wheel DATSUN B110 1973 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1973, Model line: B110, Model: DATSUN B110 1973Pages: 513, PDF Size: 28.74 MB
Page 149 of 513
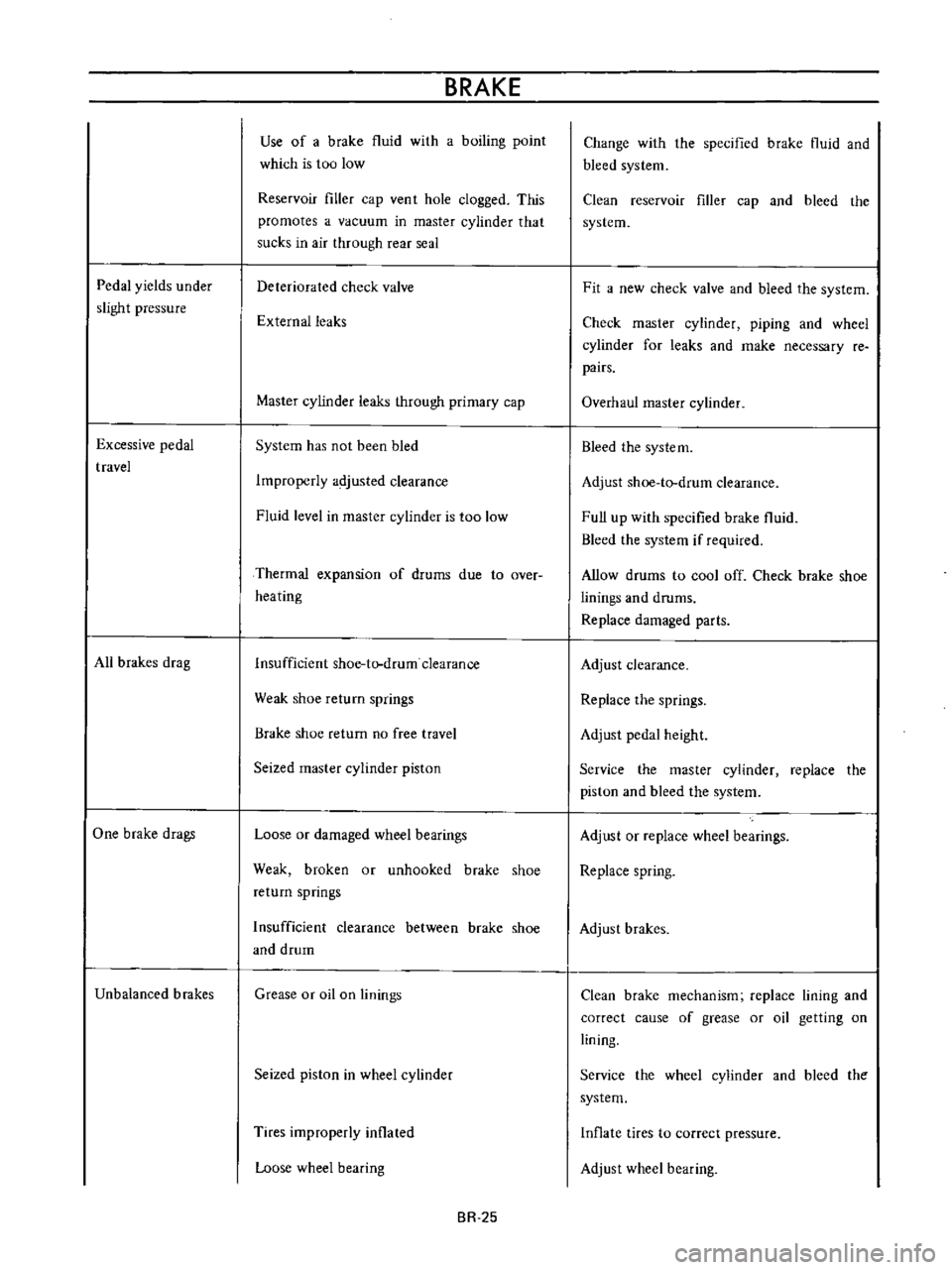
Pedal
yields
under
slight
pressure
Excessive
pedal
travel
All
brakes
drag
One
brake
drags
Unbalanced
brakes
BRAKE
Use
of
a
brake
fluid
with
a
boiling
point
which
is
too
low
Reservoir
filler
cap
ven
t
hole
clogged
This
promotes
a
vacuum
in
master
cylinder
that
sucks
in
air
through
rear
seal
Deteriorated
check
valve
External
leaks
Master
cylinder
leaks
through
primary
cap
System
has
not
been
bled
Improperly
adjusted
clearance
Fluid
level
in
master
cylinder
is
too
low
Thermal
expansion
of
drums
due
to
over
heating
Insufficient
shoe
tlrdrum
clearance
Weak
shoe
return
springs
Brake
shoe
return
no
free
travel
Seized
master
cylinder
piston
Loose
or
damaged
wheel
bearings
Weak
broken
or
unhooked
brake
shoe
return
springs
Insufficient
clearance
between
brake
shoe
and
drum
Grease
or
oil
on
linings
Seized
piston
in
wheel
cylinder
Tires
improperly
inflated
Loose
wheel
bearing
BR
25
Change
with
the
specified
brake
fluid
and
bleed
system
Clean
reservoir
filler
cap
and
bleed
the
system
Fit
a
new
check
valve
and
bleed
the
system
Check
master
cylinder
piping
and
wheel
cylinder
for
leaks
and
make
necessary
re
pairs
Overhaul
master
cylinder
Bleed
the
system
Adjust
shoe
to
drum
clearance
Full
up
with
specified
brake
fluid
Bleed
the
system
if
required
Allow
drums
to
cool
off
Check
brake
shoe
linings
and
drums
Replace
damaged
parts
Adjust
clearance
Replace
the
springs
Adjust
pedal
height
Service
the
master
cylinder
replace
the
piston
and
bleed
the
system
Adjust
or
replace
wheel
bearings
Replace
spring
Adjust
brakes
Clean
brake
mechanism
replace
lining
and
correct
cause
of
grease
or
oil
getting
on
lining
Service
the
wheel
cylinder
and
bleed
the
system
Inflate
tires
to
correct
pressure
Adjust
wheel
bearing
Page 153 of 513

v
h
o
I
7A
0
i
1
V
r
IF
1
If
r
f
A
I
A
Vi
f
f
rVl
I
2
r
Gj
r
a
DATSUN
1200
MODEL
B
11
0
SERIES
l
NISSAN
I
NISSAN
MOTOR
CO
LTD
TOKYO
JAPAN
SECTION
WT
WHEEL
AND
TIRE
WHEEl
AND
TIRE
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
WT
1
WT
5
Page 154 of 513
DESCRIPTION
MAINTENANCE
AND
SERVICE
Tire
inflation
Tubeless
tire
repair
Wheel
repair
Wear
DESCRIPTION
TIRE
SIZE
in
Standard
Optional
WHEEL
AND
TIRE
WHEEL
AND
TIRE
CONTENTS
WTl
WT2
WT2
WT2
WT2
WT2
Radial
tire
Tire
rotation
INSPECTION
Wheel
balance
Wheel
and
tire
6
00
12
4PR
Tubeless
6
00
12
4PR
with
tube
6
00
12
4PR
Snow
tire
6
00S
12
4PR
Sports
Tubeless
155SR
12
Radial
with
tube
except
for
Van
use
5
00
12
4PRULT
with
lube
front
for
Van
use
5
00
12
jPRULT
with
tube
rear
TIRE
INFLATION
PRESSURE
To
be
measured
when
tires
are
cold
kg
cm2
psi
6
00
I
2
4PR
Front
Rear
For
normal
speed
Under
100
km
h
or
60
mph
For
high
speed
Over
100
km
h
or
60
mph
155SR
12
Optional
Front
Rear
5
00
I
2
4
6PR
ULT
Optional
Front
Rear
Sedan
Coupe
1
2
1
2
17
17
1
5
1
5
22
22
1
7
1
7
24
24
Van
Van
Heavy
duty
spring
1
2
1
2
I
7
17
1
5
1
5
22
22
WTl
WT
3
WT
4
WT
4
WT
4
WT
4
Page 155 of 513
CHASSIS
Unloaded
For
normal
speed
U
nder
100
km
h
or
60
mph
F
or
high
speed
Over
100
km
h
or
60
mph
Loaded
For
normal
speed
Under
100
kmlh
or
60
mph
For
high
speed
Over
100
kmlh
or
60
mph
MAINTENANCE
AND
SERVICE
Tire
inflation
Correct
tire
pressure
is
very
importan
t
to
ease
of
steering
and
riding
comfort
This
also
reduces
driving
sound
to
a
minimum
resulting
in
longer
tire
that
is
overinfla
lion
or
underinflation
promotes
wear
at
center
tread
or
shoulder
of
tire
If
all
tires
are
inspected
frequently
and
maintained
correct
tire
pressure
it
is
possible
to
detect
sharp
material
in
the
tread
Also
the
above
check
avoids
abnormal
wear
which
invites
serious
trouble
If
tires
indicate
abnormal
or
uneven
wear
the
cause
of
trouble
should
be
detected
and
eliminated
After
inflating
tices
leakage
in
valve
should
be
check
cd
Without
valve
caps
leakage
will
occur
due
to
dirt
and
water
resulting
in
underinOation
Accordingly
whenever
tire
pressure
is
checked
be
sure
to
secure
valve
caps
and
tighten
firmly
by
hand
Tubeless
tire
repair
In
urder
to
inspect
a
leak
apply
soapy
solution
to
tire
or
submerge
tire
and
wheel
in
the
water
after
inflating
tire
to
specified
pressure
Special
inspection
for
leaks
should
12
15
17
22
1
5
1
8
22
25
1
2
2
5
I
7
36
1
5
2
8
22
40
be
carried
out
around
the
valve
wheel
rim
and
along
the
tread
Exercise
care
to
bead
and
rim
where
leakage
occurs
Wipe
out
water
from
area
which
leaks
air
bubbles
and
then
mark
the
place
with
chalk
After
remuving
the
materials
caused
puncture
seal
the
point
to
avoid
damage
to
the
tire
due
to
entrance
of
dirt
and
water
When
repairing
the
puncture
use
the
tire
repair
kits
which
are
furnished
from
tire
dealers
following
the
instructions
provided
with
the
kits
In
case
that
a
puncture
becomes
large
or
there
is
any
other
damage
on
the
tire
fabric
repair
must
be
carried
out
by
authorized
tire
dealers
Wheel
repair
Inspect
wheel
rim
flange
for
bend
or
dents
If
any
of
the
above
deterioration
is
detected
repair
should
be
made
to
secure
complete
sealing
The
flange
should
be
cleaned
by
a
wire
brush
when
rust
is
found
on
the
flange
Furthermore
if
excessive
pitting
occurs
on
the
rim
eliminate
it
with
a
file
Wear
Misalignment
When
the
front
wheels
align
in
excessive
toe
in
or
WT
2
Page 156 of 513
WHEEL
AND
TIRE
toe
out
condition
tires
scrape
the
tread
rubber
off
The
wear
of
tread
appears
feathered
edge
Center
This
wear
is
caused
by
overinllation
of
the
tire
The
inllation
pressure
must
be
kept
within
the
specified
limit
Shoulder
The
wear
may
be
caused
by
underinflation
incorrect
wheel
camber
or
continuous
high
speed
driving
on
curves
n
general
the
former
two
are
common
Because
under
I
I
I
I
1
1111
I
r
r
m
1
J
11
tHlla
tJ
I
1
1
1
I
1
Ull
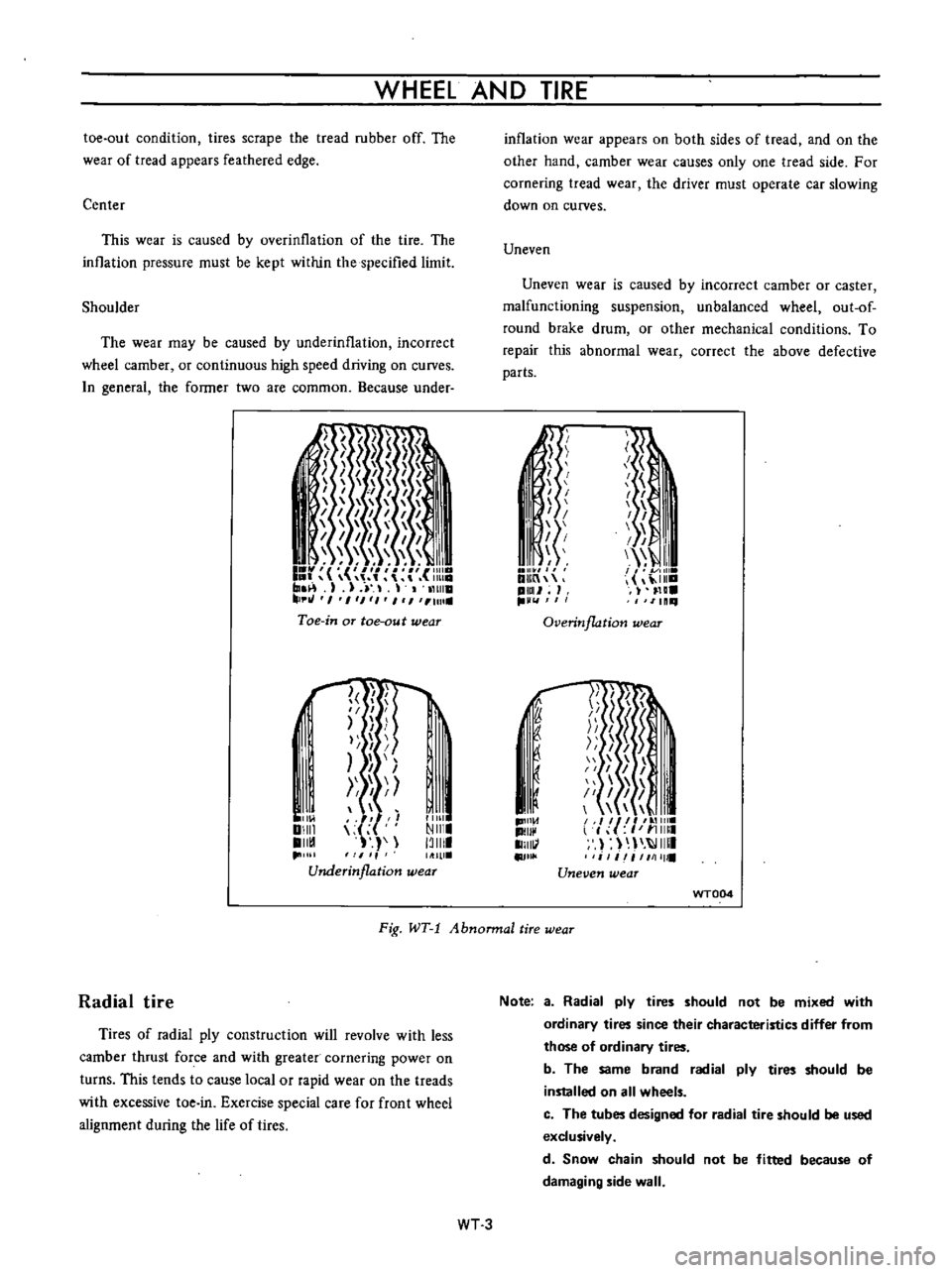
Toe
in
aT
toe
au
t
wear
l
f
I
II
I
I
I
I
Ill
Ill
Underinflation
wear
I
11
01
DIIII
II
1
11111
NIII
13111
inflation
wear
appears
on
both
sides
of
tread
and
on
the
other
hand
camber
wear
causes
only
one
tread
side
For
cornering
tread
wear
the
driver
must
operate
car
slowing
down
on
curves
Uneven
Uneven
wear
is
caused
by
incorrect
camber
or
caster
malfunctioning
suspension
unbalanced
wheel
out
of
round
brake
drum
or
other
mechanical
conditions
To
repair
this
abnormal
wear
correct
the
above
defective
parts
Ii
I
I
I
I
1
i
f
I
I
I
I
I
III
I
I
11
DlIIn
ilia
pml
H
IlLl
11111
Overinflation
wear
1D1I1
d
II
1I111
II
j
J
1
51
I
I
I
1
il
I
I
II
l
f
I
11
11111
I
IIIII
i
1
iI
1111111
Uneven
wear
f
I
I
u
WT004
Fig
WT
1
Abnonnal
tire
wear
Radial
tire
Tires
of
radial
ply
construction
will
revolve
with
less
camber
thrust
force
and
with
greater
cornering
power
on
turns
This
tends
to
cause
local
or
rapid
wear
on
the
treads
with
excessive
toe
in
Exercise
special
care
for
front
wheel
alignment
during
the
life
of
tires
Note
a
Radial
ply
tires
should
not
be
mixed
with
ordinary
tires
since
their
characteristics
differ
from
those
of
ordinary
tires
b
The
same
brand
radial
ply
tires
should
be
installed
on
all
wheels
c
The
tubes
designed
for
radial
tire
should
be
used
exclusively
d
Snow
chain
should
not
be
fitted
because
of
damaging
side
wall
WT3
Page 157 of 513
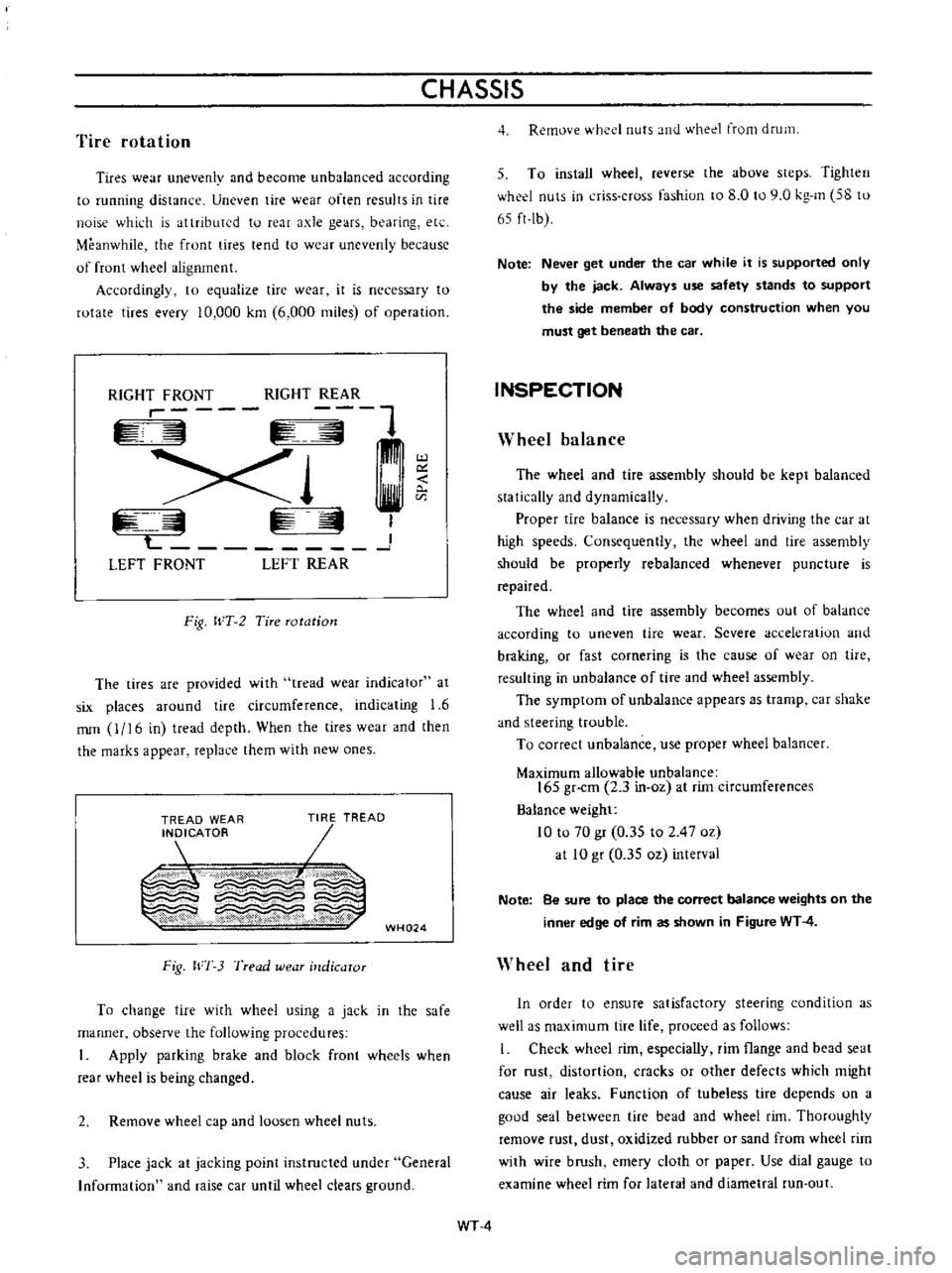
CHASSIS
Tire
rotation
Tires
wear
unevenly
and
become
unbalanced
according
to
running
distance
Uneven
tire
wear
often
results
in
tire
noise
whkh
is
attributed
to
rear
axle
gears
bearing
ell
Meanwhile
the
front
tires
tend
to
wear
unevenly
because
of
front
wheel
alignment
Accordingly
to
equalize
tire
wear
it
is
necessary
to
rotate
tires
every
10
000
km
6
000
miles
of
operation
RIGHT
FRONT
RIGHT
REAR
r
1
Xl
L
J
LEFT
FRONT
LEFT
REAR
Fig
WT
2
Tire
rotation
The
tires
are
provided
with
tread
wear
indicator
at
six
places
around
tire
circumference
indicating
1
6
nun
0
16
in
tread
depth
When
the
tires
wear
and
then
the
marks
a
ppear
replace
them
with
new
ones
TREAD
WEAR
INDICATOR
7
TREAD
m
Y
X
W
X
v
w
WH024
Fig
WI
3
Tread
wear
illdicator
To
change
tire
with
wheel
using
a
jack
in
the
safe
manner
observe
the
following
procedures
I
Apply
parking
brake
and
block
front
wheels
when
rear
wheel
is
being
changed
2
Remove
wheel
cap
and
loosen
wheel
nuts
3
Place
jack
at
jacking
point
instructed
under
General
Information
and
raise
car
until
wheel
clears
ground
4
Remove
wheel
nuts
and
whed
from
drum
5
To
install
wheel
reverse
the
above
steps
Tighten
whed
nuts
in
criss
cross
fashion
to
8
0
to
9
0
kg
m
58
to
65
ft
lb
Note
Never
get
under
the
car
while
it
is
supported
only
by
the
jack
Always
use
safety
stands
to
support
the
side
member
of
body
construction
when
you
must
get
beneath
the
car
INSPECTION
Wheel
balance
The
wheel
and
tire
assembly
should
be
kept
balanced
statically
and
dynamically
Proper
tire
balance
is
necessary
when
driving
the
car
at
high
speeds
Consequently
the
wheel
and
tire
assembly
should
be
properly
rebalanced
whenever
puncture
is
repaired
The
wheel
and
tire
assembly
becomes
out
of
balance
according
to
uneven
tire
wear
Severe
acceleration
and
braking
or
fast
cornering
is
the
cause
of
wear
on
tire
resulting
in
unbalance
of
tire
and
wheel
assembly
The
symptom
of
unbalance
appears
as
tramp
car
shake
and
steering
trouble
To
correct
unbalance
use
proper
wheel
balancer
Maximum
allowable
unbalance
165
gr
cm
2
3
in
ol
at
rim
circumferences
Balance
weight
10
to
70
gr
0
35
to
2
47
Ol
at
10
gr
0
35
Ol
interval
Note
Be
sure
to
place
the
correct
balance
weights
on
the
inner
edge
of
rim
as
shown
in
Figure
WT
4
Wheel
and
tire
In
order
to
ensure
satisfactory
steering
condition
as
well
as
maximum
tire
life
proceed
as
follows
I
Check
wheel
rim
especially
rim
flange
and
bead
seat
for
rust
distortion
cracks
or
other
defects
which
might
cause
air
leaks
Function
of
tubeless
tire
depends
on
a
good
seal
between
tire
bead
and
wheel
rim
Thoroughly
remove
rust
dust
oxidized
rubber
or
sand
from
wheel
rim
with
wire
brush
emery
cloth
or
paper
Use
dial
gauge
to
examine
wheel
rim
for
lateral
and
diametral
run
out
WT
4
Page 158 of 513
WHEEL
AND
TIRE
Note
In
replacing
tire
take
extra
care
not
to
damage
tire
bead
rim
flange
and
bead
seat
Do
not
use
tire
irons
to
force
beads
away
from
wheel
rim
flange
that
is
always
use
tire
replace
ment
device
whenever
tire
is
removed
WT005
2
Discard
when
any
of
the
following
trouble
occurs
I
Broken
or
damaged
bead
wire
2
Ply
or
tread
separation
3
Worn
febric
damage
on
tubeless
tire
4
Cracked
or
damaged
side
wall
etc
Fig
WT
4
Wheel
rim
run
out
heck
points
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
Condition
Probable
cause
Corrective
action
Wheel
wobbles
Improper
t
re
pressure
Measure
and
adjust
correctly
Damaged
tire
9f
distorted
wheel
rim
Repair
or
replace
UnbalanceiLwheel
Balance
correctly
Loose
wheel
nuts
Retighten
Worn
qr
damaged
wheel
bearing
or
excessive
play
of
wheel
bearing
Correct
play
or
replace
Improper
front
wheel
alignment
Adjust
Worn
or
damaged
ball
joint
and
link
bushing
Replace
Excessive
steering
linkage
play
or
worn
steering
lin
age
Adjust
or
replace
Loose
stcerin
linkage
connection
Retighten
the
nuts
with
the
rated
lightening
torque
or
replace
worn
parts
if
any
Broken
suspension
spring
Replace
Defective
shock
absorber
Replace
Unevenly
or
excessively
worn
tire
Improper
tire
rotation
Conduct
tire
rotation
periodically
Standard
every
10
000
km
6
000
miies
Improper
tire
pressure
Measure
and
adjust
correctly
Unbalanced
wheel
Balance
or
replace
Improperly
adjusled
brake
Readjust
correctly
WT5
Page 159 of 513
Tire
squeals
DATE
CHASSIS
Improper
wheel
alignment
Excessively
distorted
or
improperly
installed
suspension
link
High
speed
on
curves
Sudden
start
and
improper
speeding
due
to
rapid
acceleration
or
improper
brake
appli
cation
Improper
tire
pressure
Improper
front
wheel
alignment
Distorted
knuckle
or
suspension
link
Realign
Repair
correctly
or
replace
if
necessary
or
reinstall
correctly
Reduce
speed
Follow
correct
and
proper
driving
manner
Measure
and
adjust
correctly
Realign
correctly
Repair
or
replace
if
necessary
SERVICE
JOURNAL
OR
BULLETIN
REFERENCE
JOURNAL
or
BULLETIN
No
PAGE
No
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
WT
6
SUBJECT
Page 161 of 513
STEERING
DESCRIPTION
The
steering
system
consists
of
recirculating
ball
type
gear
box
and
parallelogram
linkage
These
systems
give
good
response
light
handling
and
utmost
durability
Moreover
the
steering
linkage
is
equipped
with
a
torsion
rubber
system
idler
arm
which
absorbs
shock
from
the
wheel
Check
the
lubricant
of
gear
box
every
10
000
km
6
000
miles
and
replenish
recommended
oil
as
required
The
steering
linkage
should
be
greased
up
with
wheel
bearing
grease
every
50
000
km
30
000
miles
All
necessary
service
procedures
for
the
steering
lock
system
are
described
in
the
BODY
ELECTRICAL
SECTION
of
this
manual
and
therefore
no
instruction
is
given
here
STEERING
CONTENTS
REMOVAL
DISASSEMBL
Y
Ball
nut
assembly
ST
2
ST
3
ST
4
INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
ASSEMBL
Y
AND
ADJUSTMENT
INSTALLATION
ST
4
ST
5
ST
7
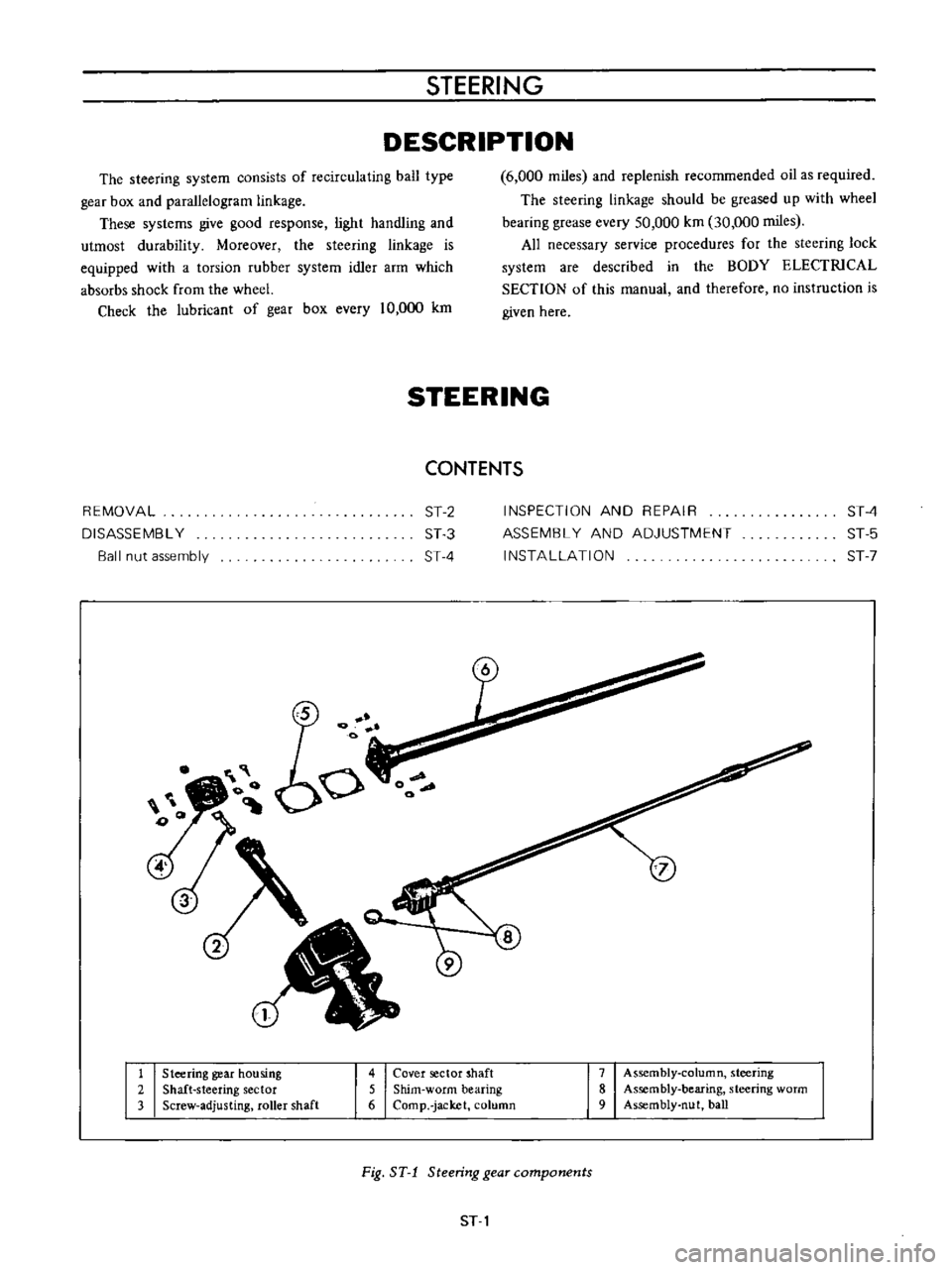
1
Steering
gear
housing
2
Shaft
steering
sector
3
Screw
adjusting
roller
shaft
4
Cover
sector
shaft
5
Shim
worm
bearing
6
Comp
jacket
column
7
Assembly
column
steering
8
Assembly
bearing
steering
worm
9
Assembly
nut
ball
Fig
ST
1
Steering
gear
components
ST
1
Page 162 of 513

Iii
I
o
t
I
I
CHASSIS
Fig
ST
2
Steering
wheel
REMOVAL
1
Remove
the
horn
ring
and
remove
the
steering
wheel
nut
and
pull
out
the
steering
wheel
by
the
use
of
a
Steer
ing
wheel
puller
ST27180000
3
Remove
the
turn
signal
and
lighting
switch
com
pletely
4
Remove
the
hand
lever
assembly
from
the
control
rod
assembly
by
unscrewing
the
fIxing
bolts
5
Remove
two
fIxing
bolts
used
to
secure
the
steering
column
to
the
instrument
panel
ST27180000
Fig
ST
3
Removing
steering
wheel
lock
nut
Note
The
horn
ring
can
be
easily
removed
by
two
bolts
2
Remove
the
steering
column
shell
Fig
ST
4
Removing
steering
column
upper
side
ST
2