automatic transmission CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004 Manual Online
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2004, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004Pages: 2585, PDF Size: 62.54 MB
Page 1854 of 2585

(15) Remove remaining retainers as shown in (Fig.
352).(16) Remove valves and springs as shown in (Fig.
353).
NOTE: Refer to Valve Body Cleaning and Inspection
for cleaning procedures.
ASSEMBLY
NOTE: If valve body assembly is reconditioned, the
PCM/TCM Quick Learn Procedure must be per-
formed. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC
CONTROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Install valves and springs as shown in (Fig.
353).
Fig. 353 Springs and Valves Location
1 - VALVE BODY 5 - MANUAL VALVE
2 - T/C REGULATOR VALVE 6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH SWITCH VALVE
3 - L/R SWITCH VALVE 7 - SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
4 - CONVERTER CLUTCH CONTROL VALVE 8 - REGULATOR VALVE
Fig. 352 Valve Retainer Location
1 - RETAINER
2 - RETAINER
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 257
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1855 of 2585
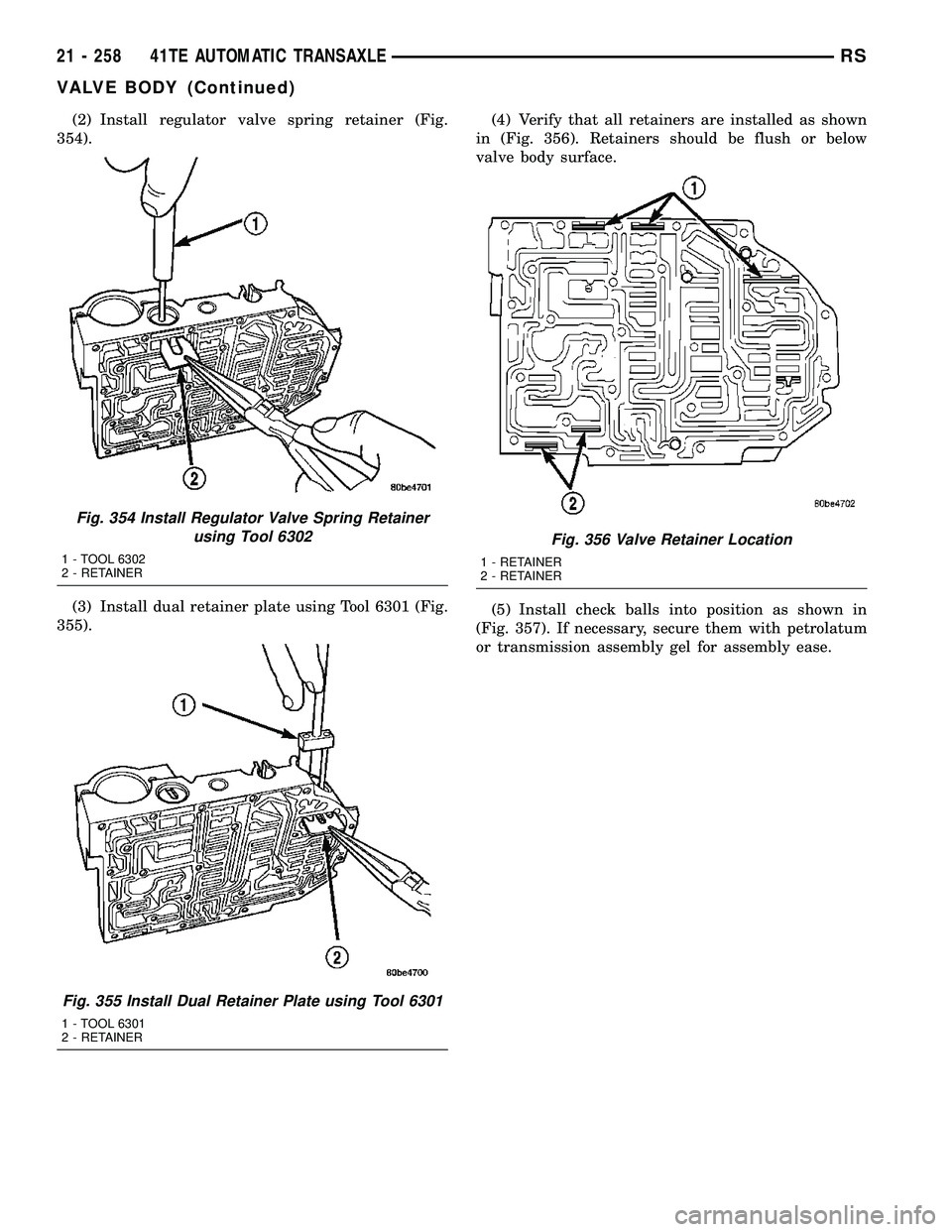
(2) Install regulator valve spring retainer (Fig.
354).
(3) Install dual retainer plate using Tool 6301 (Fig.
355).(4) Verify that all retainers are installed as shown
in (Fig. 356). Retainers should be flush or below
valve body surface.
(5) Install check balls into position as shown in
(Fig. 357). If necessary, secure them with petrolatum
or transmission assembly gel for assembly ease.
Fig. 354 Install Regulator Valve Spring Retainer
using Tool 6302
1 - TOOL 6302
2 - RETAINER
Fig. 355 Install Dual Retainer Plate using Tool 6301
1 - TOOL 6301
2 - RETAINER
Fig. 356 Valve Retainer Location
1 - RETAINER
2 - RETAINER
21 - 258 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1858 of 2585
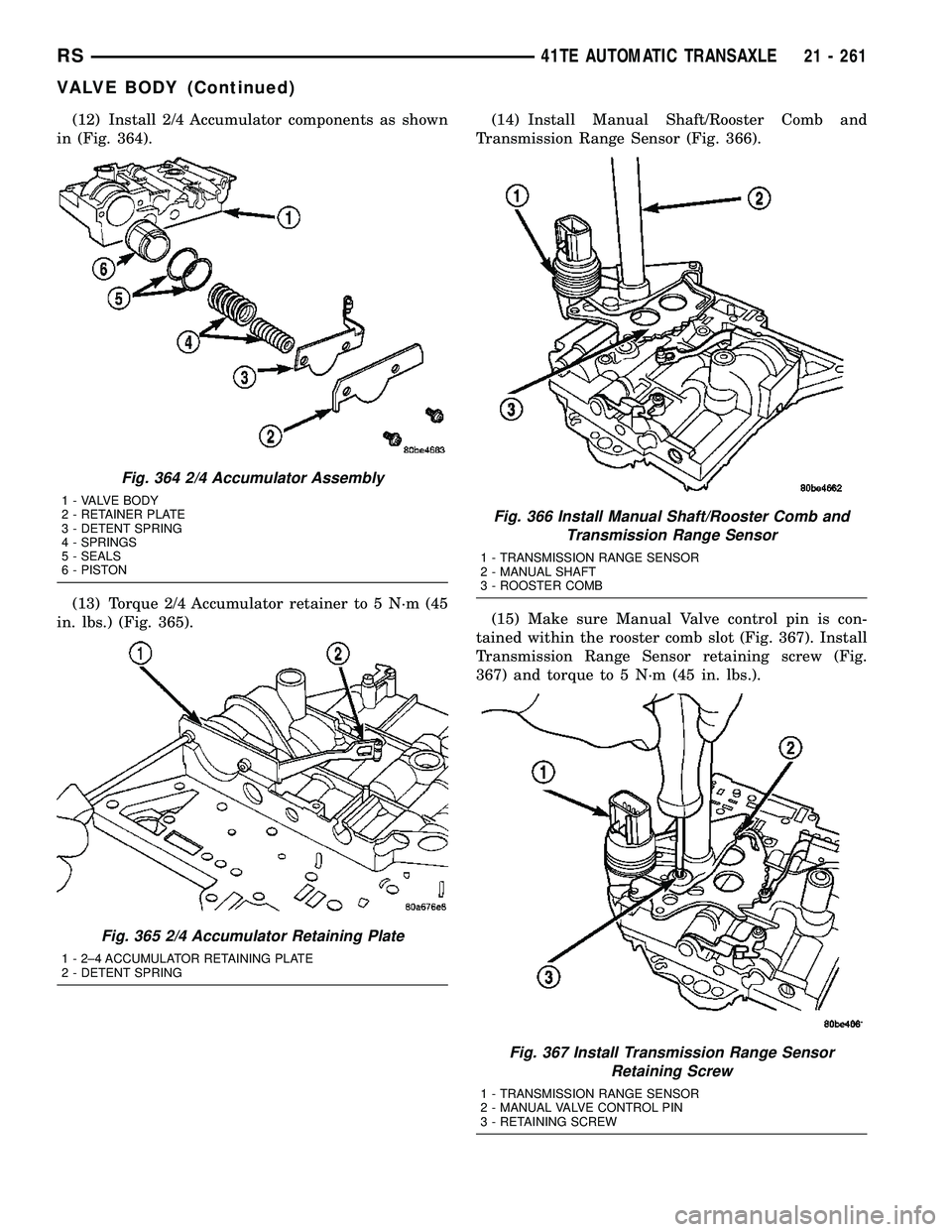
(12) Install 2/4 Accumulator components as shown
in (Fig. 364).
(13) Torque 2/4 Accumulator retainer to 5 N´m (45
in. lbs.) (Fig. 365).(14) Install Manual Shaft/Rooster Comb and
Transmission Range Sensor (Fig. 366).
(15) Make sure Manual Valve control pin is con-
tained within the rooster comb slot (Fig. 367). Install
Transmission Range Sensor retaining screw (Fig.
367) and torque to 5 N´m (45 in. lbs.).
Fig. 364 2/4 Accumulator Assembly
1 - VALVE BODY
2 - RETAINER PLATE
3 - DETENT SPRING
4 - SPRINGS
5 - SEALS
6 - PISTON
Fig. 365 2/4 Accumulator Retaining Plate
1 - 2±4 ACCUMULATOR RETAINING PLATE
2 - DETENT SPRING
Fig. 366 Install Manual Shaft/Rooster Comb and
Transmission Range Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL SHAFT
3 - ROOSTER COMB
Fig. 367 Install Transmission Range Sensor
Retaining Screw
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL VALVE CONTROL PIN
3 - RETAINING SCREW
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 261
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1859 of 2585
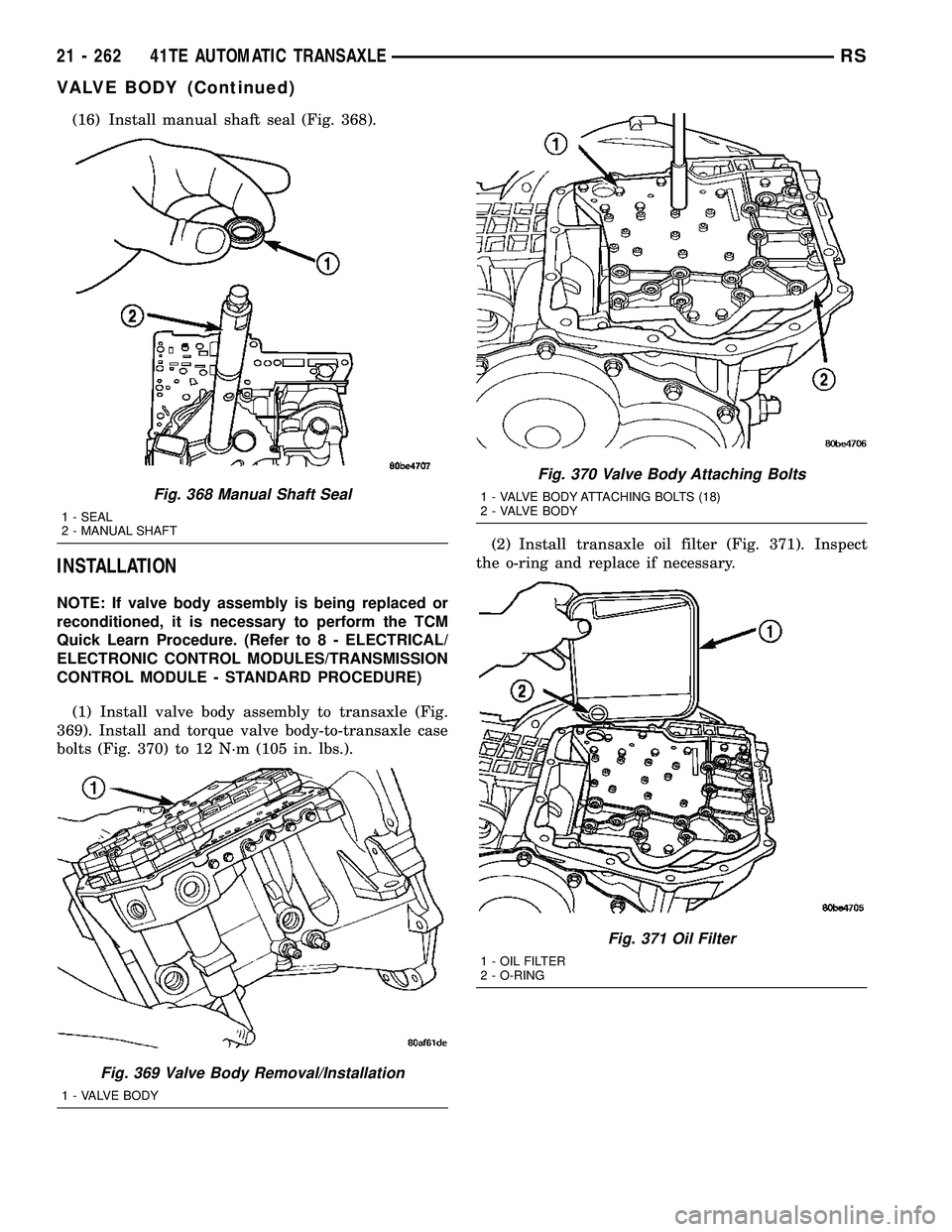
(16) Install manual shaft seal (Fig. 368).
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If valve body assembly is being replaced or
reconditioned, it is necessary to perform the TCM
Quick Learn Procedure. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION
CONTROL MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Install valve body assembly to transaxle (Fig.
369). Install and torque valve body-to-transaxle case
bolts (Fig. 370) to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).(2) Install transaxle oil filter (Fig. 371). Inspect
the o-ring and replace if necessary.
Fig. 368 Manual Shaft Seal
1 - SEAL
2 - MANUAL SHAFT
Fig. 369 Valve Body Removal/Installation
1 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 370 Valve Body Attaching Bolts
1 - VALVE BODY ATTACHING BOLTS (18)
2 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 371 Oil Filter
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - O-RING
21 - 262 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1860 of 2585
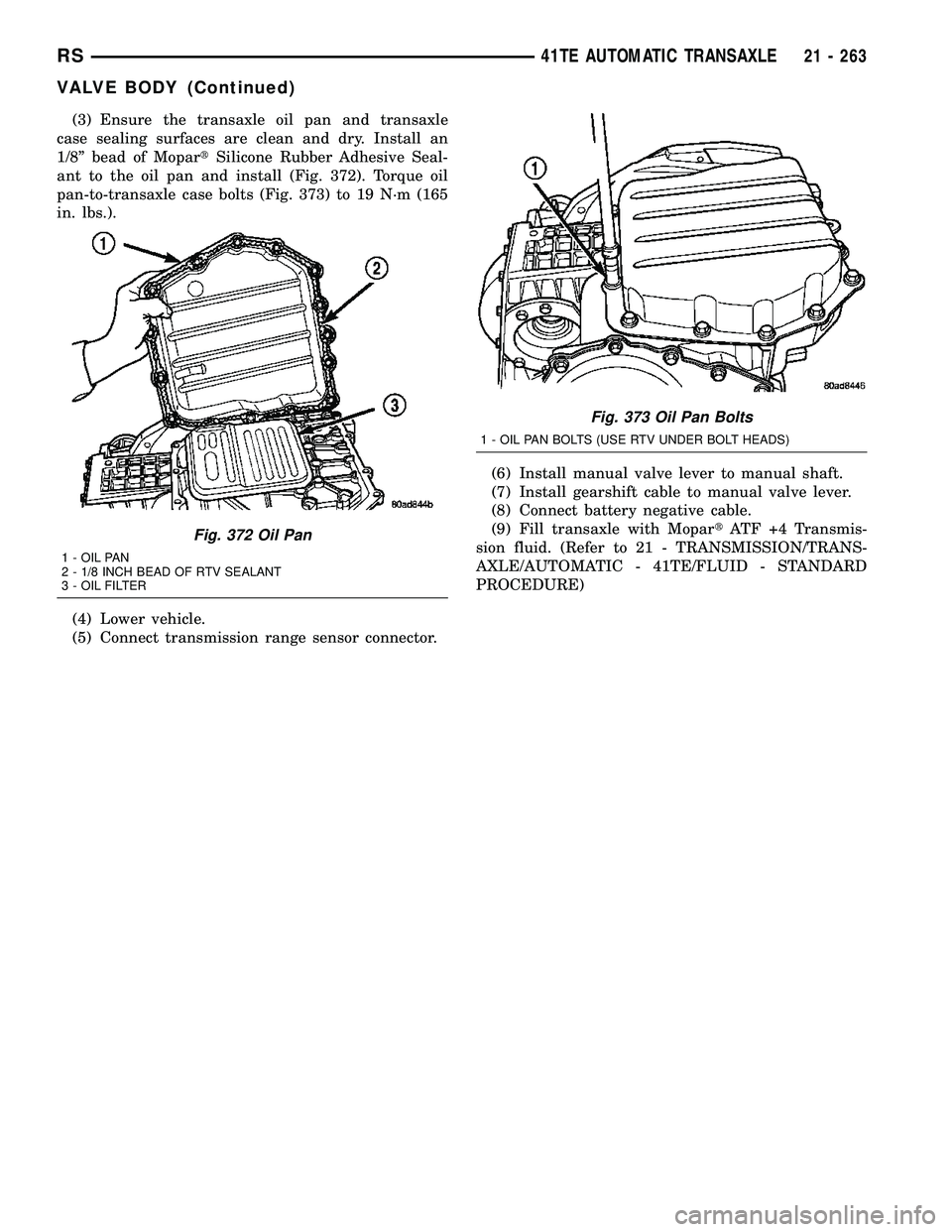
(3) Ensure the transaxle oil pan and transaxle
case sealing surfaces are clean and dry. Install an
1/8º bead of MopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Seal-
ant to the oil pan and install (Fig. 372). Torque oil
pan-to-transaxle case bolts (Fig. 373) to 19 N´m (165
in. lbs.).
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Connect transmission range sensor connector.(6) Install manual valve lever to manual shaft.
(7) Install gearshift cable to manual valve lever.
(8) Connect battery negative cable.
(9) Fill transaxle with MopartATF +4 Transmis-
sion fluid. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
Fig. 372 Oil Pan
1 - OIL PAN
2 - 1/8 INCH BEAD OF RTV SEALANT
3 - OIL FILTER
Fig. 373 Oil Pan Bolts
1 - OIL PAN BOLTS (USE RTV UNDER BOLT HEADS)
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 263
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1862 of 2585

TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE ................1
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE .............2441TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
............166
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
INPUT SHAFT DESCRIPTION ..........................1
DISASSEMBLY ..........................1
ASSEMBLY .............................5 INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
DESCRIPTION ..........................9
DISASSEMBLY .........................10
ASSEMBLY ............................17
INPUT SHAFT
DESCRIPTION
The input shaft assembly (Fig. 1) is part of the
transaxle geartrain, is driven by the clutch assembly,
and consists of the following components: ² Input Mainshaft
² 3rd Speed Gear
² 4th Speed Gear
² 3/4 Synchronizer
² 5th Input Gear
The input shaft meshes with the intermediate
shaft, and is supported by a needle bearing at the
front of the transaxle, and a sealed roller bearing at
the rear of the transaxle.
DISASSEMBLY
NOTE: When servicing the input shaft assembly, all
snap rings which are removed MUST be replaced
with new snap rings upon reassembly. The 5th gear
nut must be replaced also.
(1) Invert input shaft assembly and place in fix-
ture 8487. (2) Remove input bearing snap ring (Fig. 2).
(3) Remove input bearing. Place input shaft
assembly onto arbor press table, with the input bear-
ing supported by bearing splitter (Fig. 3). Using
adapter 8486-4, press bearing off of shaft, while
helper supports shaft to prevent dropping. (4) Place input shaft assembly back into fixture
8487. Secure fixture to bench with fasteners, or
secure to bench vise.
RS TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE21s-1
Page 1885 of 2585

40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE DESCRIPTION .........................25
OPERATION ...........................27
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - 4XTETRANSAXLE GENERAL DIAGNOSIS .......27
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TEST . . . 27
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TESTS ....................28
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH AIR PRESSURE TESTS ....................30
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TORQUE CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAKAGE . . . 31
REMOVAL .............................31
DISASSEMBLY .........................34
ASSEMBLY ............................51
INSTALLATION .........................73
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS 4XTE TRANSAXLE HYDRAULICSCHEMATICS ........................75
SPECIFICATIONS - 41TE TRANSAXLE .......87
SPECIAL TOOLS .......................89
ACCUMULATOR DESCRIPTION .........................94
OPERATION ...........................94
DRIVING CLUTCHES DESCRIPTION .........................95
OPERATION ...........................95
FINAL DRIVE DESCRIPTION .........................95
OPERATION ...........................96
DISASSEMBLY .........................96
ASSEMBLY ............................99
ADJUSTMENTS DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOADMEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT ......100
FLUID STANDARD PROCEDURE FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION CHECK . . . 102
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID ANDFILTER SERVICE .....................104
GEAR SHIFT CABLE REMOVAL ............................105
HOLDING CLUTCHES DESCRIPTION ........................106
OPERATION ..........................106
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY DISASSEMBLY ........................107
ASSEMBLY ...........................116 OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION ........................131
OPERATION ..........................131
DISASSEMBLY ........................131
ASSEMBLY ...........................132
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN DESCRIPTION ........................132
OPERATION ..........................132
SEAL - OIL PUMP REMOVAL ............................133
INSTALLATION ........................133
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID DESCRIPTION ........................133
OPERATION ..........................134
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/ TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SOLENOID ..........................135
REMOVAL ............................135
INSTALLATION ........................136
SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY DESCRIPTION ........................137
OPERATION ..........................137
REMOVAL ............................138
INSTALLATION ........................139
SPEED SENSOR - INPUT DESCRIPTION ........................140
OPERATION ..........................140
REMOVAL ............................141
INSTALLATION ........................141
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT DESCRIPTION ........................142
OPERATION ..........................142
REMOVAL ............................143
INSTALLATION ........................143
TORQUE CONVERTER DESCRIPTION ........................144
OPERATION ..........................148
REMOVAL ............................149
INSTALLATION ........................149
TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY DESCRIPTION ........................150
OPERATION ..........................150
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR DESCRIPTION ........................150
OPERATION ..........................151
REMOVAL ............................151
INSTALLATION ........................152
VALVE BODY DESCRIPTION ........................152
21s - 24 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 1887 of 2585

holding clutches: 2nd/4th gear and Low/Reverse. The
primary mechanical components of the transaxle con-
sist of the following:² Three multiple disc input clutches
² Two multiple disc holding clutches
² Four hydraulic accumulators
² Two planetary gear sets
² Hydraulic oil pump
² Valve body
² Solenoid/Pressure switch assembly
² Integral differential assembly
Control of the transaxle is accomplished by fully
adaptive electronics. Optimum shift scheduling is
accomplished through continuous real-time sensor
feedback information provided to the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) or Transmission Control Mod-
ule (TCM). The PCM/TCM is the heart of the electronic control
system and relies on information from various direct
and indirect inputs (sensors, switches, etc.) to deter-
mine driver demand and vehicle operating condi-
tions. With this information, the PCM/TCM can
calculate and perform timely and quality shifts
through various output or control devices (solenoid
pack, transmission control relay, etc.). The PCM/TCM also performs certain self-diagnos-
tic functions and provides comprehensive information
(sensor data, DTC's, etc.) which is helpful in proper
diagnosis and repair. This information can be viewed
with the DRB scan tool.
TRANSAXLE IDENTIFICATION
The 40TE transaxle is identified by a barcode label
that is fixed to the transaxle case as shown in (Fig.
2). The label contains a series of digits that can be
translated into useful information such as transaxle
part number, date of manufacture, manufacturing
origin, plant shift number, build sequence number,
etc. Refer to (Fig. 3) for identification label break-
down. If the tag is not legible or missing, the ªPKº num-
ber, which is stamped into the transaxle case behind
the transfer gear cover, can be referred to for identi-
fication. This number differs slightly in that it con-
tains the entire transaxle part number, rather than
the last three digits.
Fig. 2 Transaxle Identification Label
1 - IDENTIFICATION LABEL
Fig. 3 Identification Label Breakdown
1 - T=TRACEABILITY
2 - SUPPLIER CODE (PK=KOKOMO)
3 - COMPONENT CODE (TK=KOKOMO TRANSMISSION)
4 - BUILD DAY (344=DEC. 9)
5 - BUILD YEAR (9=1999)
6 - LINE/SHIFT CODE (3=3RD SHIFT)
7 - BUILD SEQUENCE NUMBER
8 - LAST THREE OF P/N
9 - ALPHA
10 - TRANSAXLE PART NUMBER
11 - P=PART NUMBER
21s - 26 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1888 of 2585
OPERATION
Transmission output is directed to an integral dif-
ferential by a transfer gear system in the following
input-to-output ratios:
First ............................... 2.84 : 1
Second ............................. 1.57 : 1
Third .............................. 1.00 : 1
Overdrive ........................... 0.69 : 1
Reverse ............................ 2.21 : 1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - 4XTE TRANSAXLE
GENERAL DIAGNOSIS
NOTE: Before attempting any repair on a 4XTE four-
speed automatic transaxle, check for diagnostic trou-
ble codes (DTC's) using the DRB scan tool. Refer to
the Transmission Diagnostic Procedures Manual.
Transaxle malfunctions may be caused by these
general conditions: ² Poor engine performance
² Improper adjustments
² Hydraulic malfunctions
² Mechanical malfunctions
² Electronic malfunctions
Diagnosis of these problems should always begin by
checking the easily accessible variables: fluid level and
condition, gearshift cable adjustment. Then perform a
road test to determine if the problem has been corrected
or that more diagnosis is necessary. If the problem per-
sists after the preliminary tests and corrections are com-
pleted, hydraulic pressure checks should be performed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TEST
Prior to performing a road test, verify that the
fluid level, fluid condition, and linkage adjustment
have been approved. During the road test, the transaxle should be oper-
ated in each position to check for slipping and any
variation in shifting. If the vehicle operates properly at highway speeds,
but has poor acceleration, the converter stator over-
running clutch may be slipping. If acceleration is nor-
mal, but high throttle opening is needed to maintain
highway speeds, the converter stator clutch may
have seized. Both of these stator defects require
replacement of the torque converter and thorough
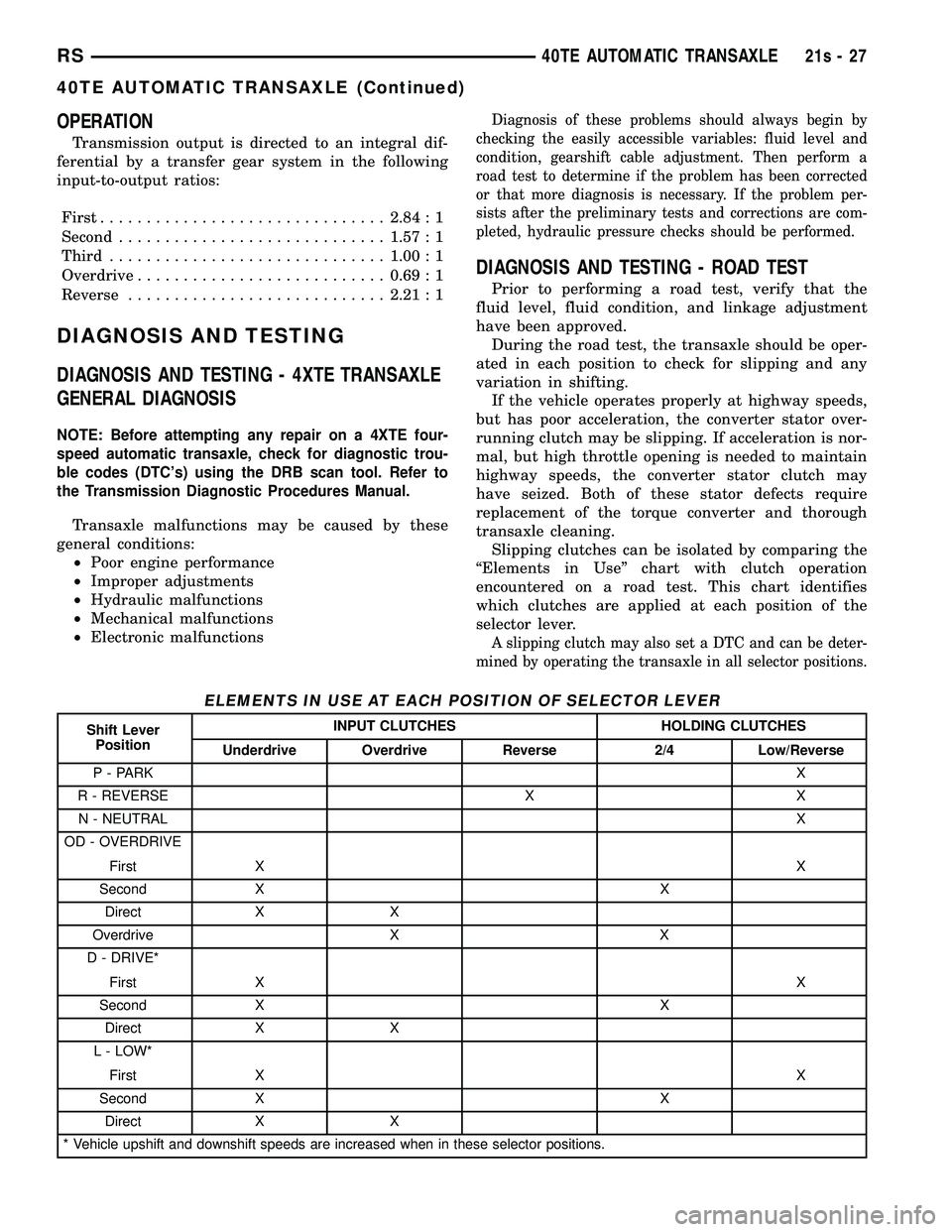
transaxle cleaning. Slipping clutches can be isolated by comparing the
ªElements in Useº chart with clutch operation
encountered on a road test. This chart identifies
which clutches are applied at each position of the
selector lever.
A slipping clutch may also set a DTC and can be deter-
mined by operating the transaxle in all selector positions.
ELEMENTS IN USE AT EACH POSITION OF SELECTOR LEVER
Shift Lever Position INPUT CLUTCHES HOLDING CLUTCHES
Underdrive Overdrive Reverse 2/4 Low/Reverse
P - PARK X
R - REVERSE X X N - NEUTRAL X
OD - OVERDRIVE
First X X
Second X X Direct X X
Overdrive X X
D - DRIVE*
First X X
Second X X Direct X X
L - LOW*
First X X
Second X X
Direct X X
* Vehicle upshift and downshift speeds are increased when in these selector positions.
RS 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s-27
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1892 of 2585
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAKAGE
When diagnosing converter housing fluid leaks,
three actions must be taken before repair: (1) Verify proper transmission fluid level.
(2) Verify that the leak originates from the con-
verter housing area and is transmission fluid. (3) Determine the true source of the leak.
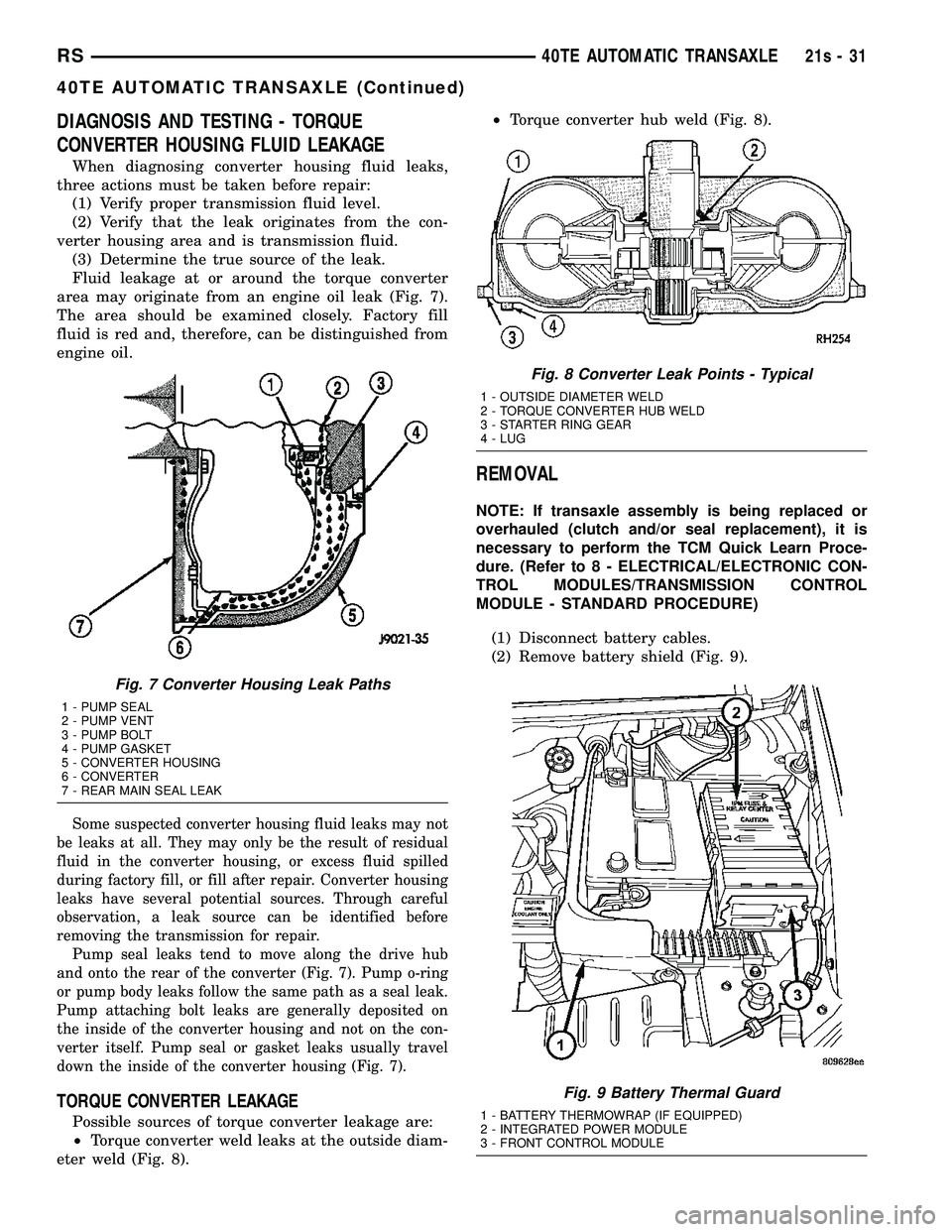
Fluid leakage at or around the torque converter
area may originate from an engine oil leak (Fig. 7).
The area should be examined closely. Factory fill
fluid is red and, therefore, can be distinguished from
engine oil.
Some suspected converter housing fluid leaks may not
be leaks at all. They may only be the result of residual
fluid in the converter housing, or excess fluid spilled
during factory fill, or fill after repair. Converter housing
leaks have several potential sources. Through careful
observation, a leak source can be identified before
removing the transmission for repair. Pump seal leaks tend to move along the drive hub
and onto the rear of the converter (Fig. 7). Pump o-ring
or pump body leaks follow the same path as a seal leak.
Pump attaching bolt leaks are generally deposited on
the inside of the converter housing and not on the con-
verter itself. Pump seal or gasket leaks usually travel
down the inside of the converter housing (Fig. 7).
TORQUE CONVERTER LEAKAGE
Possible sources of torque converter leakage are:
² Torque converter weld leaks at the outside diam-
eter weld (Fig. 8). ²
Torque converter hub weld (Fig. 8).
REMOVAL
NOTE: If transaxle assembly is being replaced or
overhauled (clutch and/or seal replacement), it is
necessary to perform the TCM Quick Learn Proce-
dure. (Refer t o 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CON-
TROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Disconnect battery cables.
(2) Remove battery shield (Fig. 9).
Fig. 7 Converter Housing Leak Paths
1 - PUMP SEAL
2 - PUMP VENT
3 - PUMP BOLT
4 - PUMP GASKET
5 - CONVERTER HOUSING
6 - CONVERTER
7 - REAR MAIN SEAL LEAK
Fig. 8 Converter Leak Points - Typical
1 - OUTSIDE DIAMETER WELD
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER HUB WELD
3 - STARTER RING GEAR
4 - LUG
Fig. 9 Battery Thermal Guard
1 - BATTERY THERMOWRAP (IF EQUIPPED)
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
RS 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s-31
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)