belt CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 959 of 1938

SWITCH STOP LAMP
1
6 GRAY
F32 18PK/DB L50 18WT/TN
V30 20DB/RD* V32 20YL/RD* Z1 20BK
K29 20WT/PK
6 5 4
3 2 1 CAV FUSED B(+)
STOP LAMP SWITCH OUTPUT SPEED CONTROL BRAKE SWITCH OUTPUT SPEED CONTROL ON/OFF SWITCH SENSE
GROUND STOP LAMP SWITCH SENSE FUNCTION CIRCUIT
* GAS
DIMMING MODULESPEED CONTROL
4BLACK1
V32 20YL/RD V38 20LB/RD L97 29PK/DB
4 3 2 1 CAV SPEED CONTROL ON/OFF SWITCH SENSE
SPEED CONTROL RELAY CONTROL PARK LAMP RELAY CONTROL
- FUNCTION
- CIRCUIT
BLACK
(BUILT-UP-EXPORT)
6 1
MODULE IMMOBILIZERSENTRY KEY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 F41 20PK/VT FUSED B(+)
2 Z2 20BK GROUND
3 F87 20WT/BK FUSED IGNITION (ST-RUN)
4- -
5 D2 20WT/BK CCD BUS (-)
6 D1 20VT/BR CCD BUS (+)
SWITCH SEAT BELT
2 1BLACK
Z1 20BK G10 18LG/RD
2 1 CAV GROUND SEAT BELT SWITCH SENSE FUNCTION CIRCUIT
VANITY MIRROR LAMPSRIGHT VISOR/
ABBLACK
F41 20PK/VT M20 20BR
B A CAV FUSED B(+) COURTESY LAMP GROUND FUNCTION CIRCUIT
SIGNAL RELAYSTOP/TURNRIGHT
BLACK4
2
3 5
2 1
GROUND STOP LAMP SWITCH OUTPUT
L605 18DG L62 18BR/RD L74 18LG Z1 18BK
Z1 18BK L50 18WT/TN L50 18WT/TN
5 4
3 CAV RIGHT COMBINATION RELAY OUTPUT RIGHT TURN SIGNAL STOP LAMP SWITCH OUTPUTFUNCTION CIRCUIT
(TRAILER TOW)
NS/GS8W-80 CONNECTOR PIN-OUTS 8W - 80 - 83
NSGS8083J988W-3
Page 970 of 1938
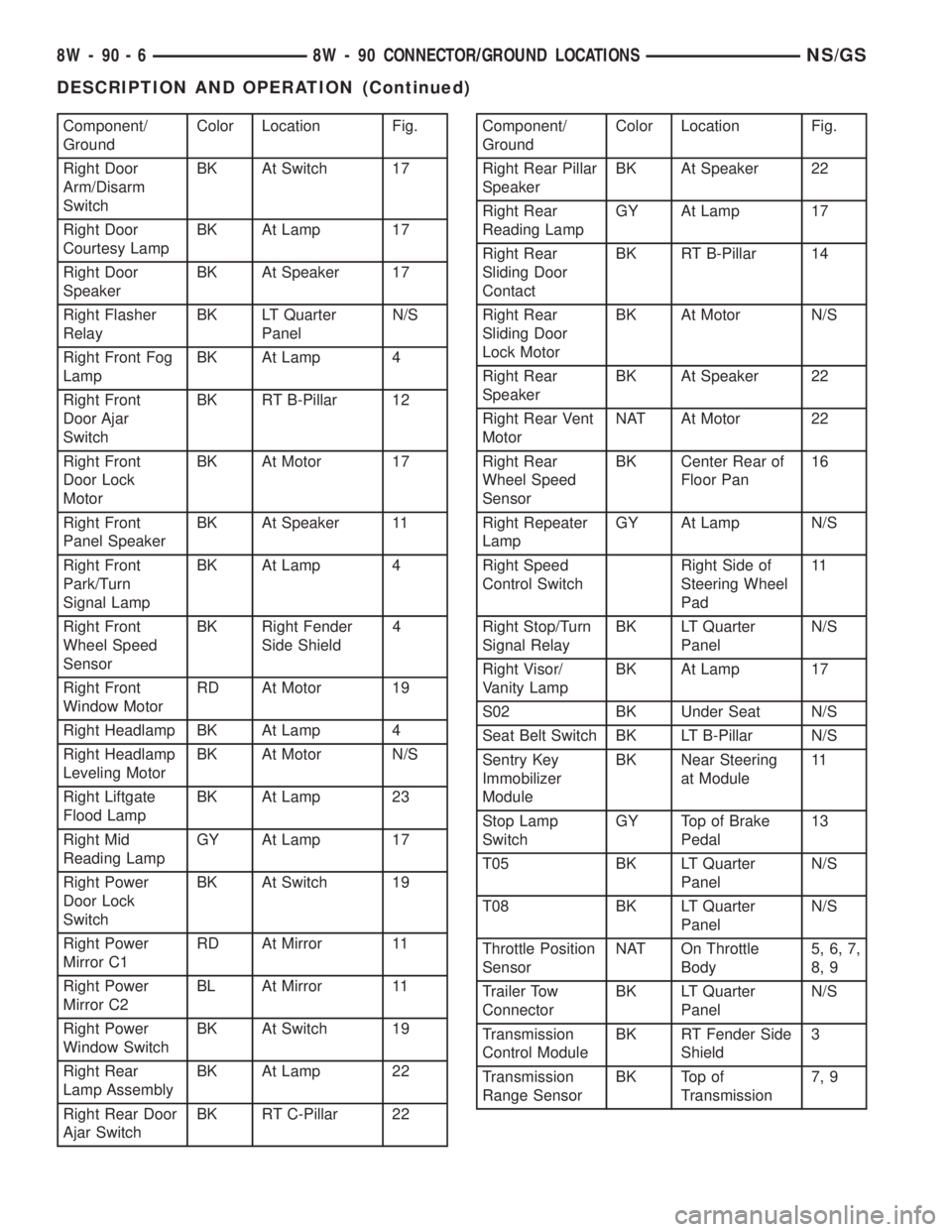
Component/
GroundColor Location Fig.
Right Door
Arm/Disarm
SwitchBK At Switch 17
Right Door
Courtesy LampBK At Lamp 17
Right Door
SpeakerBK At Speaker 17
Right Flasher
RelayBK LT Quarter
PanelN/S
Right Front Fog
LampBK At Lamp 4
Right Front
Door Ajar
SwitchBK RT B-Pillar 12
Right Front
Door Lock
MotorBK At Motor 17
Right Front
Panel SpeakerBK At Speaker 11
Right Front
Park/Turn
Signal LampBK At Lamp 4
Right Front
Wheel Speed
SensorBK Right Fender
Side Shield4
Right Front
Window MotorRD At Motor 19
Right Headlamp BK At Lamp 4
Right Headlamp
Leveling MotorBK At Motor N/S
Right Liftgate
Flood LampBK At Lamp 23
Right Mid
Reading LampGY At Lamp 17
Right Power
Door Lock
SwitchBK At Switch 19
Right Power
Mirror C1RD At Mirror 11
Right Power
Mirror C2BL At Mirror 11
Right Power
Window SwitchBK At Switch 19
Right Rear
Lamp AssemblyBK At Lamp 22
Right Rear Door
Ajar SwitchBK RT C-Pillar 22Component/
GroundColor Location Fig.
Right Rear Pillar
SpeakerBK At Speaker 22
Right Rear
Reading LampGY At Lamp 17
Right Rear
Sliding Door
ContactBK RT B-Pillar 14
Right Rear
Sliding Door
Lock MotorBK At Motor N/S
Right Rear
SpeakerBK At Speaker 22
Right Rear Vent
MotorNAT At Motor 22
Right Rear
Wheel Speed
SensorBK Center Rear of
Floor Pan16
Right Repeater
LampGY At Lamp N/S
Right Speed
Control SwitchRight Side of
Steering Wheel
Pad11
Right Stop/Turn
Signal RelayBK LT Quarter
PanelN/S
Right Visor/
Vanity LampBK At Lamp 17
S02 BK Under Seat N/S
Seat Belt Switch BK LT B-Pillar N/S
Sentry Key
Immobilizer
ModuleBK Near Steering
at Module11
Stop Lamp
SwitchGY Top of Brake
Pedal13
T05 BK LT Quarter
PanelN/S
T08 BK LT Quarter
PanelN/S
Throttle Position
SensorNAT On Throttle
Body5, 6, 7,
8, 9
Trailer Tow
ConnectorBK LT Quarter
PanelN/S
Transmission
Control ModuleBK RT Fender Side
Shield3
Transmission
Range SensorBK Top of
Transmission7, 9
8W - 90 - 6 8W - 90 CONNECTOR/GROUND LOCATIONSNS/GS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1000 of 1938

Component/
GroundColor Location Fig.
Right Rear
Sliding Door
ContactBK RT B-Pillar 14
Right Rear
Sliding Door
Lock MotorBK At Motor N/S
Right Rear
SpeakerBK At Speaker 22
Right Rear Vent
MotorNAT At Motor 22
Right Rear
Wheel Speed
SensorGY Center Rear of
Floor Pan16
Right Repeater
LampGY At Lamp N/S
Right Speed
Control SwitchRight Side of
Steering Wheel
Pad11
Right Stop/Turn
Signal RelayBK LT Quarter
PanelN/S
Right Visor/
Vanity LampBK At Lamp 17
S02 BK Under Seat N/S
Seat Belt Switch BK RT B-Pillar N/S
Sentry Key
Immobilizer
ModuleBK Near Steering
Column at
Module11
Stop Lamp
SwitchGY Top of Brake
Pedal12
T05 BK LT Quarter
PanelN/S
T08 BK RT Quarter
PanelN/SComponent/
GroundColor Location Fig.
Throttle Position
SensorNAT On Throttle
Body5, 6, 7,
8, 9
Trailer Tow
ConnectorBK LT Quarter
PanelN/S
Transmission
Control ModuleBK RT Fender Side
Shield3
Transmission
Range SensorBK Top of
Transmission7. 9
Transmission
Control
SolenoidsBK Front of
Transmission7, 9
Turbine Speed
SensorGY Front of
Transmission7, 9
Turn Signal/
Hazard SwitchBK Part of
Multifunction
Switch11
Upstream
Heated Oxygen
SensorGY Rear of Engine 5, 6, 7,
8, 9
Vehicle Speed
Control ServoBK LT Rear of
Engine
Compartment5, 6, 7,
8, 9
Vehicle Speed
SensorBK Rear of
Transmission5, 6, 8
Windshield
Wiper SwitchBK Part of
Multifunction
Switch11
Wiper Module BK LT Side of
Engine2
8W - 90 - 36 8W - 90 CONNECTOR/GROUND LOCATIONSNS/GS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1052 of 1938

made to seal the area between the bedplate and cyl-
inder block without disturbing the bearing clearance
or alignment of these components.
GASKET DISASSEMBLY
Parts assembled with form-in-place gaskets may be
disassembled without unusual effort. In some
instances, it may be necessary to lightly tap the part
with a mallet or other suitable tool to break the seal
between the mating surfaces. A flat gasket scraper
may also be lightly tapped into the joint but care
must be taken not to damage the mating surfaces.
SURFACE PREPARATION
Scrape clean or wire brush all gasket surfaces to
remove all loose material. Inspect stamped parts to
ensure gasket rails are flat. Gasket surfaces must be
free of oil and dirt. Make sure old gasket material is
removed from blind attaching holes.
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKET APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care but it's easier then using precut gas-
kets.
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 in.) diameter or less of sealant
to one gasket surface. Be certain the material sur-
rounds each mounting hole. Excess material can eas-
ily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing the material off location.
TheMopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant
gasket material or equivalent should be applied in a
continuous bead approximately 3 mm (0.120 in.) in
diameter. All mounting holes must be circled. For
corner sealing, a 3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 in.) drop
is placed in the center of the gasket contact area.
Uncured sealant may be removed with a shop towels.
Components should be torqued in place while the
sealant is still wet to the touch (within 10 minutes).
The usage of a locating dowel is recommended during
assembly to prevent smearing of material off loca-
tion.
CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET BOLT ACCESS PLUG
An Access plug is located in the right inner fender
shield. Remove the plug and insert the proper size
socket, extension and ratchet, when crankshaft rota-
tion is necessary.
ENGINE CORE PLUGS
REMOVAL
Using a blunt tool such as a drift or a screwdriver
and a hammer, strike the bottom edge of the cup
plug (Fig. 1). With the cup plug rotated, grasp firmlywith pliers or other suitable tool and remove plug
(Fig. 1).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting
as restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
INSTALLATION
Thoroughly remove all rust and clean inside of cup
plug hole in cylinder block or head. Be sure to
remove old sealer. Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole
with sealer. Make certain the new plug is cleaned of
all oil or grease. Using proper drive plug, drive plug
into hole so that the sharp edge of the plug is at
least 0.5 mm (0.020 inch.) inside the lead in chamfer
(Fig. 1).
It is in not necessary to wait for curing of the seal-
ant. The cooling system can be refilled and the vehi-
cle placed in service immediately.
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
If a loss of performance is noticed, timing belt or
chain may have skipped one or two teeth. Camshaft
and crankshaft timing should be checked. Refer to
Group 9, Engine Timing belt or chain installation.
It is important that the vehicle is operating to its
optimum performance level to maintain fuel economy
and lowest vehicle emissions. If vehicle is not operat-
ing to these standards, refer to Engine Diagnosis out-
lined is this section. The following procedures can
assist in achieving the proper engine diagnosis.
(1) Test cranking amperage draw. Refer to Group
8B, Starting.
(2) Check intake manifold for vacuum leaks.
(3) Perform cylinder compression pressure test.
Refer to Engine Diagnosis, outlined in this section.
(4) Clean or replace spark plugs as necessary and
adjust gap as specified in Group 8D, Ignition System.
Tighten to specifications.
Fig. 1 Core Hole Plug Removal
9 - 2 ENGINENS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 1057 of 1938

ENGINE DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CYLINDER COMBUSTION
PRESSURE LEAKAGE TEST.............. 8
CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST . . 7
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐMECHANICAL......... 12
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐPERFORMANCE...... 10GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 7
INSPECTION
(ENGINE OIL LEAKS IN GENERAL)......... 8
INTAKE MANIFOLD LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS..... 7
LASH ADJUSTER (TAPPET)
NOISE DIAGNOSIS...................... 8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
GENERAL INFORMATION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions.
These malfunctions may be classified as either
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise), or performance
(e.g., engine idles rough and stalls).
Refer to the Service DiagnosisÐMechanical Chart
and the Service DiagnosisÐPerformance Chart, for
possible causes and corrections of malfunctions. Refer
to Group 14, Fuel System, for the fuel system diag-
nosis.
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can-
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis
INTAKE MANIFOLD LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by
lower than normal manifold vacuum. Also, one or
more cylinders may not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN.
DO NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Spray a small stream of water (Spray Bottle) at
the suspected leak area.
(3) If a change in RPM'S, the area of the suspected
leak has been found.
(4) Repair as required.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Check engine oil level and add oil if necessary.
(2) Drive the vehicle until engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Select a route free from traf-
fic and other forms of congestion, observe all traffic
laws, and accelerate through the gears several times
briskly.
(3) Remove all spark plugs from engine. As spark
plugs are being removed, check electrodes for abnor-
mal firing indicators fouled, hot, oily, etc. Record cyl-
inder number of spark plug for future reference.
(4) Disconnect coil wire from distributor and
secure to good ground to prevent a spark from start-
ing a fire (Conventional Ignition System). For Direct
Ignition System DIS disconnect the coil connector.
(5) Be sure throttle blade is fully open during the
compression check.
(6) Insert compression gage adaptor into the #1
spark plug hole in cylinder head. Crank engine until
maximum pressure is reached on gage. Record this
pressure as #1 cylinder pressure.
(7) Repeat the previous step for all remaining cyl-
inders.
(8) Compression should not be less than (689kPa)
100 psi and not vary more than 25 percent from cyl-
inder to cylinder.
(9) If one or more cylinders have abnormally low
compression pressures, repeat the compression test.
(10) If the same cylinder or cylinders repeat an
abnormally low reading on the second compression
test, it could indicate the existence of a problem in
the cylinder in question.The recommended com-
pression pressures are to be used only as a
guide to diagnosing engine problems. An engine
should not be disassembled to determine the
NSENGINE 9 - 7
Page 1058 of 1938

cause of low compression unless some malfunc-
tion is present.
(11) Clean or replace spark plugs as necessary
and adjust gap as specified in Group 8, Electrical.
Tighten to specifications.
(12) Test resistance of spark plug cables. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical Ignition System Secondary Cir-
cuit Inspection.
(13) Test coil output voltage, primary and second-
ary resistance. Replace parts as necessary. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical Ignition System.
(14) Check fuel pump pressure at idle and differ-
ent RPM ranges. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System for
Specifications.
(15) The air filter elements should be replaced as
specified in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance,.
(16) Inspect crankcase ventilation system as out
lined in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance. For
emission controls see Group 25, Emission Controls
for service procedures.
(17) Inspect and adjust accessory belt drives refer-
ring to Group 7, Cooling System, Accessory Drive
Belts for proper adjustments.
(18) Road test vehicle as a final test.
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE RADIATOR CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Clean spark plug recesses with compressed air.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1 379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
LASH ADJUSTER (TAPPET) NOISE DIAGNOSIS
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items.
(1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause
them to be spongy.
(2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required.
(3) During this time, turn engine off and let set for
a few minutes before restarting. Repeat this several
times after engine has reached normal operating
temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor pressed into the vertical oil
passage to the cylinder head is plugged with debris.
(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Faulty lash adjuster.
a. Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head. Depress part of rocker
arm over adjuster. Normal adjusters should feel very
firm. Spongy adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
b. Remove suspected lash adjusters, and disassem-
bleDo not reuse retainer caps. Do not inter-
change parts and make sure that care and
cleanliness is exercised in the handling of parts.
c. Clean out dirt and varnish with solvent.
d. Reassemble with engine oil.
e. Check for sponginess.
f. If still spongy, replace with new adjuster.
INSPECTION (ENGINE OIL LEAKS IN GENERAL)
Begin with a through visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
9 - 8 ENGINENS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1064 of 1938

2.4L ENGINE
INDEX
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ENGINE COMPONENTS.................. 15
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION................. 14
ENGINE LUBRICATION SYSTEM............ 14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE......... 16
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY................. 20
FITTING CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS..... 18
FITTING MAIN BEARINGS................. 19
FITTING PISTON RINGS.................. 16
FITTING PISTONS....................... 16
VALVE SERVICE RECONDITION............ 21
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
BALANCE SHAFTS CARRIER ASSEMBLY..... 30
CAMSHAFT FOLLOWER.................. 30
CAMSHAFT OIL SEALÐFRONT............. 41
CAMSHAFT............................ 28
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEALÐFRONT........... 42
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEALÐREAR............ 43
CRANKSHAFT.......................... 46
CYLINDER HEAD COVER................. 28
CYLINDER HEAD........................ 34
ENGINE ASSEMBLY...................... 26
ENGINE MOUNTÐFRONT................. 23
ENGINE MOUNTÐLEFT.................. 24
ENGINE MOUNTÐREAR.................. 25
ENGINE MOUNTÐRIGHT................. 24HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTER.............. 33
OILFILTER ............................ 47
OILPAN ............................... 45
OIL PUMP............................. 47
PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD........... 49
STRUCTURAL COLLAR................... 25
TIMING BELT COVER.................... 37
TIMING BELT TENSIONER ASSEMBLY....... 40
TIMING BELT........................... 37
VALVE SPRINGS AND
VALVE SEALS IN VEHICLE............... 33
VALVES AND VALVE SPRINGS............. 35
VIBRATION DAMPER.................... 36
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
OIL PUMP............................. 50
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
OIL PUMP............................. 52
CRANKSHAFT.......................... 52
CYLINDER BLOCK....................... 54
CYLINDER HEAD........................ 51
VALVE AND VALVE SPRING................ 51
ADJUSTMENTS
ENGINE MOUNTS....................... 54
SPECIFICATIONS
2.4L ENGINE........................... 55
TORQUE CHART 2.4L.................... 57
SPECIAL TOOLS
2.4L ENGINE........................... 58
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
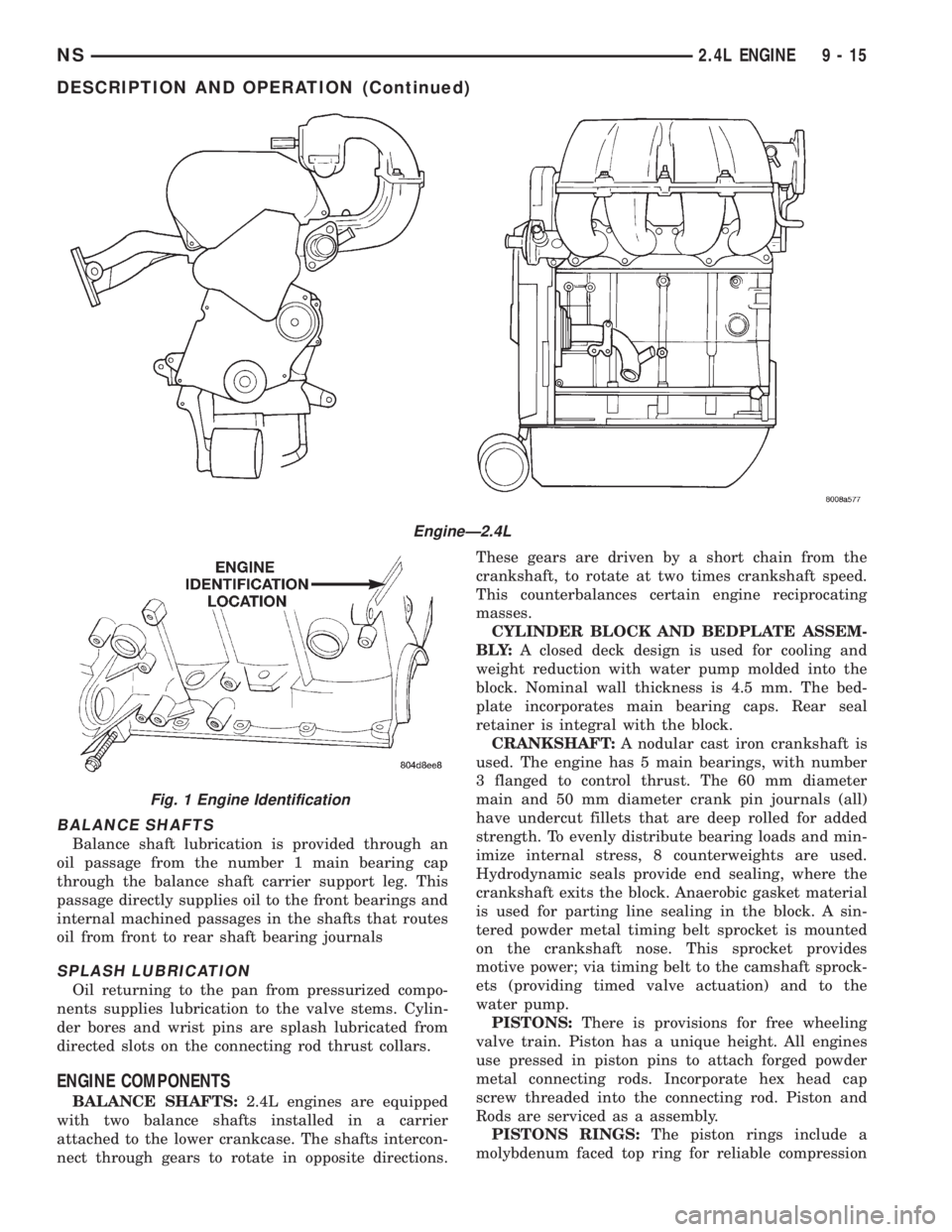
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION
The engine identification number is located on the
rear of the cylinder block (Fig. 1).
ENGINE LUBRICATION SYSTEM
OIL PAN
A structural die cast aluminum oil pan provides
lower engine protection as well as serving as the
engine oil reservoir. Oil pan is attached to block and
sealed with a gasket. The oil pickup tube has a
strainer and cover.
PRESSURE LUBRICATION
Oil drawn up through the pickup tube is pressur-
ized by the pump and routed through the full flow fil-
ter to the main oil gallery running the length of thecylinder block. Oil pickup, pump and check valve pro-
vide oil flow to the main oil gallery.
MAIN/ROD BEARINGS
A diagonal hole in each bulkhead feeds oil to each
main bearing. Drilled passages within the crankshaft
route oil from main bearing journals to connecting
rod journals.
CAMSHAFT/HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTERS
A vertical hole at the number five bulkhead routes
pressurized oil through a restrictor up past a cylin-
der head bolt to an oil gallery running the length of
the cylinder head. The camshaft journals are par-
tially slotted to allow a predetermined amount of
pressurized oil to pass into the bearing cap cavities
with small holes directed to spray lubricate the cam-
shaft lobes.
9 - 14 2.4L ENGINENS
Page 1065 of 1938
BALANCE SHAFTS
Balance shaft lubrication is provided through an
oil passage from the number 1 main bearing cap
through the balance shaft carrier support leg. This
passage directly supplies oil to the front bearings and
internal machined passages in the shafts that routes
oil from front to rear shaft bearing journals
SPLASH LUBRICATION
Oil returning to the pan from pressurized compo-
nents supplies lubrication to the valve stems. Cylin-
der bores and wrist pins are splash lubricated from
directed slots on the connecting rod thrust collars.
ENGINE COMPONENTS
BALANCE SHAFTS:2.4L engines are equipped
with two balance shafts installed in a carrier
attached to the lower crankcase. The shafts intercon-
nect through gears to rotate in opposite directions.These gears are driven by a short chain from the
crankshaft, to rotate at two times crankshaft speed.
This counterbalances certain engine reciprocating
masses.
CYLINDER BLOCK AND BEDPLATE ASSEM-
B LY:A closed deck design is used for cooling and
weight reduction with water pump molded into the
block. Nominal wall thickness is 4.5 mm. The bed-
plate incorporates main bearing caps. Rear seal
retainer is integral with the block.
CRANKSHAFT:A nodular cast iron crankshaft is
used. The engine has 5 main bearings, with number
3 flanged to control thrust. The 60 mm diameter
main and 50 mm diameter crank pin journals (all)
have undercut fillets that are deep rolled for added
strength. To evenly distribute bearing loads and min-
imize internal stress, 8 counterweights are used.
Hydrodynamic seals provide end sealing, where the
crankshaft exits the block. Anaerobic gasket material
is used for parting line sealing in the block. A sin-
tered powder metal timing belt sprocket is mounted
on the crankshaft nose. This sprocket provides
motive power; via timing belt to the camshaft sprock-
ets (providing timed valve actuation) and to the
water pump.
PISTONS:There is provisions for free wheeling
valve train. Piston has a unique height. All engines
use pressed in piston pins to attach forged powder
metal connecting rods. Incorporate hex head cap
screw threaded into the connecting rod. Piston and
Rods are serviced as a assembly.
PISTONS RINGS:The piston rings include a
molybdenum faced top ring for reliable compression
EngineÐ2.4L
Fig. 1 Engine Identification
NS2.4L ENGINE 9 - 15
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1076 of 1938

ENGINE ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Group 14, Fuel System for procedure. Remove fuel
line to fuel rail.
(2) Disconnect battery.
(3) Remove Air cleaner and hoses.
(4) Drain cooling system. Refer to Group 7, Cooling
System for procedure.
(5) Remove upper radiator hose and remove radia-
tor fans. Refer to Group 7, Cooling System for proce-
dure.
(6) Remove lower radiator hose.
(7) Disconnect automatic transmission cooler lines
and plug, if equipped.
(8) Disconnect transmission shift linkage.
(9) Disconnect throttle body linkage.
(10) Disconnect engine wiring harness.
(11) Disconnect heater hoses.
(12) Discharge Air Conditioning System. Refer to
Group 24, Air Conditioning for procedure.
(13) Hoist vehicle and remove right inner splash
shield. Remove wheels and tires.
(14) Loosen power steering belt for pump removal.
Refer to Group 7, Cooling System for procedure.
(15) Remove axle shafts. Refer to Group 2, Suspen-
sion and Driveshafts for procedure.
(16) Disconnect exhaust pipe from manifold.
(17) Remove front and rear engine mount brackets
from the body.
(18) Remove bending braces and front engine
mount bracket. Remove transmission inspection
cover.
(19) Mark flexplate to torque converter and
remove torque converter bolts.
(20) Install front engine mount bracket.
(21) Lower vehicle.
(22) Remove power steering pump. Set pump
aside.
(23) Remove A/C lines at compressor and cap.
(24) Remove ground straps to body.
(25) Raise vehicle enough to allow engine dolly
Special Tool 6135, cradle Special Tool 6710 with
Posts Special Tool 6848 and Adaptor Special Tool
8130 to be installed under vehicle (Fig. 27).
(26) Loosen cradle posts to allow movement for
proper positioning. Locate two rear posts (right side
of engine) into the holes on the engine bedplate.
Locate the two front posts (left side of engine) on the
front engine bracket and A/C compressor bracket
(Fig. 27). Lower vehicle and position cradle mounts
until the engine is resting on mounts. Tighten
mounts to cradle frame. This will keep mounts from
moving when removing or installing engine and
transmission.(27) Lower vehicle so the weight ofONLY THE
ENGINE AND TRANSMISSIONare on the cradle.
(28) Remove engine and transmission mount bolts.
(29) Raise vehicle slowly. It may be necessary to
move the engine/transmission assembly on the cradle
to allow for removal around the body.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position engine and transmission assembly
under vehicle and slowly lower the vehicle over the
engine and transmission.
(2) Align engine and transmission mounts to
attaching points. Install mounting bolts at the right
engine and left transmission mounts. Refer to proce-
dures outlined in this section.
(3) Slowly raise vehicle enough to remove the
engine dolly and cradle Special Tools 6135 and 6710.
(4) Install axle shafts. Refer to Group 2, Suspen-
sion and Driveshafts for procedure.
(5) Install transmission and engine braces and
splash shields.
(6) Connect exhaust system to manifold. Refer to
Group 11, Exhaust System and Intake Manifold for
procedure and torque specifications.
(7) Install power steering pump. Refer to Cooling
System Group 7, Accessory Drive Section for belt ten-
sion adjustment.
(8) Install A/C compressor hoses. Refer to Group
24, Heater and Air Conditioning for procedure.
(9) Install accessory drive belts. Refer to Group 7,
Cooling System Accessory Drive Section for belt ten-
sion adjustment.
(10) Install front and rear engine mounts. Refer to
this section for procedure.
(11) Install inner splash shield. Install wheels and
tires.
(12) Connect automatic transmission cooler lines,
and shift linkage. Refer to Group 21, Transmission
for procedures.
(13) Connect fuel line and heater hoses.
(14) Install ground straps. Connect engine and
throttle body connections and harnesses. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical for procedure.
(15) Connect throttle body linkage. Refer to Group
14, Fuel System for procedure.
(16) Install radiator fans. Install radiator hoses.
Fill cooling system. Refer to Group 7, Cooling System
for filling procedure.
(17) Connect battery.
(18) Install air cleaner and hoses.
(19) Install oil filter. Fill engine crankcase with
proper oil to correct level.
(20) Start engine and run until operating temper-
ature is reached.
(21) Adjust transmission linkage, if necessary.
9 - 26 2.4L ENGINENS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1078 of 1938

CYLINDER HEAD COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove upper intake manifold. Refer to Group
11, Exhaust System and Intake Manifold.
(2) Remove nuts attaching front and rear intake
manifold supports from cylinder head cover attaching
studs.
(3) Remove ignition coil pack and plug wires (Fig.
28). Remove ground strap.
(4) Remove the cylinder head cover fasteners.
(5) Remove cylinder head cover from cylinder
head.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Replace spark plug well seals when install-
ing a new cylinder head cover gasket.
(1) Clean all sealing surfaces.
(2) Install new cylinder head cover gaskets and
spark plug seals (Fig. 29).CAUTION: Do not allow oil or solvents to contact
the timing belt as they can deteriorate the rubber
and cause tooth skipping.
(3) Apply MopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Seal-
ant at the camshaft cap corners and at the top edge
of the 1/2 round seal.
(4) Install cylinder head cover assembly to head
and tighten fasteners in sequence shown in (Fig. 30).
Using the 3 step torque method:
(a) Tighten all fasteners to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.)
(b) Tighten all fasteners to 9.0 N´m (80 in. lbs.)
(c) Tighten all fasteners to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.)
(5) Install ignition coil pack and plug wires.
Tighten fasteners to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(6) Install ground strap.
(7) Install front and rear intake manifold support
brackets and attaching nuts, but do not tighten at
this time.
(8) Install upper intake manifold. Refer to Group
11, Exhaust System and Intake Manifold for proce-
dure.
(9) Final torque intake manifold support nuts to
28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
CAMSHAFT
REMOVAL
(1) Remove cylinder head cover using procedure
outlined in this section.
(2) Remove timing belt, sprockets and covers.
Refer to Timing Belt Service outlined in this section.
(3) Bearing caps are identified for location.
Remove the outside bearing caps first (Fig. 31).
(4) Loosen the camshaft bearing cap attaching
fasteners in sequence shown (Fig. 32) one camshaft
at a time.
CAUTION: Camshafts are not interchangeable. The
intake cam number 6 thrust bearing face spacing is
wider.
Fig. 28 Ignition Coil Pack and Ground Strap
Fig. 29 Cylinder Head Cover Gasket and Spark Plug
Seals
Fig. 30 Cylinder Head Cover Tightening Sequence
9 - 28 2.4L ENGINENS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)