ignition CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2004, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004Pages: 2585, PDF Size: 62.54 MB
Page 1528 of 2585

opposite preset limit or switch point. The process
then repeats itself in the opposite direction.
Short term fuel correction will keep increasing or
decreasing injector pulse-width based upon the
upstream O2 Sensor input. The maximum range of
authority for short term memory is 25% (+/-) of base
pulse-width. Short term is violated and is lost when
ignition is turned OFF.
Long Term
The second fuel correction program is the long
term adaptive memory. In order to maintain correct
emission throughout all operating ranges of the
engine, a cell structure based on engine rpm and load
(MAP) is used.
Ther number of cells varies upon the driving con-
ditions. Two cells are used only during idle, based
upon TPS and Park/Neutral switch inputs. There
may be two other cells used for deceleration, based
on TPS, engine rpm, and vehicle speed. The other
twelve cells represent a manifold pressure and an
rpm range. Six of the cells are high rpm and the
other six are low rpm. Each of these cells has a spe-
cific MAP voltage range Typical Adaptive Memory
Fuel Cells.As the engine enters one of these cells the PCM
looks at the amount of short term correction being
used. Because the goal is to keep short term at 0 (O2
Sensor switching at 0.5 volt), long term will update
in the same direction as short term correction was
moving to bring the short term back to 0. Once short
term is back at 0, this long term correction factor is
stored in memory.
The values stored in long term adaptive memory
are used for all operating conditions, including open
loop and cold starting. However, the updating of the
long term memory occurs after the engine has
exceeded approximately 170É-190É F, with fuel control
in closed loop and two minutes of engine run time.
This is done to prevent any transitional temperature
or start-up compensations from corrupting long term
fuel correction.
Long term adaptive memory can change the pulse-
width by as much as 25%, which means it can correct
for all of short term. It is possible to have a problem
that would drive long term to 25% and short term to
another 25% for a total change of 50% away from
base pulse-width calculation.
TYPICAL ADAPTIVE MEMORY FUEL CELLS
Open
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
Throttle Idle Decel
Vacuum 20 17 13 9 5 0
Above 1,984
rpm1 3 5 7 9 11 13 Drive 15
Below 1,984
rpm02 4 6 8 1012
Neutral14
MAP volt =0 1.4 2.0 2.6 3.3 3.9
Fuel Correction Diagnostics
There are two fuel correction diagnostic routines:
²Fuel System Rich
²Fuel System Lean
A DTC is set and the MIL is illuminated if the
PCM detects either of these conditions. This is deter-
mined based on total fuel correction, short term
times long term.
PROGRAMMABLE COMMUNICATIONS
INTERFACE (PCI) BUS
DESCRIPTION
The Programmable Communication Interface Mul-
tiplex system (PCI Bus) consist of a single wire. The
Body Control Module (BCM) acts as a splice to con-
nect each module and the Data Link Connector(DLC) together. Each module is wired in parallel to
the data bus through its PCI chip set and uses its
ground as the bus reference. The wiring is a mini-
mum 20 gage wire.
OPERATION
Various modules exchange information through a
communications port called the PCI Bus. The Power-
train Control Module (PCM) transmits the Malfunc-
tion Indicator Lamp (Check Engine) On/Off signal
and engine RPM on the PCI Bus. The PCM receives
the Air Conditioning select input, transaxle gear
position inputs over the PCI Bus. The PCM also
receives the air conditioning evaporator temperature
signal from the PCI Bus.
The following components access or send informa-
tion on the PCI Bus.
RSFUEL INJECTION14-21
FUEL INJECTION (Continued)
Page 1532 of 2585

CRANKSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The 2.4L crankshaft sensor is located on the rear
of the engine near the accessory drive belt (Fig. 4).
The 3.3/3.8L crankshaft sensor is located on the rear
of the transmission housing, above the differential
housing (Fig. 5). The bottom of the sensor is posi-
tioned next to the drive plate.
OPERATION
The crankshaft position sensor detects slots cut
into the transmission driveplate extension (Fig. 6).
There are 3 sets of slots. Each set contains 4 slots,
for a total of 12 slots (Fig. 7). Basic timing is set by
the position of the last slot in each group. Once the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) senses the last
slot, it determines crankshaft position (which piston
will next be at TDC) from the camshaft position sen-
sor input. The 4 pulses generated by the crankshaft
position sensor represent the 69É, 49É, 29É, and 9É
BTDC marks. It may take the PCM one engine rev-
olution to determine crankshaft position.
The PCM uses crankshaft position reference to
determine injector sequence, ignition timing and the
presence of misfire. Once the PCM determines crank-
shaft position, it begins energizing the injectors in
sequence.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Raise vehicle and support.
(3) Disconnect the electrical connector (Fig. 8).
(4) Remove crankshaft sensor bolt (Fig. 9).
(5) Remove the crankshaft sensor.
Fig. 4 CRANKSHAFT SENSOR 2.4L
Fig. 5 CRANKSHAFT SENSOR 3.3/3.8L
Fig. 6 Crankshaft Position Sensor
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
RSFUEL INJECTION14-25
Page 1535 of 2585

(3) Disconnect injector wiring connector from injec-
tor.
(4) Position fuel rail assembly so that the fuel
injectors are easily accessible (Fig. 13).
(5) Rotate injector and pull injector out of fuel rail.
The clip will stay on the injector.
(6) Check injector O-ring for damage. If O-ring is
damaged, it must be replaced. If injector is reused, a
protective cap must be installed on the injector tip to
prevent damage. Replace the injector clip if it is dam-
aged.
(7) Repeat for remaining injectors.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
The fuel rail must be removed first. Refer to Fuel
Injector Rail Removal in this section.
(1) Before installing an injector the rubber O-ring
must be lubricated with a drop of clean engine oil to
aid in installation.
(2) Install injector clip by sliding open end into the
top slot of the injector. The edge of the receiver cup
will slide into the side slots of clip.
(3) Install injector top end into fuel rail receiver
cap. Be careful not to damage O-ring during installa-
tion (Fig. 14).
(4) Repeat steps for remaining injectors.
(5) Connect fuel injector wiring.
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Before installing an injector the rubber O-ring
must be lubricated with a drop of clean engine oil to
aid in installation.(2) Install injector clip by sliding open end into the
top slot of the injector. The edge of the receiver cup
will slide into the side slots of clip (Fig. 13).
(3) Install injector top end into fuel rail receiver
cap. Be careful not to damage O-ring during installa-
tion (Fig. 13).
(4) Repeat steps for remaining injectors.
(5) Install fuel rail, refer to Fuel Rail in the Fuel
Delivery section.
(6) Connect fuel injector wiring.
(7) Install the Intake Manifold, (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION)
(8) Connect the negative battery cable.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The fuel pump relay is located in the PDC. The
inside top of the PDC cover has a label showing relay
and fuse location.
OPERATION
The fuel pump relay supplies battery voltage to the
fuel pump. A buss bar in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC) supplies voltage to the solenoid side and
contact side of the relay. The fuel pump relay power
circuit contains a fuse between the buss bar in the
PDC and the relay. The fuse is located in the PDC.
Refer to the Wiring Diagrams for circuit information.
The PCM controls the fuel pump relay by switch-
ing the ground path for the solenoid side of the relay
on and off. The PCM turns the ground path off when
the ignition switch is in the Off position. When the
ignition switch is in the On position, the PCM ener-
gizes the fuel pump. If the crankshaft position sensor
does not detect engine rotation, the PCM de-ener-
gizes the relay after approximately one second.
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The idle air control valve is mounted on the throt-
tle body. The PCM operates the idle air control valve
(Fig. 15) or (Fig. 16).
OPERATION
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed through the
idle air control valve to compensate for engine load,
coolant temperature or barometric pressure changes.
The throttle body has an air bypass passage that
provides air for the engine during closed throttle idle.
The idle air control valve regulates air flow through
the bypass passage.
Fig. 14 SERVICING FUEL INJECTOR TYPICAL
1 - FUEL INJECTOR
2 - LOCKING SLOT
3 - FUEL RAIL RECEIVER CUP
14 - 28 FUEL INJECTIONRS
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 1543 of 2585

neously then gently pull the throttle cable from
throttle bracket or if it is the slide snap design you
have to slide the locking tab out of the hole and then
slide the cable assembly out of the bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) From the engine compartment, push the hous-
ing end fitting and grommet into the dash panel.In-
stall gromment into the dash panel.
(2) Install the cable housing (throttle body end)
into the cable mounting bracket on the engine.
(3) From inside the vehicle, hold up the pedal and
install throttle cable and cable retainer in the upper
end of the pedal shaft.
(4) At the dash panel, install the cable retainer
clip between the end of the throttle cable fitting and
grommet
(5) From the engine compartment, rotate the
throttle lever wide open and install the throttle
cable.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The throttle position sensor mounts to the side of
the throttle body (Fig. 30) or (Fig. 31).The sensor
connects to the throttle blade shaft. The TPS is a
variable resistor that provides the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM) with an input signal (voltage).
OPERATION
The signal represents throttle blade position. As
the position of the throttle blade changes, the resis-
tance of the TPS changes.
The PCM supplies approximately 5 volts to the
TPS. The TPS output voltage (input signal to the
powertrain control module) represents throttle blade
position. The TPS output voltage to the PCM varies
from approximately 0.6 volt at minimum throttle
opening (idle) to a maximum of 4.5 volts at wide open
throttle.
Along with inputs from other sensors, the PCM
uses the TPS input to determine current engine oper-
ating conditions. The PCM also adjusts fuel injector
pulse width and ignition timing based on these
inputs.
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Remove the electrical connector from the Inlet
Air Temperature sensor.
(3) Remove the air cleaner box lid. Remove hose
from throttle body.
(4) Disconnect the electrical connector at TPS.
(5) Disconnect the electrical connector at IAC.
(6) Remove the throttle and speed control cables
from throttle body.
(7) Remove 3 mounting bolts from throttle body.
(8) Remove throttle body.
(9) Disconnect the purge vacuum line from the
throttle body.
(10) Remove TPS from throttle body.
Fig. 30 Throttle Position SensorÐ2.4L Engine
1 - Idle Air Control Valve
2 - Throttle Position Sensor
Fig. 31 Throttle Position SensorÐ3.3/3.8L Engine
1 - Idle Air Control Valve
2 - Throttle Position Sensor
14 - 36 FUEL INJECTIONRS
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE (Continued)
Page 1555 of 2585
COLUMN
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COLUMN
DESCRIPTION - STEERING COLUMN.......10
WARNING
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS.............10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STEERING
COLUMN............................12
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................13
SPECIFICATIONS
COLUMN TORQUE....................14
IGNITION SWITCH
REMOVAL.............................14
INSTALLATION.........................16
LOCK CYLINDER HOUSING
DESCRIPTION - IGNITION INTERLOCK......17
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................19KEY/LOCK CYLINDER
DESCRIPTION.........................20
OPERATION...........................20
REMOVAL.............................20
INSTALLATION.........................20
GEAR SHIFT LEVER
REMOVAL.............................21
INSTALLATION.........................21
SHROUD - LOWER
REMOVAL.............................21
INSTALLATION.........................22
SHROUD - UPPER
REMOVAL.............................23
INSTALLATION.........................23
STEERING WHEEL
REMOVAL.............................23
INSTALLATION.........................24
COLUMN
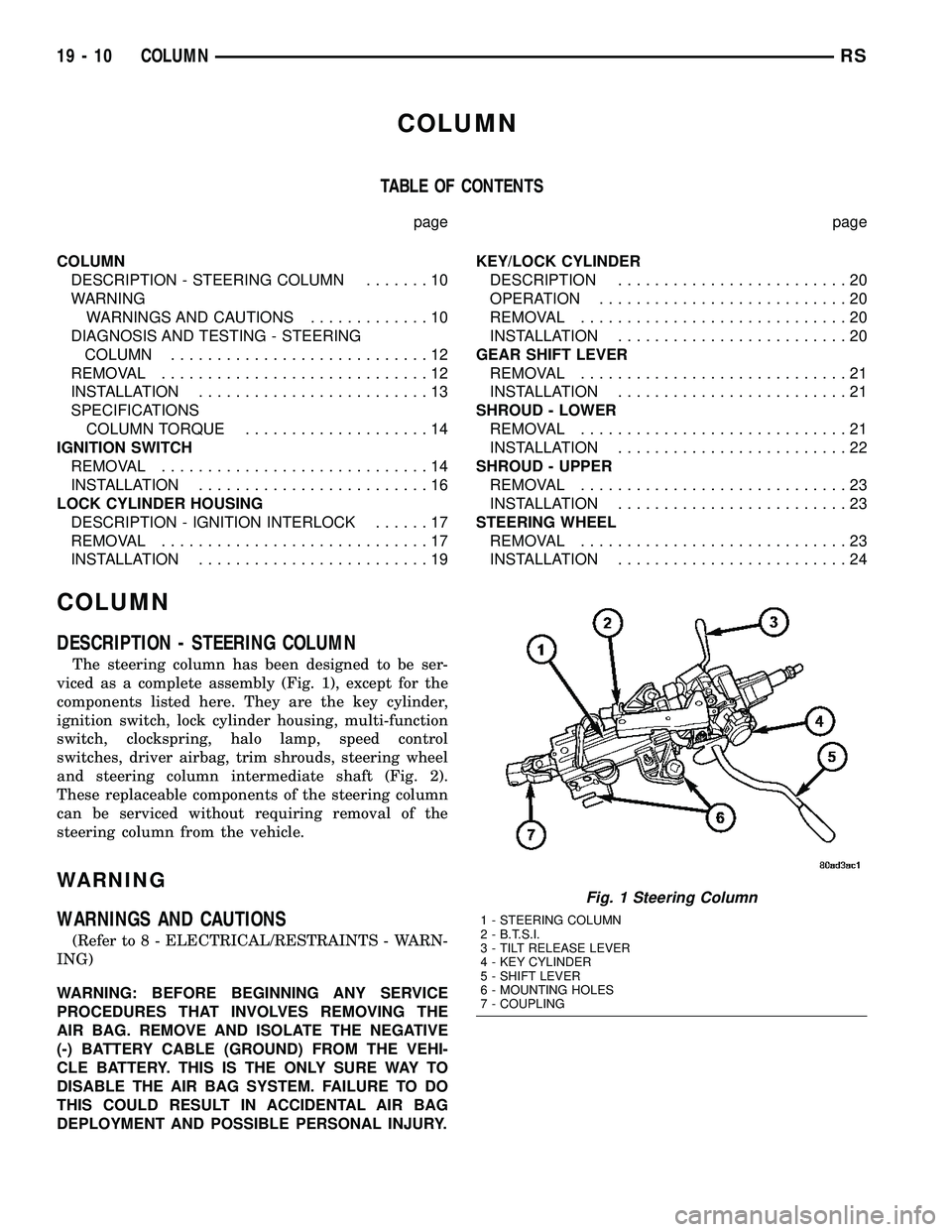
DESCRIPTION - STEERING COLUMN
The steering column has been designed to be ser-
viced as a complete assembly (Fig. 1), except for the
components listed here. They are the key cylinder,
ignition switch, lock cylinder housing, multi-function
switch, clockspring, halo lamp, speed control
switches, driver airbag, trim shrouds, steering wheel
and steering column intermediate shaft (Fig. 2).
These replaceable components of the steering column
can be serviced without requiring removal of the
steering column from the vehicle.
WARNING
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS - WARN-
ING)
WARNING: BEFORE BEGINNING ANY SERVICE
PROCEDURES THAT INVOLVES REMOVING THE
AIR BAG. REMOVE AND ISOLATE THE NEGATIVE
(-) BATTERY CABLE (GROUND) FROM THE VEHI-
CLE BATTERY. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO
DISABLE THE AIR BAG SYSTEM. FAILURE TO DO
THIS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR BAG
DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
Fig. 1 Steering Column
1 - STEERING COLUMN
2 - B.T.S.I.
3 - TILT RELEASE LEVER
4 - KEY CYLINDER
5 - SHIFT LEVER
6 - MOUNTING HOLES
7 - COUPLING
19 - 10 COLUMNRS
Page 1557 of 2585

WARNING: THE AIR BAG SYSTEM IS A SENSITIVE,
COMPLEX ELECTRO-MECHANICAL UNIT. BEFORE
ATTEMPTING TO DIAGNOSE, REMOVE OR INSTALL
THE AIR BAG SYSTEM COMPONENTS YOU MUST
FIRST DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY
NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE. THEN WAIT TWO
MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DIS-
CHARGE. FAILURE TO DO SO COULD RESULT IN
ACCIDENTAL DEPLOYMENT OF THE AIR BAG AND
POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY. THE FASTENERS,
SCREWS, AND BOLTS, ORIGINALLY USED FOR
THE AIR BAG COMPONENTS, HAVE SPECIAL
COATINGS AND ARE SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED
FOR THE AIR BAG SYSTEM. THEY MUST NEVER
BE REPLACED WITH ANY SUBSTITUTES. ANYTIME
A NEW FASTENER IS NEEDED, REPLACE WITH
THE CORRECT FASTENERS PROVIDED IN THE
SERVICE PACKAGE OR FASTENERS LISTED IN
THE PARTS BOOKS.
WARNING: SAFETY GOGGLES SHOULD BE WORN
AT ALL TIMES WHEN WORKING ON STEERING
COLUMNS.
CAUTION: Disconnect negative (ground) cable from
the battery before servicing any column compo-
nent.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to remove the pivot pins
to disassemble the tilting mechanism. Damage will
occur.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STEERING
COLUMN
For diagnosis of conditions relating to the steering
column (Refer to 19 - STEERING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING) and (Refer to 19 - STEERING - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING).
REMOVAL
NOTE: Before proceeding, (Refer to 19 - STEERING/
COLUMN - WARNING).
(1) Make sure the front wheels of the vehicle are
in the STRAIGHT AHEAD position before beginning
the column removal procedure.
(2) Disconnect negative (ground) cable from the
battery and isolate cable from battery terminal.
(3) Remove the lower shroud (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/COLUMN/LOWER SHROUD - REMOV-
AL).
(4) Remove the traction off switch.
(5) Remove the upper shroud.
(6) Remove the cluster trim bezel (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/CLUSTER BEZEL -
REMOVAL).
(7) Remove the knee blocker (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INSTRUMENT PANEL/STEERING COLUMN
OPENING COVER - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove the parking brake handle link.
(9) Remove the knee blocker reinforcement (Refer
to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/KNEE
BLOCKER - REMOVAL).
(10) Remove the airbag (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/RESTRAINTS/DRIVER AIRBAG - REMOVAL).
(11) Remove the steering wheel retaining nut.
(12) Remove the vibration damper weight.
(13) Remove the steering wheel (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/COLUMN/STEERING WHEEL -
REMOVAL). (Fig. 3)
(14) Disconnect the wiring harness connectors
from the clockspring, multi-function switch, halo
lamp, SKIM module, ignition switch and BTSI sole-
noid.
(15) Disconnect the shift cable at the lever. (Fig. 4)
(16) Remove the pinch side clip, then remove the
cable from the bracket on the column.
(17) Remove the pinch bolt coupling. (Fig. 5)
(18) Loosen the two lower mounting nuts.
(19) Remove the two upper mounting nuts
(20) Remove the steering column.
1 - CLOCKSPRING WIRING
2 - STEERING WHEEL
3 - UPPER SHROUD
4 - FIXED SHROUD
5 - SCREW
6 - STEERING COLUMN MOUNTING PLATE
7 - NUT
8 - DASH PANEL STEERING COLUMN MOUNTING BRACKET
9 - STUDS (4)
10 - STEERING COLUMN LOCKING PIN
11 - NUT/WASHER ASSEMBLY
12 - STEERING COLUMN ASSEMBLY
13 - LOWER SHROUD
14 - SCREWS
15 - STEERING WHEEL RETAINING NUT16 - STEERING WHEEL DAMPER
17 - CLOCKSPRING
18 - SCREW
19 - MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH
20 - PINCH BOLT
21 - STEERING COLUMN COUPLER
22 - PINCH BOLT RETAINING PIN
23 - DASH PANEL
24 - SILENCER SHELL
25 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT SHIELD AND SEAL
26 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
27 - ROLL PIN
28 - POWER STEERING GEAR
29 - FRONT SUSPENSION CRADLE/CROSSMEMBER
19 - 12 COLUMNRS
COLUMN (Continued)
Page 1558 of 2585
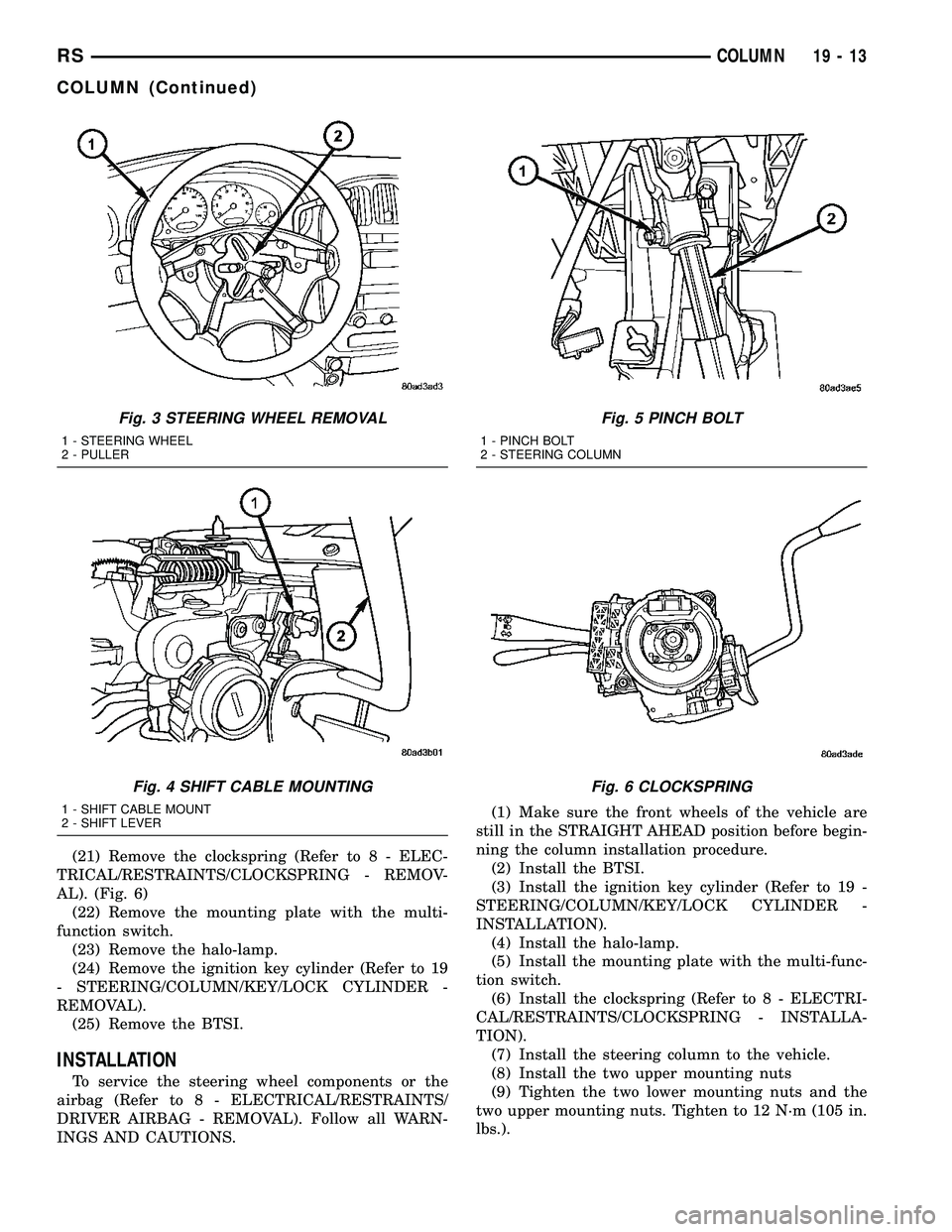
(21) Remove the clockspring (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/RESTRAINTS/CLOCKSPRING - REMOV-
AL). (Fig. 6)
(22) Remove the mounting plate with the multi-
function switch.
(23) Remove the halo-lamp.
(24) Remove the ignition key cylinder (Refer to 19
- STEERING/COLUMN/KEY/LOCK CYLINDER -
REMOVAL).
(25) Remove the BTSI.
INSTALLATION
To service the steering wheel components or the
airbag (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/
DRIVER AIRBAG - REMOVAL). Follow all WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS.(1) Make sure the front wheels of the vehicle are
still in the STRAIGHT AHEAD position before begin-
ning the column installation procedure.
(2) Install the BTSI.
(3) Install the ignition key cylinder (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/COLUMN/KEY/LOCK CYLINDER -
INSTALLATION).
(4) Install the halo-lamp.
(5) Install the mounting plate with the multi-func-
tion switch.
(6) Install the clockspring (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/RESTRAINTS/CLOCKSPRING - INSTALLA-
TION).
(7) Install the steering column to the vehicle.
(8) Install the two upper mounting nuts
(9) Tighten the two lower mounting nuts and the
two upper mounting nuts. Tighten to 12 N´m (105 in.
lbs.).
Fig. 3 STEERING WHEEL REMOVAL
1 - STEERING WHEEL
2 - PULLER
Fig. 4 SHIFT CABLE MOUNTING
1 - SHIFT CABLE MOUNT
2 - SHIFT LEVER
Fig. 5 PINCH BOLT
1 - PINCH BOLT
2 - STEERING COLUMN
Fig. 6 CLOCKSPRING
RSCOLUMN19-13
COLUMN (Continued)
Page 1559 of 2585
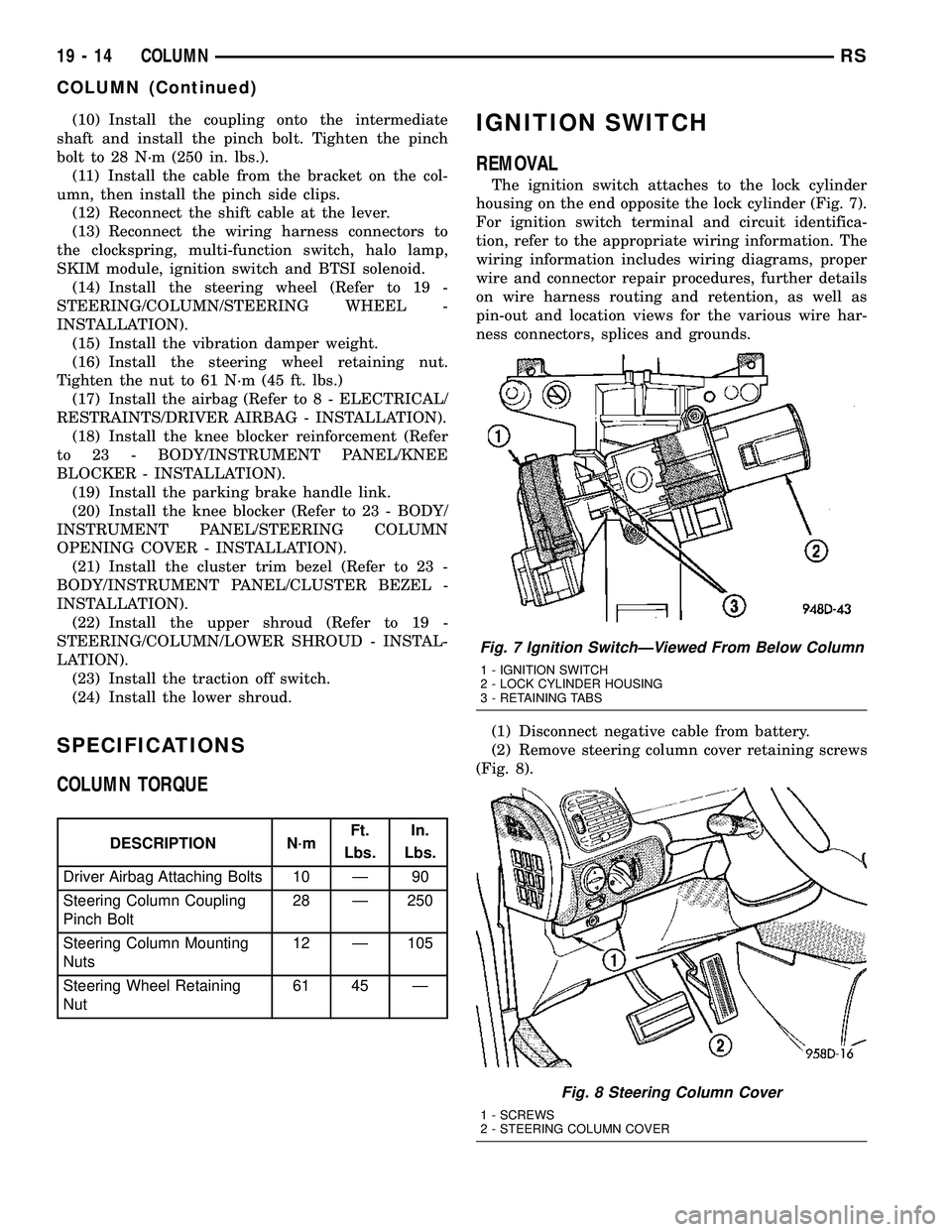
(10) Install the coupling onto the intermediate
shaft and install the pinch bolt. Tighten the pinch
bolt to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(11) Install the cable from the bracket on the col-
umn, then install the pinch side clips.
(12) Reconnect the shift cable at the lever.
(13) Reconnect the wiring harness connectors to
the clockspring, multi-function switch, halo lamp,
SKIM module, ignition switch and BTSI solenoid.
(14) Install the steering wheel (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/COLUMN/STEERING WHEEL -
INSTALLATION).
(15) Install the vibration damper weight.
(16) Install the steering wheel retaining nut.
Tighten the nut to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.)
(17) Install the airbag (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
RESTRAINTS/DRIVER AIRBAG - INSTALLATION).
(18) Install the knee blocker reinforcement (Refer
to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/KNEE
BLOCKER - INSTALLATION).
(19) Install the parking brake handle link.
(20) Install the knee blocker (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INSTRUMENT PANEL/STEERING COLUMN
OPENING COVER - INSTALLATION).
(21) Install the cluster trim bezel (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/CLUSTER BEZEL -
INSTALLATION).
(22) Install the upper shroud (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/COLUMN/LOWER SHROUD - INSTAL-
LATION).
(23) Install the traction off switch.
(24) Install the lower shroud.
SPECIFICATIONS
COLUMN TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´mFt.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Driver Airbag Attaching Bolts 10 Ð 90
Steering Column Coupling
Pinch Bolt28 Ð 250
Steering Column Mounting
Nuts12 Ð 105
Steering Wheel Retaining
Nut61 45 Ð
IGNITION SWITCH
REMOVAL
The ignition switch attaches to the lock cylinder
housing on the end opposite the lock cylinder (Fig. 7).
For ignition switch terminal and circuit identifica-
tion, refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, further details
on wire harness routing and retention, as well as
pin-out and location views for the various wire har-
ness connectors, splices and grounds.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove steering column cover retaining screws
(Fig. 8).
Fig. 7 Ignition SwitchÐViewed From Below Column
1 - IGNITION SWITCH
2 - LOCK CYLINDER HOUSING
3 - RETAINING TABS
Fig. 8 Steering Column Cover
1 - SCREWS
2 - STEERING COLUMN COVER
19 - 14 COLUMNRS
COLUMN (Continued)
Page 1560 of 2585
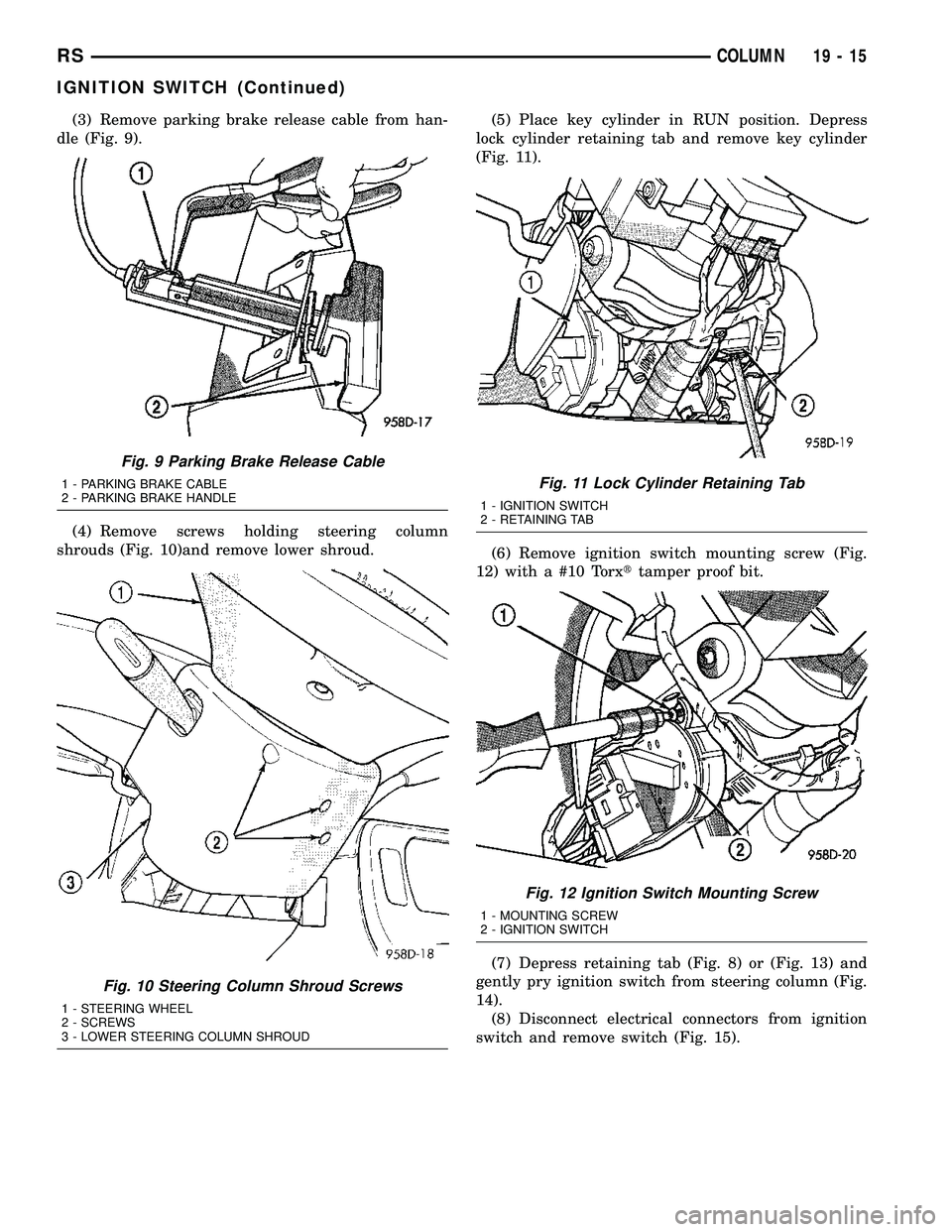
(3) Remove parking brake release cable from han-
dle (Fig. 9).
(4) Remove screws holding steering column
shrouds (Fig. 10)and remove lower shroud.(5) Place key cylinder in RUN position. Depress
lock cylinder retaining tab and remove key cylinder
(Fig. 11).
(6) Remove ignition switch mounting screw (Fig.
12) with a #10 Torxttamper proof bit.
(7) Depress retaining tab (Fig. 8) or (Fig. 13) and
gently pry ignition switch from steering column (Fig.
14).
(8) Disconnect electrical connectors from ignition
switch and remove switch (Fig. 15).
Fig. 9 Parking Brake Release Cable
1 - PARKING BRAKE CABLE
2 - PARKING BRAKE HANDLE
Fig. 10 Steering Column Shroud Screws
1 - STEERING WHEEL
2 - SCREWS
3 - LOWER STEERING COLUMN SHROUD
Fig. 11 Lock Cylinder Retaining Tab
1 - IGNITION SWITCH
2 - RETAINING TAB
Fig. 12 Ignition Switch Mounting Screw
1 - MOUNTING SCREW
2 - IGNITION SWITCH
RSCOLUMN19-15
IGNITION SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1561 of 2585

INSTALLATION
The ignition switch attaches to the lock cylinder
housing on the end opposite the lock cylinder (Fig. 7)
. For ignition switch terminal and circuit identifica-
tion, refer to the Wiring Diagrams section.
(1) Ensure the ignition switch is in the RUN posi-
tion and the actuator shaft in the lock housing is in
the RUN position.
(2) Install electrical connectors to ignition switch.
(3) Carefully install the ignition switch. The
switch will snap over the retaining tabs (Fig. 16) .
Install mounting screw (Fig. 12).
(4) Install upper and lower shrouds.(5) Install key cylinder (cylinder retaining tab will
depress only in the RUN position).
(6) Connect negative cable to battery.
(7) Check for proper operation of ignition switch
and key-in warning switch.
Fig. 13 Ignition Switch Retaining Tab
1 - IGNITION SWITCH
2 - RETAINING TAB
Fig. 14 Removing Ignition Switch
1 - IGNITION SWITCH
2 - RETAINING TAB
Fig. 15 Ignition Switch Connectors
1 - KEY IN SWITCH
2 - PRNDL SWITCH
3 - IGNITION SWITCH
Fig. 16 Ignition Switch Installation
1 - IGNITION SWITCH
2 - ACTUATOR SHAFT
3 - RETAINING TABS
19 - 16 COLUMNRS
IGNITION SWITCH (Continued)