automatic transmission CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2004, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004Pages: 2585, PDF Size: 62.54 MB
Page 1964 of 2585
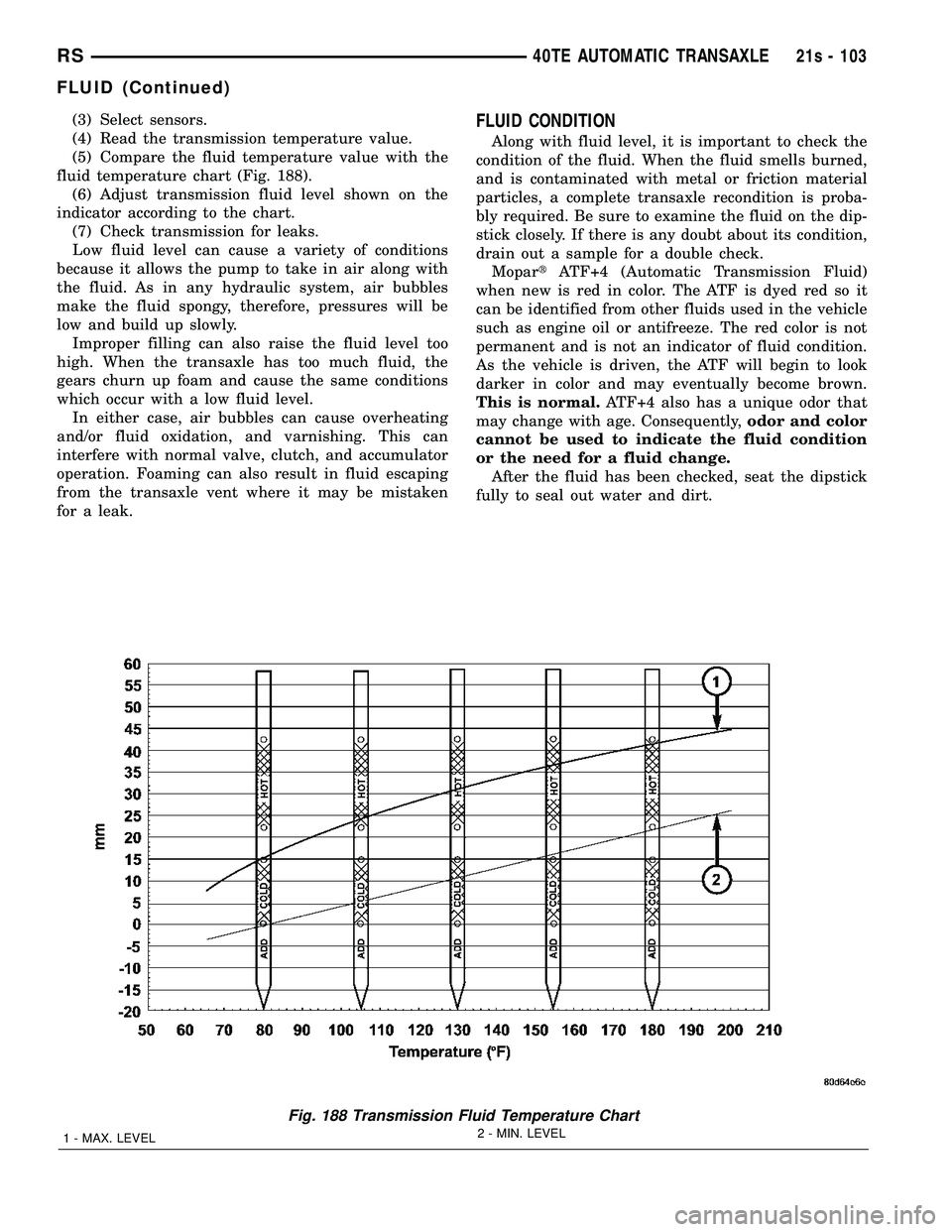
(3) Select sensors.
(4) Read the transmission temperature value.
(5) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
fluid temperature chart (Fig. 188). (6) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
indicator according to the chart. (7) Check transmission for leaks.
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly. Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the
gears churn up foam and cause the same conditions
which occur with a low fluid level. In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transaxle vent where it may be mistaken
for a leak.FLUID CONDITION
Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle recondition is proba-
bly required. Be sure to examine the fluid on the dip-
stick closely. If there is any doubt about its condition,
drain out a sample for a double check. Mopar tATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid)
when new is red in color. The ATF is dyed red so it
can be identified from other fluids used in the vehicle
such as engine oil or antifreeze. The red color is not
permanent and is not an indicator of fluid condition.
As the vehicle is driven, the ATF will begin to look
darker in color and may eventually become brown.
This is normal. ATF+4 also has a unique odor that
may change with age. Consequently, odor and color
cannot be used to indicate the fluid condition
or the need for a fluid change. After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
Fig. 188 Transmission Fluid Temperature Chart
1 - MAX. LEVEL 2 - MIN. LEVEL
RS
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s - 103
FLUID (Continued)
Page 1965 of 2585
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
SERVICE
NOTE: Refer to the maintenance schedules in
LUBRICATION and MAINTENANCE, or the vehicle
owner's manual, for the recommended maintenance
(fluid/filter change) intervals for this transaxle.
NOTE: Only fluids of the type labeled MoparTATF+4
should be used. A filter change should be made at
the time of the transmission oil change. The magnet
(on the inside of the oil pan) should also be cleaned
with a clean, dry cloth.
NOTE: If the transaxle is disassembled for any rea-
son, the fluid and filter should be changed.
FLUID/FILTER SERVICE (RECOMMENDED)
(1) Raise vehicle on a hoist. Refer to LUBRICA-
TION and MAINTENANCE for proper procedures.
Place a drain container with a large opening, under
transaxle oil pan. (2) Remove both engine mount-to-engine cross-
member cradle nuts. Using suitable screw jack and
wood block, raise engine and transmission slightly to
facilitate transaxle oil pan removal and installation. (3) Loosen pan bolts and tap the pan at one corner
to break it loose allowing fluid to drain, then remove
the oil pan. (4) Install a new filter and o-ring on bottom of the
valve body (Fig. 189). (5) Clean the oil pan and magnet. Reinstall pan
using new Mopar Silicone Adhesive sealant. Tighten
oil pan bolts to 19 N´m (165 in. lbs.). (6) Pour four quarts of Mopar tATF+4 through the
dipstick opening. (7) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes
applied, move selector lever momentarily to each
position, ending in the park or neutral position. (8) Check the transaxle fluid level and add an
appropriate amount to bring the transaxle fluid level
to 3mm (1/8 in.) below the lowest mark on the dip-
stick (Fig. 190).
(9) Recheck the fluid level after the transaxle has
reached normal operating temperature (180ÉF.). Refer
to Fluid Level and Condition Check for the proper
fluid fill procedure. (10) To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make
certain that dipstick is fully seated into the dipstick
opening.
DIPSTICK TUBE FLUID SUCTION METHOD
(ALTERNATIVE)
(1) When performing the fluid suction method,
make sure the transaxle is at full operating temper-
ature. (2) To perform the dipstick tube fluid suction
method, use a suitable fluid suction device (VaculaŸ
or equivalent). (3) Insert the fluid suction line into the dipstick
tube.
NOTE: Verify that the suction line is inserted to the
lowest point of the transaxle oil pan. This will
ensure complete evacuation of the fluid in the pan.
(4) Follow the manufacturers recommended proce-
dure and evacuate the fluid from the transaxle.
Fig. 189 Filter and O-Ring
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - O-RING
Fig. 190 Fluid Level Indicator
1 - FLUID LEVEL INDICATOR
21s - 104 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
FLUID (Continued)
Page 1966 of 2585

(5) Remove the suction line from the dipstick tube.
(6) Pour four quarts of MopartATF+4 through the
dipstick opening. (7) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes
applied, move selector lever momentarily to each
position, ending in the park or neutral position. (8) Check the transaxle fluid level and add an
appropriate amount to bring the transaxle fluid level
to 3mm (1/8 in.) below the lowest mark on the dip-
stick (Fig. 190). (9) Recheck the fluid level after the transaxle has
reached normal operating temperature (180ÉF.).
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE) (10) To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make
certain that dipstick is fully seated into the dipstick
opening.
GEAR SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery cables.
(2) Remove battery shield.
(3) Remove battery.
(4) Remove speed control servo and position out of
way. (5) Disconnect gear shift cable at manual valve
lever (Fig. 191). (6) Disconnect gear shift cable from upper mount
bracket (Fig. 191). (7) Remove instrument panel lower silencer (Fig.
192).
(8) Remove knee bolster (Fig. 193).
Fig. 191 Gearshift Cable at Transaxle - Typical
1 - MANUAL VALVE LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT CABLE
3 - UPPER MOUNT BRACKET
Fig. 192 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCER
Fig. 193 Knee Bolster
1 - KNEE BOLSTER
RS 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s - 105
FLUID (Continued)
Page 1990 of 2585
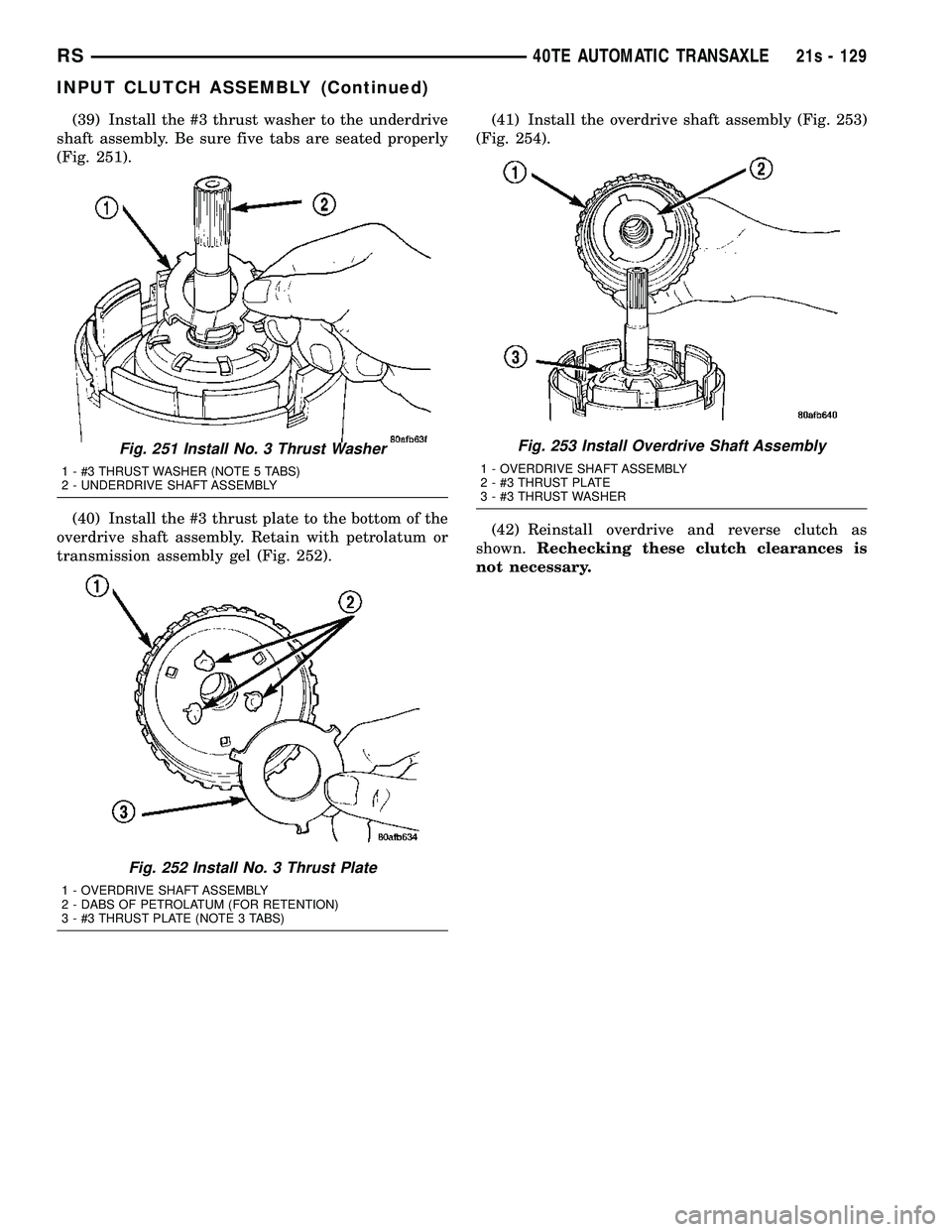
(39) Install the #3 thrust washer to the underdrive
shaft assembly. Be sure five tabs are seated properly
(Fig. 251).
(40) Install the #3 thrust plate to the bottom of the
overdrive shaft assembly. Retain with petrolatum or
transmission assembly gel (Fig. 252). (41) Install the overdrive shaft assembly (Fig. 253)
(Fig. 254).
(42) Reinstall overdrive and reverse clutch as
shown. Rechecking these clutch clearances is
not necessary.
Fig. 251 Install No. 3 Thrust Washer
1 - #3 THRUST WASHER (NOTE 5 TABS)
2 - UNDERDRIVE SHAFT ASSEMBLY
Fig. 252 Install No. 3 Thrust Plate
1 - OVERDRIVE SHAFT ASSEMBLY
2 - DABS OF PETROLATUM (FOR RETENTION)
3 - #3 THRUST PLATE (NOTE 3 TABS)
Fig. 253 Install Overdrive Shaft Assembly
1 - OVERDRIVE SHAFT ASSEMBLY
2 - #3 THRUST PLATE
3 - #3 THRUST WASHER
RS 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s - 129
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1993 of 2585
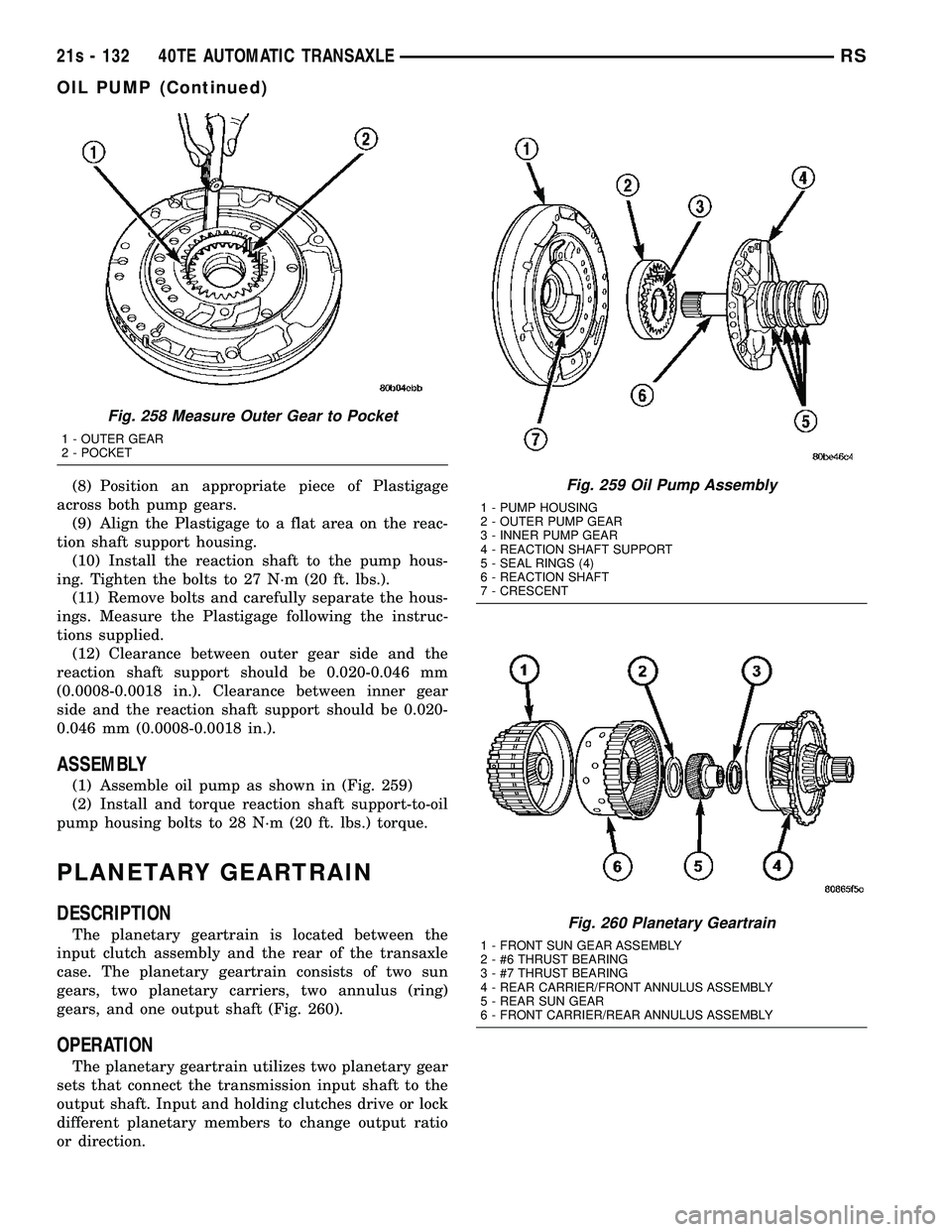
(8) Position an appropriate piece of Plastigage
across both pump gears. (9) Align the Plastigage to a flat area on the reac-
tion shaft support housing. (10) Install the reaction shaft to the pump hous-
ing. Tighten the bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.). (11) Remove bolts and carefully separate the hous-
ings. Measure the Plastigage following the instruc-
tions supplied. (12) Clearance between outer gear side and the
reaction shaft support should be 0.020-0.046 mm
(0.0008-0.0018 in.). Clearance between inner gear
side and the reaction shaft support should be 0.020-
0.046 mm (0.0008-0.0018 in.).
ASSEMBLY
(1) Assemble oil pump as shown in (Fig. 259)
(2) Install and torque reaction shaft support-to-oil
pump housing bolts to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
DESCRIPTION
The planetary geartrain is located between the
input clutch assembly and the rear of the transaxle
case. The planetary geartrain consists of two sun
gears, two planetary carriers, two annulus (ring)
gears, and one output shaft (Fig. 260).
OPERATION
The planetary geartrain utilizes two planetary gear
sets that connect the transmission input shaft to the
output shaft. Input and holding clutches drive or lock
different planetary members to change output ratio
or direction.
Fig. 258 Measure Outer Gear to Pocket
1 - OUTER GEAR
2 - POCKET
Fig. 259 Oil Pump Assembly
1 - PUMP HOUSING
2 - OUTER PUMP GEAR
3 - INNER PUMP GEAR
4 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
5 - SEAL RINGS (4)
6 - REACTION SHAFT
7 - CRESCENT
Fig. 260 Planetary Geartrain
1 - FRONT SUN GEAR ASSEMBLY
2 - #6 THRUST BEARING
3 - #7 THRUST BEARING
4 - REAR CARRIER/FRONT ANNULUS ASSEMBLY
5 - REAR SUN GEAR
6 - FRONT CARRIER/REAR ANNULUS ASSEMBLY
21s - 132 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1994 of 2585
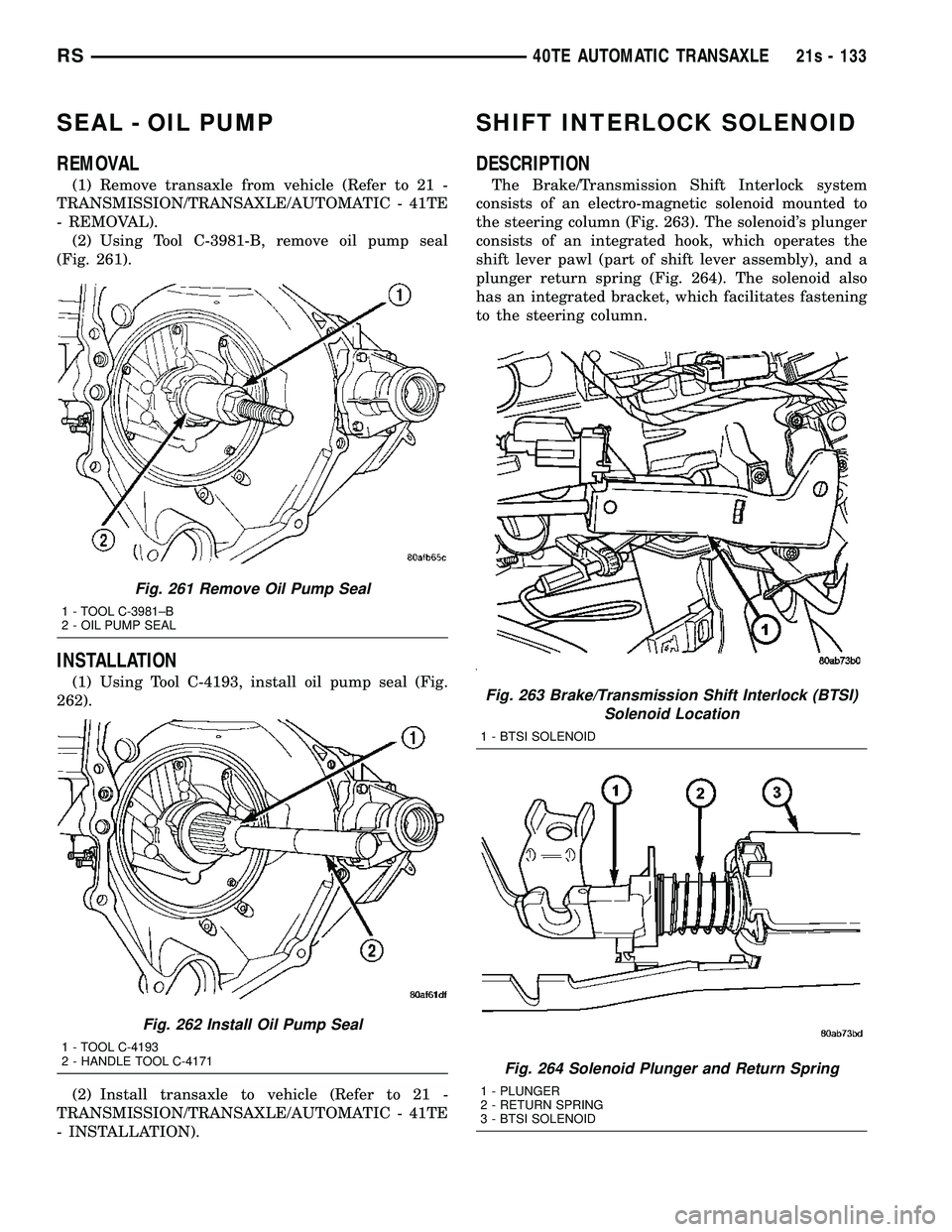
SEAL - OIL PUMP
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transaxle from vehicle (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE
- REMOVAL). (2) Using Tool C-3981-B, remove oil pump seal
(Fig. 261).
INSTALLATION
(1) Using Tool C-4193, install oil pump seal (Fig.
262).
(2) Install transaxle to vehicle (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE
- INSTALLATION).
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
The Brake/Transmission Shift Interlock system
consists of an electro-magnetic solenoid mounted to
the steering column (Fig. 263). The solenoid's plunger
consists of an integrated hook, which operates the
shift lever pawl (part of shift lever assembly), and a
plunger return spring (Fig. 264). The solenoid also
has an integrated bracket, which facilitates fastening
to the steering column.
Fig. 261 Remove Oil Pump Seal
1 - TOOL C-3981±B
2 - OIL PUMP SEAL
Fig. 262 Install Oil Pump Seal
1 - TOOL C-4193
2 - HANDLE TOOL C-4171
Fig. 263 Brake/Transmission Shift Interlock (BTSI) Solenoid Location
1 - BTSI SOLENOID
Fig. 264 Solenoid Plunger and Return Spring
1 - PLUNGER
2 - RETURN SPRING
3 - BTSI SOLENOID
RS 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s - 133
Page 1995 of 2585
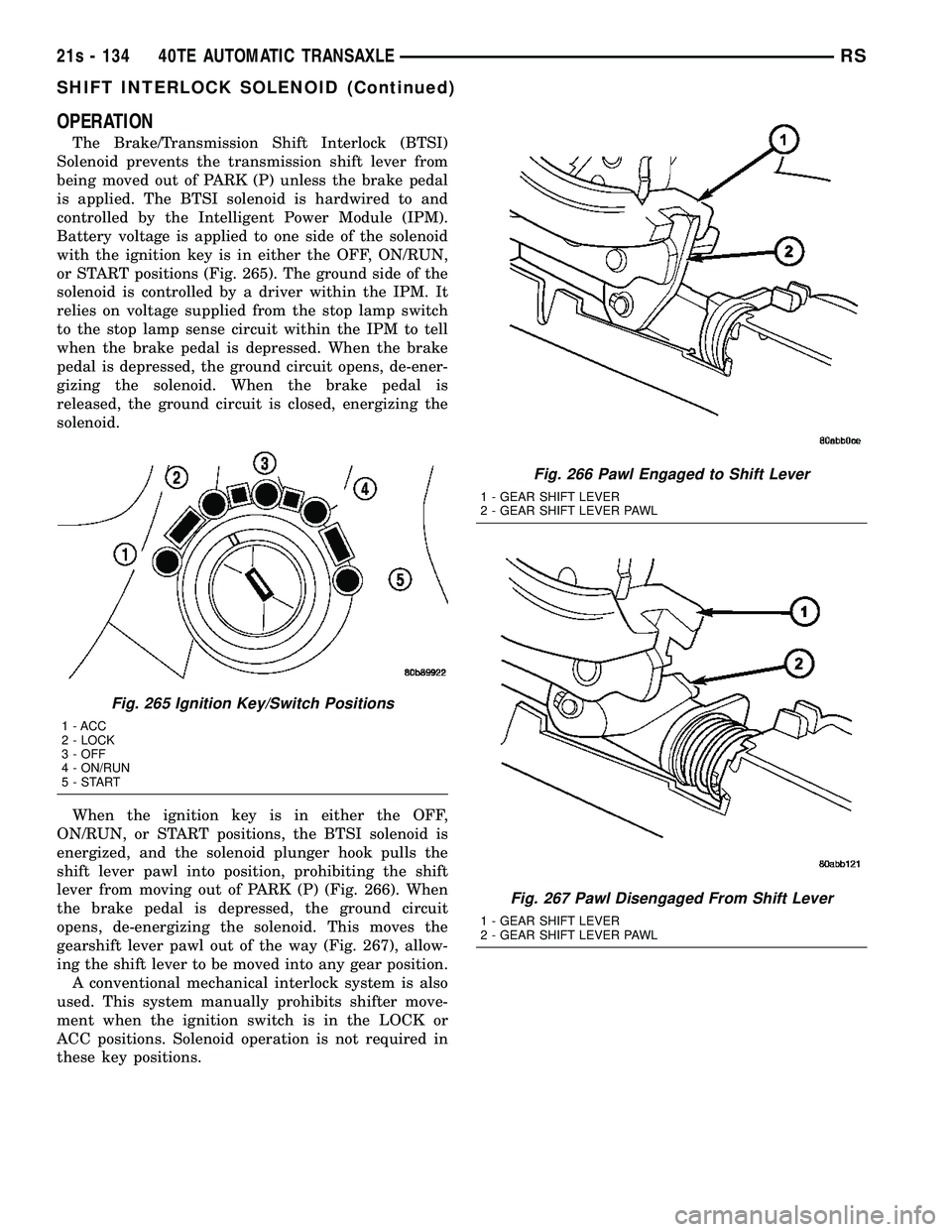
OPERATION
The Brake/Transmission Shift Interlock (BTSI)
Solenoid prevents the transmission shift lever from
being moved out of PARK (P) unless the brake pedal
is applied. The BTSI solenoid is hardwired to and
controlled by the Intelligent Power Module (IPM).
Battery voltage is applied to one side of the solenoid
with the ignition key is in either the OFF, ON/RUN,
or START positions (Fig. 265). The ground side of the
solenoid is controlled by a driver within the IPM. It
relies on voltage supplied from the stop lamp switch
to the stop lamp sense circuit within the IPM to tell
when the brake pedal is depressed. When the brake
pedal is depressed, the ground circuit opens, de-ener-
gizing the solenoid. When the brake pedal is
released, the ground circuit is closed, energizing the
solenoid.
When the ignition key is in either the OFF,
ON/RUN, or START positions, the BTSI solenoid is
energized, and the solenoid plunger hook pulls the
shift lever pawl into position, prohibiting the shift
lever from moving out of PARK (P) (Fig. 266). When
the brake pedal is depressed, the ground circuit
opens, de-energizing the solenoid. This moves the
gearshift lever pawl out of the way (Fig. 267), allow-
ing the shift lever to be moved into any gear position. A conventional mechanical interlock system is also
used. This system manually prohibits shifter move-
ment when the ignition switch is in the LOCK or
ACC positions. Solenoid operation is not required in
these key positions.
Fig. 265 Ignition Key/Switch Positions
1 - ACC
2 - LOCK
3 - OFF
4 - ON/RUN
5-START
Fig. 266 Pawl Engaged to Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
Fig. 267 Pawl Disengaged From Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
21s - 134 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 1996 of 2585
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the 9OFF 9
position. 1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park with brake
pedal applied.
2. Turn key to the
9 ON/RUN 9position. 2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9 ON/RUN 9position and
depress the brake pedal. 3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the 9LOCK 9or 9ACC 9
position. 4. Key cannot be
returned to the
9LOCK 9or
9 ACC 9position.
5. Return shifter to
9 PARK 9and try to remove
the key. 5. Key can be removed
(after returning to
9LOCK 9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of 9PARK 9. 6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of
9PARK 9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system adjustment or repair.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the 9OFF 9
position. 1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park with brake
pedal applied.
2. Turn key to the
9 ON/RUN 9position. 2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9 ON/RUN 9position and
depress the brake pedal. 3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the 9LOCK 9or 9ACC 9
position. 4. Key cannot be
returned to the
9LOCK 9or
9 ACC 9position.
5. Return shifter to
9 PARK 9and try to remove
the key. 5. Key can be removed
(after returning to
9LOCK 9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of 9PARK 9. 6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of
9PARK 9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system repair. Refer to the
appropriate Diagnostic Information.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove instrument panel lower shroud (Fig.
268).
(3) Remove knee bolster (Fig. 269).
Fig. 268 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCER
Fig. 269 Knee Bolster
1 - KNEE BOLSTER
RS 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s - 135
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 1997 of 2585
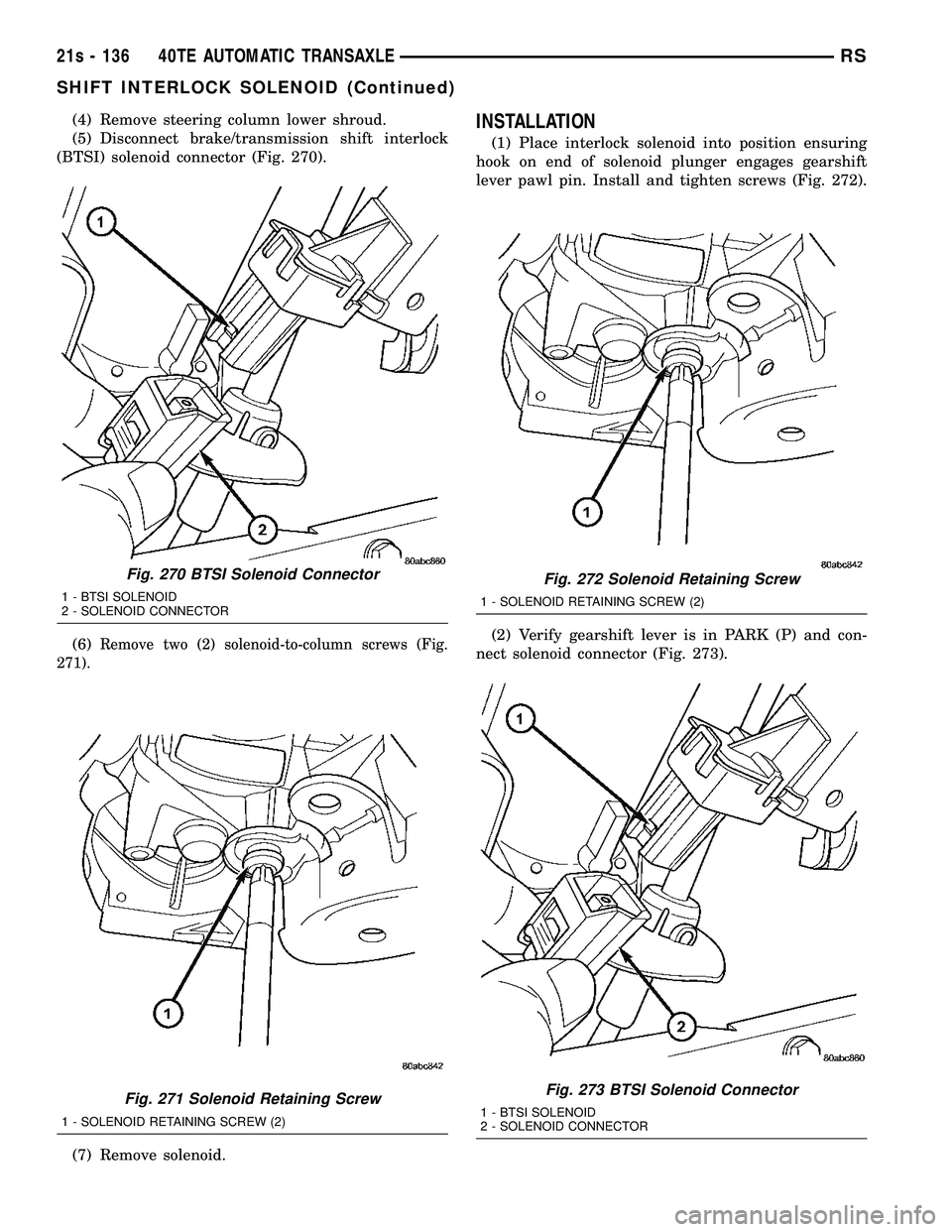
(4) Remove steering column lower shroud.
(5) Disconnect brake/transmission shift interlock
(BTSI) solenoid connector (Fig. 270).
(6)
Remove two (2) solenoid-to-column screws (Fig.
271).
(7) Remove solenoid.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place interlock solenoid into position ensuring
hook on end of solenoid plunger engages gearshift
lever pawl pin. Install and tighten screws (Fig. 272).
(2) Verify gearshift lever is in PARK (P) and con-
nect solenoid connector (Fig. 273).
Fig. 270 BTSI Solenoid Connector
1 - BTSI SOLENOID
2 - SOLENOID CONNECTOR
Fig. 271 Solenoid Retaining Screw
1 - SOLENOID RETAINING SCREW (2)
Fig. 272 Solenoid Retaining Screw
1 - SOLENOID RETAINING SCREW (2)
Fig. 273 BTSI Solenoid Connector
1 - BTSI SOLENOID
2 - SOLENOID CONNECTOR
21s - 136 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 1998 of 2585

(3) Install steering column lower shroud.
(4) Install knee bolster (Fig. 274).
(5) Install instrument panel lower silencer (Fig.
275).
(6) Connect battery negative cable.
(7) Verify proper shift interlock system operation.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 31TH/SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID -
OPERATION)
SOLENOID/PRESSURE
SWITCH ASSY
DESCRIPTION
The Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly (Fig. 276)
is external to the transaxle and mounted to the transaxle case. The assembly consists of four sole-
noids that control hydraulic pressure to the LR/CC,
2/4, OD, and UD friction elements. The reverse
clutch is controlled by line pressure from the manual
valve in the valve body. The solenoids are contained
within the Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly, and
can only be serviced by replacing the assembly.
The solenoid assembly also contains pressure
switches that monitor and send hydraulic circuit
information to the PCM/TCM. Likewise, the pressure
switches can only be service by replacing the assem-
bly.
OPERATION
SOLENOIDS
The solenoids receive electrical power from the
Transmission Control Relay through a single wire.
The PCM/TCM energizes or operates the solenoids
individually by grounding the return wire of the sole-
noid needed. When a solenoid is energized, the sole-
noid valve shifts, and a fluid passage is opened or
closed (vented or applied), depending on its default
operating state. The result is an apply or release of a
frictional element. The 2/4 and UD solenoids are normally applied,
which by design allow fluid to pass through in their
relaxed or ªoffº state. This allows transaxle limp-in
(P,R,N,2) in the event of an electrical failure. The continuity of the solenoids and circuits are
periodically tested. Each solenoid is turned on or off
depending on its current state. An inductive spike
Fig. 274 Knee Bolster
1 - KNEE BOLSTER
Fig. 275 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCER
Fig. 276 Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly
1 - SOLENOID AND PRESSURE SWITCH ASSEMBLY
RS 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s - 137
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)