check oil DATSUN 210 1979 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1979, Model line: 210, Model: DATSUN 210 1979Pages: 548, PDF Size: 28.66 MB
Page 361 of 548

BR563
Fig
BR
10
Removing
Pad
Inspection
Clean
pads
with
cleaning
solvent
CAUTION
Use
brake
fluid
to
clean
Never
use
mineral
oil
2
When
pads
are
heavily
fouled
with
oil
or
grease
or
when
pad
is
deteriorated
or
deformed
replace
it
3
If
pad
is
worn
to
less
than
the
specified
value
replace
Pad
wear
limit
Minimum
thickness
t
6
mm
0
063
in
Note
Always
replace
pads
in
pad
kit
four
pads
two
clips
four
pad
pins
and
four
pad
springs
4
Check
rotor
referring
to
Rotor
for
inspection
Installetlon
I
Clean
and
apply
P
RC
grease
on
yoke
guide
groove
of
cylinder
body
sliding
contact
portions
of
yoke
and
end
surface
of
piston
Note
a
Do
not
use
common
brake
grease
b
Be
careful
not
to
get
brake
grease
on
rotor
and
pads
2
Loosen
air
bleeder
and
push
pis
ton
B
outer
piston
in
cylinder
until
end
surface
of
piston
B
coincides
with
end
surface
of
retaining
ring
on
boot
Then
inner
pad
can
be
installed
Brake
System
BR564
Fig
BR
11
Pushing
Piston
CAUTION
Piston
can
be
easily
pushed
in
by
hand
but
if
pushed
too
far
groove
of
piston
will
go
inside
of
piston
seal
as
shown
in
Fig
BR
12
At
this
point
if
piston
is
pressured
or
moved
piston
seal
will
be
damaged
If
piston
has
been
pushed
in
too
far
remove
brake
assembly
and
disassemble
it
Then
push
piston
out
in
the
direction
shown
by
arrow
Assemble
it
again
referring
to
follow
ing
section
00
I
Normal
I
position
L
BR409
Fig
BR
12
Position
for
Pushing
Piston
3
Push
piston
A
inner
piston
in
cylinder
by
pulling
yoke
as
shown
The
outer
pad
can
then
be
installed
BRS6S
Fig
BR
13
Pulling
in
Piston
A
BR
7
4
After
installing
pads
depress
brake
pedal
several
times
and
pads
will
settle
into
proper
position
Note
When
worn
out
pads
are
re
placed
with
new
ones
brake
fluid
may
overflow
reservoir
While
re
placing
pads
keep
loosening
bleeder
to
release
brake
fluid
5
Install
wheels
and
lower
car
to
ground
REMOVAL
I
Remove
pads
Refer
to
Pad
Re
placement
2
Remove
brake
tube
from
caliper
assembly
CAUTION
When
removing
brake
tube
use
suit
able
tube
wrench
Never
use
open
end
or
adjustable
wrench
Note
Plug
up
hole
in
caliper
so
that
brake
fluid
does
not
flow
out
from
cylinder
body
3
Loosen
bolts
securing
cylinder
body
to
knuckle
spindle
and
remove
caliper
assembly
from
strut
DISASSEMBLY
I
Drain
brake
fluid
from
top
hole
of
cylinder
body
2
Push
both
pistons
A
and
B
into
cylinder
Refer
to
Pad
Replacement
3
Tap
cylinder
body
lightly
with
a
plastic
hammer
Cylinder
will
then
separate
from
yoke
BR115A
Fig
BR
14
Tapping
Cylinder
Block
Page 362 of 548
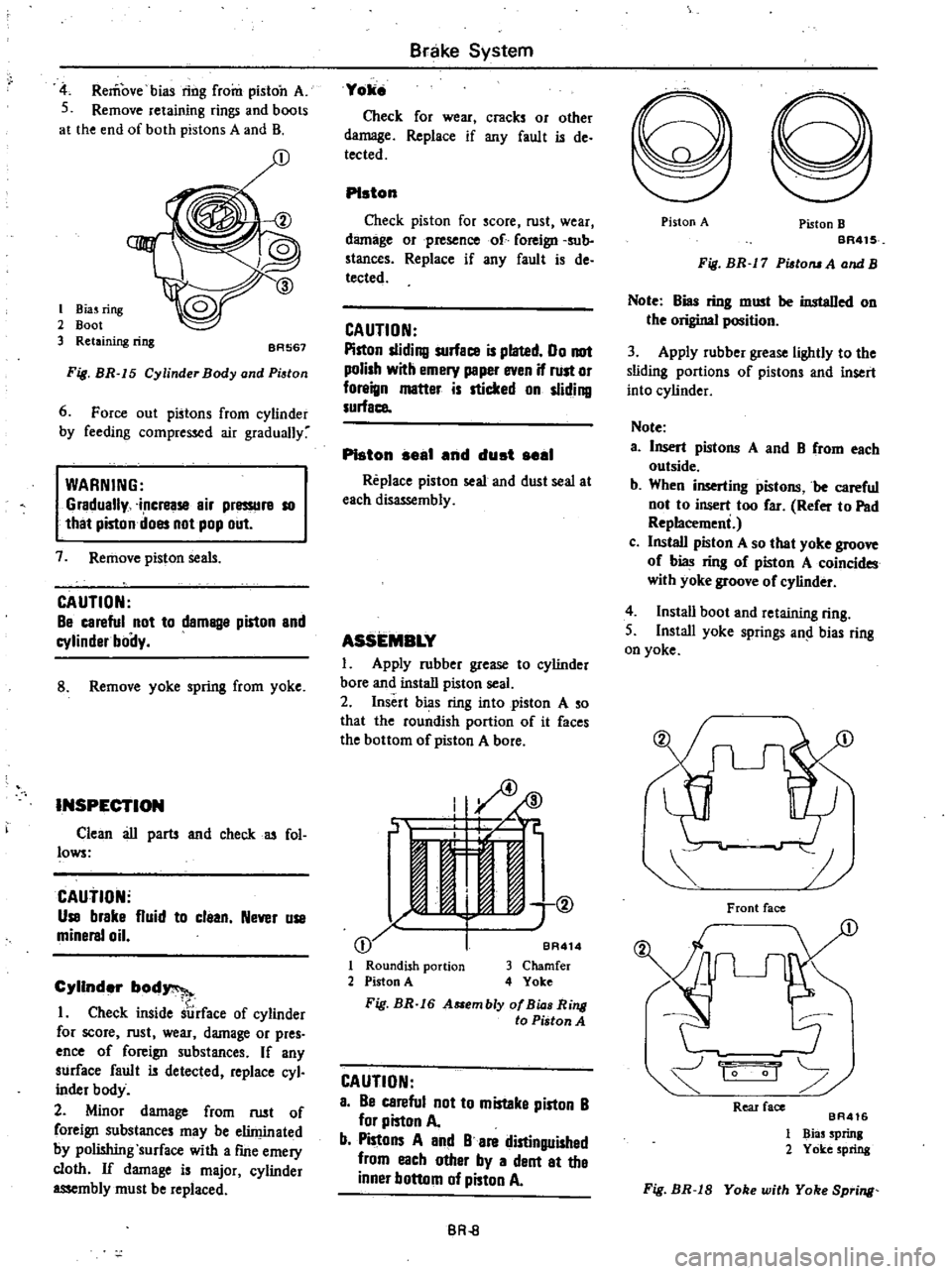
Remove
bias
ring
from
piston
A
S
Remove
retaining
rings
and
boots
at
the
end
of
both
pistons
A
and
B
I
Biuring
2
Boot
3
Retaining
ring
BA567
Fig
BR
15
Cylinder
Body
and
Pi
tan
6
Force
out
pistons
from
cylinder
by
feeding
compressed
air
gradually
WARNING
Gradually
increase
air
pressurs
10
that
piston
does
not
pop
out
7
Remove
piston
seals
CAUTION
Be
careful
not
to
damBlle
piston
and
cylinder
boily
8
Remove
yoke
spring
from
yoke
INSPECTION
Clean
au
parts
and
check
u
fol
lows
CAutiON
Use
brake
fluid
to
claan
Never
use
minersl
oil
Cylinder
bod
1
Check
inside
surface
of
cylinder
for
score
rust
wear
damage
or
pres
ence
of
foreign
substances
If
any
surface
fault
is
detected
replace
cyl
inder
body
2
Minor
damage
from
rust
of
foreign
substances
may
be
eliminated
by
polishing
surface
with
a
fme
emery
cloth
If
damage
is
major
cylinder
assembly
must
be
replaced
Brake
System
Yoke
Check
for
wear
cracks
or
other
damage
Replace
if
any
fault
is
de
tected
PIston
Check
piston
for
score
rust
wear
damage
orpresenco
of
foreign
sub
stances
Replace
if
any
fault
is
de
tected
CAUTION
Piston
sliding
surface
is
plated
00
not
polish
with
emery
peper
even
if
rust
or
foreign
matter
is
sticked
on
sliding
surface
PIston
seal
end
dust
seel
Replace
piston
seal
and
dust
seal
at
each
dis
mbly
ASSEMBLY
1
Apply
rubber
grease
to
cylinder
bore
and
install
piston
seal
2
Insert
bias
ring
into
piston
A
so
that
the
roundish
portion
of
it
faces
the
bottom
of
piston
A
bore
I
ID
J
if
C
jt
11
e
1
@
I
j
BA
I
Roundish
portion
3
Chamfer
2
Piston
A
4
Yoke
Fig
BR
16
A
embly
af
Bia
Ring
to
Piston
A
CAUTION
a
Be
careful
not
to
mistaka
piston
B
for
piston
A
b
Pistons
A
and
B
are
distinguished
from
each
other
by
a
dent
at
the
inner
bottom
of
piston
A
BR
8
Piston
A
Piston
B
BR41S
Fig
BR
17
Pisto
A
and
B
Note
Bias
ring
must
be
instaDed
on
the
original
position
3
Apply
rubber
grease
lightly
to
the
sliding
portions
of
pistons
and
insert
into
cylinder
Note
a
Insert
pistons
A
and
B
from
each
outside
b
When
inserting
pistons
be
careful
not
to
insert
too
far
Refer
to
Pad
Replacemeni
c
Install
piston
A
so
that
yoke
groove
of
bias
ring
of
piston
A
coincides
with
yoke
groove
of
cylinder
4
Instau
boot
and
retaining
ring
S
Install
yoke
springs
an
bias
ring
on
yoke
Front
face
1
1
0
Rear
face
BA416
1
Bias
Sprinl
2
Yoke
spring
Fig
BR
18
Yoke
with
Yoke
Spring
Page 365 of 548

INSPECTION
Brake
drum
I
Check
inner
diameter
of
brake
drum
to
make
sure
it
is
properly
round
and
tapered
If
it
is
not
repair
or
replace
brake
drum
Inner
diameter
Standard
diametel
203
2
mm
8
in
Maximum
diameter
204
5
mm
8
05
in
Out
of
loundness
ellipticity
less
than
0
02
mm
0
0008
in
Radial
runout
less
than
0
1
mm
0
004
in
Total
indicator
reading
Taper
less
than
0
02
mm
0
0008
in
Measured
at
a
point
40
mm
1
57
in
flam
inlet
2
Contact
surface
with
which
lin
ings
come
into
contact
should
be
fine
finished
with
No
120
to
150
sandpaper
3
Using
a
drum
racer
finish
brake
drum
by
machining
if
it
shows
any
sign
of
score
marks
partial
wear
or
stepped
wear
on
its
contact
surface
Note
After
brake
drum
has
been
completely
re
conditioned
or
re
placed
check
drum
and
shoes
for
proper
contact
pattern
Brake
e
embly
1
Replace
any
linings
which
are
cracked
worn
or
oil
stained
2
If
lining
is
worn
to
less
than
the
specified
value
replace
Lining
wear
limit
Minimum
thickness
1
5
mm
0
059
in
3
Replace
any
shoe
return
springs
which
are
broken
or
fatigued
4
Replace
fatigued
anti
rattle
spring
damaged
pin
and
or
retainer
Wheel
cylinder
I
Replace
any
cylinder
or
piston
which
is
scratched
scored
or
worn
on
its
sliding
contact
surface
Brake
System
2
Replace
worn
parts
if
piston
to
cylinder
clearance
is
beyond
limit
Piston
ta
cylinder
clearance
less
than
0
15
mm
0
0059
in
3
Replace
any
piston
cup
which
is
worn
or
otherwise
damaged
4
Replace
if
contacting
face
of
cyl
inder
and
shoe
is
worn
locally
or
in
step
5
Replace
any
damaged
dust
cover
fatigued
piston
spring
or
faulty
thread
ed
parts
6
Replace
any
tube
connector
which
is
worn
on
its
threaded
portion
INSTALLATION
Install
rear
brake
in
reverse
order
of
removal
closely
observing
the
follow
ing
1
Tighten
following
parts
to
speci
fied
torque
CAUTION
When
installing
brake
tube
use
Flare
Nut
Torque
Wrench
6694310000
ifl
Tightening
torque
Flared
nut
1
5
to
1
8
kg
m
11
to
13
fHb
Ail
bleedel
0
7
to
0
9
kg
m
15
1
to
6
5
ft
Ib
Wheel
cylinder
mounting
bolt
0
6
to
0
8
kg
m
4
3
to
5
8
ft
b
2
There
are
two
types
of
adjusters
which
have
right
thread
or
left
thread
R
H
brake
Right
thread
adjuster
L
H
brake
Left
thread
adjuster
3
Sparingly
apply
a
coat
of
brake
grease
to
the
following
points
Lubricating
points
e
Adjuster
nut
and
rod
threads
Mating
surfaces
between
adjuster
and
toggle
lever
and
pin
and
roller
BR
ll
0
J
o
BR
117
A
Fig
BR
24
Lubricating
Points
of
Adju
ter
4
Referring
to
Fig
BR
25
for
locations
of
lubricating
points
apply
a
coat
of
brake
grease
to
these
points
Exercise
care
not
to
allow
grease
to
come
into
contact
with
lining
or
ad
juster
screws
Lubricating
points
e
Contact
areas
between
wheel
cyl
inder
anchor
block
and
brake
shoe
e
Mating
surfaces
between
brake
shoe
and
brake
disc
Contact
areas
between
hand
brake
adjuster
and
brake
shoe
Contact
areas
between
brake
disc
brake
shoe
and
toggle
lever
Contact
areas
between
anti
rattle
pin
spring
retainer
and
brake
shoe
Fig
BR
25
Lubricating
Points
5
To
prevent
water
from
entering
brake
drum
apply
dry
sealant
to
brake
disc
mounting
surfaces
of
the
follow
ing
parts
Wheel
cylinder
Anti
rattle
spring
6
Make
sure
that
entire
brake
shoe
fits
in
place
7
Make
sure
that
adjuster
operates
properly
8
After
installation
is
completed
check
and
adjust
shoe
to
drum
clear
ance
by
operating
hand
brake
several
times
9
Bleed
brake
system
Page 366 of 548

BRAKE
BOOSTE
R
INSPECTION
OF
OPERATION
Checking
vecuum
pressure
I
Connect
a
vacuum
gauge
in
the
tine
between
check
velve
and
brake
booster
1
Check
valVe
2
Vacuum
gauge
BA942
Fig
BR
26
Air
Tighte
Te
Set
Up
Probable
cause
Air
leakage
at
check
valve
2
Air
leakage
at
push
rod
seal
3
Air
leakage
between
valve
body
and
seal
4
Air
leakage
at
valve
plunger
seat
5
Damaged
piping
or
joints
Air
tight
test
Under
loed
Fifteen
seconds
after
engine
is
stopped
and
brake
fully
applied
ob
serve
the
rate
of
drop
in
air
pressure
registered
by
vacuum
gauge
If
vacuum
Probable
cause
Air
leakage
at
check
valve
2
Damaged
diaphragm
3
Reaction
disc
dropped
off
4
Air
leakage
at
poppet
assembly
seat
and
valve
body
Inspec
tinK
chec
k
valve
Remove
clip
and
disconnect
hoses
Brake
System
2
Start
engine
end
merease
engine
speed
Stop
engine
when
vacuum
gauge
indicates
500
mmHg
l9
69
inHg
Air
tiKht
test
No
load
Fifteen
seconds
after
engine
is
stopped
observe
the
rate
of
drop
in
air
pressure
registered
by
vacuum
gauge
If
vacuum
pressure
drop
below
the
specified
value
refer
to
the
following
chart
to
determine
the
cause
of
failure
Maximum
vacuum
leakage
25
mmHg
0
98
inHgl
Corrective
action
Replace
check
valve
Replace
brake
booster
as
an
assembly
Repair
or
replace
pressure
drops
below
the
specified
value
refer
to
the
following
chart
to
determine
the
cause
of
failure
Maximum
vacuum
leakage
25
mmHg
0
98
inHgl
Corrective
action
Replace
check
valve
Replace
brake
booster
as
an
assembly
at
connections
The
check
valve
can
now
be
removed
BR
12
JQeL
i
l
f
BR119A
Fis
BR
27
Location
of
Check
Valllt
2
Using
a
brake
booster
testel
apply
a
vacuum
pressure
of
500
mmHg
19
69
inHg
to
the
port
of
check
valve
on
the
brake
booster
side
If
vacuum
pressure
drops
below
the
specified
value
in
15
seconds
replace
check
valve
with
a
new
one
Maximum
vacuum
leakage
01
eheck
valn
10
mmHg
0
39
inHgl
3
When
pressure
is
applied
to
the
b
rake
booster
side
of
check
valve
and
valve
does
not
open
replace
check
valve
with
a
new
one
I
0
tLLiJ
Manifold
side
Brake
booster
side
1
Spring
2
Valve
BR963
Fig
BR
28
Check
Value
4
When
installing
check
valve
be
careful
to
avoid
incorrect
connectiolU
See
Fig
DR
28
Operetlns
test
1
Connect
an
oil
pressure
gauge
to
brake
ine
at
connection
on
master
cylinder
2
Install
a
pedal
force
gauge
on
brake
pedal
3
Start
engine
end
increase
engine
speed
until
a
vacuum
pressure
of
500
mmHg
19
69
inHg
is
registered
on
vacuum
pressure
gauge
With
a
steady
vacuum
pressure
of
500
mmHg
19
69
inHg
measure
oil
pressure
with
res
pect
to
each
pedal
operating
force
Page 367 of 548

Relationship
between
oil
pressure
and
pedal
operating
force
is
illustrated
in
Fig
BR
29
If
test
results
are
not
as
specified
in
Fig
BR
29
check
brake
booster
for
condition
in
manner
des
cribed
under
Inspection
before
re
moval
of
this
unit
REMOVAL
M60
120
1
710
AA
I
1
1
110
1
560
1
v
e
100
1
420
I
90
1
280
I
1
1
80
1
140
I
Z
I
t
70
1
000
i
60
850
I
o
50
710
d
40
570
g
i
gl
j
ll
10
140
J
0
1
0
2
0
221
441
Rod
operating
force
kg
lb
Brake
System
Also
check
brake
line
for
evidence
of
fluid
leakage
Note
Detennine
whether
source
of
problem
is
in
brake
booster
or
check
valve
Before
you
reach
a
fmal
conclusion
always
inspect
check
valve
first
o
10
20
30
40
50
22
44
66
88
110
Pedal
operating
force
kg
lb
BA121A
Fig
BR
29
Performance
Diagram
of
Brake
Booster
Remo
parts
in
numerical
order
enumerated
BR593
ti
J
Fig
BR
30
Procedures
for
Removing
Brake
Booster
ADJUSTMENT
I
Adjust
the
length
of
push
rod
to
the
value
indicated
below
Length
ad
justment
of
push
rod
is
made
at
the
tip
of
push
rod
Length
A
9
75
to
10
00
mm
0
3839
to
0
3937
in
j
f
Irl
I
l
if
L
J
BA290
Fig
BR
31
Length
A
BR
13
BR288
Fig
BR
32
Adjusting
Push
Rod
Length
2
Install
clevis
Adjust
length
of
operating
rod
to
specified
value
length
B
135
mm
5
31
in
c
f
lIJ
t
t
B
BR947
Fig
BR
33
Length
B
INSTALLATION
Install
in
the
reverse
sequence
of
removaJ
IiJ
Tightening
torque
Master
cylinder
to
brake
booster
0
8
to
1
1
kg
m
5
8
to
8
0
ft
Ib
Brake
booster
to
body
0
8
to
1
1
kg
m
5
8
to
8
0
ft
lbl
Note
After
brake
boOster
is
properly
installed
in
car
conduct
an
air
tight
and
op
rational
tests
as
previously
described
Page 373 of 548
Brake
System
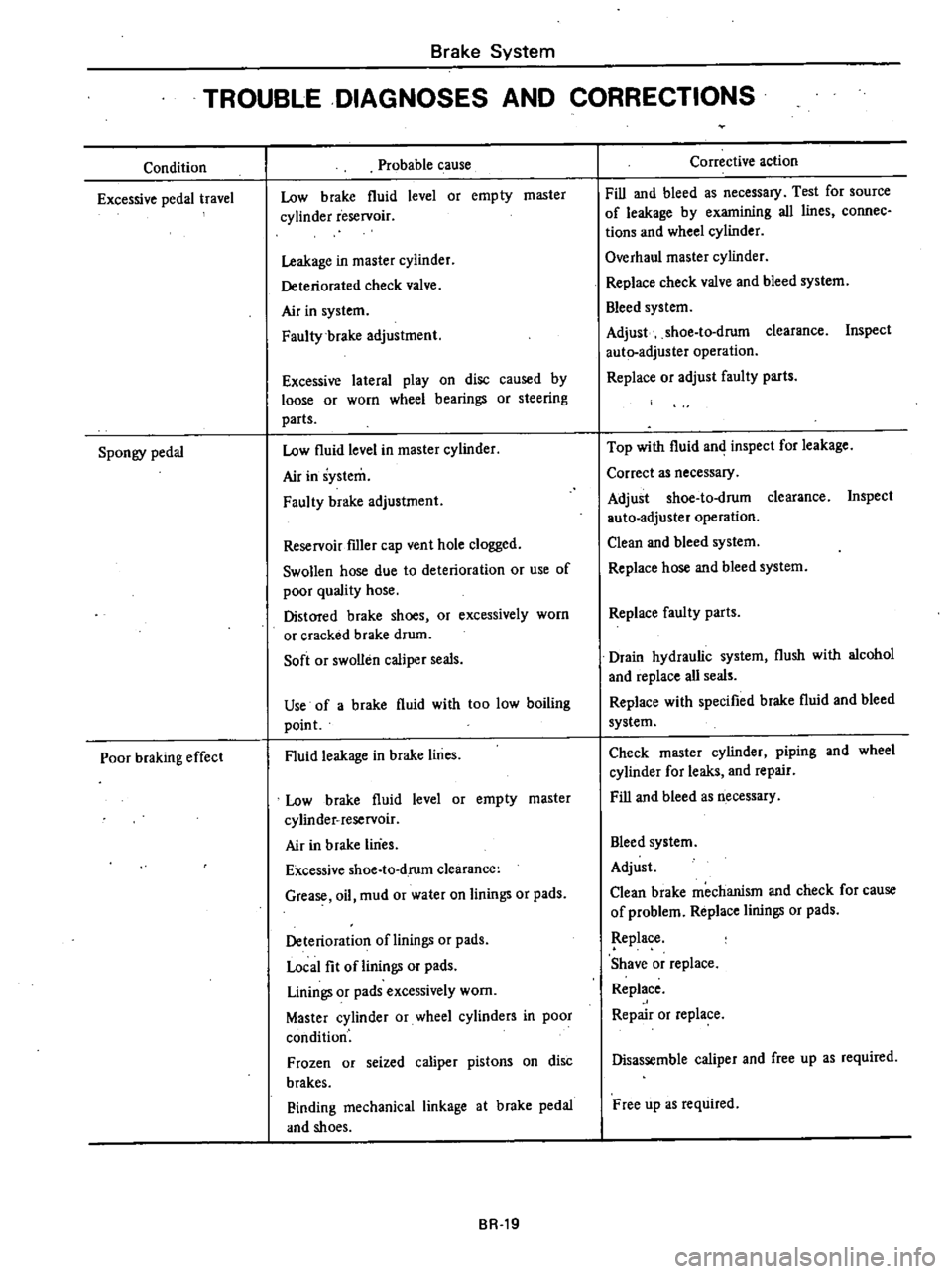
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
Condition
Excessive
pedal
travel
Spongy
pedal
Poor
braking
effect
Probable
cause
Low
brake
fluid
level
or
empty
master
cyUnder
reservoir
Leakage
in
master
cylinder
Deteriorated
check
valve
Air
in
system
Faulty
brake
adjustment
Excessive
lateral
play
on
disc
caused
by
loose
or
worn
wheel
bearings
or
steering
parts
Low
fluid
level
in
master
cylinder
Air
in
system
Faulty
brake
adjustment
Reservoir
fIller
cap
vent
hole
clogged
Swollen
hose
due
to
deterioration
or
use
of
poor
quality
hose
Distored
brake
shoes
or
excessively
worn
or
cracked
brake
drum
Soft
or
swollen
caliper
seals
Use
of
a
brake
fluid
with
too
low
boiling
point
Fluid
leakage
in
brake
lines
Low
brake
fluid
level
or
empty
master
cylinder
reservoir
Air
in
brake
lines
Excessive
shoe
to
d
rum
clearance
Grease
oil
mud
or
water
on
linings
or
pads
Deterioration
of
linings
or
pads
Local
fit
of
linings
or
pads
Linings
or
pads
excessively
worn
Master
cylinder
or
wheel
cylinders
in
poor
condition
Frozen
or
seized
caliper
pistons
on
disc
brakes
Finding
mechanical
linkage
at
brake
pedal
and
shoes
BR
19
Corrective
action
Fill
and
bleed
as
necessary
Test
for
source
of
leakage
by
examining
all
lines
connec
tions
and
wheel
cylinder
Overhaul
master
cylinder
Replace
check
valve
and
bleed
system
Bleed
system
Adjust
shoe
to
drum
clearance
Inspect
auto
adjuster
operation
Replace
or
adjust
faulty
parts
Top
with
fluid
and
inspect
for
leakage
Correct
as
necessary
Adjust
shoe
to
drum
clearance
Inspect
auto
adjuster
operation
Clean
and
bleed
system
Replace
hose
and
bleed
system
Replace
faul
ty
parts
Drain
hydraulic
system
flush
with
alcohol
and
replace
all
seals
Replace
with
specified
brake
fluid
and
bleed
system
Check
master
cylinder
p
pmg
and
wheel
cylinder
for
leaks
and
repair
Fill
and
bleed
as
necessary
Bleed
system
Adjust
Clean
brake
mechanism
and
check
for
cause
of
problem
Replace
linings
or
pads
Replace
Shave
or
replace
Replace
Repair
or
replace
Disassemble
caliper
and
free
up
as
required
Free
up
as
required
Page 374 of 548
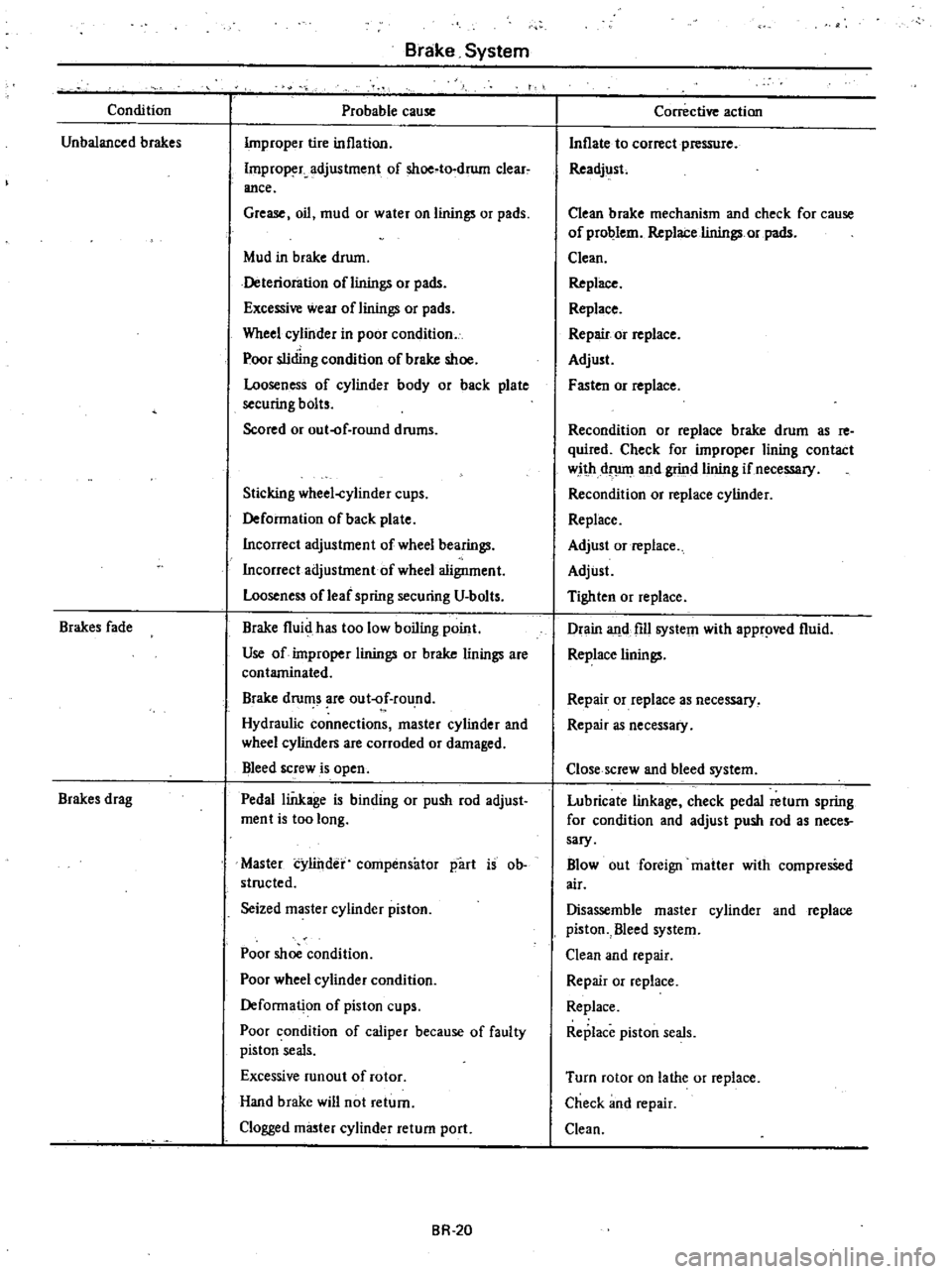
Condition
Unbalanced
brakes
Brakes
fade
Brakes
drag
Brake
System
Probable
cause
Improper
tire
inflation
Improp
r
adjustment
of
shoe
to
drum
clear
ance
Grease
oil
mud
or
water
on
linings
or
pads
Mud
in
brake
drum
Deterioration
oflinings
or
pads
Excessi
wear
of
linings
or
pads
Wheel
cylinder
in
poor
condition
Poor
sliding
condition
of
brake
shoe
Looseness
of
cylinder
body
or
back
plate
securing
bolts
Scored
or
out
f
round
drums
Sticking
wheel
cylinder
cups
Deformation
of
back
plate
Incorrect
adjustment
of
wheel
bearings
Incorrect
adjustment
of
wheel
aligoment
Looseness
of
leaf
spring
securing
U
bolts
Brake
fluid
has
too
low
boiling
point
Use
of
improper
linings
or
brake
linings
are
contaminated
Brake
drums
are
out
f
round
Hydraulic
connections
master
cylinder
and
wheel
cylinders
are
corroded
or
damaged
Bleed
screw
is
open
Pedal
linkage
is
binding
or
push
rod
adjust
ment
is
too
long
Master
cylinder
compensator
part
is
ob
structed
Seized
master
cylinder
piston
Poor
shoe
condition
Poor
wheel
cylinder
condition
Deformation
of
piston
cups
Poor
condition
of
caliper
because
of
faulty
piston
seals
Excessive
runaut
of
rotor
Hand
brake
will
not
return
Clogged
m
ter
cylinder
return
port
BR
20
Corrective
action
Inflate
to
correct
pressure
Readjust
Clean
brake
mechanism
and
check
for
cause
of
problem
Replace
linings
or
pads
Clean
Replace
Replace
Repair
or
replace
Adjust
F
ten
or
replace
Recondition
or
replace
brake
drum
as
re
quired
Check
for
improper
lining
contact
with
dflllll
and
grind
lining
if
necessary
Recondition
or
replace
cylinder
Replace
Adjust
or
replace
Adjust
Tighten
or
replace
Drain
and
fill
system
with
appr
d
fluid
Replace
linings
Repair
or
replace
as
necessary
Repair
as
necessary
Close
screw
and
bleed
system
Lubricate
linkage
check
pedal
return
spring
for
condition
and
adjust
push
rod
as
neces
sary
Blowout
foreign
matter
with
compresSed
air
Disassemble
master
cylinder
and
replace
piston
Bleed
system
Clean
and
repair
Repair
or
replace
Replace
Replace
piston
seals
Turn
rotor
on
lathe
or
replace
Check
and
repair
Clean
Page 375 of 548
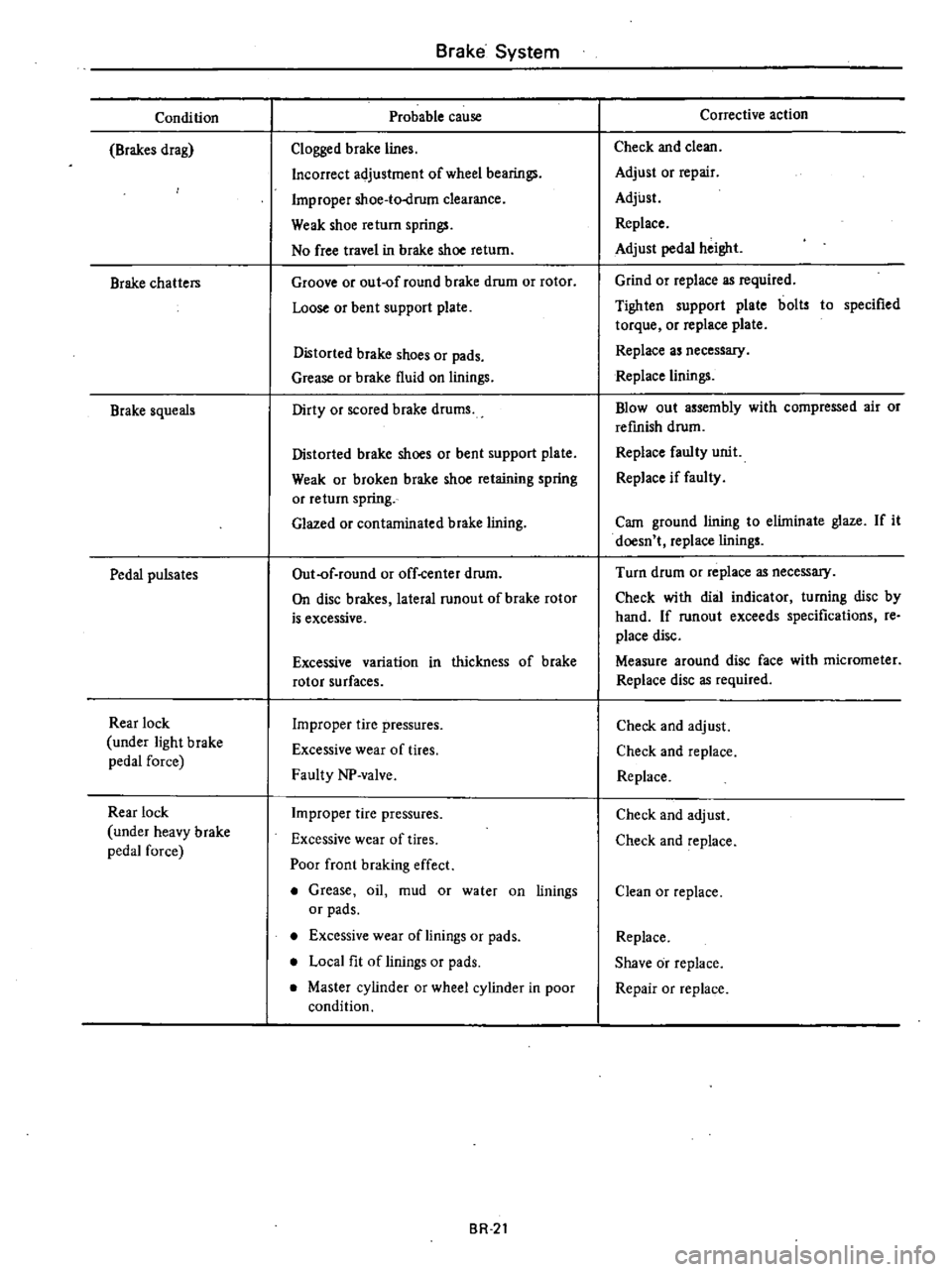
Condition
Brakes
drag
Brake
chatters
Brake
squeals
Pedal
pulsates
Rear
lock
under
light
brake
pedal
force
Rear
lock
under
heavy
brake
pedal
force
Brake
System
Probable
cause
Clogged
brake
lines
Incorrect
adjustment
of
wheel
bearings
Improper
shoe
to
drum
clearance
Weak
shoe
return
springs
No
free
travel
in
brake
shoe
return
Groove
or
out
of
round
brake
drum
or
rotor
Loose
or
bent
support
plate
Distorted
brake
shoes
or
pads
Grease
or
brake
fluid
on
linings
Dirty
or
scored
brake
drums
Distorted
brake
shoes
or
bent
support
plate
Weak
or
broken
brake
shoe
retaining
spring
or
return
spring
Glazed
or
contaminated
brake
lining
Out
of
round
or
off
center
drum
On
disc
brakes
lateral
runout
of
brake
rotor
is
excessive
Excessive
variation
in
thickness
of
brake
rotor
surfaces
Improper
tire
pressures
Excessive
wear
of
tires
Faulty
NP
valve
Improper
tire
pressures
Excessive
wear
of
tires
Poor
front
braking
effect
Grease
oil
mud
or
water
on
linings
or
pads
Excessive
wear
of
linings
or
pads
Local
fit
of
linings
or
pads
Master
cylinder
or
wheel
cylinder
in
poor
condition
BR
2t
Corrective
action
Check
and
clean
Adjust
or
repair
Adjust
Replace
Adjust
pedal
height
Grind
or
replace
as
required
Tighten
support
plate
bolts
to
specified
torque
or
replace
plate
Replace
as
necessary
Replace
linings
Blowout
assembly
with
compressed
air
or
refinish
drum
Replace
faulty
unit
Replace
if
faulty
Cam
ground
lining
to
elilninate
glaze
If
it
doesn
t
replace
linings
Turn
drum
or
replace
as
necessary
Check
with
dial
indicator
turning
disc
by
hand
If
runout
exceeds
specifications
re
place
disc
Measure
around
disc
face
with
micrometer
Replace
disc
as
required
Check
and
adjust
Check
and
replace
Replace
Check
and
adjust
Check
and
replace
Clean
or
replace
Replace
Shave
or
replace
Repair
or
replace
Page 390 of 548

CAUTION
a
Be
careful
not
to
allow
ball
nut
to
run
down
to
either
end
of
worm
The
ends
of
ball
guides
will
be
damaged
if
nut
is
rotated
until
it
stops
at
the
end
of
worm
b
00
not
detach
ball
nut
from
worm
shaft
assembly
If
necessary
replace
assembly
c
Do
not
remove
sector
shaft
bush
ings
from
steering
gear
housing
If
necessary
replace
gear
housing
assembly
d
Be
careful
not
to
allow
penetration
of
any
other
element
like
dust
or
dirt
Inspection
Wash
clean
all
the
disassembled
parts
in
cleaning
solvent
and
check
for
condition
Sector
shaft
I
Check
gear
tooth
surface
for
pitting
burrs
cracks
or
any
other
damage
and
replace
if
damaged
2
Check
sector
shaft
for
distortion
of
its
serration
and
if
necessary
re
place
In
this
case
be
8ure
to
check
gear
housing
and
steering
worm
as
sembly
for
deformation
Steering
worm
assembly
I
Inspect
ball
nut
gear
tooth
sur
face
and
replace
if
pitting
burrs
wear
or
any
other
damage
is
found
2
Ball
nut
must
rotate
smoothly
on
worm
gear
If
found
too
tight
as
sembly
should
be
replaced
Check
as
follows
I
Move
ball
nut
to
either
end
of
worm
gear
and
gradually
stand
worm
shaft
and
ball
nut
assembly
until
ball
nut
moves
downward
on
worm
gear
under
its
own
weight
2
In
the
above
test
if
ball
nut
does
not
move
freely
over
entire
stroke
assembly
may
be
damaged
Replace
with
a
new
one
Note
In
this
inspection
be
careful
not
to
damage
ball
nut
guide
tube
Steering
System
ST037
Fig
ST
22
In
pecting
Steering
Worm
and
Ball
Nut
A8sembly
Bearings
and
bushings
I
Inspect
worm
bearing
for
wear
pitting
or
any
other
damage
Replace
with
a
new
one
as
required
Note
When
replacing
worm
bearing
replace
it
as
a
set
of
bearing
and
outer
race
2
If
sector
shaft
bushings
in
gear
housing
are
found
worn
or
damaged
replace
as
an
assembly
of
gear
housing
and
bushings
Oil
seals
Discard
oil
seal
which
is
once
re
moved
Replace
oil
seal
if
sealing
lip
is
deformed
or
cracked
Also
discard
oil
seal
if
spring
is
fatigued
or
dislocated
Assembly
snd
adjustment
Assemble
steering
gear
in
reverse
order
of
disassembly
Observe
follow
ing
instructions
Clean
all
parts
2
Lubricate
bearing
turning
surface
gear
surface
gear
tooth
and
other
sliding
parts
with
clean
gear
oil
3
Fill
space
between
sealing
lips
of
new
oil
seal
with
recommended
multi
purpose
grease
and
fit
it
to
gear
housing
and
rear
cover
Note
a
To
facilitate
installation
coat
seal
contacting
face
of
oil
seal
with
gear
oil
b
Press
oil
seal
into
place
with
its
lettered
side
facing
outside
of
gear
housing
or
rear
cover
5T
7
CAUTION
Be
careful
not
to
assemble
with
any
other
element
like
dust
or
dirt
Adjustment
of
worm
bearing
preload
4
Properly
position
steering
worm
assembly
in
gear
housing
with
worm
bearings
Install
rear
cover
on
gear
housing
with
worm
bearing
shims
fJ
Tightening
torqu
Rear
coyer
2
0
to
3
0
kltm
14
to
22
ft
Ibl
Note
Be
sure
to
install
the
thicker
shUn
on
gear
housing
side
Standard
shim
total
thickness
is
1
5
mm
0
059
in
Available
worm
bearing
shUn
No
Thickness
mm
in
I
0
762
0
0300
2
0
254
0
0100
3
0
127
0
0050
4
0
050
0
0020
5
Selecting
suitable
bearing
shims
adjust
worm
bearing
preload
with
Drive
Pinion
Preload
Gauge
ST3I
27S000
Initial
turning
torque
Worm
bearing
4
0
to
6
0
kg
m
3
5
to
5
2
in
bl
Note
a
Rotate
worm
shaft
a
few
turns
in
both
directions
to
settle
worm
bear
ing
in
and
measure
preload
b
When
adjusting
worm
bearing
pre
load
add
and
then
remove
shim
s
until
correct
adjustment
is
achieved
Page 393 of 548
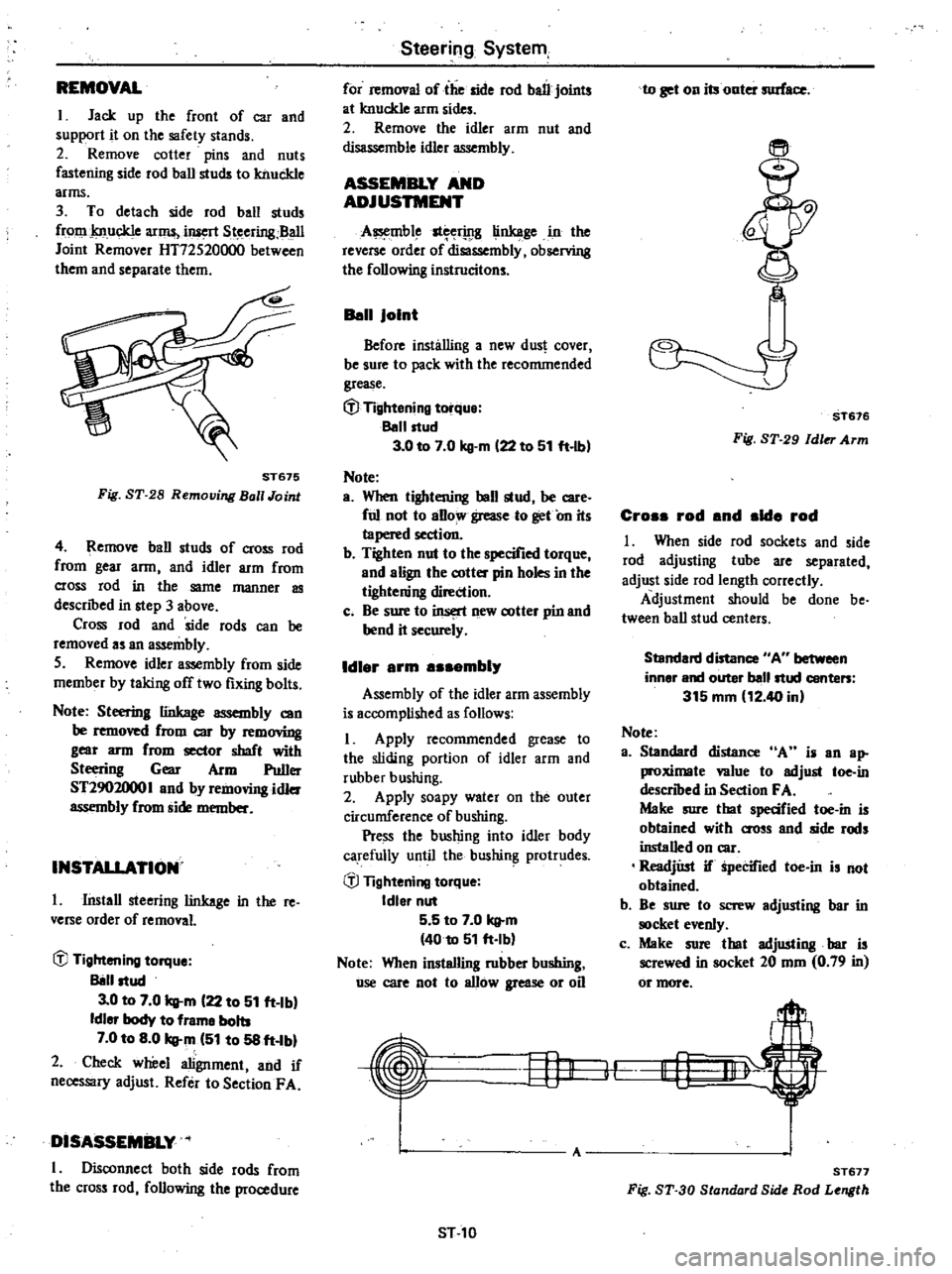
REMOVAL
I
Jack
up
the
front
of
car
and
support
it
on
the
safety
stands
2
Remove
cotter
pins
and
nuts
fastening
side
rod
ball
studs
to
knuckle
arms
3
To
detach
side
rod
ball
studs
from
knuckle
arms
iJuert
Steering
BaII
Joint
Remover
HT72520000
between
them
and
separate
them
ST675
Fig
ST
28
Remouing
Ball
Joint
4
Remove
ball
studs
of
cross
rod
from
gear
arm
and
idler
arm
from
cross
rod
in
the
same
manner
as
descnbed
in
step
3
above
Cross
rod
and
side
rods
can
be
removed
as
an
assembly
5
Remove
idler
assembly
from
side
member
by
taking
off
two
fixing
bolts
Note
Steering
linkage
assembly
can
be
removed
from
CIC
by
rem
mng
gear
arm
from
sector
shaft
with
Steering
Gear
Arm
Puller
ST2902000
I
and
by
removing
idler
assembly
from
side
member
INSTAllATION
I
Install
steering
linkage
in
the
re
verse
order
of
removal
iJJ
Tightening
torque
Il8l1ltud
3
0
to
7
0
q
m
122
to
51
ft
Ibl
Idler
body
to
frame
bolts
7
0
to
8
0
q
m
151
to
58
ft
Ibl
2
Check
wheel
alignment
and
if
necessary
adjust
Refer
to
SectionF
A
DISASSEMBLY
I
Disconnect
both
side
rods
from
the
cross
rod
following
the
procedure
Steering
System
for
removal
of
the
side
rod
ball
joints
at
knuckle
arm
sides
2
Remove
the
idler
arm
nut
and
disassemble
idler
assembly
ASSEMBLY
AND
ADJUSTMENT
A
mble
st
rwg
linkage
in
the
reverse
order
of
disassembly
observing
the
following
instrucitons
Ban
Joint
Before
installing
a
new
dus
cover
be
sure
to
pack
with
the
recommended
grease
t
J
Tightening
torque
Ballltud
3
0
to
7
0
kg
m
122
to
51
ft
lbl
Note
a
When
tightening
ball
stud
be
care
ful
not
to
aBow
grease
to
get
On
its
tapered
section
b
Tighten
nut
to
the
specified
torque
and
align
the
cotter
pin
holes
in
the
tightening
direction
c
Be
sure
to
insert
new
cotter
pin
and
bend
it
securely
Idl
r
rm
mbl
Assembly
of
the
idler
arm
assembly
is
accomplished
as
follows
I
Apply
recommended
grease
to
the
sliding
portion
of
idler
arm
and
rubber
bushing
2
Apply
soapy
water
on
the
outer
circumference
of
bushing
Pre
ss
the
bushing
into
idler
body
carefully
until
the
bushin
protrudes
iJJ
Tightening
torque
Idler
nut
5
5
to
7
0
q
m
4010
51
ft
Ib
Note
When
installing
rubber
bushing
use
care
not
to
allow
grease
or
oil
Hj1
ST
10
to
get
on
its
onter
surface
ST676
Fig
ST
29
Idler
Arm
Cro
rod
nd
Id
rod
I
When
side
rod
sockets
and
side
rod
adjusting
tube
are
separated
adjust
side
rod
length
correctly
Adjustment
should
be
done
be
tween
ball
stud
centers
Standard
distance
AU
between
inner
and
outer
ballltud
conte
315
mm
12
40
in
Note
a
Standard
distance
A
i
an
ap
proximale
value
to
adjust
toe
in
descnbed
in
Section
FA
Maire
sure
tbat
specified
toe
in
is
obtained
with
O
OSs
and
side
rods
installed
on
car
ReadjUst
if
Specified
toe
in
is
not
obtained
b
Be
sure
to
screw
adjusting
bar
in
clret
evenly
c
Make
sure
that
adjusting
bar
is
screwed
in
socket
20
mm
0
79
in
or
more
I
lf
A
ST
77
Fig
ST
30
Standard
Side
Rod
Length