engine DATSUN B110 1973 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1973, Model line: B110, Model: DATSUN B110 1973Pages: 513, PDF Size: 28.74 MB
Page 417 of 513
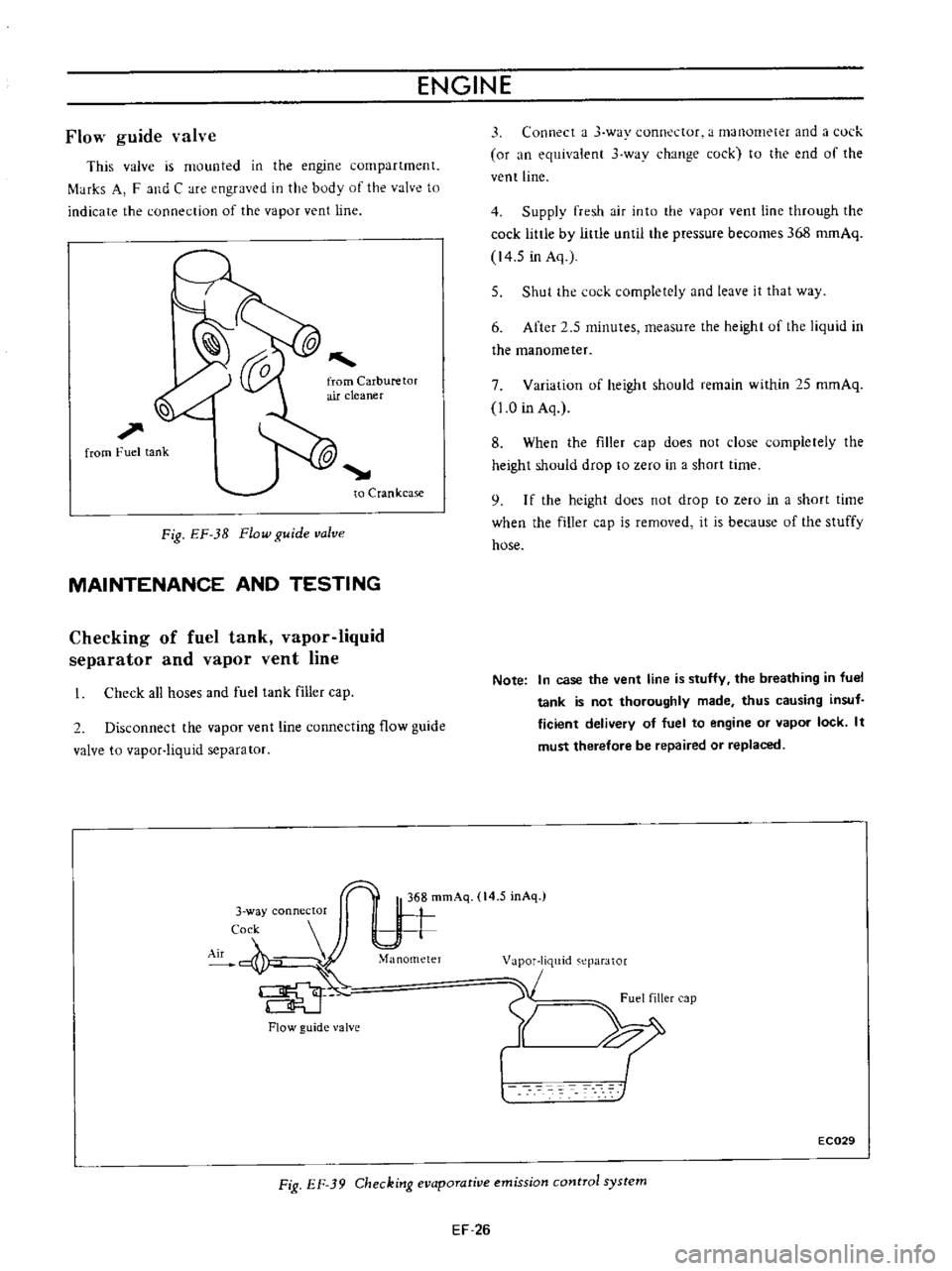
ENGINE
ffi68
mmAq
14
5
mAq
3
way
connector
Cock
II
M
nam
e
Flow
guide
valve
This
valve
is
mounted
in
the
engine
compartment
f
tHks
A
F
and
C
are
engraved
in
the
body
of
the
valve
to
indicate
the
connection
of
the
vapor
vent
line
l
l
1
from
Fuel
tank
to
Crankcase
Fig
EF
3B
Flow
guide
valve
MAINTENANCE
AND
TESTING
Checking
of
fuel
tank
vapor
liquid
separator
and
vapor
vent
line
Check
all
hoses
and
fuel
tank
filler
cap
2
Disconnect
the
vapor
vent
line
connecting
flow
guide
valve
to
vapor
liquid
separator
Flow
guide
valve
3
Connect
a
J
way
connector
a
manometer
and
a
l
ul
k
or
an
equivalent
3
wav
change
cock
to
the
end
of
the
vent
line
4
Supply
fresh
air
into
the
vapor
vent
line
through
the
cock
little
by
little
until
the
pressure
becomes
368
romAq
14
5
in
Aq
5
Shut
the
cock
completely
and
leave
it
that
way
6
After
2
5
minutes
measure
the
height
uf
the
liquid
in
the
manometer
7
Variation
of
height
should
remain
within
25
mmAq
1
0
in
Aq
8
When
the
filler
cap
does
not
close
completely
the
height
should
drop
to
zero
in
a
short
time
9
I
f
the
height
docs
not
drop
to
zero
in
a
short
time
when
the
filler
cap
is
removed
it
is
because
of
the
stuffy
hose
Note
In
case
the
vent
line
is
stuffy
the
breathing
in
fuel
tank
is
not
thoroughly
made
thus
causing
insuf
ficient
delivery
of
fuel
to
engine
or
vapor
lock
It
must
therefore
be
repaired
or
replaced
1
m
eparator
1
Fuel
filler
cap
Y
XI
EC029
Fig
EF
39
Checking
evaporative
emission
control
system
EF
26
Page 419 of 513
DATE
ENGINE
SERVICE
JOURNAL
OR
BULLETIN
REFERENCE
JOURNAL
or
BULLETIN
No
PAGE
No
SUBJECT
EF
28
Page 420 of 513
DATSUN
1200
MODEL
B
11
0
SERIES
L
NISSAN
I
NISSAN
MOTOR
CO
LTD
TOKYO
JAPAN
SECTION
EE
ENGINE
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
BATTERY
STARTING
MOTOR
CHARGING
CIRCUIT
ALTERNATOR
REGULATOR
IGNITIO
N
CIRCUIT
DISTRIBUTOR
IGNITION
COIL
SPARK
PLUG
EEl
EE
3
EE
15
EE
16
EE
23
EE
29
EE
29
EE
36
EE
37
Page 421 of 513
ENGINE
ElECTRICAL
SYSTEM
BATTERY
CONTENTS
REMOVAL
CHECKING
ELECTROLYTE
LEVEL
CHECKING
SPECIFIC
GRAVITY
EE
1
EE
l
EE
1
REMOVAL
Disconnect
the
negative
terminal
first
and
then
the
positive
terminal
2
Remove
the
retainer
nuts
and
take
off
retainer
3
Release
retainer
bolts
and
remove
battery
CHECKING
ELECTROLYTE
LEVEL
Adjust
the
electrolyte
level
in
the
battery
when
the
battery
is
in
a
fully
charged
condition
The
electrolyte
hould
maintain
its
indicated
correct
level
in
the
battery
N
water
other
than
distilled
water
should
be
added
Q
cD
I
1
Vent
plug
2
Electrolvte
3
Level
indicator
Fig
EE
1
ElectTolyte
level
CHECKING
SPECIFIC
GRAVITY
The
specific
gravity
of
the
battery
liquid
is
measured
by
means
of
a
hydrometer
When
according
to
the
table
described
later
the
charging
of
the
battery
is
below
60
percent
the
specific
gravity
is
below
1
20
as
corrected
at
200e
680F
and
also
when
the
difference
in
the
specific
CHARGING
BATTERY
FREEZING
EE
2
EE
3
gravity
of
the
individual
cells
is
above
0
025
the
battery
must
be
changed
or
adjusted
tl
f
ead
p
level
jSCale
2
II
It
I
TheTmat
gauge
I
2
Hydrometer
Fig
EE
2
Checking
specific
gTavity
Temperature
conversion
in
measuring
specific
gravity
The
standard
specific
gravity
of
the
electrolyte
is
obtained
when
the
battery
is
fully
charged
at
an
electro
lyte
temperature
of
200
e
680
F
When
temperature
rises
loe
1
80F
the
specific
gravity
decreases
0
0007
and
reversely
when
temperature
drops
loe
I
ROF
the
specific
gravity
increases
0
0007
Therefore
assuming
the
specific
gravity
at
tOe
is
St
S20
the
specific
gravity
at
200e
680F
is
calculated
according
to
the
following
expressions
S
o
St
0
0007
t
20
If
0
0007
t
20
is
X
S
o
St
X
Accordingly
if
X
is
known
beforehand
S
o
can
be
obtained
easily
The
values
of
X
are
shown
in
the
following
table
EE
1
Page 422 of 513
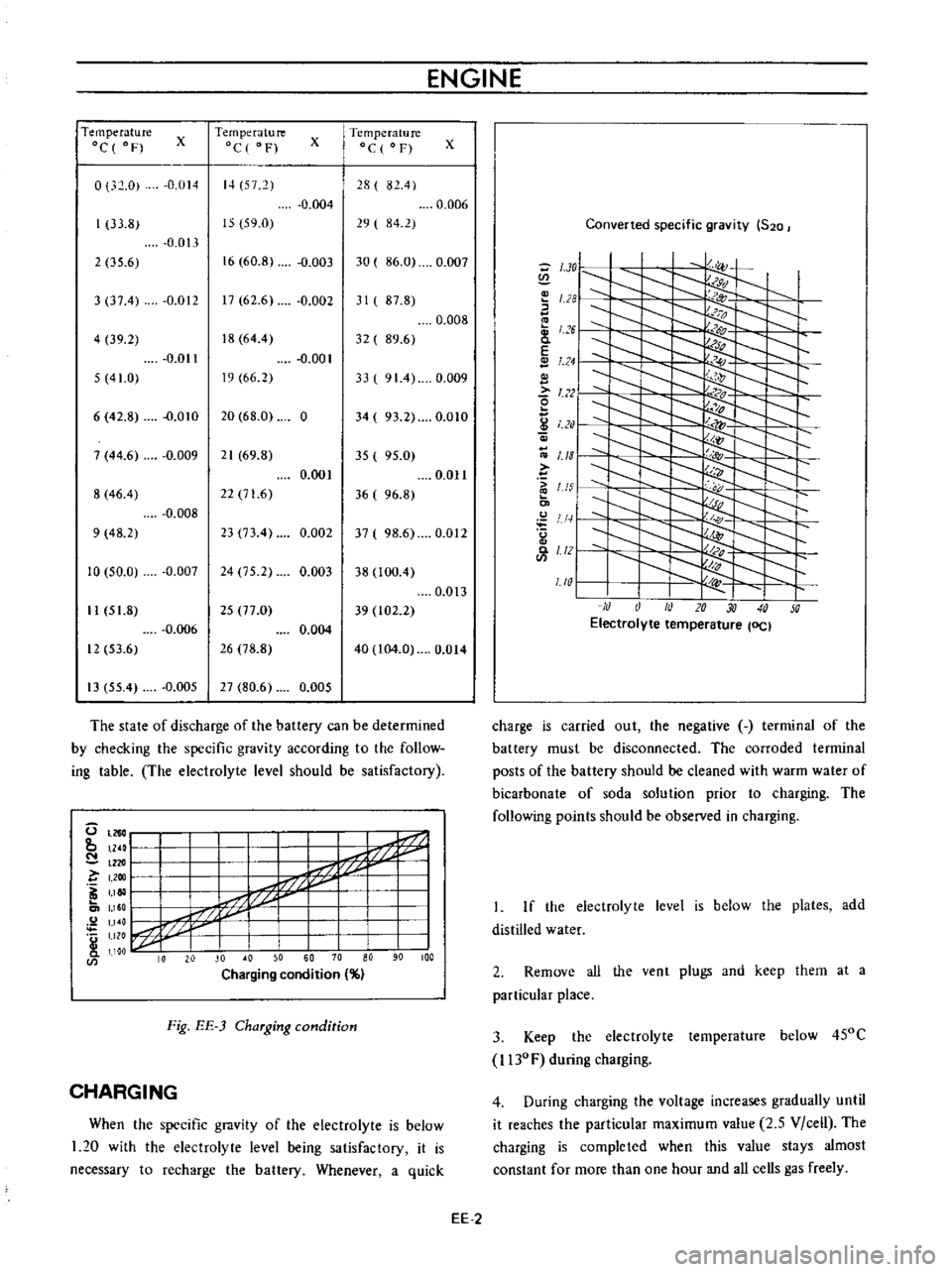
ENGINE
Temperature
Oc
of
Temperature
C
F
x
Temperature
Oc
F
x
0
32
0
0
014
14
572
28
82
4
0
004
0
006
33
8
IS
59
0
19
I
84
2
0
013
2
35
6
16
60
8
0
003
30
86
0
0
007
3
37
4
0
012
17
61
6
0
001
31
87
8
0
008
4
39
2
18
64
4
32
89
6
0
011
0
001
5
41
0
19
66
2
33
91
4
0
009
6
42
8
0
010
20
68
0
0
34
93
2
0
010
7
44
6
0
009
21
69
8
35
95
0
0
001
0
01l
8
46
4
22
71
6
36
96
8
0
008
9
48
2
23
73
4
0
002
37
98
6
0
012
10
50
0
0
007
24
75
2
0
003
38
100
4
0
013
II
51
8
25
77
0
39
t02
2
0
006
0
004
12
53
6
16
78
8
40
104
0
0
Ot4
13
55
4
0
005
27
80
6
0
005
The
state
of
discharge
of
the
battery
can
be
determined
by
checking
the
specific
gravity
according
to
the
follow
ing
table
The
electrolyte
level
should
be
satisfactory
U
tn
l
k
1
I
P
I
IZf
I
r7
42
I
bt
7
J
I
I
11
0
I
M
I
L
J
I
10
20
30
0
50
60
70
aD
90
100
Charging
condition
Fig
EE
3
Charging
condition
CHARGING
When
the
specific
gravity
of
he
electrolyte
is
below
1
20
with
the
electrolyte
level
being
satisfactory
it
is
necessary
to
recharge
the
battery
Whenever
a
quick
x
Converted
specific
gravity
520
V
9d
f
o
1
28
u
1
6
c
E
1
24
l
22
o
0
U5
S
I
1
1
2
1
10
1
NON
M
i
Electrolyte
temperature
lOCI
charge
is
carried
out
the
negative
terminal
of
the
battery
must
be
disconnected
The
corroded
terminal
posts
of
the
battery
should
be
cleaned
with
warm
water
of
bicarbonate
of
soda
solution
prior
to
charging
The
following
points
should
be
observed
in
charging
If
the
electrolyte
level
is
below
the
plates
add
distilled
water
2
Remove
all
the
vent
plugs
and
keep
them
at
a
particular
place
3
Keep
the
electrolyte
temperature
below
450C
l130F
during
charging
4
During
charging
the
voltage
increases
gradually
until
it
reaches
the
particular
maximum
value
2
5
Vice
II
The
charging
is
completed
when
this
value
stays
almost
constant
for
more
than
one
hour
and
all
cells
gas
freely
EE
2
Page 423 of 513
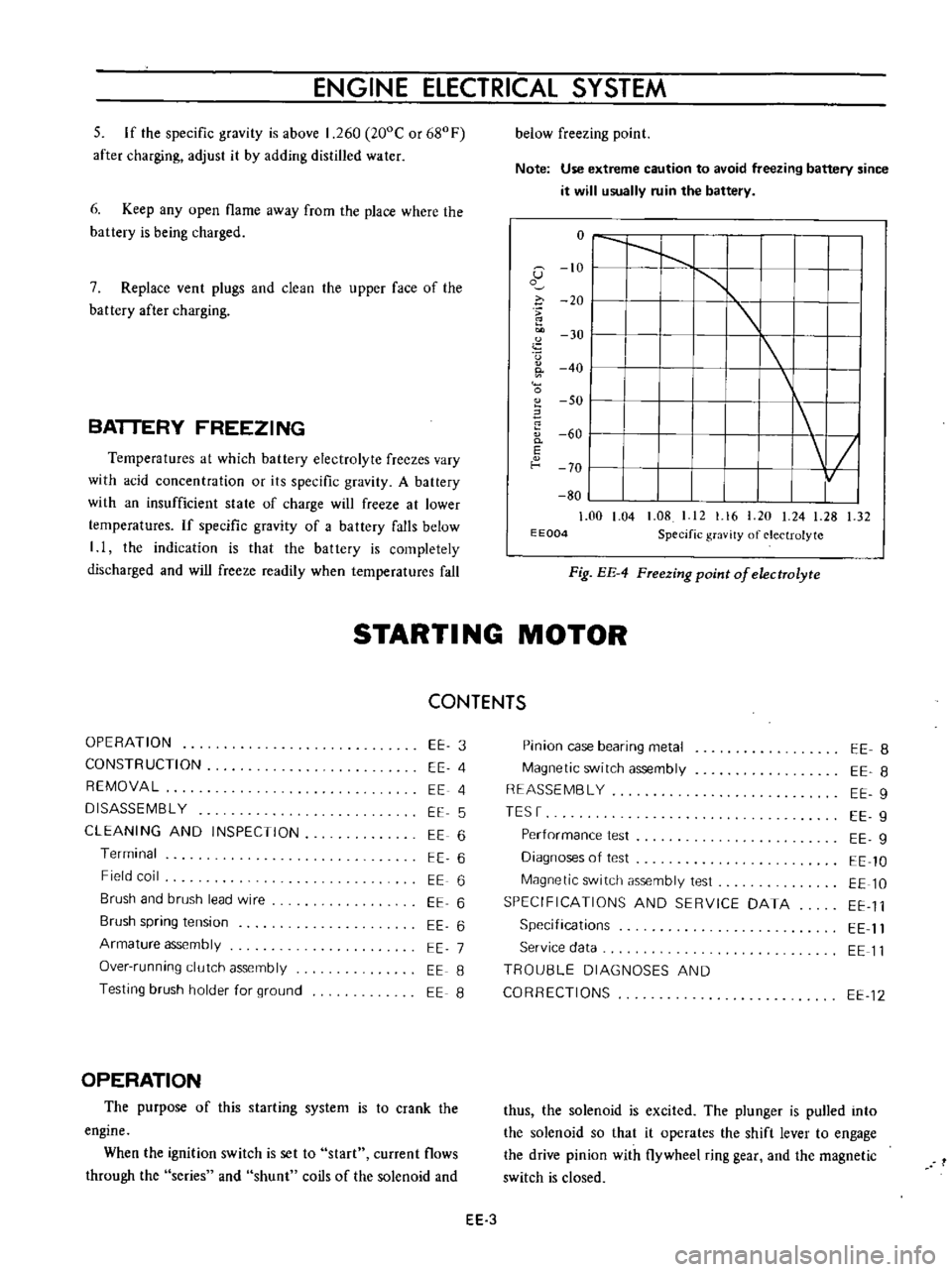
ENGINE
ElECTRICAL
SYSTEM
5
If
the
specific
gravity
is
above
1
260
200C
or
680F
after
charging
adjust
it
by
adding
distilled
water
6
Keep
any
open
flame
away
from
the
place
where
the
battery
is
being
charged
7
Replace
vent
plugs
and
clean
the
upper
face
of
the
battery
after
charging
BATTERY
FREEZING
Temperatures
at
which
battery
electrolyte
freezes
vary
with
acid
concentration
or
its
specific
gravity
A
battery
with
an
insufficient
state
of
charge
will
freeze
at
lower
temperatures
If
specific
gravity
of
a
battery
falls
below
I
I
the
indication
is
that
the
battery
is
completely
discharged
and
will
freeze
readily
when
temperatures
fall
below
freezing
point
Note
Use
extreme
caution
to
avoid
freezing
battery
since
it
will
usually
ruin
the
battery
o
I
I
1
G
10
I
1
o
i
20
I
u
30
I
I
0
40
I
0
SO
I
60
0
I
E
f
o
70
I
80
1
00
1
04
1
08
I
12
1
16
20
24
1
28
1
32
E
E004
Specific
gravity
of
electrolyte
Fig
EE
4
FTeezing
point
of
electrolyte
STARTI
NG
MOTOR
CONTENTS
OPERATION
CONSTRUCTION
REMOVAL
DISASSEMBL
Y
CLEANING
AND
INSPECTION
Terminal
Field
coil
Brush
and
brush
lead
wire
Brush
spring
tension
Armature
assembly
Over
running
clutch
assembly
Testing
brush
holder
for
ground
EE
3
EE
4
EE
4
EE
5
EE
6
EE
6
EE
6
EE
6
EE
6
EE
7
EE
8
EE
8
OPERATION
The
purpose
of
this
starting
system
is
to
crank
the
engine
When
the
ignition
switch
is
set
to
start
current
flows
through
the
series
and
shunt
coils
of
the
solenoid
and
Pinion
case
bearing
metal
Magnetic
switch
assembly
REASSEMBL
Y
TESr
Performance
test
Diagnoses
of
test
Magnetic
switch
assembly
test
SPECIFICATIONS
AND
SERVICE
DATA
Specifications
Service
data
TROU8LE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
EE
8
EE
8
EE
9
EE
9
EE
g
EE
10
EE
10
EE
11
EE
11
EE
11
EE
12
thus
the
solenoid
is
excited
The
plunger
is
pulled
into
the
solenoid
so
that
it
operates
the
shift
lever
to
engage
the
drive
pinion
with
flywheel
ring
gear
and
the
magnetic
switch
is
closed
EE
3
Page 424 of 513
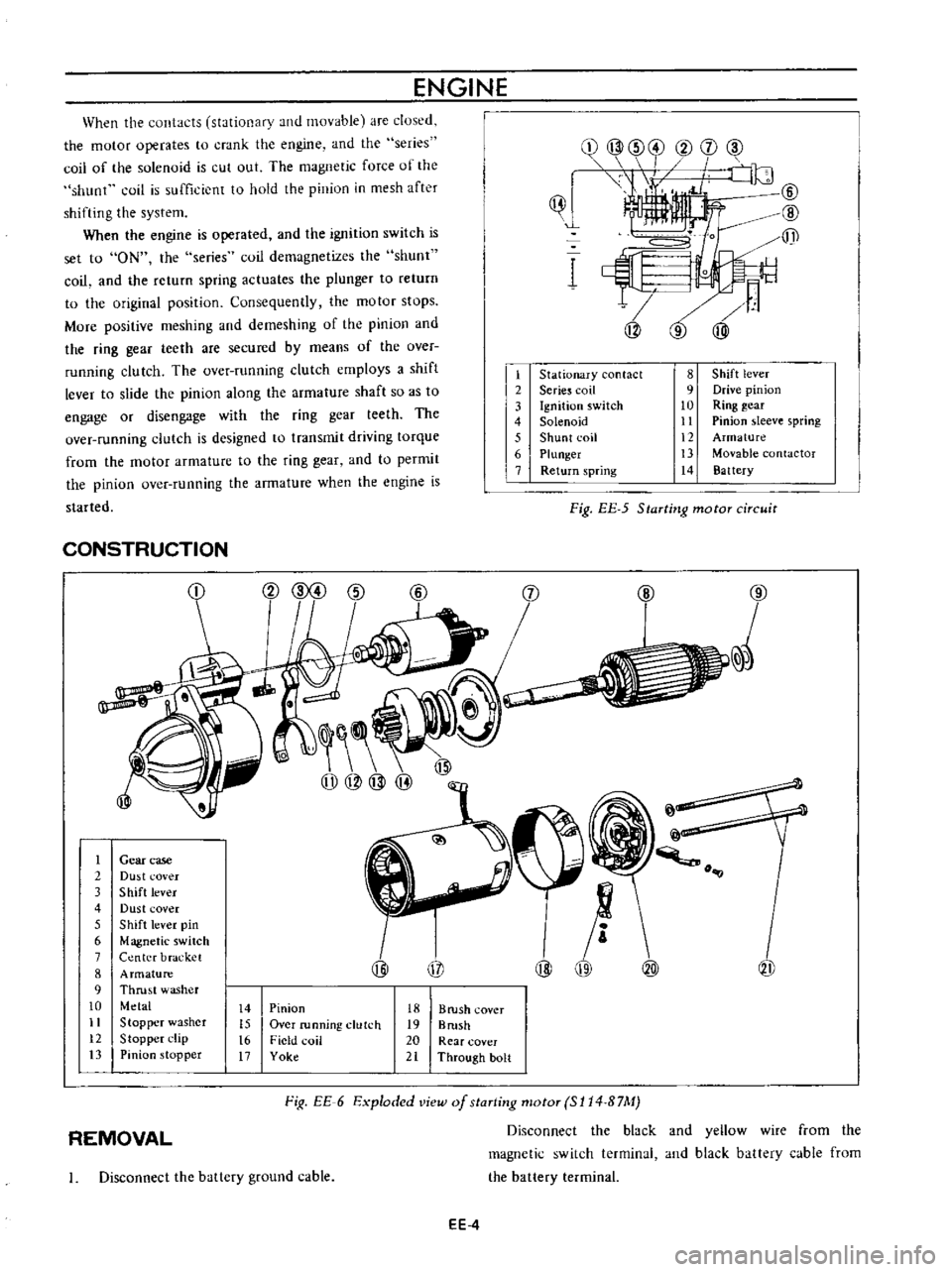
When
the
contacts
stationary
and
movable
are
dused
the
motor
operates
to
crank
the
engine
and
the
series
coil
of
the
solenoid
is
cut
out
The
magnetic
force
of
the
shunt
coil
is
sufficient
to
hold
the
pinion
in
mesh
after
shifting
the
system
When
the
engine
is
operated
and
the
ignition
switch
is
set
to
ON
the
series
coil
demagnetizes
the
shunt
coil
and
the
return
spring
actuates
the
plunger
to
return
to
the
original
position
Consequently
the
motor
stops
More
positive
meshing
and
demeshing
of
the
pinion
and
the
ring
gear
teeth
are
secured
by
means
of
the
over
running
clutch
The
over
running
clutch
employs
a
shift
lever
to
slide
the
pinion
along
the
armature
shaft
so
as
to
engage
or
disengage
with
the
ring
gear
teeth
The
over
running
clutch
is
designed
to
transmit
driving
torque
from
the
motor
armature
to
the
ring
gear
and
to
permit
the
pinion
over
running
the
armature
when
the
engine
is
started
ENGINE
ijJ
1
t
2
3
4
5
6
7
Stationary
contact
Serie
coil
Ignition
switch
Solenoid
Shunt
coil
Plunger
Return
spring
8
Shift
lever
9
Drive
pinion
10
Ring
gear
11
Pinion
sleeve
spring
12
Armature
13
Movable
contactor
14
Battery
Fig
EE
5
Starting
motor
circuit
CONSTRUCTION
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
j
@
Gear
case
Du
t
cover
Shift
lever
Dust
cover
Shift
lever
pin
Magnetic
switch
Center
bracket
Armature
Thrust
washer
Metal
Stopper
washer
Stopper
l
lip
Pinion
stopper
@
@
o
@
i
1I
@
@
@
14
15
t6
17
Pinion
Over
running
clutch
Field
coil
Yoke
18
B
rush
cover
19
Brush
20
Rear
cover
21
Through
bolt
Fig
EE
6
Exploded
view
of
staTting
motoT
SI14
B7M
Disconnect
the
black
and
yellow
wire
from
the
magnetic
switch
terminal
and
black
battery
cable
from
the
battery
terminal
REMOVAL
I
Disconnect
the
ballery
ground
cable
EE
4
Page 425 of 513
ENGINE
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
2
Remove
two
bolts
llsed
to
secure
the
starting
motor
on
the
clutch
housing
Pull
the
starter
assembly
forward
and
remove
the
starting
motor
DISASSEMBLY
Remove
the
brush
cover
and
take
out
the
brush
6
Fig
EE
7
Removing
the
brush
cover
2
Loosen
the
nut
used
to
secure
the
connecting
plate
to
the
magnetic
switch
M
terminal
Remove
two
screws
used
to
secure
the
magnetic
switch
Remove
the
cotter
pin
and
withdraw
the
shift
lever
pin
Now
remove
the
magnetic
switch
Fig
EE
8
Removing
the
magnetic
switch
assembly
3
Remove
two
through
bolts
and
rear
cover
assembly
Remove
the
yoke
assembly
by
lightly
tapping
with
a
wooden
mallet
Fig
EE
9
Removing
the
brush
cover
and
yoke
assembly
4
Withdraw
the
armature
assembly
and
shift
lever
Fig
EE
l0
Removing
the
armature
assemlby
and
shift
lever
5
Remove
the
pinion
stopper
from
the
armature
shaft
end
To
remove
the
stopper
first
remove
the
stopper
washer
and
push
the
stopper
to
the
over
running
clutch
side
and
after
removing
the
stopper
clip
remove
the
stopper
together
with
the
over
running
clutch
Withdraw
the
over
running
clutch
assembly
from
the
armature
shaft
Fig
EE
11
Removing
the
over
running
clutch
assembly
EE
5
Page 426 of 513

ENGINE
CLEANING
AND
INSPECTION
Clean
all
disassembled
parts
Be
careful
not
to
use
grease
dissolving
solvent
for
cleaning
of
the
over
running
clutch
armature
assembly
magnetic
switch
assembly
and
field
coils
since
solvent
dissolves
grease
packed
in
the
clutch
mechanism
and
damages
the
coils
or
insulators
Check
them
for
damage
or
excessive
wear
Replace
them
as
required
Terminal
Check
the
terminal
for
damage
and
wear
and
replace
if
necessary
Field
coil
Check
the
field
coil
for
insulation
If
the
coil
insulator
is
damaged
or
worn
replace
Testing
field
coil
for
continuity
Connect
test
probe
of
a
circuit
tester
or
a
resistance
counter
to
the
field
coil
positive
terminal
and
positive
brush
holder
If
the
tester
indicates
no
continuity
the
field
circuit
or
coil
is
open
O
Fig
EE
12
Cotltinuity
test
of
field
coil
Testing
field
coil
for
ground
Place
one
probe
of
a
circuit
tester
onto
the
yoke
and
the
othef
on
to
the
field
coil
positive
tenninal
If
resistance
is
read
the
field
coils
are
grounded
ol
I
Fig
EE
13
CTound
test
of
field
coil
Field
coil
test
for
short
ircuit
Un
solder
the
connected
section
of
each
coil
and
check
the
circuit
with
a
tester
in
the
same
manner
as
described
above
When
the
coil
is
defective
replace
the
coil
Brush
and
brush
lead
wire
Check
the
brush
contact
for
surface
condition
and
wear
When
the
brush
contact
is
loose
replace
the
brush
If
the
brush
is
worn
and
height
is
less
than
6
5
rom
0
2569
in
replace
it
Check
the
connection
of
the
lead
clip
and
lead
wire
for
conditions
Check
brush
holders
and
spring
clip
to
ensure
that
they
are
not
deformed
or
bent
and
properly
hold
brushes
against
the
commutator
If
the
brushes
Of
brush
holders
are
dirty
clean
Brush
spring
tension
Measure
the
brush
spring
tension
using
a
spring
scale
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
14
The
reading
should
be
approxi
mately
0
8
kg
I
76
Ib
EE
6
Page 427 of 513
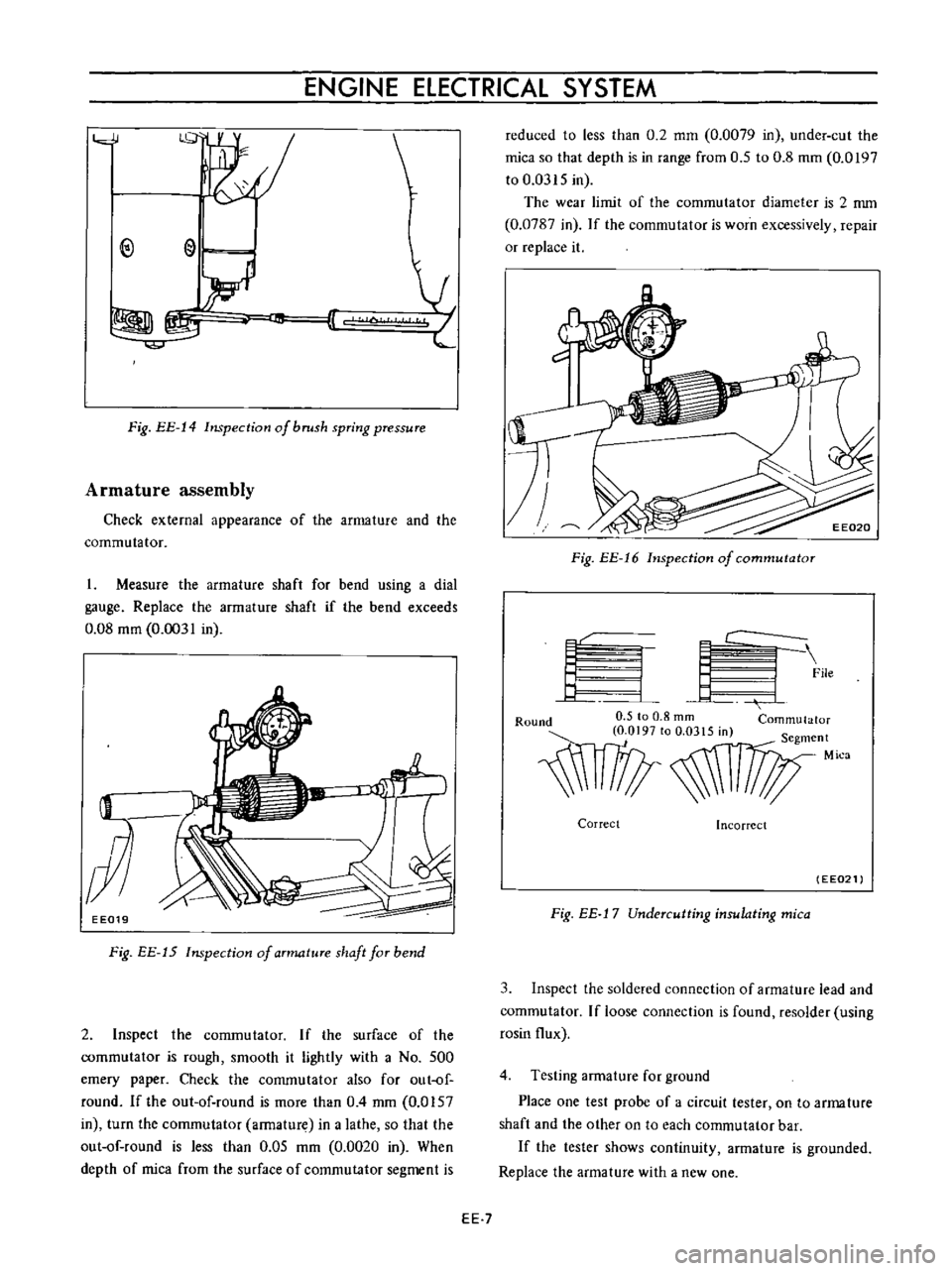
ENGINE
ElECTRICAL
SYSTEM
l
J
r
@
V
I
Fig
EE
14
Inspection
of
brush
spring
pressure
Armature
assembly
Check
external
appearance
of
the
armature
and
the
commutator
I
Measure
the
armature
shaft
for
bend
using
a
dial
gauge
Replace
the
armature
shaft
if
the
bend
exceeds
0
08
mm
0
0031
in
EE019
Fig
EE
15
Inspection
of
aTmatuTe
shaft
faT
bend
2
Inspect
the
commutator
If
the
surface
of
the
commutator
is
rough
smooth
it
lightly
with
a
No
500
emery
paper
Check
the
commutator
also
for
out
of
round
Ifthe
out
of
round
is
more
than
0
4
mm
0
0157
in
turn
the
commutator
armature
in
a
lathe
so
that
the
out
of
round
is
less
than
0
05
mm
0
0020
in
When
depth
of
mica
from
the
surface
of
commutator
segment
is
reduced
to
less
than
0
2
mm
0
0079
in
under
cut
the
mica
so
that
depth
is
in
range
from
0
5
to
0
8
mm
0
0197
to
0
0315
in
The
wear
limit
of
the
commutator
diameter
is
2
nun
0
0787
in
If
the
commutator
is
worn
excessively
repair
or
replace
it
Fig
EE
16
Inspection
of
commutator
f
L
I
C
9
File
4
J
Round
0
5
to
0
8
rom
Commutator
O
OI97tOO
0315m
S
t
egmen
1l1
Mica
Correct
Incorrect
EE021
Fig
EE
j
7
Undercutting
insulating
mica
3
Inspect
the
soldered
connection
of
armature
lead
and
commutator
If
loose
connection
is
found
resolder
using
rosin
flux
4
Testing
armature
for
ground
Place
one
test
probe
of
a
circuit
tester
on
to
arma
ture
shaft
and
the
other
on
to
each
commutator
bar
If
the
tester
shows
continuity
armature
is
grounded
Replace
the
armature
with
a
new
one
EE
7