wheel CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 191 of 1938

(4) Carefully remove the speed sensor cable from
the rear brake flex hose routing clips (Fig. 44).
(5) Remove the rear wheel speed sensor cable/
brake tube routing clips (Fig. 45). Then un-clip the
speed sensor cable from the routing clips on rear
brake tube (Fig. 45).
CAUTION: If the speed sensor has seized, due to
corrosion, do not use pliers on speed sensor head
in a attempt to remove it. Use a hammer and a
punch and tap edge of sensor, rocking the sensor
from side to side until free.
(6) Remove the wheel speed sensor attaching bolt
(Fig. 46). If sensor head does not come loose, do not
use pliers on the sensor head to loosen. Tap sensor
head from side to side to loosen.
(7) Remove the wheel speed sensor from the rear
bearing assembly.(8) Remove the speed sensor assembly from the
vehicle.
INSTALL
CAUTION: Proper installation of wheel speed sen-
sor cables is critical to continued system operation.
Be sure that cables are installed in retainers. Fail-
ure to install cables in retainers as shown in this
section may result in contact with moving parts
and/or over extension of cables, resulting in an
open circuit.
(1) Install wheel speed sensor head. Note, the plas-
tic anti rotation pin must be fully seated prior to
installing the attaching bolt.
CAUTION: Prior to installing the speed sensor
head attaching bolt, the plastic anti-rotation pin
must be fully seated into the bearing flange.
Fig. 43 Speed Sensor Cable Connection To Vehicle
Wiring Harness
Fig. 44 Speed Sensor Cable Attachment To Brake
Flex Hose
Fig. 45 Rear Speed Sensor Routing Brackets And
Clips
Fig. 46 Speed Sensor Attaching Bolt
NSBRAKES 5 - 109
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 192 of 1938

(2) Install the wheel speed sensor head attaching
bolt (Fig. 46). Tighten the attaching bolt to a torque
12 N´m (105 in. lbs.)
(3) Check the air gap between the face of the
wheel speed sensor and the top surface of the tone-
wheel. Air gap must be less then the maximum
allowable tolerance of 1.2 mm (.047 in.).
(4) Install the routing brackets attaching the speed
sensor cable and brake tube to the rear axle (Fig.
45).The rear wheel speed sensor cable should
be routed under the rear brake tube (Fig. 45).
CAUTION: When installing rear wheel speed sen-
sor cable in the routing clips on rear brake flex
hose, be sure not to damage the routing clips.
Routing clips are molded onto the hose and will
require replacement of the brake flex hose if dam-
aged during installation of the wheel speed sensor
cable.
(5) Install speed sensor cable into routing clips on
rear brake flex hose (Fig. 44).
CAUTION: The wheel speed sensor cable connec-
tors for the left and right rear wheel speed sensors
are keyed differently. Therefore, when connecting a
wheel speed sensor cable to the vehicle wiring har-
ness, do not force the connectors together. If the
connectors are forced together, damage to the con-
nectors will occur.
(6) Plug speed sensor cable connector into vehicle
wiring harness (Fig. 43).Be sure speed sensor
cable connector is fully seated and locked into
vehicle wiring harness connector.
(7) Install the speed sensor cable grommet into the
body, being sure the grommet is fully seated into the
body hole.
(8) Install the tire and wheel assembly on vehicle.
(9) Road test vehicle to ensure proper operation of
the base and ABS braking systems.
TONE WHEEL (REAR FWD)
REMOVE
(1) Raise vehicle on jackstands or centered on a
frame contact type hoist. See Hoisting in the Lubri-
cation and Maintenance section of this service man-
ual for required lifting procedure.
(2) Remove the wheel and tire assembly.
(3) Remove rear brake drum from the hub/bearing
assembly.
(4) Remove the rear wheel speed sensor from the
rear hub/bearing flange (Fig. 47). This will prevent
damage to the speed sensor during removal and
installation of the hub/bearing assembly.(5) Remove the 4 bolts (Fig. 48) attaching the hub/
bearing assembly to the flange of the rear axle.
(6) Remove the hub/bearing assembly from the
rear axle and brake support plate (Fig. 49).
Fig. 47 Rear Wheel Speed Sensor
Fig. 48 Rear Hub/Bearing Mounting Bolts
Fig. 49 Removing Rear Hub/Bearing From Axle
5 - 110 BRAKESNS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 193 of 1938

(7) Install wheel lug nuts on 3 of the wheel mount-
ing studs to protect the stud threads from damage by
the vise jaws. Mount the hub/bearing assembly in a
vise (Fig. 50). Using Puller, Special Tool C-4693
installed as shown in (Fig. 50) remove the tone wheel
from the hub/bearing assembly.
INSTALL
(1) Place hub/bearing assembly in an arbor press
supported by Receiver, Special Tool, 6062A±3 (Fig.
51). Position Driver, Special Tool 6908±1 with under-
cut side facing up (Fig. 51) on top of the tone wheel.
(2) Press the tone wheel onto the hub/bearing
assembly until it is flush with the end of hub shaft
(Fig. 52).
(3) Install the 4 hub/bearing to axle flange mount-
ing bolts into the 4 mounting holes in the flange of
the rear axle.(4) Install the rear brake support plate on the 4
mounting bolts installed in the flange of the rear
axle.
(5) Align the rear hub/bearing assembly with the 4
mounting bolts and start mounting bolts into hub/
bearing assembly. Tighten the 4 bolts in a criss-cross
pattern until the hub/bearing and brake support
plate is fully and squarely seated onto flange of rear
axle.
(6) Tighten the 4 hub/bearing mounting bolts (Fig.
48) to a torque of 129 N´m (95 ft. lbs.)
(7) Install the rear wheel speed sensor on the rear
hub/bearing flange (Fig. 47). Install the speed sensor
attaching bolt and tighten to a torque of 12 N´m (105
in. lbs.).
(8) Check the air gap between the face of the
wheel speed sensor and the top surface of the tone-
wheel. Air gap must be less then the maximum
allowable tolerance of 1.2 mm (.047 in.).
(9) Install the brake drum onto the rear hub/bear-
ing assembly.
(10) Install rear wheel and tire assembly, tighten
wheel stud nuts to 129 N´m (95 ft. lbs.).
(11) Adjust the rear brakes, (See Adjusting Service
Brakes) in Service Adjustments section in this group
of the service manual.
TONE WHEEL (REAR AWD)
The rear tone wheel on all wheel drive applications
is an integral part of each rear axle outer C/V joint.
If the rear tone wheel on an all wheel drive vehicle
requires replacement it can not be replace as a sep-
arate component of the rear axle. Tone wheel replace-
ment will require the replacement of the rear axle.
Refer to Differential And Driveline in this service
manual for the rear axle replacement procedure.
Fig. 50 Tone Wheel Removal From Hub/Bearing
Assembly
Fig. 51 Installing Tone Wheel On Hub/Bearing
Assembly
Fig. 52 Correctly Installed Tone Wheel
NSBRAKES 5 - 111
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 194 of 1938

SPECIFICATIONS
SPEED SENSOR TONE WHEEL RUNOUT
The total indicator runout allowed for both the
front and rear tone wheel measured using a dial indi-
cator is 0.15 mm (.006 in.).
WHEEL SPEED SENSOR TO TONE WHEEL
CLEARANCE
FRONT WHEEL
Minimum Clearance .35mm (.014 in.)
Maxamum Clearance 1.2 mm (.047 in.)
REAR WHEEL
Minimum Clearance .40mm (.016 in.)
Maxamum Clearance 1.2 mm (.047 in.)
BRAKE FASTENER TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION TORQUE
BRAKE TUBES:
Tube Nuts To Fittings And
Components..............17N´m(145 in. lbs.)
BRAKE HOSE:
To Caliper Banjo Bolt..........48N´m(35ft.lbs.)
Intermediate Bracket.........12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
MASTER CYLINDER:
To Vacuum Booster
Mounting Nut............25N´m(225 in. lbs.)
FIXED PROPORTIONING VALVE:
To Frame Rail Attaching
Bolts....................14N´m(125 in. lbs.)
HEIGHT SENSING PROPORTIONING VALVE:
To Mounting Bracket
Attaching Bolts...........23N´m(200 in. lbs.)
Actuator Assembly
Adjustment Nut.............5N´m(45in.lbs.)
Mounting Bracket To
Frame Rail Bolts..........17N´m(150 in. lbs.)
JUNCTION BLOCK (NON-ABS BRAKES)
To Suspension Cradle
Mounting Bolt............28N´m(250 in. lbs.)
VACUUM BOOSTER:
To Dash Panel Mounting
Nuts....................28N´m(250 in. lbs.)DESCRIPTION TORQUE
REAR WHEEL CYLINDER:
To Support Plate Mounting
Bolts.....................8N´m(75in.lbs.)
Bleeder Screw...............10N´m(80in.lbs.)
BRAKE SUPPORT PLATE:
To Rear Axle Mounting Bolts . . .130 N´m (95 ft. lbs.)
DISC BRAKE CALIPER:
Guide Pin Bolts..............41N´m(30ft.lbs.)
Bleeder Screw..............15N´m(125 in. lbs.)
ABS HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT:
Mounting Bracket To
Suspension Cradle Bolts.....28N´m(250 in. lbs.)
To Mounting Bracket Isolator
Attaching Bolts............11N´m(97in.lbs.)
CAB To HCU Mounting Screws . . .2 N´m (17 in. lbs.)
WHEEL SPEED SENSOR:
To Axle Or Steering Knuckle
Mounting Bolt............12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
PARKING BRAKE:
Pedal Assembly Mounting
Bolts....................28N´m(250 in. lbs.)
REAR HUB AND BEARING:
To Axle Mounting Bolts........129 N´m (95 ft. lbs.)
WHEEL:
Stud Lug Nut........115±156 N´m (84-115 ft. lbs.)
5 - 112 BRAKESNS
Page 195 of 1938

BRAKES
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
BASE BRAKE SYSTEM COMPONENT
DESCRIPTION........................ 1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
MASTER CYLINDER..................... 1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
MASTER CYLINDER FLUID LEVEL CHECK . . . 2REAR DRUM BRAKE ADJUSTMENT........ 1
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
BRAKE PEDAL TORQUE SHAFT ASSEMBLY . . 4
FRONT PARK BRAKE CABLE AND LEVER
ASSEMBLY-RHD&LHD VEHICLES........ 2
GENERAL INFORMATION
BASE BRAKE SYSTEM COMPONENT DESCRIPTION
The standard brake system on this vehicle contains
the same components as brake systems described in
group 5 of the service manual, with the exception of
the brake pedal system and master cylinder. These
differences are mainly related to service procedures.
The major differences are as follows:
²Use of a torque shaft assembly to transfer brake
pedal travel to the power brake booster and master
cylinder on the left side of the vehicle
²A unique power brake booster and master cylin-
der.
Refer to the Base Brake System Component
Description in the General Information section of
group 5 for more information on components used in
the base brake system.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
MASTER CYLINDER
The master cylinder used on this vehicle functions
the same as master cylinders used in other brake
systems. Refer to the Master Cylinder in the Descrip-
tion and Operation section of group 5 for more infor-
mation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
REAR DRUM BRAKE ADJUSTMENT
The rear drum brakes on front wheel drive vehicles
automatically adjust, when required, during the nor-
mal operation of the vehicle every time the brakes
are applied. Use the following procedure to test the
operation of the automatic adjuster.
Place the vehicle on a hoist with a helper in the
driver's seat to apply the brakes. Remove the access
plug from the adjustment slot in each brake support
plate to provide visual access of brake adjuster star
wheel. Disconnect parking brake cable from one side
of the vehicle at the equalizer under the vehicle at
the left frame rail. Working on the side of the vehicle
that parking brake cable is connected to, hold the
adjuster lever off the star wheel with a suitable tool,
and loosen the star wheel approximately 30 notches
in relation to the adjuster lever. This is to eliminate
the possibility that the brake is already properly
adjusted. Reconnect the parking brake cable and
repeat the procedure for the other side of the vehicle.
Fig. 1 Master Cylinder Assembly
NS/GSBRAKES 5 - 1
Page 196 of 1938

Upon application of the brake pedal, the lever
should move down, turning the star wheel. A definite
rotation of the star wheel should be seen if the auto-
matic adjuster is working properly. If no rotation of
the star wheel is observed when the pedal is consec-
utively pressed and released, the respective drum
will have to be removed and the adjuster serviced.
MASTER CYLINDER FLUID LEVEL CHECK
The master cylinder used in this vehicle has the
same fluid level markings as the master cylinders
used in other brake systems on the side of the fluid
resevoir. Refer to the Master Cylinder Fluid Level
Check in the Diagnosis and Testing section of group
5 for more information
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
FRONT PARK BRAKE CABLE AND LEVER
ASSEMBLY-RHD&LHD VEHICLES
REMOVE
(1) Raise vehicle on jackstands or centered on a
hoist. See Hoisting in the Lubrication and Mainte-
nance group of this service manual.
(2) Remove the intermediate and left rear park
brake cable from the park brake cable equalizer (Fig.
2).
(3) Remove the front park cable housing retainer
from body outrigger bracket (Fig. 3). Cable is remov-
able by sliding a 14 mm box wrench over cable
retainer and compressing the three retaining fingers.
Alternate method is to use an aircraft type hose
clamp and screwdriver.(4) Remove the two (2) retaining nuts and (2)
retaining bolts from the bottom of the parking brake/
gearshift lever bracket.
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Carefully lift the base of the gearshift boot
from the gearshift console to access the screws (Fig.
4).
Fig. 2 Park Brake Cable Attachment To Equalizer
Fig. 3 Front Park Brake Cable Attachment To Body
Fig. 4 Console and Gearshift boot
5 - 2 BRAKESNS/GS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 199 of 1938

CLUTCH
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
CLUTCH COMPONENTS.................. 1
CLUTCH DISC AND COVER APPLICATION . . . 3
CLUTCH REPLACEMENT................. 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH........ 4
CLUTCH RELEASE SYSTEM.............. 4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CLASH±INTO±REVERSE
COMPLAINTS........................ 8
CLUTCH CHATTER COMPLAINTS.......... 8
CLUTCH COVER AND DISC RUNOUT....... 8
CLUTCH DIAGNOSIS.................... 6
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH........ 4
DRIVE PLATE MISALIGNMENT............ 7
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CLUTCH ASSEMBLY (2.5L DIESEL)....... 13
CLUTCH CABLE SYSTEM Ð LHD.......... 8
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH....... 10CLUTCH RELEASE BEARING AND FORK . . . 14
HYDRAULIC CLUTCH LINKAGE SYSTEM Ð
RHD ............................... 11
MASTER CYLINDER SYSTEM
Ð RHD ............................ 12
MODULAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY (2.0L AND
2.4L GASOLINE)..................... 13
QUICK CONNECT COUPLING
Ð RHD ............................ 12
SLAVE CYLINDER ASSEMBLY
Ð RHD ............................ 12
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CLEANING PRECAUTIONS............... 15
CLUTCH CONTAMINATION.............. 15
ADJUSTMENTS
CLUTCH CABLE Ð LHD................ 16
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH....... 16
SPECIFICATIONS
CLUTCH TIGHTENING REFERENCE........ 16
GENERAL INFORMATION
CLUTCH COMPONENTS
The clutch used in the 2.0 liter and 2.4 liter gaso-
line engine is a single, dry-disc modular clutch
assembly. The modular clutch assembly combines the
pressure plate cover, pressure plate, disc, and fly-
wheel into one unit. The unit rides on the input shaft
of the transmission and is bolted to the drive plate
mounted on the rear of the crankshaft. The clutch
used in the 2.5 liter diesel engine is a conventional
clutch and pressure plate arrangement.
CLUTCH CABLE AND PEDAL Ð LHD
The clutch cable has a unique self-adjuster mecha-
nism built into the cable which compensates for
clutch disc wear. The cable requires no maintenance
or lubrication. There are no serviceable components
on the cable assembly.The clutch pedal is connected to the cable through
a plastic spacer (Fig. 1). The upper end of the clutch
pedal pivots in the pedal bracket on two nylon bush-
ings and a shaft (Fig. 2). These bushings are greased
during assembly and do not require periodic lubrica-
tion.
Fig. 1 Upstop/Spacer and Cable Ð LHD
NS/GSCLUTCH 6 - 1
Page 202 of 1938

DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
CLUTCH RELEASE SYSTEM
CLUTCH CABLE Ð LHD
The manual transaxle clutch release system has a
unique self-adjusting mechanism to compensate for
clutch disc wear (Fig. 7). This adjuster mechanism is
located within the clutch cable assembly. The preload
spring maintains tension on the cable. This tension
keeps the clutch release bearing continuously loaded
against the fingers of the clutch cover assembly.
HYDRAULIC CLUTCH Ð RHD
Leverage, clamping force, and friction are what
make the clutch work. The disc serves as the friction
element and a diaphragm spring and pressure plate
provide the clamping force. The clutch pedal, hydrau-
lic linkage, release lever and bearing provide the
leverage to disengage and engage the modular clutch
assembly.
The modular clutch assembly contains the cover,
diaphragm spring, pressure plate, disc and flywheel
in one unit. The modular clutch also uses a drive
plate and is bolted to and driven by the drive plate.
The clutch linkage uses hydraulic pressure to oper-
ate the clutch. The clutch master cylinder push rod is
connected to the clutch pedal and the slave cylinder
push rod is connected to the release lever in the
clutch housing.
Depressing the clutch pedal develops fluid pressure
in the clutch master cylinder. This pressure is trans-
mitted to the slave cylinder through a connecting
line. In turn, the slave cylinder operates the clutch
release lever.
The clutch release bearing is mounted on the
transmission front bearing retainer. The bearing is
attached to the release lever, which moves the bear-
ing into contact with the clutch cover diaphragm
spring.Slave cylinder force causes the release lever to
move the release bearing into contact with the dia-
phragm spring. As additional force is applied, the
bearing presses the diaphragm spring fingers inward
on the fulcrums. This action moves the pressure
plate rearward relieving clamp force on the disc. The
clutch disc is disengaged and not driven at this point.
The process of clutch engagement is simply the
reverse of what occurs during disengagement. Releas-
ing pedal pressure removes clutch linkage pressure.
The release bearing moves away from the diaphragm
spring which allows the pressure plate to exert
clamping force on the clutch disc.
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH
The clutch pedal position switch functions as a
safety interlock device. It prevents possible engine
cranking with the clutch engaged.
The clutch pedal position switch is wired in series
between the starter relay coil and the ignition
switch.
The clutch pedal position switch is mounted to a
bracket located behind the clutch pedal. The switch
is held in place by four plastic wing tabs.
The clutch pedal position switch IS NOT adjust-
able. The pedal blade contacts the switch in the down
position (Fig. 8).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION
SWITCH±ELECTRICAL TEST
Disconnect clutch pedal position switch harness
from instrument panel wiring harness. Using an
ohmmeter, check for continuity between the two ter-
minals in the connector on the switch harness. There
should be no continuity between the terminals when
Fig. 7 Clutch Cable Ð LHD
Fig. 8 Clutch Pedal Position Switch and
Components Ð LHD Shown
6 - 4 CLUTCHNS/GS
Page 204 of 1938
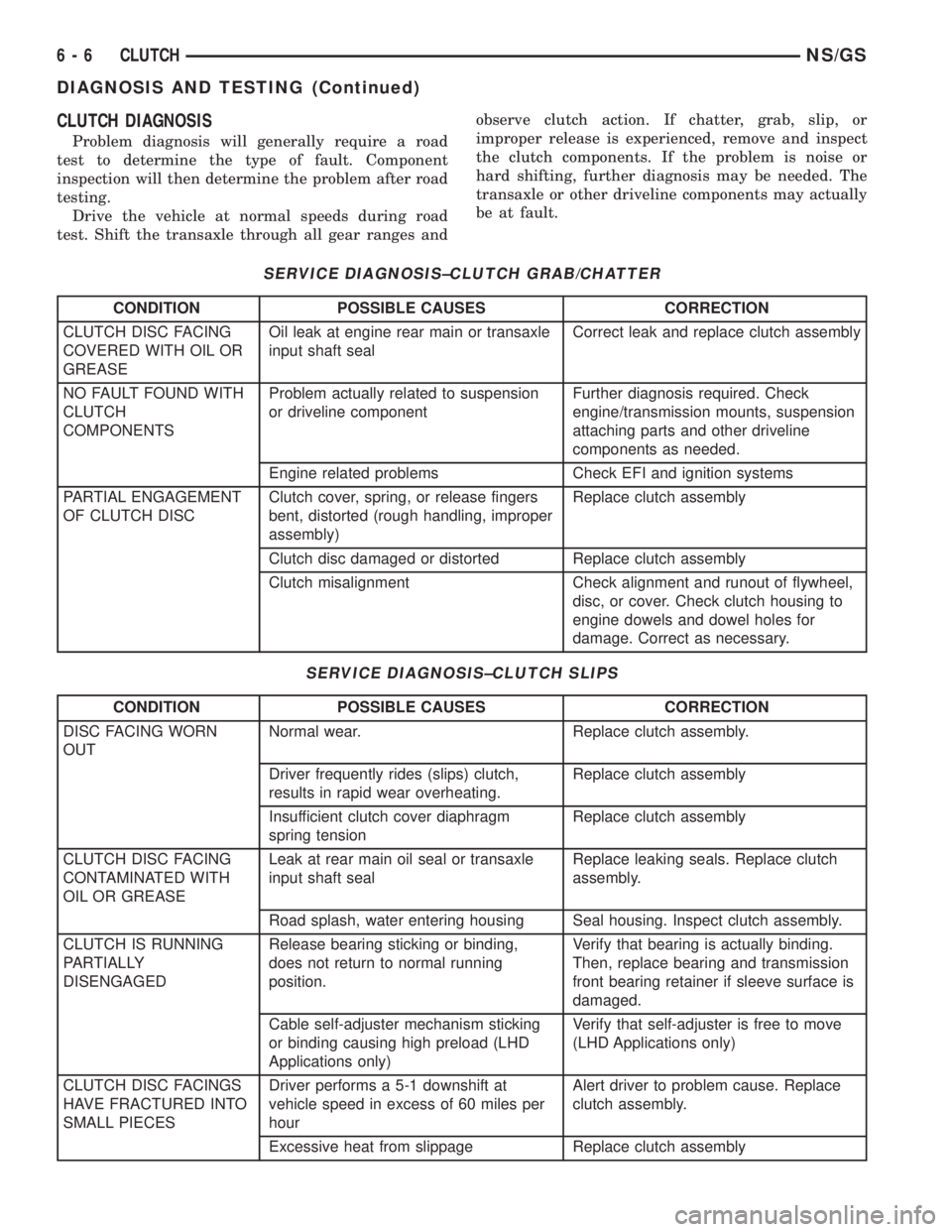
CLUTCH DIAGNOSIS
Problem diagnosis will generally require a road
test to determine the type of fault. Component
inspection will then determine the problem after road
testing.
Drive the vehicle at normal speeds during road
test. Shift the transaxle through all gear ranges andobserve clutch action. If chatter, grab, slip, or
improper release is experienced, remove and inspect
the clutch components. If the problem is noise or
hard shifting, further diagnosis may be needed. The
transaxle or other driveline components may actually
be at fault.
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS±CLUTCH GRAB/CHATTER
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
CLUTCH DISC FACING
COVERED WITH OIL OR
GREASEOil leak at engine rear main or transaxle
input shaft sealCorrect leak and replace clutch assembly
NO FAULT FOUND WITH
CLUTCH
COMPONENTSProblem actually related to suspension
or driveline componentFurther diagnosis required. Check
engine/transmission mounts, suspension
attaching parts and other driveline
components as needed.
Engine related problems Check EFI and ignition systems
PARTIAL ENGAGEMENT
OF CLUTCH DISCClutch cover, spring, or release fingers
bent, distorted (rough handling, improper
assembly)Replace clutch assembly
Clutch disc damaged or distorted Replace clutch assembly
Clutch misalignment Check alignment and runout of flywheel,
disc, or cover. Check clutch housing to
engine dowels and dowel holes for
damage. Correct as necessary.
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS±CLUTCH SLIPS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
DISC FACING WORN
OUTNormal wear. Replace clutch assembly.
Driver frequently rides (slips) clutch,
results in rapid wear overheating.Replace clutch assembly
Insufficient clutch cover diaphragm
spring tensionReplace clutch assembly
CLUTCH DISC FACING
CONTAMINATED WITH
OIL OR GREASELeak at rear main oil seal or transaxle
input shaft sealReplace leaking seals. Replace clutch
assembly.
Road splash, water entering housing Seal housing. Inspect clutch assembly.
CLUTCH IS RUNNING
PARTIALLY
DISENGAGEDRelease bearing sticking or binding,
does not return to normal running
position.Verify that bearing is actually binding.
Then, replace bearing and transmission
front bearing retainer if sleeve surface is
damaged.
Cable self-adjuster mechanism sticking
or binding causing high preload (LHD
Applications only)Verify that self-adjuster is free to move
(LHD Applications only)
CLUTCH DISC FACINGS
HAVE FRACTURED INTO
SMALL PIECESDriver performs a 5-1 downshift at
vehicle speed in excess of 60 miles per
hourAlert driver to problem cause. Replace
clutch assembly.
Excessive heat from slippage Replace clutch assembly
6 - 6 CLUTCHNS/GS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 205 of 1938

SERVICE DIAGNOSIS±IMPROPER CLUTCH RELEASE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
CLUTCH DISC BINDS ON
INPUT SHAFT SPLINESClutch disc hub splines damaged during
installationClean, smooth, and lubricate disc and
shaft splines. Replace clutch assembly
and/or input shaft if splines are severely
damaged.
Input shaft splines rough, damaged. Clean input shaft splines. Then lube.
Corrosion or rust formations on splines
of input shaft and discClean input shaft splines and disc
splines, then lube
CLUTCH DISC RUSTED
TO FLYWHEEL AND/OR
PRESSURE PLATEOccurs in vehicles stored or not driven
for extended period of time. Also occurs
after steam cleaning if vehicle is not
used for extended period.Replace clutch assembly
CLUTCH WILL NOT
DISENGAGE PROPERLYDisc bent, distorted during transaxle
installationReplace clutch assembly
Clutch cover diaphragm spring damaged
during transaxle installationReplace clutch assembly
Release fork and (or) bushings
damagedReplace fork and (or) bushings if worn or
damaged
Clutch cable binding or routed
incorrectlyCheck and correct cable routing
Self-adjuster in cable not functioning
properly, resulting in excess cable slackPull on cable conduit at transaxle (as if
disconnecting cable) to check adjuster
operation
Clutch pedal travel restricted Verify clutch pedal can travel all the way
to the downstop on the bracket
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS±CLUTCH PEDAL NOISE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
CLUTCH PEDAL MAKES
REPEATED9POP9NOISE
IN THE FIRST INCH OF
TRAVELSelf-adjusting mechanism in cable
defective (LHD Applications)Replace clutch cable (LHD Applications)
CLUTCH PEDAL
SQUEAKS WHEN
DEPRESSED TO FLOORPedal bushings worn out or inadequate
lubricationReplace or lubricate bushings
Clutch pedal assist spring fittings worn
outReplace assist spring fittings
Clutch release shaft bushings in the
bellhousing are worn outReplace release shaft and bushings
DRIVE PLATE MISALIGNMENT
Common causes of misalignment are:
²Heat warping
²Mounting drive plate on a dirty crankshaft
flange
²Incorrect bolt tightening
²Improper seating on the crankshaft shoulder
²Loose crankshaft boltsClean the crankshaft flange before mounting the
drive plate. Dirt and grease on the flange surface
may misalign the flywheel, causing excessive runout.
Use new bolts when mounting drive plate to crank-
shaft. Tighten drive plate bolts to specified torque
only. Over-tightening can distort the drive plate hub
causing excessive runout.
NS/GSCLUTCH 6 - 7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)