DATSUN B110 1973 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1973, Model line: B110, Model: DATSUN B110 1973Pages: 513, PDF Size: 28.74 MB
Page 341 of 513
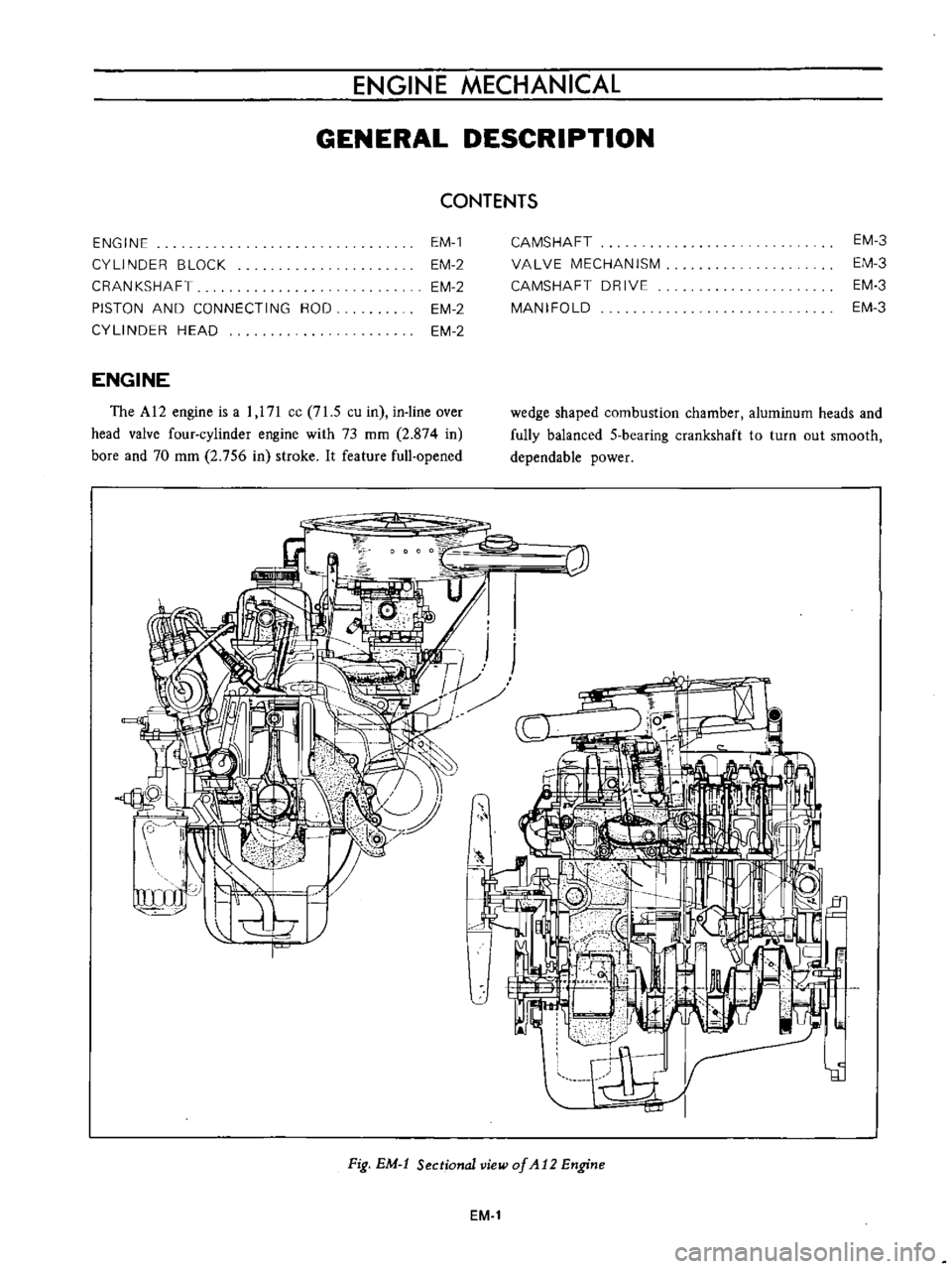
ENGINE
MECHANICAL
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION
CONTENTS
ENGINE
CYLINDER
BLOCK
CRAN
KSHAFT
PISTON
AND
CONNECTING
ROD
CYLINDER
HEAD
EM
EM
2
EM
2
EM
2
EM
2
CAMSHAFT
VALVE
MECHANISM
CAMSHAFT
DRIVE
MANIFOLD
EM
3
EM
3
EM
3
EM
3
ENGINE
The
AI2
engine
is
a
1
171
cc
71
5
cu
in
in
line
over
head
valve
four
cylinder
engine
with
73
mm
2
874
in
bore
and
70
mm
2
756
in
stroke
It
feature
full
opened
wedge
shaped
combustion
chamber
aluminum
heads
and
fully
balanced
5
bearing
crankshaft
to
turn
out
smooth
dependable
power
c
Ii
I
l
1
nun
y
r
r
Fig
EM
t
Sectional
view
of
At2
Engine
EM
1
Page 342 of 513
ENGINE
CYLINDER
BLOCK
The
cylinder
block
in
a
mono
block
special
casting
structure
adopts
five
bearing
support
system
The
A
12
Engine
is
provided
with
baffle
plate
and
steel
net
to
reduce
oil
consumption
the
steel
net
scoops
oil
j
y
r
0
Q
0
T
Fig
EM
2
Cylinder
block
Fig
EM
3
Cylinder
block
CRANKSHAFT
The
crankshaft
is
made
of
special
forged
steel
and
provided
with
a
high
capacity
balance
weight
The
crankshaft
improves
engine
quietness
and
durability
t
high
speed
operation
The
main
bearing
are
lubricated
from
oil
holes
which
intersect
the
main
oil
gallery
in
parallel
with
the
cylinder
bores
v
Fig
EM
4
Crankshaft
PISTON
AND
CONNECTING
ROD
The
newly
designed
lightweight
piston
is
of
cast
aluminum
slipper
skirt
type
The
A
12
Engine
uses
concave
head
pistons
The
piston
pin
is
of
a
special
steel
hollow
type
and
is
connected
to
the
piston
in
a
full
floating
fit
and
to
the
connecting
rod
in
press
fit
The
connecting
rod
is
made
of
forged
steeL
Full
pressure
lubrication
is
directed
to
the
connecting
rods
through
drilled
oil
passages
from
the
adjacent
main
bearing
journal
Oil
holes
on
the
connecting
rod
journals
are
designed
so
that
oil
is
supplied
to
give
maximum
lubrication
just
before
full
bearing
load
is
applied
J
oO
o
e
Fig
EM
5
Piston
and
connecting
rod
CYLINDER
HEAD
The
cylinder
head
is
made
of
light
and
strong
aluminum
alloy
with
good
cooling
efficiency
A
special
aluminum
bronze
valve
seat
is
used
on
the
intake
valve
while
a
special
cast
valve
seat
is
installed
on
the
exhaust
valve
These
parts
are
hot
press
fitted
EM
2
Page 343 of 513
ENGINE
MECHANICAL
Fig
EM
6
Cylinder
head
CAMSHAFT
Camshaft
is
made
of
special
cast
iron
and
supported
by
five
cannshaft
bearings
1
1
f
r
f
r
I
Fig
EM
Camshaft
Camshaft
bearings
are
lubricated
from
oil
holes
which
intersect
the
main
oil
gallery
of
the
cylinder
block
Concentric
passages
are
drilled
in
the
front
and
rear
parts
of
the
camshaft
for
supplying
oil
to
each
cam
lobe
through
an
oil
hole
drilled
in
the
base
circle
of
each
lobe
Lubricant
is
supplied
to
the
front
oil
gallery
from
2nd
camshaft
bearing
and
to
the
rear
oil
gallery
from
4th
camshaft
bearing
From
the
center
camshaft
bearing
lubricant
is
supplied
to
the
valve
rocker
shaft
through
the
center
locker
shaft
bracket
VALVE
MECHANISM
The
valve
system
has
push
rod
type
rocker
arm
which
uses
the
single
type
valve
springs
a
Fig
EM
8
Vol
mechanism
CAMSHAFT
DRIVE
The
camshaft
is
driven
with
a
double
row
roller
chain
which
is
driven
by
the
crankshaft
Tension
of
the
chain
is
controlled
by
the
chain
tensioner
which
is
operated
with
spring
and
oil
pressure
The
rubber
shoe
type
tensioner
insulates
vibration
of
the
chain
and
controls
tension
of
the
chain
Fig
EM
9
Comshdft
drive
chain
MANIFOLD
The
intake
manifold
is
a
mono
block
aluminum
cast
The
exhaust
manifold
is
made
of
a
cast
iron
The
semi
dual
exhaust
system
which
combines
exhaust
gas
flow
at
the
point
of
exhaust
pipe
connection
improves
exhausting
efficiency
The
exhaust
manifold
has
a
heat
control
valve
which
assures
stable
and
smooth
engine
running
after
starting
during
cold
season
The
manifold
is
connected
to
the
exhaust
pipe
by
flanges
which
completely
eliminate
exhaust
leaking
EM
3
Page 344 of 513
ENGINE
Fig
EM
IO
Intake
manifold
Fig
EM
12
Intake
and
exhaust
manifolds
Fig
EM
It
Exhaust
manifold
ENGINE
DISASSEMBLY
CONTENTS
CLEANING
AND
INSPECTION
DISASSEMBL
Y
EM
4
EM
5
PISTON
AND
CONNECTING
ROD
CYLINDER
HEAD
EM
7
EM
7
CLEANING
AND
INSPECTION
breakage
rust
damage
and
loss
Clean
the
engine
thoroughly
before
disassembly
Before
cleaning
the
engine
remove
the
electrical
parts
and
plug
up
the
carburetor
air
horn
to
avoid
intrusio
n
of
foreign
matter
2
Cylinder
block
Check
thoroughly
the
water
jacket
for
cracks
and
breakage
3
Clutch
howing
Check
for
cracks
1
The
engine
exterior
Check
the
covers
and
bolts
for
4
Oil
pan
Check
for
excessive
rust
EM
4
Page 345 of 513

ENGINE
MECHANICAL
I
I
J
I
v
Fig
EM
13
Engine
on
engine
stand
DISASSEMBLY
1
Mount
engine
assembly
on
engine
stand
I
Remove
the
engine
mounting
bracket
R
H
2
Install
the
engine
attachment
3
Mount
the
engine
on
the
stand
Engine
stand
ST050
10000
Engine
attachment
ST05270000
2
Remove
the
alternator
and
engine
mounting
bracket
L
H
side
3
Remove
the
crankshaft
pulley
4
Remove
the
oil
pump
together
with
the
oil
ftIter
Fig
EM
14
Oil
pump
removal
5
Remove
the
high
tension
cable
with
the
distributor
cap
on
6
Remove
the
spark
plugs
7
Remove
the
distributor
assembly
8
Remove
the
carburetor
9
Remove
the
rocker
cover
10
Remove
the
thermostat
housing
Fig
EM
15
Thermostat
housing
removal
I
L
Remove
the
manifolds
Fig
EM
16
Manifolds
removal
12
Remove
the
water
pump
EM
5
Page 346 of 513
ENGINE
l
JJ
l
Ii
Fig
EM
t7
Water
pump
r
1
13
Remove
the
fuel
pump
14
Remove
the
rocker
shaft
assembly
and
push
rods
Fig
EM
18
Rocker
shaft
assembly
removal
IS
Remove
the
cylinder
head
assembly
Fig
EM
19
Cylinder
head
bolts
removal
sequence
16
Invert
the
engine
17
Remove
the
oil
pan
and
oil
strainer
Fig
EM
20
Oil
stromer
removal
18
Remove
the
timing
chain
cover
and
the
chain
tensioner
19
Remove
the
crankshaft
and
camshaft
sprockets
together
with
the
timing
chain
Fig
EM
21
Timing
chain
cover
removal
20
Rotate
the
engine
a
quarter
turn
and
remove
the
piston
and
connecting
rod
assembly
Take
off
the
con
necting
rod
bearings
at
the
same
time
and
keep
them
in
order
EM
6
Page 347 of 513
ENGINE
MECHANICAL
Fig
EM
22
Piston
and
conMcting
rod
assembly
removal
21
Rotate
the
engine
a
quarter
turn
and
remove
the
flywheeL
22
Remove
the
main
bearing
cap
and
the
rear
oil
seal
Fig
EM
2J
Rear
oil
seal
removal
23
Remove
the
crankshaft
24
Remove
the
baffie
plate
and
the
crank
case
net
Fig
EM
24
Baffle
plate
and
net
removal
25
Remove
the
camshaft
after
taking
ofT
the
camshaft
plate
Fig
EM
25
Camshaft
plate
removal
26
Remove
the
valve
lifter
PISTON
AND
CONNECTING
ROD
1
Remove
the
piston
rings
with
a
ring
remover
2
Press
out
the
piston
pin
with
a
piston
pin
remover
and
an
arbor
press
Piston
pin
press
oland
STl3040000
ST13040000
EM103
Fig
EM
26
Piston
pin
removal
CYLINDER
HEAD
Remove
the
valves
using
a
valve
lifter
Valve
lifter
STl2070000
EM
Page 348 of 513
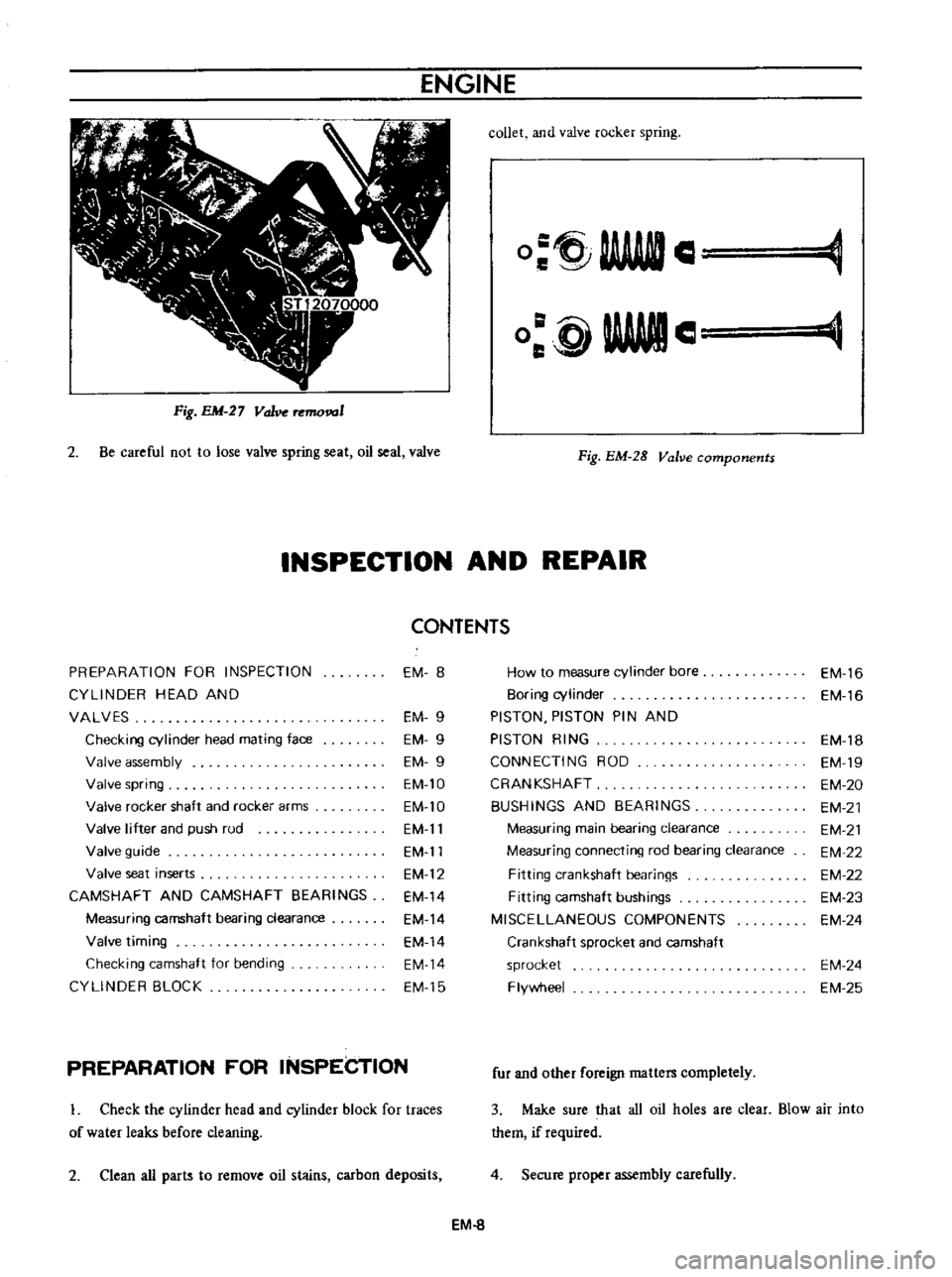
ENGINE
J
I
r
I
I
J
fj
7
L
j
8
if
d1
I
ilfi
3
c
7
I
t
j
v
1
Ji
Fig
EM
27
Valve
mo
1
2
Be
careful
not
to
lose
valve
spring
seat
oil
seal
valve
collet
and
valve
rocker
spring
O
tj
AAAftIl
C
e
WWII
o
glAWle
Fig
EM
28
Valve
components
INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
CONTENTS
PREPARATION
FOR
INSPECTION
EM
8
How
to
measure
cylinder
bore
EM
16
CYLlNOER
HEAD
AND
80ring
cylinder
EM
16
VALVES
EM
9
PISTON
PISTON
PIN
AND
Checking
cylinder
head
mating
face
EM
9
PISTON
RING
EM
18
Valve
assembly
EM
9
CONNECTING
ROD
EM
19
Valve
spring
EM
10
CRANKSHAFT
EM
20
Valve
rocker
shaft
and
rockei
arms
EM
lO
BUSHINGS
AND
BEARINGS
EM
21
Valve
lifter
and
push
rud
EM
11
Measuring
main
bearing
clearance
EM
21
Valve
guide
EM
11
Measuring
connecting
rod
bearing
clearance
EM
22
Valve
seat
inserts
EM
12
Fitting
crankshaft
bearings
EM
22
CAMSHAFT
AND
CAMSHAFT
BEARINGS
EM
14
Fitting
camshaft
bushings
EM
23
Measuring
camshaft
bearing
clearance
EM
14
MISCELLANEOUS
COMPONENTS
EM
24
Valve
timing
EM
14
Crankshaft
sprocket
and
camshaft
Checking
camshaft
for
bending
EM
14
sprocket
EM
24
CYLlNOER
BLOCK
EM
15
Flywheel
EM
25
PREPARATION
FOR
INSPECTION
L
Check
the
cylinder
head
and
cylinder
block
for
traces
of
water
leaks
before
cleaning
2
Clean
all
parts
to
remove
oil
stains
carbon
deposits
fur
and
other
foreign
matters
completely
3
Make
sure
that
all
oil
holes
are
clear
Blow
air
into
them
if
required
4
Secure
proper
assembly
carefully
EM
8
Page 349 of 513
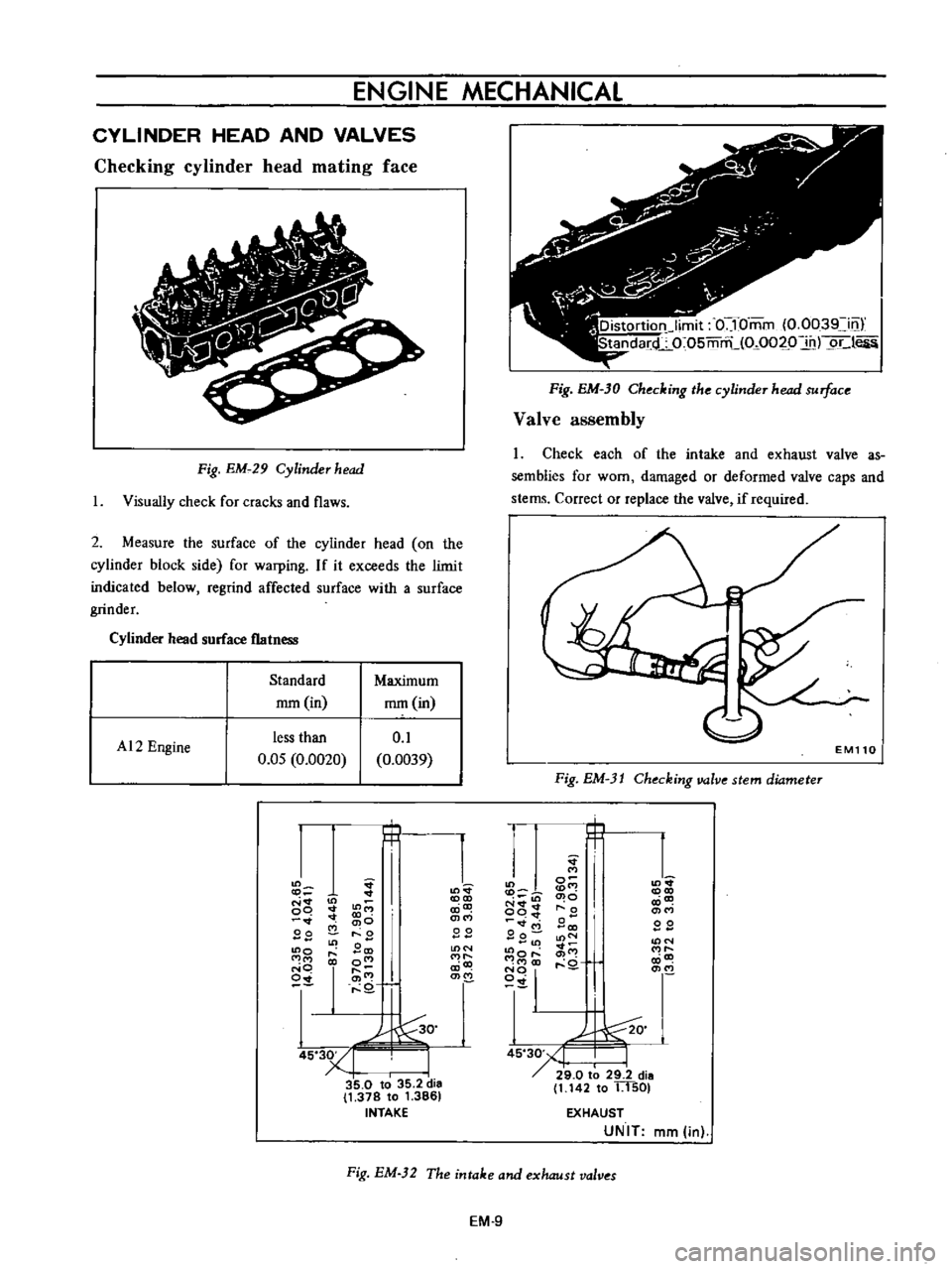
ENGINE
MECHANICAL
CYLINDER
HEAD
AND
VALVES
Checking
cylinder
head
mating
face
Fig
EMc29
Cylinder
head
I
Visually
check
for
cracks
and
flaws
2
Measure
the
surface
of
the
cylinder
head
on
the
cylinder
block
side
for
warping
If
it
exceeds
the
limit
indicated
below
regrind
affected
surface
with
a
surface
grinder
Cylinder
head
surface
flatness
Standard
Maximum
rom
in
mm
in
AI2
Engine
less
than
0
1
O
OS
0
0020
0
0039
t
C
in
00
co
0
00
2
0
Sco
co
0
0
i
Q
coco
a
ilt
BE
mIX
2
00
5
3YI
I
35
0
to
35
2
dia
1
378
to
1
3861
INTAKE
Fig
EM
30
Checking
the
cylinder
head
surface
Valve
a88embly
I
Check
each
of
the
intake
and
exhaust
valve
asc
semblies
for
wom
damaged
or
deformed
valve
caps
and
stems
Correct
or
replace
the
valve
if
required
l
EM110
Fig
EM
31
Chuking
valve
stem
diameter
t
L
coco
CO
co
BE
Ln
oq
q
od
M
2
g
tOo
18co1
O
c
0
DO
o
0
0
co
o
CO
co
J00
45
30
1
I
I
2
9
0
t
29
2
dia
1
142
to
1
l501
EXHAUST
UNIT
mm
in
Fig
EM
32
The
intake
and
exhaust
valves
EM
9
Page 350 of 513
ENGINE
2
The
valve
face
or
valve
stem
end
surface
should
be
refaced
by
using
a
valve
grinder
Notes
a
Deflection
of
seat
surface
against
axis
should
be
0
03
mm
0
0012
in
or
less
b
Correctness
of
right
angle
and
out
of
round
should
be
0
01
mm
0
0004
in
or
I
c
EM111
Fig
EM
33
Valve
grinder
Note
When
the
a1ve
head
has
been
reduced
to
0
5
mm
0
0197
in
or
I
in
thickn
replace
the
al
e
Grinding
allowance
for
the
alve
stem
end
surface
is
0
5
mm
10
0197
in
or
I
Valve
spring
I
Measure
the
free
length
and
the
tension
of
each
spring
If
the
measured
value
exceeds
the
specified
limit
replace
the
spring
Spring
specifications
Free
length
46
5
mm
1
831
in
38
7
rom
at
23
9
kg
1
524
in
at
52
7Ib
Valve
closed
Valve
open
30
2
rom
at
58
5
kg
1
19
in
at
1291b
EM
l0
2
Check
each
spring
for
deformation
with
a
square
Any
springs
with
deflection
of
1
6
mm
0
0630
in
or
more
must
be
replaced
EM113
Fig
EM
34
Valve
spring
test
Valve
rocker
shaft
and
rocker
arm
I
Check
the
valve
rocker
shaft
and
rocker
arm
for
seizure
and
wear
and
repair
or
replace
as
required
Valve
rocker
arm
to
shaft
oil
clearance
0
02
to
0
05
mm
0
0008
to
0
0020
in
2
When
valve
contact
surface
of
the
valve
rocker
arm
is
worn
excessively
in
step
repair
by
means
of
a
valve
grinder
or
replace
Grinding
allowance
for
valve
contact
surface
of
the
valve
rocker
arm
is
0
5
rom
0
0197
in
or
less
t
Fig
EM
3S
val
Tocker
shaft