acc DAEWOO LACETTI 2004 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: LACETTI, Model: DAEWOO LACETTI 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 1135 of 2643
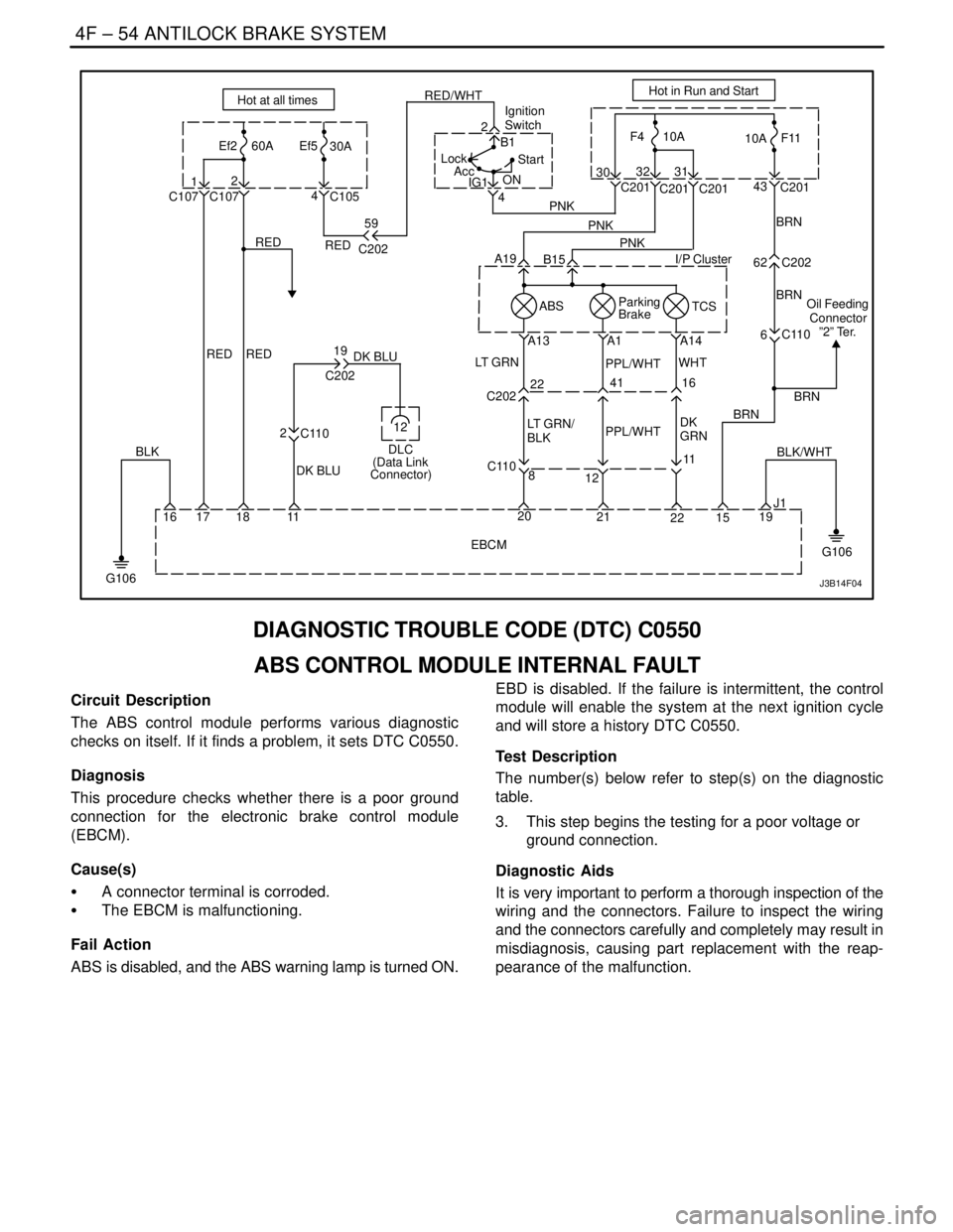
4F – 54IANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
J3B14F04
60A Ef230A Ef5
2
42
C107 C105
2
C110
G106
A19
A13 A1 A14
C110 C202
C202WHT LT GRN
DK
GRN LT GRN/
BLK
BLK
DK BLUDK BLU
PPL/WHT
PPL/WHT ABS
TCS Parking
Brake
Hot at all times
RED REDRED/WHT
Ignition
Switch
RED
RED
I/P Cluster
EBCM8
20
22 2216 41
1211
18 1621
1
C107
10A F410AF11
32 31
43
6 62 C201
C201 C201C201
C110 C202
Hot in Run and Start
30
4
1711
C202
15
B15
DLC
(Data Link
Connector)12
G106
BLK/WHTOil Feeding
Connector
”2” Ter.
BRNBRN BRN
BRN PNK PNK PNK
19J1
59B1
ONStart Lock
Acc
IG1
19
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) C0550
ABS CONTROL MODULE INTERNAL FAULT
Circuit Description
The ABS control module performs various diagnostic
checks on itself. If it finds a problem, it sets DTC C0550.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks whether there is a poor ground
connection for the electronic brake control module
(EBCM).
Cause(s)
S A connector terminal is corroded.
S The EBCM is malfunctioning.
Fail Action
ABS is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is turned ON.EBD is disabled. If the failure is intermittent, the control
module will enable the system at the next ignition cycle
and will store a history DTC C0550.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
3. This step begins the testing for a poor voltage or
ground connection.
Diagnostic Aids
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of the
wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the wiring
and the connectors carefully and completely may result in
misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with the reap-
pearance of the malfunction.
Page 1137 of 2643
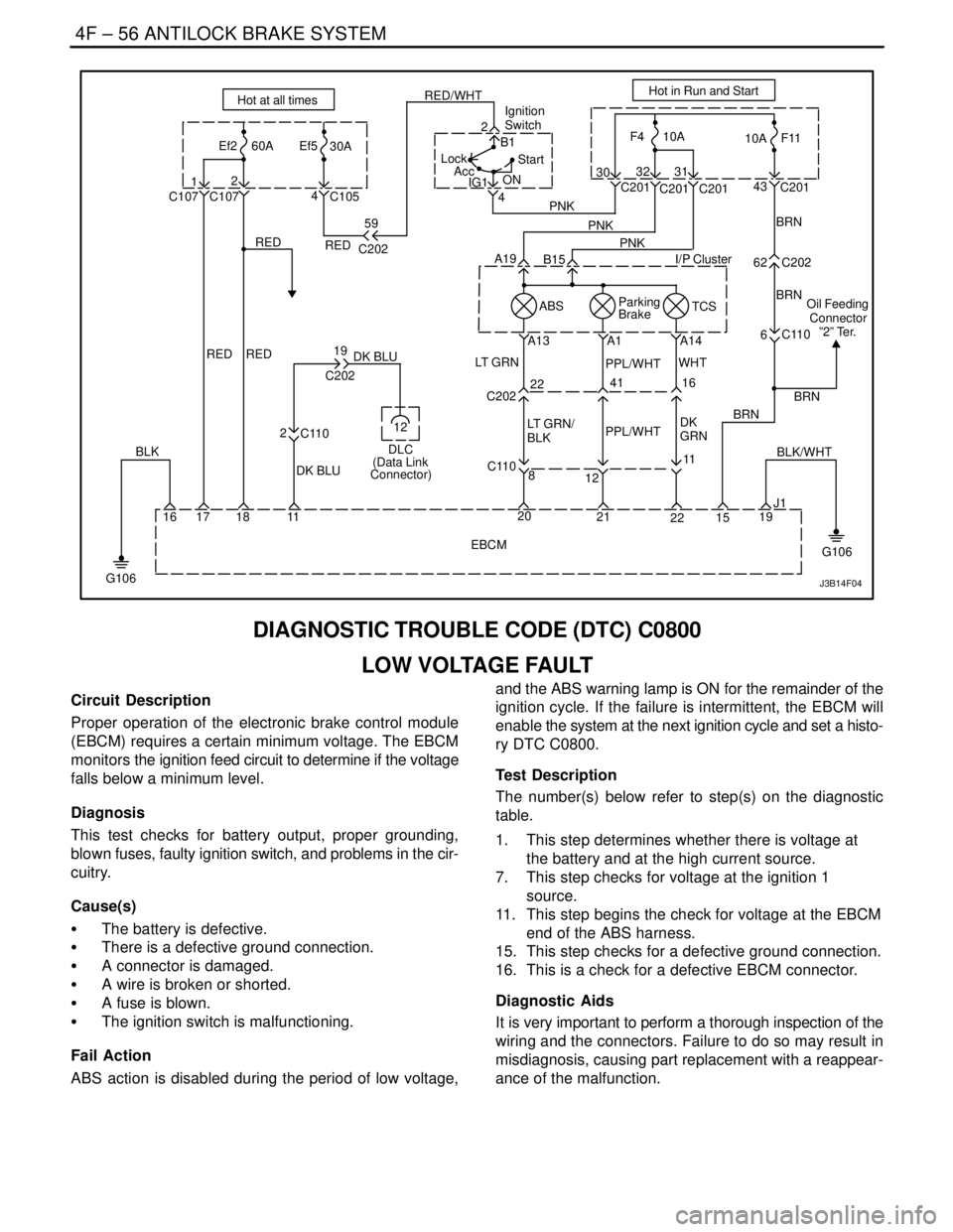
4F – 56IANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
J3B14F04
60A Ef230A Ef5
2
42
C107 C105
2
C110
G106
A19
A13 A1 A14
C110 C202
C202WHT LT GRN
DK
GRN LT GRN/
BLK
BLK
DK BLUDK BLU
PPL/WHT
PPL/WHT ABS
TCS Parking
Brake
Hot at all times
RED REDRED/WHT
Ignition
Switch
RED
RED
I/P Cluster
EBCM8
20
22 2216 41
1211
18 1621
1
C107
10A F410AF11
32 31
43
6 62 C201
C201 C201C201
C110 C202
Hot in Run and Start
30
4
1711
C202
15
B15
DLC
(Data Link
Connector)12
G106
BLK/WHTOil Feeding
Connector
”2” Ter.
BRNBRN BRN
BRN PNK PNK PNK
19J1
59B1
ONStart Lock
Acc
IG1
19
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) C0800
LOW VOLTAGE FAULT
Circuit Description
Proper operation of the electronic brake control module
(EBCM) requires a certain minimum voltage. The EBCM
monitors the ignition feed circuit to determine if the voltage
falls below a minimum level.
Diagnosis
This test checks for battery output, proper grounding,
blown fuses, faulty ignition switch, and problems in the cir-
cuitry.
Cause(s)
S The battery is defective.
S There is a defective ground connection.
S A connector is damaged.
S A wire is broken or shorted.
S A fuse is blown.
S The ignition switch is malfunctioning.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled during the period of low voltage,and the ABS warning lamp is ON for the remainder of the
ignition cycle. If the failure is intermittent, the EBCM will
enable the system at the next ignition cycle and set a histo-
ry DTC C0800.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. This step determines whether there is voltage at
the battery and at the high current source.
7. This step checks for voltage at the ignition 1
source.
11. This step begins the check for voltage at the EBCM
end of the ABS harness.
15. This step checks for a defective ground connection.
16. This is a check for a defective EBCM connector.
Diagnostic Aids
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of the
wiring and the connectors. Failure to do so may result in
misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with a reappear-
ance of the malfunction.
Page 1141 of 2643

4F – 60IANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR
ON–VEHICLE SERVICE
SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
CAUTION : Brake fluid may irritate eyes and skin. In
case of contact, take the following actions:
S Eye contact – rinse thoroughly with water.
S Skin contact – wash with soap and water.
S Ingestion – consult a physician immediately.
CAUTION : To help avoid personal injury due to poor
braking, DO NOT tap into the vehicle’s brake system
to operate a trailer brake system.
Notice : When fasteners are removed, always reinstall
them at the same location from which they were removed.
If a fastener needs to be replaced, use the correct part
number fastener for that application. If the correct part
number fastener is not available, a fastener of equal size
and strength (or stronger) may be used. Fasteners that
are not reused, and those requiring thread–locking com-
pound will be called out. The correct torque values must
be used when installing fasteners that require them. If the
above procedures are not followed, parts or system dam-
age could result.
Notice : Use only DOT 3 equivalent hydraulic brake fluid.
The use of DOT 5 (silicone) brake fluid is not recom-
mended. Reduced brake performance or durability may
result.
Notice : Avoid spilling brake fluid on any of the vehicle’s
painted surfaces, wiring, cables, or electrical connectors.
Brake fluid will damage paint and electrical connections.
If any fluid is spilled on the vehicle, flush the area with wa-
ter to lessen the damage.
Computer System Service Precautions
Take care to avoid electronic brake control module
(EBCM) circuit overloading. In testing for opens or shorts,
do not ground or apply voltage to any circuit unless
instructed to do so by the diagnostic procedure. Test cir-
cuits only with a high–impedance multimeter. Never re-
move or apply power to any control module with the igni-
tion switch in the ON position. Always turn the ignition to
the OFF position before removing or connecting battery
cables, fuses, or connectors.
General Service Precautions
S Disconnect the EBCM connector before performing
any vehicle welding work using an electric arc weld-
er.
S Do not attempt to disassemble any component des-
ignated as nonserviceable. The hydraulic modulator
and the EBCM can be separated from each other
and replaced separately but cannot be serviced.
They have no replaceable parts, and there is no
access to the components they contain.
Page 1146 of 2643

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 4F – 65
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND SYSTEM
OPERATION
BASIC KNOWLEDGE REQUIRED
Before using this section, it is important that you have a ba-
sic knowledge of the following items. Without this knowl-
edge, it will be difficult to use the diagnostic procedures
contained in this section.
S Basic Electrical Circuits : You should understand
the basic theory of electricity and know the mean-
ing of voltage, current (amps), and resistance
(ohms). You should understand what happens in a
circuit with an open or shorted wire. You should be
able to read and understand a wiring diagram.
S Use of Circuit Testing Tools : You should know how
to use a test light and how to bypass components
to test circuits using fused jumper wires. You should
be familiar with a digital multimeter. You should be
able to measure voltage, resistance, and current,
and be familiar with the controls and how to use
them correctly.
ABS SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The ABS 5.3 Antilock Braking System (ABS) consists of
a conventional hydraulic brake system plus antilock com-
ponents. The conventional brake system includes a vacu-
um booster, master cylinder, front disc brakes, rear lead-
ing/trailing drum brakes, interconnecting hydraulic brake
pipes and hoses, brake fluid level sensor and the BRAKE
indicator.
The ABS components include a hydraulic unit, an elec-
tronic brake control module (EBCM), two system fuses,
four wheel speed sensors (one at each wheel), intercon-
necting wiring, the ABS indicator, the EBD indicator (which
is connected to the parking lamp) and the rear disk brakes.
See “ABS Component Locator” in this section for the gen-
eral layout of this system.
The hydraulic unit with the attached EBCM is located be-
tween the surge tank and the fire wall on the left side of the
vehicle.
The basic hydraulic unit configuration consists of hydraulic
check valves, two solenoid valves for each wheel, a hy-
draulic pump, two accumulators, and two damper. The hy-
draulic unit controls hydraulic pressure to the front calipers
and rear wheel cylinders by modulating hydraulic pressure
to prevent wheel lockup.
Nothing in the hydraulic unit or the EBCM is serviceable.
In the event of any failure, the entire ABS unit with at-
tached EBCM must be replaced. For more information, re-
fer to ”Base Braking Mode” and ”Antilock Braking Mode”
in this section.
BASE BRAKING MODE
The baseline braking mode of the ABS 5.3 system used
in this vehicle is a diagonal split system. In this system,
one master cylinder circuit supplies pressure to the right
front and the left rear brakes; the other circuit supplies
pressure to the left front and the right rear brakes. All
valves in the hydraulic modulator are in their normal, non–
energized positions as shown in the drawings found in
”ABS System Components” in this section.
Page 1147 of 2643
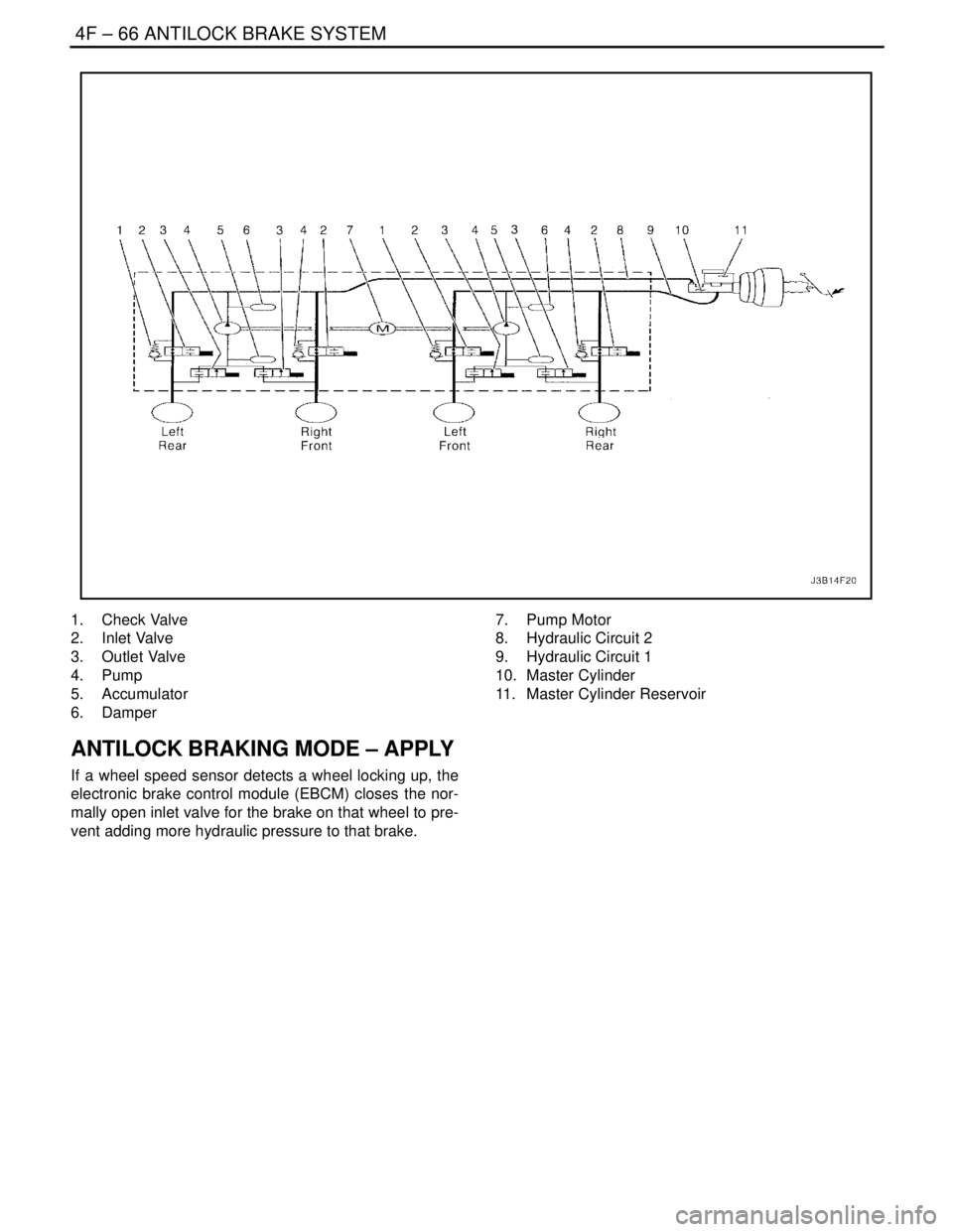
4F – 66IANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
1. Check Valve
2. Inlet Valve
3. Outlet Valve
4. Pump
5. Accumulator
6. Damper7. Pump Motor
8. Hydraulic Circuit 2
9. Hydraulic Circuit 1
10. Master Cylinder
11. Master Cylinder Reservoir
ANTILOCK BRAKING MODE – APPLY
If a wheel speed sensor detects a wheel locking up, the
electronic brake control module (EBCM) closes the nor-
mally open inlet valve for the brake on that wheel to pre-
vent adding more hydraulic pressure to that brake.
Page 1350 of 2643

SECTION : 5A1
ZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CAUTION : Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool
or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable will help
prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in LOCK unless otherwise noted.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION5A1–3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ZF 4HP 16 Automatic Transaxle 5A1–3. . . . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Components 5A1–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SPECIFICATIONS5A1–5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Specifications 5A1–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Gear Ratio 5A1–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fluid Capacity 5A1–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fastener Tightening Specifications 5A1–5. . . . . . . . . .
Shift Speed Chart 5A1–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Line Pressure 5A1–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SPECIAL TOOLS5A1–9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Special Tools Table 5A1–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SCHEMATIC AND ROUTING DIAGRAMS5A1–11 . . .
Transaxle Control Module (1 of 2) 5A1–11. . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Control Module (2 of 2) 5A1–12. . . . . . . . . .
Shift Mode Diagram 5A1–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Flow Diagram 5A1–17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
COMPONENT LOCATOR5A1–33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Identification Information 5A1–33. . . . . . . .
Torque Converter 5A1–34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Housing 5A1–35. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Oil Pump 5A1–36. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rear Cover & Oil Pan Cover 5A1–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Parking Lever 5A1–38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input Shaft & Shift Gear 5A1–39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Valve Body 5A1–41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Gear Shift Control 5A1–42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION AND PROCEDURES
DIAGNOSIS5A1–43 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Basic Knowledge Required 5A1–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Functional Check Procedure 5A1–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Line Pressure Check Procedure 5A1–43. . . . . . . . . . .
Clutch Plate Diagnosis 5A1–45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cooler Flushing and Flow Test 5A1–45. . . . . . . . . . . . . Transaxle Fluid Level Service Procedure 5A1–45. . . .
Electrical/Garage Shift Test 5A1–47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Road Test Procedure 5A1–47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Torque Converter Lock–Up Clutch(TCC)
Diagnosis 5A1–48. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TCM Initialization Procedure 5A1–50. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Shift Speed Chart 5A1–51. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Internal Wiring Harness Check 5A1–51. . . . . . . . . . . .
Transaxle Wiring Harness Connector 5A1–54. . . . . . .
Symptom Diagnosis 5A1–56. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS5A1–60
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Identification 5A1–60
DTC P0562 – System Voltage Low 5A1–68. . . . . . . . .
DTC P0563 – System Voltage High 5A1–71. . . . . . . .
DTC P0601 – Internal Control Module Memory
Checksum Error 5A1–74. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0603 – Internal Control Module Keep
Alive Memory(KAM) Error 5A1–76. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0604 – Internal Control Module Random
Access Memory(RAM) Error 5A1–78. . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0606 – Transaxle Control Module
Processor Fault 5A1–80. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0703 – Brake Switch Circuit
Malfunction 5A1–83. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0705 – Transmission Range Sensor
Circuit Malfunction(PRNDL Input) 5A1–86. . . . . . . .
DTC P0710 – Transmission Fluid Temperature
Sensor Circuit Malfunction 5A1–89. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0715 – Input Speed Sensor(ISS) Circuit
Malfunction 5A1–92. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0716 – Input Speed Sensor(ISS) Circuit
Range/Performance 5A1–95. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0717 – Input Speed Sensor(ISS) Circuit
No Signal 5A1–98. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0720 – Output Speed Sensor(OSS)
Circuit Malfunction 5A1–101. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0721 – Output Speed Sensor(OSS)
Circuit Range/Performance 5A1–104. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 1352 of 2643

ZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A1 – 3
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Important Measurement/Adjustment 5A1–230. . . . . . .
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND SYSTEM
OPERATION5A1–232 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Mechanical Components 5A1–232. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electronical Components 5A1–236. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TCM Inputs That Affect the 4HP 16
Transaxle 5A1–241. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
INTRODUCTION
ZF 4HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
The ZF 4 HP 16 is a four–speed automatic transaxle de-
signed for cars with front–wheel drive and a transversely
mounted engine.
The transaxle has a hydrodynamic torque converter with
a controlled slip lock–up clutch.
A planetary gear train establishes the mechanical gear ra-
tios. The integral constant ratio can be adapted to the en-
gine’s power output and the vehicle’s weight. The elec-
tronic–hydraulic control makes controlled power shifts and
various shift programs possible. In selector lever position
”P”, the output is locked mechanically.The special feature of this transaxle is that it operates with-
out freewheels. Shifting between individual gears takes
place by means of overlapping clutch engagement and re-
lease.
The advantage of overlap shifting is as follows:
– The transaxle can be of more compact design
and is lighter on account of the absence of free-
wheels and the lower number of shift elements
– Lower drag losses, i.e. higher efficiency
– Lower peak torques acting on the components
and driveline.
However, overlap shifting necessitates high–performance
hardware and software, and precision engine signals.
Page 1392 of 2643

ZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A1 – 43
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION AND
PROCEDURES DIAGNOSIS
BASIC KNOWLEDGE REQUIRED
You must be familiar with some basic electronics to use
this section of the Service Manual. They will help you to
follow diagnostic procedures.
Notice : Lack of the basic knowledge of this transaxle
when performing diagnostic procedures could result in in-
correct diagnostic performance or damage to transaxle
components.
Do not, under any circumstances, attempt to diagnose a
transaxle problem without this basic knowledge.
Notice : If a wire is probed with a sharp instrument and not
properly sealed afterward, the wire will corrode and an
open circuit will result.
Diagnostic test probes are now available that allow you to
probe individual wires without leaving the wire open to the
environment. These probe devices are inexpensive and
easy to install, and they permanently seal the wire from
corrosion.
Special Tools
You should be able to use a Digital Volt Meter (DVM), a cir-
cuit tester, jumper wires or leads and a line pressure gauge
set.
The functional check procedure is designed to verify the
correct operation of electronic components in the trans-
axle.
This will eliminate the unnecessary removal of transaxle
components.
FUNCTIONAL CHECK PROCEDURE
Begin with the Functional Check Procedure which pro-
vides a general outline of how to diagnose automatic
transaxle. The following functional check procedure will in-
dicate the proper path of diagnosing the transaxle by de-
scribing the basic checks and then referencing the loca-
tions of the specific checks.
S Check the fluid level according to the Fluid Level
Service Procedure.
S Check the transaxle for fluid leaks.
S Check if the transaxle fluid is not burnt by color and
smell.
S Ensure that the transaxle is not in Limp Home
Mode(LHM).
S Check the battery terminals and the ground con-
nections for corrosion or looseness.
S Check that the cooler flow is not restricted.S Check all electrical connections for tightness.
S Use on–board diagnostic tool or a scan tool to see
if any transaxle trouble codes have been set. Refer
to the appropriate ”Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)”
information and repair the vehicle as directed. After
repairing the vehicle, perform the road test and
verify that the code has not set again.
S Perform the Electrical/Garage Shift Tests.
S Perform the Road Test Procedure in this section.
S Inspect the oil and check for metal or other contam-
inants in the oil pan.
LINE PRESSURE CHECK
PROCEDURE
The 4HP 16 A/T uses a trochoid type oil pump to produce
hydraulic pressure, and a pressure control solenoid (sole-
noid 1) to control that pressure at the pressure regulator
valve, after it leaves the pump. The transaxle pressure
control solenoid is controlled by an electrical signal that
ranges from 0 to 12 volts corresponds to minimum line
pressure (approx. 89.9 to 124.7 psi (6.2 to 8.6 bar)) and
0 volt corresponds to a maximum line pressure (approx.
221.9 to 252.4 psi (15.3 to 17.4 bar)) in all range.
Line pressures are calculated for two sets of gear ranges
– Drive–Park–Neutral and Reverse. This allow the trans-
axle line pressure to be appropriate for different pressure
needs in different gear ranges:
Gear
Range
Solenoid
1RPMPressure
Drive,
ReverseOff2,500221.9~252.4psi
(15.3~17.4 bar)
On2,50017.4~269.8psi
(1.2~18.6 bar)
Neutral,
ParkOff2,500221.9~252.4psi
(15.3~17.4 bar)
On2,50089.9~269.8 psi
(6.2~18.6 bar)
Before performing a line pressure check, verify that the
pressure control solenoid is receiving the correct electrical
signal from the TCM:
1. Install a scan tool.
2. Start the engine and set parking brake.
3. Check for a stored pressure control solenoid diag-
nostic trouble code, and other diagnostic trouble
codes.
Page 1393 of 2643
5A1 – 44IZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
4. Repair vehicle, if necessary.
Inspect:
S Fluid level.
S Manual linkage.
Install or Connect:
S Scan tool (scanner)
S Oil pressure gauge at line pressure port (clutch B or
E ports on transaxle case)
5. Put gear selector in Park and set the parking brake.6. Start engine and allow it to warm up at idle.
7. Access the ”Solenoid 1 Control Mode” on the scan-
ner.
8. Switching solenoid 1 ON/OFF, accelerating the en-
gine to 2,500rpm, and then read the line pressure
at the each gear.
9. Compare data to the Drive–Park–Neutral line pres-
sure chart below.
Notice : Total test running time should not exceed 2 min-
utes, or transaxle damage could occur.
CAUTION : Brake must be applied at all times to pre-
vent unexpected vehicle motion.
If pressure readings differ greatly from the line pressure
chart, refer to the Diagnosis Charts contained in this sec-
tion.
Notice : Clutch damage may occur.
The scanner is only able to control the pressure control so-
lenoid in Park and Neutral with the vehicle stopped.
This protects the clutches from extremely high or low pres-
sures in Drive or Reverse rang.
Gear Range
SolenoidLine
Pressure B PortE Port
Park / NeutralONLOW90~124.7 psi (6.2~8.6 bar)
OFFHIGH221.9~252.3 ps
i (15.3~17.4 bar)
ReverseONLOW90~124.7 psi (6.2~8.6 bar)
OFFHIGH221.9~252.3 psi
(15.3~17.4 bar)
DriveONLOW90~124.7 psi (6.2~8.6 bar)
OFFHIGH137.7~162.4 psi
(9.5~11.2 bar)
3ONLOW90~124.7 psi (6.2~8.6 bar)90~124.7 psi (6.2~8.6 bar)
OFFHIGH221.9~252.3 psi
(15.3~17.4 bar)137.7~162.4 psi
(9.5~11.2 bar)
2ONLOW90~124.7 psi (6.2~8.6 bar)
OFFHIGH137.7~162.4 psi
(9.5~11.2 bar)
1ONLOW90~124.7 psi (6.2~8.6 bar)
OFFHIGH221.9~252.3 psi
(15.3~17.4 bar)
Page 1395 of 2643

5A1 – 46IZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
sible, drive the vehicle for a few kilometers (N–D,
N–R, shift until two gear). This will allow the trans-
axle to be within the correct temperature range.
Transaxle fluid level should be checked at tempera-
ture 20 to 45°C (68 to 113°F).
CAUTION : Removal of the fluid filler plug when the
transaxle fluid is hot may cause injury if fluid drains
from the filler hole.
2. Switch off accessories, especially air conditioner,
heater.
3. With the brake pedal pressed, move the gear shift
control lever through the gear ranges, pausing a
few seconds in each range. Return the gearshift
lever to P(Park). Turn the engine OFF.
4. Park the vehicle on a hoist, inspection pit or similar
raised level surface. The vehicle must be level to
obtain a correct fluid level measurement.
5. Place a fluid container below the fluid filler plug.
6. Clean all dirt from around the fluid filler plug.
Remove the fluid filler plug. Clean the filler plug and
check that there is no damage to the ”O” ring.
S If fluid drains through the filler hole the transaxle
may have been overfilled. When the fluid stops
draining the fluid level is correct. Install the fluid
filler plug and tighten it to 45NSm(34 lb–ft).
S If fluid does not drain through the filler hole, the
transaxle fluid level may be low. Lower the ve-
hicle, and start the vehicle in P(Park) with the
parking brake and the brake applied. With the
engine idling, move the gear shift lever through
the gear ranges, pausing a few seconds in each
range and adding the fluid until gear application
is felt. Return the gear shift lever to P(Park).
Turn the engine OFF and raise the vehicle.
Check if the fluid level is aligned with the bottom
of the filler hole. If not, add a small quantity of
fluid to the correct level. Install the fluid filler
plug and tighten it to 45NSm(34 lb–ft).
7. When the fluid level checking procedure is com-
pleted, wipe any fluid around the filler plug with a
rag or shop towel.
Fluid Level Set After Service
1. Depending on the service procedure performed,
add the following amounts of fluid through the filler
plug hole prior to adjusting the fluid level:
Oil pan removal – 4 liters (4.23 quarts)
Converter removal – 2 liters ( 2.11 quarts)
Overhaul – 6.9liters (7.3 quarts)
Oil drain plug removal – 4 liters (4.23 quarts)
2. Follow steps 1 through 4 of the Fluid Level Diagno-
sis Procedure.
3. Clean all dirt from around the fluid filler plug.
Remove the fluid filler plug. Clean the filler plug and
check that there is no damage to the ”O” ring.
4. Lower the vehicle with the filler plug still removed
and start the vehicle in P(Park) with the parking
brake and the brake applied. With the engine idling,move the gear shift lever through the gear ranges,
pausing a few seconds in each range and adding
the fluid until gear application is felt. Then add an
additional 0.5 liters of fluid. Return the gear shift
lever to P(Park). Turn the engine OFF and raise the
vehicle. Install the fluid filler plug and tighten it to
45NSm (34 lb–ft).
5. Drive the vehicle at 2.2 miles(3.5km) to 2.8
miles(4.5 km) with light throttle so that the engine
does not exceed 2500 rpm. This should result in
the transaxle temperature being in the range 20 to
45°C (68 to 11°F). With the brake applied, move
the shift lever through the gear ranges, pausing a
few seconds in each range at the engine idling.
6. Return the gear shift lever to P(Park). Turn the en-
gine OFF and raise the vehicle on the hoist, if appli-
cable, ensuring the vehicle is level. When the three
minutes passed after the engine stopped, remove
the filler plug. Check if the fluid level is aligned with
the bottom of the filler hole. If not, add a small
quantity of fluid to the correct level. Install the fluid
filler plug and tighten it to 45NSm (34 lb–ft).
7. Wipe any fluid around the filler plug with a rag or
shop towel.
Fluid Leak Diagnosis and Repair
The cause of most external leaks can generally be Lo-
cated and repaired with the transaxle in the vehicle.
Methods for Locating Leaks
General Method
1. Verify that the leak is transaxle fluid.
2. Thoroughly clean the suspected leak area.
3. Drive the vehicle for approximately 25 km (15
miles) or until the transaxle reaches normal operat-
ing temperature (88°C, 190°F).
4. Park the vehicle over clean paper or cardboard.
5. Turn the engine OFF and look for fluid spots on the
paper.
6. Make the necessary repairs to correct the leak.
Powder Method
1. Thoroughly clean the suspected leak area.
2. Apply an aerosol type powder (foot powder) to the
suspected leak area.
3. Drive the vehicle for approximately 25 km (15
miles) or until the transaxle reaches normal operat-
ing temperature (88°C, 190°F).
4. Turn the engine OFF.
5. Inspect the suspected leak area and trace the leak
path through the powder to find the source of the
leak.
6. Make the necessary repairs.
Dye and Black Light Method
1. Add dye to the transaxle though the transaxle fluid
filler plug. Follow the manufacturer’s recommenda-
tion for the amount of dye to be used.
2. Use the black light to find the fluid leak.
3. Make the necessary repairs.