engine DODGE NEON 1999 Service Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 301 of 1200

CHECKING FOR DIAGNOSTIC CODES
When trying to verify a speed control system elec-
tronic malfunction: Connect a DRB scan tool if avail-
able to the data link connector. The connector is
located at left side of the steering column, and at
lower edge of the panel.
(1) A speed control malfunction may occur without
a diagnostic code being indicated.
Refer to Group 25, for further information and use-
age of the DRB scan tool and a more complete list of
Diagnostic Trouble Code.
SPEED CONTROL SLOWS DOWN BY ITSELF
Test vehicle speed sensor, refer to group 8E. If sen-
sor fails replace sensor, if it passes perform the fol-
lowing test:
(1) Perform the speed control switch test on the
DECEL switch, if it fails replace switch.
(2) If the switch passes, conduct the vacuum sup-
ply test.
(3) If it passes, conduct the servo vacuum test. If it
fails replace servo.
(4) If continuity, replace the PCM.
SPEED CONTROL ELECTRICAL TEST
Electronic speed control systems may be tested
using two different methods. One involves use of aDRB. If this test method is desired, refer to the Pow-
ertrain Diagnostic Test Procedures for charging and
speed control system manual.
The other test method uses a volt/ohm meter. The
volt/ohm meter method is described in the following
tests.
If any information is needed concerning wiring,
refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams (Fig. 4).
CAUTION: When test probing for voltage or conti-
nuity at electrical connectors, care must be taken
not to damage connector, terminals, or seals. If
these components are damaged, intermittent or
complete system failure may occur.
When electrical connections are removed, corrosion
should be removed from electrical terminals and a
light coating of Mopar Multi-Purpose Grease, or
equivalent, applied. Inspect connectors for damage
terminals.
A poor connection can cause a complete or inter-
mittent malfunction and is also the only connection
in the circuit, that can not be tested. For this reason,
a loose connection may be misdiagnosed as a compo-
nent malfunction.
SPEED CONTROL DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
Hex Code DRB Scan Tool Display Description of Diagnostic Trouble Code
23No Vehicle Speed Sensor
SignalNo vehicle distance (speed) sensor signal detected during
road load conditions.
OFSpeed Control Solenoid
CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the Speed Control
vacuum or vent solenoid circuits.
56MUX S/C Switch High Speed Control switch input above the maximum acceptable
voltage.
57MUX S/C Switch Low Speed Control switch input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
52S/C Power Relay Or 12V
Driver CircuitMalfunction detected with power feed to speed control servo
solnoids.
Check Engine Lamp will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
8H - 4 VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEMPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 303 of 1200

OVERSHOOT/UNDERSHOOT FOLLOWING SPEED
CONTROL SET
If the operator repeatedly presses and releases the
set button with their foot off of the accelerator (a ªlift
foot setº to begin speed control operation), the vehicle
may accelerate and exceed the desired set speed by
up to 5 MPH (8 km/h) and then decelerate to less
than the desired set speed before finally achieving
the desired set speed.
The Speed Control has an adaptive strategy that
compensates for vehicle-to-vehicle variations in speed
control cable lengths. When the speed control is set
with the vehicle operators foot off of the accelerator
pedal, the speed control thinks there is excessive
speed control cable slack and adapts. If the lift foot
sets are continually used, the speed control over-
shoot/undershoot condition will develop.
To ªunlearnº the overshoot/undershoot condition,
the vehicle operator has to press and release the set
button while maintaining the desired set speed with
the accelerator pedal (not decelerating or accelerat-
ing), and then turn the cruise control switch to the
OFF position (or press the CANCEL button if
equipped) after waiting 10 seconds. This procedure
must be performed approximately 10±15 times to
completely unlearn the overshoot/undershoot condi-
tion.
SERVO VACUUM TEST
(1) Turn ignition switch to the ON position with-
out starting engine. Activate speed control ON
switch.
(2) Disconnect the four-way electrical connector
and the vacuum harness at the servo (Fig. 5).
(3) Connect a jumper wire from Pin 3 of the servo
to Pin 3 of the wire connector.
(4) Ground Pins 2 and 4 in the servo. Do not con-
nect pin 1.
(5) Connect a hand held vacuum pump to the vac-
uum nipple and apply 10 - 15 inches of vacuum.
(6) If servo pulls cable, replace servo.
(7) Ground Pin 1 on servo.
(8) Check that the throttle cable pulls in and holds
as long as the vacuum pump is connected. After one
minute, check if cable is still holding. If cable does
not hold replace the servo.
(9) Disconnect jumper from pin 3. Cable should
return to rest position. If not, replace servo.
(10) Connect 4 way electrical connector and vac-
uum harness to servo.
SPEED CONTROL SWITCH TEST
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic
Manual for switch test valves.
STOP LAMP SWITCH TEST
(1) Remove the stop lamp switch refer to Stop
Switch Removal/Installation in this section. Discon-
nect connector from stop lamp switch (Fig. 6). Using
an ohmmeter, switch continuity may be checked as
follows:
(2) With switch plunger released, there should be
continuity between Pin 5 and Pin 6.
(3) With switch plunger depressed, there should be
continuity:
²Between Pin 1 and Pin 2.
²Between Pin 3 and Pin 4.
(4) If the above results are not obtained, the stop
lamp switch is defective or out of adjustment.
Fig. 5 Servo Harness Connector
Fig. 6 Stop Lamp Wiring
8H - 6 VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEMPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 305 of 1200

(c) If continuity is OK between cavity 62 and
cavity 1, repair open circuit between cavity 2 of the
stop lamp switch connector and ground.
(6) Using an ohmmeter, check continuity from cav-
ity 76 on PCM connector to ground with the trans-
mission in park or neutral. If no continuity, test TRS/
Park-Neutral switch and switch wiring
(7) Turn speed control and ignition switch OFF.
(8) Unplug the BLACK 40-way connector from the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
(9) Using an ohmmeter, check continuity from cav-
ity 3 of servo connector to cavity 5 on the PCM con-
nector.
(a) If continuity is OK, replace PCM. Check cir-
cuit for short to ground before replacing PCM.
(b) If no continuity, remove stop lamp switch
and conduct Stop Lamp Switch Test. If test fails,
adjust or replace as necessary.
(c) If switch passes, measure continuity from
cavity 4 of stop lamp switch connector to cavity 3
of servo connector. Repair open circuit if necessary.
(d) If continuity is OK, measure continuity from
cavity 3 of stop lamp switch to cavity 5 of PCM
connector. Repair open circuit as necessary.
(e) Install PCM connectors onto PCM and speed
control servo connector to servo.
VACUUM SUPPLY TEST
(1) Disconnect vacuum hose at the servo and
install a vacuum gauge in the hose (Fig. 9).
(2) Start engine and observe gauge at idle. Vac-
uum gauge should read at least ten inches of mer-
cury. Shut off engine, the vacuum should continue to
hold 10 inches of mercury.
(3) If vacuum does not meet this requirement,
check and correct the following vacuum leaks in the
vacuum lines, check valve, vacuum reservoir or poor
engine performance.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
For diagnosis and testing of the Vehicle Speed Sen-
sor (VSS), refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diag-
nostic Procedures service manual. Also refer to the
DRB scan tool.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SPEED CONTROL SERVO
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from servo.
(2) Disconnect vacuum hoses from servo
(3) Remove 2 nuts retaining cable to servo.
(4) Remove hair pin holding cable to servo.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install hairpin to cable at servo.
(2) Install 2 nuts at cable to servo and servo
bracket, tighten to 7 N´m (60 ins. lbs.).
(3) Connect electrical connector to servo.
(4) Connect vacuum hose to servo
SPEED CONTROL SWITCH
The speed control switches are mounted in the
steering wheel and wired through the clock spring
device under the airbag module (Fig. 1).
WARNING: IF REMOVAL OF AIRBAG MODULE IS
NECESSARY, REFER TO GROUP 8M, RESTRAINT
SYSTEMS.
REMOVAL
(1) Turn off ignition.
(2) Remove two screws from side of each switch.
(3) Rock switch away from airbag and steering
wheel.
(4) Disconnect two-way electrical connector.
(5) Repeat for the other switch.
INSTALLATION
For installation reverse above procedures.
STOP LAMP SWITCH
REMOVAL
Remove the switch from the bracket by depressing
the brake pedal and rotating the switch in a counter-
clockwise direction approximately 30 degrees. Pull
the switch rearward and remove from bracket. Dis-
connect wiring harness connector.
INSTALLATION
Before installing the switch, reset the adjustable
switch plunger by pulling on the plunger head until
Fig. 9 Vacuum Gauge TestÐTypical
8H - 8 VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEMPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 331 of 1200
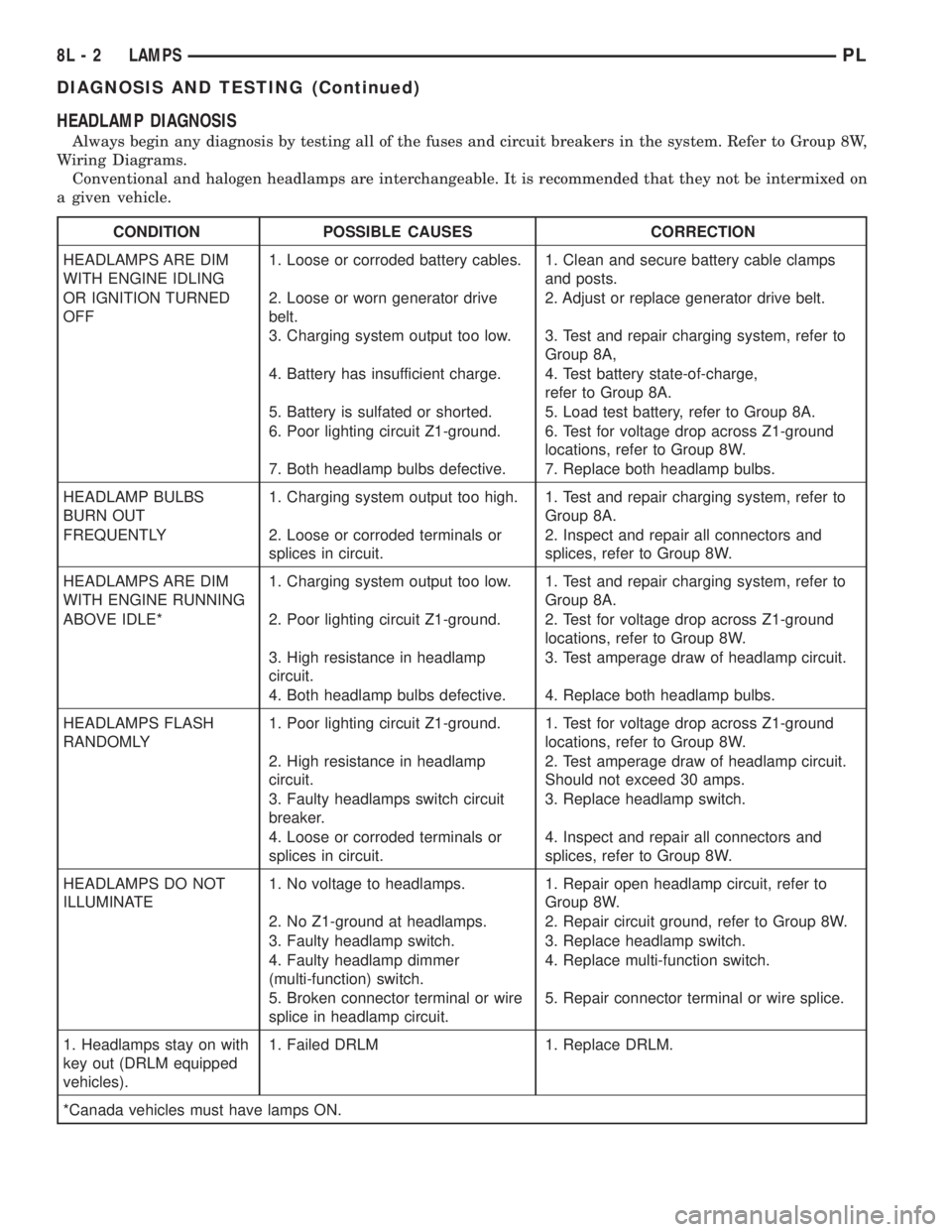
HEADLAMP DIAGNOSIS
Always begin any diagnosis by testing all of the fuses and circuit breakers in the system. Refer to Group 8W,
Wiring Diagrams.
Conventional and halogen headlamps are interchangeable. It is recommended that they not be intermixed on
a given vehicle.
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
HEADLAMPS ARE DIM
WITH ENGINE IDLING1. Loose or corroded battery cables. 1. Clean and secure battery cable clamps
and posts.
OR IGNITION TURNED
OFF2. Loose or worn generator drive
belt.2. Adjust or replace generator drive belt.
3. Charging system output too low. 3. Test and repair charging system, refer to
Group 8A,
4. Battery has insufficient charge. 4. Test battery state-of-charge,
refer to Group 8A.
5. Battery is sulfated or shorted. 5. Load test battery, refer to Group 8A.
6. Poor lighting circuit Z1-ground. 6. Test for voltage drop across Z1-ground
locations, refer to Group 8W.
7. Both headlamp bulbs defective. 7. Replace both headlamp bulbs.
HEADLAMP BULBS
BURN OUT1. Charging system output too high. 1. Test and repair charging system, refer to
Group 8A.
FREQUENTLY 2. Loose or corroded terminals or
splices in circuit.2. Inspect and repair all connectors and
splices, refer to Group 8W.
HEADLAMPS ARE DIM
WITH ENGINE RUNNING1. Charging system output too low. 1. Test and repair charging system, refer to
Group 8A.
ABOVE IDLE* 2. Poor lighting circuit Z1-ground. 2. Test for voltage drop across Z1-ground
locations, refer to Group 8W.
3. High resistance in headlamp
circuit.3. Test amperage draw of headlamp circuit.
4. Both headlamp bulbs defective. 4. Replace both headlamp bulbs.
HEADLAMPS FLASH
RANDOMLY1. Poor lighting circuit Z1-ground. 1. Test for voltage drop across Z1-ground
locations, refer to Group 8W.
2. High resistance in headlamp
circuit.2. Test amperage draw of headlamp circuit.
Should not exceed 30 amps.
3. Faulty headlamps switch circuit
breaker.3. Replace headlamp switch.
4. Loose or corroded terminals or
splices in circuit.4. Inspect and repair all connectors and
splices, refer to Group 8W.
HEADLAMPS DO NOT
ILLUMINATE1. No voltage to headlamps. 1. Repair open headlamp circuit, refer to
Group 8W.
2. No Z1-ground at headlamps. 2. Repair circuit ground, refer to Group 8W.
3. Faulty headlamp switch. 3. Replace headlamp switch.
4. Faulty headlamp dimmer
(multi-function) switch.4. Replace multi-function switch.
5. Broken connector terminal or wire
splice in headlamp circuit.5. Repair connector terminal or wire splice.
1. Headlamps stay on with
key out (DRLM equipped
vehicles).1. Failed DRLM 1. Replace DRLM.
*Canada vehicles must have lamps ON.
8L - 2 LAMPSPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 332 of 1200

FOG LAMP
FOG LAMP DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
FOG LAMPS ARE DIM WITH
ENGINE IDLING OR IGNITION
TURNED OFF.1. Loose or corroded battery cables. 1. Clean and secure battery cable
clamps and posts.
2. Loose or worn generator drive
belt.2. Adjust or replace generator drive
belt.
3. Charging system output too low. 3. Test and repair charging system.
Refer to Group 8A,
4. Battery has insufficient charge. 4. Test battery state-of -charge.
Refer to Group 8A.
5. Battery is sulfated or shorted. 5. Load test battery. Refer to Group
8A.
6. Poor lighting circuit Z1-ground. 6. Test for voltage drop across
Z1-ground locations. Refer to Group
8W.
FOG LAMP BULBS BURN OUT
FREQUENTLY1. Charging system output too high. 1. Test and repair charging system.
Refer to Group 8A.
2. Loose or corroded terminals or
splices in circuit.2. Inspect and repair all connectors
and splices. Refer to Group 8W.
FOG LAMPS ARE DIM WITH
ENGINE RUNNING ABOVE IDLE1. Charging system output too low. 1. Test and repair charging system.
Refer to Group 8A.
2. Poor lighting circuit Z1-ground. 2. Test for voltage drop across
Z1-ground locations. Refer to Group
8W.
3. High resistance in fog lamp
circuit.3. Test amperage draw of fog lamp
circuit.
FOG LAMPS FLASH RANDOMLY 1. Poor lighting circuit Z1-ground. 1. Test for voltage drop across
Z1-ground locations. Refer to Group
8W.
2. High resistance in fog lamp
circuit.2. Test amperage draw of fog lamp
circuit.
3. Faulty fog lamp switch. 3. Replace fog lamp switch.
4. Loose or corroded terminals or
splices in circuit.4. Inspect and repair all connectors
and splices. Refer to Group 8W.
FOG LAMPS DO NOT
ILLUMINATE1. Blown fuse for fog lamp. 1. Replace fuse. Refer to Group 8W.
2. No Z1-ground at fog lamps. 2. Repair circuit ground. Refer to
Group 8W.
3. Faulty fog lamp switch. 3. Replace fog lamp switch.
4. Broken connector terminal or wire
splice in fog lamp circuit.4. Repair connector terminal or wire
splice.
5. Defective or burned out bulb. 5. Replace bulb.
PLLAMPS 8L - 3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 351 of 1200
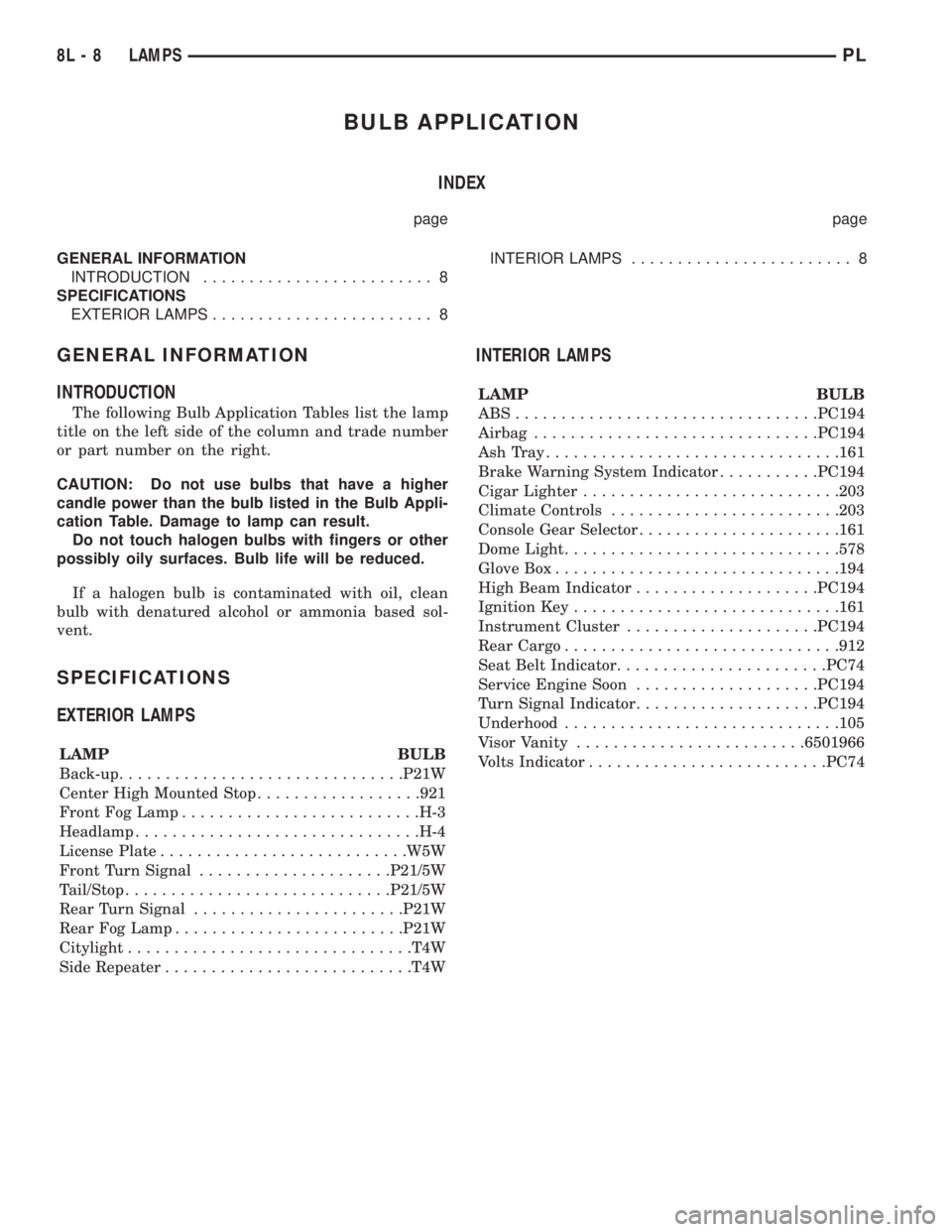
BULB APPLICATION
INDEX
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION......................... 8
SPECIFICATIONS
EXTERIOR LAMPS........................ 8INTERIOR LAMPS........................ 8
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
The following Bulb Application Tables list the lamp
title on the left side of the column and trade number
or part number on the right.
CAUTION: Do not use bulbs that have a higher
candle power than the bulb listed in the Bulb Appli-
cation Table. Damage to lamp can result.
Do not touch halogen bulbs with fingers or other
possibly oily surfaces. Bulb life will be reduced.
If a halogen bulb is contaminated with oil, clean
bulb with denatured alcohol or ammonia based sol-
vent.
SPECIFICATIONS
EXTERIOR LAMPS
LAMP BULB
Back-up...............................P21W
Center High Mounted Stop..................921
Front Fog Lamp..........................H-3
Headlamp...............................H-4
License Plate...........................W5W
Front Turn Signal.....................P21/5W
Tail/Stop.............................P21/5W
Rear Turn Signal.......................P21W
Rear Fog Lamp.........................P21W
Citylight...............................T4W
Side Repeater...........................T4W
INTERIOR LAMPS
LAMP BULB
ABS.................................PC194
Airbag...............................PC194
AshTray................................161
Brake Warning System Indicator...........PC194
Cigar Lighter............................203
Climate Controls.........................203
Console Gear Selector......................161
Dome Light..............................578
Glove Box...............................194
High Beam Indicator....................PC194
Ignition Key.............................161
Instrument Cluster.....................PC194
Rear Cargo..............................912
Seat Belt Indicator.......................PC74
Service Engine Soon....................PC194
Turn Signal Indicator....................PC194
Underhood..............................105
Visor Vanity.........................6501966
Volts Indicator..........................PC74
8L - 8 LAMPSPL
Page 374 of 1200

parking lamps out put. Press the panic button and
check for a voltage pulse (Fig. 2).
(2) If no voltage pulse is measured, replace the
receiver. If voltage OK, repair circuit to the parking
lamps as necessary.
(3) Connect the meter to Pin 5 of the black connec-
tor and to ground to test head lamps out put. Press
the panic button and check for a voltage pulse (Fig.
2).
(4) If no voltage pulse is measured, replace the
receiver. If voltage OK, repair circuit to the head
lamps as necessary.
REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY SYSTEM
When trouble shooting problems with the Remote
Keyless Entry System, always verify that the power
door lock/unlock switches are functional. If the doors
do not lock/unlock refer to Group 8W, Wiring Dia-
gram for Pin and wiring locations.
If the following items do not work:
²Remote keyless entry system
²Radio/clock
²Door lock switches
A blown fuse is the probable cause. Check fuses 2,
3 and 11 in the fuse block. To check for a blown fuse,
pull the fuse out slightly, but maintain contact
between the fuse terminals and the terminals in fuse
block. Using the voltmeter probe, check both termi-
nals for 12 volts. If only one terminal measures bat-
tery voltage, the circuit breaker is defective and must
be replaced. If neither terminal measures battery
voltage, check the high current fuses 3 and 11 in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). The PDC is located
in the engine compartment. If fuse(s) are NOT OK,
replace fuse(s) or repair as necessary. If fuses are
OK, check for an open or shorted circuit to the Power
Distribution Center, repair as needed.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
HORN CHIRP CANCELLATION
During the programming operation the horn chirp
can be disabled or enable using the following proce-
dure. One or both transmitters can be program to be
disabled or enable.
(1) Retrieve the programming line from the upper
edge of the passenger side cowl trim panel upper
edge. The RKE Programming Line is a green wire
with a red bullet connector.
(2) Using a jumper wire, ground the RKE pro-
gramming line.
(3) Turn ignition switch to the ON position.
(4) Press any button on the transmitter. The locks
will cycle to confirm programming,
(5) To disable or enable horn chirp press the lock
button on the transmitter four times and the hornwill sound to confirm programming. Press the lock
button on the second transmitter four times and the
horn will sound to confirm programming.
(6) Disconnect the programming line from ground.
This returns the system to its normal operation
mode.
(7) Replace any removed components. Return pro-
gramming line chirpto its original position. Check for
system operation.
PANIC FUNCTION CANCELLATION
During the programming operation the panic func-
tion can be disabled or enable using the following
procedure. One or both transmitters can be program
to be disabled or enable.
(1) Retrieve the programming line from the upper
edge of the passenger side cowl trim panel. The RKE
Program Line is a green wire with a red bullet con-
nector.
(2) Using a jumper wire, ground the RKE Pro-
gramming Line.
(3) Turn ignition switch to the ON position.
(4) Press any button on the transmitter. The locks
will cycle to confirm programming,
(5) To disable or enable panic function press the
panic button on the transmitter four times and the
horn will sound to confirm programming. Press the
panic button on the second transmitter four times
and the horn will sound to confirm programming.
(6) Disconnect the programming line from ground.
This returns the system to its normal operation
mode.
(7) Replace any removed components. Return the
programming line to its original position. Check for
system operation.
PROGRAM REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY MODULE
(1) Retrieve the programming line from the upper
edge of the passenger side cowl trim panel. The RKE
Programming Line is a green wire with a red bullet
connector.
(2) Using a jumper wire, ground the RKE pro-
gramming line.
(3) Turn ignition switch to the ON position.
(4) Press any button on the transmitter to set
code. The locks will cycle to confirm programming. If
there is a second transmitter it must be set at this
time. Press any button on the second transmitter and
wait for the locks to cycle to confirm programming.
(5) Disconnect the programming line from ground.
This returns the system to its normal operation
mode.
(6) Replace all removed components. Return pro-
gramming line to its original position. Check for sys-
tem operation.
PLPOWER DOOR LOCKS 8P - 5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 376 of 1200

IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM
CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
IMMOBILIZER RECEIVER................ 1
IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM.................. 1
IMMOBILIZER TRANSMITTER............. 2
POWER-UP MODE...................... 2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
IMMOBILIZER DIAGNOSIS............... 2SERVICE PROCEDURES
VEHICLE IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM.......... 3
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
IMMOBILIZER RECEIVER................ 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM
The Immobilizer system includes the following
unique items:
²An immobilizer module receiver that controls
system operation and also controls the RKE and Illu-
minated entry systems, if equipped.
²An encoded Crankshaft Position Sensor for the
ignition system. The Immobilizer module decodes the
signal from the crankshaft so the PCM can recognize
it as a valid Crankshaft Position Sensor signal, and
allow the engine to run.
²A wiring harness that interconnects the crank-
shaft sensor, the immobilizer receiver, and the PCM.
²Two key fob transmitters.
The Immobilizer System prevents unauthorized
operation of the vehicle by disabling the engine and
starter. The system will NOT allow the vehicle to
start unless the UNLOCK button on the RKE trans-
mitter is pressed. The system will be activated after
turning the ignition switch to the OFF position and
using one of the following methods.
(1) Press the LOCK button on the RKE transmit-
ter.
(2) LOCK the doors by pressing a power lock but-
ton switch.
(3) LOCK the driver or passenger door using the
key.
²The Security light will flash, for about 16 sec-
onds, indicating that the engine and starter will be
disabled.
²The Security light remaining on, indicates the
system is not operational.
²The Immobilizer will activate automatically
within 10 minutes of the ignition switch being in the
OFF position, whether the vehicle has been locked or
unlocked.²An attempt to start the vehicle without pressing
the UNLOCK button on the RKE transmitter will
result in a warning chime and the Security light
flashing.
NOTE: The ignition switch must be in the OFF posi-
tion in order for the system to be activated, whether
the doors are closed or not.
IMMOBILIZER RECEIVER
The immobilizer receiver is programmed to
respond to the Lock and Unlock radio signals issued
by the immobilizer transmitters. The receiver will
only respond to the radio signals of transmitters (up
to four) whose vehicle access codes have been stored
in the receiver's electronic memory. The receiver is
programmed at the assembly plant with the vehicle
access codes of the two transmitters that are shipped
with the vehicle.
The immobilizer receiver also has a central pro-
cessing unit, which contains the immobilizer system
logic. The programming in the immobilizer receiver
allows the system to learn and retain transmitter
vehicle access codes, as well as to communicate with
the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) and/or the
DRB scan tool on the Chrysler Collision Detection
(CCD) data bus network.
The CCD data bus network allows the sharing of
sensor information. This helps to reduce wiring har-
ness complexity, reduce internal controller hardware,
and reduce component sensor current loads. At the
same time, the CCD data bus network provides
increased reliability and enhanced diagnostic capabil-
ities.
Each immobilizer transmitter has a different vehi-
cle access code, which must be programmed into the
memory of the immobilizer receiver in the vehicle in
order to operate the immobilizer system. A DRB scan
tool must be used to program new or additional
PLIMMOBILIZER SYSTEM 8Q - 1
Page 377 of 1200

transmitter vehicle access codes into the memory of
the immobilizer receiver. Refer to the Vehicle Theft
Security System menu item on the DRB scan tool for
the procedures.
The immobilizer receiver recognizes the Lock and
Unlock signals received from the programmed immo-
bilizer transmitters. If the code sent by the key fob
transmitter is recognized as valid by the Immobilizer
module, it will decode the Crankshaft Position Sensor
signal, enable the starter circuit, and allow the
engine to run.
The immobilizer receiver is mounted to the dash
panel with a hook and loop fastener patch. It is
located behind the instrument cluster and above the
heater-A/C housing. The receiver is connected to the
dash panel cross-body wiring harness. (Fig. 1)
For diagnosis of the vehicle immobilizer receiver or
the CCD data bus, a DRB scan tool is required. Refer
to the Vehicle Theft Security System menu item of
the DRB scan tool for the procedures. The immobi-
lizer receiver contains no servicable parts. If faulty,
the unit must be replaced.
IMMOBILIZER TRANSMITTER
The vehicle immobilizer system includes two trans-
mitters that are supplied with the vehicle when it isshipped from the factory. Each of the two transmit-
ters is equipped with two buttons labeled with Inter-
national Standards Organization (ISO) symbols for
Lock, and Unlock. Two spare batteries (enough for
one transmitter) are also shipped with the transmit-
ters. The transmitters are equipped with a key ring
and are designed to serve as a key fob. The operating
range of the radio frequency transmitter signal is up
to 7 meters (23 feet) from the immobilizer receiver.
Each transmitter has a different vehicle access
code, which must be programmed into the memory of
the immobilizer receiver in the vehicle in order to
operate the immobilizer system. The two transmit-
ters shipped with the vehicle have their vehicle
access codes programmed into the receiver at the fac-
tory. A DRB scan tool must be used to program new
or additional transmitter vehicle access codes into
the memory of the immobilizer receiver. Refer to the
Vehicle Theft Security System menu item on the
DRB scan tool for the procedures.
Each transmitter operates on two Duracell DL2016
(or equivalent) batteries. Typical battery life is from
one to two years.
POWER-UP MODE
When the vehicle immobilizer system senses that
the vehicle battery has been disconnected and recon-
nected, it enters its power-up mode. If the immobi-
lizer system was armed prior to the battery
disconnect, the system remains armed when the bat-
tery is reconnected.
If the immobilizer system was disarmed prior to
the battery disconnect, the system will remain dis-
armed if the battery is reconnected within five min-
utes. The system will passively arm itself when the
battery is reconnected more than five minutes after a
battery disconnect or failure. After any passive arm-
ing, the system will have to be actively disarmed
using one of the transmitters.
The power-up mode logic also applies if the battery
goes dead, and battery jump-starting is attempted.
The engine no-run feature will prevent the engine
from operating until the vehicle immobilizer system
has been actively disarmed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
IMMOBILIZER DIAGNOSIS
Refer to the 1998 PL Powertrain Diagnostic Man-
ual for complete diagnostic procedures of the immo-
bilizer system.
Fig. 1 Immobilizer Module Location
8Q - 2 IMMOBILIZER SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 400 of 1200

TERMINOLOGY
This a list of terms with there definitions used in
the wiring diagrams.
Built-Up-Export...........Vehicles Built For Sale
In Markets Other Than North America
Except-Built-Up-Export.....Vehicles Built For Sale
In North America
LHD..................Left Hand Drive Vehicles
RHD.................Right Hand Drive Vehicles
ATX . . . .Automatic Transmission-Front Wheel Drive
MTX .....Manual Transmission-Front Wheel Drive
AT......Automatic Transmission-Rear Wheel Drive
MT .......Manual Transmission-Rear Wheel Drive
SOHC............Single Over Head Cam Engine
DOHC.............Dual Over Head Cam Engine
CONNECTOR INFORMATION
CAUTION: Not all connectors are serviced. Some
connectors are serviced only with a harness. A typ-
ical example might be the Supplemental Restraint
System connectors. Always check parts availability
before attempting a repair.
IDENTIFICATION
In-line connectors are identified by a number, as
follows:
²In-line connectors located on theengine com-
partment harnessareC100series numbers.
²Connectors located on theinstrument panel
harnessareC200series numbers.
²Connectors located on thebody harnessare
C300series numbers.
²Jumper harness connectorsareC400series
numbers.
²Grounds and ground connectorsare identi-
fied with aªGºand follow the same series number-
ing as the in-line connector.
Component connectors are identified by the compo-
nent name instead of a number (Fig. 2). Multiple
connectors on a component use a C1, C2, etc. identi-
fier (Fig. 3).
LOCATIONS
Section 8W-90 contains connector/ground location
illustrations. The illustrations contain the connector
name (or number)/ground number and component
identification. Connector/ground location charts in
Section 8W-90 reference the illustration number for
components and connectors.
Section 8W-80 shows each connector and the cir-
cuits involved with that connector. The connectors
are identified using the name/number on the Dia-
gram pages.
SPLICE LOCATIONS
Splice Location charts in Section 8W-70 show the
entire splice, and provide references to other sections
the splice serves.
Section 8W-95 contains illustrations that show the
general location of the splices in each harness. The
illustrations show the splice by number, and provide
a written location.
NOTES, CAUTIONS, and WARNINGS
Throughout this group additional important infor-
mation is presented in three ways; Notes, Cautions,
and Warnings.
NOTESare used to help describe how switches or
components operate to complete a particular circuit.
They are also used to indicate different conditions
that may appear on the vehicle. For example, an
up-to and after condition.
CAUTIONSare used to indicate information that
could prevent making an error that may damage the
vehicle.
WARNINGSprovide information to prevent per-
sonal injury and vehicle damage. Below is a list of
general warnings that should be followed any time a
vehicle is being serviced.
WARNING: ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES FOR
EYE PROTECTION.
WARNING: USE SAFETY STANDS ANYTIME A PRO-
CEDURE REQUIRES BEING UNDER A VEHICLE.
Fig. 2 Component Identification
Fig. 3 Connector Identification
PL8W - 01 GENERAL INFORMATION 8W - 01 - 7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)