDRAULIC CIRCUITS AND VALVE OPERATION......5-20
ABS BRAKING-BUILD PRESSURE............... 5-20
BUILD/DECAY VALVES..................... 5-20
ABS BRAKING-DECAY PRESSURE...............5-22
BUILD/DECAY VALVES..................... 5-22
NORMAL BRAKING....................... 5-20
BUILD/DECAY VALVES.....................5-20
MAJOR COMPONENTS...................... 5-14
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE CAB.............5-14
MASTER CYLINDER AND VACUUM BOOSTER.........5-14
MODULATOR AND PUMP MOTOR/ASSEMBLY.........5-14
WHEEL SPEED SENSORS.................... 5-14
MECHANICAL DIAGNOSTICS AND SERVICE
PROCEDURES
.......................... 5-24
INTERMITTENT FAULTS.....................5-24
SPECIAL SERVICE TOOL....................5-24
DRB DIAGNOSTIC TESTER...................5-24
NORMAL BRAKE SYSTEM FUNCTION.............5-14
ON-CAR ABS BRAKE SYSTEM SERVICE...........5-25
CHECKING BRAKE FLUID LEVEL................ 5-25
GENERAL SERVICE PRECAUTIONS...............5-25
SPECIFICATIONS......................... 5-46
SYSTEM SELF-DIAGNOSTICS..................5-15
VEHICLE PERFORMANCE.................... 5-15
WARNING SYSTEMS OPERATION...............5-16
NORMAL OPERATION OF WARNING LAMP..........5-16
GENERAL INFORMATION .....................5-1
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM CONTROL VALVES .........5-10
GENERAL INFORMATION.................... 5-10
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURES........5-11
BRAKE WARNING SYSTEM................... 5-11
CHECKING BRAKE WARNING SWITCH UNIT...........5-11
TESTING ANTILOCK PROPORTIONING VALVES........5-11
PRESSURE DIFFERENTIAL WARNING LIGHT SWITCH. . . 5-10
SERVICE ADJUSTMENTS .....................5-3
Page 43 of 2438

TOWING RECOMMENDATIONS
RECOMMENDED TOWING EQUIPMENT
To avoid damage to bumper fascia and air dams
use of a wheel lift or flat bed towing device (Fig. 8) is
recommended. When using a wheel lift towing de-
vice, be sure the unlifted end of disabled vehicle has
at least 100 mm (4 in.) ground clearance. If mini-
mum ground clearance cannot be reached, use a tow-
ing dolly. If a flat bed device is used, the approach
angle should not exceed 15 degrees.
GROUND CLEARANCE
CAUTION: If vehicle is towed with wheels removed,
install lug nuts to retain brake drums or rotors.
A towed vehicle should be raised until lifted wheels
are a minimum 100 mm (4 in) from the ground. Be
sure there is adequate ground clearance at the oppo-
site end of the vehicle, especially when towing over
rough terrain or steep rises in the road. If necessary,
remove the wheels from the lifted end of the vehicle
and lower the vehicle closer to the ground, to in-
crease the ground clearance at the opposite end of
the vehicle. Install lug nuts on wheel attaching studs
to retain brake drums or rotors.
LOCKED VEHICLE TOWING
When a locked vehicle must be towed with the
front wheels on the ground, use a towing dolly or flat
bed hauler.
FLAT TOWING WITH TOW BAR
² 4-speed automatic transaxle vehicles can be flat
towed at speeds not to exceed 72 km/h (44 mph) for
not more than 160 km (100 miles). The steering col-
umn must be unlocked and gear selector in neutral.
² 3-speed automatic transaxle vehicles can be flat
towed at speeds not to exceed 40 km/h (25 mph) for
not more than 25 km (15 miles). The steering column
must be unlocked and gear selector in neutral.
² Manual transaxle vehicles can be flat towed at any
legal highway speed with no distance restrictions.
The steering column must be unlocked and gear se-
lector in neutral. WARNING: DO NOT ALLOW TOWING ATTACH-
MENT DEVICES TO CONTACT THE FUEL TANK OR
LINES, FUEL LEAK CAN RESULT. DO NOT LIFT OR TOW VEHICLE BY FRONT OR
REAR BUMPER, OR BUMPER ENERGY ABSORBER
UNITS. DO NOT VENTURE UNDER A LIFTED VEHICLE IF
NOT SUPPORTED PROPERLY ON SAFETY
STANDS. DO NOT ALLOW PASSENGERS TO RIDE IN A
TOWED VEHICLE. USE A SAFETY CHAIN THAT IS INDEPENDENT
FROM THE TOWING ATTACHMENT DEVICE.
CAUTION: Do not damage brake lines, exhaust sys-
tem, shock absorbers, sway bars, or any other un-
der vehicle components when attaching towing
device to vehicle. Remove or secure loose or protruding objects
from a damaged vehicle before towing. Refer to state and local rules and regulations be-
fore towing a vehicle. Do not allow weight of towed vehicle to bear on
lower fascia, air dams, or spoilers.
TOWINGÐFRONT WHEEL LIFT
Chrysler Corporation recommends that a vehicle be
towed with the front end lifted, whenever possible.
TOWINGÐREAR WHEEL LIFT
If a front wheel drive vehicle cannot be towed with
the front wheels lifted, the rear wheels can be lifted
provided the following guide lines are observed.
CAUTION: Do not use steering column lock to se-
cure steering wheel during towing operation.
² Unlock steering column and secure steering wheel
in straight ahead position with a clamp device de-
signed for towing.
² Verify that front drive line and steering compo-
nents are in good condition.
² 4-speed automatic transaxle vehicles can be towed
at speeds not to exceed 72 km/h (44 mph) for not
more than 160 km (100 miles). The gear selector
must be in neutral position.
² 3-speed automatic transaxle vehicles can be towed
at speeds not to exceed 40 km/h (25 mph) for not
more than 25 km (15 miles). The gear selector must
be in neutral position.
² 3-speed automatic transaxle vehicles can be towed
at speeds not to exceed 40 km/h (25 mph) for not
more than 25 km (15 miles). The gear selector must
be in neutral position.
Fig. 8 Recommended Towing Devices
Ä LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 7
Page 59 of 2438

SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS
CONTENTS
page page
AUTOMATIC AIR LOAD LEVELING SYSTEM . 59
AUTOMATIC AIR SUSPENSION ............ 73
DRIVESHAFTS ......................... 25
FRONT SUSPENSION ..................... 2
FRONT SUSPENSION SERVICE PROCEDURES . 5 GENERAL INFORMATION
.................. 1
REAR (STUB) AXLE ALIGNMENT ALL MODELS ............................ 89
REAR SUSPENSION ..................... 50
SPECIFICATIONS ....................... 91
GENERAL INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references may be made to
a particular vehicle by letter or number designation.
A chart showing the breakdown of these designations
is included in the Introduction section at the front of
this Service Manual. An independent MacPherson Type front suspension
is used on these vehicles. Vertical shock absorbing
struts attach to the upper fender reinforcement and the steering knuckle to provide upper steering
knuckle position. Lower control arms are attached
inboard to a crossmember and outboard to the steer-
ing knuckle through a ball joint to provide lower
steering knuckle position. During steering maneu-
vers, the strut (through a pivot bearing in the upper
retainer) and the steering knuckle turn as an assem-
bly (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Front Suspension (Typical)
Ä SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS 2 - 1
Page 63 of 2438

FRONT SUSPENSION SERVICE PROCEDURES INDEX
page page
Ball Joints .............................. 13
Hub and Bearing Assembly ................. 20
Knuckle (Front Suspension) ................. 16
Lower Control Arm ....................... 10
Lower Control Arm Pivot Bushings ........... 11 Shock Absorbers (Strut Damper)
............. 10
Strut Damper Assembly ..................... 7
Suspension Coil Springs .................... 9
Sway Bar .............................. 14
Wheel Alignment .......................... 5
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
Front wheel alignment is the proper adjustment of
all interrelated front suspension angles. These angles
are what affects the running and steering of the
front wheels of the vehicle. The method of checking front alignment will vary
depending on the type of equipment being used. The
instructions furnished by the manufacturer of the
equipment should always be followed. With the ex-
ception that the alignment specifications recom-
mended by Chrysler Corporation be used. There are six basic factors which are the founda-
tion to front wheel alignment. These are height,
caster, camber, toe-in, steering axis inclination and
toe-out on turns. Of the six basic factors only camber
and toe in are mechanically adjustable (Fig. 1)
CAUTION: Do not attempt to modify any suspen-
sion or steering components by heating or bending
of the component.
Wheel alignment adjustments and checks should be
made in the following sequence. (1) Camber
(2) Toe
Camber is the number of degrees the top of the
wheel is tilted inward or outward from true vertical.
Inward tilt is negative camber. Outward tilt is posi-
tive camber. Excessive camber is a tire wear factor: negative
camber causes wear on the inside of the tire, while
positive camber causes wear to the outside. Toe
is measured in degrees or inches and is the
distance the front edges of the tires are closer (or far-
ther apart) than the rear edges. See Front Wheel
Drive Specifications for Toesettings.
PRE-ALIGNMENT
Before any attempt is made to change or correct
the wheel alignment factors. The following inspection
and necessary corrections must be made on those
parts which influence the steering of the vehicle. (1) Check and inflate tires to recommended pres-
sure. All tires should be the same size and in good
condition and have approximately the same wear.
Note type of tread wear which will aid in diagnosing,
see Wheels and Tires, Group 22. (2) Check front wheel and tire assembly for radial
runout. (3) Inspect lower ball joints and all steering link-
age for looseness. (4) Check for broken or sagged front and rear
springs. Front suspension must only be checked after the
vehicle has had the following checked or adjusted.
Tires set to recommended pressures, full tank of fuel,
no passenger or luggage compartment load and is on
a level floor or alignment rack. Just prior to each alignment reading. The vehicle
should be bounced (rear first, then front) by grasping
bumper at center and jouncing each end an equal
number of times. Always release bumpers at bottom
of down cycle.
Ä SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS 2 - 5
Page 65 of 2438

WHEEL ALIGNMENT SERVICE PROCEDURE
CAMBER AA, AJ BODIES (1) Prepare vehicle as described in the Pre-Align-
ment procedure. (2) Loosen cam and knuckle bolts (each side) (Fig.
2). (3) Rotate cam bolt (Fig. 2) to move top of wheel in
or out to specified camber. (4) Tighten the cam bolts and nuts to 100 N Im (75
ft. lbs.) plus1/4 turn beyond specified torque.
CAMBER AC, AG, AP, AY BODIES (1) Prepare vehicle as described in the Pre-Align-
ment procedure. (2) Position vehicle on alignment equipment and
read camber as instructed by equipment manufactur-
er's procedure. (3) Using extensions and appropriate tools. Re-
move the strut assembly to steering knuckle attach-
ing bolts from vehicle (Fig. 2). Replace the original
attaching bolts with the bolts provided in the align-
ment, Cam And Bolt Service Package. (4) Rotate the alignment adjusting cam bolt, (Fig.
2) to obtain the specified camber setting for the ve-
hicle. See the Specifications Section at the end of this
group for the camber setting for the vehicle being
serviced. (5) Using the appropriate extensions and tools.
Carefully reach around the tire and tighten the
knuckle bolts enough to hold the camber setting.
Finish by tightening the bolts to 100 N Im (75 ft.lbs.)
plus 1/4 turn beyond specified torque.
TOE
(1) Prepare vehicle as described in the Pre-Align-
ment procedure. (2) Center steering wheel and hold with steering
wheel clamp. (3) Loosen tie rod locknuts. Rotate rods to align toe
to specifications (Fig. 3).
CAUTION: Do not twist tie rod to steering gear rub-
ber boots during adjustment. (4) Tighten tie rod locknuts to 75 N Im (55 ft.lbs.)
torque. (5) Adjust steering gear to tie rod boots at tie rod.
(6) Remove steering wheel clamp.
STRUT DAMPER ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
(1) Loosen wheel nuts.
(2) Raise vehicle, see Hoisting in Lubrication and
Maintenance, Group 0. (3) Remove wheel and tire assembly.
Where service procedure includes assembly of
original strut (shock absorber) to original
knuckle. Mark cam adjusting bolt (Fig. 4), on
AA, and AJ bodies only. Mark outline of strut
on knuckle as shown in (Fig. 1). on AC, AG, AP
and AY bodies. (4) Remove cam bolt, knuckle bolt(s), washer
plate(s) and brake hose to damper bracket retaining
screw (Fig. 4). (5) Remove strut damper to fender shield mount-
ing nut washer assemblies.
Fig. 2 Alignment Adjustment Locations
Fig. 3 Front Wheel Toe Adjustment
Ä SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS 2 - 7
Page 67 of 2438

(a) Severe deterioration of rubber isolator; re-
tainers for cracks and distortion and bond failure of
retainers and rubber isolators. (b) Bearings for binding.
(c) Shock Absorber for flat spots over full stroke
also see, Shock Absorbers, (strut damper).
ASSEMBLE (STRUT DAMPER)
(1) Mount the strut assembly in a vertical position.
(2) Place the compressed spring onto the strut as-
sembly, so the end of the coil is seated in the seat re-
cess in lower spring mount (Fig. 9). (3) Install the dust shield, isolator (if so equipped)
jounce bumper, spacer (as required), and spring seat
onto the top of the strut shaft (Fig. 8). (4) Position top spring seat alignment tab correctly
with respect to bottom bracket (Fig. 9). (5) Install the rebound retainer and shaft nut (Fig.
8). (6) Tighten the strut shaft nut using, Strut Rod
Socket And Holder, Special Tool L-4558. Torque strut
shaft nut to 75 N Im (55 ft. lbs.) plus 1/4 turn (Fig. 10).
WARNING: THIS STEP MUST BE DONE BEFORE
SPRING COMPRESSOR, SPECIAL TOOL C-4838 IS
RELEASED FROM THE COIL SPRING.
(7) Verify coil spring is aligned correctly with respect
to bottom bracket (Fig. 9). (8) Release Spring Compressor Tool C-4838.
SUSPENSION COIL SPRINGS
Springs are rated separately for each side of vehicle
depending on optional equipment and type of service.
During service procedures where both springs are
removed, mark springs (Chalk, Tape, etc.) (Fig. 11) to
ensure installation in original position. If the coils
springs require replacement. Be sure that the
springs needing replacement, are replaced with
springs meeting the correct load rating for the
vehicle and its specific options. During service procedures requiring the re-
moval or installation of a coil spring with Spring
Fig. 7 Loosening Strut Assembly Shaft Nut
Fig. 8 Mount Assembly
Fig. 9 Spring Seat Alignment Notch Position to Bracket
Fig. 10 Tighten Strut Rod Nut with Tool
Ä SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS 2 - 9
Page 68 of 2438
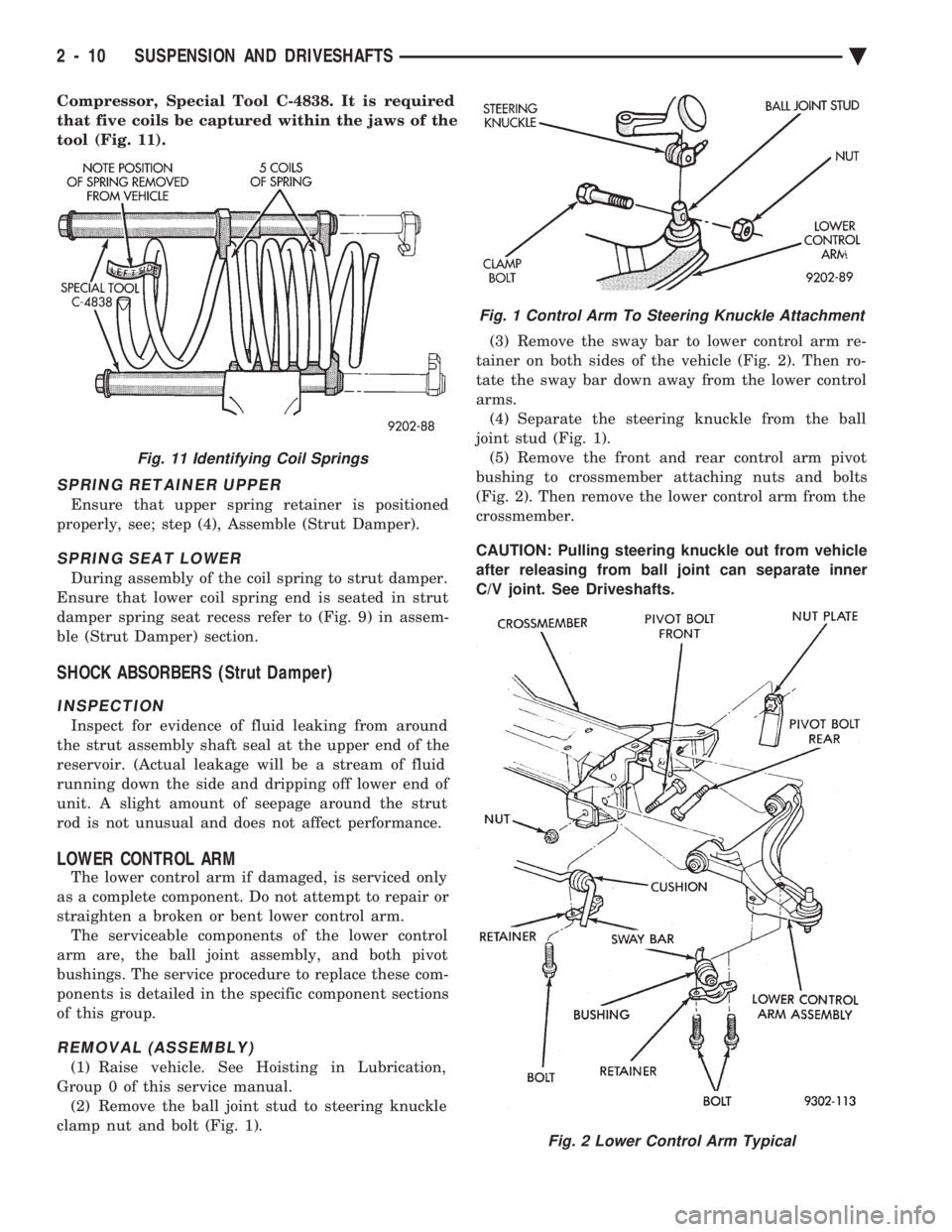
Compressor, Special Tool C-4838. It is required
that five coils be captured within the jaws of the
tool (Fig. 11).
SPRING RETAINER UPPER
Ensure that upper spring retainer is positioned
properly, see; step (4), Assemble (Strut Damper).
SPRING SEAT LOWER
During assembly of the coil spring to strut damper.
Ensure that lower coil spring end is seated in strut
damper spring seat recess refer to (Fig. 9) in assem-
ble (Strut Damper) section.
SHOCK ABSORBERS (Strut Damper)
INSPECTION
Inspect for evidence of fluid leaking from around
the strut assembly shaft seal at the upper end of the
reservoir. (Actual leakage will be a stream of fluid
running down the side and dripping off lower end of
unit. A slight amount of seepage around the strut
rod is not unusual and does not affect performance.
LOWER CONTROL ARM
The lower control arm if damaged, is serviced only
as a complete component. Do not attempt to repair or
straighten a broken or bent lower control arm. The serviceable components of the lower control
arm are, the ball joint assembly, and both pivot
bushings. The service procedure to replace these com-
ponents is detailed in the specific component sections
of this group.
REMOVAL (ASSEMBLY)
(1) Raise vehicle. See Hoisting in Lubrication,
Group 0 of this service manual. (2) Remove the ball joint stud to steering knuckle
clamp nut and bolt (Fig. 1). (3) Remove the sway bar to lower control arm re-
tainer on both sides of the vehicle (Fig. 2). Then ro-
tate the sway bar down away from the lower control
arms. (4) Separate the steering knuckle from the ball
joint stud (Fig. 1). (5) Remove the front and rear control arm pivot
bushing to crossmember attaching nuts and bolts
(Fig. 2). Then remove the lower control arm from the
crossmember.
CAUTION: Pulling steering knuckle out from vehicle
after releasing from ball joint can separate inner
C/V joint. See Driveshafts.
Fig. 11 Identifying Coil Springs
Fig. 1 Control Arm To Steering Knuckle Attachment
Fig. 2 Lower Control Arm Typical
2 - 10 SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS Ä