ECU DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: NUBIRA, Model: DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 243 of 2643

ENGINE ELECTRICAL 1E – 29
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
3. Position the rotor assembly shaft with the drive end
frame in the slip ring end assembly until the gap
between the outer lace and the end frame casting
is 1.9 mm (0.075 inch).
4. Install the generator through–bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the generator through–bolts to 10 NSm (89 lb–
in).
5. Position the fan, the collars, and the pulley on the
rotor shaft and secure with the nut.
Tighten
Tighten the generator drive end bearing nut to 81 NSm
(60 lb–ft).
6. Install the generator. Refer to ”Generator”in the
On–Vehicle Service section.
7. Weld the brush holder terminal to the regulator ter-
minal, if removed.
8. Fix the brush holder with the retainer pin, and weld
the regulator/brush holder assembled terminal to
the rectifier terminal.
9. Apply silicone grease between the bridge and the
end frame for radiation purposes.
10. Fasten the screws holding the rectifier regulator/
brush holder assembly to the end frame.
11. Punch the new baffle with the pin into the brush.
Notice : Take care to prevent damage to the vehicle by
protecting the diode in the rectifier bridge from excessive
heat while welding.
12. Weld the connectors of the rectifier bridge.
Page 282 of 2643

1F – 36IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
MULTIPLE ECM INFORMATION SENSOR DTCS SET
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) monitors various sen-
sors to determine engine operating conditions. The ECM
controls fuel delivery, spark advance, transaxle operation,
and emission control device operation based on the sen-
sor inputs.
The ECM provides a sensor ground to all of the sensors.
The ECM applies 5 volts through a pull–up resistor and
monitors the voltage present between the sensor and the
resistor to determine the status of the Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT) sensor, the Intake Air Temperature
(IAT) sensor. The ECM provides the Exhaust Gas Recir-
culation (EGR) Pintle Position Sensor, the Throttle Posi-
tion (TP) sensor, the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
sensor, and the Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor with a 5 volt
reference and a sensor ground signal. The ECM monitors
the separate feedback signals from these sensors to de-
termine their operating status.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure to inspect the ECM and the engine grounds for be-
ing secure and clean.
A short to voltage in one of the sensor circuits can cause
one or more of the following DTCs to be set: P0108,
P0113, P0118, P0123, P1106, P1111, P1115, P1121,
P0463, P0533.
If a sensor input circuit has been shorted to voltage, en-
sure that the sensor is not damaged. A damaged sensor
will continue to indicate a high or low voltage after the af-
fected circuit has been repaired. If the sensor has been
damaged, replace it.
An open in the sensor ground circuit between the ECM and
the splice will cause one or more of the following DTCs to
be set: P0107, P0108, P0113, P0118, P0122, P0123,
P1106, P1111, P1115, P1121, P0462, P0532.
A short to ground in the 5 volt reference circuit or an open
in the 5 volt reference circuit between the ECM and the
splice will cause one or more of the following DTCs to be
set: P0107, P0112, P0117, P0122, P1107, P1112, P1114,
P1122, P0462, P0532.Check for the following conditions:
S Inspect for a poor connection at the ECM. Inspect
harness connectors for backed–out terminals, im-
proper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or
damaged terminals, and poor terminal–to–wire con-
nection.
S Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the har-
ness appears to be OK, observe an affected sen-
sor ’s displayed value on the scan tool with the igni-
tion ON and the engine OFF while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the af-
fected sensors. A change in the affected sensor’s
displayed value will indicate the location of the fault.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The Powertrain On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) Sys-
tem Check prompts the technician to complete
some basic checks and store the freeze frame and
failure records data on the scan tool if applicable.
This creates an electronic copy of the data taken
when the malfunction occurred. The information is
then stored on the scan tool for later reference.
9. A faulty EGR valve can leak a small amount of cur-
rent from the ignition feed circuit to the 5 volt refer-
ence circuit. If the problem does not exist with the
EGR valve disconnected, replace the EGR valve.
0. If a sensor input circuit has been shorted to voltage,
ensure that the sensor has not been damaged. A
damaged IAT or ECT sensor will continue to indi-
cate a high voltage or low temperature after the
affected circuit has been repaired. A damaged ACT,
TP, MAP, Fuel Tank Pressure, or EGR Pintle Posi-
tion sensor will indicate a high or low voltage or
may be stuck at a fixed value after the affected cir-
cuit has been repaired. If the sensor has been dam-
aged, replace it.
21. The replacement ECM must be reprogrammed.
Refer to the latest Techline procedure for ECM re-
programming.
Page 360 of 2643

1F – 114IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0107
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR LOW
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) uses the Manifold Ab-
solute Pressure (MAP) sensor to control the fuel delivery
and the ignition timing. The MAP sensor measures the
changes in the intake manifold pressure, which results
from engine load (intake manifold vacuum) and the rpm
changes; and converts these into voltage outputs. The
ECM sends a 5 volt–reference voltage to the MAP sensor.
As the manifold pressure changes, the output voltage of
the MAP sensor also changes. By monitoring the MAP
sensor output voltage, the ECM knows the manifold pres-
sure. A low–pressure (low voltage) output voltage will be
about 1.0 to 1.5 volts at idle, while higher pressure (high
voltage) output voltage will be about 4.5 to 4.8 at wide
open throttle (WOT). The MAP sensor is metric pressure,
allowing the ECM to make adjustments for different alti-
tudes.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S This DTC can be stored in ”key–on” status.
(Case A)
S When the engine idling.
S No throttle position(TP) sensor MTIA fail conditions
present.
S Engine speed(rpm) is less than 2,500rpm.
S The MAP is less than 12.0 kPa.
(Case A)
S When the engine part load.
S The engine revolution speed is less than 4,000rpm.S No Throttle Position (TP) Sensor fails conditions
present.
S The Throttle Position (TP) angle greather than
30.0°.
S The MAP is less than 11.5 kPa.
S An open or low voltage condition exists.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The coolant fan turns ON.
S The ECM will substitutes a fixed MAP value and
use TP to control the fuel delivery (the scan tool will
not show defaulted)
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
With the ignition ON and the engine stopped, the manifold
pressure is equal to atmosphere pressure and the signal
voltage will be high.
Page 363 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 117
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0108
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR HIGH
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) uses the Manifold Ab-
solute Pressure (MAP) sensor to control the fuel delivery
and the ignition timing. The MAP sensor measures the
changes in the intake manifold pressure, which results
from engine load (intake manifold vacuum) and the rpm
changes; and converts these into voltage outputs. The
ECM sends a 5 volt–reference voltage to the MAP sensor.
As the manifold pressure changes, the output voltage of
the MAP sensor also changes. By monitoring the MAP
sensor output voltage, the ECM knows the manifold pres-
sure. A low–pressure (low voltage) output voltage will be
about 1.0 to 1.5 volts at idle, while higher pressure (high
voltage) output voltage will be about 4.5 to 4.8 at wide
open throttle (WOT). The MAP sensor is metric pressure,
allowing the ECM to make adjustments for different alti-
tudes.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S This DTC can be stored in ”key–on” status.
S When the engine idling.
S Engine speed is greater than 700rpm.
S No throttle position sensor (TPS) fail conditions
present.
S The MAP is greater than 95kPA.
S A high voltage condition exists.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.S A history DTC is stored.
S The ECM will substitutes a fixed MAP value and
use TP to control the fuel delivery (the scan tool will
not show defaulted)
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
With the ignition ON and the engine stopped, the manifold
pressure is equal to atmosphere pressure and the signal
voltage will be high.
The ECM as an indication of vehicle altitude uses this in-
formation. Comparison of this reading with a known good
vehicle with the same sensor is a good way to check the
accuracy of a suspect sensor. Readings should be the
same ±0.4volt.
If a DTC P0108 is intermittent, refer to ”Manifold Absolute
Pressure Check” in this section for further diagnosis.
If the connections are OK monitor the manifold absolute
pressure(MAP) sensor signal voltage while moving re-
lated connectors and the wiring harness. If the failure is in-
duced, the display on the scan tool will change. This may
help to isolate the location of an intermittent malfunction.
Page 366 of 2643

1F – 120IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
J3B11F51
BRNORN
/BLK
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0112
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR LOW VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor uses a thermis-
tor to control the signal voltage to the engine control mod-
ule (ECM). The ECM supplies a 5 volt reference voltage
and a ground to the sensor. When the air is cold, the resist-
ance is high ; therefore IAT sensor signal voltage will be
high. If the intake air is warm, resistance is low ; therefore
the IAT sensor signal voltage will be low.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S IAT voltage is less than 0.01V.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.S The ECM will default to 605C(1405F) for intake air
temperature. The scan tool will not show the de-
faulted value.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for 10 sec-
onds.
Diagnostic Aids
If the vehicle is at ambient temperature, compare the IAT
sensor to the engine coolant temperature(ECT) sensor.
The IAT sensor and the ECT sensor should be relatively
close to each other. Use the temperature vs. Resistance
Values table to evaluate the possibility of a skewed sensor.
Refer to ”Temperature vs. Resistance” in this section.
Page 368 of 2643

1F – 122IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
J3B11F51
BRNORN
/BLK
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0113
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR HIGH VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor uses a thermis-
tor to control the signal voltage to the engine control mod-
ule (ECM). The ECM supplies a 5 volt reference voltage
and a ground to the sensor . when the air is cold, the resist-
ance is high ; therefore IAT sensor signal voltage will be
high. If the intake air is warm, resistance is low ; therefore
the IAT sensor signal voltage will be low.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S IAT voltage is less than 4.99V.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.S The ECM will default to 605C(1405F) for intake air
temperature. The scan tool will not show the de-
faulted value.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for 10 sec-
onds.
Diagnostic Aids
S If the vehicle is at ambient temperature, compare
the IAT sensor to the engine coolant temperature
(ECT) sensor. The IAT sensor and the ECT sensor
should be relatively close to each other.
S Use the temperature vs. Resistance Values table to
evaluate the possibility of a skewed sensor. Refer
to ”Temperature vs. Resistance” in this section.
Page 371 of 2643
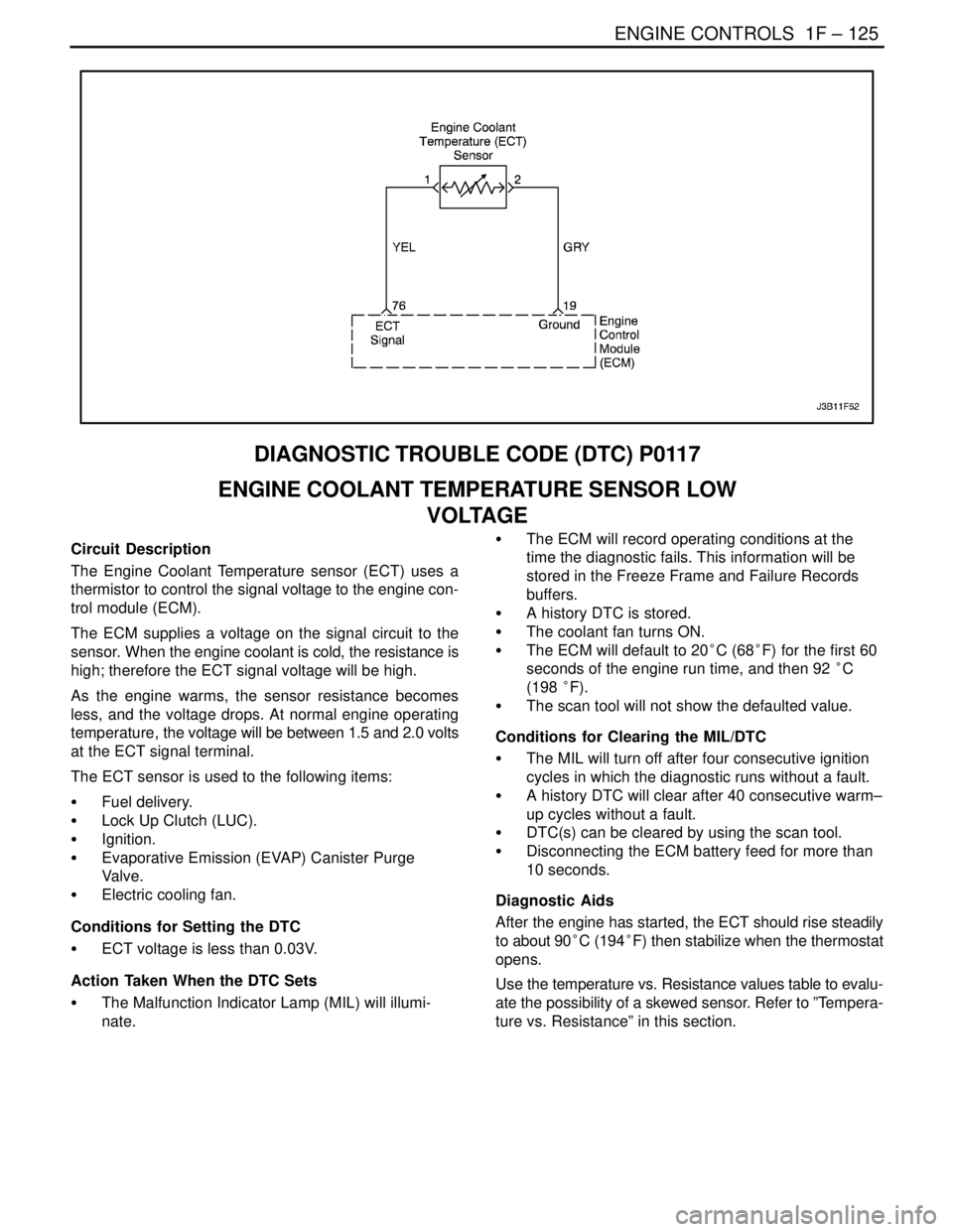
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 125
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0117
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR LOW
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Engine Coolant Temperature sensor (ECT) uses a
thermistor to control the signal voltage to the engine con-
trol module (ECM).
The ECM supplies a voltage on the signal circuit to the
sensor. When the engine coolant is cold, the resistance is
high; therefore the ECT signal voltage will be high.
As the engine warms, the sensor resistance becomes
less, and the voltage drops. At normal engine operating
temperature, the voltage will be between 1.5 and 2.0 volts
at the ECT signal terminal.
The ECT sensor is used to the following items:
S Fuel delivery.
S Lock Up Clutch (LUC).
S Ignition.
S Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Canister Purge
Valve.
S Electric cooling fan.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S ECT voltage is less than 0.03V.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The coolant fan turns ON.
S The ECM will default to 20°C (68°F) for the first 60
seconds of the engine run time, and then 92 °C
(198 °F).
S The scan tool will not show the defaulted value.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
After the engine has started, the ECT should rise steadily
to about 90°C (194°F) then stabilize when the thermostat
opens.
Use the temperature vs. Resistance values table to evalu-
ate the possibility of a skewed sensor. Refer to ”Tempera-
ture vs. Resistance” in this section.
Page 374 of 2643
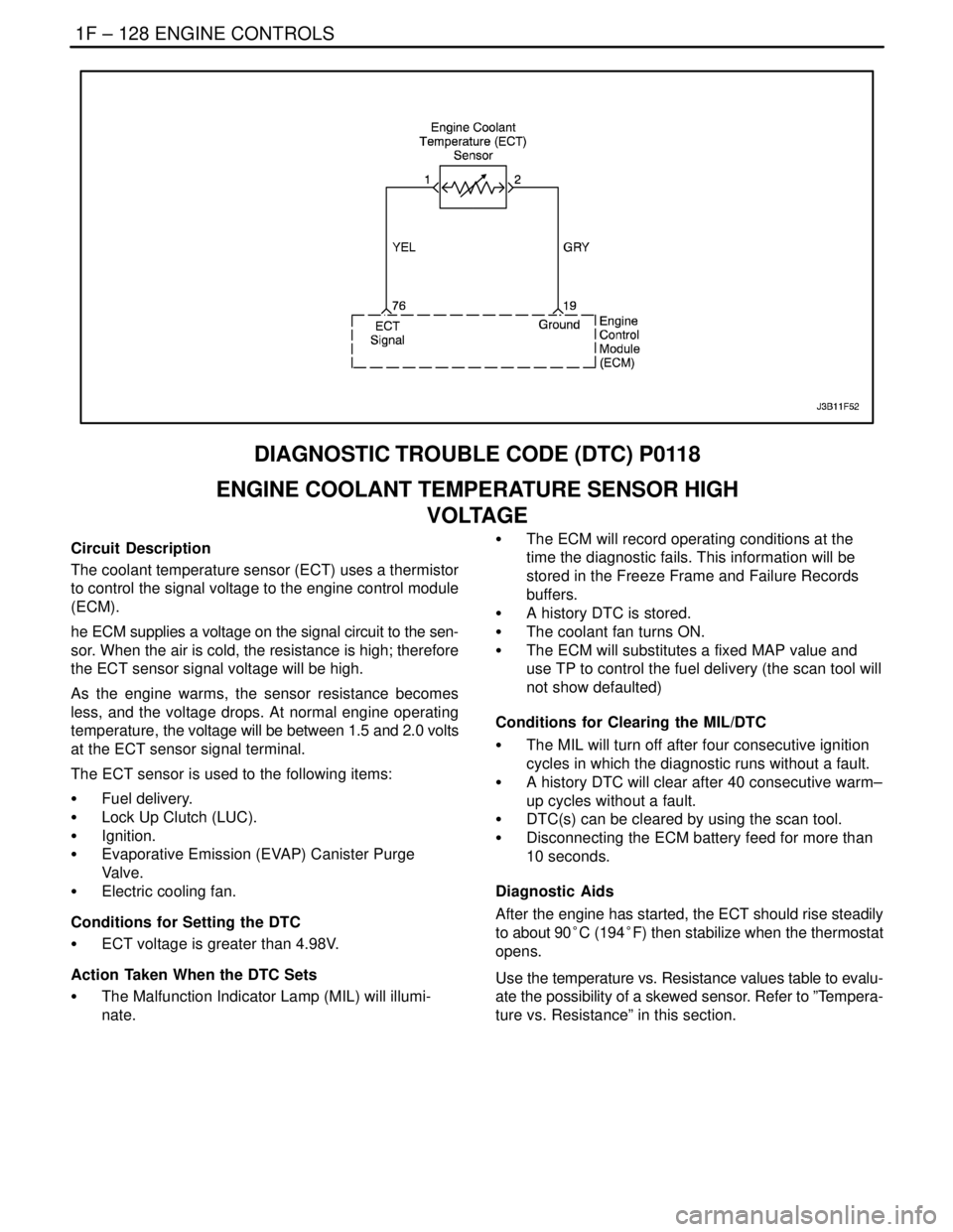
1F – 128IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0118
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR HIGH
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The coolant temperature sensor (ECT) uses a thermistor
to control the signal voltage to the engine control module
(ECM).
he ECM supplies a voltage on the signal circuit to the sen-
sor. When the air is cold, the resistance is high; therefore
the ECT sensor signal voltage will be high.
As the engine warms, the sensor resistance becomes
less, and the voltage drops. At normal engine operating
temperature, the voltage will be between 1.5 and 2.0 volts
at the ECT sensor signal terminal.
The ECT sensor is used to the following items:
S Fuel delivery.
S Lock Up Clutch (LUC).
S Ignition.
S Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Canister Purge
Valve.
S Electric cooling fan.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S ECT voltage is greater than 4.98V.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The coolant fan turns ON.
S The ECM will substitutes a fixed MAP value and
use TP to control the fuel delivery (the scan tool will
not show defaulted)
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
After the engine has started, the ECT should rise steadily
to about 90°C (194°F) then stabilize when the thermostat
opens.
Use the temperature vs. Resistance values table to evalu-
ate the possibility of a skewed sensor. Refer to ”Tempera-
ture vs. Resistance” in this section.
Page 377 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 131
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0122
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR LOW VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The aim of the MTIA (Main Throttle Idle Actuator) is to con-
trol the idle speed with the throttle body itself. The throttle
is motorized for low opening angle (05, 195). The charac-
teristics of the airflow are not the same for low and high
opening angles. As a matter of fact, the gradient of the
mass air flow function of TPS is lower for small angles that
permits to be more precise during the idle speed control.
Out of idle speed the throttle is actuated mechanically by
a classical bowdencable.
The throttle position sensor (TPS) provides a voltage sig-
nal that changes in relation to the throttle plate angle. The
signal voltage will vary from about nearly 5.0 V at idles to
about 0.2V to 0.4 V at wide–open throttle. The TPS is one
of the most important inputs used by the ECM for fuel con-
trol and other functions such as idle, wide open throttle,
deceleration enleanment, and acceleration enrichment.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S TPS voltage is less than 0.3V.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The coolant fan turns ON.
S The ECM will default to 20°C (68°F) for the first 60
seconds of the engine run time, and then 92 °C
(198 °F).
S The scan tool will not show the defaulted value.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
If the DTC P0122 cannot be duplicated, the information in-
cluded in the Freeze Frame data can be useful. Use the
scan tool DTC information data to determine the status of
the DTC. If the DTC occurs intermittently, using the DTC
P0121 diagnostic table may help isolate the problem.
Page 380 of 2643

1F – 134IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0123
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR HIGH VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The aim of the MTIA (Main Throttle Idle Actuator) is to con-
trol the idle speed with the throttle body itself. The throttle
is motorized for low opening angle (05, 195). The charac-
teristics of the airflow are not the same for low and high
opening angles. As a matter of fact, the gradient of the
mass air flow function of TPS is lower for small angles that
permits to be more precise during the idle speed control.
Out of idle speed the throttle is actuated mechanically by
a classical bowdencable.
The throttle position sensor (TPS) provides a voltage sig-
nal that changes in relation to the throttle plate angle. The
signal voltage will vary from about nearly 5.0 V at idles to
about 0.2V to 0.4 V at wide–open throttle. The TPS is one
of the most important inputs used by the ECM for fuel con-
trol and other functions such as idle, wide open throttle,
deceleration enleanment, and acceleration enrichment.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S TPS voltage is greater than 4.8V.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.S A history DTC is stored.
S The coolant fan turns ON.
S The ECM will default to 20°C (68°F) for the first 60
seconds of the engine run time, and then 92 °C
(198 °F).
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
If the DTC P0123 cannot be duplicated, the information in-
cluded in the Freeze Frame data can be useful. Use the
scan tool DTC information data to determine the status of
the DTC. If the DTC occurs intermittently, using the DTC
P0121 diagnostic table may help isolate the problem.
With the ignition ON and the throttle at closed position the
voltage should read between 0.20 V and 0.90V and in-
crease steadily to over 4.5V at WOT.
DTCs P0123 and P0113 stored at the same time could be
the result of an open sensor ground circuit.