check engine DATSUN 210 1979 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1979, Model line: 210, Model: DATSUN 210 1979Pages: 548, PDF Size: 28.66 MB
Page 37 of 548
Engine
Tune
up
Condition
Probable
cause
Overheat
Improper
fuel
mixture
Floor
temp
ture
too
high
California
and
FU
model
Problem
in
fuel
system
Refer
to
Inspec
tion
of
Fuel
System
Problem
in
ignition
system
Refer
to
In
spection
oflgnition
System
Corrective
action
Previously
mentioned
Check
the
fuel
system
Check
and
repair
Check
and
repair
SPECIAL
SERVICE
TOOL
Kent
Moore
No
Tool
number
tool
name
Reference
page
or
Fig
No
STl9320000
Oil
filter
wrench
125664
Page
ET
3
ET
23
Kent
Moore
No
Tool
number
tool
name
Reference
page
or
Fig
No
Page 40 of 548
PRELIMINARY
CLEANING
AND
INSPECTION
Before
disassembling
engine
ob
serve
the
following
items
I
Prior
to
disassembling
check
outer
parts
for
sign
of
leak
past
their
gasketed
surfaces
2
Check
carburetor
and
fuel
pump
for
condition
fuel
hoses
for
deteriora
t
ion
cracks
or
otherwise
leakage
of
fuel
past
their
jointed
or
connected
surfaces
3
Wipe
dust
and
mud
off
engine
4
Inspect
outer
parts
for
visual
faults
and
broken
or
missing
parts
such
as
bolts
and
nuts
5
Check
piping
and
electrical
cir
cuits
for
deterioration
breakage
fittings
discontinuity
or
insulation
DISASSEMBLY
To
remove
engine
from
car
refer
to
Section
ER
for
Removal
1
Remove
starting
motor
then
re
move
transmission
from
engine
2
Remove
clutch
assembly
3
Remove
alternator
fan
belt
alter
nator
bracket
and
alternator
adjusting
bar
4
Remove
idler
pulley
air
pump
belt
and
idier
pulley
bracket
If
so
equipped
Note
Loosen
idler
pulley
nut
and
belt
adjusting
bolt
in
that
order
@
1
Idler
pulley
nut
2
Belt
adjusting
bolt
3
Air
pump
belt
4
Idler
pulley
bracket
EM527
Fig
EM
2
Removing
Idle
Pulley
Air
Pump
Belt
and
Idle
Pulley
Bracket
Engine
Mechanical
ENGINE
DISASSEMBLY
5
Remove
air
pump
pulley
air
pump
and
air
pump
bracket
If
so
equipped
6
Remove
fan
fan
spacer
and
pul
ley
7
Remove
oil
level
gauge
8
Remove
distributor
cap
and
high
tension
cables
as
an
assembly
9
Disconnect
distributor
vacuum
line
from
distributor
and
remove
dis
tributor
10
Disconnect
fuel
line
from
carbu
retor
II
Remove
fuel
pump
and
fuel
line
12
Remove
water
outlet
and
thermostat
13
Remove
engine
mounting
brack
et
R
H
14
Remove
oil
pump
and
filter
as
sembly
EL043
Fig
EM
3
Removing
Oil
Pump
15
Remove
spark
plugs
16
Install
Engine
Attachment
KVlOI02500
to
cylinder
block
using
engine
f1
ounling
bracket
R
H
attach
ing
studs
fuel
pump
attaching
studs
and
alternator
bracket
attaching
bolt
holes
17
Mount
engine
on
Engine
Stand
ST050I
SOOO
Fig
EM
4
EM
3
18
Remove
engine
mounting
brack
et
L
H
19
Disconnect
air
vacuum
and
blow
by
hoses
from
air
cleaner
20
Remove
air
cleaner
and
air
cleaner
brackets
21
Remove
vacuum
control
valve
assembly
and
bracket
as
a
unit
22
Remove
carburetor
and
baffle
plate
23
Remove
E
G
R
control
valve
24
Remove
intake
and
exhaust
manifold
assemblies
EM528
Fig
EM
5
Removing
Manifold
25
Remove
P
C
V
hose
pipe
con
nector
to
control
valve
26
Remove
rocker
cover
27
Loosen
valve
rocker
adjusting
nut
and
turn
adjusting
screws
out
to
disengage
push
rods
Then
evenly
loosen
rocker
shaft
bolts
28
Remove
rocker
shaft
assembly
EM453
Fig
EM
6
Removing
Rocker
Shaft
Assembly
29
Withdraw
push
rods
and
keep
them
in
correct
order
1
30
Loosen
cylinder
head
bolts
a
little
at
a
time
in
the
sequence
shown
in
Fig
EM
and
remove
cylinder
head
Page 42 of 548
CYLINDER
HEAD
I
Using
Valve
lifter
STl2070000
compress
valve
spring
and
remove
valve
collet
2
Release
Valve
Lifter
and
remove
spring
retainer
spring
oil
seal
spring
seat
and
valve
PREPARATION
FOR
INSPECTION
I
8efore
cleaning
check
for
signs
of
water
and
oille
s
2
Clean
oil
and
carbon
deposits
from
all
parts
They
should
be
clean
from
gaskets
and
sealant
3
Clean
all
oil
holes
with
solvent
and
dry
with
compressed
air
Make
sure
that
they
are
not
restricted
CYLINDER
HEAD
AND
VALVE
CHECKING
CYLINDER
HEAD
MATING
FACE
I
Make
a
visual
check
for
cracks
and
flaws
2
Measure
surface
of
cylinder
head
on
cylinder
block
sid
for
warpage
If
beyond
designated
limit
correct
s
rface
with
a
surface
grinder
Warpage
of
urfece
Less
than
0
1
mm
0
004
in
EM108
Fig
EM
IS
Checking
Cylinder
Head
Surface
Engine
Mechanical
EM462
Fig
EM
16
Removing
Value
3
Place
valve
components
in
order
INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
Note
Surface
grinding
limit
The
grinding
limit
of
cylinder
head
is
determined
by
the
cylinder
block
grinding
in
an
engine
Depth
of
cylinder
head
grinding
is
A
Depth
of
cylinder
block
grinding
is
6B
The
limit
is
as
follows
A
B
0
2
mm
0
008
in
VALVE
i
Check
each
of
the
intake
and
exhaust
valve
for
worn
damaged
or
deformed
valve
caps
or
stems
Correct
or
replace
the
valve
that
is
faulty
For
standard
size
of
valve
refer
to
Service
Data
and
Specifications
2
Valve
face
or
valve
stem
end
surface
should
be
refaced
by
using
a
valve
grinder
Note
When
valve
head
has
been
worn
down
to
0
5
mm
0
020
in
in
thickness
replace
the
valve
Grinding
allowance
for
valve
stem
end
surface
is
0
5
mm
0
020
in
or
less
c
EM111
Fig
EM
19
Regrinding
Valve
Face
EM
5
C
vO@
lll@8
C
CQ8@
a
EM463
Fig
EM
17
Valve
Components
Note
Take
care
not
to
lose
valve
spring
seat
oil
seal
valve
collet
and
valve
rocker
guide
VALVE
SPRING
I
Check
valve
spring
for
squareness
using
a
steel
square
and
surface
plate
If
spring
is
out
of
square
S
more
than
specified
limit
replace
with
new
ones
Out
of
square
S
Less
than
1
6
mm
0
063
inl
L
1
EM296
Fig
EM
20
Measuring
Spring
Sguareness
2
Measure
the
free
length
and
the
tension
of
each
spring
If
the
measured
value
exceeds
the
specified
limit
re
place
spring
Refer
to
Service
Data
and
pecifica
tions
EMl13
Fig
EM
21
Measuring
Spring
Teruion
Page 43 of 548
VALVE
GUIDE
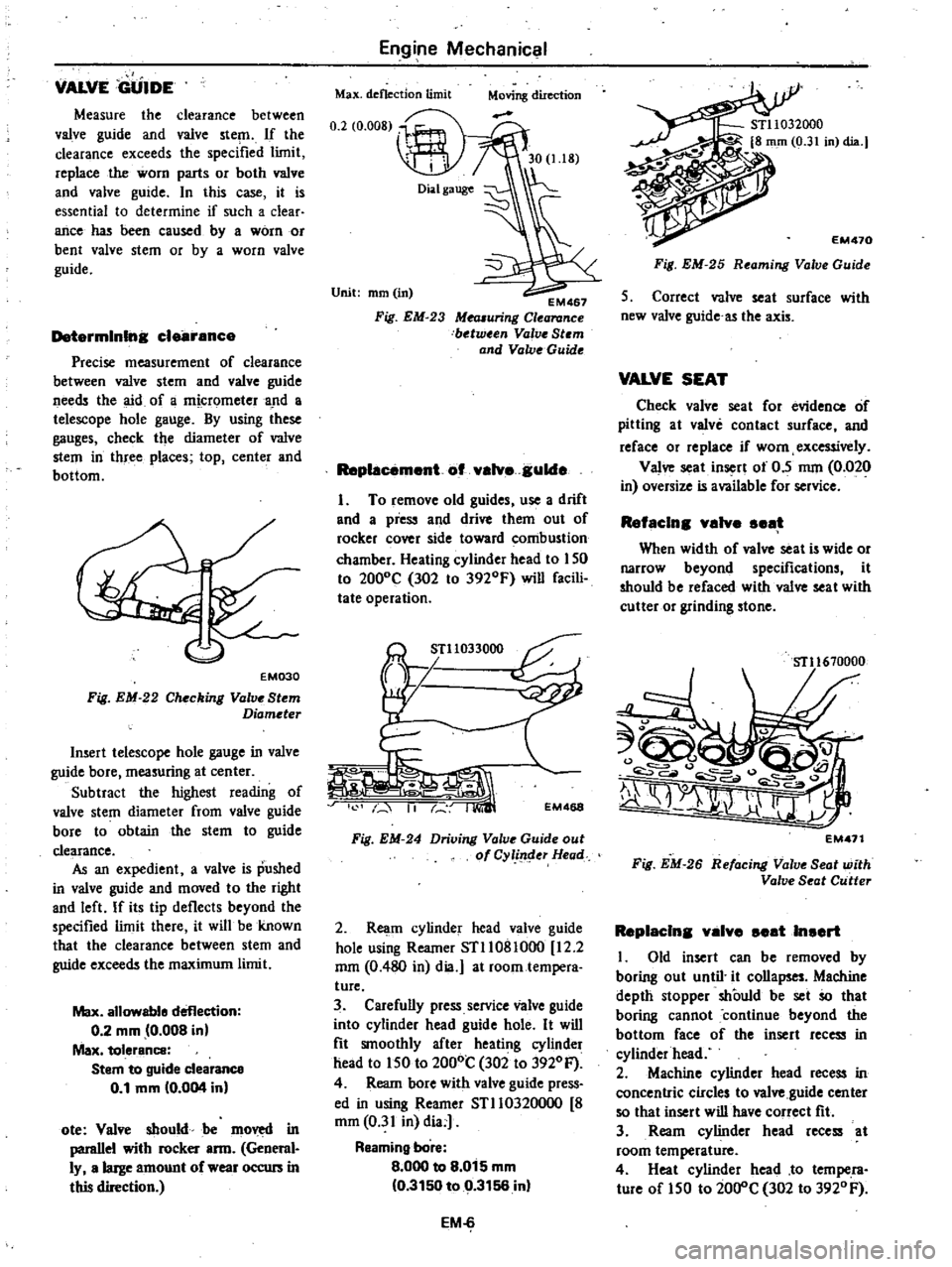
Measure
the
clearance
between
valve
guide
and
valve
stern
If
the
clearance
exceeds
the
specified
limit
replace
the
worn
parts
or
both
valve
and
valve
guide
In
this
case
it
is
essential
to
determine
if
such
a
clear
ance
has
been
caused
by
a
worn
or
bent
valve
stem
or
by
a
worn
valve
guide
Determining
clearance
Precise
measurement
of
clearance
between
valve
stem
and
valve
guide
needs
the
aid
of
a
micrometer
and
a
telescope
hole
gauge
By
using
these
gauges
check
the
diameter
of
valve
stem
in
three
places
top
center
and
bottom
EM030
Fig
EM
22
Checking
Valve
Stem
Diameter
Insert
telescope
hole
gauge
in
valve
guide
bore
measuring
at
center
Subtract
the
highest
reading
of
valve
stem
diameter
from
valve
guide
bore
to
obtain
the
stem
to
guide
clearance
As
an
expedient
a
valve
is
pushed
in
valve
guide
and
moved
to
the
right
and
left
If
its
tip
deflects
beyond
the
specified
limit
there
it
will
be
known
that
the
clearance
between
stem
and
guide
exceeds
the
maximum
limit
Max
allowabl
deflection
0
2
mm
0
008
in
Max
tolerance
Stem
to
guide
clearance
0
1
mm
10
004
in
ote
Valve
sbould
be
moved
in
paraIlel
with
rocker
ann
General
ly
a
large
amount
of
wear
occurs
in
this
direction
Engine
Mechanical
Max
deflection
limit
Unit
mm
in
EM467
Mea6uring
Clearance
between
Valve
Stem
and
Valve
Guide
Fig
EM
23
Replacement
of
valve
julde
I
To
remove
old
guides
use
a
drift
and
a
pie
and
drive
them
out
of
rocker
cover
side
toward
combustion
chamber
Heating
cylinder
head
to
I
SO
to
200
C
302
to
392
F
will
facili
tate
operation
T11033000
EM468
1
II
Fig
EM
24
Driving
Valve
Guide
out
of
Cylinder
Head
2
Ream
cylinder
head
valve
guide
hole
using
Reamer
STlI081000
12
2
mrn
0
480
in
dia
at
room
tempera
ture
3
Carefully
press
service
Valve
guide
into
cylinder
head
guide
hole
It
will
fit
smoothly
after
heating
cylinder
head
to
ISO
to
200
302
to
392
F
4
Ream
bore
with
valve
guide
press
ed
in
using
Reamer
STll0320000
8
mm
0
31
in
dia
Reaming
bore
8
000
to
8
015
mm
0
3150
to
0
3156
in
EM
6
EM470
Fig
EM
25
Reaming
Valve
Guide
5
Correct
va1ve
seat
surface
with
new
valve
guide
as
the
axis
VALVE
SEAT
Check
valve
seat
for
evidence
of
pitting
at
valve
contact
surface
and
reface
or
replace
if
worn
excessively
Valve
seat
insert
of
0
5
mm
0
020
in
oversize
is
available
for
service
Refaclng
valve
seat
When
width
of
valve
seat
is
wide
or
narrow
beyond
specifications
it
should
be
refaced
with
valve
seat
with
cutter
or
grinding
stone
iIT11670000
EM411
Fig
EM
26
Refacing
Valve
Seat
with
Valve
Seat
Cutter
Replaclna
valve
seat
Insert
I
Old
insert
can
be
removed
by
boring
out
until
it
collapses
Machine
depth
stopper
should
be
set
So
that
boring
cannot
continue
beyond
the
bottom
face
of
the
insert
recess
in
cylinderhead
2
Machine
cylinder
head
recess
in
concentric
circles
to
valve
guide
center
so
that
insert
will
have
correct
fit
3
Ream
cylinder
head
recess
at
room
temperature
4
Heat
cylinder
head
to
tempera
ture
of
150
to
200
C
302
to
3920F
Page 44 of 548

5
Fit
insert
ensuring
that
it
seats
on
bottom
face
of
its
recess
6
Newly
fitted
valve
seat
should
be
cut
or
ground
with
suitable
seat
cutter
or
grinding
stone
7
Apply
smalliunount
of
fine
grind
ing
compound
to
valve
contacting
face
and
put
valve
into
guide
Lap
valve
against
its
seat
ntil
proper
valve
seat
ing
is
obtained
Remove
valve
and
clean
valve
and
valve
seat
VALVE
ROCKER
ARM
1
AND
SHAFT
I
Check
rocker
arm
bore
and
shaft
for
scores
or
scuffs
2
Check
clearance
between
each
rocker
arm
and
shaft
by
measuring
inner
diameter
of
rocker
arm
bore
and
outer
diameter
of
shaft
If
either
clearance
is
not
within
spec
ification
replace
rocker
arm
and
or
shaft
3
Check
valve
end
contact
surface
of
rocker
arm
for
abnormal
wear
or
scuffs
VALVE
LIFTER
AND
PUSH
ROD
I
Check
valve
lifter
for
wear
or
scuffs
Check
bottom
end
of
valve
lifter
to
make
sure
it
has
a
slight
convex
Replace
valve
lifters
that
are
scored
worn
or
have
unsmooth
bot
tom
2
Check
clearance
between
lifter
hole
on
cylinder
block
and
valve
lifter
Replace
valve
lifter
if
clearance
ex
ceeds
wear
limit
3
Check
push
rod
for
bending
and
damage
Check
end
of
push
rod
for
rough
ness
or
excessive
wear
CAMSHAFT
AND
CAMSHAFT
BEARING
CAMSHAFT
BEARING
CLEARANCE
Journal
diameters
should
be
check
ed
with
a
micrometer
and
bearings
with
an
inside
dial
gauge
Measure
ments
should
then
be
compared
to
Engine
Mechanical
determine
whether
bearings
are
worn
If
worn
beyond
0
15
mm
0
0059
in
replace
using
Camshaft
Bearing
Drift
STl6Il0000
In
press
fitting
a
new
bearing
make
certain
that
oil
holes
in
block
and
bearing
are
properly
aligned
EM474
Fig
EM
27
Measuring
Camshaft
Bearing
Inner
Diameter
CAUTION
a
After
replacing
all
bearings
finish
bearing
inner
diameters
by
line
bor
ing
b
I
nstall
welch
plug
into
cylinder
block
applying
sealant
EM475
Fig
EM
28
Replacing
Cam
haft
Bearings
CAMSHAFT
ALIGNMENT
I
Check
camshaft
camshaft
journal
and
earn
surface
for
bending
wear
or
damage
If
fault
is
beyond
limits
replace
affected
parts
2
A
bend
value
is
one
half
of
the
reading
obtained
when
camshaft
is
turned
one
full
revolution
with
a
dial
gauge
applied
to
the
cen
ter
journal
Camshaft
bend
Total
indicator
reading
Less
than
0
10
mm
0
0039
in
EM
7
s
EM476
Fig
EM
29
Checking
Cam
haft
Bend
3
Camshaft
end
play
can
be
check
ed
by
installing
camshaft
camshaft
locating
plate
and
camshaft
sprocket
in
thier
respective
p
sitions
End
play
can
then
be
checked
with
a
dial
guage
or
feeler
gauge
If
end
play
exceeds
the
specified
limit
replace
locating
plate
Max
tolerance
of
camshaft
end
pley
0
10
mm
0
0039
in
EM477
Fig
EM
3D
Checking
Cam
haft
End
Play
VALVE
TIMING
This
diagram
applies
to
all
cyl
inders
If
any
valve
is
found
beyond
specifications
one
possibility
is
that
earn
lobe
is
worJ
1
or
damaged
exces
sively
calling
for
replacement
of
cam
shaft
CYLINDER
BLOCK
I
Visually
check
cylinder
block
for
cracks
or
flaws
2
Measure
top
of
cylinder
block
cylinder
head
mating
face
for
warp
age
If
warpage
exceeds
limits
correct
it
Warpage
of
cylinder
block
surface
Less
than
0
10
mm
0
0039
in
Page 45 of 548
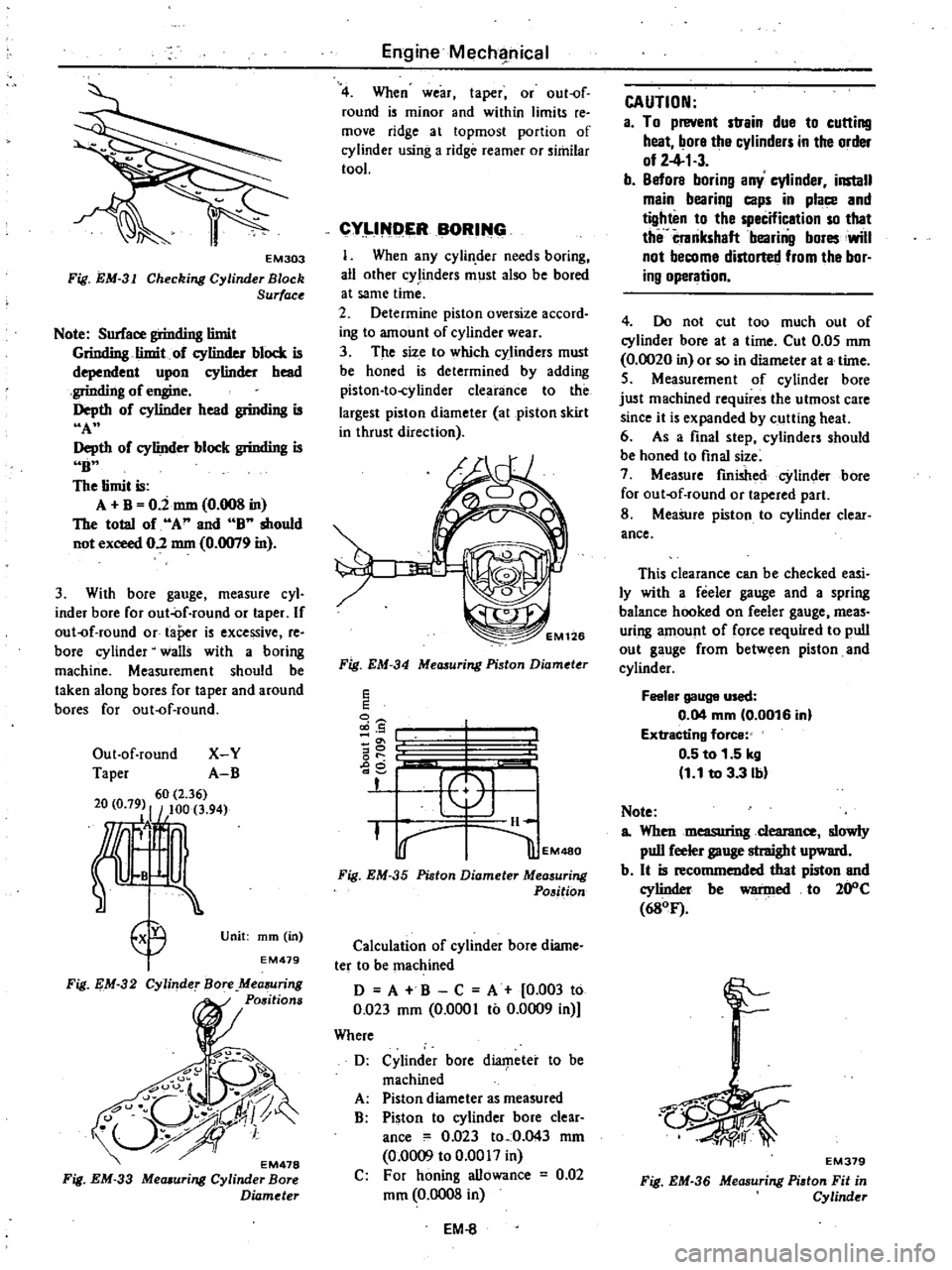
EM303
Fig
EM
31
Checking
Cylinder
Block
Surface
Note
Surface
grinding
6mit
Grinding
limit
of
cylinder
block
is
dependent
upon
cylinder
bead
grinding
of
engjne
Depth
of
cylinder
head
grinding
is
A
Depth
of
cylinder
block
b
1
b
is
U
The
limit
is
A
B
O
imm
0
008
in
The
total
of
A
and
B
should
not
exceed
0
2
mm
0
0079
in
3
With
bore
gauge
measure
cyl
inder
bore
for
out
of
round
or
taper
If
out
f
round
or
taPer
is
excessive
re
bore
cylinder
walls
with
a
boring
machine
Measurement
should
be
taken
along
bores
for
taper
and
around
bores
for
out
f
round
Out
of
round
X
Y
Taper
A
B
60
2
36
20
0
79
I
100
3
94
Ii
B
E9
I
Unit
mm
in
EM479
Fig
EM
32
Cylinder
Bore
Mea
uring
Positions
EM478
Fig
EM
33
Mecuuring
Cylinder
Bore
Diameter
Engine
Mecha
hical
4
When
wear
taper
or
out
of
round
is
minor
and
within
limits
re
move
ridge
at
topmost
portion
of
cylinder
using
a
ridge
reamer
or
similar
tool
CYLlND
ER
BORING
I
When
any
cylin
der
needs
boring
all
other
cY
linders
must
also
be
bored
at
same
time
2
Determine
piston
oversize
accord
ing
to
amount
of
cylinder
wear
3
The
size
to
which
c
linders
must
be
honed
is
determined
by
adding
piston
to
cylinder
clearance
to
the
largest
piston
diameter
at
piston
skirt
in
thrust
direction
f
EM126
Fig
EM
34
Measuring
Piston
Diameter
E
E
5
g
or
ge
I
PI
H
i
I
lEM480
Fig
EM
35
Piston
Diameter
Measuring
Position
Calculation
of
cylinder
bore
diame
ter
to
be
machined
D
A
B
C
A
0
003
to
0
023
mm
0
0001
to
0
0009
in
Where
D
Cylinder
bore
diaIpeter
to
be
machined
A
Piston
diameter
as
measured
B
Piston
to
cylinder
bore
clear
ance
0
023
to
0
043
mm
0
0009
to
0
0017
in
C
For
honing
allowance
0
02
mm
0
0008
in
EM
8
CAUTION
a
To
prevent
strain
due
to
cutting
heat
bore
the
cylinders
in
the
order
of
2
4
1
3
b
Before
boring
any
cylinder
install
main
bearing
caps
in
place
and
tighten
to
the
specification
so
that
the
crankshaft
bearing
bores
will
not
become
distorted
from
the
bor
ing
operation
4
Do
not
cut
too
much
out
of
cylinder
bore
at
a
time
Cut
0
05
mm
0
0020
in
or
so
in
diameter
at
a
time
5
Measurement
of
cylinder
bore
just
machined
requires
the
utmost
care
since
it
is
expanded
by
cutting
heal
6
As
a
final
step
cylinders
should
be
honed
to
final
size
7
Measure
finished
cylinder
bore
for
out
of
round
or
tapered
part
8
Measure
piston
to
cylinder
clear
ance
This
clearance
can
be
checked
easi
ly
with
a
feeler
gauge
and
a
spring
balance
hooked
on
feeler
gauge
meas
uring
amount
of
force
required
to
pull
out
gauge
from
between
piston
and
cylinder
Feeler
gauge
used
0
04
mm
0
0016
inl
Extracting
force
0
5
to
1
51rg
1
1
to
3
3
b
Note
a
Whenmeasuringcleanmce
slowly
pull
feeler
gauge
straight
upward
b
It
is
recommended
that
piston
and
cylinder
be
warmed
to
20
C
680F
r
EM379
Fig
EM
36
Measuring
Pi
ton
Fit
in
Cylinder
Page 46 of 548

Note
If
cylinder
bore
has
worn
beyond
the
wear
limit
use
cylinder
liner
Undersize
cylinder
liners
are
avail
able
for
service
Interference
fit
of
cylinder
liner
in
cylinder
block
ahould
be
0
08
to
0
09
mm
0
003
I
to
0
0035
in
PISTON
PISTON
PIN
AND
PISTON
RING
I
Remove
carbon
from
piston
and
ring
grooves
with
a
carbon
scraper
and
a
curved
steel
wire
The
wire
will
be
useful
in
cleaning
bottom
land
of
ring
groove
Clean
out
oil
slots
in
bottom
land
of
oil
ring
groove
2
Check
for
damage
scratches
and
wear
Replace
if
fault
is
detected
3
Measure
side
clearance
of
rings
in
ring
grooves
as
each
ring
is
installed
If
side
clearance
exceeds
the
speci
fied
limit
replace
piston
together
with
piston
ring
Max
tolerance
of
side
clearance
0
1
mm
0
0039
in
Engine
Mechanical
u
EM482
Fig
EM
38
Measuring
Ring
Gap
Note
a
When
piston
ring
only
is
to
be
replaced
without
cylinder
bore
be
ing
corrected
measure
the
gap
at
the
bottom
of
cylinder
where
the
wear
is
minor
b
Oversize
piston
rings
are
available
for
service
0
5
mm
0
020
in
1
0
mm
0
039
in
oversize
5
Measure
piston
pin
hole
in
rela
tion
to
the
outer
diameter
of
pin
If
wear
exceeds
limit
replace
piston
pin
together
with
piston
on
which
it
is
installed
Piston
pin
to
piston
clearance
O
OOS
to
0
012
mm
0
0003
to
0
0005
in
Note
Determine
the
fitting
of
piston
pin
into
piston
pin
hole
to
such
an
extent
that
it
can
be
pressed
smoothly
by
fmger
at
room
tem
perature
This
piston
pin
must
be
a
tight
press
fit
into
connecting
rod
EM481
Fig
EM
37
Me
suring
Piston
Ring
Side
Clearance
4
Measure
ring
gap
with
a
feeler
gauge
placing
ring
squarely
in
cyl
inder
Ring
should
be
placed
to
diameter
at
upper
or
lower
limit
of
ring
travel
If
ring
gap
exceeds
the
specified
limit
replace
ring
Max
tolerance
of
ring
gap
1
0
mm
0
039
in
EM131
Fig
EM
39
Piston
Pin
Fitting
CONNECTING
ROD
1
If
a
connecting
rod
has
any
flaw
on
either
side
of
thrust
face
and
large
end
correct
or
replace
it
Bend
and
torsion
per
100
mm
3
94
in
length
Less
than
0
05
mm
0
0020
in
EM
9
EM133
Fig
EM
40
Checking
Rod
Alignment
2
Check
connecting
rod
for
bend
or
torsion
using
a
connecting
rod
aligner
If
bend
or
torsion
exceeds
limit
cor
rect
or
replace
3
When
replacing
connecting
rod
select
rod
so
weight
difference
be
tween
new
and
old
ones
is
within
5
gr
0
180z
4
Install
connecting
rods
with
bear
iogs
on
to
corresponding
crank
pins
and
measure
thrust
clearance
If
meas
ured
value
exceeds
limit
replace
con
necting
rod
Max
tolerance
of
big
end
play
0
4
mm
0
016
in
l
Big
end
play
l
t
t
EM483
Fig
EM
41
Checking
Big
End
Pwy
CRANKSHAFT
I
Repair
or
replace
as
required
If
faults
are
minor
correct
with
fine
crocus
cloth
2
Check
with
a
micrometer
journals
and
crank
pins
for
taper
and
out
of
round
Measurement
should
be
taken
along
journals
for
taper
and
around
journals
for
out
of
round
If
out
of
round
or
taper
exceeds
the
specified
limit
replace
or
repair
Page 48 of 548
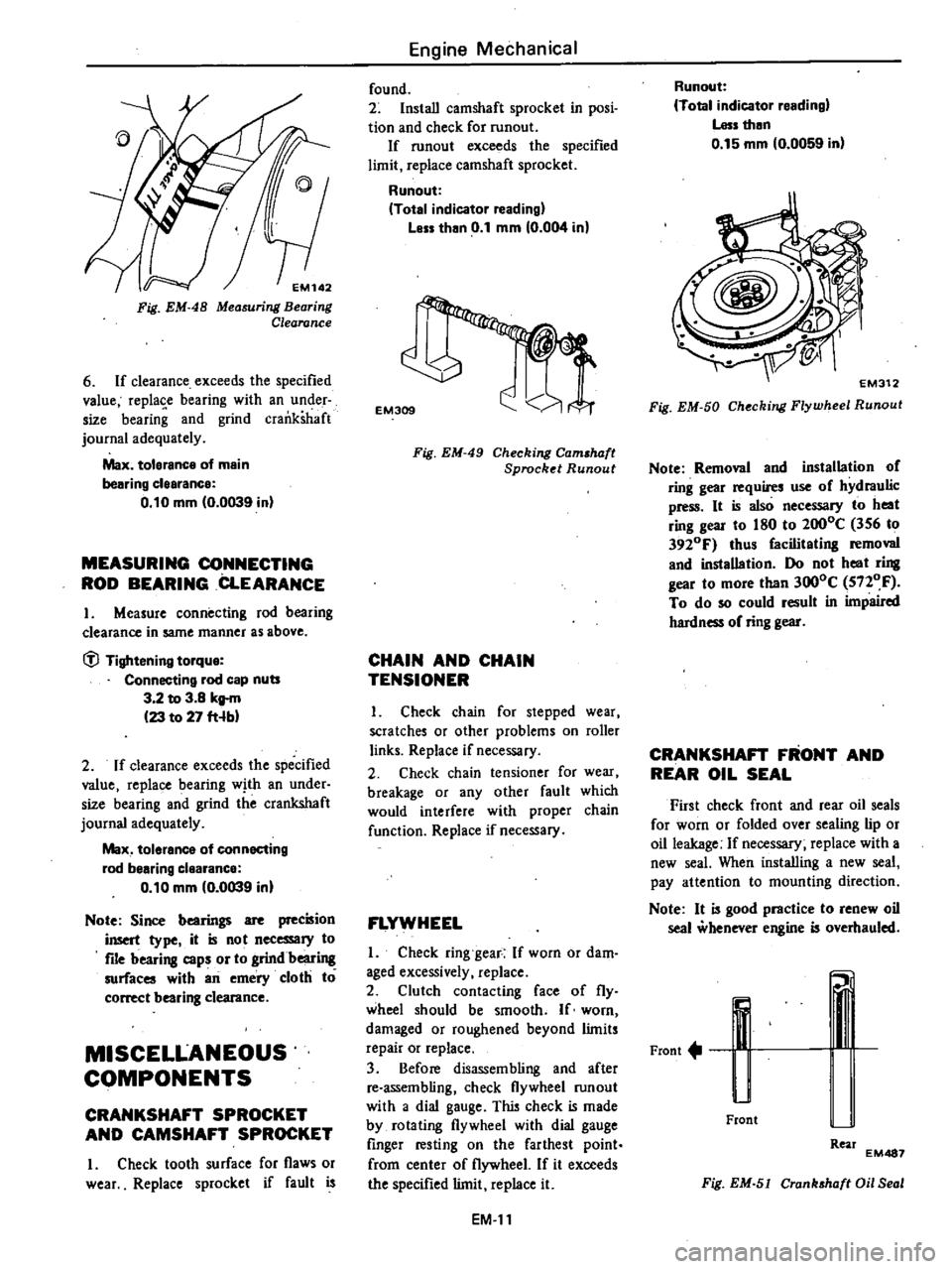
EM142
Fig
EM
48
Measuring
Bearing
Clearance
6
If
clearance
exceeds
the
specified
value
replase
bearing
with
an
under
size
bearing
and
grind
crankshaft
journal
adequately
Max
tolerance
of
main
bearing
clearance
0
10
mm
0
0039
in
MEASURING
CONNECTING
ROD
BEARING
CLEARANCE
I
Measure
connecting
rod
bearing
clearance
in
same
manner
as
above
tfl
Tightening
torque
Connecting
rod
cap
nuts
3
2
to
3
8
kg
m
23
to
27
fHb
2
If
clearance
exceeds
the
specified
value
replace
bearing
with
an
under
size
bearing
and
grind
the
crankshaft
journal
adequately
Max
tolerance
of
connecting
rod
bearing
clearance
0
10
mm
0
0039
in
Note
Since
bearings
are
precision
insert
type
it
is
not
necessary
to
file
bearing
caps
or
to
grindbeari
surfaces
with
an
emery
cloth
to
correct
bearing
clearance
MISCELLANEOUS
COMPONENTS
CRANKSHAFT
SPROCKET
AND
CAMSHAFT
SPROCKET
I
Check
tooth
surface
for
flaws
or
wear
Replace
sprocket
if
fault
is
Engine
Mechanical
found
2
Install
camshaft
sprocket
in
posi
tion
and
check
for
runout
If
runout
exceeds
the
specified
limit
replace
camshaft
sprocket
Runout
Total
indicator
reading
Less
than
0
1
mm
0
004
in
EM309
Fig
EM
49
Checking
Cam
haft
Sprocket
Runout
CHAIN
AND
CHAIN
TENSIONER
I
Check
chain
for
stepped
wear
scratches
or
other
problems
on
roller
links
Replace
if
necessary
2
Check
chain
tensioner
for
wear
breakage
or
any
other
fault
which
would
interfere
with
proper
chain
function
Replace
if
necessary
FLYWHEEL
I
Check
ring
gear
If
worn
or
dam
aged
excessively
replace
2
Clutch
contacting
face
of
fly
wheel
should
be
smooth
If
worn
damaged
or
roughened
beyond
limits
repair
or
replace
3
Before
disassembling
and
after
re
assembling
check
flywheel
run
out
with
a
dial
gauge
This
check
is
made
by
rotating
flywheel
with
dial
gauge
finger
resting
on
the
farthest
point
from
center
of
flywheel
If
it
exceeds
the
specified
limit
replace
it
EM
II
Runout
Total
indicator
reading
Less
then
0
15
mm
0
0059
in
Fig
EM
50
Checking
Flywheel
Runout
Note
Removal
and
installation
of
ring
gear
requires
use
of
hydraulic
press
It
is
also
necessary
to
heat
ring
gear
to
180
to
2000C
356
to
3920F
thus
facilitating
removal
and
installation
Do
not
heat
ring
gear
to
more
than
3000C
5nOF
To
do
so
could
result
in
impaired
hardness
of
ring
gear
CRANKSHAFT
FRONT
AND
REAR
OIL
SEAL
First
check
front
and
rear
oil
seals
for
worn
or
folded
over
sealing
lip
or
oil
leakage
If
necessary
replace
with
a
new
seal
When
installing
a
new
seal
pay
attention
to
mounting
direction
Note
It
is
good
practice
to
renew
oil
seal
whenever
engine
is
overhauled
Front
u
Front
Rear
EM487
Fig
EM
51
Cranhhaft
Oil
Seal
Page 49 of 548
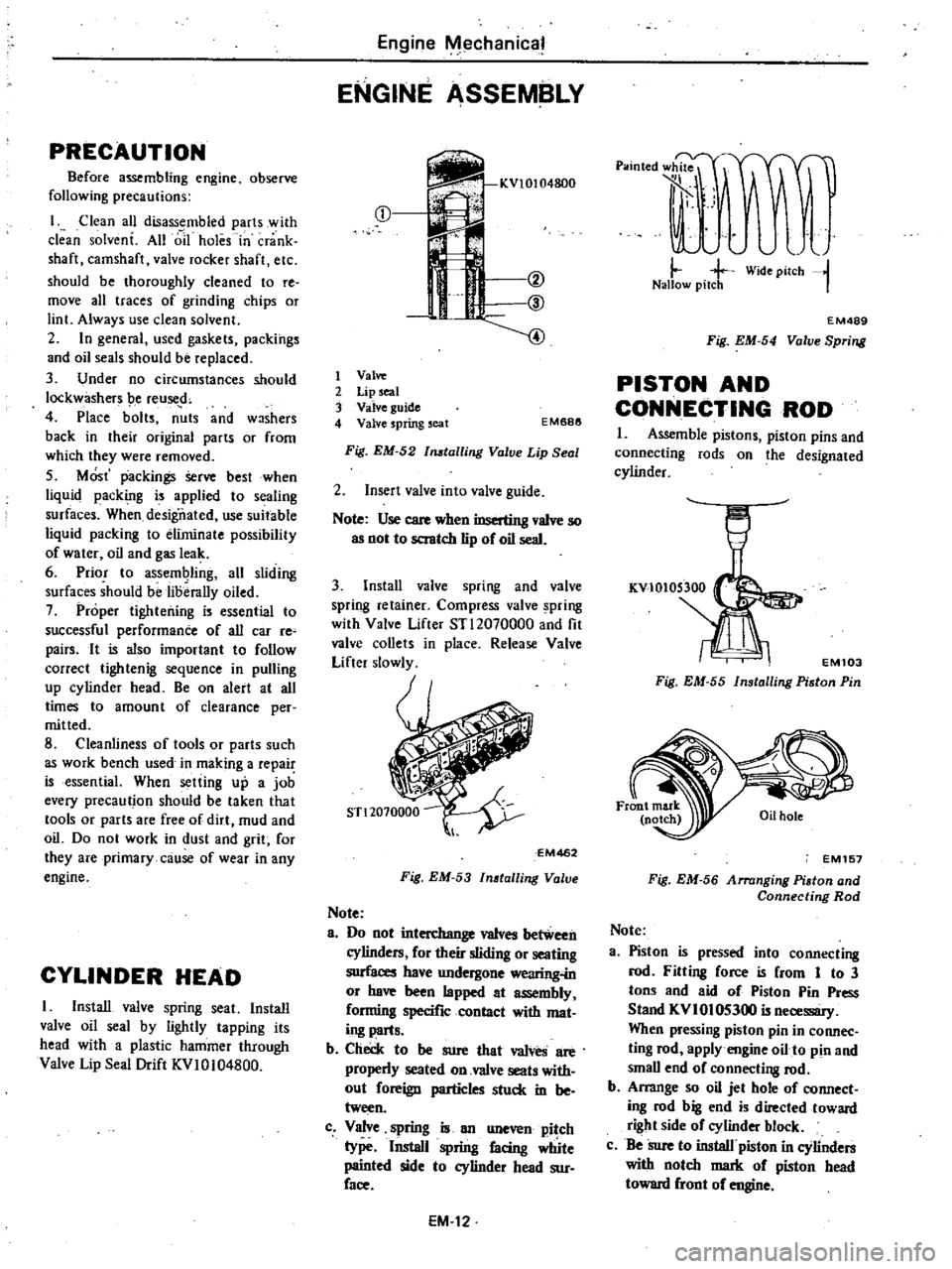
PRECAUTION
Before
assembling
engine
observe
following
precautions
I
Clean
all
disass
mbled
parts
with
clean
solvent
All
611
holes
in
crank
shaft
camshaft
valve
rocker
shaft
etc
should
be
thoroughly
cleaned
to
re
move
all
traces
of
grinding
chips
or
lint
Always
use
clean
solvent
2
In
general
used
gaskets
packings
and
oil
seals
should
be
replaced
3
Under
no
circumstances
should
lockwashers
be
reuse
d
4
Place
bolts
nuts
and
woshers
back
in
their
original
parts
or
from
which
they
were
removed
5
MOst
packing
Serve
best
when
liquid
packing
is
applied
to
sealing
surfaces
When
desigiiated
use
suitable
liquid
packing
to
eliminate
possibility
of
water
oil
and
gas
leak
6
Prior
to
assemQling
all
sliding
surfaces
should
be
lioerally
oiled
7
Proper
tightening
is
essential
to
successful
performanCe
of
all
car
re
pairs
It
is
also
important
to
follow
correct
tightenig
sequence
in
pulling
up
cylinder
head
Be
on
alert
at
all
times
to
amount
of
clearance
per
mitted
8
Cleanliness
of
tools
or
parts
such
as
work
bench
used
jn
making
a
repai
is
essential
When
setting
up
a
job
every
precaution
should
be
taken
that
tools
or
parts
are
free
of
dirt
mud
and
oil
Do
not
work
in
dust
and
grit
for
they
are
primary
cause
of
wear
in
any
engine
CYLINDER
HEAD
I
Install
valve
spring
seat
Install
valve
oil
seal
by
lightly
tapping
its
head
with
a
plastic
hammer
through
Valve
Lip
Seal
Drift
KVI0104800
Engine
Mechanical
ENGINE
ASSEMBLY
m
f
if
@
@
4
1
Valve
2
Lip
seal
3
Valve
guide
4
Valve
spring
seat
EM688
Fig
EM
52
tailing
Valve
Lip
Seal
2
Insert
valve
into
valve
guide
Note
Use
care
when
inserting
valve
so
as
not
to
scratch
lip
of
oil
seal
3
Install
valve
spring
and
valve
spring
retainer
Compress
valve
pring
with
Valve
Lifter
STl2070000
and
fit
valve
collets
in
place
Release
Valve
Lifter
slowly
EM462
Fig
EM
53
Inatalling
Valve
Note
8
Do
not
interchange
valves
between
cylinders
for
their
sliding
or
seating
surfaces
have
undergone
wearing
in
or
have
been
lapped
at
assembly
forming
specific
contact
with
mat
ing
parts
b
Check
to
be
sure
that
valves
are
properly
seated
on
valve
seats
with
out
foreign
particles
stuck
in
be
tween
c
Valve
spring
is
an
uneven
pitch
type
Install
spring
facing
Wte
painted
side
to
cylinder
head
sur
face
EM
12
p
lOted
l
rJF
t
A
J
il
j
j
Wide
pilCh
l
Nallow
pitch
I
EM489
Fig
EM
54
Valve
Spring
PISTON
AND
CONNECTING
ROD
I
Assemble
pistons
piston
pins
and
connecting
rods
on
the
designated
cylinder
EM103
Fig
EM
55
Installing
Piston
Pin
EM157
Fig
EM
56
Arranging
Piaton
and
Connecting
Rod
Note
3
Piston
is
pressed
into
connecting
rod
Fitting
force
is
from
1
to
3
tons
and
aid
of
Piston
Pin
Press
Stand
KVI
01
05300
is
necessary
When
pressing
piston
pin
in
connec
ting
rod
apply
engine
oil
to
pin
and
small
end
of
connecti
8
rod
b
Arrange
so
oil
jet
hole
of
connect
ing
rod
big
end
is
directed
toward
right
side
of
cylinder
block
c
Be
Sure
to
install
piston
in
cylinders
with
notch
mark
of
piston
head
toward
front
of
engine
Page 51 of 548
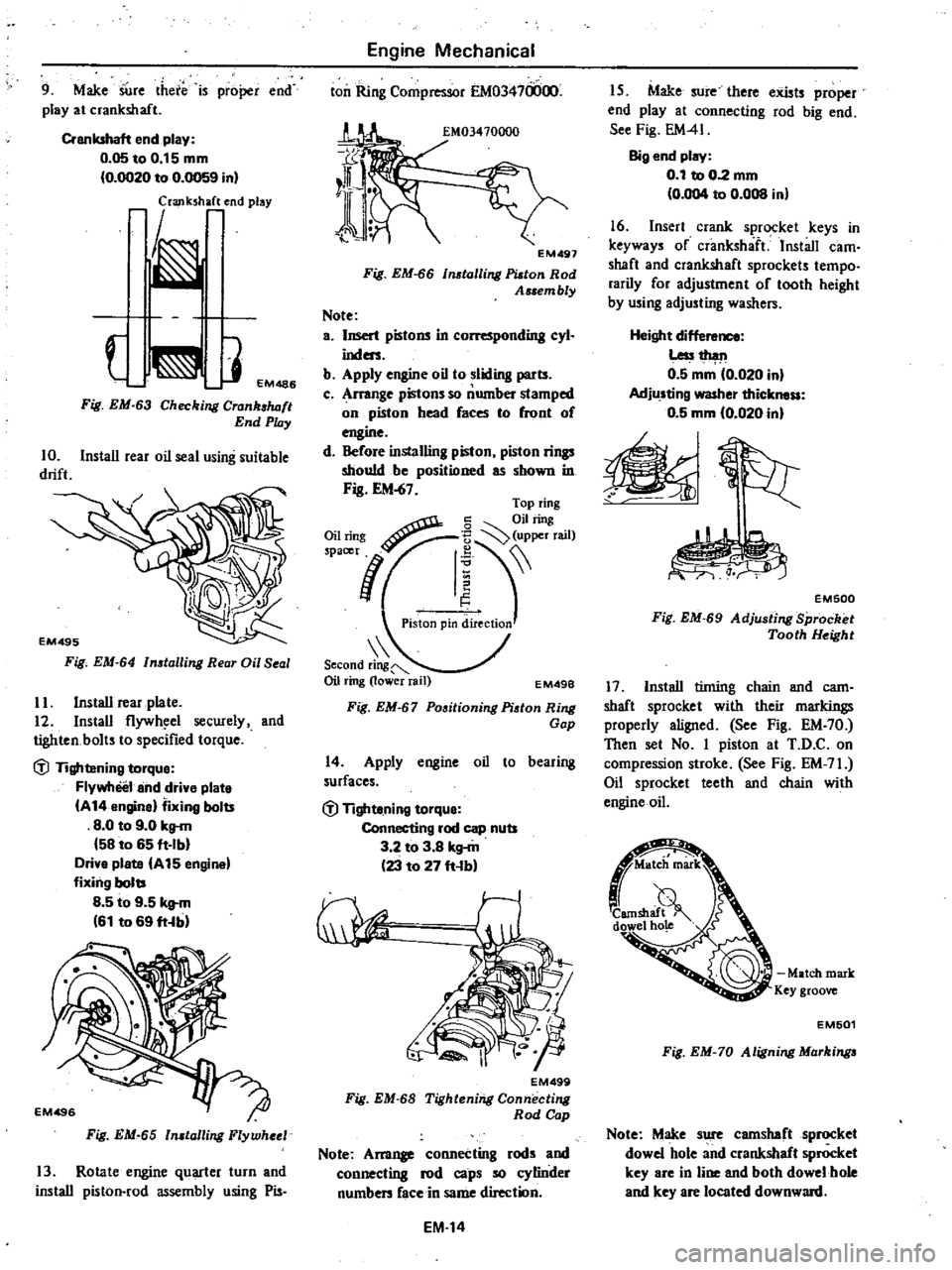
9
Make
SUre
there
is
proper
end
play
at
crankshaft
Crankshaft
end
play
0
05toO
15mm
0
OO20
to
0
0059
in
laJlk
h
end
play
J
EM486
Fig
EM
63
Checking
Crank
luJft
End
Play
10
Install
rear
oil
seal
using
suitable
drift
Fig
EM
64
n
talling
Rear
Oil
Seal
II
Install
rear
plate
12
Install
flywh
el
secwely
and
tighten
bolts
to
specified
torque
dl
Tightening
torque
Flywheel
and
drive
plate
A
14
engine
fixing
bolts
8
0
to
9
0
kg
m
58
to
65
ft
Ib
Drive
plate
A
15
engine
fixing
bolts
8
5
to
9
5
kg
m
61
to
69
ft
b
Fig
EM
65
n
talling
Flywheel
13
Rotate
engine
quarter
turn
and
install
piston
rod
assembly
using
Pis
Engine
Mechanical
ton
Ring
Compressor
EM03470000
EM497
Fig
EM
66
tolling
Platon
Rod
Assem
bly
Note
a
Insert
pistons
in
L
r
nding
cyl
inders
b
Apply
engine
oil
to
sliding
parts
c
Arrange
pistons
so
number
stamped
on
piston
head
faces
to
front
of
engine
d
Before
installing
piston
piston
rings
should
be
positioned
as
shown
in
Fig
EM
67
Second
ring
Oil
ring
lower
rail
EM49B
Fig
EM
67
Positioning
Piston
Ring
Gap
14
Apply
engine
oil
to
bearing
surfaces
dl
Tighte
ning
torque
Connecting
rod
cap
nuts
3
2
to
3
8
kg
m
23
to
27
ft
b
EM499
Fig
EM
68
Tightening
Connecting
Rod
Cap
Note
Am11
connecting
rods
and
connecting
rod
caps
so
cylinder
numben
face
in
same
direction
EM
14
I
S
Make
sure
there
exists
proper
end
play
at
connecting
rod
big
end
See
Fig
EM41
Big
end
play
0
1
to
0
2
mm
0
004
to
0
008
in
16
Insert
crank
sprocket
keys
in
keyways
of
crankshaft
Install
cam
shaft
and
crankshaft
sprockets
tempo
rarily
for
adjustment
of
tooth
height
by
using
adjusting
washers
Height
dif
Less1
h
l11
0
5
mm
0
020
in
Adjusting
washer
thickness
0
5
mm
10
020
in
EM500
Fig
EM
69
Adju
ting
Sprocket
Tooth
Height
17
Install
tinting
chain
and
cam
shaft
sprocket
with
their
markings
properly
aligned
See
Fig
EM
70
Then
set
No
I
piston
at
T
D
C
on
compression
stroke
See
Fig
EM
71
Oil
sprocket
teeth
and
chain
with
engine
oil
Match
mark
Key
groove
EM501
Fig
EM
70
Aligning
Markinga
Note
Make
sure
camshaft
sprocket
dowel
hole
and
crankshaft
sprocket
key
are
in
line
and
both
dowel
hole
and
key
are
located
downward