ignition DODGE NEON 1999 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 655 of 1200
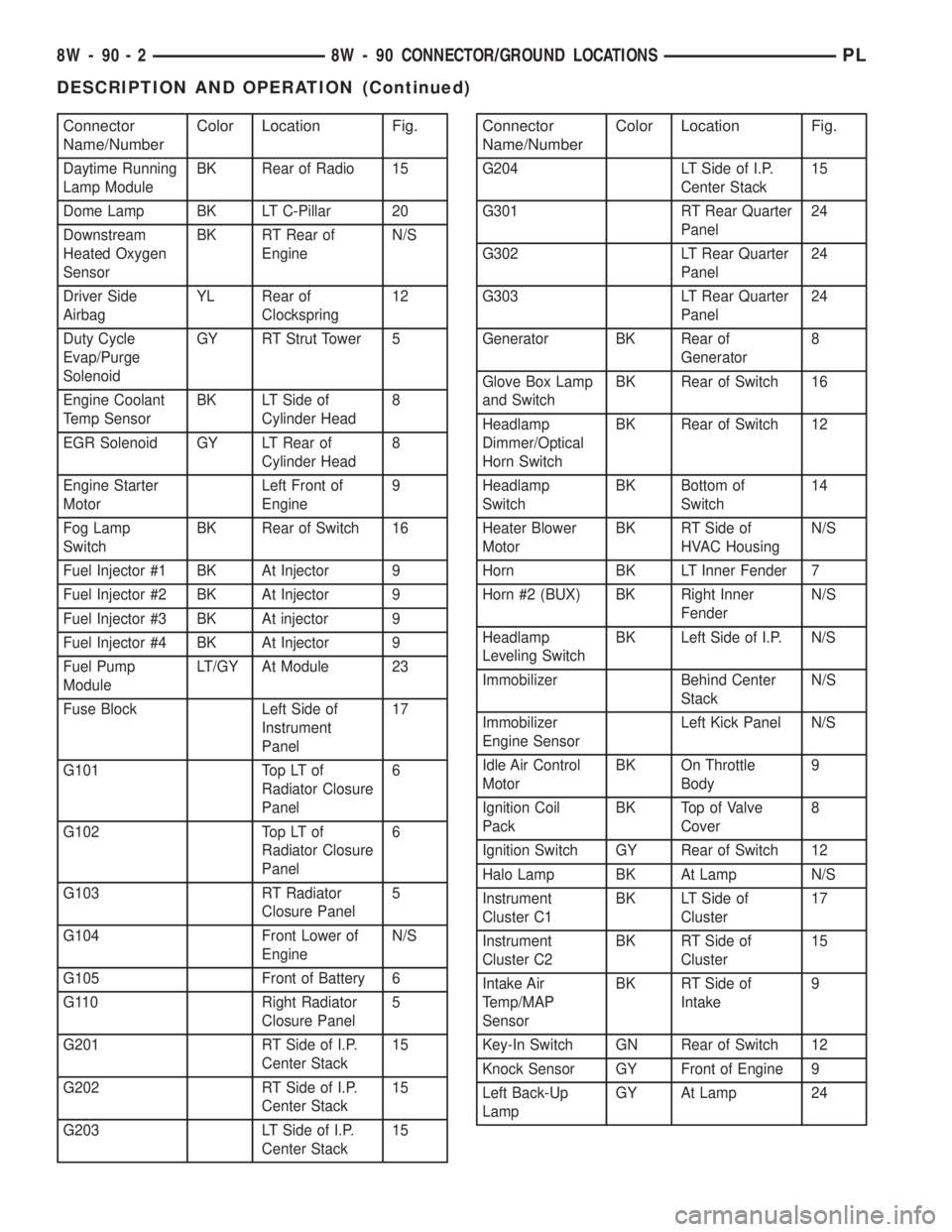
Connector
Name/NumberColor Location Fig.
Daytime Running
Lamp ModuleBK Rear of Radio 15
Dome Lamp BK LT C-Pillar 20
Downstream
Heated Oxygen
SensorBK RT Rear of
EngineN/S
Driver Side
AirbagYL Rear of
Clockspring12
Duty Cycle
Evap/Purge
SolenoidGY RT Strut Tower 5
Engine Coolant
Temp SensorBK LT Side of
Cylinder Head8
EGR Solenoid GY LT Rear of
Cylinder Head8
Engine Starter
MotorLeft Front of
Engine9
Fog Lamp
SwitchBK Rear of Switch 16
Fuel Injector #1 BK At Injector 9
Fuel Injector #2 BK At Injector 9
Fuel Injector #3 BK At injector 9
Fuel Injector #4 BK At Injector 9
Fuel Pump
ModuleLT/GY At Module 23
Fuse Block Left Side of
Instrument
Panel17
G101 Top LT of
Radiator Closure
Panel6
G102 Top LT of
Radiator Closure
Panel6
G103 RT Radiator
Closure Panel5
G104 Front Lower of
EngineN/S
G105 Front of Battery 6
G110 Right Radiator
Closure Panel5
G201 RT Side of I.P.
Center Stack15
G202 RT Side of I.P.
Center Stack15
G203 LT Side of I.P.
Center Stack15
Connector
Name/NumberColor Location Fig.
G204 LT Side of I.P.
Center Stack15
G301 RT Rear Quarter
Panel24
G302 LT Rear Quarter
Panel24
G303 LT Rear Quarter
Panel24
Generator BK Rear of
Generator8
Glove Box Lamp
and SwitchBK Rear of Switch 16
Headlamp
Dimmer/Optical
Horn SwitchBK Rear of Switch 12
Headlamp
SwitchBK Bottom of
Switch14
Heater Blower
MotorBK RT Side of
HVAC HousingN/S
Horn BK LT Inner Fender 7
Horn #2 (BUX) BK Right Inner
FenderN/S
Headlamp
Leveling SwitchBK Left Side of I.P. N/S
Immobilizer Behind Center
StackN/S
Immobilizer
Engine SensorLeft Kick Panel N/S
Idle Air Control
MotorBK On Throttle
Body9
Ignition Coil
PackBK Top of Valve
Cover8
Ignition Switch GY Rear of Switch 12
Halo Lamp BK At Lamp N/S
Instrument
Cluster C1BK LT Side of
Cluster17
Instrument
Cluster C2BK RT Side of
Cluster15
Intake Air
Temp/MAP
SensorBK RT Side of
Intake9
Key-In Switch GN Rear of Switch 12
Knock Sensor GY Front of Engine 9
Left Back-Up
LampGY At Lamp 24
8W - 90 - 2 8W - 90 CONNECTOR/GROUND LOCATIONSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 677 of 1200
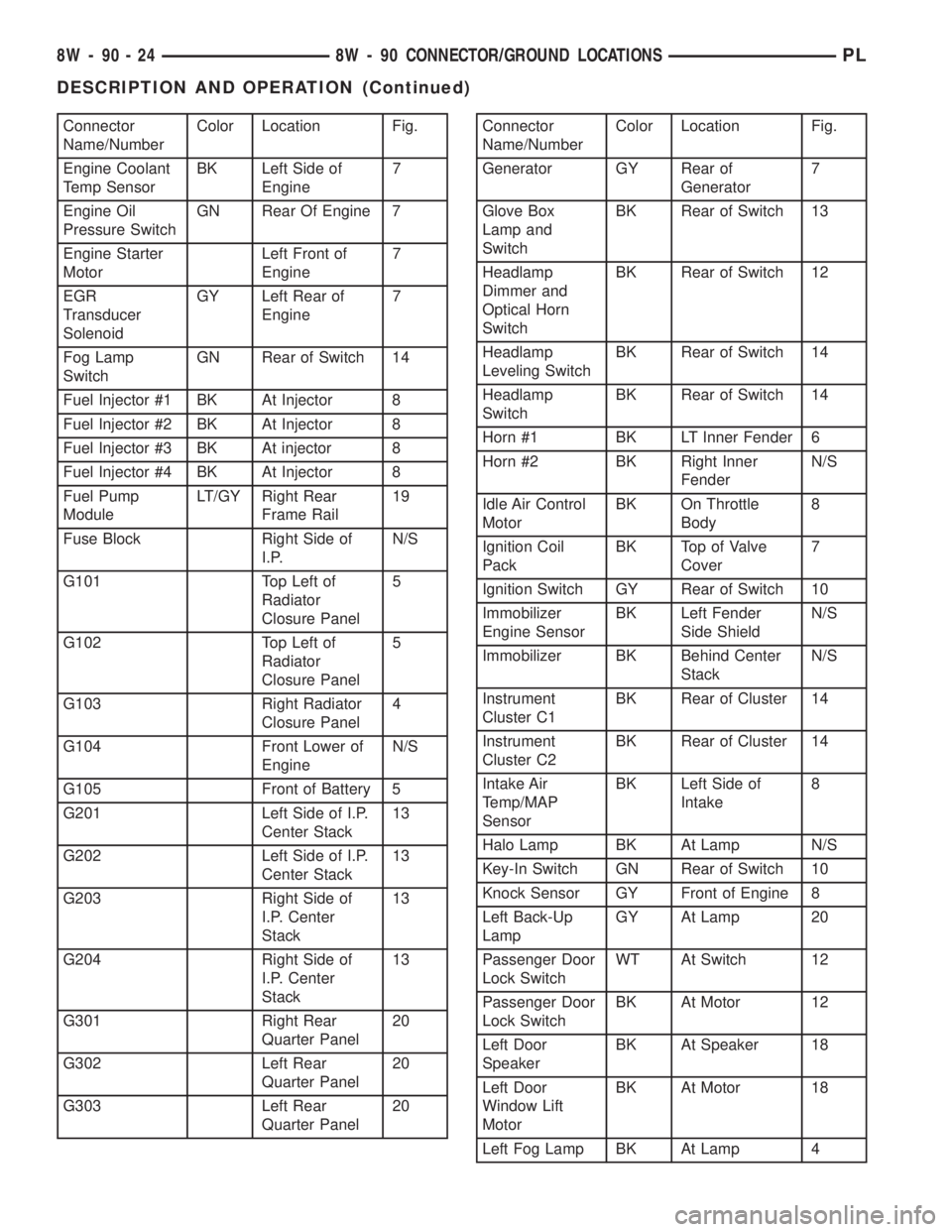
Connector
Name/NumberColor Location Fig.
Engine Coolant
Temp SensorBK Left Side of
Engine7
Engine Oil
Pressure SwitchGN Rear Of Engine 7
Engine Starter
MotorLeft Front of
Engine7
EGR
Transducer
SolenoidGY Left Rear of
Engine7
Fog Lamp
SwitchGN Rear of Switch 14
Fuel Injector #1 BK At Injector 8
Fuel Injector #2 BK At Injector 8
Fuel Injector #3 BK At injector 8
Fuel Injector #4 BK At Injector 8
Fuel Pump
ModuleLT/GY Right Rear
Frame Rail19
Fuse Block Right Side of
I.P.N/S
G101 Top Left of
Radiator
Closure Panel5
G102 Top Left of
Radiator
Closure Panel5
G103 Right Radiator
Closure Panel4
G104 Front Lower of
EngineN/S
G105 Front of Battery 5
G201 Left Side of I.P.
Center Stack13
G202 Left Side of I.P.
Center Stack13
G203 Right Side of
I.P. Center
Stack13
G204 Right Side of
I.P. Center
Stack13
G301 Right Rear
Quarter Panel20
G302 Left Rear
Quarter Panel20
G303 Left Rear
Quarter Panel20Connector
Name/NumberColor Location Fig.
Generator GY Rear of
Generator7
Glove Box
Lamp and
SwitchBK Rear of Switch 13
Headlamp
Dimmer and
Optical Horn
SwitchBK Rear of Switch 12
Headlamp
Leveling SwitchBK Rear of Switch 14
Headlamp
SwitchBK Rear of Switch 14
Horn #1 BK LT Inner Fender 6
Horn #2 BK Right Inner
FenderN/S
Idle Air Control
MotorBK On Throttle
Body8
Ignition Coil
PackBK Top of Valve
Cover7
Ignition Switch GY Rear of Switch 10
Immobilizer
Engine SensorBK Left Fender
Side ShieldN/S
Immobilizer BK Behind Center
StackN/S
Instrument
Cluster C1BK Rear of Cluster 14
Instrument
Cluster C2BK Rear of Cluster 14
Intake Air
Temp/MAP
SensorBK Left Side of
Intake8
Halo Lamp BK At Lamp N/S
Key-In Switch GN Rear of Switch 10
Knock Sensor GY Front of Engine 8
Left Back-Up
LampGY At Lamp 20
Passenger Door
Lock SwitchWT At Switch 12
Passenger Door
Lock SwitchBK At Motor 12
Left Door
SpeakerBK At Speaker 18
Left Door
Window Lift
MotorBK At Motor 18
Left Fog Lamp BK At Lamp 4
8W - 90 - 24 8W - 90 CONNECTOR/GROUND LOCATIONSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 694 of 1200
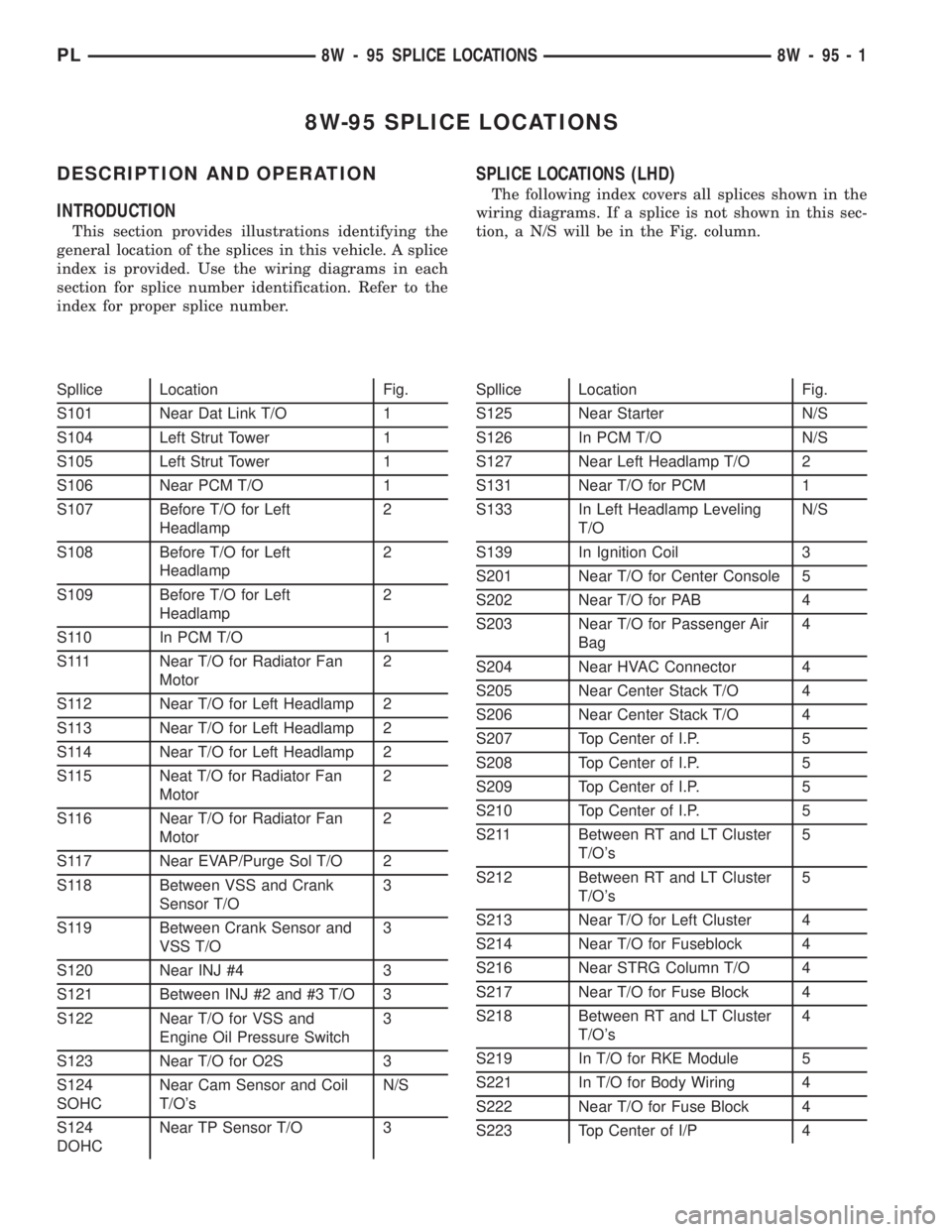
8W-95 SPLICE LOCATIONS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
INTRODUCTION
This section provides illustrations identifying the
general location of the splices in this vehicle. A splice
index is provided. Use the wiring diagrams in each
section for splice number identification. Refer to the
index for proper splice number.
SPLICE LOCATIONS (LHD)
The following index covers all splices shown in the
wiring diagrams. If a splice is not shown in this sec-
tion, a N/S will be in the Fig. column.
Spllice Location Fig.
S101 Near Dat Link T/O 1
S104 Left Strut Tower 1
S105 Left Strut Tower 1
S106 Near PCM T/O 1
S107 Before T/O for Left
Headlamp2
S108 Before T/O for Left
Headlamp2
S109 Before T/O for Left
Headlamp2
S110 In PCM T/O 1
S111 Near T/O for Radiator Fan
Motor2
S112 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S113 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S114 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S115 Neat T/O for Radiator Fan
Motor2
S116 Near T/O for Radiator Fan
Motor2
S117 Near EVAP/Purge Sol T/O 2
S118 Between VSS and Crank
Sensor T/O3
S119 Between Crank Sensor and
VSS T/O3
S120 Near INJ #4 3
S121 Between INJ #2 and #3 T/O 3
S122 Near T/O for VSS and
Engine Oil Pressure Switch3
S123 Near T/O for O2S 3
S124
SOHCNear Cam Sensor and Coil
T/O'sN/S
S124
DOHCNear TP Sensor T/O 3Spllice Location Fig.
S125 Near Starter N/S
S126 In PCM T/O N/S
S127 Near Left Headlamp T/O 2
S131 Near T/O for PCM 1
S133 In Left Headlamp Leveling
T/ON/S
S139 In Ignition Coil 3
S201 Near T/O for Center Console 5
S202 Near T/O for PAB 4
S203 Near T/O for Passenger Air
Bag4
S204 Near HVAC Connector 4
S205 Near Center Stack T/O 4
S206 Near Center Stack T/O 4
S207 Top Center of I.P. 5
S208 Top Center of I.P. 5
S209 Top Center of I.P. 5
S210 Top Center of I.P. 5
S211 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's5
S212 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's5
S213 Near T/O for Left Cluster 4
S214 Near T/O for Fuseblock 4
S216 Near STRG Column T/O 4
S217 Near T/O for Fuse Block 4
S218 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's4
S219 In T/O for RKE Module 5
S221 In T/O for Body Wiring 4
S222 Near T/O for Fuse Block 4
S223 Top Center of I/P 4
PL8W - 95 SPLICE LOCATIONS 8W - 95 - 1
Page 704 of 1200
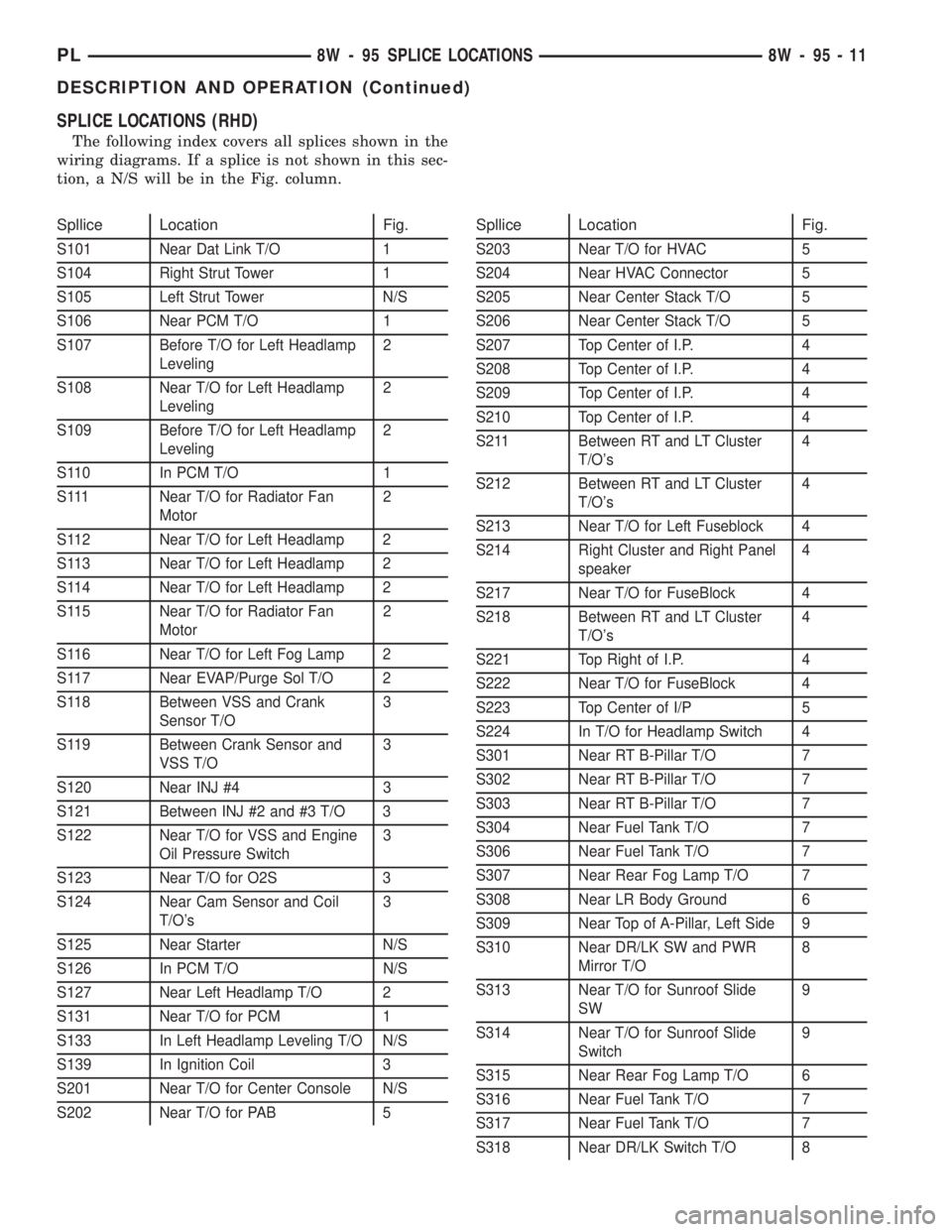
SPLICE LOCATIONS (RHD)
The following index covers all splices shown in the
wiring diagrams. If a splice is not shown in this sec-
tion, a N/S will be in the Fig. column.
Spllice Location Fig.
S101 Near Dat Link T/O 1
S104 Right Strut Tower 1
S105 Left Strut Tower N/S
S106 Near PCM T/O 1
S107 Before T/O for Left Headlamp
Leveling2
S108 Near T/O for Left Headlamp
Leveling2
S109 Before T/O for Left Headlamp
Leveling2
S110 In PCM T/O 1
S111 Near T/O for Radiator Fan
Motor2
S112 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S113 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S114 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S115 Near T/O for Radiator Fan
Motor2
S116 Near T/O for Left Fog Lamp 2
S117 Near EVAP/Purge Sol T/O 2
S118 Between VSS and Crank
Sensor T/O3
S119 Between Crank Sensor and
VSS T/O3
S120 Near INJ #4 3
S121 Between INJ #2 and #3 T/O 3
S122 Near T/O for VSS and Engine
Oil Pressure Switch3
S123 Near T/O for O2S 3
S124 Near Cam Sensor and Coil
T/O's3
S125 Near Starter N/S
S126 In PCM T/O N/S
S127 Near Left Headlamp T/O 2
S131 Near T/O for PCM 1
S133 In Left Headlamp Leveling T/O N/S
S139 In Ignition Coil 3
S201 Near T/O for Center Console N/S
S202 Near T/O for PAB 5
Spllice Location Fig.
S203 Near T/O for HVAC 5
S204 Near HVAC Connector 5
S205 Near Center Stack T/O 5
S206 Near Center Stack T/O 5
S207 Top Center of I.P. 4
S208 Top Center of I.P. 4
S209 Top Center of I.P. 4
S210 Top Center of I.P. 4
S211 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's4
S212 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's4
S213 Near T/O for Left Fuseblock 4
S214 Right Cluster and Right Panel
speaker4
S217 Near T/O for FuseBlock 4
S218 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's4
S221 Top Right of I.P. 4
S222 Near T/O for FuseBlock 4
S223 Top Center of I/P 5
S224 In T/O for Headlamp Switch 4
S301 Near RT B-Pillar T/O 7
S302 Near RT B-Pillar T/O 7
S303 Near RT B-Pillar T/O 7
S304 Near Fuel Tank T/O 7
S306 Near Fuel Tank T/O 7
S307 Near Rear Fog Lamp T/O 7
S308 Near LR Body Ground 6
S309 Near Top of A-Pillar, Left Side 9
S310 Near DR/LK SW and PWR
Mirror T/O8
S313 Near T/O for Sunroof Slide
SW9
S314 Near T/O for Sunroof Slide
Switch9
S315 Near Rear Fog Lamp T/O 6
S316 Near Fuel Tank T/O 7
S317 Near Fuel Tank T/O 7
S318 Near DR/LK Switch T/O 8
PL8W - 95 SPLICE LOCATIONS 8W - 95 - 11
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 715 of 1200

assure gasket rails are flat. Flatten rails with a ham-
mer on a heavy steel plate if required. Gasket sur-
faces must be free of oil and dirt. Make sure old
gasket material is removed from blind attaching
holes.
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKET APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care but it's easier then using precut gas-
kets.
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 inch.) diameter or less of seal-
ant to one gasket surface. Be certain the material
surrounds each mounting hole. Excess material can
easily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing material off the location.
The MopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant gas-
ket material or equivalent should be applied in a con-
tinuous bead approximately 3 mm (0.120 inch) in
diameter. All mounting holes must be circled. For
corner sealing, a 3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 inch.)
drop is placed in the center of the gasket contact
area. Uncured sealant may be removed with a shop
towel. Components should be torqued in place while
the sealant is still wet to the touch (within 10 min-
utes). The usage of a locating dowel is recommended
during assembly to prevent smearing material off the
location.
CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET BOLT ACCESS PLUG
An Access plug is located in the right inner fender
shield. Remove the plug and insert the proper size
socket, extension and ratchet, when crankshaft rota-
tion is necessary.
ENGINE CORE PLUGS
REMOVAL
Using a blunt tool such as a drift or a screwdriver
and a hammer, strike the bottom edge of the cup
plug (Fig. 1). With the cup plug rotated, grasp firmly
with pliers or other suitable tool and remove plug
(Fig. 1).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting
as restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
INSTALLATION
Thoroughly remove all rust and clean inside of cup
plug hole in cylinder block or head. Be sure to
remove old sealer. Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole
with sealer. Make certain the new plug is cleaned of
all oil or grease. Using proper drive plug, drive plug
into hole so that the sharp edge of the plug is atleast 0.5 mm (0.020 inch.) inside the lead in chamfer
(Fig. 1).
It is in not necessary to wait for curing of the seal-
ant. The cooling system can be refilled and the vehi-
cle placed in service immediately.
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
If a loss of performance is noticed, timing belt or
chain may have skipped one or two teeth. Camshaft
and crankshaft timing should be checked. Refer to
Group 9, Engine Timing belt or chain installation.
It is important that the vehicle is operating to its
optimum performance level to maintain fuel economy
and lowest vehicle emissions. If vehicle is not operat-
ing to these standards, refer to Engine Diagnosis out-
lined is this section. The following procedures can
assist in achieving the proper engine diagnosis.
(1) Test cranking amperage draw. Refer to Group
8B, Starting.
(2) Check intake manifold for vacuum leaks.
(3) Perform cylinder compression pressure test.
Refer to Engine Diagnosis, outlined in this section.
(4) Clean or replace spark plugs as necessary and
adjust gap as specified in Group 8D, Ignition System.
Tighten to specifications.
(5) Test resistance of spark plug cables. Refer to
Group 8D, Ignition System.
(6) Test ignition coils primary and secondary resis-
tance. Replace parts as necessary. Refer to Group 8D,
Ignition System.
(7) Check fuel pump pressure at idle and different
RPM ranges. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System for
Specifications.
(8) The air filter elements should be replaced as
specified in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance.
(9) Inspect crankcase ventilation system as out-
lined in Group 25, Emission Control Systems.
(10) Road test vehicle as a final test.
Fig. 1 Core Hole Plug Removal
9 - 2 ENGINEPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 720 of 1200

ENGINE DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE
LEAKAGE TEST........................ 8
CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST . . 7
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐMECHANICAL......... 11
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐPERFORMANCE...... 10GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 7
INSPECTION (ENGINE OIL LEAKS IN
GENERAL)............................ 8
INTAKE MANIFOLD LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS..... 7
LASH ADJUSTER (TAPPET) NOISE DIAGNOSIS.. 8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
GENERAL INFORMATION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions.
These malfunctions may be classified as either
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise), or performance
(e.g., engine idles rough and stalls).
Refer to the Service DiagnosisÐMechanical Chart
and the Service DiagnosisÐPerformance Chart, for
possible causes and corrections of malfunctions. Refer
to Group 14, Fuel System, for the fuel system diag-
nosis.
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can-
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis
INTAKE MANIFOLD LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by
lower than normal manifold vacuum. Also, one or
more cylinders may not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN.
DO NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Spray a small stream of water (Spray Bottle) at
the suspected leak area.
(3) If a change in RPM'S, the area of the suspected
leak has been found.
(4) Repair as required.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Check engine oil level and add oil if necessary.
(2) Drive the vehicle until engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Select a route free from traf-
fic and other forms of congestion, observe all traffic
laws, and accelerate through the gears several times
briskly.
(3) Remove all spark plugs from engine. As spark
plugs are being removed, check electrodes for abnor-
mal firing indicators fouled, hot, oily, etc. Record cyl-
inder number of spark plug for future reference.
(4) Disconnect coil wire from distributor and
secure to good ground to prevent a spark from start-
ing a fire (Conventional Ignition System). For Direct
Ignition System DIS disconnect the coil connector.
(5) Be sure throttle blade is fully open during the
compression check.
(6) Insert compression gage adaptor into the #1
spark plug hole in cylinder head. Crank engine until
maximum pressure is reached on gage. Record this
pressure as #1 cylinder pressure.
(7) Repeat the previous step for all remaining cyl-
inders.
(8) Compression should not be less than (689kPa)
100 psi and not vary more than 25 percent from cyl-
inder to cylinder.
(9) If one or more cylinders have abnormally low
compression pressures, repeat the compression test.
(10) If the same cylinder or cylinders repeat an
abnormally low reading on the second compression
test, it could indicate the existence of a problem in
the cylinder in question.The recommended com-
pression pressures are to be used only as a
guide to diagnosing engine problems. An engine
should not be disassembled to determine the
PLENGINE 9 - 7
Page 721 of 1200

cause of low compression unless some malfunc-
tion is present.
(11) Clean or replace spark plugs as necessary
and adjust gap as specified in Group 8, Electrical.
Tighten to specifications.
(12) Test resistance of spark plug cables. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical Ignition System Secondary Cir-
cuit Inspection.
(13) Test coil output voltage, primary and second-
ary resistance. Replace parts as necessary. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical Ignition System.
(14) Check fuel pump pressure at idle and differ-
ent RPM ranges. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System for
Specifications.
(15) The air filter elements should be replaced as
specified in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance,.
(16) Inspect crankcase ventilation system as out
lined in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance. For
emission controls see Group 25, Emission Controls
for service procedures.
(17) Inspect and adjust accessory belt drives refer-
ring to Group 7, Cooling System, Accessory Drive
Belts for proper adjustments.
(18) Road test vehicle as a final test.
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE RADIATOR CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Clean spark plug recesses with compressed air.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1 379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
LASH ADJUSTER (TAPPET) NOISE DIAGNOSIS
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items.
(1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause
them to be spongy.
(2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required.
(3) During this time, turn engine off and let set for
a few minutes before restarting. Repeat this several
times after engine has reached normal operating
temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor pressed into the vertical oil
passage to the cylinder head is plugged with debris.
(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Faulty lash adjuster.
a. Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head. Depress part of rocker
arm over adjuster. Normal adjusters should feel very
firm. Spongy adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
b. Remove suspected rocker arms (sohc) or lash
adjuster (dohc) and replace.
INSPECTION (ENGINE OIL LEAKS IN GENERAL)
Begin with a through visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.
9 - 8 ENGINEPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 723 of 1200
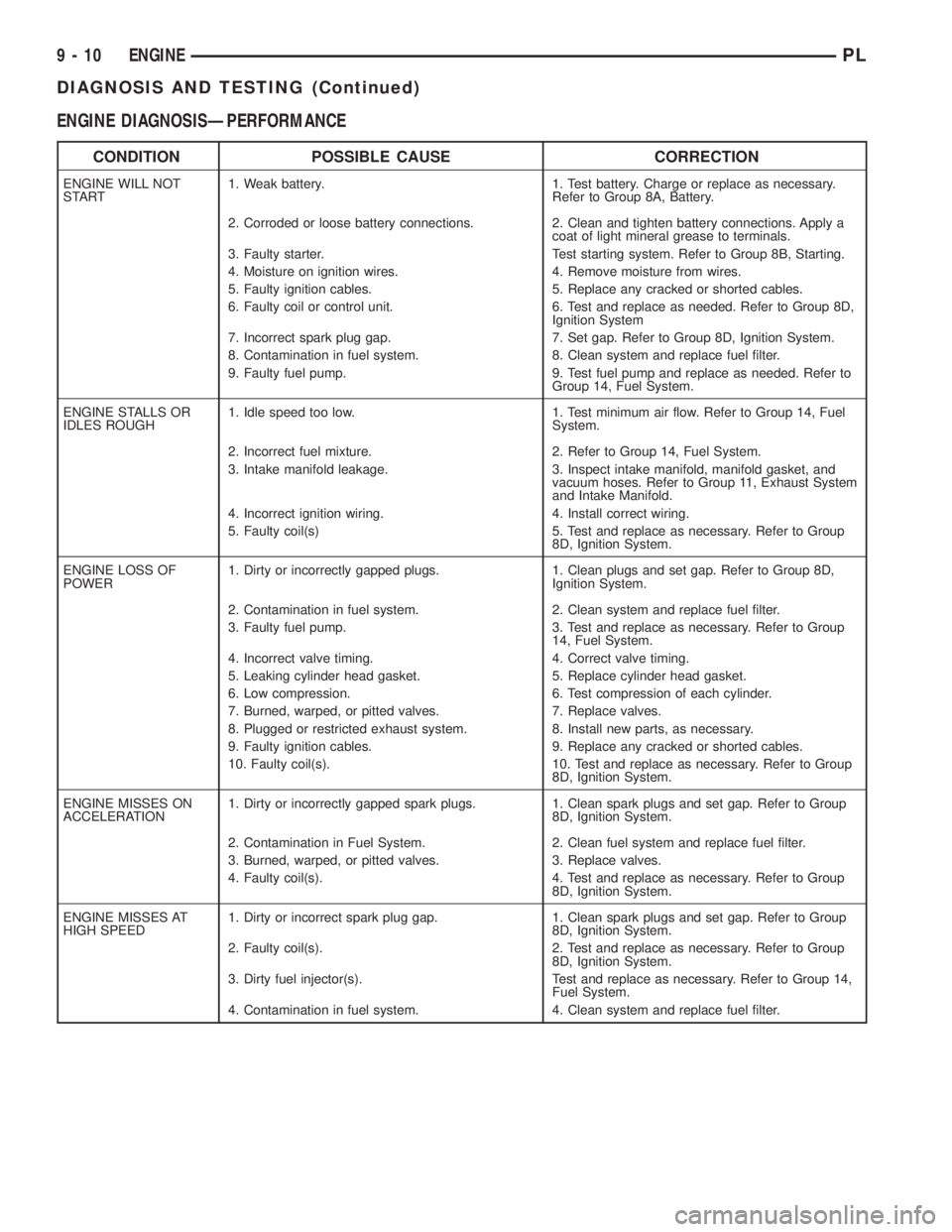
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐPERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT
START1. Weak battery. 1. Test battery. Charge or replace as necessary.
Refer to Group 8A, Battery.
2. Corroded or loose battery connections. 2. Clean and tighten battery connections. Apply a
coat of light mineral grease to terminals.
3. Faulty starter. Test starting system. Refer to Group 8B, Starting.
4. Moisture on ignition wires. 4. Remove moisture from wires.
5. Faulty ignition cables. 5. Replace any cracked or shorted cables.
6. Faulty coil or control unit. 6. Test and replace as needed. Refer to Group 8D,
Ignition System
7. Incorrect spark plug gap. 7. Set gap. Refer to Group 8D, Ignition System.
8. Contamination in fuel system. 8. Clean system and replace fuel filter.
9. Faulty fuel pump. 9. Test fuel pump and replace as needed. Refer to
Group 14, Fuel System.
ENGINE STALLS OR
IDLES ROUGH1. Idle speed too low. 1. Test minimum air flow. Refer to Group 14, Fuel
System.
2. Incorrect fuel mixture. 2. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System.
3. Intake manifold leakage. 3. Inspect intake manifold, manifold gasket, and
vacuum hoses. Refer to Group 11, Exhaust System
and Intake Manifold.
4. Incorrect ignition wiring. 4. Install correct wiring.
5. Faulty coil(s) 5. Test and replace as necessary. Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System.
ENGINE LOSS OF
POWER1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped plugs. 1. Clean plugs and set gap. Refer to Group 8D,
Ignition System.
2. Contamination in fuel system. 2. Clean system and replace fuel filter.
3. Faulty fuel pump. 3. Test and replace as necessary. Refer to Group
14, Fuel System.
4. Incorrect valve timing. 4. Correct valve timing.
5. Leaking cylinder head gasket. 5. Replace cylinder head gasket.
6. Low compression. 6. Test compression of each cylinder.
7. Burned, warped, or pitted valves. 7. Replace valves.
8. Plugged or restricted exhaust system. 8. Install new parts, as necessary.
9. Faulty ignition cables. 9. Replace any cracked or shorted cables.
10. Faulty coil(s). 10. Test and replace as necessary. Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System.
ENGINE MISSES ON
ACCELERATION1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped spark plugs. 1. Clean spark plugs and set gap. Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System.
2. Contamination in Fuel System. 2. Clean fuel system and replace fuel filter.
3. Burned, warped, or pitted valves. 3. Replace valves.
4. Faulty coil(s). 4. Test and replace as necessary. Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System.
ENGINE MISSES AT
HIGH SPEED1. Dirty or incorrect spark plug gap. 1. Clean spark plugs and set gap. Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System.
2. Faulty coil(s). 2. Test and replace as necessary. Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System.
3. Dirty fuel injector(s). Test and replace as necessary. Refer to Group 14,
Fuel System.
4. Contamination in fuel system. 4. Clean system and replace fuel filter.
9 - 10 ENGINEPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 734 of 1200

(8) Install A/C compressor and hoses. Refer to
Group 24, Heater and Air Conditioning for procedure.
(9) Install accessory drive belts. Refer to Group 7,
Cooling System Accessory Drive Section for belt ten-
sion adjustment.
(10) Install front engine mount. Refer to this sec-
tion for procedure.
(11) Manual transmission: Install power hop
damper.
(12) Install inner splash shield. Install wheels and
tires.
(13)Manual Transmission:Connect clutch cable
and linkages. Refer to Group 6, Manual Transaxle
Clutch.
(14)Automatic Transmission:Connect shifter
and kickdown linkage. Refer to Group 21, Transaxle
for procedures.
(15) Connect fuel line and heater hoses.
(16) Install ground straps. Connect engine and
throttle body connections and harnesses. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical for procedure.
(17) Connect throttle body linkage. Refer to Group
14, Fuel System for procedure.
(18) Install radiator and shroud assembly. Install
radiator hoses. Fill cooling system. Refer to Group 7,
Cooling System for filling procedure.
(19) Install battery tray and battery. Set Power-
train Control Module (PCM) into place.
(20) Install air cleaner and hoses.
(21) Install oil filter. Fill engine crankcase with
proper oil to correct level.
(22) Perform camshaft and crankshaft timing
relearn procedure as follows:
²Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
²Turn the ignition switch on and access the ªmis-
cellaneousº screen.
²Select ªre-learn cam/crankº option and follow
directions on DRB screen.
(23) Start engine and run until operating temper-
ature is reached.
(24) Adjust transmission linkage, if necessary.
CYLINDER HEAD COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove air cleaner inlet duct (Fig. 17)
(2) Remove ignition coil pack (Fig. 18).
(3) Remove the cylinder head cover bolts.
(4) Remove cylinder head cover from cylinder
head.
INSTALLATION
Before installation, clean cylinder head and cover
mating surfaces. Make certain the cylinder head
cover mating surface is flat.
(1) Install new cylinder head cover gasket.
CAUTION: Do not allow oil or solvents to contact
the timing belt as they can deteriorate the rubber
and cause tooth skipping.
(2) Install cover assembly to head and tighten fas-
teners to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(3) Install ignition coil pack. Tighten fasteners to
23 N´m (200 in. lbs.).
SPARK PLUG TUBE
(1) Remove cylinder head cover. Refer to procedure
outlined in this section.
(2) Using locking pliers remove the tube from the
cylinder head (Fig. 19). Discard old tube.
(3) Clean area around spark plug with Mopart
parts cleaner or equivalent.
Fig. 17 Inlet Duct Removal
Fig. 18 Ignition Coil Pack
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 21
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 736 of 1200

²Zero the dial indicator.
²Move camshaft forward to limits of travel and
read dial indicator.
²End play travel: 0.13 - 0.33 mm (0.005 - 0.013
in.).
(5) Install front camshaft seal. Camshaft must be
installed before the camshaft seal is installed. Refer
to procedure outlined in this section.
(6) Install cylinder head. Refer to procedure out-
lined in this section.
(7) Install rear timing belt cover.
(8) Install camshaft sprocket and tighten to 115
N´m (85 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install timing belt tensioner and timing belt.
Refer to procedures outlined in this section.
(10) Install rocker arm assemblies in correct order
as removed. Tighten the rocker arm assemblies in
sequence shown in (Fig. 22) to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(11) Install cylinder head cover and tighten fasten-
ers to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(12) Install ignition coil pack and ignition cables.(13) Perform camshaft and crankshaft timing
relearn procedure as follows:
²Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
²Turn the ignition switch on and access the ªmis-
cellaneousº screen.
²Select ªre-learn cam/crankº option and follow
directions on DRB screen.
ROCKER ARM/HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove cylinder head cover using procedure
outlined in this section.
(2) Identify the rocker arm shaft assemblies before
removal.
(3) Loosen the attaching fasteners. Remove rocker
arm shaft assemblies from cylinder head.
(4) Identify the rocker arms spacers and retainers
for reassembly. Disassemble the rocker arm assem-
blies by removing the attaching bolts from the shaft
(Fig. 23).
(5) Slide the rocker arms and spacers off the shaft.
Keep the spacers and rocker arms in the same loca-
tion for reassembly.
Fig. 21 Camshaft End Play
Fig. 22 Rocker Arm Shaft Tightening Sequence
Fig. 23 Rocker Arm Shaft Assemblies
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 23
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)