ignition DODGE NEON 1999 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 5 of 1200

²Replace air cleaner element.
²Replace spark plugs.
²Change automatic transmission fluid.
37,500 Miles (60 000 km) or at 30 months
²Change engine oil.
45,000 Miles (72 000 km) or at 36 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Flush and replace engine coolant at 36 months,
regardless of mileage.
52,500 Miles (84 000 km) or at 42 months
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if not done at
36 months.
60,000 Miles (96 000 km) or at 48 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Check and replace, if necessary***, the PCV
valve.**
²Lubricate front suspension upper ball joints.
²Replace drive belts.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Replace ignition cables.
²Replace spark plugs.
²Change automatic transmission fluid.
67,500 Miles (108 000 km) or at 54 months
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
75,000 Miles (120 000 km) or at 60 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if it has been
30,000 miles (48 000 km) or 24 months since last
change.
82,500 Miles (132 000 km) or at 66 months
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if it has been
30,000 miles (48 000 km) or 24 months since last
change.
90,000 Miles (144 000 km) or at 72 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Check and replace, if necessary***, the PCV
valve.**
²Lubricate front suspension upper ball joints.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Replace air cleaner air cleaner element.
²Replace spark plugs.
²Change automatic transmission fluid.
97,500 Miles (156 000 km) or at 78 months
²Change engine oil.
105,000 Miles (168 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace engine timing belt
²Adjust drive belt tension.
SCHEDULE ± B
NOTE: * Follow this schedule if you usually operate
your vehicle under one or more of the following
conditions. Change the automatic transmission
fluid and filter every 15,000 miles (24 000 km) if you
usually operate your vehicle under one of the con-
ditions marked with an *.
3,000 Miles (5 000 km)
²Change engine oil
6,000 Miles (10 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Replace engine oil filter.
9,000 Miles (14 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake lining.
12,000 Miles (19 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Replace engine oil filter.
15,000 Miles (24 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Inspect and replace, if required, the air
cleaner element.
²Change automatic transaxle fluid and filter.
Adjust the bands.*
18,000 Miles (29 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
21,000 Miles (34 000 km)
²Change engine oil
0 - 4 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 6 of 1200

24,000 Miles (38 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Replace engine oil filter.
27,000 Miles (43 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
30,000 Miles (48 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Check and replace, if necessary, the PCV
valve.**
²Lubricate front suspension upper ball joints.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Replace spark plugs.
²Change automatic transmission fluid and filter.
Adjust the bands.*
33,000 Miles (53 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
36,000 Miles (58 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Flush and replace engine coolant.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
39,000 Miles (62 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
42,000 Miles (67 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
45,000 Miles (72 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
²Inspect and replace, if necessary, the air
cleaner element.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Change automatic transaxle fluid and filter.
Adjust the bands.*
48,000 Miles (77 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
51,000 Miles (82 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace engine coolant.
54,000 Miles (86 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
57,000 Miles (91 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
60,000 Miles (96 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Check and replace, if necessary***, the PCV
valve.**
²Lubricate front suspension upper ball joints.
²Replace drive belts.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Replace ignition cables.
²Replace spark plugs.
²Change automatic transaxle fluid and filter.
Adjust the bands.*
63,000 Miles (101 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
66,000 Miles (106 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
69,000 Miles (110 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
72,000 Miles (115 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
75,000 Miles (120 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Inspect and replace, if necessary, the air
cleaner element.
²Change automatic transaxle fluid and filter.
Adjust the bands.*
78,000 Miles (125 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
81,000 Miles (130 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace the engine coolant.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
84,000 Miles (134 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
87,000 Miles (139 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
PLLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 5
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 8 of 1200

JUMP STARTING, TOWING AND HOISTING
INDEX
page page
SERVICE PROCEDURES
HOISTING RECOMMENDATIONS............ 9JUMP STARTING PROCEDURE.............. 7
TOWING RECOMMENDATIONS.............. 8
SERVICE PROCEDURES
JUMP STARTING PROCEDURE
WARNING: REVIEW ALL SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
AND WARNINGS IN GROUP 8A, BATTERY/START-
ING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS. DO NOT
JUMP START A FROZEN BATTERY, PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT. DO NOT JUMP START WHEN
MAINTENANCE FREE BATTERY INDICATOR DOT IS
YELLOW OR BRIGHT COLOR. DO NOT JUMP
START A VEHICLE WHEN THE BATTERY FLUID IS
BELOW THE TOP OF LEAD PLATES. DO NOT
ALLOW JUMPER CABLE CLAMPS TO TOUCH
EACH OTHER WHEN CONNECTED TO A BOOSTER
SOURCE. DO NOT USE OPEN FLAME NEAR BAT-
TERY. REMOVE METALLIC JEWELRY WORN ON
HANDS OR WRISTS TO AVOID INJURY BY ACCI-
DENTAL ARCING OF BATTERY CURRENT. WHEN
USING A HIGH OUTPUT BOOSTING DEVICE, DO
NOT ALLOW BATTERY VOLTAGE TO EXCEED 16
VOLTS. REFER TO INSTRUCTIONS PROVIDED
WITH DEVICE BEING USED.
CAUTION: When using another vehicle as a
booster, do not allow vehicles to touch. Electrical
systems can be damaged on either vehicle.
TO JUMP START A DISABLED VEHICLE:
(1) Raise hood on disabled vehicle and visually
inspect engine compartment for:
²Battery cable clamp condition, clean if necessary.
²Frozen battery.
²Yellow or bright color test indicator, if equipped.
²Low battery fluid level.
²Generator drive belt condition and tension.
²Fuel fumes or leakage, correct if necessary.
CAUTION: If the cause of starting problem on dis-
abled vehicle is severe, damage to booster vehicle
charging system can result.
(2) When using another vehicle as a booster
source, park the booster vehicle within cable reach.
Turn off all accessories, set the parking brake, placethe automatic transmission in PARK or the manual
transmission in NEUTRAL and turn the ignition
OFF.
(3) On disabled vehicle, place gear selector in park
or neutral and set park brake. Turn off all accesso-
ries.
(4) Connect jumper cables to booster battery. RED
clamp to positive terminal (+). BLACK clamp to neg-
ative terminal (-). DO NOT allow clamps at opposite
end of cables to touch, electrical arc will result.
Review all warnings in this procedure.
(5) On disabled vehicle, connect RED jumper cable
clamp to positive (+) terminal. Connect BLACK
jumper cable clamp to engine ground as close to the
ground cable attaching point as possible (Fig. 1).
(6) Start the engine in the vehicle which has the
booster battery, let the engine idle a few minutes,
then start the engine in the vehicle with the dis-
charged battery.
CAUTION: Do not crank starter motor on disabled
vehicle for more than 15 seconds, starter will over-
heat and could fail.
(7) Allow battery in disabled vehicle to charge to
at least 12.4 volts (75% charge) before attempting to
start engine. If engine does not start within 15 sec-
onds, stop cranking engine and allow starter to cool
(15 min.), before cranking again.
Fig. 1 Jumper Cable Clamp Connections
PLLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 7
Page 88 of 1200

boosters differ at the interface to the master cylinder.
If the power brake booster requires replacement be
sure it is replaced with the correct part.
The power brake booster can be identified by the
tag attached to the body of the booster assembly (Fig.
16). This tag contains the following information: The
production part number of the power booster assem-
bly, the date it was built, who manufactured it, and
brake sales code.
NOTE: The power brake booster assembly is not a
repairable part and must be replaced as a complete
unit if it is found to be faulty in any way. The power
booster vacuum check valve is not repairable but
can be replaced as an assembly.The power brake booster reduces the amount of
force required by the driver to obtain the necessary
hydraulic pressure to stop vehicle.
The power brake booster is vacuum operated. The
vacuum is supplied from the intake manifold on the
engine through the power brake booster check valve
(Fig. 16).
As the brake pedal is depressed, the power booster
input rod moves forward (Fig. 17). This opens and
closes valves in the power booster, allowing atmo-
spheric pressure to enter on one side of a diaphragm.
Engine vacuum is always present on the other side.
This difference in pressure forces the output rod of
the power booster (Fig. 17) out against the primary
piston of the master cylinder. As the pistons in the
master cylinder move forward this creates the
hydraulic pressure in the brake system.
Different engine options available for this vehicle
require that different vacuum hose routings be used.
The power brake vacuum booster assembly mounts
on the engine side of the dash panel. It is connected
to the brake pedal by the input push rod (Fig. 17). A
vacuum line connects the power booster to the intake
manifold. The master cylinder is bolted to the front
of the power brake vacuum booster assembly.
RED BRAKE WARNING LAMP
The red Brake warning lamp is located in the
instrument panel cluster and is used to indicate a
low brake fluid condition or that the parking brake is
applied. In addition, the brake warning lamp is
turned on as a bulb check by the ignition switch
when the ignition switch is placed in the crank posi-
tion. Problems with this system will generally be of
the type where the warning lamp fails to turn on
when it should, or remains on when it should not.
The warning lamp bulb is supplied a 12 volt igni-
tion feed anytime the ignition switch is on. The bulb
is then illuminated by completing the ground circuit
Fig. 14 Master Cylinder For Antilock Brake
Equipped Vehicles
Fig. 15 Non-ABS Master Cylinder Primary And
Secondary Ports
Fig. 16 Power Brake Booster Identification
PLBRAKES 5 - 7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 122 of 1200

MASTER CYLINDER
REMOVE
CAUTION: On ABS equipped vehicles, vacuum in
power booster must be pumped down before
removing master cylinder to prevent booster from
sucking in any contamination. This can be done
simply by pumping the brake pedal until a firm
pedal is achieved, with the ignition off.
(1) On ABS equipped vehicles, be sure engine is
not running, and pump the brake pedal until a firm
pedal is achieved (4-5 strokes).
(2) Remove vehicle wiring harness connector, from
brake fluid level sensor, in master cylinder brake
fluid reservoir (Fig. 103).
(3) Disconnect the primary and secondary brake
tubes from the master cylinder (Fig. 104) and (Fig.
105). Install plugs at all open brake tube outlets on
master cylinder assembly.(4) On vehicles equipped with ABS, clean area
where master cylinder attaches to booster using a
suitable brake cleaner product such as Mopar Brake
Parts Cleaner or an equivalent.
(5) Remove the 2 nuts (Fig. 106) attaching master
cylinder housing to power brake vacuum booster.
(6) Slide master cylinder assembly straight out of
the power brake vacuum booster.
CAUTION: On vehicles equipped with ABS, the
master cylinder is used to create the seal for hold-
ing vacuum in the power brake vacuum booster.
The vacuum seal in the front of the power brake
vacuum booster (Fig. 107) MUST be replaced when-
ever the master cylinder is removed from the power
brake vacuum booster.
(7) If vehicle is equipped with ABS, remove vac-
uum seal (Fig. 107) located in the front of the power
brake vacuum booster. Vacuum seal is removed by
Fig. 102 Caliper Guide Pin Bolts
Fig. 103 Master Cylinder Fluid Level Sensor
Fig. 104 Primary And Secondary Brake Tubes W/O
ABS Brakes
Fig. 105 Primary And Secondary Brake Tubes With
ABS Brakes
PLBRAKES 5 - 41
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 125 of 1200

VACUUM BOOSTER
REMOVE
CAUTION: On ABS equipped vehicles, vacuum in
power booster must be pumped down before
removing master cylinder to prevent booster from
sucking in any contamination. This can be done
simply by pumping the brake pedal until a firm
pedal is achieved, with the ignition off.
(1) On ABS equipped vehicles, with engine not
running, pump the brake pedal until a firm pedal is
achieved (4-5 strokes).
(2) Remove vehicle wiring harness connector from
brake fluid level sensor located in master cylinder
brake fluid reservoir (Fig. 114).
(3) Disconnect the primary and secondary brake
tubes from the master cylinder (Fig. 115) and (Fig.
116). Install plugs at all open brake tube outlets on
master cylinder assembly.(4) On vehicles equipped with ABS, clean area
where master cylinder attaches to booster using a
suitable brake cleaner such as Mopar Brake Parts
Cleaner or an equivalent.
(5) Remove the 2 nuts (Fig. 117) attaching master
cylinder housing to power brake vacuum booster.
(6) Slide master cylinder assembly straight out of
the power brake vacuum booster.
CAUTION: On vehicles equipped with ABS, the
master cylinder is used to create the seal for hold-
ing vacuum in the power brake vacuum booster.
The vacuum seal in the front of the power brake
vacuum booster (Fig. 118) MUST be replaced when-
ever the master cylinder is removed from the power
brake vacuum booster.
(7) If vehicle is equipped with ABS, remove vac-
uum seal (Fig. 118) located in the front of the power
Fig. 114 Master Cylinder Fluid Level Sensor
Fig. 115 Primary And Secondary Brake Tubes W/O
ABS Brakes
Fig. 116 Primary And Secondary Brake Tubes With
ABS Brakes
Fig. 117 Master Cylinder Mounting To Vacuum
Booster
5 - 44 BRAKESPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 151 of 1200

This is accomplished by a sophisticated system of
electrical and hydraulic components. As a result,
there are a few performance characteristics that may
at first seem different but should be considered nor-
mal. These characteristics are discussed below.
NORMAL BRAKING SYSTEM FUNCTION
Under normal braking conditions, the ABS System
functions the same as a standard brake system with
a diagonally split master cylinder and conventional
vacuum assist.
ABS SYSTEM OPERATION
If a wheel locking tendency is detected during a
brake application, the brake system will enter the
ABS mode. During ABS braking, hydraulic pressure
in the four wheel circuits is modulated to prevent
any wheel from locking. Each wheel circuit is
designed with a set of electric solenoids to allow mod-
ulation, although for vehicle stability, both rear
wheel solenoids receive the same electrical signal.
During an ABS stop, the brakes hydraulic system
is still diagonally split. However, the brake system
pressure is further split into four control channels.
During antilock operation of the vehicle's brake sys-
tem the front wheels are controlled independently
and are on two separate control channels and the
rear wheels of the vehicle are controlled together.
The system can build and release pressure at each
wheel, depending on signals generated by the wheel
speed sensors (WSS) at each wheel and received at
the Controller Antilock Brake (CAB).
ABS operation is available at all vehicle speeds
above 3 to 5 mph. Wheel lockup may be perceived at
the very end of an ABS stop and is considered nor-
mal.
VEHICLE HANDLING PERFORMANCE DURING
ABS BRAKING
It is important to remember that an antilock brake
system does not shorten a vehicle's stopping distance
under all driving conditions, but does provide
improved control of the vehicle while stopping. Vehi-
cle stopping distance is still dependent on vehicle
speed, weight, tires, road surfaces and other factors.
Though ABS provides the driver with some steer-
ing control during hard braking, there are conditions
however, where the system does not provide any ben-
efit. In particular, hydroplaning is still possible when
the tires ride on a film of water. This results in the
vehicles tires leaving the road surface rendering the
vehicle virtually uncontrollable. In addition, extreme
steering maneuvers at high speed or high speed cor-
nering beyond the limits of tire adhesion to the road
surface may cause vehicle skidding, independent of
vehicle braking. For this reason, the ABS system is
termed Antilock instead of Anti-Skid.
NOISE AND BRAKE PEDAL FEEL
During ABS braking, some brake pedal movement
may be felt. In addition, ABS braking will create
ticking, popping and/or groaning noises heard by the
driver. This is normal due to pressurized fluid being
transferred between the master cylinder and the
brakes. If ABS operation occurs during hard braking,
some pulsation may be felt in the vehicle body due to
fore and aft movement of the suspension as brake
pressures are modulated.
At the end of an ABS stop, ABS will be turned off
when the vehicle is slowed to a speed of 3±4 mph.
There may be a slight brake pedal drop anytime that
the ABS is deactivated, such as at the end of the stop
when the vehicle speed is less then 3 mph or during
an ABS stop where ABS is no longer required. These
conditions will exist when a vehicle is being stopped
on a road surface with patches of ice, loose gravel or
sand on it. Also stopping a vehicle on a bumpy road
surface will activate ABS because of the wheel hop
caused by the bumps.
TIRE NOISE AND MARKS
Although the ABS system prevents complete wheel
lock-up, some wheel slip is desired in order to
achieve optimum braking performance. Wheel slip is
defined as follows, 0 percent slip means the wheel is
rolling freely and 100 percent slip means the wheel is
fully locked. During brake pressure modulation,
wheel slip is allowed to reach up to 25 to30%. This
means that the wheel rolling velocity is 25 to 30%
less than that of a free rolling wheel at a given vehi-
cle speed. This slip may result in some tire chirping,
depending on the road surface. This sound should not
be interpreted as total wheel lock-up.
Complete wheel lock up normally leaves black tire
marks on dry pavement. The ABS System will not
leave dark black tire marks since the wheel never
reaches a fully locked condition. Tire marks may
however be noticeable as light patched marks.
START UP CYCLE
When the ignition is turned on, a popping sound
and a slight brake pedal movement may be noticed.
Additionally, when the vehicle is first driven off a
humming may be heard and/or felt by the driver at
approximately 20 to 40 kph (12 to 25 mph). The ABS
warning lamp will also be on for up to 5 seconds
after the ignition is turned on. All of these conditions
are a normal function of ABS as the system is per-
forming a diagnosis check.
5 - 70 BRAKESPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 155 of 1200

integral part of the rear wheel hub and bearing
assembly. The speed sensor air gap on both applica-
tions is NOT adjustable.
The four Wheel Speed Sensors are serviced individ-
ually. The front Tone Wheels are serviced as an
assembly with the outboard constant velocity joint.
The rear Tone Wheels are serviced as an assembly
with the rear hub and bearing assembly.
Correct ABS system operation is dependent on
accurate wheel speed signals. The vehicle's wheels
and tires must all be the same size and type to gen-
erate accurate signals. Variations in wheel and tire
size can produce inaccurate wheel speed signals.
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKES (CAB)
The Controller Antilock Brakes (CAB) is a micro-
processor based device which monitors the ABS sys-
tem during normal braking and controls it when the
vehicle is in an ABS stop. The CAB is mounted to the
bottom of the HCU (Fig. 10). The CAB uses a 25 way
electrical connector on the vehicle wiring harness.
The power source for the CAB is through the ignitionswitch in the Run or On position.THE (CAB) IS ON
THE CCD BUS
The primary functions of the (CAB) are:
(1) Detect wheel locking or wheel slipping tenden-
cies by monitoring the speed of all four wheels of the
vehicle.
(2) Control fluid modulation to the wheel brakes
while the system is in an ABS mode or the traction
control system is activated.
(3) Monitor the system for proper operation.
(4) Provide communication to the DRB Scan Tool
while in diagnostic mode.
(5) Store diagnostic information.
The CAB continuously monitors the speed of each
wheel through the signals generated by the wheel
speed sensors to determine if any wheel is beginning
to lock. When a wheel locking tendency is detected,
the CAB commands the CAB command coils to actu-
ate. The CAB command coils then open and close the
valves in the HCU which modulate brake fluid pres-
sure in some or all of the hydraulic circuits. The CAB
continues to control pressure in individual hydraulic
circuits until a locking tendency is no longer present.
The ABS system is constantly monitored by the
CAB for proper operation. If the CAB detects a fault,
it will turn on the Amber ABS Warning Lamp and
disable the ABS braking system. The normal base
braking system will remain operational.
The CAB contains a self-diagnostic program which
will turn on the Amber ABS Warning Lamp when a
ABS system fault is detected. Faults are then stored
in a diagnostic program memory. There are multiple
fault messages which may be stored in the CAB and
displayed through the DRB Scan Tool. These fault
messages will remain in the CAB memory even after
the ignition has been turned off. The fault messages
can be read and or cleared from the CAB memory by
a technician using the DRB Scan Tool. The fault
occurrence and the fault code will also be automati-
Fig. 8 Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Fig. 9 Rear Wheel Speed Sensor With Disc Brakes
Fig. 10 Controller Antilock Brake (CAB)
5 - 74 BRAKESPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 156 of 1200

cally cleared from the CAB memory after the identi-
cal fault has not been seen during the next 255 key
cycles of vehicle operation.
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE INPUTS
²Four wheel speed sensors.
²Stop lamp switch.
²Ignition switch.
²System relay voltage.
²Ground.
²Diagnostics Communications (CCD)
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE OUTPUTS
²ABS warning lamp actuation.
²Diagnostic communication. (CCD)
ABS WARNING LAMP (YELLOW)
The ABS system uses a yellow colored ABS Warn-
ing Lamp. The ABS warning lamp is located on the
lower left side of the instrument pane. The purpose
of the warning lamp is discussed in detail below.
The ABS warning lamp will turn on when the CAB
detects a condition which results in a shutdown of
ABS function. When the ignition key is turned to the
on position, the ABS Warning Lamp is on until the
CAB completes its self tests and turns the lamp off
(approximately 4 seconds after the ignition switch is
turned on). Under most conditions, when the ABS
warning lamp is on, only the ABS function of the
brake system is affected. The standard brake system
and the ability to stop the car will not be affected
when only the ABS warning lamp is on.
The ABS warning lamp is controlled by the CAB.
The CAB turns on the yellow ABS warning lamp by
grounding the circuit.
HYDRAULIC CIRCUITS AND VALVE OPERATION
Through the following operation descriptions the
function of the various hydraulic control valves in the
ABS will be described. The fluid control valves men-
tioned below, control the flow of pressurized brake
fluid to the wheel brakes during the different modes
of ABS braking.
For explanation purposes, all wheel speed sensors
except the right front are sending the same wheel
speed information. The following diagrams show only
the right front wheel in a antilock braking condition.
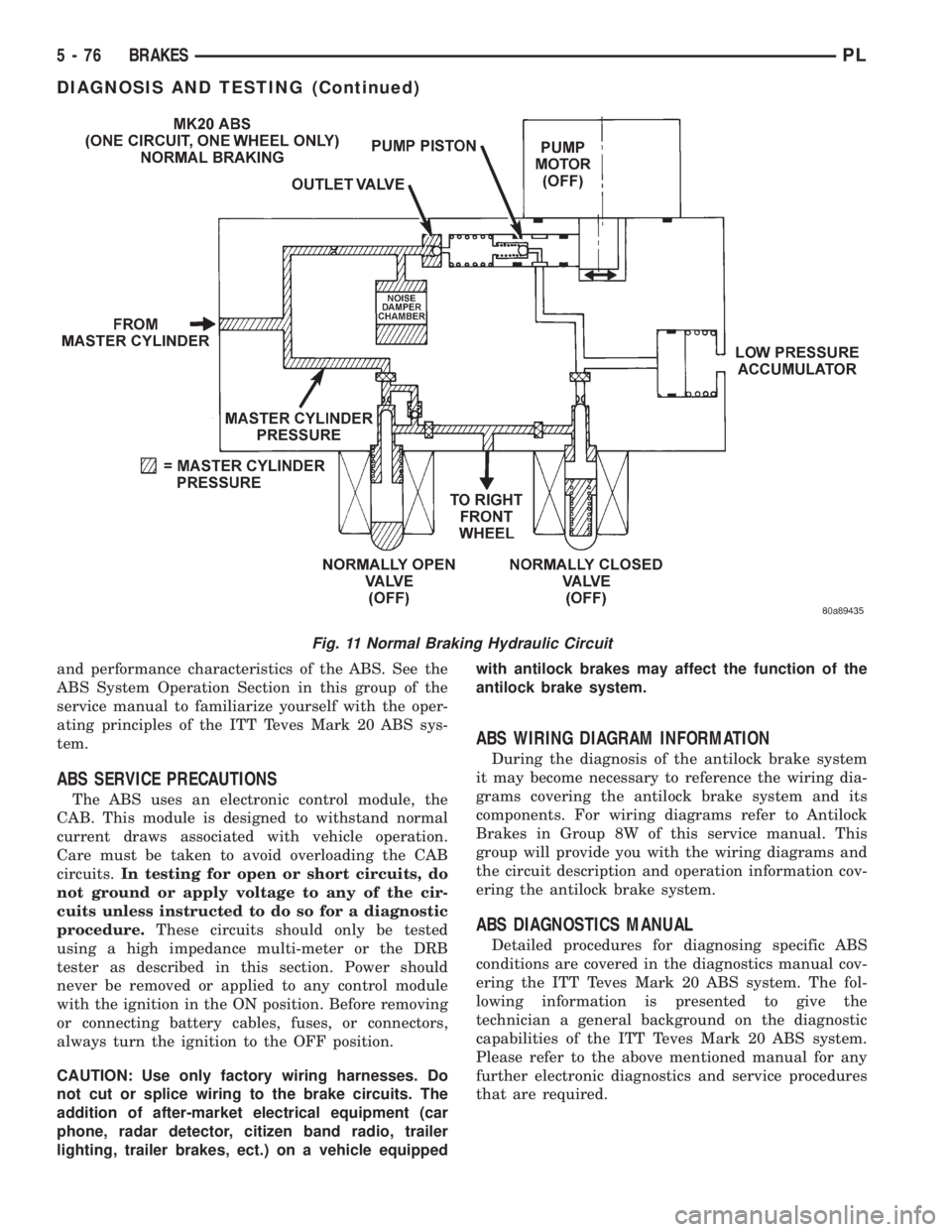
NORMAL BRAKING HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT AND
SOLENOID VALVE FUNCTION
This condition is the normal operation of the vehi-
cles base brake hydraulic system. The hydraulic sys-
tem circuit diagram (Fig. 11) shows a situation where
no wheel spin or slip is occurring relative to the
speed of the vehicle. The driver is applying the brake
pedal to build pressure in the brake hydraulic system
to apply the brakes and stop the vehicle.
TEVES MARK 20 ABS CIRCUIT AND
SOLENOID VALVE FUNCTION
This hydraulic circuit diagram (Fig. 12) shows the
vehicle in the ABS braking mode. This hydraulic cir-
cuit (Fig. 12) shows a situation where one wheel is
slipping because the driver is attempting to stop the
vehicle at a faster rate than the surface the vehicle's
tires are on will allow. The normally open and nor-
mally closed valves modulate the brake hydraulic
pressure as required. The pump/motor is switched on
so that the brake fluid from the low pressure accu-
mulators is returned to the master cylinder circuits.
The brake fluid will then be routed to either the mas-
ter cylinder or the wheel brake depending on the
position of the normally open valve.
TEVES MARK 20 SECONDARY ABS CIRCUIT
AND SOLENOID VALVE FUNCTION
This hydraulic circuit diagram (Fig. 13) shows the
vehicle in the ABS braking mode. This hydraulic cir-
cuit (Fig. 13) shows a situation where one wheel is
slipping because the driver is attempting to stop the
vehicle at a faster rate than the surface the vehicle's
tires are on will allow. The normally open and nor-
mally closed valves modulate the brake hydraulic
pressure as required. The pump/motor is switched on
so that the brake fluid from the low pressure accu-
mulators is returned to the master cylinder circuits.
The brake fluid will then be routed to either the mas-
ter cylinder or the wheel brake depending on the
position of the normally open valve. A volume of 1.2
cc's of brake fluid is taken in by the lip seal saver
(Fig. 13) to protect the lip seals on the piston of the
master cylinder.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
ABS GENERAL DIAGNOSTICS INFORMATION
This section contains the information necessary to
diagnose the ITT Teves Mark 20 ABS Brake System.
Specifically, this section should be used to help diag-
nose conditions which result in any of the following:
(1) ABS Warning Lamp turned on.
(2) Brakes Lock-up on hard application
Diagnosis of base brake conditions which are obvi-
ously mechanical in nature should be directed to
Group 5 Brakes in this service manual. This includes
brake noise, brake pulsation, lack of power assist,
parking brake, Red BRAKE Warning Lamp lighting,
or vehicle vibration during normal braking.
Many conditions that generate customer com-
plaints may be normal operating conditions, but are
judged to be a problem due to not being familiar with
the ABS system. These conditions can be recognized
without performing extensive diagnostic work, given
adequate understanding of the operating principles
PLBRAKES 5 - 75
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 157 of 1200
and performance characteristics of the ABS. See the
ABS System Operation Section in this group of the
service manual to familiarize yourself with the oper-
ating principles of the ITT Teves Mark 20 ABS sys-
tem.
ABS SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
The ABS uses an electronic control module, the
CAB. This module is designed to withstand normal
current draws associated with vehicle operation.
Care must be taken to avoid overloading the CAB
circuits.In testing for open or short circuits, do
not ground or apply voltage to any of the cir-
cuits unless instructed to do so for a diagnostic
procedure.These circuits should only be tested
using a high impedance multi-meter or the DRB
tester as described in this section. Power should
never be removed or applied to any control module
with the ignition in the ON position. Before removing
or connecting battery cables, fuses, or connectors,
always turn the ignition to the OFF position.
CAUTION: Use only factory wiring harnesses. Do
not cut or splice wiring to the brake circuits. The
addition of after-market electrical equipment (car
phone, radar detector, citizen band radio, trailer
lighting, trailer brakes, ect.) on a vehicle equippedwith antilock brakes may affect the function of the
antilock brake system.
ABS WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATION
During the diagnosis of the antilock brake system
it may become necessary to reference the wiring dia-
grams covering the antilock brake system and its
components. For wiring diagrams refer to Antilock
Brakes in Group 8W of this service manual. This
group will provide you with the wiring diagrams and
the circuit description and operation information cov-
ering the antilock brake system.
ABS DIAGNOSTICS MANUAL
Detailed procedures for diagnosing specific ABS
conditions are covered in the diagnostics manual cov-
ering the ITT Teves Mark 20 ABS system. The fol-
lowing information is presented to give the
technician a general background on the diagnostic
capabilities of the ITT Teves Mark 20 ABS system.
Please refer to the above mentioned manual for any
further electronic diagnostics and service procedures
that are required.
Fig. 11 Normal Braking Hydraulic Circuit
5 - 76 BRAKESPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)