battery DATSUN 210 1979 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1979, Model line: 210, Model: DATSUN 210 1979Pages: 548, PDF Size: 28.66 MB
Page 15 of 548

DATSUN
210
Model
8310
Series
SECTIONET
ET
ENGINE
TUNE
UP
CONTENTS
EMISSION
CONTROL
DEVICES
BASIC
MECHANICAL
SYSTEM
ADJUSTING
INTAKE
AND
EXHAUST
VALVE
CLEARANCE
CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTING
DRIVE
BELTS
CHANGING
ENGINE
OIL
REPLACING
01
L
FI
L
TER
CHANGING
ENGINE
COOLANT
CHECKING
COOLING
SYSTEM
HOSES
AND
CONNECTIONS
CHECKING
ENGINE
COMPRESSION
IGNITION
AND
FUEL
SYSTEM
CHECKING
BATTERY
CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTING
IGNITION
TIMING
CHECKING
IGNITION
WIRING
CHECKING
AND
REPLACING
SPARK
PLUGS
CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTING
CARBURETOR
IDLE
RPM
AND
MIXTURE
RATIO
CHECKING
CHOKE
MECHANISM
Choke
plate
and
linkage
CHECKING
FUEL
SHUT
OFF
SYSTEM
FU
models
ET
2
ET
3
ET
3
ET
3
ET
3
ET
3
ET
4
ET
4
ET
4
ET
5
ET
5
ET
5
ET
6
ET
6
ET
7
ET
9
ET
9
REPLACING
FUEL
FILTER
ET
10
CHECKING
FUEL
LINES
Hoses
piping
connections
etc
ET
10
REPLACING
AIR
CLEANER
FILTER
ETlO
CHECKING
AUTOMATIC
TEMPERATURE
CONTROL
AIR
CLEANER
ET
10
EMISSION
CONTROL
SYSTEM
ET
11
CHECKING
VACUUM
FITTING
HOSES
AND
CONNECTIONS
ET
11
REPLACING
AIR
PUMP
AIR
CLEANER
FILTER
Except
FU
models
and
Canada
models
E
1122i
REPLACING
AIR
INDUCTION
VALVE
FILTER
FU
models
and
Canada
models
E
tlil1r2
C
REPLACING
PCV
VALVE
AND
FILTER
ETf
CHECKING
VENTI
LATION
HOSES
E1P12
CHECKING
VAPOR
LINES
Eli
J2
CHECKING
FUEL
TANK
VACUUM
RELIEF
I
f
III
VALVE
ET
13
REPLACING
CARBON
CANISTER
W
FILTER
ET
d
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
ET
14
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
ET
16
SPECIAL
SERVICE
TOOL
ET
23
Page 19 of 548
sion
pressure
chances
are
that
piston
rings
are
worn
or
damaged
2
If
pressure
stays
low
the
likeli
hood
is
that
valve
is
sticking
or
seating
Engine
Tune
up
improperly
3
If
cylinder
compression
in
any
two
adjacent
cylinders
is
low
and
if
adding
oil
does
not
help
the
compres
sion
there
is
leakage
past
the
gasketed
surface
Oil
and
water
in
combustion
cham
bers
can
result
from
this
problem
IGNITION
AND
FUEL
SYSTEM
CHECKING
BATTERY
I
Remove
six
vent
plugs
and
check
electrolyte
level
in
each
battery
cell
If
necessary
pour
distilled
water
Overflow
Correct
Shortage
t
t
j
t
t
t
EE358
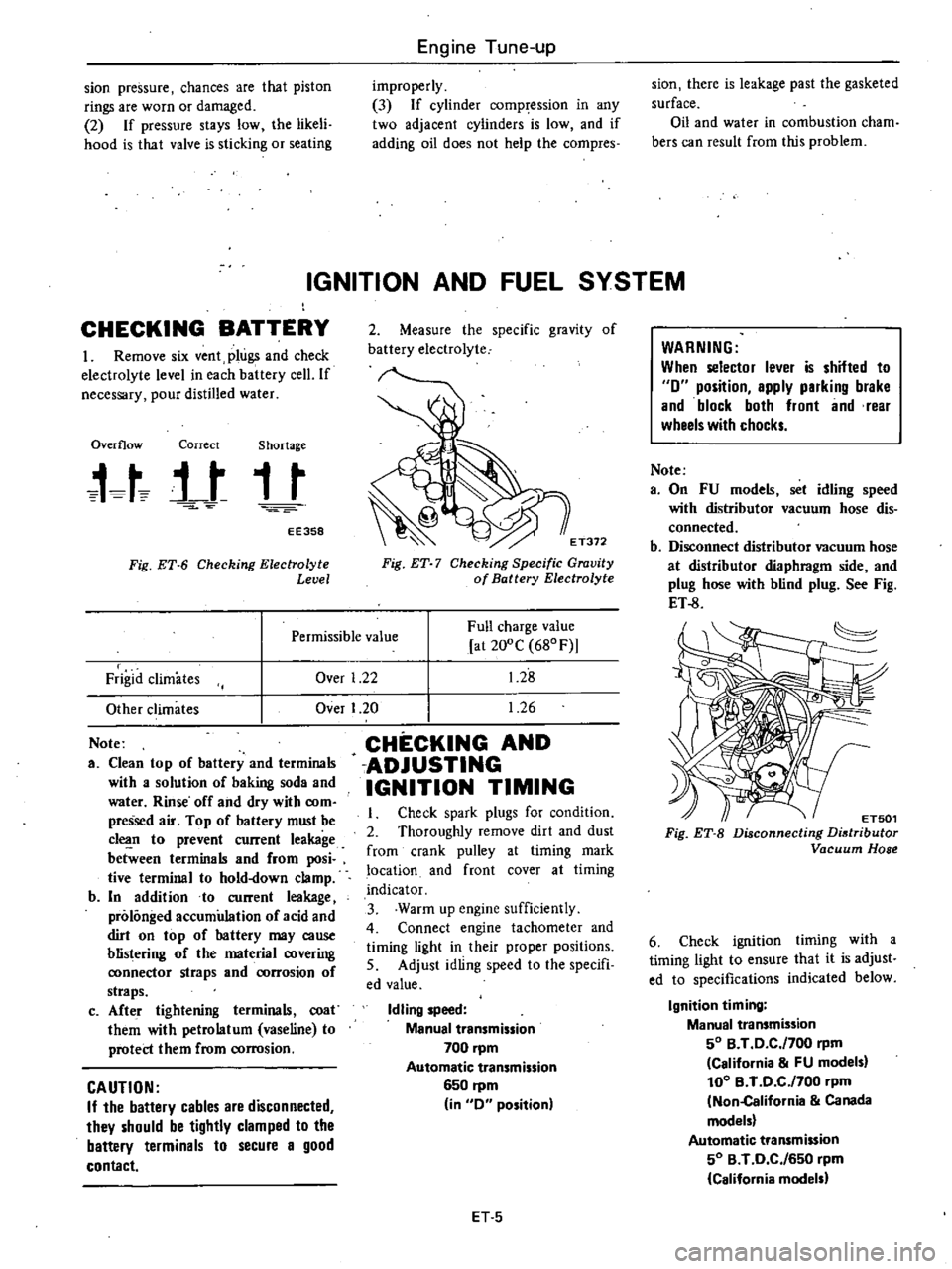
Fig
ET
6
Checking
Electrolyte
Level
2
Measure
the
specific
gravity
of
battery
electrolyte
E
T372
Fig
ET
7
Checking
Specific
Gravity
of
Battery
Electrolyte
Over
1
22
Full
charge
value
at
200C
680F
1
28
1
26
Permissible
value
Frigid
climates
Other
climates
Note
a
Clean
top
of
battery
and
terminals
with
a
solution
of
baking
soda
and
water
Rinse
off
and
dry
with
com
pressed
air
Top
of
battery
must
be
c1
n
to
prevent
current
leakage
between
terminals
and
from
posi
tive
terminal
to
hold
down
clamp
b
In
addition
to
current
leakage
prolonged
accumulation
of
acid
and
dirt
on
top
of
hattery
may
cause
blistering
of
the
material
covering
ronnector
straps
and
rorrosion
of
straps
c
Afte
r
tightening
terminals
coat
them
with
petrolatum
vaseline
to
protect
them
from
corrosion
CAUTION
If
the
battery
cables
are
disconnected
they
should
be
tightly
clamped
to
the
battery
terminals
to
secure
a
good
contact
Over
I
20
CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTING
IGNITION
TIMING
Check
spark
plugs
for
condition
2
Thoroughly
remove
dirt
and
dust
from
crank
pulley
at
timing
mark
location
and
front
cover
at
timing
indicator
3
Warm
up
engine
sufficiently
4
Connect
engine
tachometer
and
timing
light
in
their
proper
positions
5
Adjust
idling
speed
to
the
specifi
ed
value
Idling
speed
Manual
transmission
700
pm
Automatic
transmission
6S0
rpm
in
0
position
ET
S
WARNING
When
selector
lever
is
shifted
to
0
position
apply
parking
brake
and
block
both
front
and
rear
wheels
with
chocks
Note
a
On
FU
models
set
idling
speed
with
distributor
vacuum
hose
dis
connected
b
Disconnect
distributor
vacuum
hose
at
distributor
diaphragm
side
and
plug
hose
with
blind
plug
See
Fig
ET
8
ET501
Fig
ET
B
Disconnecting
Distributor
Vacuum
Hose
6
Check
ignition
timing
with
a
timing
light
to
ensure
that
it
is
adjust
ed
to
specifications
indicated
below
Ignition
timing
Manual
transmission
SO
B
T
0
C
f700
rpm
California
FU
models
100
B
T
0
C
f700
pm
Non
California
Canada
models
Automatic
transmission
SO
B
T
0
C
f6S0
rpm
California
models
Page 28 of 548
Engine
T
une
up
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
INSpECTION
AND
ADJUSTMENT
Basic
mechanical
s
stem
Valve
clearance
Hot
Intake
Exhaust
Drive
belt
deflection
Fan
Air
pump
Air
COo9itioner
compressor
Applied
thumb
pressure
Engine
oil
capacity
AI4
engine
wmi
oil
filter
Without
oil
filter
A
15
engine
With
oil
fIlter
Without
oil
filter
Radiator
cap
relief
pressure
Cooling
system
leakage
testing
pressure
Water
capacity
Without
heater
With
heater
Compression
pressure
at
350
rpm
Standard
Minimum
Battery
specific
gravity
at
200C
680F
Frigid
climates
Other
climates
mm
in
mm
in
0
35
0
014
0
5
O
QI
i
mm
in
mm
in
mm
in
kg
lb
liters
US
qt
lmp
qt
8
to
12
0
31
to
0
47
8
to
12
0
31
to
0
47
8
to
12
0
31
to
0
47
10
22
37
3Ji
3
Y
IT
3
2Ji
kgfcm2
psi
kg
cm2
psi
33
3
Ji
2
Ji
2
8
3
2
f
0
9
13
1
6
23
liters
US
qt
lmp
qt
5
2
5
f
4
MfT
5
0
5Y
4
AfT
5
9
6Y
5
MfT
57
6
5
AfT
liters
US
qt
lmp
qt
kgfcm2
psi
kgfcm2
psi
13
5
192
12
5
178
1
28
1
26
ET11
Page 30 of 548

Engine
Tune
up
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
Condition
Probable
cause
CANNOT
CRANK
ENGINE
OR
SLOW
CRANKING
Improper
grade
oil
Discharged
battery
Faulty
battery
Loose
fan
belt
Malfunction
in
charge
system
Wiring
connection
loose
in
starting
circuit
F
ul1Y
ignition
switch
Faulty
starter
motor
Trouble
shooting
procedure
on
starting
circuit
Switch
on
the
starting
motor
with
light
ON
WheJlIJght
gOO
off
or
Ii
J1S
considerably
a
Check
battery
b
Check
connection
and
cable
c
Check
starter
motor
When
light
stays
bright
Corrective
action
Replace
with
proper
grade
oil
Charge
battery
Replace
Adjust
Inspect
Correct
Repair
or
replace
Repair
or
replace
a
Check
wlflng
connection
between
battery
and
starter
motor
b
Check
ignition
switch
c
Check
starter
motor
ENGINE
WILL
CRANK
NOR
LLY
BUT
WILL
NOT
START
In
this
case
the
following
trouble
causes
may
exist
but
in
many
cases
ignition
system
or
fuel
system
is
in
trouble
19
ition
syst
m
in
trouble
FII
1
system
in
trowb
Val
mechanism
do
not
work
properly
Low
compression
Trouble
shooting
procedure
Check
spark
plug
firstly
by
following
procedure
Disconnect
high
tension
cable
from
one
spark
plug
and
hold
it
about
10
mm
0
39
in
from
the
engine
metal
part
and
crank
the
engine
Good
spark
occurs
a
Check
spark
plug
b
Checkignition
timing
c
Check
fuel
system
d
Check
cylinder
compression
Check
the
current
now
in
primary
circuit
Very
high
current
Inspect
primary
circuit
for
short
Check
breaker
point
operation
except
tran
sistor
ignition
system
No
spark
occurs
ET
l
6
Page 95 of 548
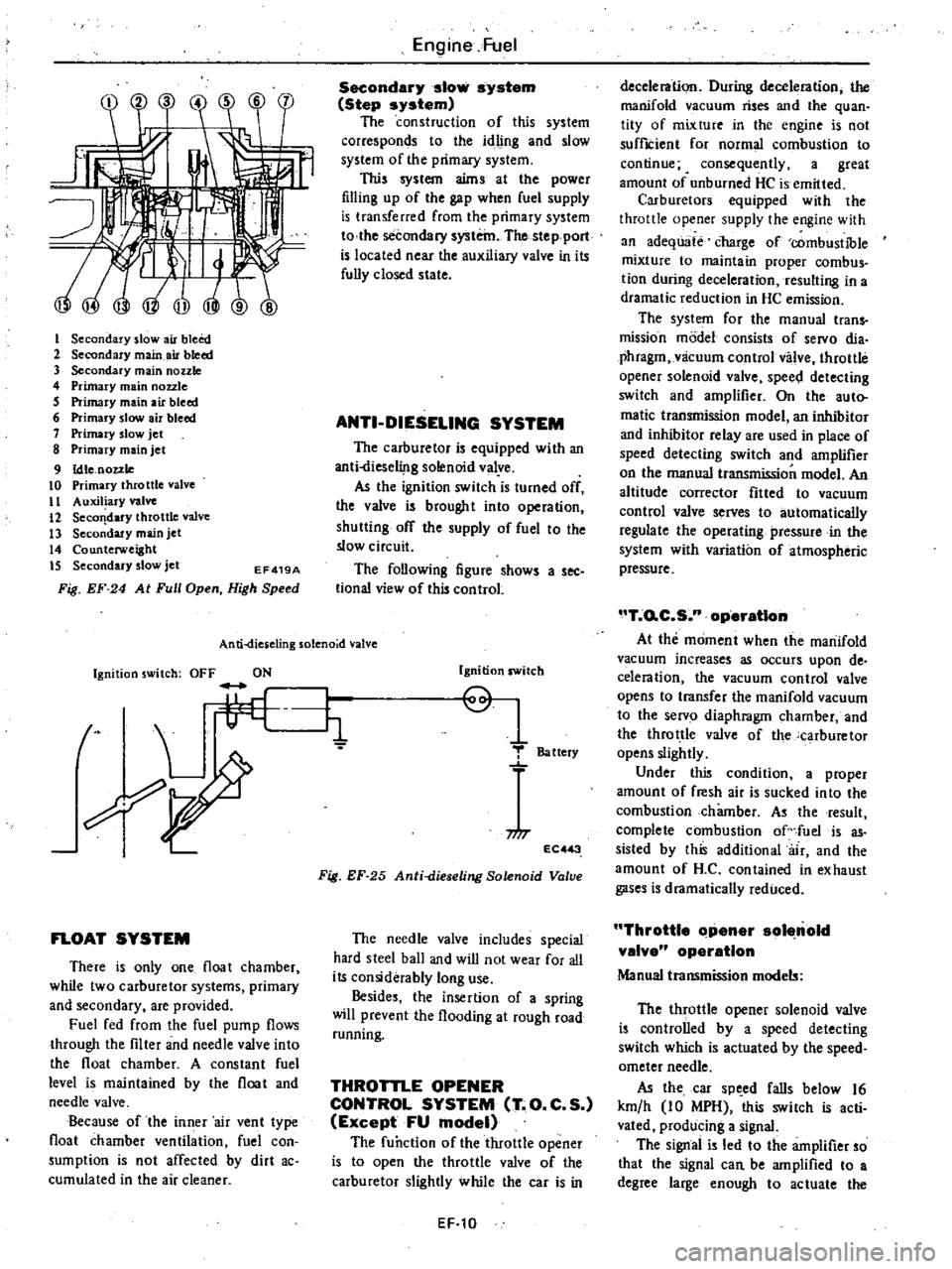
I
Secondary
slow
air
bleed
2
Secondary
main
air
bleed
3
Secondary
main
nozzle
4
Primary
main
nozzle
5
Primary
main
air
bleed
6
Primary
slow
air
bleed
7
Primary
slow
jet
8
Primary
main
jet
9
Idle
nozzle
10
Primary
throttle
valve
II
Auxiliary
valve
12
Seco
dary
throttle
valve
13
Secondary
main
jet
14
Counterweight
IS
Secondary
slow
jet
EF419A
Fig
EF
24
At
Full
Open
High
Speed
Engine
Fuel
Secondary
slow
system
Step
system
The
construction
of
this
system
corresponds
to
the
idling
and
slow
system
of
the
primary
system
This
system
aims
at
the
power
filling
up
of
the
gap
when
fuel
supply
is
transferred
from
the
primary
system
to
the
secondary
system
The
stepport
is
located
near
the
auxiliary
valve
in
its
fully
closed
state
ANTI
DIESELING
SYSTEM
The
carburetor
is
equipped
with
an
anti
liese1i
lg
solenoid
valye
As
the
ignition
switch
is
turned
off
the
valve
is
brought
into
operation
shutting
off
the
supply
of
fuel
to
the
slow
circuit
The
following
figure
shows
a
see
tional
view
of
this
control
An
ti
dies
eling
solenoid
valve
Ignition
switch
OFF
ON
t
L
li
FLOAT
SYSTEM
There
is
only
one
float
chamber
while
two
carburetor
systems
primary
and
secondary
are
provided
Fuel
fed
from
the
fuel
pump
flows
through
the
filter
and
needle
valve
into
the
float
chamber
A
constant
fuel
level
is
maintained
by
the
float
and
needle
valve
Because
of
the
inner
air
vent
type
float
chamber
ventilation
fuel
con
sumption
is
not
affected
by
dirt
ac
cumulated
in
the
air
cleaner
Ignition
switch
Q
1
T
Battery
niT
EC
3
Fig
EF
25
Anti
dieseling
Solenoid
Valve
The
needle
valve
includes
special
hard
steel
ball
and
wiD
not
wear
for
all
its
considerably
long
use
Besides
the
insertion
of
a
spring
will
prevent
the
flooding
at
rough
road
running
THROTTLE
OPENER
CONTROL
SYSTEM
T
O
C
S
Except
FU
model
The
function
of
the
throttle
opener
is
to
open
the
throttle
valve
of
the
carburetor
slightly
while
the
car
is
in
EF
10
deceleration
During
deceleration
the
manifold
vacuum
rises
and
the
quan
tity
of
mixture
in
the
engine
is
not
suffICient
for
normal
combustion
to
continue
4
consequently
a
great
amount
of
unburned
HC
is
emitted
Carburetors
equipped
with
the
throttle
opener
supply
the
engine
with
an
adequate
charge
of
combustible
mixture
to
maintain
proper
combus
tion
during
deceleration
resulting
in
a
dramatic
reduction
in
HC
emission
The
system
for
the
manual
trans
mission
model
consists
of
servo
dia
phragm
vlicuum
control
valve
throttle
opener
solenoid
valve
spee
l
detecting
switch
and
amplifier
On
the
auto
matic
transmission
model
an
inhibitor
and
inhibitor
relay
are
used
in
place
of
speed
detecting
switch
and
amplifier
on
the
manual
transmission
model
An
altitude
corrector
fitted
to
vacuum
control
valve
serves
to
automatically
regulate
the
operating
pressure
in
the
system
with
variation
of
atmospheric
pressure
T
o
C
S
n
operatIon
At
the
moment
when
the
manifold
vacuum
increases
as
occurs
upon
de
celeration
the
vacuum
control
valve
opens
to
transfer
the
manifold
vacuum
to
the
servo
diaphragm
chamber
and
the
throttle
valve
of
the
carburetor
opens
slightly
Under
this
condition
a
proper
amount
of
fresh
air
is
sucked
into
the
combustion
chamber
As
the
result
complete
combustion
of
fuel
is
as
sisted
by
this
additional
air
and
the
amount
of
H
C
contained
in
exhaust
gases
is
dramatically
reduced
Throttle
Clpener
sol
nold
valve
operation
Manual
transmission
models
The
throttle
opener
solenoid
valve
is
controlled
by
a
speed
detecting
switch
which
is
actuated
by
the
speed
ometer
needle
As
the
car
sp
ed
falls
below
16
km
h
10
MPH
this
switch
is
acti
vated
producing
a
signal
The
signal
is
led
to
the
amplifier
so
that
the
signal
can
be
amplified
to
a
degree
large
enough
to
actuate
the
Page 96 of 548
throttle
opener
solenoid
valve
The
throttle
opener
solenoid
valve
is
actuated
and
the
servo
diaphragm
chamber
is
opened
to
the
atmosphere
In
this
case
the
seIVo
diaphragm
does
not
opera
te
Engine
Fuel
Automatic
transmission
models
As
long
as
the
shift
lever
is
in
the
N
or
p
position
the
inhibitor
switch
on
the
transmission
is
turned
on
and
the
throttle
opener
solenoid
valve
is
actuated
Under
this
condition
the
seIVo
diaphragm
does
not
operate
because
of
the
same
reason
as
men
tioned
for
the
manual
transmission
model
ON
Car
peed
betow
t6
km
h
to
mph
OFF
Car
peed
above
16
km
h
to
mph
To
intake
manifold
j
lJl
11
1
ti
i
ljn
L
o
1
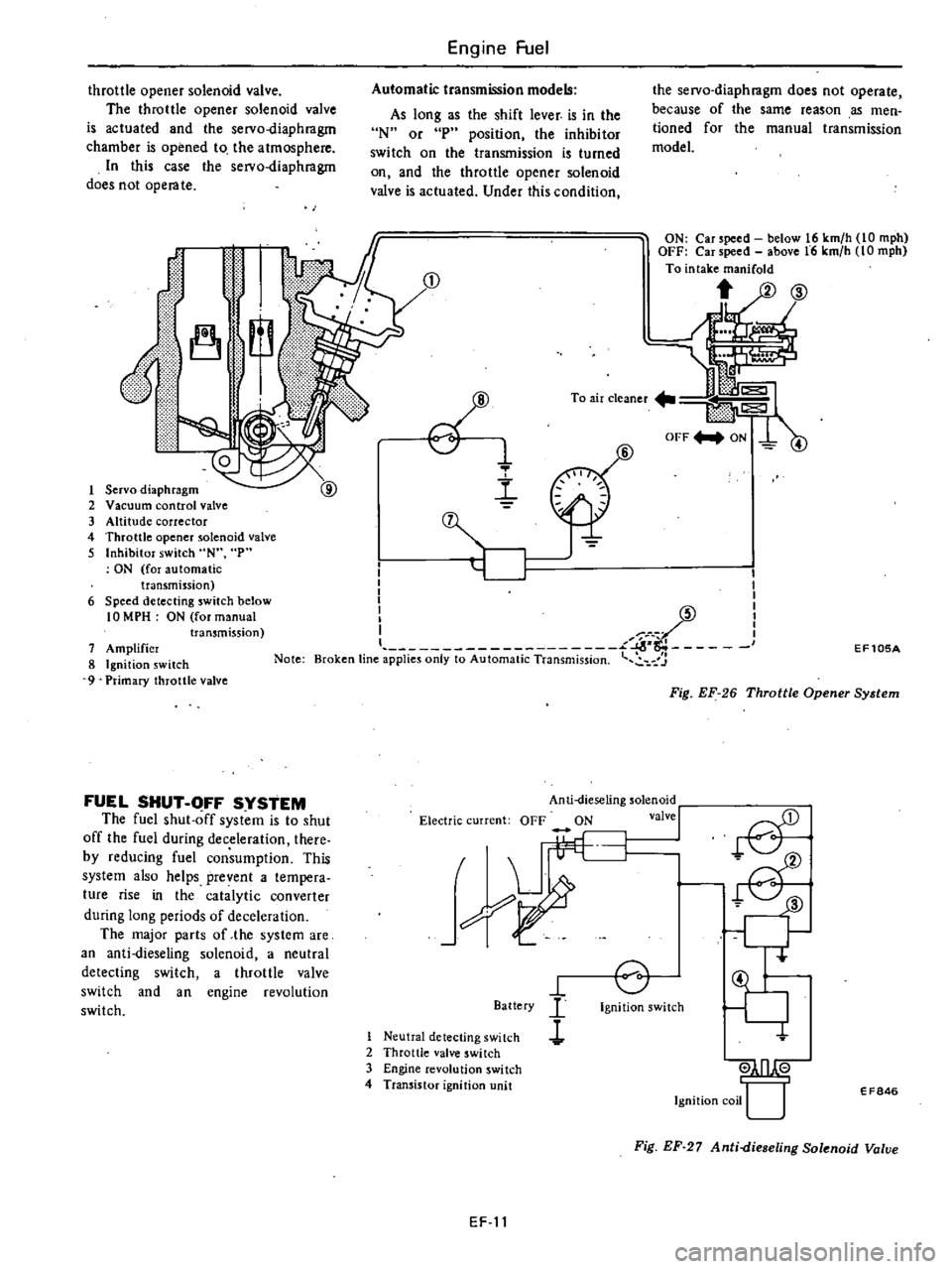
Servo
diaphragm
2
Vacuum
control
valve
3
Altitude
corrector
4
Throttle
opener
solenoid
valve
5
Inhibitor
switch
N
p
ON
for
automatic
transmission
6
Speed
detecting
switch
below
10
MPH
ON
for
manual
transmission
7
Amplifier
8
Ignition
switch
9
Primary
throttle
valve
Note
FUEL
SHUT
OFF
SYSTEM
The
fuel
shut
off
system
is
to
shut
off
the
fuel
during
deceleration
there
by
reducing
fuel
consumption
This
system
also
helps
prevent
a
tempera
ture
rise
in
the
catalytic
converter
during
long
periods
of
deceleration
The
major
parts
of
the
system
are
an
anti
dieseling
solenoid
a
neutral
detecting
switch
a
throttle
valve
switch
and
an
engine
revolution
switch
e
1
l
6
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
l
L
I
Broken
tine
applies
only
to
Automatic
Transmission
7
Anti
dieseling
solenoid
Electric
current
OFF
ON
valve
I
I
h
L
Battery
I
Neutral
detecting
switch
l
2
Throttle
valve
switch
3
Engine
revolution
switch
4
Transistor
ignition
unit
o
Ignition
switch
EF105A
Fig
EF
26
Throttle
Opener
System
ill
Ignition
coil
U
EF846
Fig
EF
27
Anti
dieseling
Solenoid
Valve
EF
11
Page 102 of 548
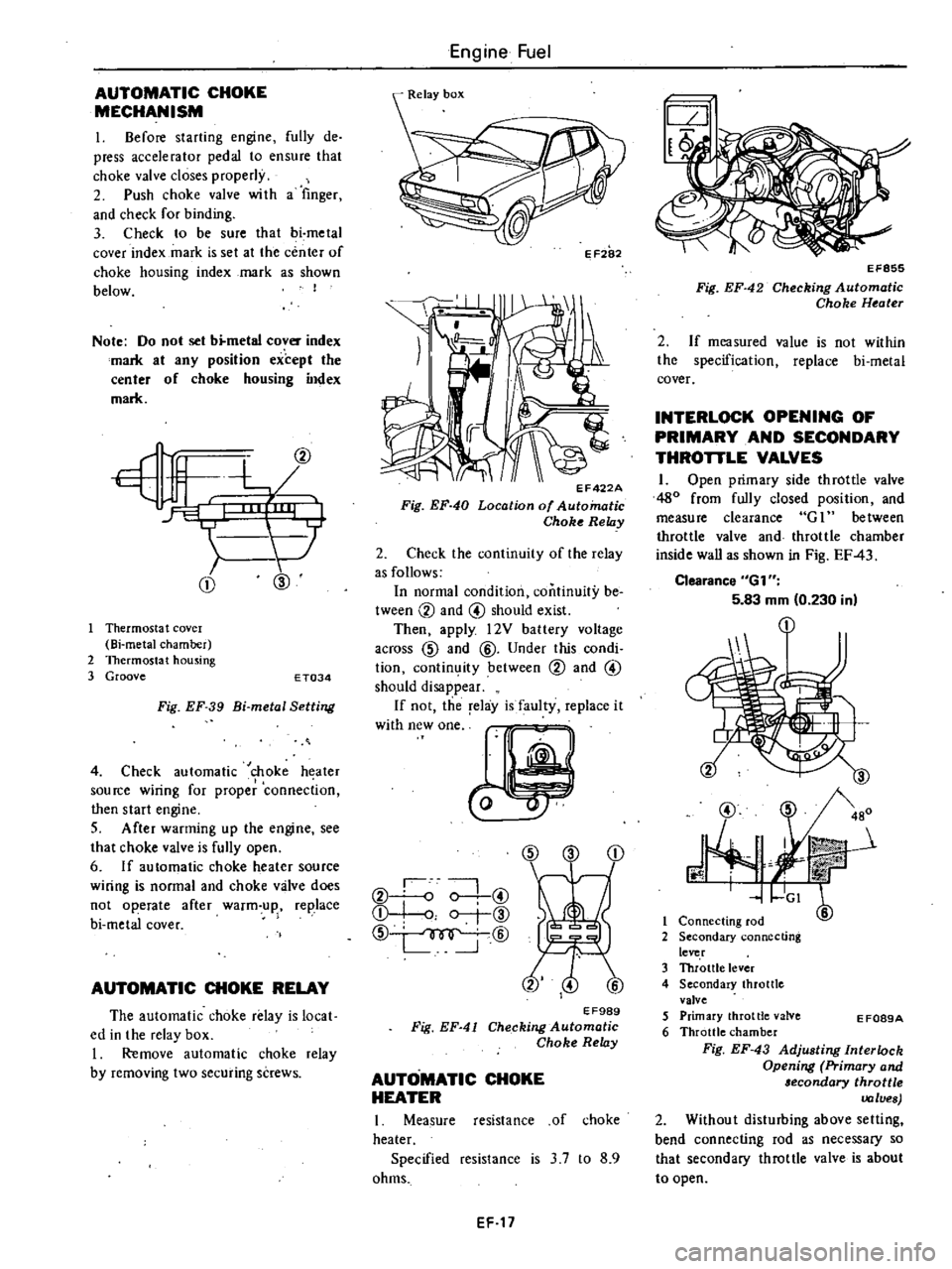
AUTOMATIC
CHOKE
MECHANISM
I
Before
starting
engine
fully
de
press
accelerator
pedal
to
ensure
that
choke
valve
closes
properly
2
Push
choke
valve
wi
th
a
finger
and
check
for
binding
3
Check
to
be
sure
that
bi
metal
cover
index
mark
is
set
at
the
center
of
choke
housing
index
mark
as
shown
below
I
Note
Do
not
set
b
metal
cover
index
mark
at
any
position
except
the
center
of
choke
housing
index
mark
CD
@
Thermosta
t
covel
Bi
metal
chamber
2
Thermostat
housing
3
Groove
E
T034
Fig
EF
39
Bi
metal
Setting
4
Check
automatic
choke
heater
source
wiring
for
proper
connection
then
start
engine
S
After
warming
up
the
engine
see
that
choke
valve
is
fully
open
6
If
automatic
choke
heater
source
wiring
is
normal
and
choke
valve
does
not
operate
after
warm
up
replace
bi
metal
cover
AUTOMATIC
CHOKE
RELAY
The
automatic
choke
relay
is
local
ed
in
the
relay
box
I
Remove
automatic
choke
relay
by
removing
two
securing
screws
Engine
Fuel
II
EF422A
Fig
EF
40
Location
of
Automatic
Choke
Relay
2
Check
the
continuity
of
the
relay
as
follows
In
normal
condition
continuity
be
tween
CV
and
@
should
exist
Then
apply
l2V
battery
voltage
across
CID
and
@
Under
this
condi
tion
contin
ity
between
CV
and
@
should
disappear
If
not
the
relay
is
faulty
replace
it
W
hWO
CID
CD
CV
o
0
@
Q
I
o
r
@
CID
@
EF989
Fig
EF
41
Checking
Automatic
Choke
Relay
AUTOMATIC
CHOKE
HEATER
I
Measure
resistance
of
choke
heater
Specified
resistance
is
3
7
to
8
9
ohms
EF
17
EF855
Fig
EF
42
Checking
Automatic
Choke
Heater
2
If
measured
value
is
not
within
the
specification
replace
bi
metal
cover
INTERLOCK
OPENING
OF
PRIMARY
AND
SECONDARY
THROTTLE
VALVES
1
Open
primary
side
throttle
valve
480
from
fully
closed
position
and
measure
clearance
G
1
between
throttle
valve
and
throttle
chamber
inside
wall
as
shown
in
Fig
EF
43
Clearance
6G1
5
83
mm
0
230
in
@
J
3
480
r
mit
GI
6
1
Connecting
rod
2
Secondary
connecting
lever
3
Throttle
lever
4
Secondary
throttle
valve
5
Primary
throttle
valve
6
Throttle
chamber
Fig
EF
43
Adjusting
Interlock
Opening
Primary
and
lecondary
throttle
values
2
Without
disturbing
above
setting
bend
connecting
rod
as
necessary
so
that
secondary
throttle
valve
is
about
to
open
E
F089A
Page 104 of 548
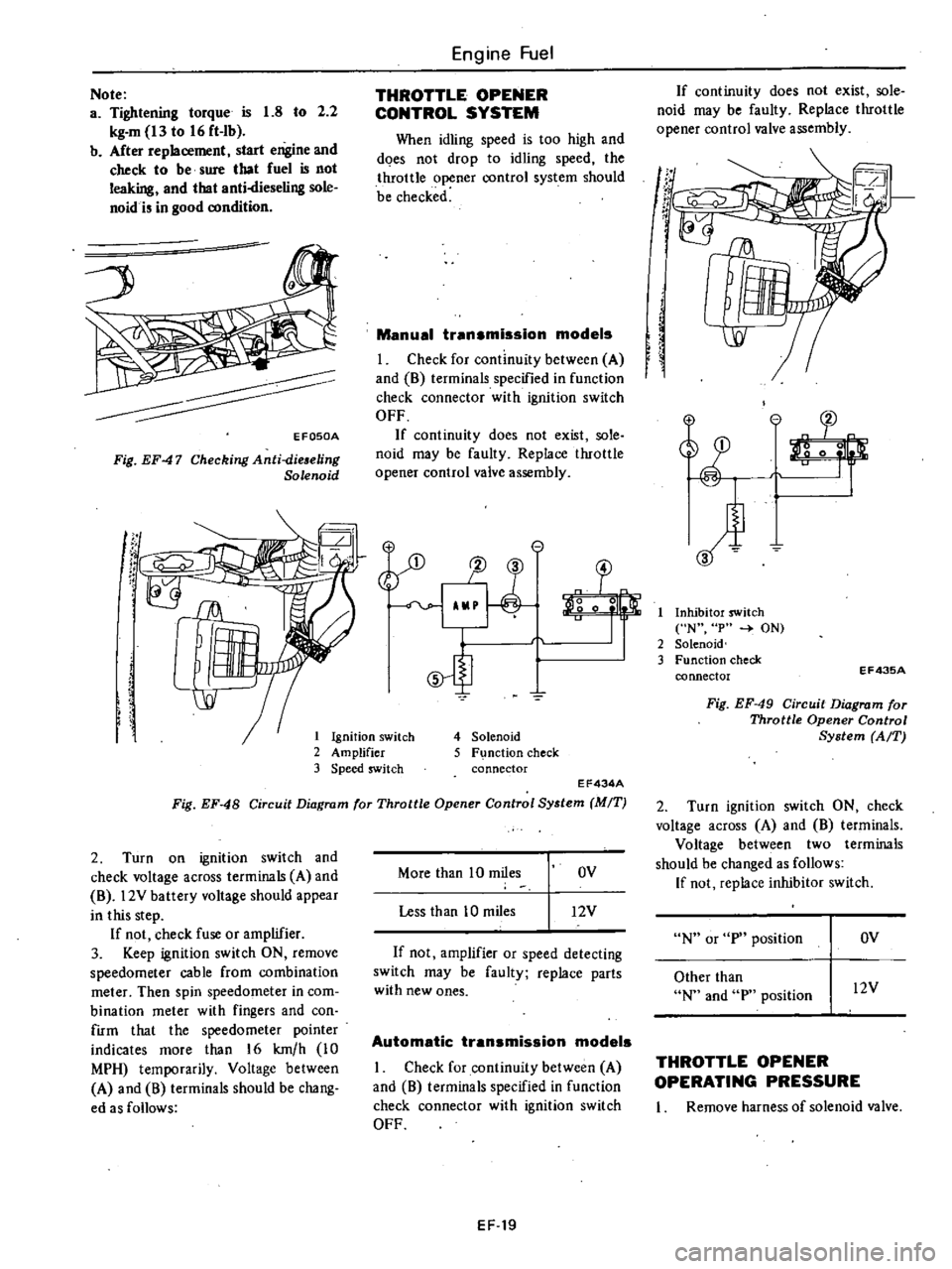
1
Ignition
switch
2
Amplifier
3
Speed
switch
Note
a
Tightening
torque
is
1
8
to
2
2
kg
m
13
to
16
ft
Ib
b
After
replacement
start
engine
and
check
to
be
sure
that
fuel
is
not
leaking
and
that
anti
dieseling
sole
noid
i
in
good
condition
EFOSOA
Fig
EF47
Checking
Anti
dieaeling
Solenoid
l
SJ
Engine
Fuel
THROTTLE
OPENER
CONTROL
SYSTEM
When
idling
speed
is
too
high
and
does
not
drop
to
idling
speed
the
throttle
opener
control
system
should
be
checked
Manual
transmission
models
I
Check
for
continuity
between
A
and
8
terminals
specified
in
function
check
connector
with
ignition
switch
OFF
If
continuity
does
not
exist
sole
noid
may
be
faulty
Replace
throttle
opener
control
valve
assembly
e
1J
3
o
0
5
4
Solenoid
5
F
nction
check
connector
EF434A
Fig
EF
48
Circuit
Diagram
for
Throttle
Opener
Control
System
MIT
2
Turn
on
ignition
switch
and
check
voltage
across
terminals
A
and
8
l2V
battery
voltage
should
appear
in
this
step
If
not
check
fuse
or
amplifier
3
Keep
ignition
switch
ON
remove
speedometer
cable
from
combination
meter
Then
spin
speedometer
in
com
bination
meter
with
fingers
and
con
firm
that
the
speedometer
pointer
indicates
more
than
16
km
h
10
MPH
temporarily
Voltage
between
A
and
8
terminals
should
be
chang
ed
as
follows
More
than
10
miles
OV
Less
than
10
miles
12V
If
not
amplifier
or
speed
detecting
switch
may
be
faulty
replace
parts
with
new
ones
Automatic
transmission
models
I
Check
for
continuity
between
A
and
8
terminals
specified
in
function
check
connector
with
ignition
switch
OFF
EF
19
If
continuity
does
not
exist
sole
noid
may
be
faulty
Replace
throttle
opener
control
valve
assembly
If
t
r
If
I
Inhibitor
switch
N
p
ON
2
Solenoid
3
Function
check
connector
EF43SA
Fig
EF
49
Circuit
Diagram
for
Throttle
Opener
Control
System
AfT
2
Turn
ignition
switch
ON
check
voltage
across
A
and
8
terminals
Voltage
between
two
terminals
should
be
changed
as
follows
If
not
replace
inhibitor
switch
N
or
p
position
OV
Other
than
N
and
p
position
l2V
THROTTLE
OPENER
OPERATING
PRESSURE
I
Remove
harness
of
solenoid
valve
Page 146 of 548
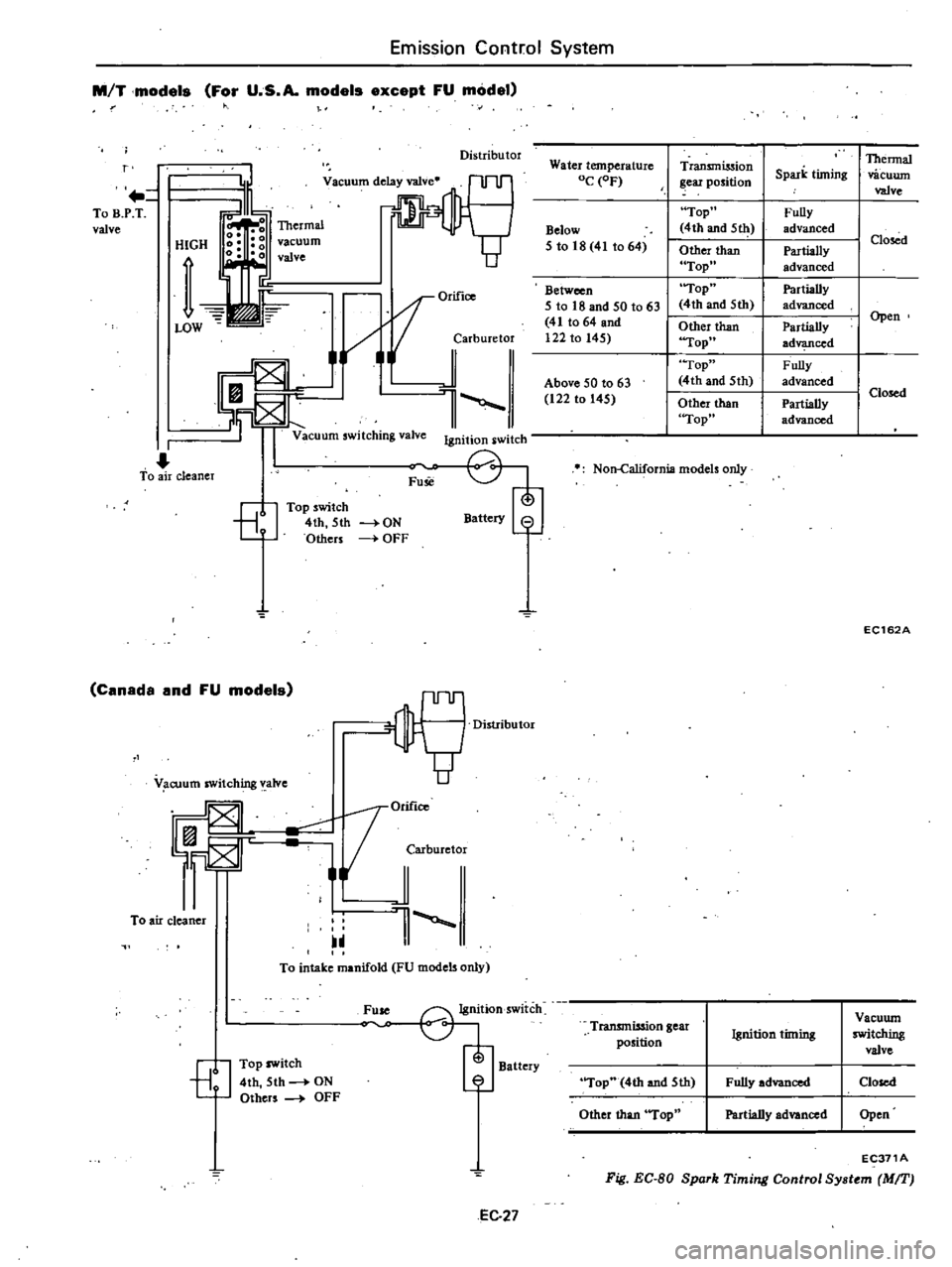
Emission
Control
System
M
T
models
For
U
S
A
models
except
FU
model
Distributor
r
To
B
P
T
valve
HIGH
vacuum
valve
OrifiCO
i
jarburetor
l
Vacuum
switching
valve
Ignition
switch
I
To
air
cleaner
Fuse
8
Top
switch
4th
5th
Others
Battery
8
ON
OFF
Canada
and
FU
models
OM
1orifico
F
JCMburetor
To
air
cleaner
1
V
cuum
switching
valve
To
intake
manifold
FU
models
only
Fuse
G1j
Ignition
switch
Battery
7
EJ
Top
switch
4th
5th
ON
Others
OFF
EC
27
Water
temperature
OC
OF
Below
5
to
18
41
to
64
Between
I
5
to
18
and
50
t063
41
to
64
and
I
122
to
145
I
I
Above
50
to
63
122
to
145
Transmission
ear
position
Top
4th
and
5111
Other
than
Top
Top
4th
and
5th
Other
than
Top
Top
4th
and
5th
Other
than
Top
Non
California
models
only
Thermal
Spark
timing
vacuwn
valve
Fully
advanced
I
Closed
Partially
advanced
Partially
I
advanced
Partially
I
Open
ad
ced
Fully
I
advanced
I
Closed
Partially
advanced
EC162A
Transmission
gear
Vacuwn
Ignition
timing
switching
position
valve
Top
4th
and
5th
Fully
advanced
Closed
Other
than
Top
Partially
advanced
Open
EC371A
Fig
EC
BO
Spork
Timing
Control
Sy
tem
MIT
Page 147 of 548
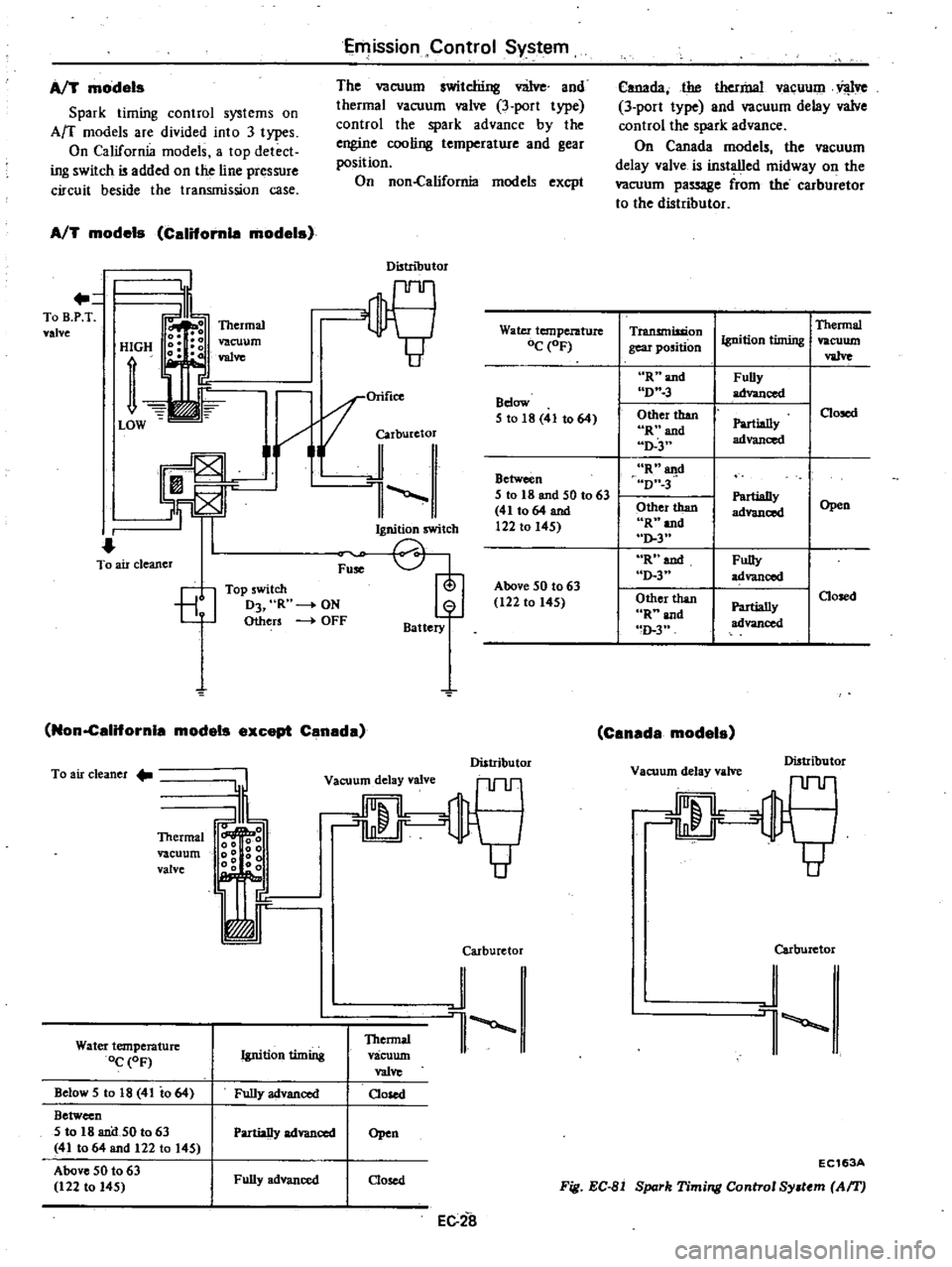
Emission
Control
System
AfT
models
Spark
timing
control
systems
on
Arc
models
are
divided
into
3
types
On
California
models
a
top
detect
ing
switch
i3
added
on
the
line
pressure
circuit
beside
the
transmission
case
The
vacuum
switching
v
iJve
and
thermal
vacuum
valve
3
port
type
control
the
spark
advance
by
the
engine
cooling
temperature
and
gear
position
On
non
California
models
excpt
AfT
models
Califomle
models
Distributor
To
B
P
T
valve
1
Orifice
i1J
1
ICh
OJ
L
J
To
air
cleaner
Fu
EJ
Top
5witch
D3
R
ON
Others
4
OFF
Battery
Non
californla
models
except
Canada
To
air
cleaner
l
o
o
0
Ig
o
g
00
00
00
r
Vacuum
delay
valve
Thermal
vacuum
valve
Water
temperature
OC
OF
Thennal
vacuum
valve
Oosed
Ignition
timing
Below
5
10
18
41
io
64
Between
5
to
IB
and
50
to
63
411064
and
122
10
145
Above
50
to
63
122
to
145
Fully
advanced
PartiaDy
advanced
Open
Fully
advanced
Oosed
EC2a
Water
temperature
OC
oF
Bdow
51018
41
to
64
Between
5
to
18
and
50
10
63
411064
and
12210145
Above
50
to
63
122
to
145
Distributor
Carburetor
J
l
Canada
the
thermal
vaCUUDl
Vl
lve
3
port
type
and
vacuum
delay
valve
control
the
spark
advance
On
Canada
models
the
vacuum
delay
valve
is
installed
midway
on
the
vacuum
passage
from
the
carburetor
to
the
distributor
Transmission
gear
position
Thermal
vacuum
va1ve
Ignition
timing
R
and
D
3
FuBy
advanced
Other
than
Rnand
D
3
Oosed
Partially
advanced
R
a
gd
D
3
Other
than
R
and
0
3
Partially
advanced
Open
R
aud
D
3
Fully
advanced
Other
than
R
and
m
3
Oosed
Partially
advanced
Canada
models
Vacuum
delay
valve
Distributor
Carburetor
J
l
EC163A
Fig
EC
81
Spark
Timing
Control
Sy
tem
Af1
J