checking oil DATSUN 210 1979 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1979, Model line: 210, Model: DATSUN 210 1979Pages: 548, PDF Size: 28.66 MB
Page 52 of 548
m
k
camSM9tJ
down
hole
Key
groove
EM767
Fig
EM
11
Setting
No
I
Piston
atT
D
C
18
Tighten
camshaft
sprocket
bolt
ifl
Tightening
torque
Camshaft
sprocket
bolt
4
to
4
8
kg
m
29
to
35
fHbl
EM502
Fig
EM
72
Tightening
Camshaft
Sprocket
Bolt
19
Install
chain
tensioner
and
tight
en
tensioner
attaching
bolts
ifl
Tightening
torque
Tensioner
enaching
bolt
0
6
to
0
8
kg
m
14
3
to
5
8
ft
b
EM503
Fig
EM
73
Installing
Chain
Tensioner
20
Check
projection
L
of
ten
sioner
spindle
If
projection
L
exceeds
the
speci
fied
limit
replace
chain
Engine
Mechanical
Correct
projection
L
Less
than
15
mm
0
59
inl
lEM504
Fig
EM
74
Checking
Projection
of
Tf
nsioner
Spindle
21
Correctly
install
oil
thrower
in
front
of
camshaft
sprocket
22
Press
new
oil
seal
in
timing
chain
cover
F
ran
t
cover
oil
seal
should
be
replaced
when
front
cover
is
disassem
bled
23
Install
timing
chain
cover
with
gasket
in
place
Note
When
inatalling
oil
seal
apply
coating
of
engine
oil
to
mating
shaft
to
prevent
scratches
and
fold
ed
lip
Also
apply
coating
of
oil
to
periphery
of
oil
seal
ifl
Tightening
torque
Timing
chain
cover
bolts
0
5
to
0
7
kg
m
3
6
to
5
1
ft
Ib
Z5
1
o
j
I
t
f
4
EM455
Fig
EM
75
Installing
Timing
Chain
Covtr
24
Install
water
pump
with
gasket
in
place
ifl
Tightening
torque
Water
pump
attaching
bolts
0
9
to
1
4
kg
m
16
5
to
10
1
ft
bl
25
Install
crank
pulley
then
con
firm
and
set
No
I
piston
at
T
D
C
on
compression
stroke
EM
15
ifl
Tightening
torque
Crank
pulley
nut
15to
20
kg
m
108
to
145
ft
b
26
Invert
engine
Install
oil
stniiner
and
oil
pan
using
new
gasket
and
oil
seal
Note
Give
coating
of
sealant
to
seam
between
oil
pan
gasket
and
oil
pan
oil
seal
ifl
Tightening
torque
Oil
pan
bolts
0
4
to
0
6
kg
m
12
9
to
4
3
ft
lb
27
Install
gasket
and
cylinder
head
Note
Do
not
apply
sealant
to
any
other
part
of
cylinder
block
and
head
surface
28
Tighten
cylinder
head
bolts
ifl
Tightening
torque
Cylinder
head
bolts
7
0
to
7
5
kg
m
51
to
54
ft
IM
Note
a
One
of
cylinder
head
bolts
is
smal
ler
in
diameter
than
others
and
has
a
hollow
head
It
should
be
install
ed
on
right
side
center
of
cylinder
head
b
Tightening
should
be
made
in
two
or
three
steps
finally
torquing
to
specification
c
Retighten
cylinder
head
bolt
after
engine
has
been
warmed
up
Refer
to
Carburetor
Idle
R
P
M
and
Mixture
Ratio
EF
Section
for
Adjustment
and
Inspection
EM505
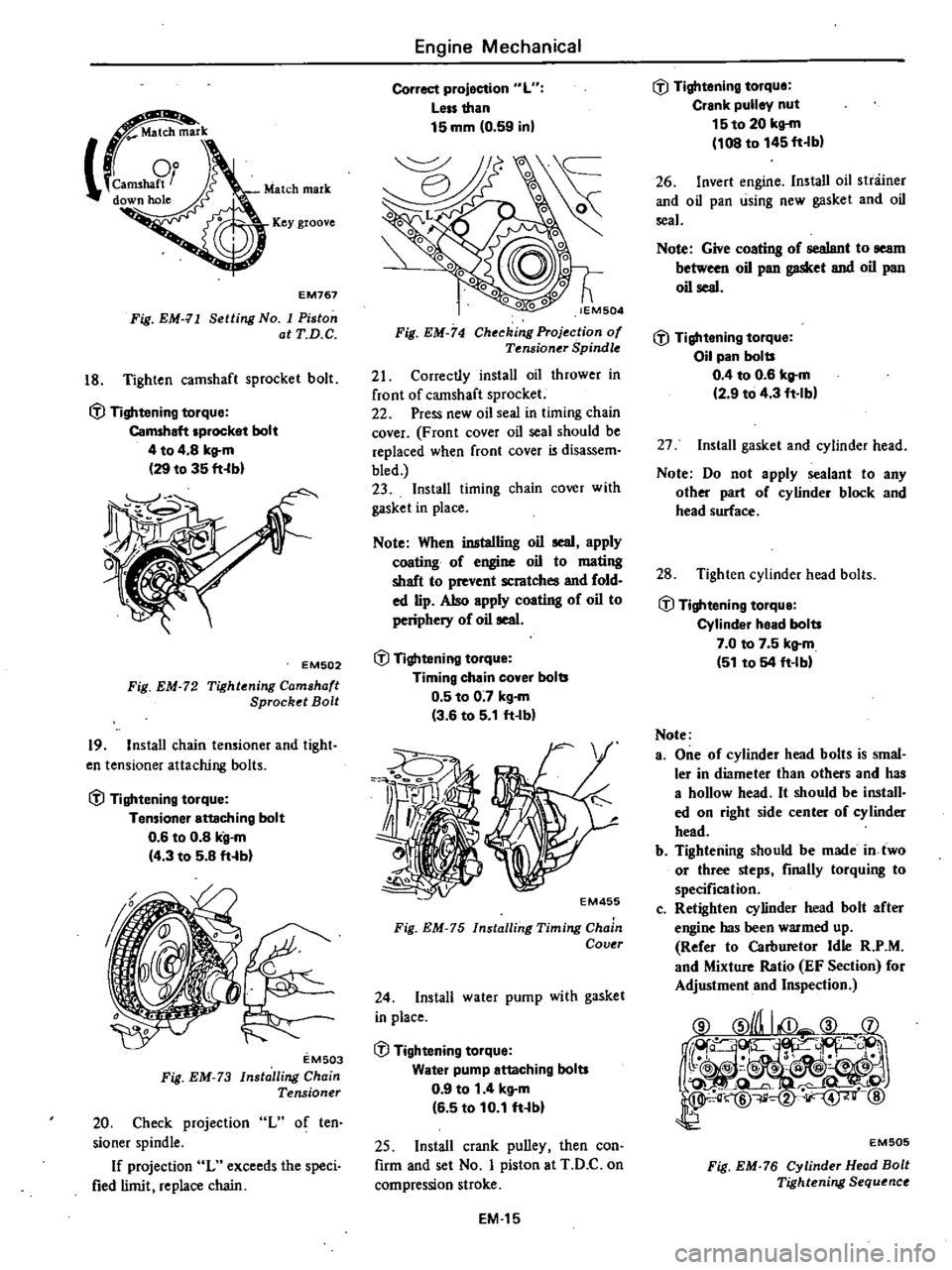
Fig
EM
76
Cylinder
Head
Bolt
Tightening
Sequence
Page 75 of 548
OIL
PUMP
The
oil
pump
and
filter
assembly
is
bolted
to
the
right
side
of
the
cylinder
block
and
can
be
removed
with
the
engine
in
pl
c
The
oil
pump
which
is
driven
by
a
gear
on
the
camshaft
has
the
full
flow
element
type
filter
in
stalled
to
the
oil
pump
cover
REMOVAL
I
Place
a
suitable
container
under
oil
pump
2
Remove
three
bolts
attaching
oil
pump
and
filter
assembly
and
with
draw
assembly
3
Separate
oil
filter
from
oil
pump
4
Ciean
off
old
gasket
from
mating
surfaces
i
E
L043
F
EL
2
R
moving
Oil
Pump
Asso
mbly
INSTALLATION
I
Install
oil
filter
to
oil
pump
2
Locate
oil
pump
and
filter
as
sembly
or
cylinder
block
using
a
spacer
and
new
gasket
Secure
with
three
bolts
l
l
Tightening
torque
Oil
pump
securing
bolts
0
9
to
1
4
kg
m
6
5
to
10
1
ft
lbl
3
Check
oil
level
and
add
oil
if
necessary
4
Start
engine
and
check
for
oil
leaks
5
Remove
the
container
Engine
Lubrication
System
DISASSEMBLY
AND
ASSEMBLY
I
Remove
bolt
securing
pump
cover
to
pump
body
Separate
pump
cover
from
pump
body
2
Slide
out
outer
rotor
from
pump
body
3
Remove
oil
pressure
regulator
plug
washer
shim
spring
and
valve
4
Assemble
oil
pump
in
reverse
order
of
disassembly
Note
a
When
placing
oil
pump
in
a
vice
use
extreme
care
not
to
distort
pump
body
and
cover
in
the
jaws
b
Do
not
pull
out
drive
shaft
pin
securing
drive
shaft
and
inner
rotor
Shaft
is
press
fitted
to
rotor
with
the
pin
caulked
EL044
Fig
EL
3
Oil
Pump
l
l
Tightening
torque
Oil
pump
cove
bolt
0
39
to
0
5
2
kltm
2
8
to
3
8
ti
Ib
Regulator
valve
plug
4
0
to
5
0
kltm
29
to
36
ft
bl
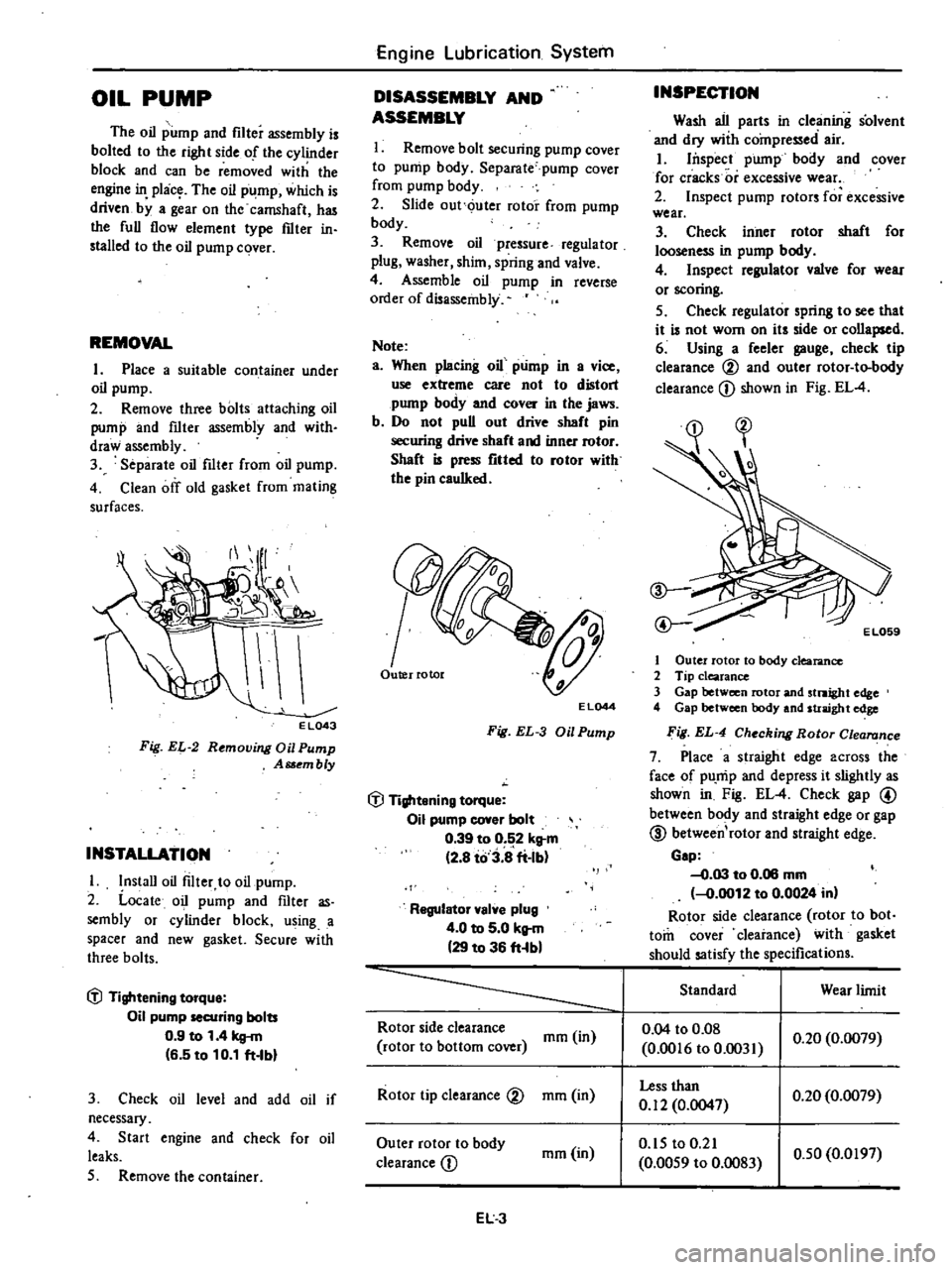
INSPECTION
Wash
all
parts
in
cleaning
solvent
and
dry
wiih
compressed
air
I
hispect
pump
body
and
cover
for
cracks
or
excessive
wear
2
Inspect
pump
rotors
for
excessive
wear
3
Check
inner
rotor
shaft
for
looseness
in
pump
body
4
Inspect
regulator
valve
for
wear
or
scoring
5
Check
regulator
spring
to
see
that
it
is
not
worn
on
its
side
or
collapsed
6
Using
a
feeler
gauge
check
tip
clearance
00
and
outer
rotor
to
body
clearance
CD
shown
in
Fig
EL
4
EL059
1
Outer
rotor
to
body
clearance
2
Tip
clearance
3
Gap
between
rotor
and
stnight
edge
4
Gap
between
body
and
straight
edge
ig
EL
4
Checking
Rotor
Clea
nce
7
Place
a
straight
edge
across
the
face
of
pU
mp
and
depress
it
slightly
as
shown
in
Fig
EL
4
Check
gap
@
between
body
and
straight
edge
or
gap
@
between
rotor
and
straight
edge
Gap
0
03
to
0
06
mm
0
0012
to
0
0024
in
Rotor
side
clearance
rotor
to
bot
tom
cover
clearance
with
gasket
should
satisfy
the
specifications
Standard
Wear
limit
Rotor
side
clearance
mm
in
0
04
to
0
08
rotor
to
bottom
cover
0
0016
to
0
031
0
20
0
0079
Rotor
tip
clearance
V
mm
in
Less
than
0
20
0
0079
0
12
0
0047
Outer
rotor
to
body
mm
in
0
15
to
0
21
0
50
0
0197
clearance
CD
0
0059
to
0
083
EL3
Page 82 of 548
Cooling
System
TEM
COUPLlNG
Non
Califomia
model
equipped
with
air
conditioning
Tem
coupling
is
a
type
of
fan
coupling
which
is
provided
with
a
temperature
control
system
The
conventional
coupling
always
slips
the
fan
at
a
high
speed
under
a
constant
ratio
regardless
of
the
engine
cooling
requirement
The
slipping
ratio
of
the
Tem
coupling
however
is
properly
changed
with
the
cooling
requirement
ON
denotes
that
cooling
is
required
and
the
fan
operates
up
to
about
2
900rpm
When
high
cooling
is
not
required
during
cold
season
with
the
engine
warmed
up
etc
the
oper
ation
is
placed
under
OFF
condition
and
the
fan
slips
at
about
2
050
rpm
The
coiled
bimetal
thermostat
installed
on
the
front
center
portion
of
the
Tem
coupling
detects
temperature
of
air
passing
through
the
radiator
The
air
temperature
is
directly
relative
to
the
engine
coolant
tempera
ture
and
the
inside
slide
valve
is
opened
or
closed
as
required
and
thus
the
ON
OFF
control
is
performed
When
the
air
temperature
rises
the
bimetal
is
expanded
and
the
valve
is
opened
silicone
oil
is
forwarded
to
the
groove
that
transmits
torque
and
the
system
is
placed
under
ON
con
dition
When
the
valve
closes
silicone
oil
is
not
supplied
to
the
groove
oil
in
the
groove
is
accumulated
on
the
Tem
coupling
periphery
due
to
the
centrifu
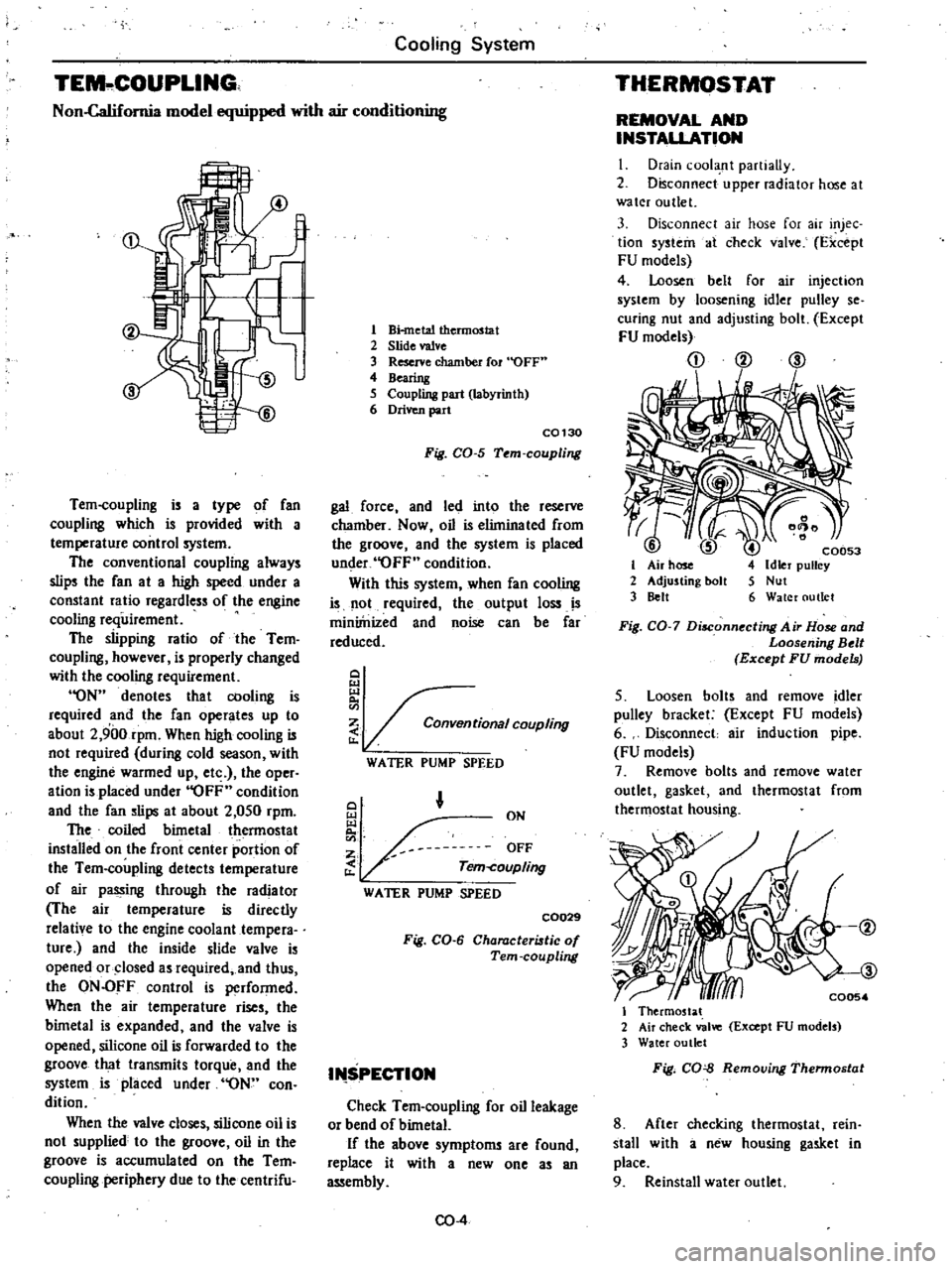
1
Bi
metal
thermostat
2
Slide
valve
3
Reserve
chamber
fOl
OFF
4
Bearing
5
Coupling
part
labyrinth
6
Driven
part
C0130
Fig
CO
5
Tem
coupling
gal
force
and
led
into
the
reserve
chamber
Now
oil
is
eliminated
from
the
groove
and
the
system
is
placed
under
OFF
condition
With
this
system
when
fan
cooling
is
not
required
the
output
loss
IS
miniinized
and
noise
can
be
far
reduced
Q
i
tionalCOUPling
WATER
PUMP
SPEED
Q
ON
OFF
Tem
coupling
WATER
PUMP
SPEED
C0029
Fig
CO
6
Characteristic
of
Tern
coupling
I
SPECTION
Check
Tem
coupling
for
oil
leakage
or
bend
of
bimetaL
If
the
above
symptoms
are
found
replace
it
with
a
new
one
as
an
assembly
CO
4
THERMOSTAT
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
I
Drain
cool
nt
partiaUy
2
Disconnect
upper
radiator
hose
at
water
outlet
3
Disconnect
air
hose
for
air
injec
tion
systein
at
check
valve
Fxcept
FU
models
4
Loosen
belt
for
air
injechon
system
by
loosening
idler
pulley
se
curing
nut
and
adjusting
bolt
Except
FU
models
CD
@
ID
I
2
3
C0053
Idler
pulley
Nut
Water
outlet
Fig
CO
7
Disconnecting
Air
Hose
and
Loosening
Belt
Except
FU
models
5
Loosen
bolts
and
remove
idler
pulley
bracket
Except
FU
models
6
Disconnect
air
induction
pipe
FU
models
7
Remove
bolts
and
remove
water
outlet
gasket
and
thermostat
from
thermostat
housing
I
Thermostat
2
Air
check
valve
Except
FU
models
3
Water
outlet
Fig
CO
Removing
Thennostat
8
After
checking
thermostat
rein
stall
with
a
new
housing
gasket
in
place
9
Reinstall
water
outlet
Page 125 of 548
Emission
Control
System
CRANKCASE
EMISSION
CONTROL
SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
This
system
returns
blow
by
gas
to
both
the
intake
manifold
and
carbure
tor
aitdeaner
The
positive
crankcase
ventilation
P
C
v
valve
is
provided
to
conduct
crankcase
blow
by
gas
to
the
intake
manifold
During
partial
throttle
operation
of
the
engine
the
intake
manifold
sucks
the
blow
by
gas
through
the
P
C
V
valve
Normally
the
capacity
of
the
valve
is
sufficient
to
handle
any
blow
by
and
a
small
amount
of
ventilating
air
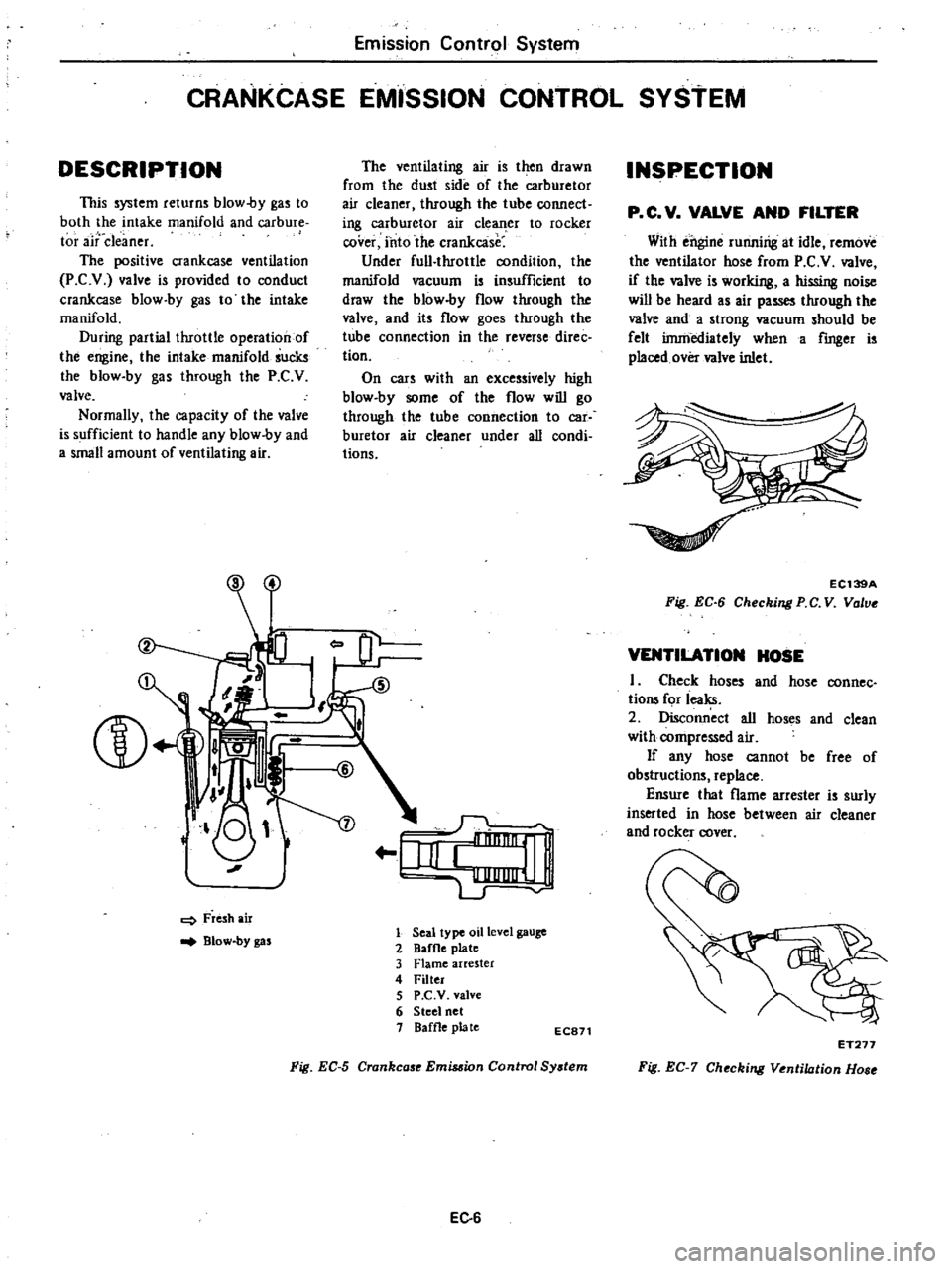
L
J
J
o
I
Fresh
air
Blow
by
gas
The
ventilating
air
is
then
drawn
from
the
dust
side
of
the
carburetor
air
cleaner
through
the
tube
connect
ing
carburetor
air
cle
er
to
rocker
cover
into
the
crankcase
Under
full
throttle
condition
the
manifold
vacuum
is
insufficient
to
draw
the
blow
by
flow
through
the
valve
and
its
flow
goes
through
the
tube
connection
in
the
reverse
direc
tion
On
cars
with
an
excessively
high
blow
by
some
of
the
flow
will
go
through
the
tube
connection
to
car
buretor
air
cleaner
under
all
condi
tions
r
IiI
e
1
LJ
1
Seal
type
oil
level
gauge
2
DafOe
plate
3
Flame
arrester
4
Filter
5
P
C
V
valve
6
Steel
net
1
Baffle
plate
EC871
Fig
EC
5
Crankcase
Emis
ion
Control
Sy
tem
EC
6
INSPECTION
p
C
V
VALVE
AND
FILTER
With
ei
gine
runnirig
at
idle
remove
the
ventilator
hose
from
P
C
V
valve
if
the
valve
is
working
a
hissing
noise
wiD
be
heard
as
air
passes
through
the
valve
and
a
strong
vacuum
should
be
felt
irnniediately
when
a
fmger
is
placed
over
valve
inlet
EC139A
Fig
EC
6
Checking
PC
V
Vo
ve
VENTILATION
HOSE
I
Check
hoses
and
hose
connec
tions
for
ieaks
2
oisconn
ct
all
hoses
and
clean
with
compressed
air
If
any
hose
cannot
be
free
of
obstructions
replace
Ensure
that
flame
arrester
is
surly
inserted
in
hose
between
air
cleaner
and
rocker
rover
ET277
Fig
EC
7
Checking
Ventilation
Hose
Page 128 of 548

Remove
snap
ring
CD
and
lock
bolt
@
and
the
following
parts
can
be
detached
from
heat
control
valve
shaft
Key
ID
Counterweight
@
Thermostat
spring
@
Coil
spring
@
Note
As
previously
descnbed
heat
control
valve
j
is
welded
to
valve
shaft
@
at
exhaust
manifold
and
cannot
be
disassembled
To
install
reverse
the
removal
procedure
INSPECTION
1
With
engine
stopped
visually
check
the
quick
heat
manifold
system
for
the
following
items
I
Check
heat
control
valve
for
malfunction
due
to
break
of
key
that
locates
counterweight
to
valve
shaft
2
Rotate
heat
control
valve
shaft
with
fingers
and
check
for
binding
between
shaft
and
bushing
in
closing
and
opening
operation
of
heat
control
valve
If
any
binding
is
felt
in
rotating
operation
move
valve
shaft
in
the
rotation
direction
several
times
If
this
operation
does
not
correct
binding
condition
it
is
due
to
seizure
between
shaft
and
bushing
and
exhaust
mani
fold
should
be
replaced
as
an
assem
bly
Emission
Control
System
Counterweight
Heat
control
valve
Stopper
pin
EC249
Fig
EC
IO
Checking
Heat
Control
Valve
Movement
2
Run
engine
and
visually
check
counterweight
to
see
if
it
operates
properly
I
When
engine
speed
is
increased
discharge
pressure
of
exhaust
gases
causes
counterweight
to
move
down
ward
clockwise
2
For
some
time
after
starting
engine
in
cold
weather
counterweight
turns
counterclockwise
until
it
comes
into
contact
with
stopper
pin
installed
to
exhaust
manifold
EC
9
Counterweight
gradually
moves
down
clockwise
as
engine
warms
up
and
ambient
temperature
goes
higher
around
exhaust
manifold
If
it
does
not
move
at
all
check
and
replace
thermostat
spring
AIR
INJECTION
SYSTEM
A
I
S
DESCRIPTION
The
Air
Injection
System
A
I
S
is
adopted
on
U
S
A
models
except
FU
models
and
injects
compressed
air
secondary
air
coming
from
the
air
pump
into
the
exhaust
port
of
the
cylinder
head
to
reduce
hydrocarbons
He
and
carbon
monoxide
CO
in
exhaust
gas
through
recombustion
There
are
two
types
of
Air
Injection
System
Fresh
outside
air
is
drawn
by
the
air
pump
through
the
air
pump
air
cleaner
Compressed
air
is
injected
into
the
exhaust
manifold
through
the
check
valve
The
A
B
valve
supplies
air
from
the
carburetor
air
cleaner
to
the
intake
manifold
so
as
to
prevent
after
fire
during
deceleration
The
amount
of
injected
air
is
con
trolled
by
C
A
C
valve
California
models
or
air
relief
valve
Non
California
models
Page 144 of 548

INSPECTION
Entire
system
I
Make
a
thorough
vjsual
check
of
E
G
R
control
system
If
necessary
wipe
away
oil
to
facilitate
inspection
If
any
hoses
are
cracked
or
broken
replace
2
With
engine
stopped
inspect
E
G
R
control
valve
for
any
indication
of
binding
or
sticking
by
moving
dia
phragm
of
control
valve
upwards
with
a
finger
3
With
engine
running
inspect
E
G
R
control
valve
and
thermal
vacu
um
valve
for
normal
operation
1
When
engine
coolant
tempera
tun
is
low
Make
sure
that
E
G
R
control
valve
does
not
operate
when
engine
speed
is
increased
from
idling
to
3
000
to
3
500
rpm
Place
a
finger
on
the
diaphragm
of
E
G
R
control
valve
to
check
for
valve
operation
EC773
Fig
EC
73
Checking
E
G
R
Control
2
When
engine
coolant
tempera
tureishigh
Emission
Control
System
Make
sure
that
E
G
R
control
valve
operates
when
engine
speed
is
in
creased
from
idling
to
3
000
to
3
500
rpm
Place
fingers
on
the
diaphragm
of
E
G
R
control
valve
to
check
for
valve
operation
If
E
G
R
control
valve
does
not
operate
check
as
follows
Disconnect
one
end
E
G
R
control
valve
side
of
vacuum
hose
connect
ing
ihermal
vacuum
valve
to
E
G
R
control
valve
Increase
engine
speed
from
idling
to
3
000
to
3
500
rpm
Make
sure
that
thermal
vacuum
valve
is
open
2
port
type
or
closed
3
port
type
and
that
car
buretor
vacuum
is
present
at
the
end
E
G
R
control
valve
side
of
vacuum
hose
If
vacuum
is
weak
or
not
present
at
all
replace
thermal
vacuum
valve
If
vacuum
is
present
check
E
G
R
control
valve
or
B
P
T
valve
If
any
difficulty
is
encountered
in
judging
the
condition
of
any
com
ponent
during
above
inspection
check
the
questionable
component
in
dependently
as
follows
U
S
A
models
Ie
EC160A
Canada
models
ET429
Fig
EC
74
Checking
Vacuum
of
E
G
R
Control
Valve
EC
25
E
G
R
control
valve
Dismount
E
G
R
control
valve
from
engine
I
Apply
vacuum
to
E
G
R
control
valve
referring
to
the
following
figure
If
the
valve
moves
to
full
position
it
is
normal
E
G
R
control
valve
will
remain
open
for
more
than
30
seconds
after
vacuum
has
cut
off
5t
orr
rl
1
1
Fig
EC
75
EC129A
Checking
E
G
R
Control
Valve
2
Visually
check
E
G
R
control
wive
for
damage
wrinkle
or
deforma
tion
3
Clean
the
seating
surface
of
E
G
R
control
valve
with
a
brush
and
compressed
air
and
remove
foreign
matter
from
around
the
valve
and
port
Fig
EC
76
Cleoning
E
G
R
Control
Valve
Thermal
vacuum
valve
3
port
type
Remove
thermal
vacuum
valve
from
engine
Inhale
air
from
port
ofE
G
R
system
and
check
to
be
sure
that
thermal
vacuum
valve
opens
or
closes
in
response
to
its
temperature
Thermal
vacuum
valve
dosing
temperature
Above
50
to
630
C
122
to
1450
F
Page 152 of 548

e
In
o
L
1
Ignition
switch
2
Vacuum
switching
v3
lve
3
Top
detecting
switch
4
Function
check
connector
EC330A
i
Fig
EC
99
Checking
Top
Detecting
l
Switch
Vacuum
dela
valve
Remove
vacUum
delay
valve
2
Blow
air
from
th
port
of
the
distributor
side
The
vacuum
delay
valve
is
in
go
ij
condition
if
the
air
flows
through
the
valve
3
Try
again
from
the
opposit
side
of
the
valve
Th
valve
is
in
goo
condition
if
th
a
flow
resistance
is
greater
than
the
step
2
abov
Distributor
side
Carburetor
side
Distribu
tor
side
Carburetor
side
EC346
Fig
EC
100
Checking
Vocuum
Dewy
Valve
Emission
Control
Syst
m
4
If
the
condition
of
spark
delay
valve
is
questionable
dip
port
into
a
cup
filled
with
water
Blow
air
from
brown
face
side
Small
air
bubbles
should
appear
CAUTION
Be
c
areful
to
avoid
entry
of
oil
or
dirt
into
valve
7
E
C279
Fig
EC
101
Checking
Vacuum
D
lDy
Valve
CATALYTIC
CONVERTER
California
dels
DESCRIPTION
1
The
catalytic
converter
accelerates
the
chemical
reaction
of
hydrocarbons
CD
0
He
and
carbon
monoxide
O
in
the
exhaust
gas
and
changes
them
into
non
harmful
carbon
dioxide
C02
and
water
H20
This
chemical
reac
tiOD
process
requires
the
proper
a
mount
of
air
which
is
supplied
by
the
air
pump
Refer
to
the
item
AJ
S
This
air
is
called
secondary
air
The
Catalytic
converter
is
mounted
0
the
models
destinbd
for
California
OPERATION
Exhaust
gas
emitted
from
the
en
gine
contains
some
harmful
substances
due
to
incomplete
combustion
in
the
combustion
chamber
The
air
injection
stem
i
designed
to
reduce
the
con
tent
of
such
substances
in
the
exhaust
gas
In
this
system
the
secondary
air
is
led
from
the
ch
ck
valve
and
injected
in
o
the
exhaust
manifold
With
this
injection
of
the
secondary
air
hydro
carbons
He
and
carbon
monoxide
CO
in
the
exhaust
gas
are
gradually
oxidized
with
oxygen
02
in
the
secondary
air
and
converted
into
nOD
harmful
carbon
dioxide
C02
and
water
HP
The
catalytic
converter
further
cleans
engine
exhaust
gas
Through
catalytic
action
it
changes
residual
hydrocarbons
and
carbon
monoxide
contained
in
exhaust
gas
into
carbon
dioxide
and
water
before
exhaust
gas
is
discharged
to
the
atmosphere
0
Secondary
air
Carbon
monoxide
hydrocarbon
Carbon
dioxide
gas
Nater
EC
i
A
I
Front
tube
2
Catalytic
converter
3
Center
tube
4
Main
murner
EC
33
EC215
Fig
EC
I02
Function
of
Catalytic
Converter
Page 153 of 548

REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
I
Jack
up
the
car
Note
Apply
parking
brake
and
place
wheel
chocks
2
Remove
screws
securing
lower
shelter
of
catalytic
converter
Loosen
flange
bolt
connecting
catalytic
converter
to
front
and
rear
exhaust
tube
Catalytic
converter
assembly
can
then
be
taken
out
3
Installation
i
in
the
reverse
se
quence
of
removal
CAUTION
a
Be
careful
not
to
damage
catalytic
co
when
handliilg
b
Never
wet
catalyzer
with
water
oil
etc
t
J
Tightening
torque
Catalyti
converter
bolts
2
6
to
3
4
kg
m
19
to
25
ft
lb
Emission
Control
System
EC075A
EC076A
Fig
EC
103
Removing
Catalytic
Converter
INSPECTION
PrelimInary
In
pectlon
Vi
ually
check
condition
of
all
component
parts
including
hose
tubes
and
wires
replace
if
necessary
Refer
to
Air
Injection
System
for
inspection
EC
34
Catalytic
converter
Whether
catalytic
converter
is
nor
mal
or
not
can
e
checked
by
ob
serving
variation
in
CO
percentage
The
checking
procedure
is
as
follows
Apply
parking
brake
Shift
gears
into
Neutral
for
manual
transmis
sion
and
N
or
P
for
automatic
transmission
position
I
Adjust
engine
idling
speed
and
CO
percentage
Refer
to
Adjusting
Carburetor
Idle
RPM
and
Mixture
Ratio
for
adjustment
2
Race
engine
1
500
to
2
000
rpm
two
or
three
times
under
no
load
and
make
sure
that
specified
CO
percent
age
obtained
3
Remove
cap
and
connect
air
hose
to
air
check
valve
If
idling
speed
increases
readjust
it
to
specified
speed
with
throttle
adjusting
screw
4
Warm
up
engine
for
about
four
minutes
at
2
000
pm
under
no
load
S
Measure
Ci
percentage
at
idling
speed
After
stepAhas
been
complet
ed
wait
for
one
minute
before
making
CO
percentage
measurement
6
If
CO
percentage
measured
in
step
5
is
less
than
0
3
the
catalytic
converter
is
normaL
7
If
CO
percentage
measured
in
step
5
is
over
0
3
recheck
AJ
S
and
1
replace
air
check
valVe
The
perform
inspection
steps
4
and
S
8
If
CO
percentage
is
still
over
0
3
in
step
7
catalyt
iC
converter
i
mal
functioning
Replace
catalytic
con
verter
Page 159 of 548

DATSUN
210
Model
8310
Series
SECTIONEE
ENGINE
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
CONTENTS
BATTERY
CHECKING
ELECTROLYTE
LEVEL
CHECKING
SPECIFIC
GRAVITY
CHARGING
INSTALLATION
STARTING
MOTOR
STARTING
CIRCUIT
CONSTRUCTION
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
DISASSEMBL
Y
CLEANING
AND
INSPECTION
ASSEMBL
Y
TEST
CHARGING
CIRCUIT
ALTERNATOR
DESCRIPTION
REMOVAL
DISASSEMBLY
INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
ASSEMBLY
ALTERNATOR
TEST
REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION
INSPECTION
IGNITION
CIRCUIT
EE
2
EE
2
EE
2
EE
3
EE
3
EE
4
EE
4
EE
5
EE
6
EE
6
EE
6
EE
8
EE
8
EE
10
EE
13
EE
13
EE
14
EE
14
EE
14
EE
16
EE
17
EE
1B
EE
18
EE
18
EE
20
DESCRIPTION
DISTRIBUTOR
CONSTRUCTION
CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTMENT
I
ISASSEMBL
Y
AND
ASSEMBLY
IC
IGNITION
UNIT
DESCRIPTION
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
CHECKING
IC
IGNITION
SYSTEM
IGNITION
COIL
SPARK
PLUG
INSPECTION
CLEANING
AND
REGAP
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
INSPECTION
AND
ADJUSTMENT
TIGHTENING
TORQUE
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
I
BATTERY
II
STARTING
MOTOR
III
ALTERNATOR
Including
voltage
regulator
IV
IGNITION
CIRCUIT
EE
20
EE
22
EE
22
EE
23
EE
23
EE
24
EE
24
EE
25
EE
25
EE
28
EE
29
EE
29
EE
29
EE
30
EE
30
EE
31
EE
33
EE
34
EE
34
EE
35
EE
36
EE
37
Page 181 of 548

CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTMENT
CAP
AND
ROTOR
HEAD
Cap
and
rotor
head
should
be
in
spected
periodically
as
specified
in
the
Main
teoanee
Schedule
Remove
cap
and
clean
all
dust
and
carbon
deposits
from
cap
and
rotor
from
time
to
time
If
cap
is
cracked
or
is
leaking
replace
wi
th
a
new
one
ADVANCE
MECHANISMS
SpecHlcatlons
Refer
to
Service
Data
and
Specifica
tions
for
distributor
Vacuum
advance
mechanism
mechanical
parts
If
vacuum
advance
mechanism
fails
to
operate
properly
check
for
the
followin
B
items
and
correct
the
mal
function
as
required
I
Check
vacuum
inlet
for
signs
of
leakage
at
its
connection
If
necessary
retighten
or
replace
with
a
new
one
2
Check
vacuum
diaphragm
for
air
leak
If
leak
is
found
replace
vacuum
controUer
assembly
3
Inspect
breaker
plate
for
smooth
moving
If
plate
does
not
move
smoothly
this
condition
could
be
due
to
sticky
steel
balls
or
pivot
Apply
grease
to
steel
halls
or
if
necessary
replace
breaker
plate
as
an
assembly
Centrifugal
advance
mechanical
parts
When
cause
of
engine
malfunction
is
traced
to
centrifugal
advance
mecha
nical
parts
use
distributor
tester
to
check
its
characteristics
If
nothing
is
wrong
with
its
charac
teristics
conceivable
causes
are
faulty
or
abnormal
wear
of
driving
part
or
others
So
do
not
disassemble
it
In
the
event
of
improper
character
istics
check
closely
rotor
shaft
assem
bly
governor
weight
and
shaft
If
any
of
the
above
parts
are
mal
functioning
replace
the
parts
Engine
Electrical
System
DISASSEMBLY
AND
ASSEMBLY
DISASSEMBLY
I
Take
off
cap
and
remove
rotor
head
2
Remove
Ie
ignition
unit
Refer
to
IC
Ignition
Unit
for
removal
and
in
stallation
3
Remove
stator
and
magnet
by
removing
stator
securing
screws
4
Remove
vacuum
controller
by
removing
securing
screws
EE746
Fig
EE
59
Removing
Vacuum
Controller
5
Using
two
pry
bars
or
suitable
puller
pry
reluctor
from
shaft
CAUTION
When
removing
reluctor
be
careful
not
10
distort
or
damage
the
teeth
6
Remove
roll
pin
7
Remove
pick
up
coil
assembly
8
Remove
breaker
plate
setscrews
and
remove
breaker
plate
assembly
EE703
Fig
EE
60
Removing
Breaker
Plate
Setscrews
9
Punch
knock
pin
out
and
remove
pinion
EE
23
EE704
Fig
EE
61
Removing
Knock
Pin
10
Remove
rotor
shaft
and
drive
shaft
assembly
EE705
Fig
EE
62
Removing
Rotor
Shaft
and
Drive
Shaft
Assembly
11
Mark
rotor
shaft
and
drive
shaft
Remove
packing
from
the
top
of
rotor
shaft
and
unscrew
rotor
shaft
setscrew
Remove
rotor
shaft
EE706
Fig
EE
63
Removing
Rotor
Shaft
12
Mark
one
of
the
governor
springs
and
its
bracket
Also
mark
one
of
the
governor
weights
and
its
pivot
pins
13
Carerully
unhook
and
remove
governor
springs
14
Remove
governor
weights
A
r
ply
grease
to
guvernor
weights
after
disassembling