Electrical DATSUN 210 1979 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1979, Model line: 210, Model: DATSUN 210 1979Pages: 548, PDF Size: 28.66 MB
Page 164 of 548
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
Disconnect
battery
ground
cable
Disconnect
harness
connector
and
battery
cable
at
magnetic
switch
2
Remove
bolts
securing
starting
motor
to
transmission
case
Pull
start
iog
motor
forward
and
remove
it
3
Inst
1I
starting
motor
in
reverse
order
of
removal
DISASSEMBLY
NON
REDUCTION
GEAR
TYPE
I
Disconnect
connecting
plate
from
M
terminal
of
magnetic
switch
Re
move
two
screws
securing
magnetic
switch
and
remove
magnetic
switch
assembly
2
Remove
dust
cover
E
ring
and
thrust
washer
s
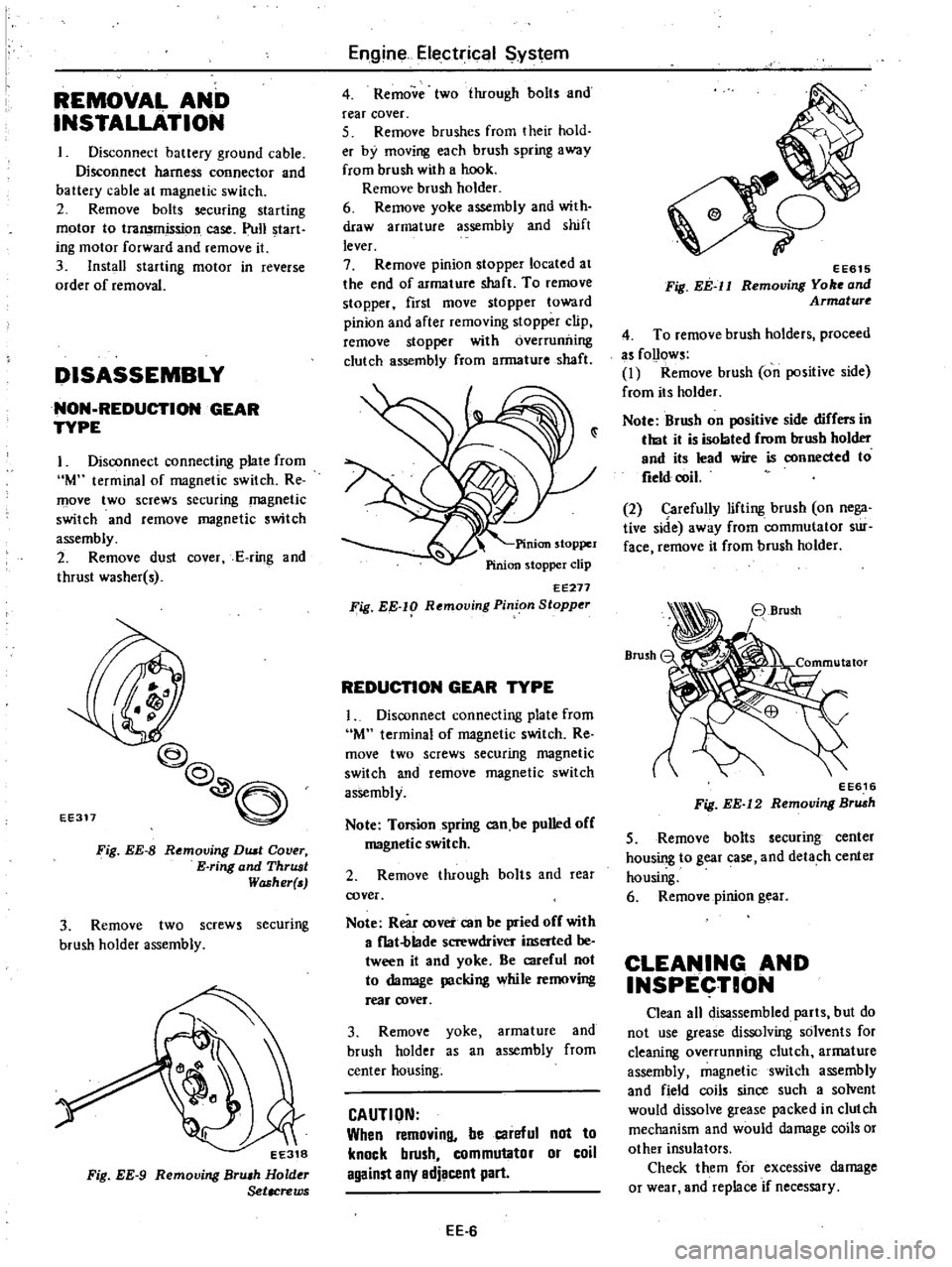
EE311
@@
O
Fig
EE
8
Removing
DUll
Cover
E
ring
and
ThrUJJt
Washer
3
Remove
two
screws
securing
brush
holder
assembly
EE318
Fig
EE
9
Removing
Bru
h
Hold
Setacrews
Engine
Electrical
ystem
4
Remove
two
ihrough
bolts
and
rear
cover
5
Remove
brushes
from
their
hold
er
by
moving
each
brush
spring
away
from
brush
with
a
hook
Remove
brush
holder
6
Remove
yoke
assembly
and
with
draw
armature
assembly
and
shift
lever
7
Remove
pinion
stopper
located
at
the
end
of
armature
shaft
To
remove
stopper
first
move
stopper
toward
pinion
and
after
removing
stopper
clip
remove
stopper
with
overruniling
clutch
assembly
from
armature
shaft
EE271
Fig
EE
lg
Rf
moving
Pinion
Stopper
REDUCTION
GEAR
TYPE
1
Disconnect
connecting
plate
from
M
terminal
of
magnetic
switch
Re
move
two
screws
securing
magnetic
switch
and
remove
magnetic
switch
assembly
Note
Torsion
spring
can
be
pulled
off
magnetic
switch
2
Remove
through
baIts
and
rea
cover
Note
Rear
cover
can
be
pried
off
with
a
f1at
blade
screwdriver
inserted
be
tween
it
and
yoke
Be
careful
not
to
damage
packing
while
removing
reaf
cover
3
Remove
yoke
armature
and
brush
holder
as
an
assembly
from
center
housing
CAUTION
When
removing
be
careful
not
to
knock
brush
commutator
or
coil
against
any
adjacent
part
EE
6
o
7
EE615
Fig
EE
ll
Removing
Yo
and
Armature
4
To
remove
brush
holders
proceed
as
follows
I
Remove
brush
on
positive
side
from
its
holder
Note
Brush
on
positive
side
differs
in
that
it
is
isolated
from
brush
holder
and
its
lead
wire
is
connected
to
field
coil
2
Carefully
lifting
brush
on
nega
tive
side
away
from
commutator
sur
face
remove
it
from
brush
holder
EE616
Fig
EE
12
Removing
Br
h
5
Remove
bolts
securing
center
housing
to
gear
case
and
detach
center
housing
6
Remove
pinion
gear
CLEANING
AND
INSPECTION
Clean
all
disassembled
parts
but
do
not
use
grease
dissolving
solvents
for
cleaning
overrunning
clutch
armature
assembly
magnetic
switch
assembly
and
field
coils
since
such
a
solvent
would
dissolve
grease
packed
in
clutch
mechanism
and
would
damage
coils
or
other
insulators
Check
them
for
excessive
damage
or
wear
and
replace
if
necessary
Page 165 of 548
TERMINAL
Check
terminal
for
damage
and
wear
and
replace
magnetic
switch
assembly
if
necessary
FIELD
COIL
Check
field
coil
for
insulation
If
the
insulation
of
oil
is
damaged
or
worn
it
should
be
replaced
Testing
field
coil
for
continuity
Connect
the
probe
of
a
circuit
tester
or
an
ohmmeter
to
field
coil
two
positive
terminal
of
positive
brush
holder
If
tester
shows
no
continuity
field
circuit
or
coil
is
open
Replace
it
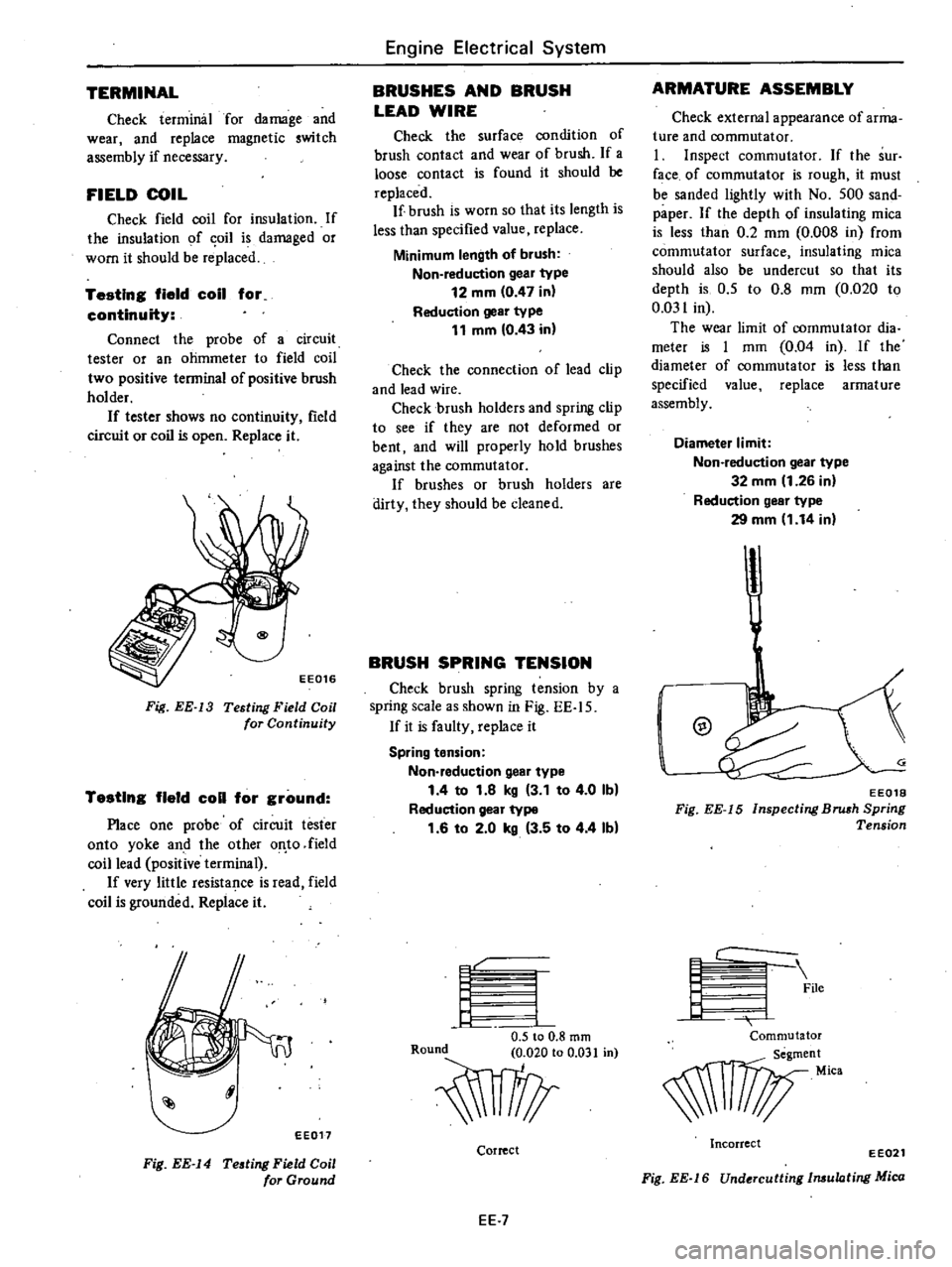
Fig
EE
13
Testing
Field
Coil
for
Continuity
Testing
field
coli
for
ground
Place
one
probe
of
circuit
tester
onto
yoke
and
the
other
of
to
field
coil
lead
positive
terminal
If
very
little
resistance
is
read
field
coil
is
grounded
Replace
it
I
EE017
Fig
EE
14
Testing
Field
Coil
for
Ground
Engine
Electrical
System
BRUSHES
AND
BRUSH
LEAD
WIRE
Check
the
surface
condition
of
brush
contact
and
wear
of
brush
If
a
loose
contact
is
found
it
should
be
replaced
If
brush
is
worn
so
that
its
length
is
less
than
specified
value
replace
Minimum
length
of
brush
Non
reduction
gear
type
12
mm
0
47
in
Reduction
gear
type
11
mm
0
43
in
Check
the
connection
of
lead
clip
and
lead
wire
Check
brush
holders
and
spring
clip
to
see
if
they
are
not
deformed
or
bent
and
will
properly
hold
brushes
against
the
commutator
If
brushes
or
brush
holders
are
dirty
they
should
be
cleaned
BRUSH
SPRING
TENSION
Check
brush
spring
tension
by
a
spring
scale
as
shown
in
Fig
EE
l
5
If
it
is
faulty
replace
it
Spring
tension
Non
reduction
geaf
type
1
4
to
1
8
kg
3
1
to
4
0
Ib
Reduction
gear
type
1
6
to
2
0
kg
3
5
to
4
4
Ib
I
r
4
1
0
5
to
0
8
rom
O
iO
Correct
EE
7
ARMATURE
ASSEMBLY
Check
external
appearance
of
arma
ture
and
oommutator
I
Inspect
commutator
If
the
sur
face
of
commutator
is
rough
it
must
be
sanded
lightly
with
No
500
sand
paper
If
the
depth
of
insulating
mica
is
less
than
0
2
mm
0
008
in
from
commutator
surface
insulating
mica
should
also
be
undercut
so
that
its
depth
is
0
5
to
0
8
mm
0
020
to
0
031
in
The
wear
limit
of
commutator
dia
meter
is
I
mm
0
04
in
If
the
diameter
of
commutator
is
less
than
specified
value
replace
armature
assembly
Diameter
limit
Non
reduction
gear
type
32
mm
1
26
in
Reduction
gear
type
29
mm
1
14
in
I
@
EE018
Fig
EE
15
Inspecting
Bnah
Spring
Tension
c
I
File
Commutator
nt
I
1
11
Mica
Incorrect
EE021
Fig
EE
16
Undercutting
Imulating
Mica
Page 166 of 548

2
Inspect
silldered
conneetibn
of
armature
lead
and
commutator
If
loose
connection
is
found
solder
it
using
resin
flux
3
Armature
test
for
ground
Using
a
circuit
tester
place
one
test
probe
onto
armature
core
or
shaft
and
other
onto
each
commutator
bar
If
tester
shows
continuity
armature
is
grounded
and
must
be
replaced
L
L
I
EE022
F
EE
17
Teating
Armature
for
Ground
4
Check
armature
for
short
by
plac
ing
it
on
armature
tester
growler
with
a
piece
of
iron
over
arma
t
ure
core
rotating
armature
If
the
plate
vibrates
armature
is
shorted
jeBel
EE023
Fig
EE
18
Testing
Armature
or
Short
5
Check
armature
for
continuity
by
placing
probes
of
tester
on
two
seg
ments
side
by
side
If
tester
shows
no
continuity
the
circuit
is
open
OVERRUNNING
CLUTCH
ASSEMBLY
Inspect
pinion
assembly
and
screw
sleeve
or
reduction
gear
Screw
sleeve
must
slide
freely
along
armature
shaft
splines
or
pinion
gear
shaft
must
slide
freely
through
reduction
gear
If
dam
age
is
found
or
resistance
except
nor
mal
resistance
due
to
spring
felt
when
sliding
it
must
be
repaired
Inspect
pinion
teeth
If
excessive
rubbing
is
found
on
teeth
replace
Flywheel
ring
gear
also
must
be
inspected
Engine
Electrical
System
@
ll
EE278
Fig
EE
19
Overrunning
Clutch
Assembly
1
Pinion
gear
2
Reduction
gear
EE617
Fig
EE
20
Pinion
and
Reduction
Gear
Overrunni11C
Clutch
AS5em
bly
BRUSH
HOLDER
TEST
FOR
GROUND
Using
a
circuit
tester
place
one
test
probe
onto
negative
side
of
brush
holder
and
another
onto
positive
side
If
tester
shows
continuity
brush
hold
er
is
shorted
to
ground
Replace
brush
holder
EE025
Fig
EE
21
Testing
Brush
for
Ground
BEARING
METAL
Non
reduction
gear
type
spect
bearing
metal
for
wear
or
side
play
If
the
clearance
between
bearing
metal
and
armature
shaft
is
more
than
0
2
mm
0
008
in
replace
metal
EE
8
BAI
L
BEARING
Reduction
gear
type
Holding
outer
race
with
finger
rotate
bearing
to
see
if
there
is
any
play
or
bind
If
necessary
replace
bearing
MAGNETic
SWITCH
ASSEMBLY
I
Using
a
circuit
tester
check
con
tinuity
between
S
terminal
of
mag
netic
switch
and
switch
body
metal
If
continuity
does
not
exist
shunt
coil
is
opened
Replace
switch
assembly
2
In
the
same
manner
as
above
check
continuity
between
terminals
S
and
M
If
continuity
does
not
exist
series
coil
is
opened
Replace
switch
assembly
ASSEMBLY
Reassemble
starting
motor
in
re
verse
sequence
of
disassembly
When
assembling
be
sure
to
apply
grease
to
gear
case
and
rear
cover
bearing
metal
and
apply
oil
lightly
to
pinion
TEST
PERFORMANCE
TEST
Starter
motor
should
be
subjected
to
a
no
load
test
whenever
it
has
been
overhauled
to
ensure
that
its
perfo
rmance
will
be
satisfactory
when
installed
on
engine
Starter
motor
should
also
be
subjected
to
the
test
when
the
cause
of
abnormal
operation
is
to
be
determined
A
brief
outline
of
the
test
is
given
below
No
loadtest
Connect
starting
motor
in
series
willi
specified
12
volts
battery
and
an
ammeter
capable
of
indicating
1
000
amperes
Specified
current
draw
and
rev6lu
tion
in
this
test
are
shown
in
Sp
ci
Cications
Page 167 of 548
Starting
motor
S
DIAGNOSES
OF
TEST
I
Low
speed
with
no
load
and
high
current
draw
may
result
from
the
following
I
Tight
dirty
or
worn
bearings
2
Bent
armature
shaft
or
loosened
field
probe
3
Shorted
armature
Check
armature
further
4
A
grounded
armature
or
field
a
Remove
input
terminal
b
Raise
two
negative
side
brushes
from
commutator
c
Using
a
circuit
tester
place
one
probe
onto
input
terminal
and
the
other
onto
yoke
d
If
tester
indicates
continuity
raise
the
other
two
brushes
and
check
field
and
armature
separately
to
deter
mine
whether
field
or
armature
is
grounded
2
Failure
to
operate
with
high
cur
rent
draw
may
be
caused
by
the
following
I
A
grounded
or
open
field
coil
Inspect
the
connection
and
trace
circuit
with
a
circuit
tester
2
Armature
coil
does
not
operate
Inspect
commutator
for
excessive
burning
In
this
case
arc
may
occur
on
damaged
commutator
when
motor
is
operated
with
no
load
3
Burned
out
commutator
bar
Weak
brush
spring
tension
broken
Engine
Electrical
System
Switch
Battery
Vultmeter
Ammeter
EE738
Fig
EE
22
No
load
Testing
brush
spring
rubber
bush
thrust
out
of
mica
in
commuta
tor
or
a
loose
contact
between
brush
and
conunuta
tor
would
cause
commutator
bar
to
burn
3
Low
current
draw
and
low
no
load
speed
would
cause
high
internal
resistance
due
to
loose
connections
damaged
leads
dirty
commutator
and
causes
listed
on
item
2
3
MAGNETIC
SWITCH
ASSEMBLY
TEST
Switch
2
1
6
11
p
IB
b
I
Battery
Starter
motor
EE351
Fig
EE
23
Circuit
of
Magnetic
Switch
Assembly
Test
If
the
starting
motor
check
is
OK
check
magnetic
switch
assem
bly
Connect
cables
between
negative
battery
terminal
and
start
ing
motor
M
terminal
positive
battery
terminal
and
starting
motor
8
terminal
connecting
a
switch
in
series
as
shown
above
EE
9
Non
reduction
gear
type
With
the
switch
on
push
pinion
back
to
remove
all
slack
and
measure
the
clearance
between
pinion
front
edge
and
pinion
stopper
Clearance
L
0
3
to
2
5
mm
0
012
to
0
098
in
EE644
Fig
EE
24
Measuring
Clearance
l
Reduction
gear
type
Compare
difference
2
in
height
of
pinion
when
it
is
pushed
out
with
magnetic
switch
energized
and
when
it
is
pulled
out
by
hand
until
it
touches
stopper
Difference
L
0
3
to
1
5
mm
0
012
to
0
059
in
Pull
out
by
hand
until
pinion
stops
Push
out
1
1
n
11
r
L
Difference
EE688
Fig
EE
25
Measuri
g
Difference
L
If
necessary
adjust
it
by
changing
or
adding
adjusting
washer
s
Adjust
ing
washers
are
available
into
two
different
sizes
0
5
mm
0
020
in
and
0
8
mm
0
031
in
Page 168 of 548
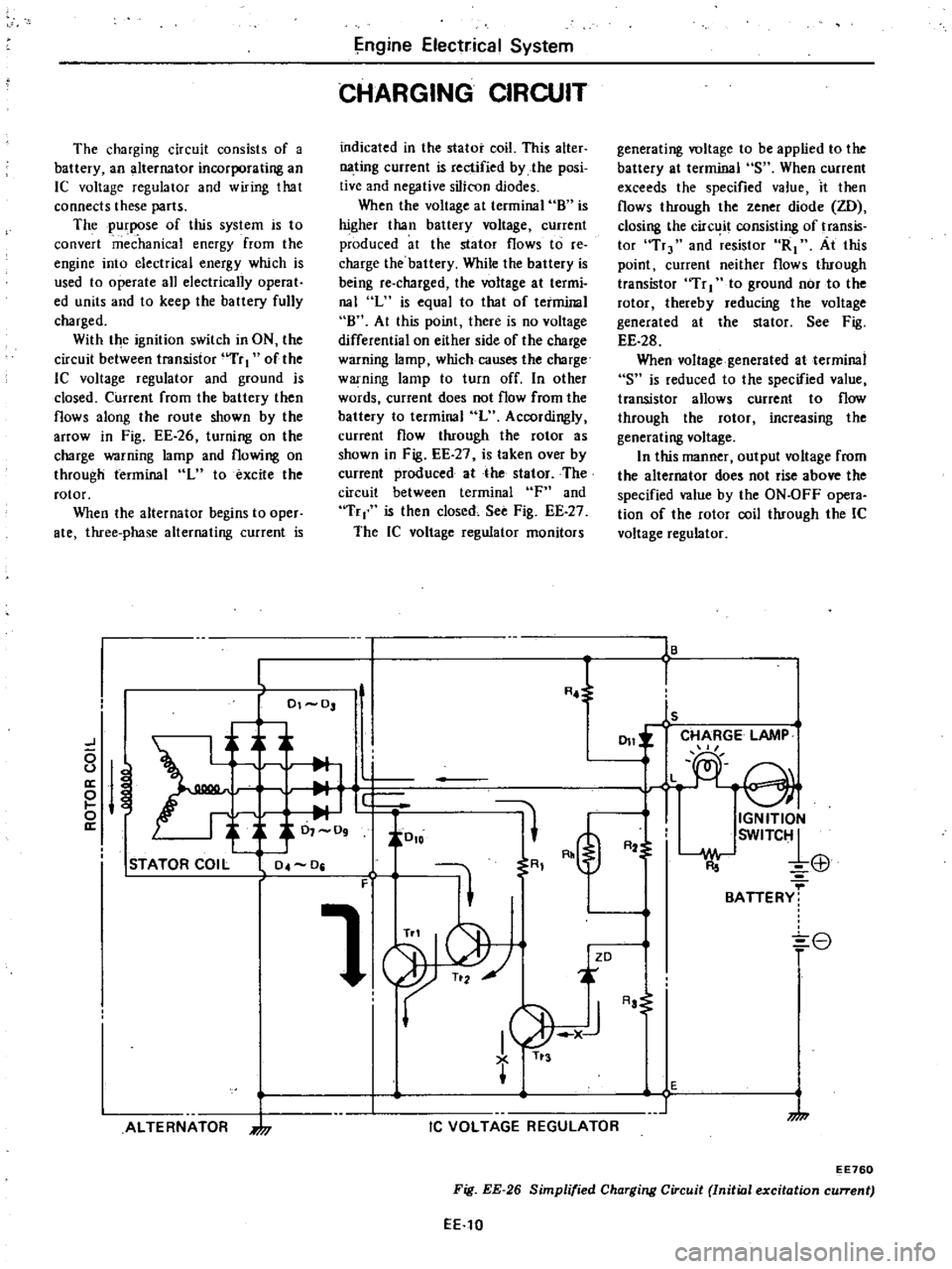
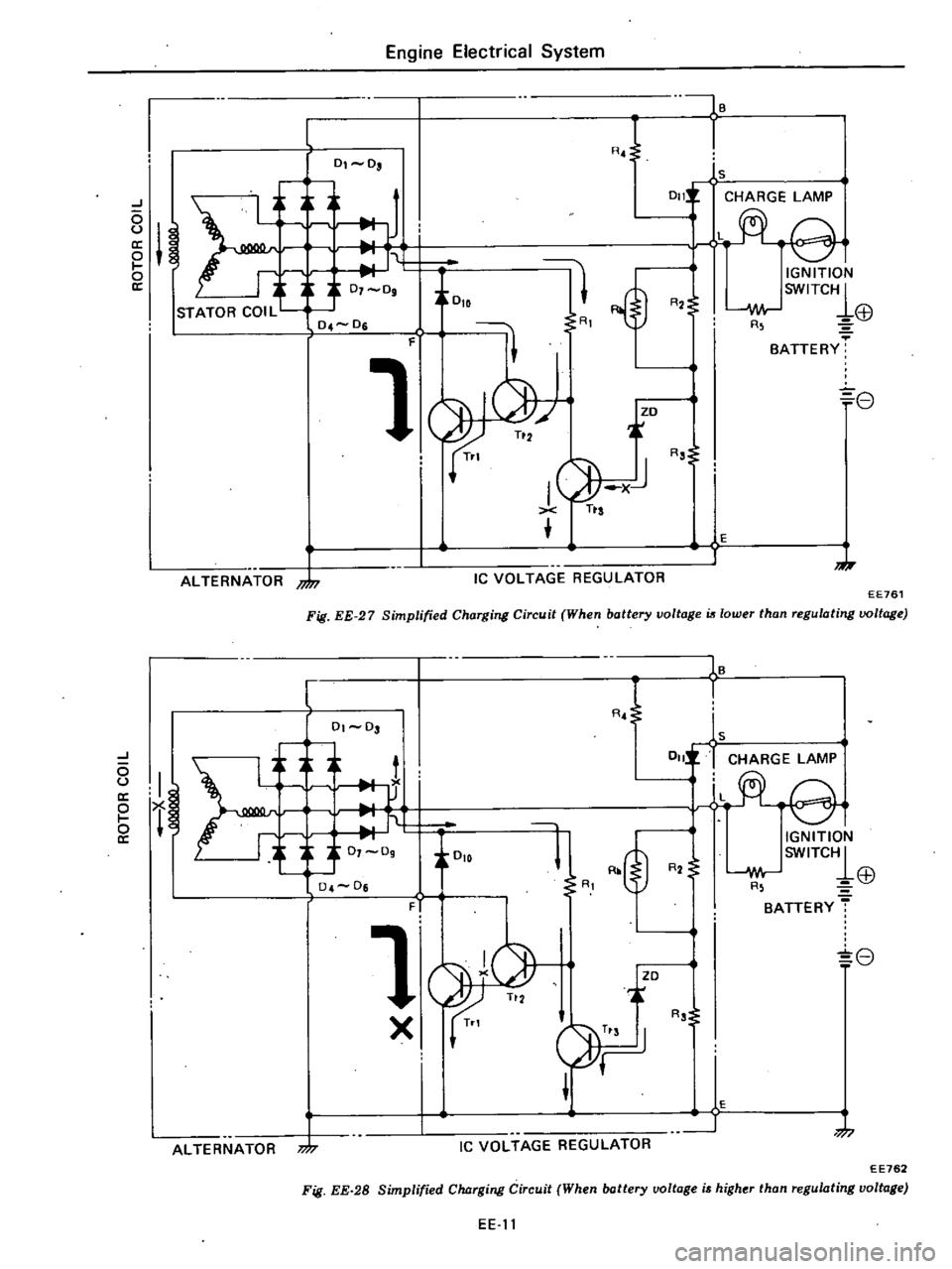
The
charging
circuit
consists
of
a
battery
an
alternator
incorporating
an
IC
voltage
regulator
and
wiring
that
connects
these
parts
The
purpose
of
this
system
is
to
convert
mec
hanka
energy
from
the
engine
into
electrical
energy
which
is
used
to
operate
all
electrically
operat
ed
units
and
to
keep
the
battery
fully
charged
With
the
ignition
switch
in
ON
the
circuit
between
transistor
uTr
I
of
the
lC
voltage
regulator
and
ground
is
closed
Current
from
the
battery
then
flows
along
the
route
shown
by
the
arrOW
in
Fig
EE
26
turning
on
the
charge
warning
lamp
and
flowing
on
through
terminal
L
to
excite
the
rotor
When
the
alternator
begins
to
oper
ate
three
phase
alternating
current
is
ngine
Elect
ical
System
CHARGING
CIRCUIT
indicated
in
the
stator
coil
This
alter
nating
current
is
rectified
by
the
posi
tive
and
negative
silicon
diodes
When
the
voltage
at
terminal
8
is
higher
than
battery
voltage
current
produced
at
the
stator
flows
to
re
charge
the
battery
While
the
battery
is
being
re
charged
the
voltage
at
termi
nal
L
is
equal
to
that
of
terminal
8
At
this
point
there
is
no
voltage
differential
on
either
side
of
the
charge
warning
lamp
which
causes
the
charge
warning
lamp
to
turn
off
In
other
words
current
does
not
flow
from
the
battery
to
terminal
L
Accordingly
current
flow
through
the
rotor
as
shown
in
Fig
EE
27
is
taken
over
by
current
produced
at
the
stator
The
circuit
between
terminal
F
and
Tr
is
then
closed
See
Fig
EE
27
The
IC
voltage
regulator
monitors
generating
voltage
to
be
applied
to
the
battery
at
terminal
S
When
current
exceeds
the
specified
value
it
then
flows
through
the
zener
diode
ZD
closing
the
circ
it
consisting
of
transis
tor
Tr
and
resistor
R1
At
this
point
current
neither
flows
through
transistor
Tr
I
to
ground
nor
to
the
rotor
thereby
reducing
the
voltage
generated
at
the
stator
See
Fig
EE
28
When
voltage
generated
at
terminal
S
is
reduced
to
the
specified
value
transistor
allows
current
to
flow
through
the
rotor
increasing
the
generating
voltage
In
this
manner
output
voltage
from
the
alternator
does
not
rise
above
the
specified
value
by
the
ON
OFF
opera
tion
of
the
rotor
coil
through
the
IC
voltage
regulator
16
L
R
l
I
01
0
ls
CHARGE
LAMP
J
011
L
e
0
u
a
M
e
i
J
0
io
o
IGNITION
a
0
09
SWITC1
R2
El1
STATOR
COIL
04
0
R
F
1
BATTERY
8
ZD
ALTERNATOR
7
I
1
AJ
TI
3
IC
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
Aa
E
1
7
EE760
Fig
EE
26
Simplified
Charging
Circuit
Initial
excitation
current
EE
10
Page 169 of 548
J
o
u
o
ll
ALTERNATOR
nJn
l
0
0
Engine
Electrical
System
F
00IB
RJ
1
1s
0111
CHARGE
LAMP
rt
ei
tOlD
11
1
IGNITION
SWITC1
R2
i
I
oJor
EB
R
BATTERY
f
3
07
09
0
4
0
1
8
r
I
G
XiJ
Tts
R
o
s
o
E
1
J
IC
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
Fig
EE
27
Simplified
Charging
Circ14it
When
battery
voltage
is
lower
than
regulating
voltage
EE761
I
h
it
r
f
1
0
0
J
o
U
ll
o
I
o
cr
ALTERNATOR
m
l
01
03
1
X
RJ
16
I
1s
OIlI
r
CHARGE
LAMP
L
l
@
R2
IGNITION
SWITCH1
w
Lp
R
l
Q7
BATTERY
T
8
T
F
i
R
j
JZO
RS
E
J
7
Ie
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
EE762
Fig
EE
28
Simplified
Cluzrging
Circuit
When
battery
voltage
i
higher
than
regulating
voltage
EE
11
Page 170 of 548
FUSIBLE
LINK
FUSIBLE
LINK
f
BATTERY
@@
V
R
@@
G
G
FUSleLE
ImrnI
LI
NK
MTI
I
En
g
n
l
Electrical
Syst
lOl
IGNITION
SWITCH
FUSE
lOA
o
v
FUSE
lOA
C
V
L@@
BAT
f
L
S
BI
I
I
sl
fRO
L
I
I
F
I
EI
i
K
a
ALTERNATOR
lE
Ie
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
I
I
L
WR
I
1
d
I
t
J
t
IGNITION
WR
SWITCH
BW
U
0
AUTO
CHOKE
RELAY
G
1
WR
J
I
00
00
gg
1
00
VR
1
E
lDID
I
@
O
BAT
mID
W
J
WR
W
FUSE
BLOCK
CHARGE
WARNING
LAMP
5J
BL
Note
@
V
@
California
models
Non
Qilifomo
18
models
FU
models
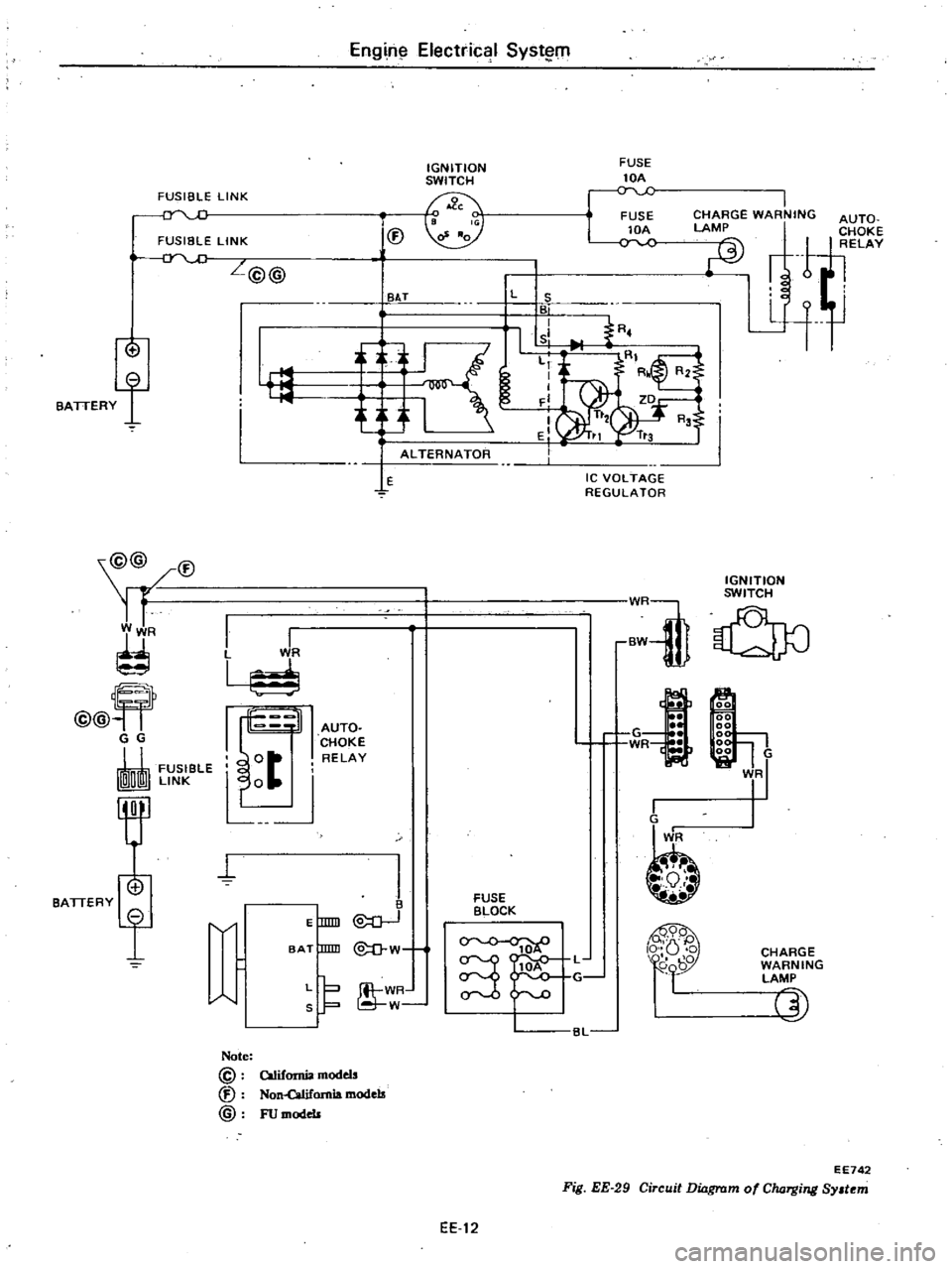
Fig
EE
29
Circuit
Dinrswr
EE742
mofCIuJ
Tg
ng
Sy
t
m
EE
12
Page 171 of 548
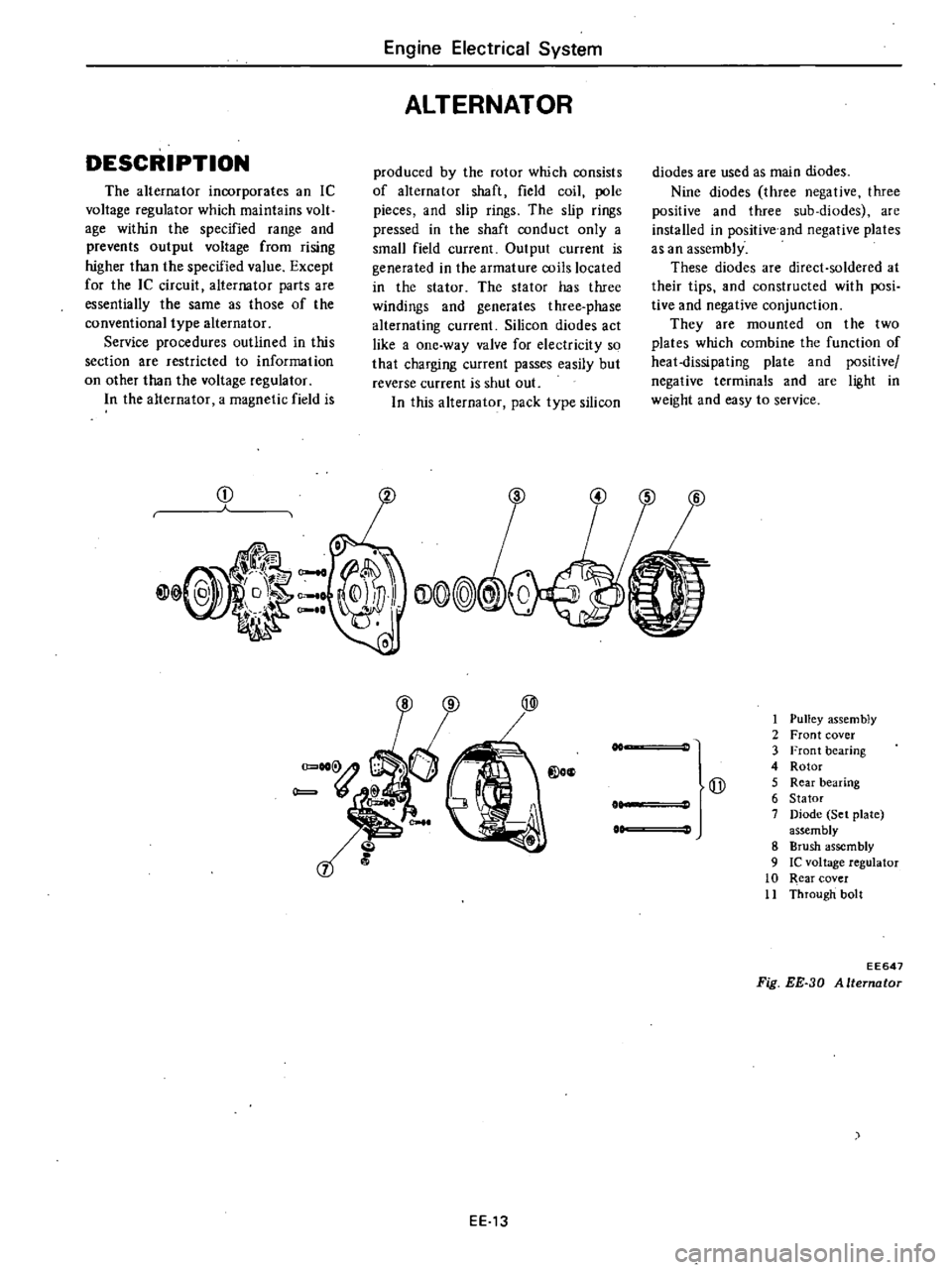
DESCRIPTION
The
alternator
incorporates
an
Ie
voltage
regulator
which
maintains
volt
age
within
the
specified
range
and
prevents
output
voltage
from
rising
higher
than
the
specified
value
Except
for
the
Ie
circuit
alternator
parts
are
essentially
the
same
as
those
of
the
conventional
type
alternator
Service
procedures
outlined
in
this
section
are
restricted
to
information
on
other
than
the
voltage
regulator
In
the
alternator
a
magnetic
field
is
CD
Engine
Electrical
System
ALTERNATOR
produced
by
the
rotor
which
consists
of
alternator
shaft
field
coil
pole
pieces
and
slip
rings
The
slip
rings
pressed
in
the
shaft
conduct
only
a
small
field
current
Output
current
is
generated
in
the
armature
coils
located
in
the
stator
The
stator
has
three
windings
and
generates
three
phase
alternating
current
Silicon
diodes
act
like
a
one
way
valve
for
electricity
so
that
charging
current
passes
easily
but
reverse
current
is
shut
out
In
this
alternator
pack
type
silicon
diodes
are
used
as
main
diodes
Nine
diodes
three
negative
three
positive
and
three
sub
diodes
are
installed
in
positive
and
negative
plates
as
an
assembly
These
diodes
are
direct
soldered
at
their
tips
and
constructed
with
posi
tive
and
negative
conjunction
They
are
mounted
on
the
two
plates
which
combine
the
function
of
heat
dissipating
plate
and
positive
negative
terminals
and
are
light
in
weight
and
easy
to
service
EE13
1
Pulley
assem
bly
2
Front
cover
3
Front
bearing
4
Rotor
Qj
5
Rear
bearing
6
Stator
7
Diode
Set
plate
assembly
8
Brush
assembly
9
Ie
voltage
regulator
10
Rear
cover
11
Through
bolt
EE647
Fig
EE
30
Alternator
Page 172 of 548
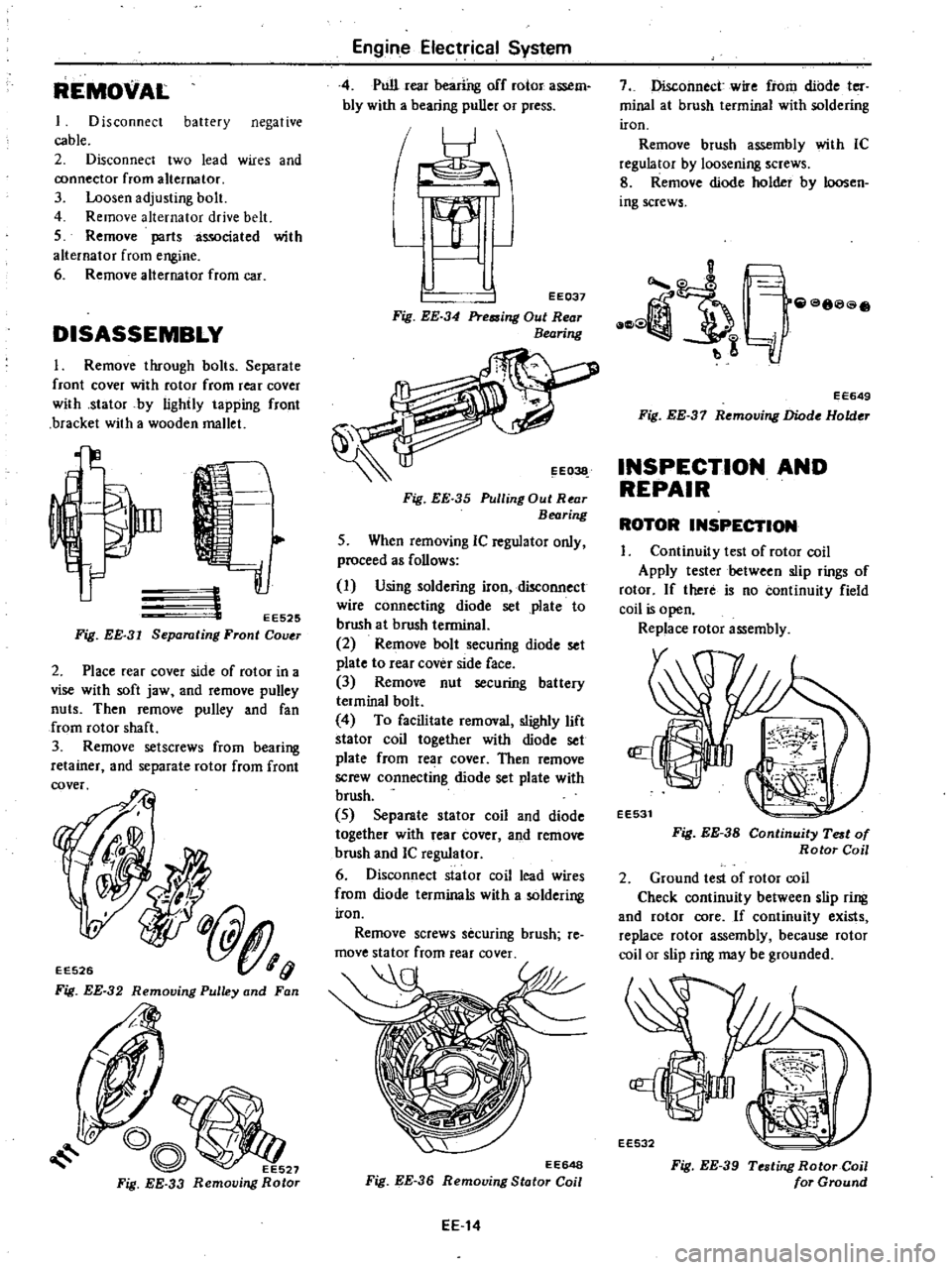
REMOVAL
1
Disconnect
battery
negative
cable
2
Disconnect
two
lead
wires
and
oonnector
from
alternator
3
Loosen
adjusting
bolt
4
Remove
alternator
drive
belt
5
Remove
parts
associated
with
alternator
from
engine
6
Remove
alternator
from
car
DISASSEMBLY
I
Remove
through
bolts
Separate
front
cover
with
rotor
from
rear
cover
with
stator
by
lightly
tapping
front
bracket
with
a
wooden
mallet
rnJ
J
i
EE525
Separating
Front
COI
T
Fig
EE
31
2
Place
rear
cover
side
of
rotor
in
a
vise
with
soft
jaw
and
remove
pulley
nuts
Then
remove
pulley
and
fan
from
rotor
shaft
3
Remove
setscrews
from
bearing
retainer
and
separate
rotor
from
front
EE526
Fig
EE
32
Removing
Pulley
and
Fan
tr
s
0
27
Fig
EE
33
Removing
Rotor
Engine
Electrical
System
4
Pull
rear
bearfug
off
rotor
assem
bly
with
a
bearing
puller
or
press
EE037
Fig
EE
34
Pressing
Out
Rear
Bearing
I
EO
Fig
EE
35
Pulling
Out
Rear
Bearing
5
When
removing
IC
regulator
only
proceed
as
follows
I
Using
soldering
iron
disconnect
wire
connecting
diode
set
plate
to
brush
at
brush
terminal
2
Remove
bolt
securing
diode
set
plate
to
rear
cover
side
face
3
Remove
nut
securing
battery
terminal
bolt
4
To
facilitate
removal
s1ighly
lift
stator
coil
together
with
diode
set
plate
from
re
r
cover
Then
remove
screw
connecting
diode
set
plate
with
brush
5
Separate
stator
coil
and
diode
together
with
rear
cover
and
remove
brush
and
IC
regulator
6
Disconnect
stator
coil
lead
wires
from
diode
terminals
with
a
soldering
iron
Remove
screws
securing
brush
re
move
stator
from
rear
cover
EE648
Fig
EE
36
Removing
Stator
Coil
EE
14
7
Disconnect
wire
from
diode
tor
minal
at
brush
terminal
with
soldering
iron
Remove
brush
assembly
with
IC
regulator
by
loosening
screws
8
Remove
diode
holder
by
loosen
ing
screws
acefii
li
E
E649
Fig
EE
37
Removing
Diode
Holder
INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
ROTOR
INSPECTION
I
Continuity
test
of
rotor
coil
Apply
tester
between
slip
rings
of
rotor
If
there
is
no
continuity
field
coil
is
open
Replace
rotor
assembly
Fig
EE
38
Continuity
Test
of
Rotor
Coil
2
Ground
test
of
rotor
coil
Check
continuity
between
slip
ring
and
rotor
core
If
continuity
exists
replace
rotor
assembly
because
rotor
coil
or
slip
ring
may
be
grounded
EE532
Fig
EE
39
Te
ting
Rotor
Coil
for
Ground
Page 173 of 548
INSPECTION
OF
STATOR
Continuity
test
Stator
is
normal
when
there
is
continuity
between
individual
stator
coil
terminals
When
there
is
no
conti
nuity
between
individual
terminals
cable
is
broken
Replace
stator
assembly
EE533
Fig
EE
40
Testing
Stator
for
Continuity
2
Ground
test
If
each
lead
wire
of
stator
coil
including
neutral
wire
is
not
conduc
tive
with
stator
core
condition
is
satisfactory
If
there
is
continuity
stator
coil
is
grounded
EE534
Fig
EE
41
Testing
Stator
for
Ground
INSPECTION
OF
DIODE
Perform
a
continuity
test
on
diodes
in
both
directions
using
an
ohmmeter
There
are
six
main
diodes
and
tluee
sub
diodes
attached
to
set
plate
Three
main
diodes
are
attached
to
positive
EEl
plate
and
three
others
to
negative
8
plate
Three
sub
diodes
are
attached
to
terminals
The
continuity
test
should
be
per
formed
on
each
diode
between
the
terminal
and
plate
Engine
Electrical
System
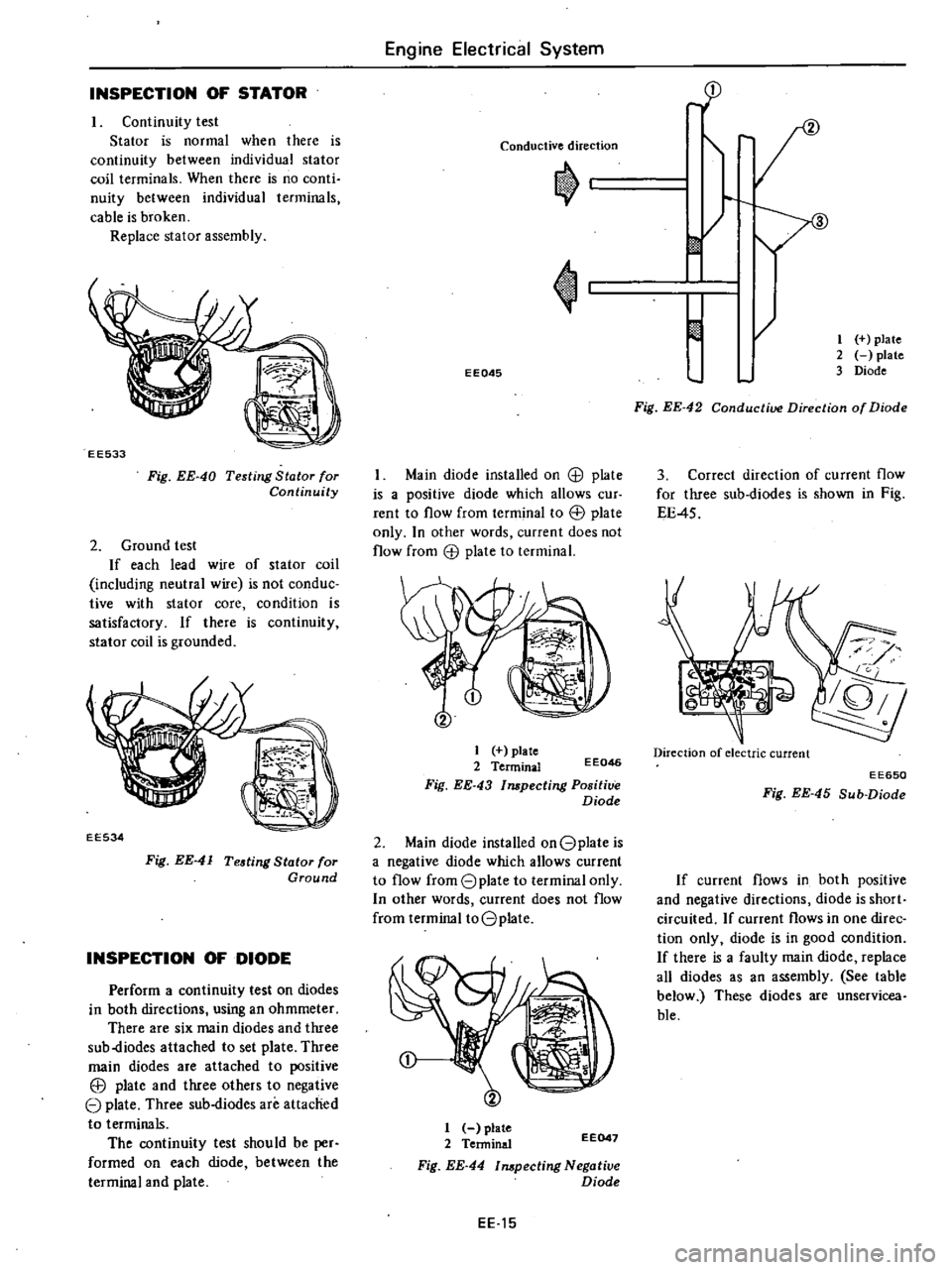
Conductive
direction
EE045
Main
diode
installed
on
8
plate
is
a
positive
diode
which
allows
cur
rent
to
flow
from
terminal
to
EEl
plate
only
In
other
words
current
does
not
flow
from
8
plate
to
terminal
1
plate
2
Terminal
Fig
EE
43
Impecting
Positive
Diode
EE046
2
Main
diode
installed
on
Gplate
is
a
negative
diode
which
allows
current
to
flow
from
Gplate
to
terminal
only
In
other
words
current
does
not
flow
from
terminal
toGplate
1
plate
2
Tenninal
Fig
EE
44
Impecting
Negatiue
Diode
EE047
EE
15
rp
m
1
plate
2
ptate
3
Diode
Fig
EE
42
Conductive
Direction
of
Diode
3
Correct
direction
of
current
flow
for
three
sub
diodes
is
shown
in
Fig
EE
4S
Direction
of
electric
current
EE650
Fig
EE
45
Sub
Diode
If
current
flows
in
both
positive
and
negative
directions
diode
is
short
circuited
If
current
flows
in
one
direc
tion
only
diode
is
in
good
condition
If
there
is
a
faulty
main
diode
replace
all
diodes
as
an
assembly
See
table
below
These
diodes
are
unservicea
ble