rear axle CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 4 of 1938

INTRODUCTION
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
BODY CODE PLATE...................... 1
FASTENER IDENTIFICATION................ 4
INTERNATIONAL VEHICLE CONTROL AND
DISPLAY SYMBOLS..................... 4METRIC SYSTEM........................ 7
TORQUE REFERENCES................... 7
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER.......... 1
VEHICLE SAFETY CERTIFICATION LABEL..... 1
VIN CHECK DIGIT........................ 1
GENERAL INFORMATION
VEHICLE SAFETY CERTIFICATION LABEL
A vehicle safety certification label (Fig. 1) is located
on the rear shut face of the driver's door. This label
indicates date of manufacture (month and year),
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR), Gross Axle
Weight Rating (GAWR) front, Gross Axle Weight Rat-
ing (GAWR) rear and the Vehicle Identification Num-
ber (VIN). The Month, Day and Hour of manufacture
is also included.
When it is necessary to contact the manufacturer
regarding service or warranty, the information on the
Vehicle Safety Certification Label would be required.
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER
The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) can be
viewed through the windshield at the upper left cor-
ner of the instrument panel, near the left windshield
pillar (Fig. 2). The VIN consists of 17 characters in a
combination of letters and numbers that provide spe-
cific information about the vehicle. Refer to VIN
Code Breakdown Chart for decoding information.
VIN CHECK DIGIT
To protect the consumer from theft and possible
fraud, the manufacturer is required to include a
Check Digit at the ninth position of the Vehicle Iden-
tification Number. The check digit is used by the
manufacturer and government agencies to verify the
authenticity of the vehicle and official documenta-
tion. The formula to use the check digit is not
released to the general public.
BODY CODE PLATE
LOCATION AND DECODING
The Body Code Plate (Fig. 3) is located in the
engine compartment on the radiator closure panel
crossmember. There are seven lines of information on
the body code plate. Lines 4, 5, 6, and 7 are not used
to define service information. Information reads from
left to right, starting with line 3 in the center of the
plate to line 1 at the bottom of the plate.Fig. 1 Vehicle Safety Certification Label
Fig. 2 Vehicle Identification Number (VIN Plate)
NSINTRODUCTION 1
Page 15 of 1938
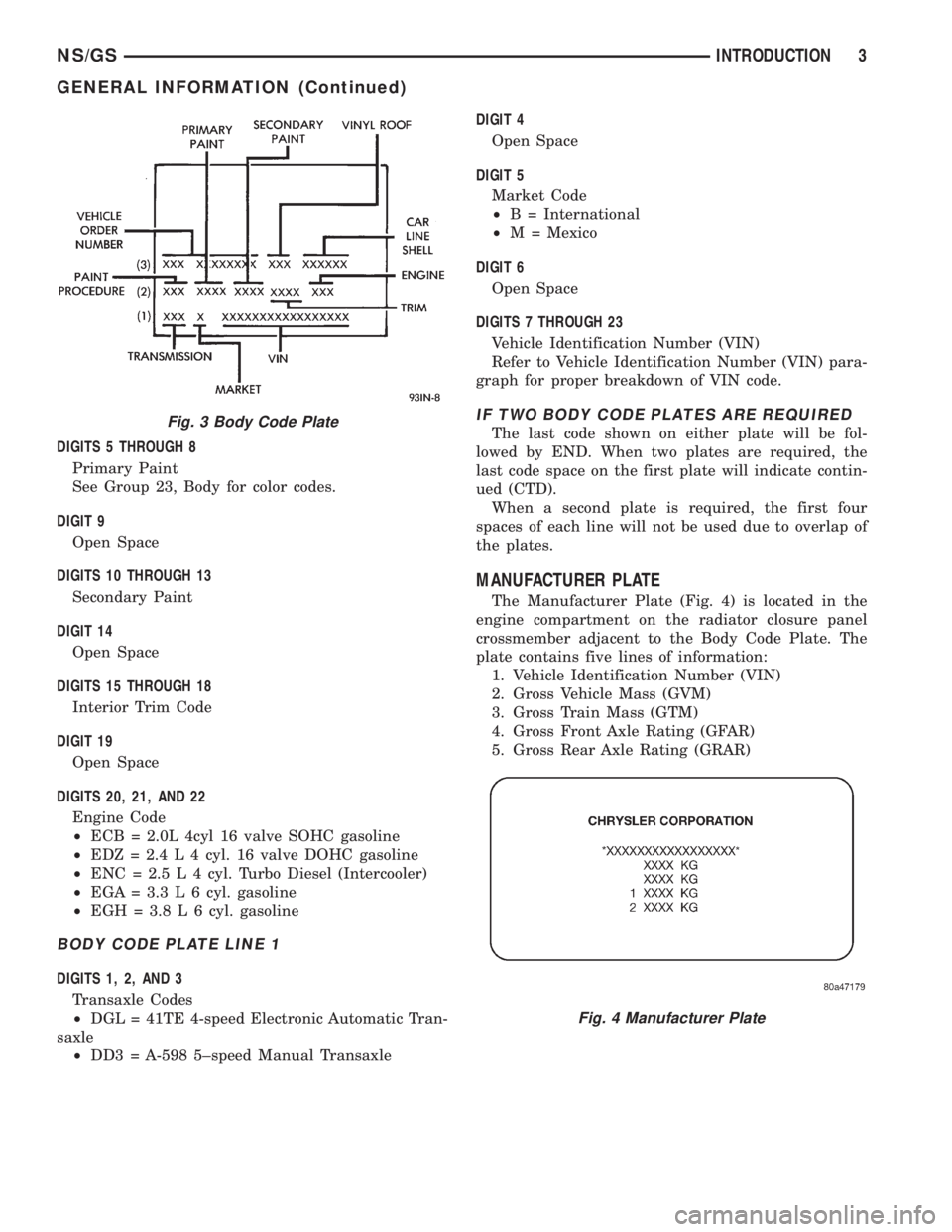
DIGITS 5 THROUGH 8
Primary Paint
See Group 23, Body for color codes.
DIGIT 9
Open Space
DIGITS 10 THROUGH 13
Secondary Paint
DIGIT 14
Open Space
DIGITS 15 THROUGH 18
Interior Trim Code
DIGIT 19
Open Space
DIGITS 20, 21, AND 22
Engine Code
²ECB = 2.0L 4cyl 16 valve SOHC gasoline
²EDZ = 2.4 L 4 cyl. 16 valve DOHC gasoline
²ENC = 2.5 L 4 cyl. Turbo Diesel (Intercooler)
²EGA = 3.3 L 6 cyl. gasoline
²EGH = 3.8 L 6 cyl. gasoline
BODY CODE PLATE LINE 1
DIGITS 1, 2, AND 3
Transaxle Codes
²DGL = 41TE 4-speed Electronic Automatic Tran-
saxle
²DD3 = A-598 5±speed Manual TransaxleDIGIT 4
Open Space
DIGIT 5
Market Code
²B = International
²M = Mexico
DIGIT 6
Open Space
DIGITS 7 THROUGH 23
Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
Refer to Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) para-
graph for proper breakdown of VIN code.
IF TWO BODY CODE PLATES ARE REQUIRED
The last code shown on either plate will be fol-
lowed by END. When two plates are required, the
last code space on the first plate will indicate contin-
ued (CTD).
When a second plate is required, the first four
spaces of each line will not be used due to overlap of
the plates.
MANUFACTURER PLATE
The Manufacturer Plate (Fig. 4) is located in the
engine compartment on the radiator closure panel
crossmember adjacent to the Body Code Plate. The
plate contains five lines of information:
1. Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
2. Gross Vehicle Mass (GVM)
3. Gross Train Mass (GTM)
4. Gross Front Axle Rating (GFAR)
5. Gross Rear Axle Rating (GRAR)
Fig. 3 Body Code Plate
Fig. 4 Manufacturer Plate
NS/GSINTRODUCTION 3
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 22 of 1938

²Replace spark plugs.
²Replace ignition cables.
²Inspect serpentine drive belt, replace if neces-
sary. This maintenance is not required if belt was
previously replaced.
²Drain and refill automatic transaxle fluid and
replace filter. Adjust band, if so equipped. (See note)
²Change AWD power transfer unit fluid.
78,000 Miles (125 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
81,000 Miles (130 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect brake linings.
²Flush and replace engine coolant.
84,000 Miles (134 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Change AWD overrunning clutch and rear car-
rier fluid.
87,000 Miles (139 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
90,000 Miles (144 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Check PCV valve and replace if necessary.
Not required if previously changed. *
²Inspect serpentine drive belt, replace if neces-
sary. This maintenance is not required if belt was
previously replaced.
²Drain and refill automatic transmission fluid
and replace filter. Adjust bands, if so equipped. (See
note)
²Change AWD power transfer unit fluid.
²Inspect tie rod ends and boot seals.
²Inspect brake linings.
93,000 Miles (149 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
96,000 Miles (154 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
99,000 Miles (158 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect brake linings.
102,000 Miles (163 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
105,000 Miles (168 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect air cleaner element. Replace as
necessary.
²Inspect serpentine drive belt, replace if neces-
sary. This maintenance is not required if belt was
previously replaced.
²Drain and refill automatic transmission fluid
and filter. Adjust bands, if so equipped. (See note)
²Change AWD power transfer unit fluid.
²Change AWD overrunning clutch and rear car-
rier fluid.
108,000 Miles (173 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect brake linings.
111,000 Miles (178 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace engine coolant.
114,000 Miles (182 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
117,000 Miles (187 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect brake linings.
120,000 Miles (192 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Inspect PCV valve. Replace as necessary. *
²Inspect serpentine drive belt. Not required if
replaced at 75,000, 90,000 or 105,000 miles.
²Drain and refill automatic transmission fluid
and replace filter. Adjust bands, if so equipped.
²Change AWD power transfer unit fluid.
²Inspect tie rod ends and boot seals.
* This maintenance is recommended by Chrysler to
the owner but is not required to maintain the war-
ranty on the PCV valve.
** If California vehicle, this maintenance is recom-
mended by Chrysler to the owner but is not required
to maintain the warranty of the timing belt.
NOTE: Operating vehicle more than 50% in heavy
traffic during hot weather, above 90ÉF (32ÉC), using
vehicle for police, taxi, limousine type operation or
trailer towing require the more frequent transaxle
service noted in Schedule ± B. Perform these ser-
vices if vehicle is usually operated under these con-
ditions.
Inspection and service should also be performed
anytime a malfunction is observed or suspected.
0 - 6 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCENS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 24 of 1938

DISCONNECT CABLE CLAMPS AS FOLLOWS:
²Disconnect BLACK cable clamp from engine
ground on disabled vehicle.
²When using a Booster vehicle, disconnect
BLACK cable clamp from battery negative terminal.
Disconnect RED cable clamp from battery positive
terminal.
²Disconnect RED cable clamp from battery posi-
tive terminal on disabled vehicle.
TOWING RECOMMENDATIONS
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
WARNING: DO NOT ALLOW TOWING ATTACH-
MENT DEVICES TO CONTACT THE FUEL TANK OR
LINES, FUEL LEAK CAN RESULT.
DO NOT LIFT OR TOW VEHICLE BY FRONT OR
REAR BUMPER, OR BUMPER ENERGY ABSORBER
UNITS.
DO NOT GO UNDER A LIFTED VEHICLE IF NOT
SUPPORTED PROPERLY ON SAFETY STANDS.
DO NOT ALLOW PASSENGERS TO RIDE IN A
TOWED VEHICLE.
USE A SAFETY CHAIN THAT IS INDEPENDENT
FROM THE TOWING ATTACHMENT DEVICE.
CAUTION: Do not damage brake lines, exhaust sys-
tem, shock absorbers, sway bars, or any other
under vehicle components when attaching towing
device to vehicle.
Do not attach towing device to front or rear sus-
pension components.
Do not secure vehicle to towing device by the use
of front or rear suspension or steering components.
Remove or secure loose or protruding objects
from a damaged vehicle before towing.
Refer to state and local rules and regulations
before towing a vehicle.
Do not allow weight of towed vehicle to bear on
lower fascia, air dams, or spoilers.
RECOMMENDED TOWING EQUIPMENT
To avoid damage to bumper fascia and air dams
use of a flat bed towing device or wheel lift (Fig. 2) is
recommended. When using a wheel lift towing device,
be sure the disabled vehicle has at least 100 mm (4
in.) ground clearance. If minimum ground clearance
cannot be reached, use a towing dolly. If a flat bed
device is used, the approach angle should not exceed
15 degrees.
GROUND CLEARANCE
CAUTION: If vehicle is towed with wheels
removed, install lug nuts to retain brake drums or
rotors.
A towed vehicle should be raised until the lifted
wheels are a minimum 100 mm (4 in.) from the
ground. Be sure there is at least 100 mm (4 in.)
clearance between the tail pipe and the ground. If
necessary, remove the wheels from the lifted end of
the vehicle and lower the vehicle closer to the
ground, to increase the ground clearance at the rear
of the vehicle. Install lug nuts on wheel attaching
studs to retain brake drums or rotors.
LOCKED VEHICLE TOWING
When a locked vehicle must be towed with the
front wheels on the ground, use a towing dolly or flat
bed hauler.
FLAT TOWING WITH TOW BAR
²3-speed automatic transaxle vehicles can be flat
towed at speeds not to exceed 40 km/h (25 mph) for
not more than 25 km (15 miles). The steering column
must be unlocked and gear selector in neutral.
²4-speed electronic automatic transaxle vehicles
can be flat towed at speeds not to exceed 72 km/h (44
mph) for not more than 160 km (100 miles). The
steering column must be unlocked and gear selector
in neutral.
FLAT BED TOWING TIE DOWNS
CAUTION: Do not tie vehicle down by attaching
chains or cables to suspension components or
engine mounts, damage to vehicle can result.
NS vehicles can be tied to a flat bed device using
the reinforced loops located under the front and rear
bumpers on the drivers side of the vehicle. There are
also four reinforced elongated holes for T or R-hooks
located on the bottom of the front frame rail torque
Fig. 2 Recommended Towing Devices
0 - 8 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCENS
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 25 of 1938

boxes behind the front wheels and forward of the
rear wheels inboard of the rocker panel weld seam.
TOWINGÐFRONT WHEEL LIFT
Chrysler Corporation recommends that a vehicle be
towed with the front end lifted, whenever possible. A
90 cm (36 in.) length of 4x4 wood beam can be placed
between the wheel lift device and the bottom of the
fascia to prevent damage to vehicle during the lifting
operation. The beam can removed after lifting the
front of the vehicle.
TOWINGÐREAR WHEEL LIFT
If a vehicle cannot be towed with the front wheels
lifted, the rear wheels can be lifted provided the fol-
lowing guide lines are observed.
CAUTION: Do not use steering column lock to
secure steering wheel during towing operation.
²On AWD vehicles, all four wheels must be free to
rotate. Use towing dollies at unlifted end of vehicle.
²Unlock steering column and secure steering
wheel in straight ahead position with a clamp device
designed for towing.
²3-speed automatic transaxle vehicles can be flat
towed at speeds not to exceed 40 km/h (25 mph) for
not more than 25 km (15 miles). The steering column
must be unlocked and gear selector in neutral.
²4-speed electronic automatic transaxle vehicles
can be flat towed at speeds not to exceed 72 km/h (44
mph) for not more than 160 km (100 miles). The
steering column must be unlocked and gear selector
in neutral.
HOISTING RECOMMENDATIONS
Refer to Owner's Manual provided with vehicle for
proper emergency jacking procedures.
WARNING: THE HOISTING AND JACK LIFTING
POINTS PROVIDED ARE FOR A COMPLETE VEHI-
CLE. WHEN THE ENGINE OR REAR SUSPENSION
IS REMOVED FROM A VEHICLE, THE CENTER OF
GRAVITY IS ALTERED MAKING SOME HOISTING
CONDITIONS UNSTABLE. PROPERLY SUPPORT ORSECURE VEHICLE TO HOISTING DEVICE WHEN
THESE CONDITIONS EXIST.
CAUTION: Do not position hoisting device on sus-
pension components or front crossmember, dam-
age to vehicle can result.
TO HOIST OR JACK VEHICLE SEE(Fig. 3).
Vehicles with factory installed ground effects are
equipped with front and rear hoisting pads. These
pads are stamped, ªHoist Pointº.
Fig. 3 HOISTING AND JACKING POINTS
NSLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 9
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 31 of 1938

JUMP STARTING, HOISTING AND TOWING
INDEX
page
SERVICE PROCEDURES
TOWING RECOMMENDATIONS............. 5
SERVICE PROCEDURES
TOWING RECOMMENDATIONS
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
WARNING: DO NOT ALLOW TOWING ATTACH-
MENT DEVICES TO CONTACT THE FUEL TANK OR
LINES, FUEL LEAK CAN RESULT.
DO NOT LIFT OR TOW VEHICLE BY FRONT OR
REAR BUMPER, OR BUMPER ENERGY ABSORBER
UNITS.
DO NOT GO UNDER A LIFTED VEHICLE IF NOT
SUPPORTED PROPERLY ON SAFETY STANDS.
DO NOT ALLOW PASSENGERS TO RIDE IN A
TOWED VEHICLE.
USE A SAFETY CHAIN THAT IS INDEPENDENT
FROM THE TOWING ATTACHMENT DEVICE.
CAUTION: Do not damage brake lines, exhaust sys-
tem, shock absorbers, sway bars, or any other
under vehicle components when attaching towing
device to vehicle.
Do not attach towing device to front or rear sus-
pension components.
Do not secure vehicle to towing device by the use
of front or rear suspension or steering components.
Remove or secure loose or protruding objects
from a damaged vehicle before towing.
Refer to state and local rules and regulations
before towing a vehicle.
Do not allow weight of towed vehicle to bear on
lower fascia, air dams, or spoilers.
RECOMMENDED TOWING EQUIPMENT
To avoid damage to bumper fascia and air dams
use of a flat bed towing device or wheel lift (Fig. 1) is
recommended. When using a wheel lift towing device,
be sure the disabled vehicle has at least 100 mm (4
in.) ground clearance. If minimum ground clearance
cannot be reached, use a towing dolly. If a flat bed
device is used, the approach angle should not exceed
15 degrees.
GROUND CLEARANCE
CAUTION: If vehicle is towed with wheels
removed, install lug nuts to retain brake drums or
rotors.
A towed vehicle should be raised until the lifted
wheels are a minimum 100 mm (4 in.) from the
ground. Be sure there is at least 100 mm (4 in.)
clearance between the tail pipe and the ground. If
necessary, remove the wheels from the lifted end of
the vehicle and lower the vehicle closer to the
ground, to increase the ground clearance at the rear
of the vehicle. Install lug nuts on wheel attaching
studs to retain brake drums or rotors.
LOCKED VEHICLE TOWING
When a locked vehicle must be towed with the
front wheels on the ground, use a towing dolly or flat
bed hauler.
FLAT TOWING WITH TOW BAR
²4-speed electronic automatic transaxle vehicles
can be flat towed at speeds not to exceed 72 km/h (44
mph) for not more than 160 km (100 miles). The
steering column must be unlocked and gear selector
in neutral.
FLAT BED TOWING TIE DOWNS
CAUTION: Do not tie vehicle down by attaching
chains or cables to suspension components or
engine mounts, damage to vehicle can result.
Fig. 1 Recommended Towing Devices
NS/GSLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 5
Page 32 of 1938

NS vehicles can be tied to a flat bed device using
the reinforced loops located under the front and rear
bumpers on the drivers side of the vehicle. There are
also four reinforced elongated holes for T or R-hooks
located on the bottom of the front frame rail torque
boxes behind the front wheels and forward of the
rear wheels inboard of the rocker panel weld seam.
TOWINGÐFRONT WHEEL LIFT
Chrysler International recommends that a vehicle
be towed with the front end lifted, whenever possible.
A 90 cm (36 in.) length of 4x4 wood beam can be
placed between the wheel lift device and the bottom
of the fascia to prevent damage to vehicle during the
lifting operation. The beam can removed after lifting
the front of the vehicle.
TOWINGÐREAR WHEEL LIFT
If a vehicle cannot be towed with the front wheels
lifted, the rear wheels can be lifted provided the fol-
lowing guide lines are observed.
CAUTION: Do not use steering column lock to
secure steering wheel during towing operation.
²On AWD vehicles, all four wheels must be free to
rotate. Use towing dollies at unlifted end of vehicle.
²Unlock steering column and secure steering
wheel in straight ahead position with a clamp device
designed for towing.
²4-speed electronic automatic transaxle vehicles
can be flat towed at speeds not to exceed 72 km/h (44
mph) for not more than 160 km (100 miles). The
steering column must be unlocked and gear selector
in neutral.
TOWINGÐTOW HOOKS
WARNING: Do not use the tow hook to lift the vehi-
cle off the ground.
A tow-hook bolt, located in the rear interior trim
storage compartment (with jack), is provided with
your vehicle. The tow hook is used for towing the
vehicle with all four wheels on the ground only. It
can be attached to the vehicle through an opening in
the lower front fascia. The tow hook must be fully
seated to the attach bracket through the lower front
fascia as shown. If the tow hook is not fully seated to
the attach bracket the vehicle should not be towed.
NOTE: The tow hook bolt protective plug must be
removed from the tow hook bracket prior to bolt
attachment. The tow hook is used ONLY for towing
the vehicle with all four wheels on the ground.
Fig. 2
0 - 6 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCENS/GS
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 44 of 1938

STEERING KNUCKLE
The front suspension knuckle is not a repairable
component of the vehicles front suspensionIT MUST
BE REPLACED.If bent, broken or damaged in any
way, do not attempt to straighten or repair the steer-
ing knuckle.
Service replacement of the front hub/bearing
assembly can be done with the front steering knuckle
remaining on the vehicle.
LOWER CONTROL ARM
If damaged, the lower control arm casting is ser-
viced only as a complete component. Inspect lower
control arm for signs of damage from contact with
the ground or road debris. If lower control arm shows
any sign of damage, inspect lower control arm for
distortion.Do not attempt to repair or straighten
a broken or bent lower control arm.
The serviceable components of the lower control
arm are: the ball joint assembly, ball joint assembly
grease seal and control arm bushings. Inspect both
control arm bushings for severe deterioration, and
replace if required. Inspect ball joint per inspection
procedure in this section of the service manual and
replace if required. Service procedures to replace
these components are detailed in the specific compo-
nent removal and installation sections in this group
of the service manual.
BALL JOINT (LOWER)
With the weight of the vehicle resting on the road
wheels, grasp the grease fitting as shown in (Fig. 5)
and with no mechanical assistance or added force
attempt to rotate the grease fitting.
If the ball joint is worn the grease fitting will
rotate easily. If movement is noted, replacement of
the ball joint is recommended.
STABILIZER BAR
Inspect for broken or distorted sway bar bushings,
bushing retainers, and worn or damaged sway bar to
strut attaching links. If sway bar to front suspension
cradle bushing replacement is required, bushing can
be removed from sway bar by opening slit and peel-
ing bushing off sway bar.
HUB AND BEARING ASSEMBLY
The condition of the front hub and bearing assem-
bly is diagnosed using the inspection and testing pro-
cedure detailed below.
The bearing contained in the Unit III front hub/
bearing assembly will produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise will generally
change when the bearings are loaded. A road test of
the vehicle is normally required to determine the
location of a worn or damaged bearing.
Find a smooth level road surface and bring the
vehicle up to a constant speed. When vehicle is at a
constant speed, swerve the vehicle back and forth
from the left and to the right. This will load and
unload the bearings and change the noise level.
Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise is
usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 m.p.h..
SERVICE PROCEDURES
SUSPENSION CRADLE THREAD REPAIR
PROCEDURE
WARNING: When performing this procedure use
only the thread inserts which are specified in the
Mopar Parts Catalog for this repair procedure.
These thread inserts have been specifically devel-
oped for this application and use of other types of
thread inserts can result in an inferior long term
repair.
The threaded holes in the front suspension cradle,
if damaged, can repaired by installing a Heli-Coilt
thread insert.
The threaded holes that are repairable using the
thread insert, are the lower control arm rear bushing
retainer mounting bolt holes, routing bracket attach-
ing locations for the power steering hoses, and brake
hose attachment holes.
This repair procedure now allows the threaded
holes in the suspension crossmember to be repaired,
eliminating the need to replace the crossmember if
damage occurs to one of the threaded holes.
The thread inserts for this application are specified
by part number in the Mopar Parts Catalog.Do not
use a substitute thread insert.
The specific tools and equipment required to install
the thread insert are listed below. Refer to the
Fig. 5 Checking Ball Joint Wear
2 - 12 SUSPENSIONNS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 52 of 1938

(7) Loosen but do not remove the pivot bolt (Fig.
32) attaching the front bushing of the lower control
arm to the front suspension cradle.
(8) Remove retainer (Fig. 33) attaching rear bush-
ing of lower control arm to front suspension cradle.
CAUTION: Make location reference marks where
the front suspension cradle is mounted against the
front frame rails before loosening and lowering the
cradle. This is required so the cradle can be re-in-
stalled in the design location to achieve proper
front suspension alignment.
(9) Loosen but not fully removing the 2 left side
suspension cradle to frame rail attaching bolts (Fig.
34).
NOTE: When removing the left lower control arm
from the vehicle, the front suspension cradle needsto be lowered for the pivot bolt to clear the tran-
saxle.
(10) Lower the left front corner of the suspension
cradle until pivot bolt will clear end of transaxle (Fig.
35). Remove the pivot bolt and the lower control arm
from the cradle.
INSTALL
NOTE: If the left lower control arm is being
installed on the vehicle the front suspension cradle
needs to be lowered for the pivot bolt to clear the
transaxle.
(1) Position lower control arm assembly into front
suspension cradle.If installing the left lower con-
trol arm, pry down on the left front corner of
the suspension cradle until the pivot bolt clears
the end of the transaxle (Fig. 35).Install pivot
bolt attaching front bushing of lower control arm to
front
Fig. 32 Lower Control Arm Bushing To Cradle Pivot
Bolt
Fig. 33 Control Arm Bushing To Suspension Cradle
Retainer
Fig. 34 Suspension Cradle To Frame Rail Mounting
Bolts
Fig. 35 Lowering Front Suspension Cradle
2 - 20 SUSPENSIONNS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 58 of 1938

CAUTION: Wheel bearing damage will result if
after loosening hub nut, vehicle is rolled on the
ground or the weight of the vehicle is allowed to be
supported by the tires.
(3) With the aid of a helper applying the brakes to
keep the front hub from turning,loosen but do not
removethe hub nut.The hub and driveshaft are
splined together through the knuckle (bearing)
and retained by the hub nut.
(4) Raise vehicle on jack stands or centered on a
frame contact type hoist. See Hoisting in the Lubri-
cation and Maintenance section of this manual, for
the required lifting procedure to be used for this
vehicle.
(5) Remove wheel lug nuts, and front tire and
wheel assembly.
(6) Remove front disc brake caliper to steering
knuckle attaching bolts. (Fig. 54).
(7) Remove disc brake caliper assembly from steer-
ing knuckle. Caliper is removed by first rotating top
of caliper away from steering knuckle, and then
removing bottom of caliper out from under machined
abutment. (Fig. 55)
(8) Support disc brake caliper assembly using a
wire hook, (Fig. 56)do not hang caliper assembly
by hydraulic hose.
(9) Remove the braking disc from the front hub/
bearing assembly.
(10) Remove the retaining nut and the washer
(Fig. 57) from the end of the stub axle.
(11) Remove the four hub and bearing assembly
mounting bolts from the rear of steering knuckle
(Fig. 58).
(12) Remove the hub and bearing assembly from
the steering knuckle (Fig. 59).
Fig. 54 Front Disc Brake Caliper Mounting Bolts
Fig. 55 Brake Caliper Assembly Removal/Installation
Fig. 56 Supporting Brake Caliper
Fig. 57 Hub/Bearing To Stub Axle Retaining Nut And
Washer
2 - 26 SUSPENSIONNS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)